1. Introduction
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) positioning, known for providing absolute positioning information, holds a pivotal role in navigation [
1]. With the ongoing evolution of technologies like unmanned driving and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), GNSS has found integration into numerous navigation systems, either as a core module or a vital data source. Despite typically receiving signals from more than four satellites in most scenarios, urban environments pose challenges due to obstructions or non-line-of-sight factors, resulting in positioning errors of tens of meters [
2]. This issue arises because researchers frequently employ outlier detection methods to eliminate specific satellite pseudorange, inadvertently increasing the risk of inadequate satellite availability.
Furthermore, considering the continuity of satellite reception data across epochs, can leveraging information from previous historical epochs enhance state estimation accuracy? In scenarios where pseudorange information is unavailable, at the current epoch, is it possible to establish a virtual constrain? And let this virtual constraint serves to fortify the integrity of the graph optimization model?
In the previous data processing approaches, Kalman filtering stands as a cornerstone in state estimation both in the GNSS positioning or GNSS/IMU integration system. In a straightforward GNSS model, its state prediction equation relies on recursive assumptions from the previous epoch. For instance, in surveying applications, it assumes constancy in the positions of measurement points, while for mobile carriers, it commonly adopts either a constant velocity model or dead reckoning assumptions [
3]. Filtering incorporates historical prior information encapsulated within the previous epoch's state, which is subsequently propagated to the current epoch through the aforementioned assumption models' state transition equation. By amalgamating this prior knowledge with present measurement information, an optimal estimation outcome is achieved [
4,
5]. However, due to uncertainties in practical applications, recent data processing methods have been leaning towards optimization theory, especially graph optimization theory (FGO).
Filtering theory confronts the challenge of diminished estimation performance stemming from the inclusion of interfered measurement data [
6]. For example, during the current epoch, certain measurement information may be tainted by interference, rendering it inaccurately detected or identified [
7]. Consequently, the estimated value for that epoch will display notable bias, and the state transition equation will indiscriminately propagate this flawed information to subsequent epochs. Typically, a substantial number of measurement epochs are requisite to alleviate or eradicate this detrimental influence.
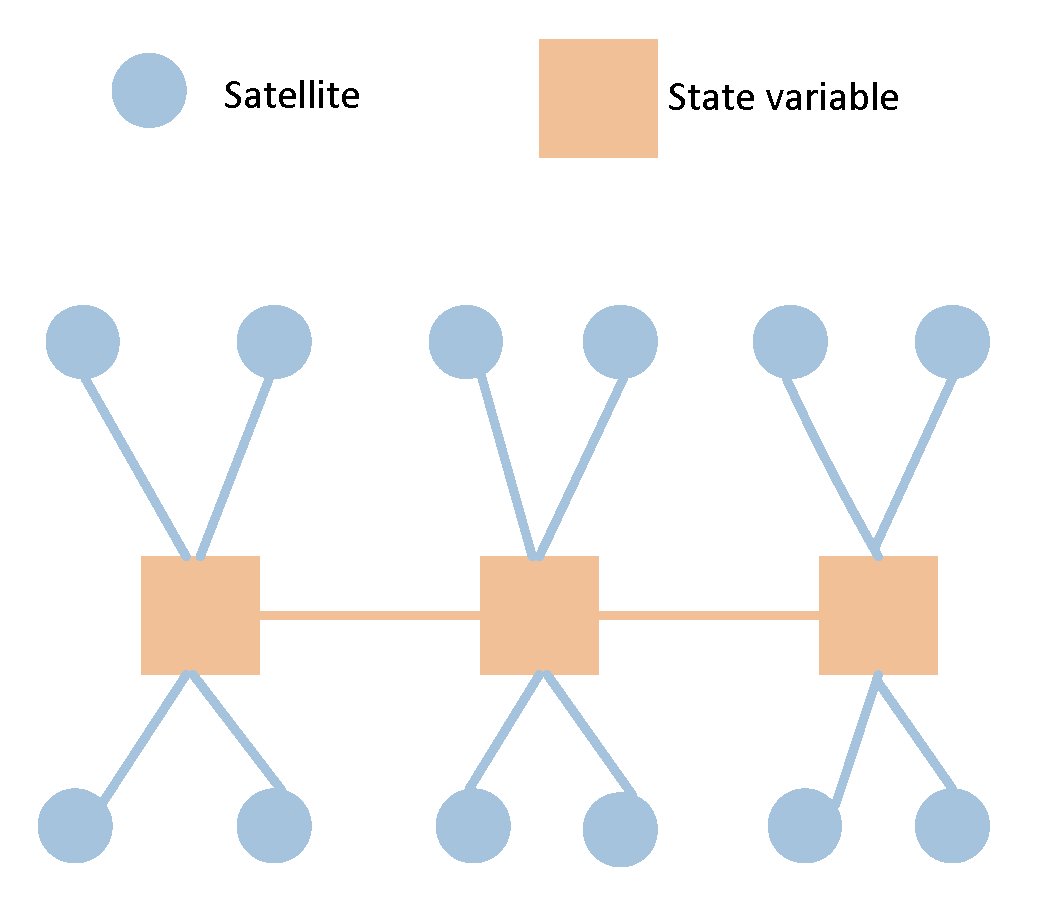
In contrast, within graph optimization models, an interfered measurement represents merely one edge among a multitude of constraints within the model. Its effect on the overall state is constrained, and the duration of its influence frequently depends on the extent of the optimization window. This concept is elucidated in
Figure 1.
In recent years, there are many cases of applying FGO technology to GNSS positioning and navigation field. A multi-sensor fusion graph optimization model based on GNSS, INS, and LiDAR has been proposed and compared with Google's Cartographer [
8]. Results from land vehicle tests demonstrate significant enhancements over traditional GNSS/INS methods. Additionally, the graph optimization model has been consistently compared with the Kalman filter method[
9], highlighting the robust estimation through multiple iterations and better exploration of time correlation between measurements and states.In the field of real-time kinematic (RTK), the superiority of the graph optimization method has also been demonstrated[
10]. By effectively utilizing pseudorange, carrier-phase, and Doppler measurements, this method improves positioning accuracy compared to filtering-based estimators. In the realm of real-time data processing and 3D mapping, the graph optimization method has been proven to significantly reduce errors. Evaluations in Hong Kong urban areas demonstrate substantial error reduction using this approach[
11]. To address the degradation of GNSS signals caused by the urban canyon effect, the use of factor graphs and robust optimization techniques for GNSS data processing is investigated [
12]. Additionally, the open-source library GTSAM is utilized to accelerate the solution process, significantly enhancing the practical applicability of the graph optimization method. Additionally, the factor graph optimization method has demonstrated high reliability in addressing outlier issues caused by multipath effects and NLOS scenarios[
13,
14]. In real-time vehicle positioning and mapping scenarios [
15], the graph optimization method has achieved promising results by integrating information from different sensors.
Based on a review of pioneering work, an initial summary can be derived: no matter in the FGO model of GNSS/IMU —where nodes are constrained by IMU[
16], or a single satellite positioning model—where nodes are constrained by constant velocity[
17], the pseudorange measurements act as edges on single epoch nodes. By adjusting the receiver's positions along the trajectory, it is possible to minimize the overall pseudorange measurement errors, given that satellite positions remain fixed. This raises a pertinent question: can a satellite's position at a specific moment be observed by multiple pose points, thereby allowing poses to reuse satellite position information? Motivated by this inquiry, this paper explores a graph optimization method for constructing constraints using virtual pseudoranges, i.e., a virtual constraint in FGO. The contributions are primarily in three areas:
A method for establishing virtual pseudorange constraints is proposed, and a corresponding FGO model is developed to support this approach.
A comparative analysis between the proposed model and GNSS/IMU and SLAM models is conducted. Additionally, the differences in the marginalization processes among these models are analyzed.
Utilizing real-world GNSS/IMU data, pseudoranges are artificially replaced with the virtual constraint created using the proposed method. The results from this method are then compared against the original FGO results to demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the model.
