1. Introduction
Big data technology has become a significant tool in the advancement of contemporary society and has made a significant contribution to China's economic development as a result of the growth of Internet and information technology. Big data technology differs from traditional data forms in three key ways: large data volume, varied data types, and fast generation speed Y. Wang (2020) [
1]. These differences open up enormous potential for growth for many business domains, including marketing and sales, human resources, e-commerce, and human resources in Asia, as well as launching Chinese businesses into a completely new developmental stage, The state of business management development in relation to big data, enterprise manufacture, and creation tends to make big data technology use more commonplace in enterprise business management. The relationship between companies and consumers is gradually approaching a balanced state as a result of the use of big data to alter the generation and dissemination of information. This includes increasing the reciprocal impact between businesses and consumers as well as improving the fairness, transparency, and justice between the growth of business operations and consumer activities [
2].
The primary source of massive amounts information on the Internet is user-generated data and information. This effectively replaces the traditional "closed" management model, increases interactivity between consumer and enterprise production activities, and lets consumers use the Internet platform to manage enterprise business processes. In order for enterprise operation and environmental operation to progressively move in the direction of the network, information technology, and dynamic development, they prefer to utilize big data technology in a dynamic manner to enterprise business management , The system has greater effects on modern enterprise manufacture management and business administration due to the current state of enterprise management, the "network ecosystem" formed by social networking network users, cooperative businesses, and competitors, so that business production management and company management gradually show both horizontally and vertically joint [
3]. The system has a bigger influence on contemporary enterprise supply management and business leadership, causing these two areas of development to progressively exhibit two different types of situations: vertical and horizontal joint First, from the perspective of a horizontal alliance, a networked business model can alter the nature of competition between enterprise organizations, improve cross-regional cooperation, and eventually create a "virtual enterprise" or "enterprise alliance"; second, from the perspective of a vertical cooperation, enterprise groups are interconnected by commercial supply chains, thus strengthening ties between related businesses and fostering mutual benefit and symbiosis. As a result, the supply chain progressively moves in the direction of a value chain and eventually becomes a network ecological chain, by utilizing big data technology in business management, organizations can progressively shift their market demands towards accuracy and real-time responses. This allows them to fully utilize the vast amount of information available on the Internet to establish a dependable theoretical foundation for their decision-making processes. Because of the Internet, businesses can use it to capture a variety of business data, gather detailed information about customer behavior, quantify the work that goes into enterprise performance assessments, and increase the accuracy of the data used in business decision-making. However, as society has developed, consumer quirks have changed significantly [
1,
4].
Products from the company are cut and rearranged in accordance with current trends in development and customer needs, Recent advances in big data and cloud computing, as well as the advancement of chip technologies like Microprocessor & the university, have all contributed to the explosive growth of artificial intelligence technology. Artificial Intelligence technology will be expanded in the field of enterprise company management in the future, that will finally make company business management more adaptable. This will help enterprise business management better adapt to the requirements of future development. Furthermore, in this overall context, the integration of AI and corporate business management will showcase additional features that cater to demand rather than just highlighting the interplay between different kinds of financial data, not just to enhance transaction efficiency but also to lower operating costs by concentrating on the customer's product experience [
4,
5].
Figure 1.
AI with business management.
Figure 1.
AI with business management.
Considering future development, the advancement of artificial intelligence enables company business management services and goods to become even more intimately connected to the user scene, comprehending user needs and continuously introducing workable solutions to satisfy the needs of various users rather than just a technical product. This allows for the achievement of a major technological breakthrough, as the majority of company business management products have consistent quality specifications and stable commodity prices. As a result, the function that artificial intelligence at this time is primarily reflected in the personal operation of the operation, On the other hand, corporate business management is primarily focused on service quality, which allows artificial intelligence technology to have more room to grow and become the dominant trend in the future. This paper examines the state of business management advancement in Asia and suggests using artificial intelligence and big data technologies in enterprise business management. It also suggests a new model that will open up new avenues for company business management development [
2,
5].
Figure 2.
the purpose and elements of the organization's business management process.
Figure 2.
the purpose and elements of the organization's business management process.
