1. Introduction
Untreatable multidrug-resistant infections are becoming more common, causing an alarming number of deaths [
1]. To address this issue, scientists are exploring alternative methods to develop drugs that can target cell components or mechanisms that are less prone to mutation, resulting in resistance [
2,
3]. Among the new antimicrobial substances being developed, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) show great potential as a new source of effective antimicrobial activity [
4,
5,
6].
AMPs, also known as host defense peptides, are the oldest innate immune defense factors [
7] and play a crucial role in the natural immune system of the host [
8]. Recent studies have revealed that AMPs use unique antimicrobial mechanisms that differ from those of antibiotics commonly used in clinical infections [
9,
10,
11]. There are a variety of AMPs that bind to microbes through low-affinity targets, a condition that greatly reduces the chance of generating antimicrobial resistance [
12]. The AMPs are categorized according to their effect on the bacterial membrane or membrane proteins[
13,
17]. Under stress conditions, the occurrence of mutations in these areas is reduced, thus decreasing the chance of developing resistance[
17,
20,
21,
22]. In light of these properties, the AMPs have the potential to be used as drugs to treat infections caused by microorganisms [
23,
25].
It has been shown that the designed AMP LR
GG (LLRLLRRGGRRLLRLL-NH2), which tends to form an α-helical structure in membrane-mimetic environments [
26], exhibits effective antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria when used in combination with ciprofloxacin, colistin, and other antibiotics. This combination has been found to reverse the ciprofloxacin-resistant phenotype of
Pasteurella multocida and increase 512-fold the antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin against this bacterium (unpublished data from our laboratory).
The chemically synthesized peptide LRGG has been found to damage the bacterial outer membrane by targeting lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and disrupting the Fe3+ transport system involving the inner membrane permease protein FecD, thereby significantly improving the efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of animals infected with multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and Pasteurella multocida. The LRGG peptide can also trigger membrane potential hyperpolarization and intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in pathogenic bacteria, leading to synergistic bactericidal effects. However, neither isolation nor chemical synthesis of AMPs is a good choice for clinical application. In fact, the isolation of natural AMPs from hosts is impractical due to their low concentration and complicated purification procedure, while the use of synthetic AMPs is limited by the high costs of their chemical synthesis.
Currently, the most effective strategy to produce AMPs on a large scale is the biological expression[
27,
28] with the expression in
Escherichia coli being the most commonly used method in light of its low production costs, short incubation period, and ease of control[
29,
30]. However, the production of AMPs composed of only ten to a dozen amino acids in prokaryotic expression systems can be challenging [
31]. An additional drawback is that AMPs produced within prokaryotes can result in cell inhibition. To avoid this problem and increase the AMPs production rate, a larger protein tag, such as green fluorescence protein (GFP), can be fused to AMPs [
32,
33]GFP is commonly used as a protein label and can also be used for easily observable expression detection[
34,
35].
In this study, the GFP was tandemly fused with the N' terminus of AMP LR
GG and cloned and inserted into the pQE80
Escherichia coli expression vector to act as a precursor protein, and a target site for the TEV protease was inserted between the GFP fusion protein-encoding gene and the LR
GG, thus enabling the fusion label to be easily removed during purification. The cleavage site affects only one amino acid of the main protein chain with minimal impact on the protein properties [
36]. In this study, the effects of AMP LR
GG expression on the cell membrane and DNA of gram-negative bacteria were also investigated through tests of the permeability of the inner and outer membranes, cell membrane potential, and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
The chemically synthesized AMP LR
GG (LLRLLRRGGRRLLRLL-NH2) is a fully designed peptide. purches from Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd.
Table 1.
Strains and Plasmids.
Table 1.
Strains and Plasmids.
| Strains |
Source |
|
Eschericha coli stellar component cell |
Takara |
| Transetta component cell |
Takara |
|
E.coli ATCC 25922 |
Preserved by the Pharmacology and Toxicology Laboratory of Jilin Agricultural University |
|
S. pullorum NCTC5776 |
|
K.Pneumoniae CMCC 46117 |
|
P.aeruginosa ATCC27853 |
|
S.flexneri CMCC51572 |
|
S.aureus ATCC 25923 |
|
S. faecalis ATCC 29212 |
| Plasmids |
|
| pQE-80-Kan |
Qiagen |
| pMD-18T |
Takara |
| pTZ18U-GFP |
Takara |
Table 2.
Primers used in this study.
Table 2.
Primers used in this study.
| Gene |
Primer |
Sequence (5′- 3′) |
| linear pQE Vector |
pQE-VT-F |
GTAAAAGCTTAATTAGCTGAGCTTGGACTCC |
| pQE-VT-R |
CATATCTCTAGAGGATCCGTGATGGTG |
| GFP |
GFP-F |
CTAGAGATATGCGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCACTG |
| GFP-R |
AAGATTCTCATACTTGTATAGTTCATCCATGCCATGTGTAATCCC |
| LRGG
|
LRGG-F1 |
CTTACAGCAGACGCAGCAGACGACGGCCGCCACGACGCAG |
| LRGG-R1 |
GAGAATCTTTATTTTCAGGGCCTGCTGCGTCTGCTGCGTCGTGGCGGC |
| TEV cleavage site + LRGG
|
TEV-LRGG-F2 |
GAGAATCTTTATTTTCAGGGCCTGCTGCGTCTGCTGCGTCGTGGCGGC |
| TEV-LRGG-R2 |
TTACAGCAGACGCAGCAGACGACGGCCGCCACGACGCAG |
| validation primers |
M13-F |
AGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACG |
| M13-R |
GAGCGGATAACAATTTCACAC |
| pQE30+ |
GTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCAC |
| pQE30- |
CTGAACAAATCCAGATGGAG |
2.2. Acquisition of Target Genes
- (1)
To target the GFP gene, we designed GFP-F and GFP-R primers from the plasmid pTZ18U-GFP previously constructed in the laboratory. PrimeStar Max DNA Polymerase was used to amplify the GFP gene via PCR, with the plasmid pTZ18U-GFP serving as the template.