2. Methodology
2.1. Virtual Jconstraints Establishment from Pesudorange
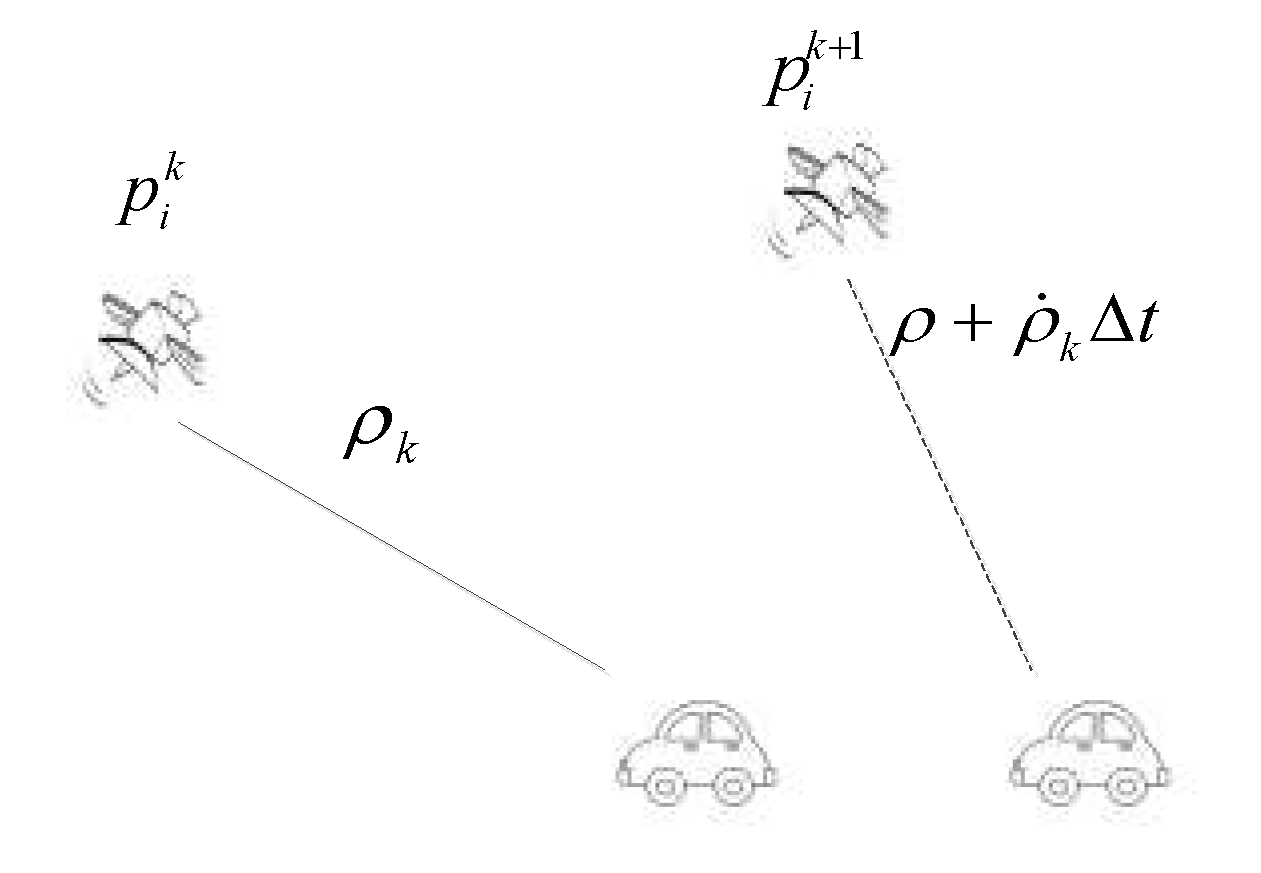
The pseudorange measurement constraints for satellites are all based on the current epoch. Indeed, since satellites are in motion, there wouldn't exist two pseudorange measurements from different epochs targeting the same satellite position, resulting in two measurement constraints. Considering two consecutive epochs with a time interval of Δt, during the first epoch, a suite of data comprising the satellite's position, pseudorange, and pseudorange rate is acquired. Consequently, it is presumed that the satellite's position at the second epoch can be extrapolated based on the elapsed time interval, which is a strong assumption. The design process of this section is illustrated in
Figure 2.
The pseudorange can be expressed as:
The is pseudoraange of satellite i, the is position of satellite i during signal transmission, the is position of the receiver during signal reception, the is clock difference of the receiver, and the is cumulative errors of this satellite are all factors to consider.
While the pseudorange can be expressed as:
and are the velocities of the i-th satellite and receiver, respectively, expressed in ECEF coordinate system. indicates receiver clock drift. is the set of all errors.
In dynamic environments, the variation in pseudorange rates may become more pronounced. Hence, persisting with the utilization of the pseudorange rate from the preceding epoch at the subsequent epoch constitutes a week assumption. Nonetheless, owing to the typically modest time interval between two epochs and the constrained displacement of the carrier during this period, we deem this assumption to remain reasonable. It’s shown in
Figure 3.
Most significantly, when the number of satellites is inadequate, the satellite constraint equations for each pose point are insufficiently constrained. In such scenarios, it is usually to replace an unknown variable with constant value, in most case it’s the clock bias, by referencing the clock bias value from the preceding epoch. Despite the clock bias being relatively stable, it exerts influence on all pseudorange measurements during that epoch. Hence, the virtual constraints play a pivotal role in resolving a full-rank constraint problem.
For the same satellite, the subsequent pseudorange approximation can be derived from the previous pseudorange at time ttt and its rate, as shown in equation 3.
The variable k represents the current time, while denotes the duration required to transition from time k to time k+1.
2.2. Graph Model Construction with Virtual Constraints
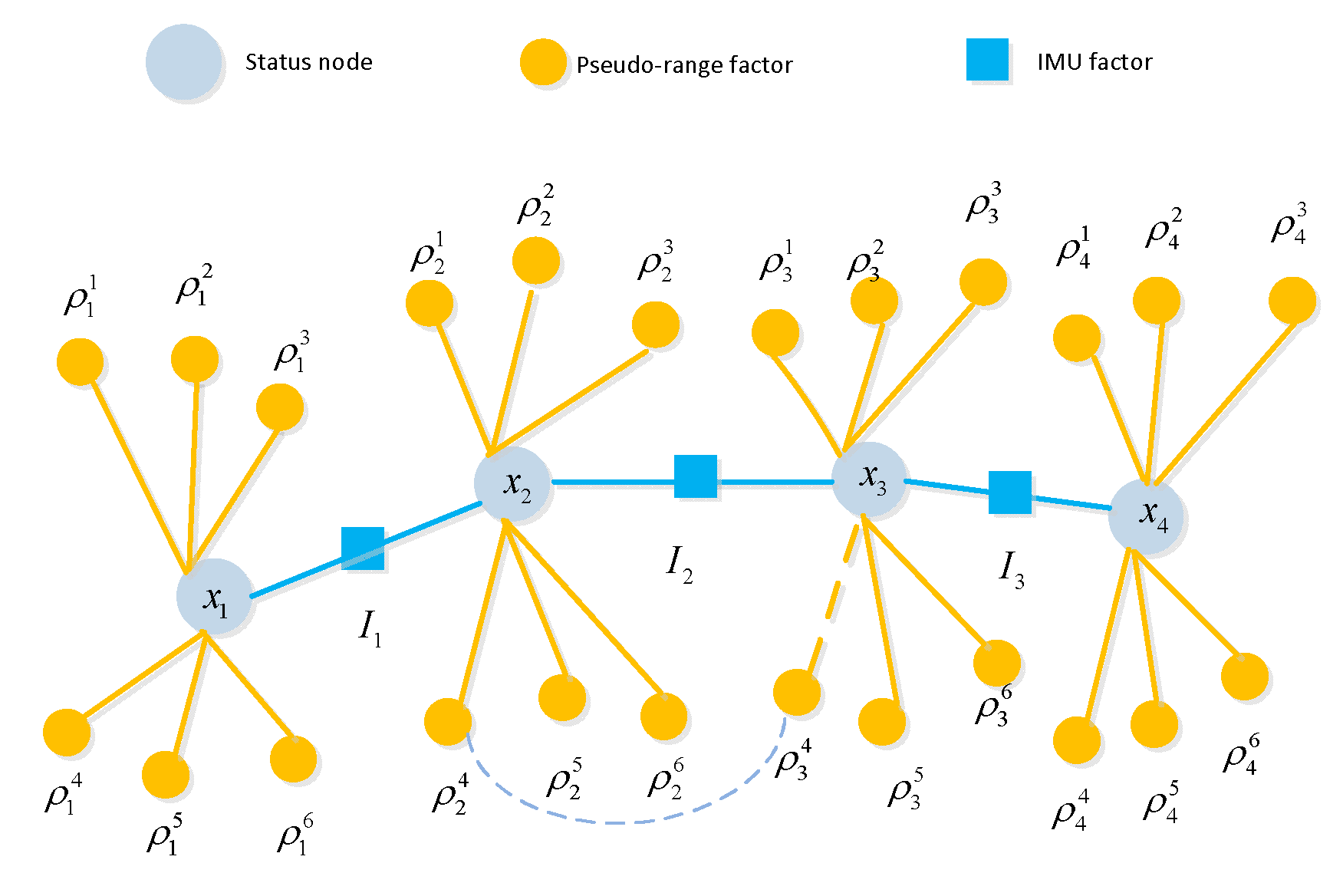
A complete GNSS/IMU graph optimization model consists IMU factors, pseudorange factors, and the state (position) of the carrier, which can be depicted in
Figure 4. The IMU factors accomplish motion constraint measurements between two adjacent nodes of the carrier, while the pseudorange factors provide absolute measurement constraints on the carrier's position at a given moment.