2. Aim of the Study
By fusing AI technology with business leadership, we aim to further deepen the comprehension of AI by relevant personnel by focusing on analyzing the application path of AI innovation to business management and, finally, clarifying the future expansion direction of AI technological advances in business management. Our goal is to increase our comprehension of AI technology [
5,
6].
This paper analyzes the state of company and enterprise managerial growth today and suggests applying artificial intelligence and big data technologies to enterprise management tasks. It also suggests a new model that will introduce new development possibilities as well as developments to the field of enterprise management.
2.1. Benefits and Benefits of AI Technologies in Managing the Business of Large Companies
The way organizations run has been completely transformed by artificial intelligence (AI), especially when it comes to handling enormous volumes of data. Businesses can gain a great deal by utilizing AI technology, which improve productivity, judgment, and general performance [
7] . The following are some of the main advantages of AI for firms managing massive data:
Improved insights and analysis of data.
Effectiveness of Operations.
Tailored Client Experience.
Security and Fraud Detection.
Management of Human Resources.
Lowering Expenses.
Product Development and Creativity.
2.2. The Proposed Method
A modern computer network and other technologies are used to gather, organize, and store all types of data produced in the day-to-day management and operation of businesses. This information is then used as a reference basis for preparing and selection of multiple business management tasks and related decision-making programs. This is known as an enterprise management information system.
Although each enterprise has its own unique set of business processes, the development of a company management information system must begin with the business processes within the enterprise. For production enterprises, these processes include product development, sourcing materials, processing production, and other related activities [
8,
7]. Establishing a management information system via an examination of the organization's entire business process is crucial since enterprise management encompasses material management, manufacturing control, and various additional management facets. The relentless growth of the social economy has made enterprise competition increasingly intense; Businesses focus more on the close relationships they have with their clients; it's critical to improve