- (2)
To target the gene sequence of the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG, the primers LR
GG-F1 and LR
GG-R1 were designed. Follow the seamless cloning method to construct plasmids, as shown in
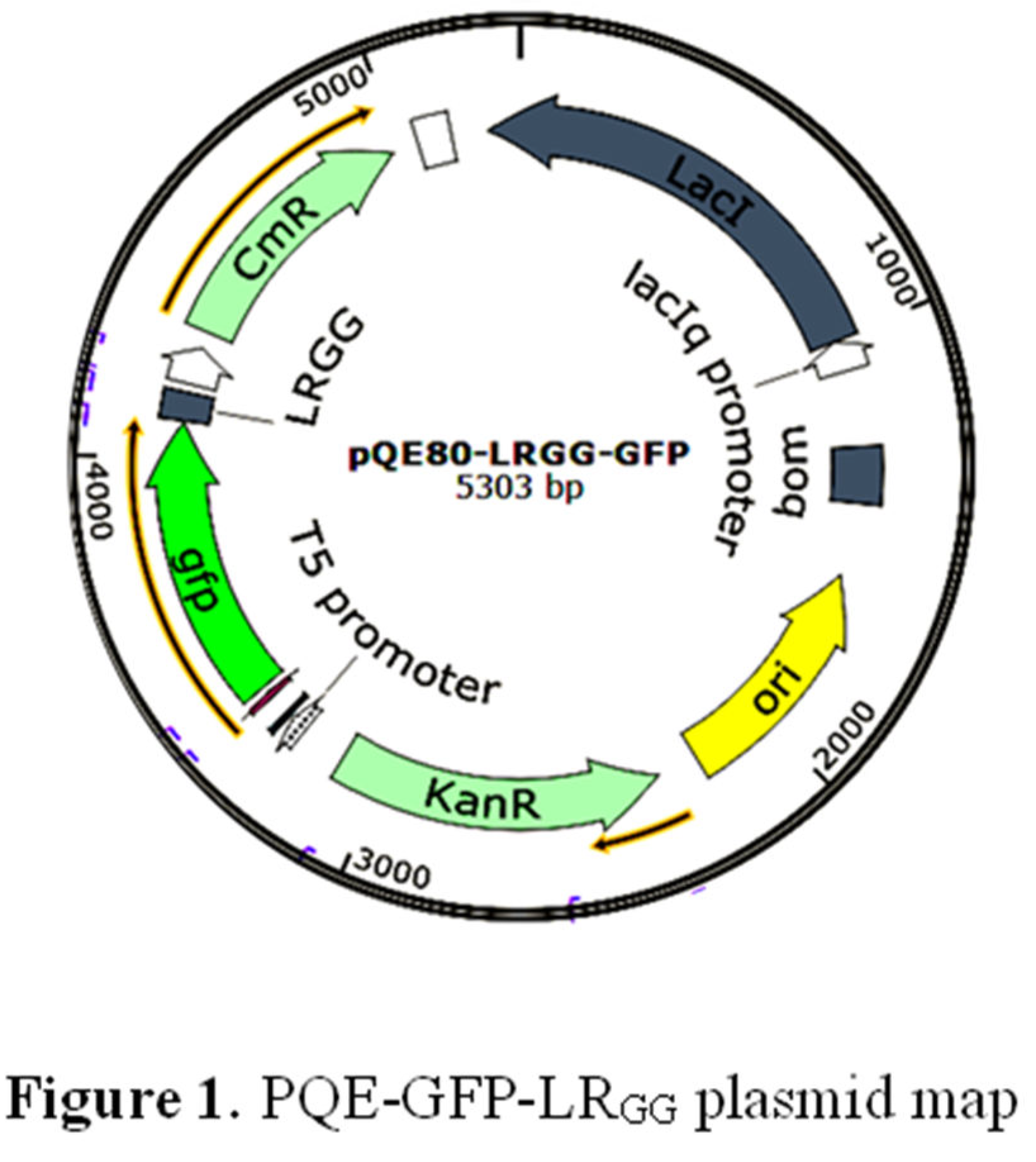
Figure 1.
2.3. Construction of pQE-GFP-LRGG Expression Vector
- (1)
To construct the pQE-GFP-LRGG vector, three gene fragments were amplified.
- (2)
The gfp gene was amplified by PCR reaction using the primers GFP-F and GFP-R primers, and the pTZ18U-GFP plasmid served as the template.
- (3)
To synthesize the Tev site and LRGG sequence, two oligonucleotides (TEV-LRGG-F2 and TEV-LRGG-R2) were mixed at a 1:1 ratio in a PCR reaction buffer. The mixture was denatured at 95℃ and annealed by reducing the temperature by one degree per minute from 95℃ to 25℃ within 70 minutes. This process yielded a double-stranded LRGG DNA sequence containing with the TEV target site.
- (4)
The linearized pQE80 vector was amplified by PCR using the pQE-VT-F and pQE-VT-R primers and the pQE80-KAN plasmid as a template.
The LRGG expression vector was created using the Seamless Cloning technique. In this process, the gfp gene fragment was placed in front of the fusion protein. A TEV cleavage site was added between the gfp and the LRGG fragment. These fragments were then placed behind the T5 promoter, and the His tag sequence was located in the pQE80-KAN vector. These genes were fused and connected through approximately 15 bp of complementary gene fragments. To carry out seamless cloning, a 20 μL reaction mixture consisting of 100 ng of gfp fragment, 50 ng of Tev site-LRGG fragment, 100 ng of linearized pQE80-KAN vector, and 4 μL of seamless enzyme was prepared. The reaction mixture was incubated for 15 minutes at 50°C and then placed on ice. The construct was then transformed into Stellar competent cells (Takara). Following the manufacturer’s protocol, the cells were plated onto LB plates containing 50 μg/ml kanamycin and incubated overnight. Positive clones were screened using PCR reaction of test primers pQE30+ and pQE30- and DNA sequencing. The positive clone was then grown, and the expression vector was extracted and transformed into Transgene (DE3) competent cells.
2.4. Expression and Purification of Fusion Protein GFP-LRGG
The transformed clone, verified by sequencing, was placed in 20 mL of LB medium containing 50 μg/mL kanamycin. 180 rpm, incubated overnight at 37℃. When the optical density reached 0.5, protein expression was induced by 0.2 mM IPTG. After an additional 4 hours of incubation, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 8,000 rpm at 4℃ and the cell pellet was stored at -80℃.
To obtain the GFP-LRGG fusion protein, the E. coli cells were lysed using a sonicator at 18 W for six rounds of 30-second bursts in Buffer A (20 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.4, 5% glycerol, 500 mM NaCl). The samples were supplemented immediately before use with 6 mM β-Mercaptoethenol, 0.1 mM Benzamidine, and 0.1 mM PMSF. The lysate was passed through a Ni-NTA 6FF column. Proteins with no affinity for the column were eluted with Buffer A containing 50 mM imidazole, whereas the fusion protein was eluted with Buffer A containing 300 mM imidazole. The fractions containing the fusion protein detected by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis were pooled and dialyzed against buffer A to eliminate imidazole, and the fusion protein was concentrated, analyzed with a BCA test kit, and stored at -80℃.
2.5. Cleavage of the Fusion Protein and Purification of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
The TEV protease was used to cleave the GFP-LR
GG fusion protein [
37] in a reaction mixture consisting of 100 μL of 10X TEV Buffer supplemented with 50 μL of recombinant TEV protease (1 mg/mL from Beyotime Co., Ltd.) and 40 μg of the fusion protein GFP-LR
GG (1 mg/mL). After 16 hours of incubation at 16°C, the 6x His-tag remained upstream of the GFP, while no His-tag remained linked to LR
GG. Using a Ni-NTA affinity column, the two products of the digestion of the fusion protein were separated by passage through an affinity column that was able to retain the 6x His-GFP while allowing the LR
GG peptide to pass through upon elution with 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) buffer containing 200 mL of glycerol and 500 mM sodium chloride. 300 mM imidazole. The effluent containing GFP-LR
GG was dialyzed against buffer A containing 50% glycerol. After checking its purity by Tricine-SDS‒PAGE, the protein was stored at -80°C.