2.2.1. IMU Factor
Without considering the influence of the Earth's angular velocity due to its rotation, maintaining a constant value for gravity, and employing a prediction-error modeling approach, the following conclusions can be drawn. The IMU measurements between two adjacent measurement frames are fused into a constraint, ensuring alignment between the processed IMU information and GNSS data. The angular velocity and acceleration measurement model of the IMU is as follows:
Where
and
are respectively measured values and real values in the carrier coordinate system,
represents the gyroscope noise,
represents the zero bias of the gyroscope;
represents the acceleration in the carrier coordinate system, and
is the state transition matrix.
represents the true value of acceleration,
is the weight vector;
represents the zero bias of acceleration and
represents the noise of acceleration. The differential equation of IMU kinematics can be obtained as follows:
Its discrete form is derived from Euler integral:
Substitute equation (7) to (8), it obtains:
Where
and
represent discrete forms of noise. The simplified kinematic equation of the state quantity of the IMU measurement model from
to
is as follows:
Where,
indicates the interval between two consecutive IMU data moments:
The state at time
, can be deduced from
as
Where,
and
represents the state value and measurement value at the moment
,
represents the deviation of the inertial device;
represents a simplified map function of equation 7. Then the error function of IMU can be expressed as follow equation , and
is the IMU covariance matrix:
This is the pre-integration factor of the IMU, which represents the spatial position constraints between two adjacent states. It includes the angular deviations between the two states, which ultimately manifest as spatial displacement between them. This spatial displacement is indirectly related to the pseudorange measurements.
2.2.2. GNSS Pseudorange Factor
The GNSS receiver receives signals from multiple satellites at a given epoch,
is the receiver's current position under the ECEF system, and
is the satellite's position in the ECEF coordinate system. Then its GNSS factor can be expressed as:
Then the error equation of GNSS can be obtained from the given satellite measurement[
18]:
In the equation 10, represents the pseudorange result calculated based on the estimated position of the carrier and the satellite's position, while represents the instantaneous pseudorange information calculated using the receiver's measurements, ephemeris data, and receiver clock bias. The virtual constraint is still established using the clock bias at the current epoch, whereas the satellite position and measurement data are extrapolated from the information of the preceding epoch.
3.1.3. Graph Model Analysis Akin to SLAM Model
In this section, the proposed graph model will be analyzed in comparison with the traditional graph models used in SLAM. The reason for this lies in the numerous similarities between the newly constructed graph model and those in SLAM, despite certain differences. And graph models were first extensively researched and applied in the field of SLAM, including derivative libraries such as iSAM[
19] and GTSAM[
20]. Consequently, the subsequent solution and processing procedures can leverage some of the operations utilized in SLAM.
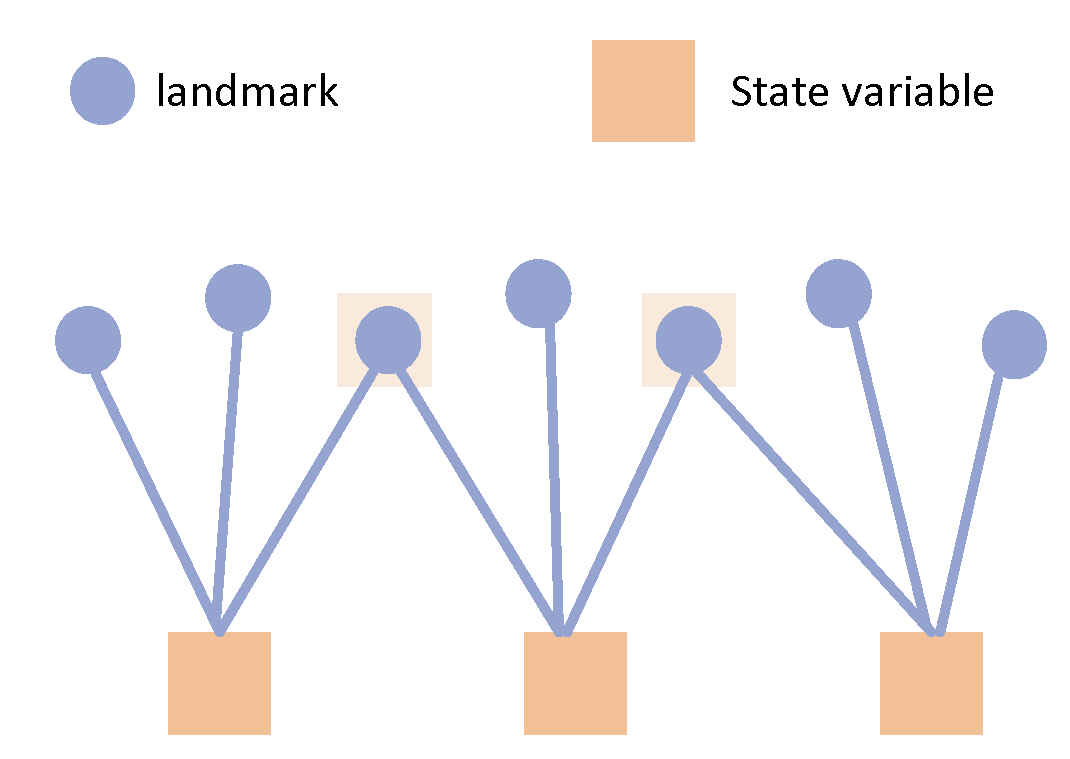
First of all, in the SLAM diagram, landmarks are variables to be estimated, meaning their poses are not fixed. In contrast, in the typical GNSS/IMU diagram model, the positions of the satellites are fixed. However, it is important to note that there is a clock bias variable among the estimation variables. Due to the introduction of this unknown variable, the entire process can be likened to the positional uncertainty of the satellite, but this uncertainty is transmitted to the carrier as a clock bias. The clock bias is also compensated by multiplying it by the speed of light to obtain the pseudorange. In other words, due to the relativity of motion, although the satellite positions are fixed, considering the existence of the clock bias variable, the satellite positions in the graph model serve a role very similar to that of landmarks in the SLAM graph model.
Unlike the SLAM model, where the carrier can freely adjust the distance between itself and each observed landmark—such that landmark1 can be adjusted by 0.1 meters and landmark2 by 0.2 meters—in the GNSS/IMU graph model, the clock bias affects the distance to each satellite equally at a given moment. Thus, when the value of the clock bias is estimated, its conversion to distance will be equivalent applied for each pseudorange at one time epoch.