these interactions and interactions as well as sustain positive client relations. In order to improve corporate decision-making management, businesses must simultaneously adapt their modes of operation and perform thorough analyses of pertinent management information and statistics in light of the expanding e-commerce industry. As a result, in order to satisfy the corporate management requirements, several management jobs, such customer management, must be taken into consideration when building the management data system platform [
9,
10].
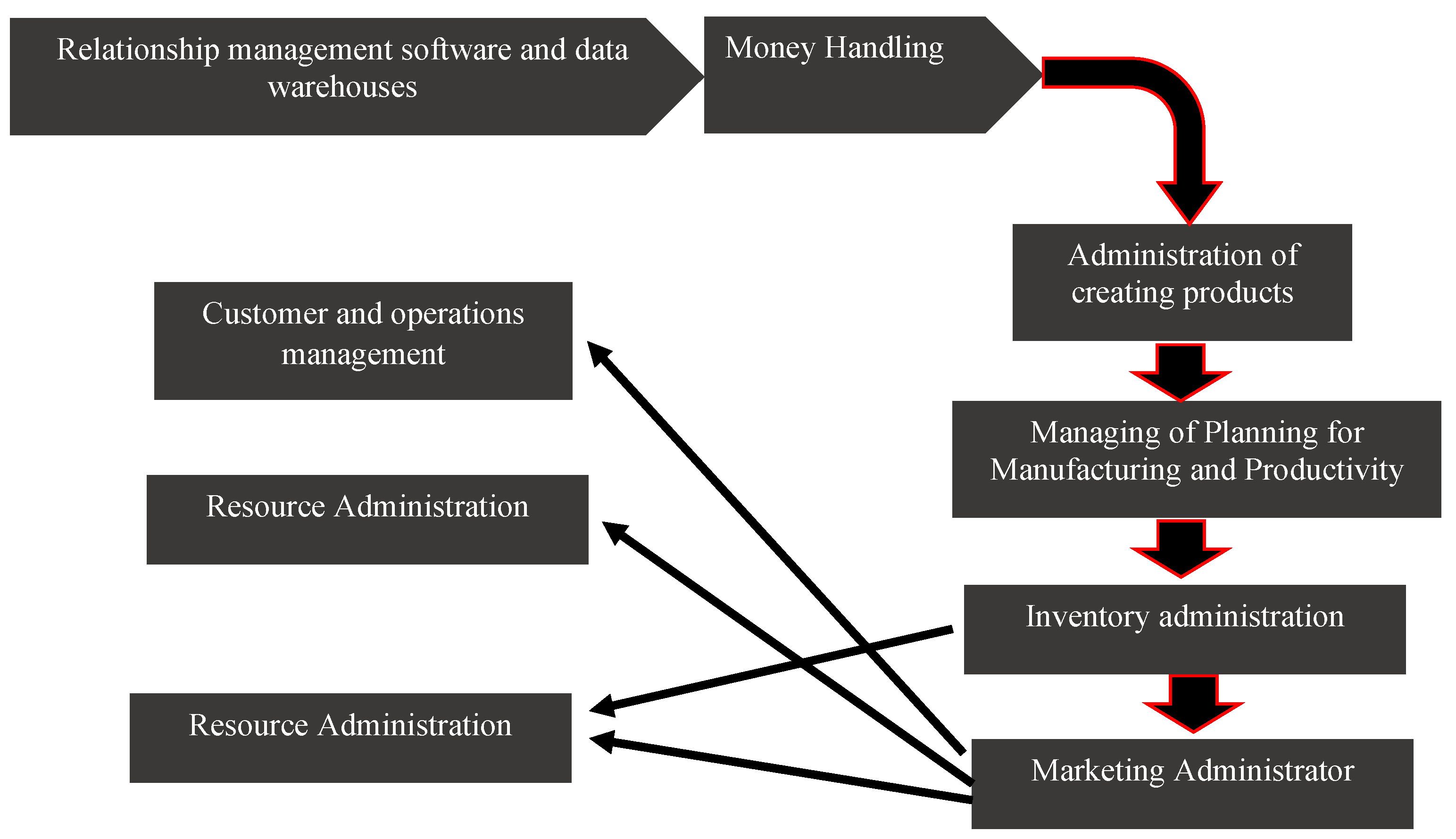
Figure 3.
Diagrammatic representation of the construction model.
Figure 3.
Diagrammatic representation of the construction model.
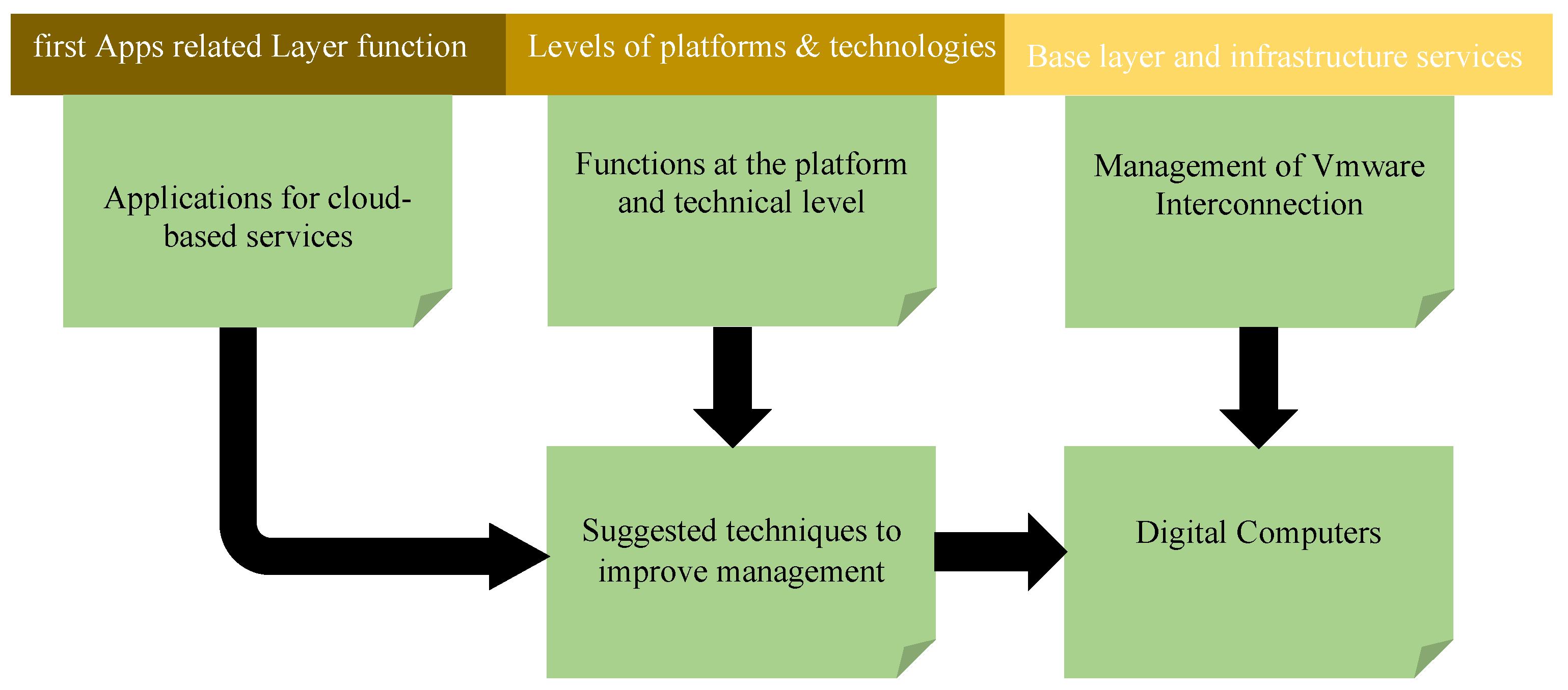
Cloud computing is a network-based service that uses hardware and software to give consumers access to the internet. Its capacity to share resources and grow dynamically defines it. In online computing systems, virtualization is a crucial technology that makes it possible to virtualize different IT resources. Platform, application, and infrastructure layers are all part of the platform layer [
11]. A data center and the virtualization of system resources are prerequisites for the infrastructure equipment layer, which uses virtual technology to virtualize hardware resources. This makes it possible to use resources more effectively and cut expenses [
12].
Computer and API code libraries are among the settings for app creation and testing that users can access through the platform layer. Applications such as inventory control systems and financial control systems that are operating on the platform are included in the application layer. To identify which apps are appropriate for computing services in the cloud and cloud migration, the management database must be integrated with business information management requirements and application load, The application layer, base layer assistance, and service layer services make up the suggested cloud computing model. Internal resources must be integrated with the enterprise's unique circumstances, application load specifications, virtual solutions, business models, scientific deployment, and security settings in order to create a comprehensive cloud computing platform. Users should be able to customize their operating environment at the platform layer, and for a complete management solution, software applications should be moved to the application layer [
10,
13].
Figure 4.
Business company leadership and massive amounts of data.
Figure 4.
Business company leadership and massive amounts of data.