2.6. Determination of the Antibacterial Activity of Fusion Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
The minimal inhibitory concentrations against various bacteria displayed by peptides expressed in prokaryotes and chemically synthesized were determined by the broth microdilution method. Two replicates were set up by placing 100 μL of the two antimicrobial peptides (approximately 1024 μg/mL each) in the first rows of the 96-well plates. followed by serial two-fold dilutions to achieve final peptide concentrations ranging from 512 to 1 μg/mL. The strains kept at −80°C were reactivated, plated and incubated overnight at 37°C. Single colonies were picked, inoculated into 5 mL of MH medium and cultured until they reached OD600 = 0.5. The bacterial suspensions were then diluted to 1 × 105 CFU/mL, and 50 μL was added to wells 1 – 11. Then, 50 μL and 100 μL of deionized water were added to wells 11 and 12, respectively, to provide a positive and a negative control. The concentration of peptide present in the first non-turbid well in which bacterial growth was inhibited was taken as the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC). This experiment was repeated three times.
2.7. Determination of the Bactericidal Kinetic Curve of Fusion Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
To determine the bactericidal kinetic curve of in vivo-expressed and synthetic peptide, the bacterial suspension was mixed with two peptides to obtain a final peptide concentration corresponding to 4 × MIC. The plate was then shaken at 37℃ and 180 rpm, taking 50 μL aliquots of the bacterial suspension every 20 min and diluting them two-fold with sterile PBS buffer before they were spread evenly on LB-containing solid media and incubated overnight at 37℃ (12 h-16 h). The number of colonies on each plate was counted, and the number of colonies at 30-300 was taken as the control group. The group not exposed to the antimicrobial peptide was used as a control. The experiment was repeated three times, and the bactericidal kinetic curve was plotted.
2.8. Environmental Sensitivity of Fusion Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
The efficacy of the chemically synthesized and in vivo-expressed LRGG peptide were tested for their efficacy against E. coli ATCC 25922 under various conditions, such as heat and different pH conditions, before determining in triplicate their minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) in triplicate. In one case, the peptides were placed in ice-cold water at 0°C and heated to 37°C and 100°C for 30 minutes each, and their efficacy was compared to that of an untreated control group. This process was repeated three times. In another case, the peptides were exposed for one hour to pH values of 4, 6, 8, and 10, and their activity was compared to that of an untreated control group. In another set of experiments, the peptides were mixed and incubated with 1 mg/mL of four different proteases. After inactivation of the enzymes, the peptides were tested for their efficacy against E. coli ATCC 25922. The peptides were also tested after mixing with various salt solutions and concentrations of fetal bovine serum at concentrations ranging from 5% to 50%. In all cases, the MIC were determined in triplicate using untreated antimicrobial peptides as controls.
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assay of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
The cytotoxicity of both in vivo expressed and synthesized LRGG peptides was determined using the CCK-8 colorimetric assay on RAW 264.7 and Vero cells. To ensure consistency, before addition to the cell culture plate the in vivo expressed peptide was diluted with synthetic peptide LRGG using deionized water to achieve a 1-128 μg/mL concentration gradient. The peptides were then incubated with the cells for 16 hours at 37℃ in a 5% CO2 incubator, with two sets of replicates for each assay. After incubation, 10 μL of 10% CCK solution was added to each well and incubated for 4 hours at 37 ℃ in a 5% CO2 incubator. The OD450 was measured, and the process was repeated three times for accuracy.
2.10. Hemolytic Activity Assay of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
To obtain a suspension containing 2% red blood cells, 15 mL of sheep blood was collected in a tube containing 0.2% sodium heparin anticoagulant and centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 10 min. After discarding the supernatant, the red blood cell pellet was collected, washed twice with sterile PBS, and resuspended in PBS. The expressed peptide was then diluted with deionized water containing synthetic LRGG to achieve a final concentration with the same gradient as the MIC value (1-128 μg/mL). After the erythrocyte suspension was incubated with the antimicrobial peptide LRGG for one hour at 37°C, the mixture from each well of the 96-well plate was aspirated and centrifuged at 1000 × g for 10 min. The absorbance of the supernatant was then measured at 570 nm, with three repeats and averaging. Finally, the hemolytic index was calculated as follows: Hemolytic index (%) = (O.D. peptide - O.D. PBS)/(O.D. TritonX - 100 - O.D. PBS) × 100%.
2.11. Embryotoxicity of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG in Zebrafish
In this experiment, AB-strain zebrafish embryos were introduced to express and synthesize the antimicrobial peptide LRGG at a concentration of 1 × MIC. A sodium dehydroacetate solution of 200 μg/mL served as the positive control, while the negative control group contained only culture medium. The embryos were cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for approximately 2–3 days, and their morphology after fertilization was observed using a light microscope.
2.12. Inner and Outer Membrane Permeability Tests
To measure the effectiveness of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG, bacterial suspensions were prepared with 1.5 mM ONPG buffer at an ABS O.D. of 600 = 0.5. The experiment was conducted by adding varying concentrations of the expressed antimicrobial peptide LRGG (1/2 – 4 MIC) to the same volume of Eschericha coli ATCC25922 bacterial solution successively plated in 96-well plates. PBS was added to the control group. The absorbance was then measured at ABS O.D. = 420 nm using a microplate reader at 5-minute intervals for 50 minutes.
To determine the permeability of the bacterial membrane, NPN, a fluorescent dye that cannot enter a bacterial membrane with an intact structure, was used [
38]. First, black 96-well plates were used, and the same volume of bacterial suspension and different concentrations of expressed antimicrobial peptides were added. PBS was added to the control group, and 1 mM NPN fluorescent dye was added to reach a final concentration of 10 μM. The plates were then incubated in the dark at room temperature for 30 minutes, and their O.D. values were measured with a fluorescence microplate reader using an excitation wavelength of 350 nm and an emission wavelength of 420 nm.
The formula used to calculate the outer membrane permeability was
NPN absorption (%) = (Fobs-F0)/(F100-F0) × 100%.
Where Fobs is the fluorescence value measured in the presence of antimicrobial peptides and F0 is the fluorescence value of the negative control. F100 is the fluorescence value of the positive control. The experiment was conducted in triplicate for each group.
2.13. Effect of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG on the Bacterial Plasma Membrane Potential
To determine whether the expressed antimicrobial peptide LRGG can break bacterial cytoplasmic membranes, diSC3-5 was used as a fluorescent dye to monitor changes in membrane potential. A bacterial suspension was prepared and adjusted to an ABS O.D. of 600 = 0.5. Next, the same volume of bacterial suspension and varying concentrations of expressed antimicrobial peptide LRGG (1-8 MIC) were added to black 96-well plates. A control group was established using PBS, and diSC3-5 dye was added to a final concentration of 0.4 μM and incubated at room temperature in the dark for one hour. Changes in absorbance values between 0 to 1500 s were measured using a fluorescence microplate reader at excitation (622 nm) and emission (670 nm) wavelengths.
2.14. DNA Gel Retardation Assay
The Eschericha coli ATCC25922 genome was extracted, and its concentration was determined to be OD260/OD280 = 1.8 ~ 2.0. Genomic DNA (400 ng) and the expressed antimicrobial peptide LRGG at final concentrations ranging from 1 ~ 512 μM were incubated at 37℃ for 1 h and verified by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Data analysis The experimental data obtained in this study were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 8.0 software. The data are presented as the means and standard deviations.