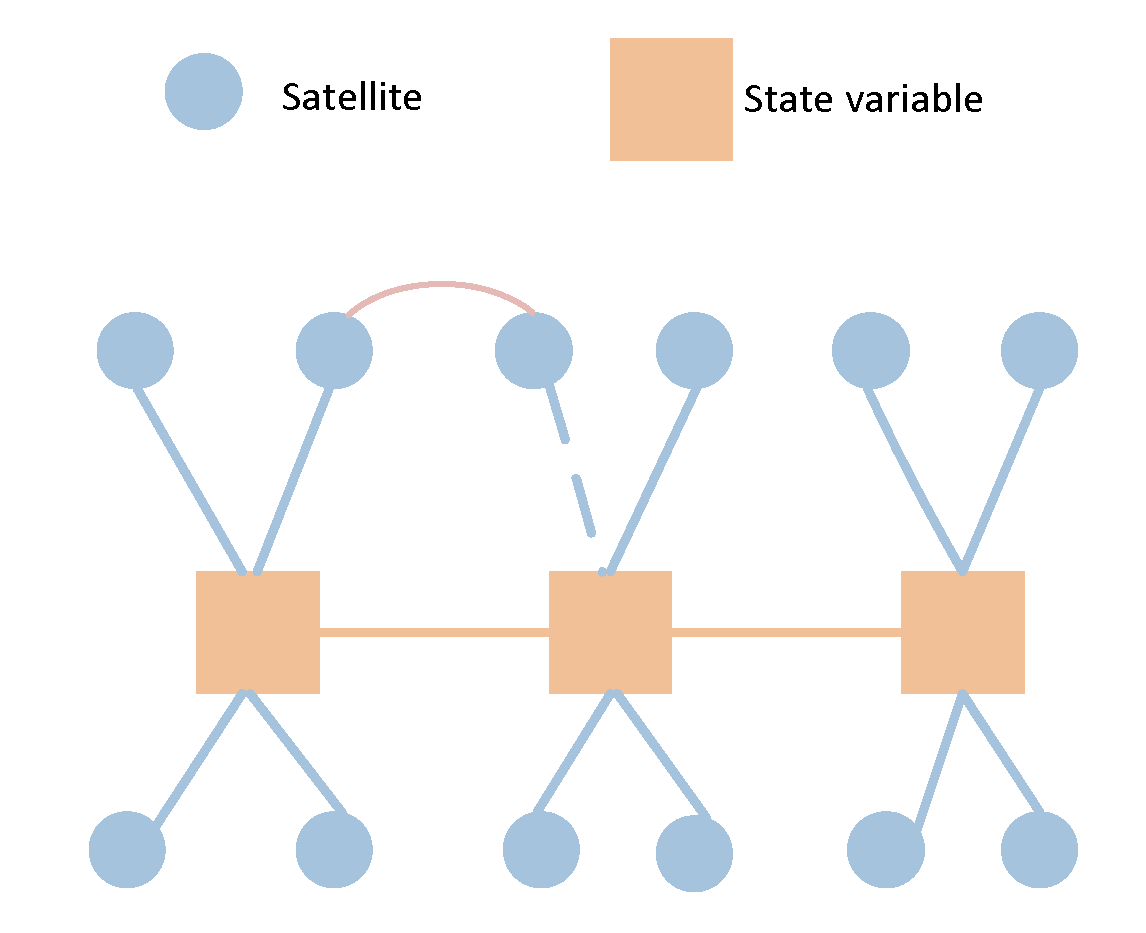
In the SLAM graph, a landmark can be observed by multiple nodes, i.e., observed multiple times. However, in the GNSS/IMU model, the satellite position data observed at one moment is not utilized by another moment, hence there is no co-observation relationship. The model proposed in this paper differs from the traditional GNSS/IMU graph optimization model. In the traditional model, the pose of the carrier at any given moment and its associated satellites are independent, meaning they are only associated with that specific moment and not with satellites from other moments. However, in the model proposed in this paper, virtual satellite positions are derived from previous moments. Therefore, when constructing such virtual constraints, there is a mapping association between one satellite (with the same PRN) at different times. Consequently, there exists a factor between these two satellite nodes, as illustrated in
Figure 4, with dash line connection. Once the virtual constrain between current and previous satellite poses is build, there will be a correlation in the information matrix, unlike SLAM model, where the landmarks are independent, with the part corresponding to landmarks in the matrix maintains a sparse diagonal characteristic.
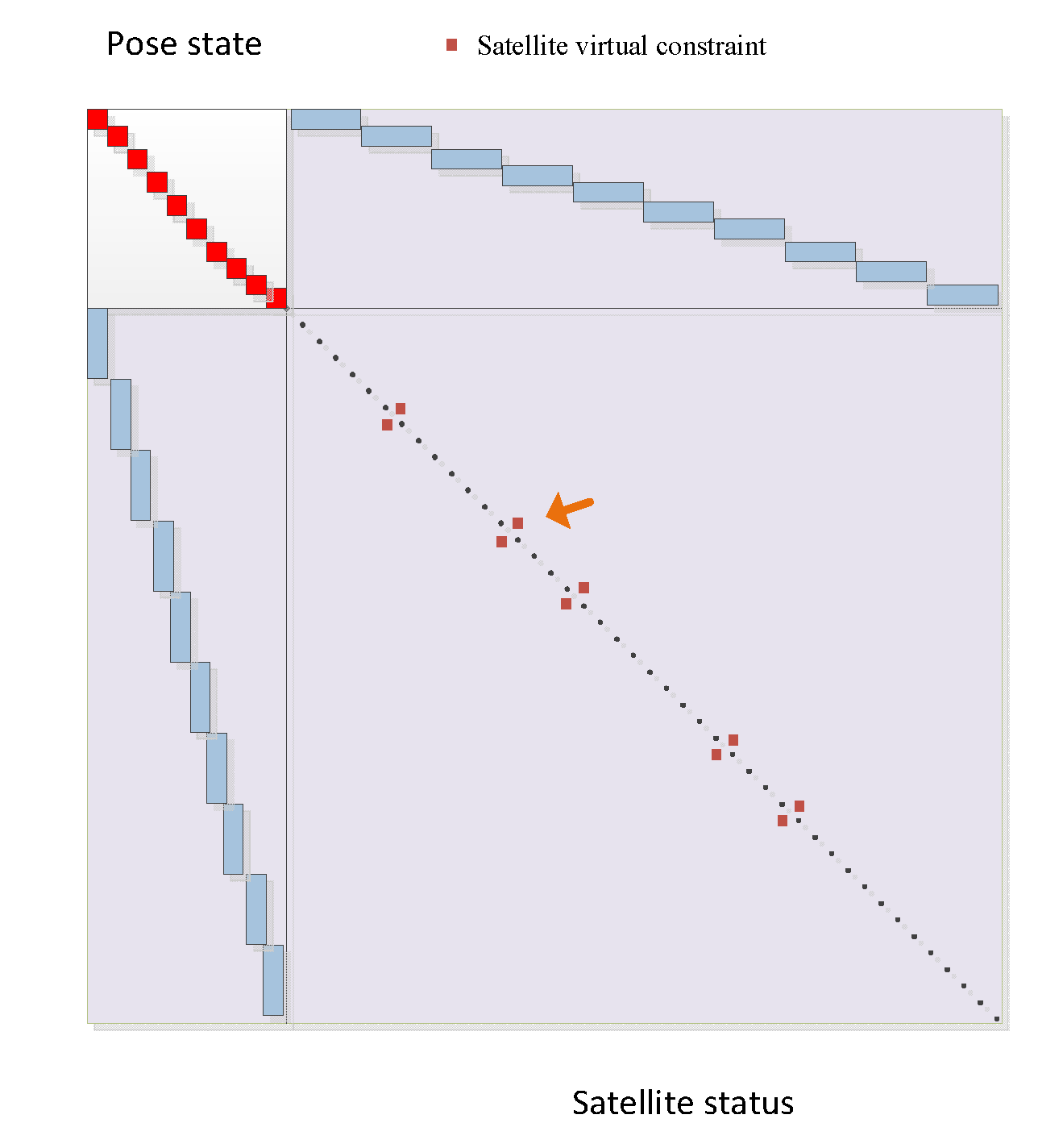
If the structure of the SLAM information matrix is analogized, treating the satellite positions at different times with different PRN as independent node variables and placing them uniformly on the right side of the information matrix, there will be an association between the same satellite at different times. Consequently, this part of the matrix will no longer be purely diagonal, as shown in
Figure 5.
2.2.3. Marginalization
The marginalization process in traditional GNSS graph models is quite straightforward. The satellite is isolated because the pseudorange from satellites is observed only at one state, and not observed in other states as shown in
Figure 5. So if a state is prepared to be removed from the sliding window filter (SWF), it can be discarded directly without affecting the other states in the win6dow, as this state is isolated.