2.2. Our Algorithm
Determining the degree of mistake in enterprise business management accounting information is essential to achieving error correction of such data. Consequently, the neural network-based correction of mistakes of corporate company management accounting data is proposed in this research [
14]. Let us assume that the data set for enterprise business management accountancy is configured as: w=T
where n is the total amount of accounting data points in the data set and W is the composition factor. The accounting and financial accounting data detection set's +e error X is stated as:
where u stands for the detection factor for accounting data. Decompose W and obtain prior to the accounting and financial accounting data mistake detection [
12].
where Q denotes the expected value and H on the lower triangular matrix. Determine W's variance matrix. The expected value is defined as:
The expression for the decomposition of singular of wc into the final individual values and the initial m-v singular values is:
where v indicates the number of rows in the constraint matrix, G indicates the orthogonal outputting basis vector, and Z represents the diagonal input basis vector made up of W columns [
15]. The value of v determined by the computation above is +e, or the number of minimal eigenvalues close to 1. The data set's +e error result can be found as:
Convolutional neural networks are used to identify correlations between data, errors, and data and errors after the data errors have been obtained. The associations between data are then utilized as a foundation for rectifying the data mistakes [
16,
17].
The following is the mathematical description of formula for factor correlation analysis using the chi square test:
where f0 ij is the observation frequency and fe ij is the intended frequency, and r is the number of rows and c is the number of cells in the contingency table.) The following formula can be used to determine the predicted frequency of fe:
The total of line inspection frequencies is represented by RT, whereas the sum of column observation frequencies is represented by CT [
18].
Based on the chi square statistics derived from the aforementioned formulas, it is evident that in cases where the observed frequency and the expected frequency coincide, the least chi square statistic is zero. This suggests that the two variables are entirely uncorrelated and independent of each other. The greater the difference between the observed and expected frequencies, the greater degree of correlation and the larger a chi square statistic that can be produced [
19].