The genome of Eschericha coli ATCC25922 was isolated, and its concentration was determined to be OD260/OD280 = 1.8 ~ 2.0 Genomic DNA (400 ng) and the expressed LRGG were incubated at 37℃ for one hour at final concentrations ranging from 1 ~ 512 μM. The results were verified via 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. To analyze the data obtained in this study, GraphPad Prism 8.0 software was used for statistical analysis. The data are presented as the mean and standard deviation.
3. Results
3.1. Construction of the pQE-GFP-LRGG Expression Vector
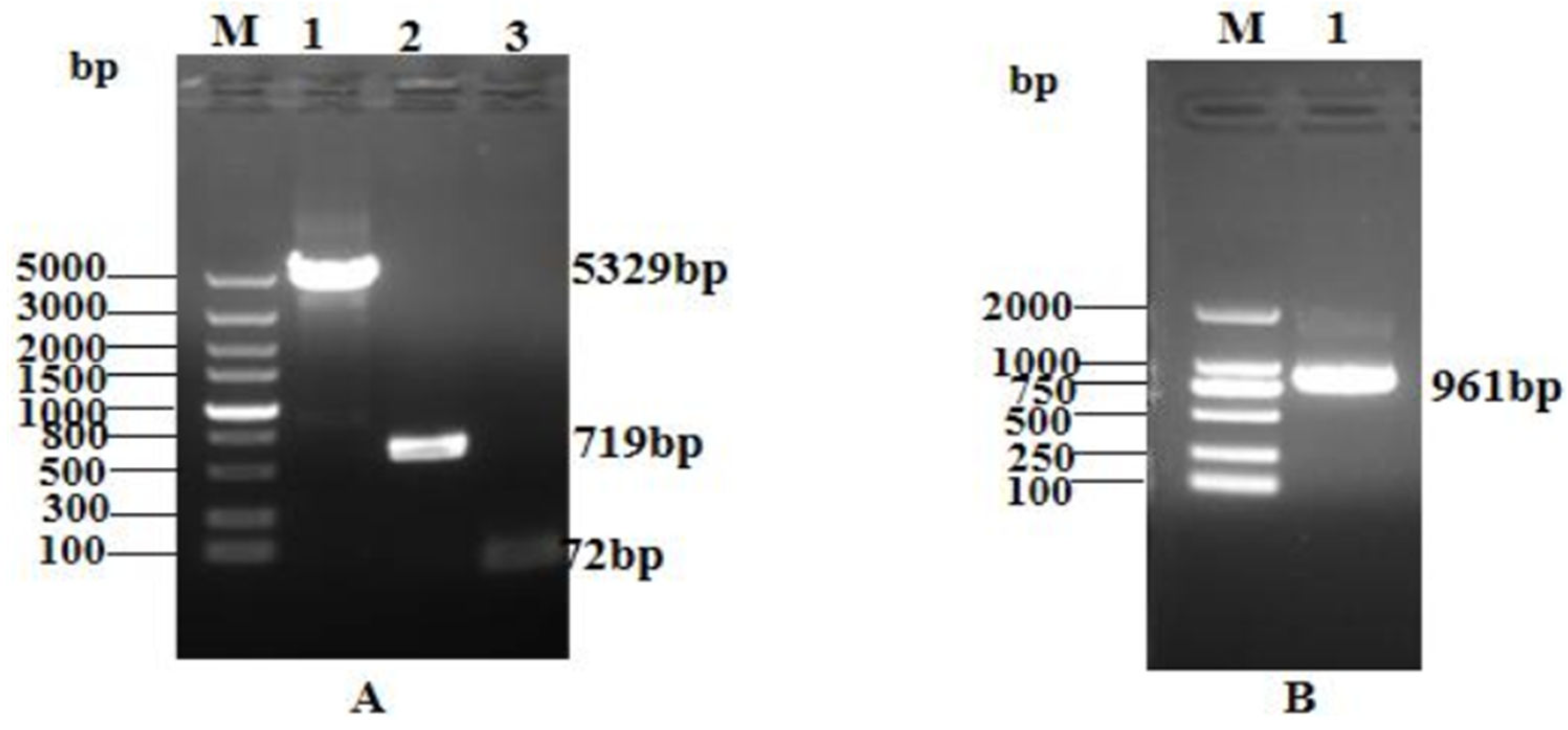
Agarose gel electrophoresis analysis of the linearized pQE80-KAN vector, GFP gene, and TEV site LR
GG gene sequences confirmed that their fragment length were 5329 bp, 719 bp, and 72 bp, respectively (
Figure 2A). PCR identification of the transformed competent clones using the primers pQE30+ and pQE30- revealed the expected band size of 961 bp for the GFP + LR
GG + TEV restriction sites, as shown in (
Figure 2B). These results validated the successful construction of the prokaryotic expression vector pQE-GFP-LR
GG.
3.2. Expression and Purification of the Fusion Protein GFP-LRGG
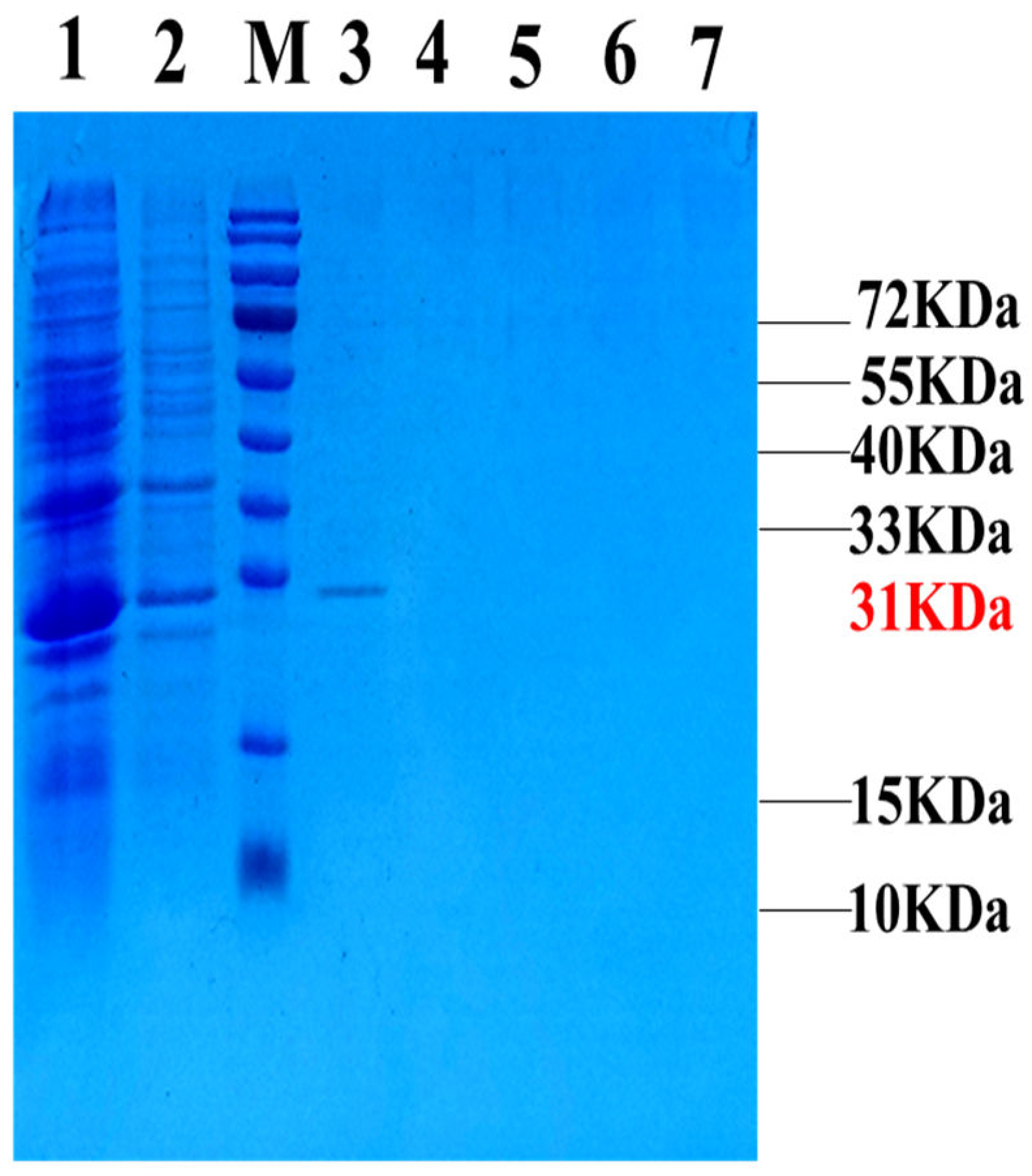
The expression and purification of all the samples were verified through SDS‒PAGE, and the corresponding results are shown in (
Figure 3). Notably, the target band measuring 31 kDa was found in lane 3, indicating that GFP-LR
GG, the intended protein, could be eluted with 300 mM imidazole. Additionally, the concentration of the purified target protein was quantified to be 4.7 mg/L using a BCA kit.