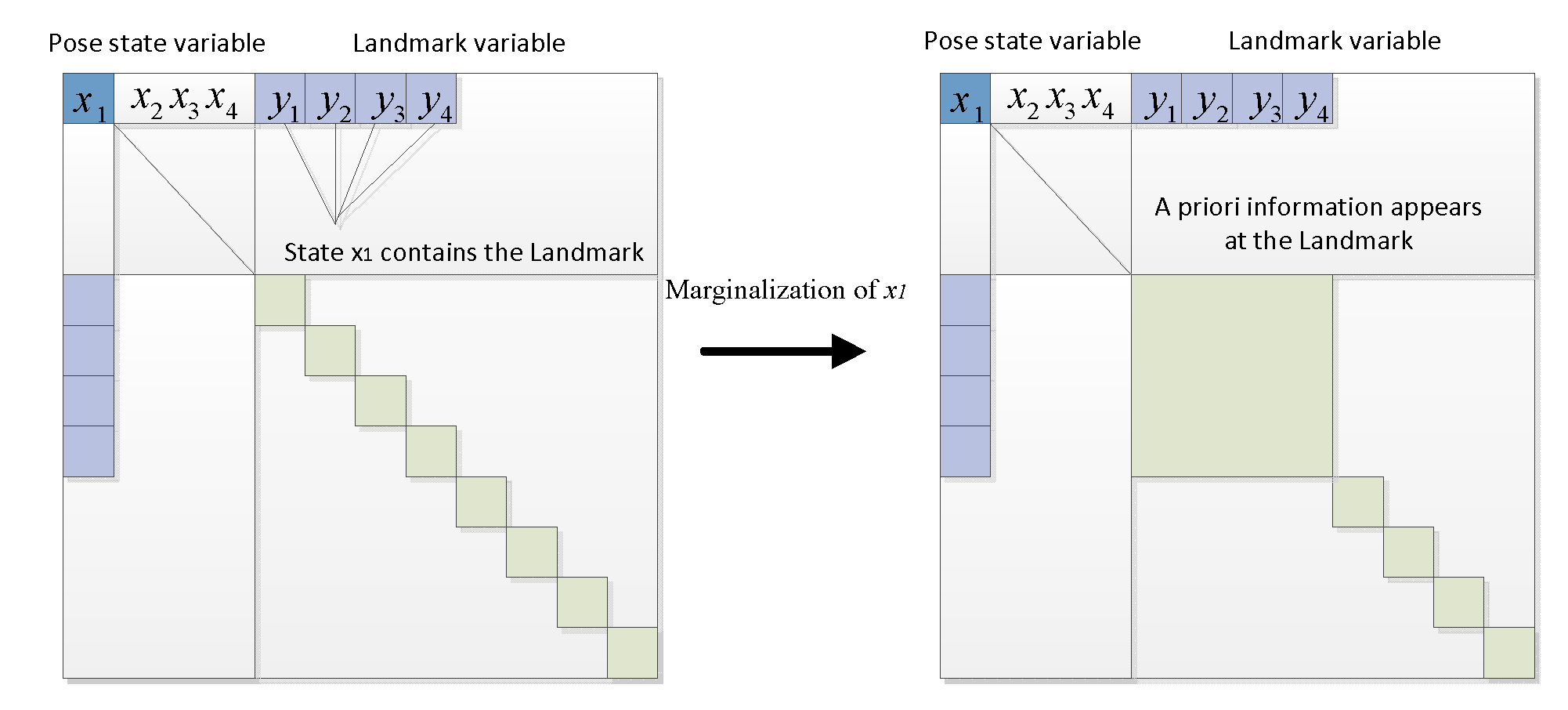
However, in a SLAM graph model, when the first state is to be removed, it is no longer isolated due to the fact that a landmark can be observed by multiple states, as shown in
Figure 7. Due to the fact that the marginalized state observed some landmarks, these landmarks gain prior information indicating that where they should be given the current state of
.
Typically, this prior information is transferred to the retained states through the operation of a Schur complement. This process involves multiplying the first row of the information matrix by a coefficient and adding it to the rows below the partition line to eliminate the non-zero block in the first column. Subsequently, the first column is used to eliminate the non-zero block in the first row. However, this operation results in the Landmark-Landmark portion of the information matrix being filled with additional information, causing it to no longer remain a diagonal block as shown in
Figure 8.
In the virtual constraint model proposed in this paper, the virtual satellite positions are constrained with associations from previous time steps. Therefore, during the marginalization process, it is necessary to simultaneously transform the priors of both the state-state and Satellite-Satellite sections as shown in
Figure 9. The positions of the satellites are determined through ephemeris and satellite time. In fact, if accurate time information is available, the satellite positions can be considered precise. Thus, the mapping error from one time step to another essentially represents the temporal error between the two epochs. However, satellite motion is nonlinear, it is difficult to represent the mapping with an analytical function that uses time as a variable.
Therefore, in the marginalization process of this model, the state and corresponding observed satellite position information from the previous epoch will be removed. The prior for the satellite positions that need to establish virtual constraints is treated as an uncertainty, which is separated from the overall error minimization model,as shown in equation11. The covariance for this part is set based on the accuracy of the receiver's oscillator.
3. Experiments and Results