Convolutional neural networks are used to build the data classification model based on the errors in the financial accounting data that were identified previously. The financial accounting data is then used as the model's input quantity, and feature vector analysis of the data is used to ascertain the relationship between the variables in the financial accounting data, The layer that pools features and the convolutional portion in the model are primarily in charge of processing the financial accounting data, and the specificity of the data relationship is taken into account when redesigning the connection between the two layers. Assume that the model's input of financial accounting data is DA, where a represents the data's i-th sequence. Use Ai to represent the series sequence matrix AI. Then, convolutionally operate the data to produce another vector, p, which is represented as:
where K represents the convolution layer's weight matrix and 1≤j≤|DA| − k + 1. The convolution process of the financial accounting data is defined as follows: filters are used to capture the various aspects of the input data and where 1≤i≤n. Convolution of the model's layers yields +e matrix P Ϗ̈p1, p2,..., pn [
21]. Pooling layer treatment is used to obtain the vector that is being segmented after +e matrix P is divided into three parts, pi. {{ΔL=Δ_s L+Δ_o L.}} yb=L
By calculating the dot product, the +e category label equivalent to data DA is found. The class vector of that group label is then found and merged into the category matrix TA. It is possible to ascertain the inter-data link based on each data type. The repair of the data error is realized if the data error and the relationship of the data are understood. Error correction for enterprise financial data is put into practice. The aforementioned study indicates that the error of financial accounting data is calculated as the total of accounting error and random error: η_ij=max(p_(i.j) ).
2.3. The Results