3.3. Cutting of the Fusion Protein and Purification of the Antibacterial Peptide LRGG
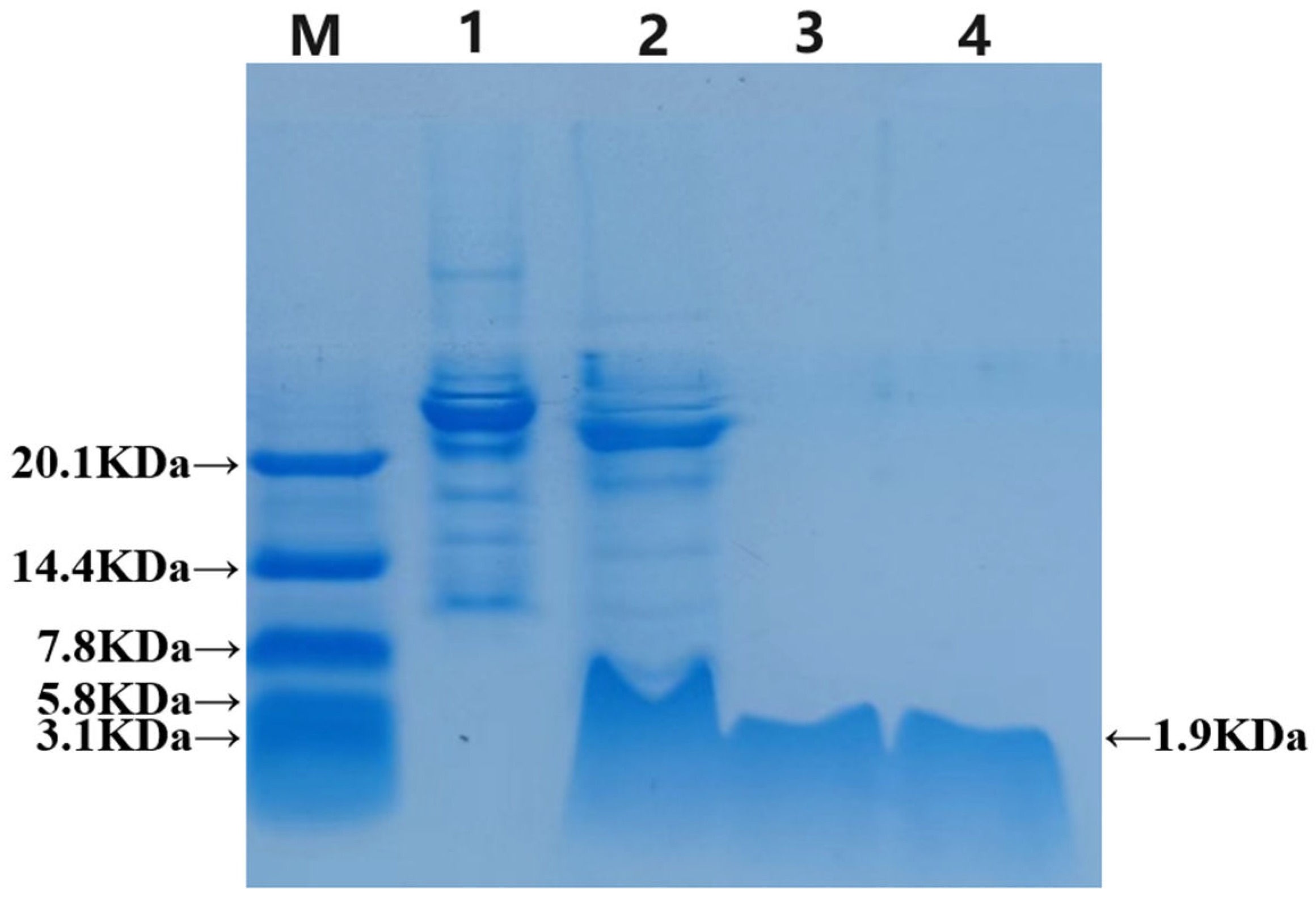
The recombinant TEV enzyme cleaved the GFP, which was subsequently purified using a Ni-NTA column and analyzed via Tricine-SDS‒PAGE electrophoresis. In
Figure 4, the results show that the strip in lane 2 is slightly lower than the pre-cut strip in lane 1 and has the same height as the strip passing through the liquid. This indicates that the fusion label was successfully removed, leaving behind a band with a minimal molecular weight consistent with the chemical synthesis of LR
GG in lane 4. To summarize, the recombinant TEV enzyme cleaved the GFP, and the prokaryotic-expressed antimicrobial peptide LR
GG was successfully purified through multiple purification methods. The concentration of the protein, as measured by the BCA reagent kit, was an average of 1.4 mg/L.
3.4. Determination of the Bacteriostatic Activity and Kinetics Curve of Fusion-Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
This study employed the microdilution method to assess the minimum inhibitory concentrations of both the expressed and synthetic LRGG peptides.
Table 3 presents the results, which reveal that LR
GG antimicrobial peptides demonstrate exceptional broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria, surpassing their efficacy against Gram-positive bacteria. Notably, the MIC of prokaryotic-expressed and chemically synthesized antimicrobial peptides were found to be similar, while the fusion protein showed no antibacterial activity.
3.5. Environmental Sensitivity of Fusion Expressed Peptide LRGG
Temperature and pH stability: Based on the data presented in
Table 4, both the expressed and chemically synthesized LR
GG demonstrated remarkable temperature and pH stability. Specifically, the MIC value of these peptides increased by four-fold at 100℃ and by two-fold and four-fold at pH 10. These findings demonstrate that LR
GG exhibits excellent stability under conditions that are typically considered harsh, highlighting its potential as a promising candidate for various applications.