To better validate the algorithm's effectiveness, MATLAB was utilized for evaluation. As computational efficiency issues have not yet been considered, classic computational libraries like g2o and GTSAM were bypassed. To validate the proposed method's effectiveness, the paper employs a tightly-coupled open-source framework[
21], tested using a set of handcart experiment data which collect in XuZhou city , China. The dataset includes reference solutions outputted by the Inertial Explorer software in IMU/RTK mode, preprocessed GNSS observations, preprocessed IMU observations, and dual GNSS antenna orientation data. The hardware parameters is configured as follows:
Table 1.
System hardware configuration settings.
Table 1.
System hardware configuration settings.
| Title 1 |
Title 2 |
| GNSS Signal Frequency (Hz) |
1 |
| IMU Frequency (Hz) |
125 |
| Gyroscope Bias (rad/s) |
0.0005 |
|
) |
80 |
| Carrier-to-Noise Ratio Threshold |
30 |
| Operation Time (s) |
292 |
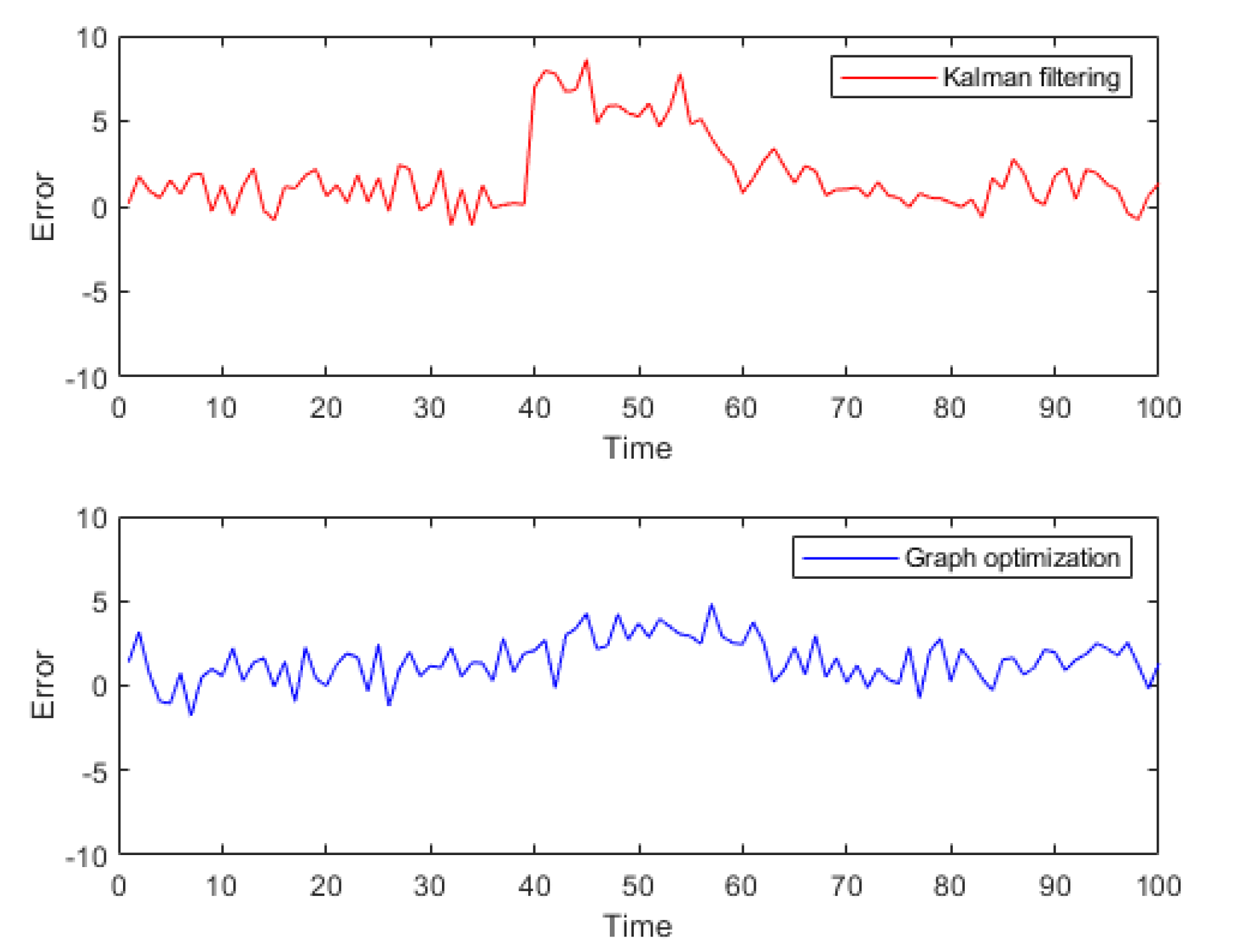
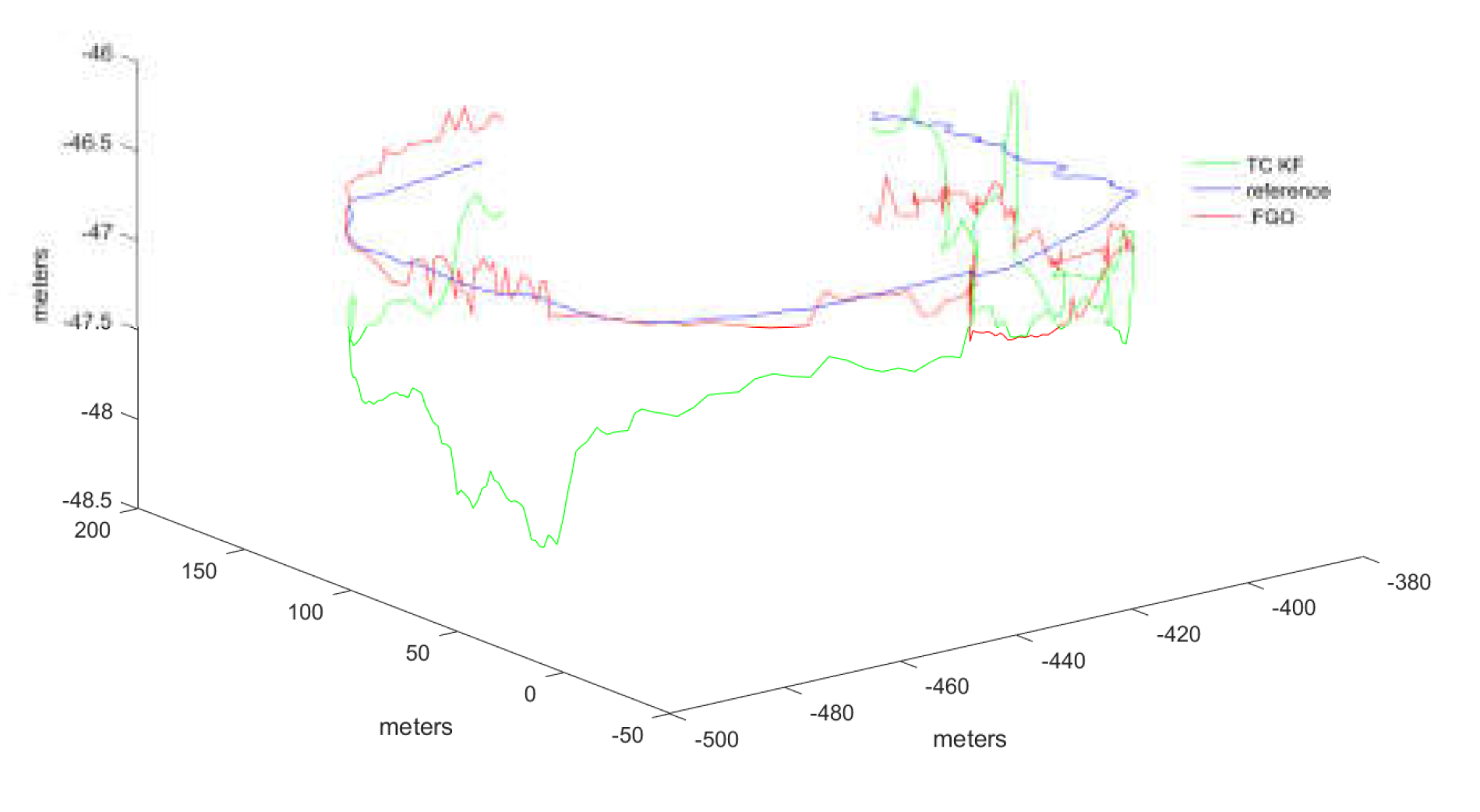
The output results from the commercial software Inertial Explorer are used as the reference trajectory. Initially, the trajectory calculation results of the FGO method and the Kalman filtering method from the open-source framework were tested. The results are shown in
Figure 10.
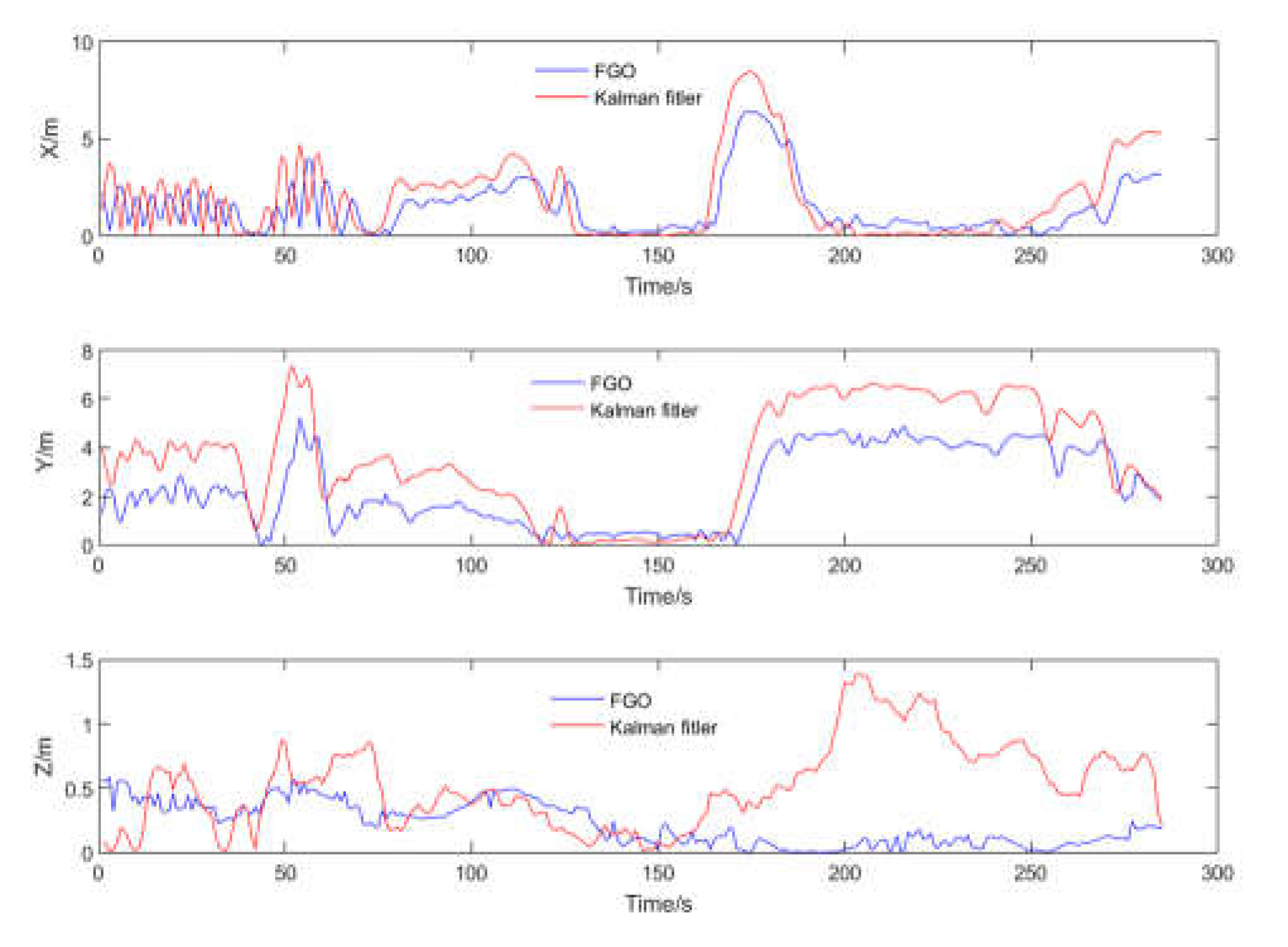
To better validate the trajectory error comparison, the adopted comparison method includes the error in each direction of the carrier coordinate system, as well as the overall trajectory's Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). RMSE provides a more intuitive measure of the overall trajectory error. Compared to the reference trajectory, the tightly coupled Kalman filtering method exhibited greater fluctuations and was more directly influenced by measurement values. In contrast, the FGO method demonstrated better stability in trajectory tracking. The error trends for the three axes are displayed in
Figure 11.
It should be noted that the vertical fluctuations in the Z-axis of the trajectory shown in the figures appear large due to the different scale ratios used for display. This was done to better illustrate the comparative differences in the trajectories. However, the overall trend of the trajectory distribution remains unchanged. Additionally, to provide a more direct comparison of errors, the results of both methods were statistically compared with the reference trajectory. The error statistics which contains the 3 directions RMSE are presented in
Table 2.