The targeted organizations' regional business database provided the data for the sample under study, which has a 20-year time series. There are 83 indicators in the data, comprising 31 industrial or macro indicators, 50 finance indicators, and one preset indicator. The 3050 customers in the data sample consist of 3000 good customers and 60 poor customers, in this investigation, no pertinent metric evaluation was carried out. First, the neural network that can successfully avoid the effects of strong indicator correlation because of its features of weight sharing and local connectivity; Second, make sure the input data meets the size requirements; Third, the rationale is that the purpose of this study is not to examine indicators.
Table 1 displays the sample allocation of information table [
19].
First is to standardize the initial data. To create the standardized data set, the raw data of small companies that were taken out of the database were standardized. Standardized processing is not covered in detail because it is not the study's main emphasis [
20].
Unbalanced sample processing is step two. The imbalanced sample processing procedure in this work is carried out via a MATLAB r2015a software. The smote method is used to create new defaulted samples from the defaulted samples, bringing the overall number of refused and no defaulted samples to a ratio of a one to one.
The complete sample N is split into training population N1 and test example N2 at random for this article. The test group ratio is split into seven and three among them.
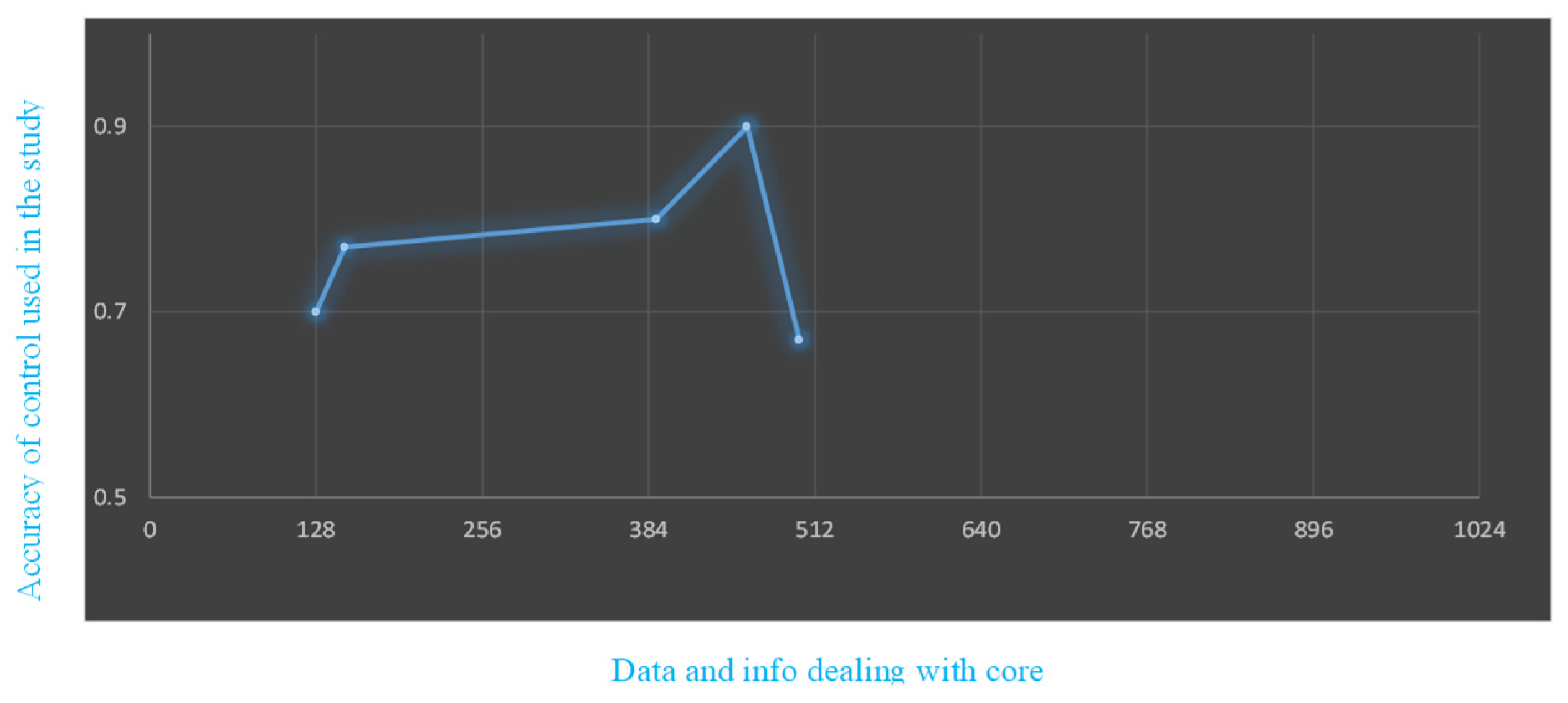
Figure 5.
Impact of multilayer core 2 level on training set prejudiced accuracy.
Figure 5.
Impact of multilayer core 2 level on training set prejudiced accuracy.
The whole sample N is split into learning sample N1 and assessment sample N2 at random for this paper [
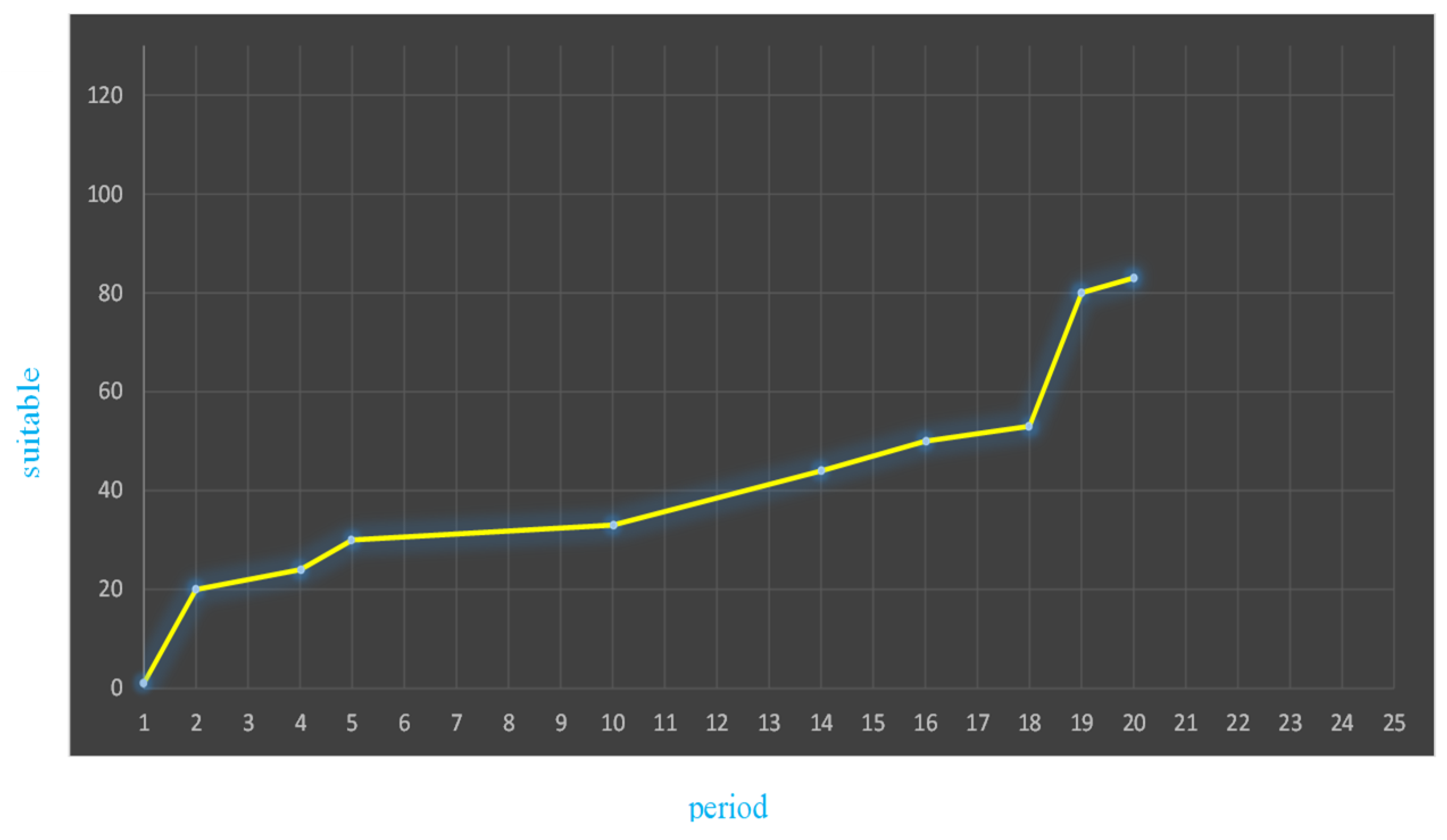
21]. The test set's ratio is split between them into seven: three. By contrasting Table 2's neural networks and models with more conventional approaches, we may as can be observed, the S-VM models developed in this study have substantially higher accuracy values for G-mean, Type mistakes, B-M, M-K, AI, and AUC compared to four standard default descriptor models—SVM, NB, and LDA.