According to the data presented in
Table 5, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of melittin was substantially greater than the MIC of protease-treated melittin. This finding highlights the importance of proteases in reducing the stability of melittin. Furthermore, it has been reported that the peptide LR
GG is unstable in the presence of proteases.
Salt Ion Stability: Given the abundance of salt ions present in physiological environments, it is important to assess the MIC values of the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG when expressed versus chemically synthesized in various salt ion environments. As demonstrated in
Table 6, compared with those in the control, the MICs of the prokaryotic-expressed and chemically synthesized peptides in a 150 mM NaCl solution decreased by only two- to fourfold. Therefore, it can be concluded that both the expressed and chemically synthesized peptide LR
GG possess commendable salt ion stability.
Serum stability: The MIC for peptide LR
GG, both expressed and chemically synthesized, were assessed against
Eschericha coli ATCC25922 at various serum concentrations. The results are presented in
Table 7. Notably, the MIC for LR
GG fluctuates at serum concentrations of 20% to 50%, ultimately increasing four fold. Conversely, the MIC values for melittin plateaued at 128 at a 10% concentration, demonstrating minimal antibacterial activity. These findings suggest that the serum environment has little impact on the antibacterial effectiveness of LR
GG, regardless of its method of synthesis.
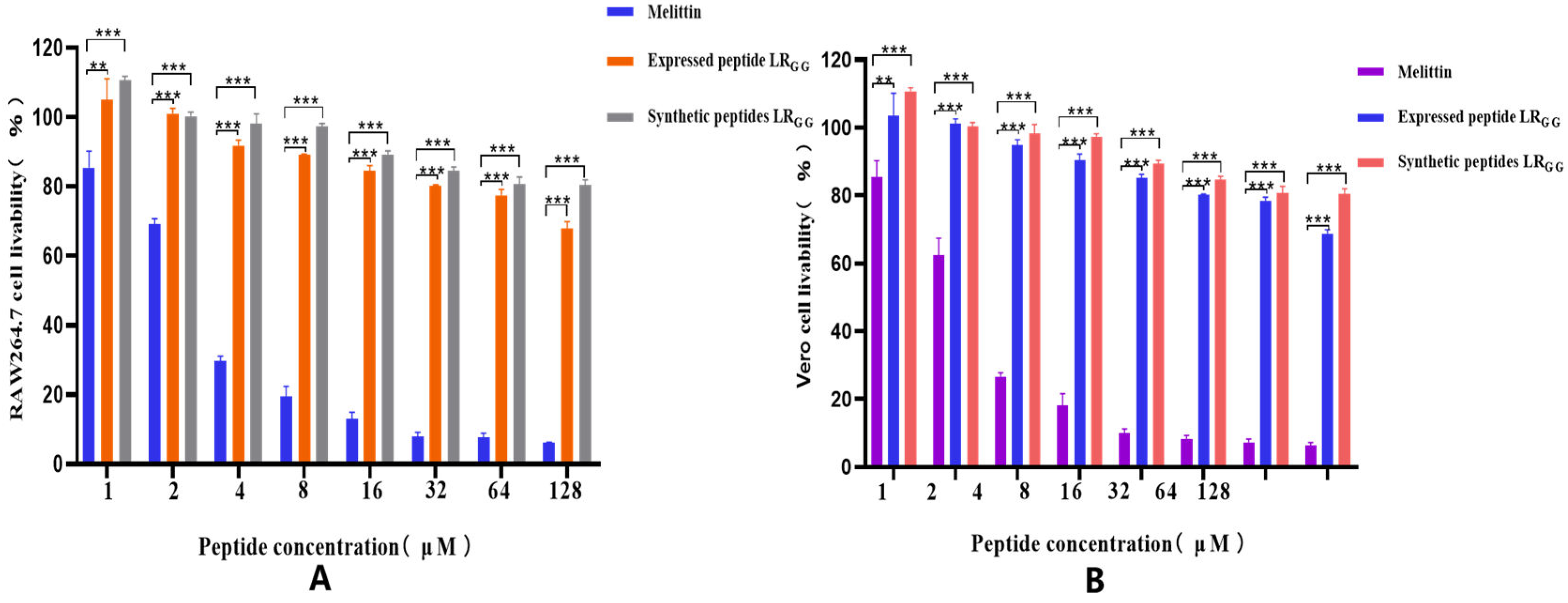
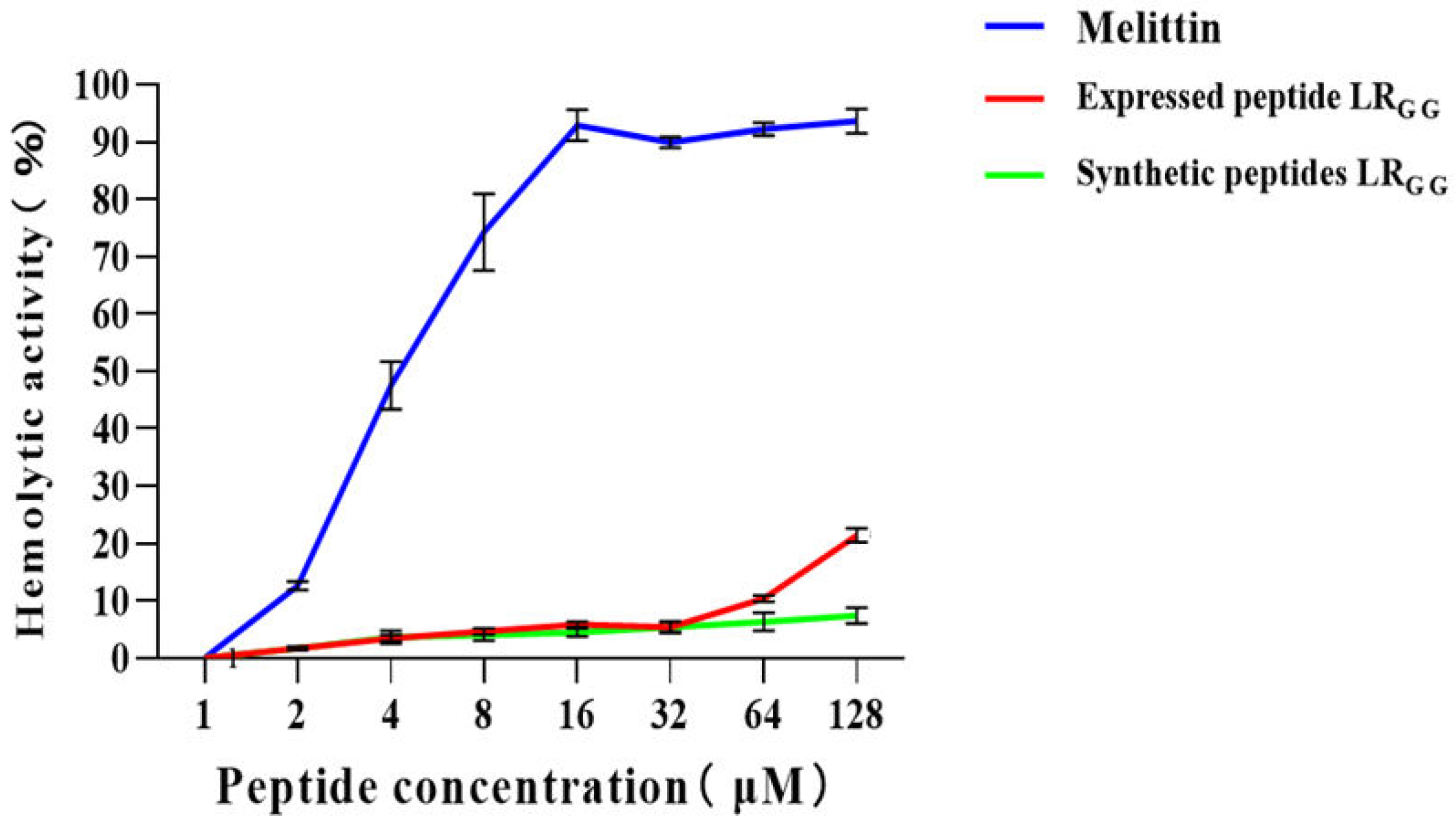
3.6. Cytotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG
The effectiveness of the expressed and synthetic peptides LR
GG against RAW264.7 and Vero cell was evaluated, as demonstrated in (
Figure 5). At MIC values of 1 - 64, the chemically synthesized antimicrobial peptide exhibited a slightly higher cell survival rate compared to the prokaryotic-expressed antimicrobial peptide. However, both the expressed and synthetic peptides showed over 80% cell survival rate against RAW264.7 and Vero cells, in contrast to the control melittin. Compared with that of the melittin control, the hemolytic activity of chemically synthesized LR
GG was less than 10% compared to the melittin control at MIC values of 1-64 μg/mL, as shown in (
Figure 6). The hemolytic activity of the expressed LR
GG was slightly more than 10% at 64 μg/mL, but the hemolytic index was less than 10% at the lowest inhibitory concentration. The comparable cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity of LR
GG-expressed and chemically synthesized LR
GG demonstrated that the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG has excellent cell selectivity at minimum inhibitory concentrations.