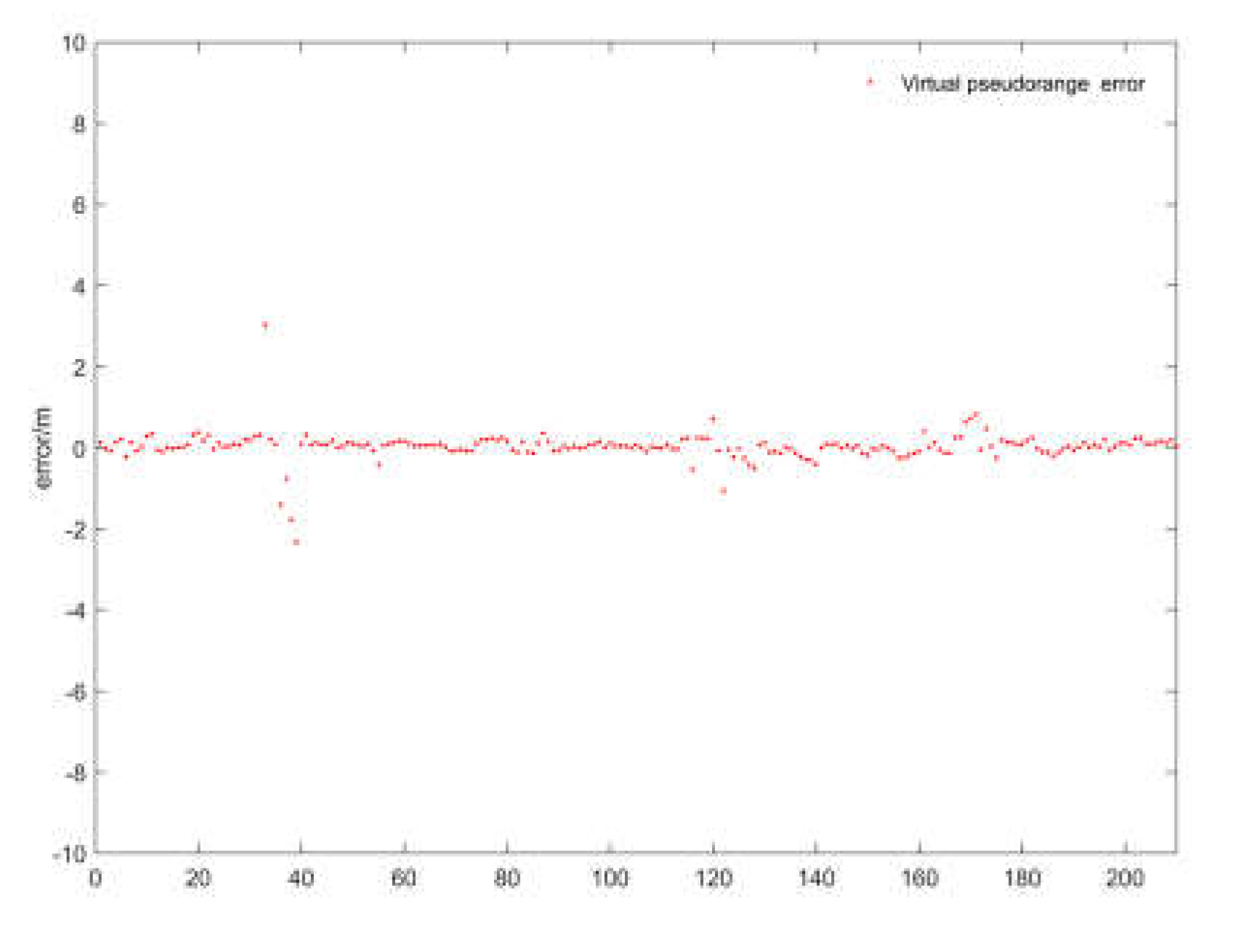
Next, to verify the actual performance of the virtual pseudorange constraint and examine whether its inclusion significantly affects the navigation system error, we compare the positioning results with and without the virtual constraints and conduct an error analysis. First, the difference between the virtual pseudorange and the real pseudorange is validated by comparing the virtual pseudorange with the measured pseudorange. In the test data, 213 pseudorange measurements were randomly selected. The pseudorange for the next time step was constructed using virtual constraints and compared with the real pseudorange measured at the next time step. The error results are shown in
Figure 12.
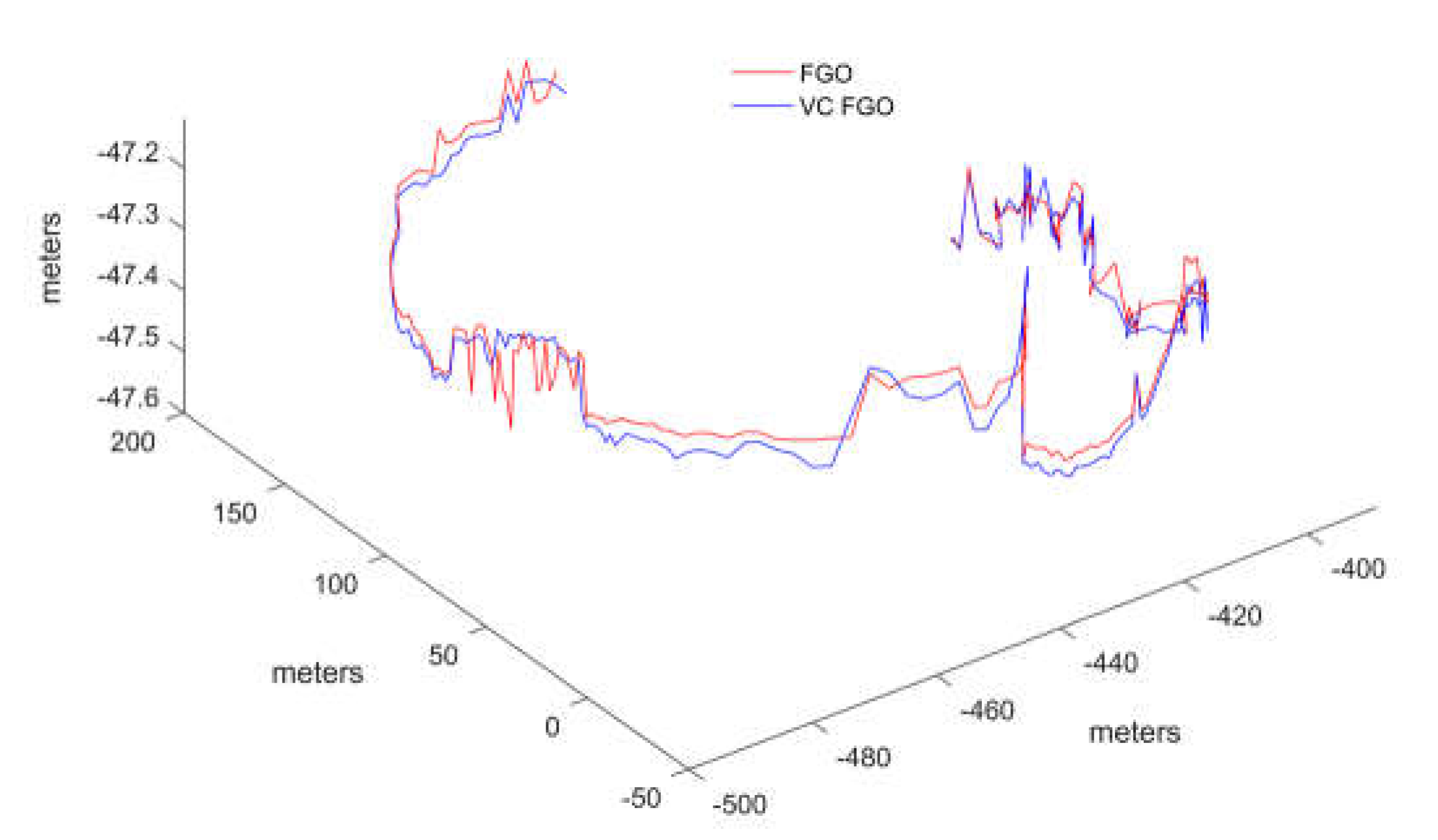
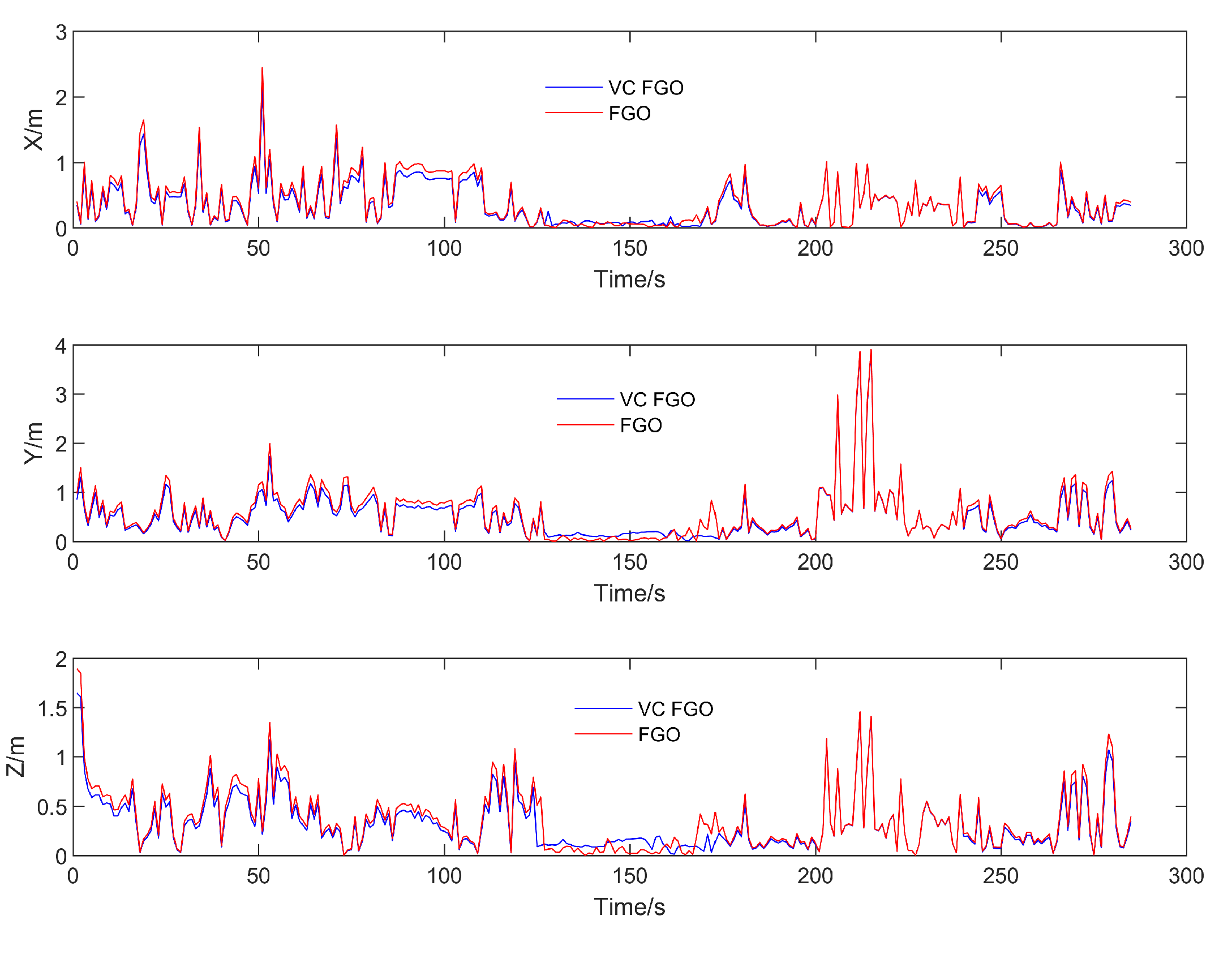
The error trend shown in the figure indicates that most of the errors between the virtual pseudorange and the real pseudorange are within 1 meter. In the test data, the maximum error does not exceed 4 meters. When these virtual pseudorange constraints are injected into the graph model, replacing the original real pseudorange, the resulting impact on positioning differences is shown in
Figure 13. Extending from the differences in pseudorange to the final positioning results, the numerical differences are significantly smaller compared to the differences between the FGO results and the Kalman filter results. If the reference trajectory is included, the comparison between the two would appear even more aligned due to scale. To highlight the details of the comparison, the trajectory only displays the comparison between the FGO with virtual constraints (VC FGO) and the original FGO. From the trend perspective, VC FGO exhibits good consistency.
Similarly, to better quantify the positioning differences between the two methods, the component values in the three-axis directions were compared with the reference trajectory.
The RMSE errors and error variation rates for the three axes compared to the reference trajectory are shown in the table.
The error distribution trend and statistical results indicate that the positioning result differences between VC FGO and FGO are not significant. The RMSE error in the horizontal axes is within 2%, and in the vertical Z-axis, it is within 5%.
4. Conclusions
To address the decline in pseudorange measurement accuracy caused by GNSS system multipath and NLOS effects, which can lead to decreased positioning accuracy and insufficient satellite numbers, this paper proposes a virtual pseudorange constraint-based graph optimization model. This method is based on a GNSS/IMU integrated navigation system. The paper explores and analyzes three main aspects: the establishment of virtual pseudoranges, graph model construction, and marginalization processing. Performance evaluation of this method was conducted using an open-source integrated navigation framework and a set of real-world data. The results show that the positioning differences between the virtual constraint FGO and the original FGO are within 5%, demonstrating the high feasibility of the method. This approach shows significant potential for maintaining graph integrity and ensuring comprehensive estimation accuracy. In future work, the authors will further investigate the relationship between sustained prediction time and positioning accuracy, as well as the feasibility of constructing multiple virtual constraints simultaneously.
Author Contributions
The paper provide by seven authors, the authors contributions as follows: Conceptualization, Haiyang Qiu; Data curation, Yun Zhao; Funding acquisition, Haiyang Qiu, Hui Wang; Methodology, Haiyang Qiu and Lei Wang; Project administration, Haiyang Qiu; Software, Yun Zhao; Supervision, Hui Wang, Lei Wnag; Writing – original draft, Yun Zhao; Writing – review & editing, Yun Zhao. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52101358, 41906154), Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program So-cial Development Project (BE2022783).
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to gratitude any reviewers who have made comments on this article