Figure 6.
The suggested slope chart for enhancing success.
Figure 6.
The suggested slope chart for enhancing success.
3. Conclusion
To summaries, the advancement of computer technology has led to the emergence of Internet, Internet of Things, cloud computing, and big data technologies. These technologies have tremendously boosted modern business company management work and have the potential to significantly alter the management concept of large, modern enterprises. They can also improve business organizational operations, optimize enterprise marketing decision-making, integrate consumer behaviors production mode, and improve the bluntness and intuitiveness of company’s business operations.
It has the power to significantly alter the way large corporations think about management, improve the way industry organizations conduct business, maximize their marketing strategies, incorporate consumer behavior into production, improve the directness and understanding of corporate administration, and support the growth and reform of the market economy. The use of cloud computing architecture-based enterprise business management systems can address more than just the drawbacks of conventional enterprise business management systems, but also support the management system's reliability and timeliness, increase troubleshooting effectiveness, and improve the system's overall performance. As such, it makes sense to use and promote the system in corporate business management. In order to completely enhance the firm business management system's overall performance and guarantee that the system can operate more effectively, staff members should enhance the system design, execute excellent system debugging, and bolster system testing and maintenance, we intend to carry out research on neural networks with recurrent neurons and knowledge graphs in the future to investigate the importance of massive data and intelligent techniques for enterprise business management.