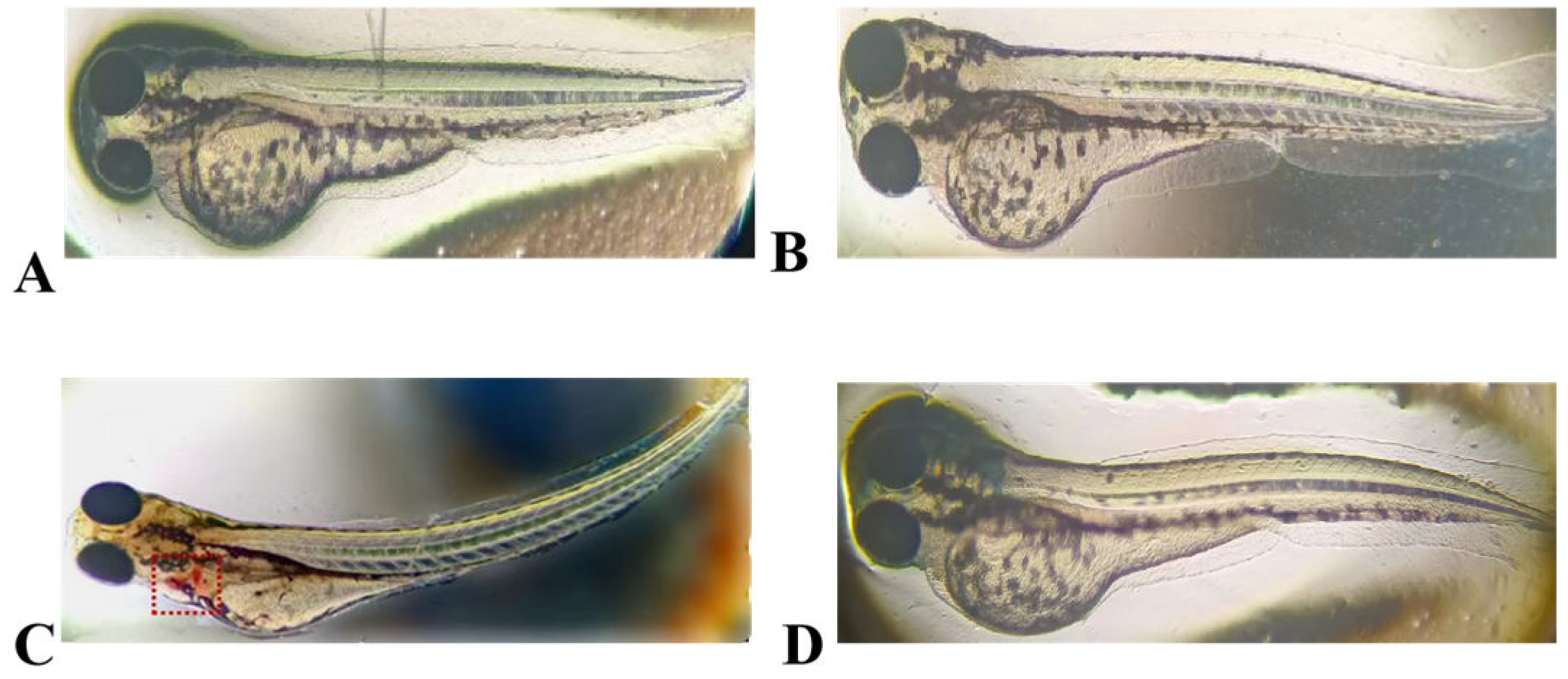
3.7. Embryotoxicity of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG in Zebrafish
The results of embryotoxicity tests conducted on zebrafish that were exposed to LR
GG expression and chemically synthesized antimicrobial peptide are shown in
Figure 7. The hearts of zebrafish that were exposed to LR
GG expression (a positive control) with high concentrations of sodium dehydroacetate (200 μg/mL) showed significant hemorrhage and severe bending of the fish. Conversely, exposure to expressed LR
GG and chemically synthesized LR
GG at a concentration of 1 × MIC, comparable to that of the negative control, did not change the morphology of the zebrafish. These results indicate that neither the expressed nor chemically synthesized antimicrobial peptide LR
GG had any toxic effects on zebrafish.