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ai Qingsong, Zhang Baocheng, Yuan Yunbin et al. Evaluation and mitigation of the influence of pseudorange biases on GNSS satellite clock offset estimation[J]. Measurement, 2022, 193.
- Wen W, Hsu L T. Towards robust GNSS positioning and real-time kinematic using factor graph optimization[C]//2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2021: 5884-5890.
- Zhang Xiaohong, ZHANG Yuantai, Zhu Feng, et al. Factor Graph Optimization Method of GNSS positioning in complex urban Scenarios and its resistance Analysis [J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Department of Information Learning edition),2023,48(7):1050-1057. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y ,Liu F ,Liu H , et al. A Real‐Time and Fast LiDAR–IMU–GNSS SLAM System with Point Cloud Semantic Graph Descriptor Loop‐Closure Detection [J]. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2023, 5 (10): .
- C S N ,N M C ,T A . Analysis of GNSS and IMU Sensor Data Fusion Using the Unscented Kalman Filter Method on Medical Drones in Open Air [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2023, 1250 (1):.
- Kaczmarek Adrian, Rohm Witold, Klingbeil Lasse et al. Experimental 2D extended Kalman filter sensor fusion for low-cost GNSS/IMU/Odometers precise positioning system[J]. Measurement, 2022, 193.
- McGrath Timothy and Stirling Leia. Body-Worn IMU Human Skeletal Pose Estimation Using a Factor Graph-Based Optimization Framework.[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 20(23).
- Chang L, Niu X, Liu T, et al. GNSS/INS/LiDAR-SLAM integrated navigation system based on graph optimization[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1009.
- Wen W, Pfeifer T, Bai X, et al. Factor graph optimization for GNSS/INS integration: A comparison with the extended Kalman filter[J]. NAVIGATION: Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2021, 68(2): 315-331.
- Suzuki, T. Time-relative RTK-GNSS: GNSS loop closure in pose graph optimization[J]. IEEE robotics and automation letters, 2020, 5(3): 4735-4742.
- Zhang G, Ng H F, Wen W, et al. 3D mapping database aided GNSS based collaborative positioning using factor graph optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(10): 6175-6187.
- Li W, Cui X, Lu M. A robust graph optimization realization of tightly coupled GNSS/INS integrated navigation system for urban vehicles[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2018, 23(6): 724-732.
- Wen W, Zhang G, Hsu L T. GNSS outlier mitigation via graduated non-convexity factor graph optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 71(1): 297-310.
- Jiang C, Chen Y, Xu B, et al. Vector tracking based on factor graph optimization for GNSS NLOS bias estimation and correction[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(17): 16209-16221.
- Das A, Elfring J, Dubbelman G. Real-time vehicle positioning and mapping using graph optimization[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(8): 2815.
- Weiqiang, Fu,Shupeng, Hu,Changhai et al. Development and Test of GNSS/IMU-Based Speed Measurement Device for Agricultural Machinery[C]//.Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Agriculture 2017(ICIA2017) PartI.,2017:455-466.
- Jiang C, Chen S, Chen Y, et al. GNSS vector tracking method using graph optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 68(4): 1313-1317.
- Wen W, Kan Y C, Hsu L T. Performance comparison of GNSS/INS integrations based on EKF and factor graph optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2019). 2019: 3019-3032.
- Kaess M, Ranganathan A, Dellaert F. iSAM: Incremental smoothing and mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(6): 1365-1378.
- Dellaert, F. Factor graphs and GTSAM: A hands-on introduction[J]. Georgia Institute of Technology, Tech. Rep, 2012, 2: 4.
- Groves P, D. Principles of GNSS, inertial, and multisensor integrated navigation systems, [Book review][J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2015, 30(2): 26-27. https://githubcom/benzenemo/TightlyCoupledINSGNSS.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).