References
- Y. Wang, Y. Shi, M. Cai, and W. Xu, “Predictive control of air-fuel ratio in aircraft engine on fuel-powered unmanned aerial vehicle using fuzzy-RBF neural network,” J Franklin Inst, vol. 357, no. 13, pp. 8342–8363, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Mishina, S. Sato, Y. Yoshida, D. Hisano, and A. Maruta, “Eigenvalue-Domain Neural Network Demodulator for Eigenvalue-Modulated Signal,” Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 39, no. 13, pp. 4307–4317, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Kumar, M. W. A. Talib, S. Srivastava, and R. Iqbal, “Network modelling and computation of quickest path for service-level agreements using bi-objective optimization,” Int J Distrib Sens Netw, vol. 15, no. 10, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Pradeep Raj, P. Manimegalai, P. Ajay, and J. Amose, “Lipid Data Acquisition for devices Treatment of Coronary Diseases Health stuff on the Internet of Medical Things,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing Ltd, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Jianbo and X. Cao, “Factors Affecting the Evolution of Advanced Manufacturing Innovation Networks Based on Cloud Computing and Multiagent Simulation,” Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2021. Hindawi Limited, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Bashir, M. M. Naqshbandi, and R. Farooq, “Business model innovation: a systematic review and future research directions,” International Journal of Innovation Science, vol. 12, no. 4. Emerald Group Holdings Ltd., pp. 457–476, Dec. 04, 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Pan, C. Han, M. Song, and M. Wang, “The Impact of Information Technology Investment on the Performance of Apparel Manufacturing Enterprises: Based on the Moderating Effect of Equity Concentration,” IEEE Trans Eng Manag, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 1365–1373, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Lindgren, “Multi Business Model Innovation in a World of Smart Cities with Future Wireless Technologies,” Wirel Pers Commun, vol. 113, no. 3, pp. 1423–1435, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. V. Surkova and Y. A. Mazhaiskii, “Assessing the Financial Performance of Aviation Enterprises,” Russian Engineering Research, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 983–986, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Lin, “Financial Performance Management System and Wireless Sharing Network Optimization of Listed Enterprises under BPNN,” Mobile Information Systems, vol. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Vlahovic, A. Brljak, and M. Pejic-Bach, “Ontology-Based Analysis of Website Structure for Benchmarking in Retail Business,” International Journal of Web Portals, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–19, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Kamalraj, S. Neelakandan, M. Ranjith Kumar, V. Chandra Shekhar Rao, R. Anand, and H. Singh, “Interpretable filter based convolutional neural network (IF-CNN) for glucose prediction and classification using PD-SS algorithm,” Measurement (Lond), vol. 183, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Jain, A. Khunteta, and S. Srivastava, “Churn Prediction in Telecommunication using Logistic Regression and Logit Boost,” in Procedia Computer Science, Elsevier B.V., 2020, pp. 101–112. [CrossRef]
- T. Xu, Y. Ma, and K. Kim, “Telecom churn prediction system based on ensemble learning using feature grouping,” Applied Sciences (Switzerland), vol. 11, no. 11, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- De Caigny, K. Coussement, K. W. De Bock, and S. Lessmann, “Incorporating textual information in customer churn prediction models based on a convolutional neural network,” Int J Forecast, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 1563–1578, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Al-Mashraie, S. H. Chung, and H. W. Jeon, “Customer switching behavior analysis in the telecommunication industry via push-pull-mooring framework: A machine learning approach,” Comput Ind Eng, vol. 144, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. P. D. Cyril, J. R. Beulah, N. Subramani, P. Mohan, A. Harshavardhan, and D. Sivabalaselvamani, “An automated learning model for sentiment analysis and data classification of Twitter data using balanced CA-SVM,” , vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 386–395, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Singh et al., “Artificial intelligence based quality of transmission predictive model for cognitive optical networks,” Optik (Stuttg), vol. 257, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Sreekala, C. P. D. Cyril, S. Neelakandan, S. Chandrasekaran, R. Walia, and E. O. Martinson, “Capsule Network-Based Deep Transfer Learning Model for Face Recognition,” Wirel Commun Mob Comput, vol. 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Neelakandan, D. Paulraj, P. Ezhumalai, and M. Prakash, “A Deep Learning Modified Neural Network(DLMNN) based proficient sentiment analysis technique on Twitter data,” Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 415–434, 2024. [CrossRef]
- B. N. M. K. and K. . M. F. L. M. Akimova, “Formation Of the System of Financial-Information Support of Environmentally-Oriented Management of The Enterprise,” 2020. Accessed: May 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://eds.p.ebscohost.com/eds/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=0&sid=f0d811f4-4bcb-49ec-a9c8-a51a75b8cc94%40redis.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).