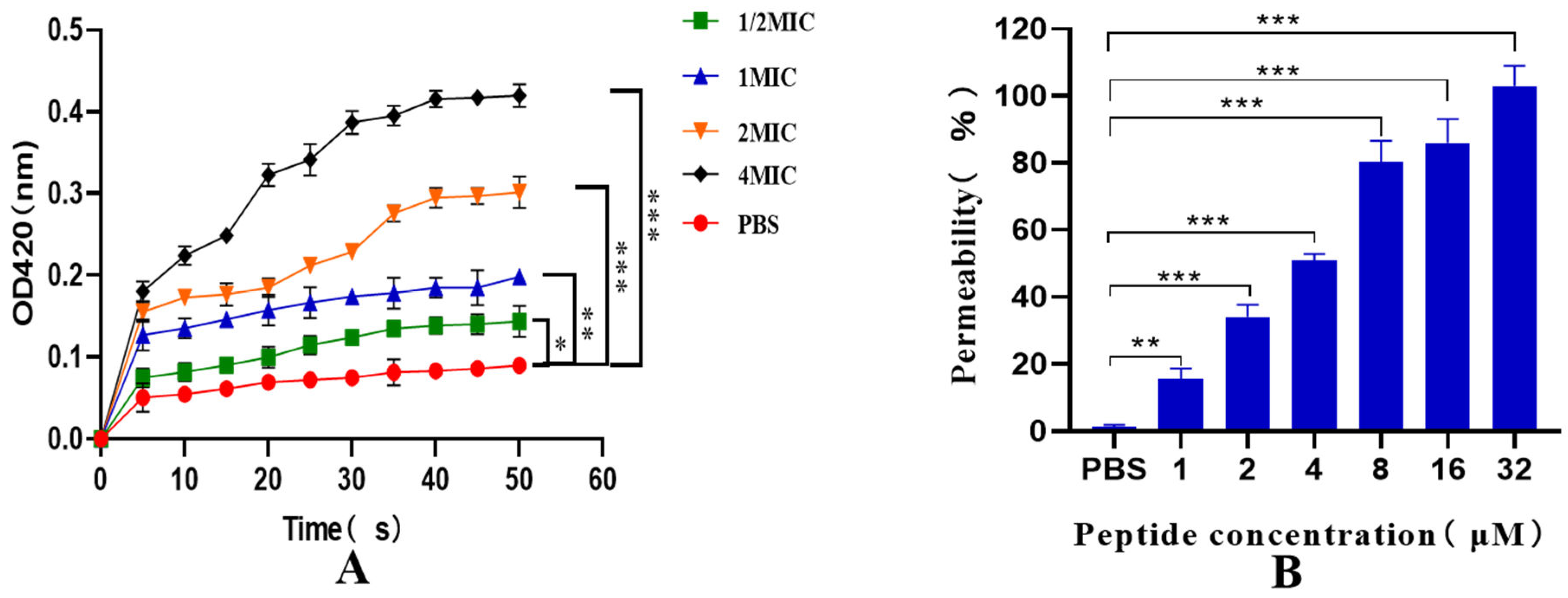
3.8. Inner and outer Membrane Permeability Tests
As depicted in
Figure 8A, the permeability of the inner membrane of the recombinant antimicrobial peptide LR
GG increased within 0-50 minutes, which further increased with increasing dose and prolonged exposure. These results indicate that the prokaryotic-expressed antimicrobial peptide LR
GG effectively ruptures the inner membrane of bacterial cells at the minimum inhibitory concentration. Additionally, as illustrated in
Figure 8B, the peptide was able to penetrate the outer membrane of cells in a concentration-dependent manner at concentrations ranging from 1-32 μM. Notably, when the concentration of LR
GG exceeded 8 µM, the outer membrane permeability was observed to be more than 80%. These findings suggest that the prokaryotic-expressed antimicrobial peptide LR
GG can effectively destroy the bacterial cell outer membrane at the minimum inhibitory concentration.
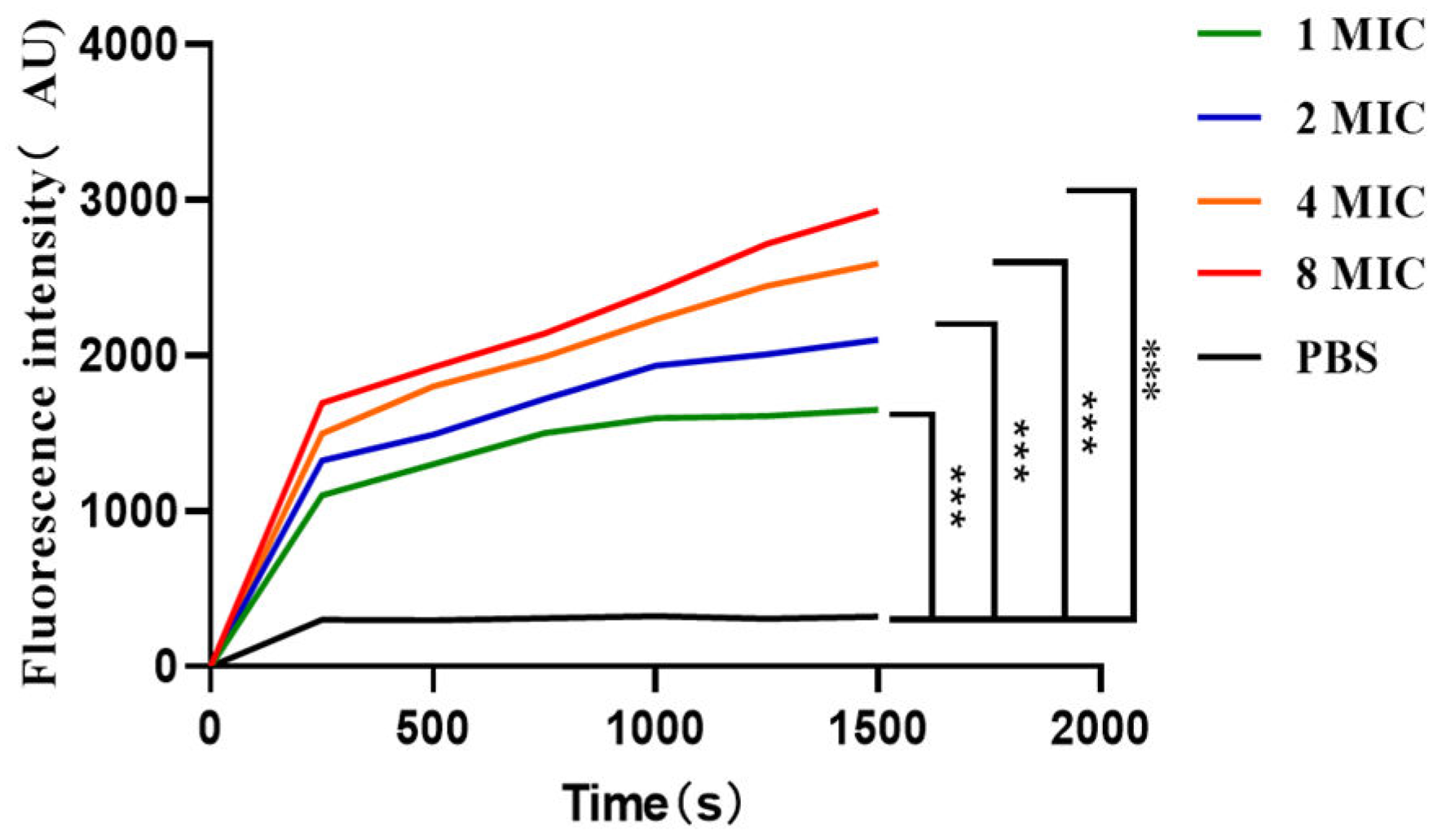
3.9. Effect of the Antimicrobial Peptide LRGG on the Bacterial Plasma Membrane Potential
According to
Figure 9, when the diSC3-5 fluorescent dye enters the cell membrane, it can form non-luminescent polymers [
39]. However, if the cell membrane is destroyed, the previously entered diSC3-5 will flow out and be detected through its fluorescence value. Over time and concentration within 0-1500 s at 1-8 MIC, the fluorescence value of prokaryotic-expressed antimicrobial peptide LR
GG gradually increased, indicating its impact on the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane potential. This further confirmed that the expressed peptide LR
GG is capable of destroying the bacterial cell membrane.
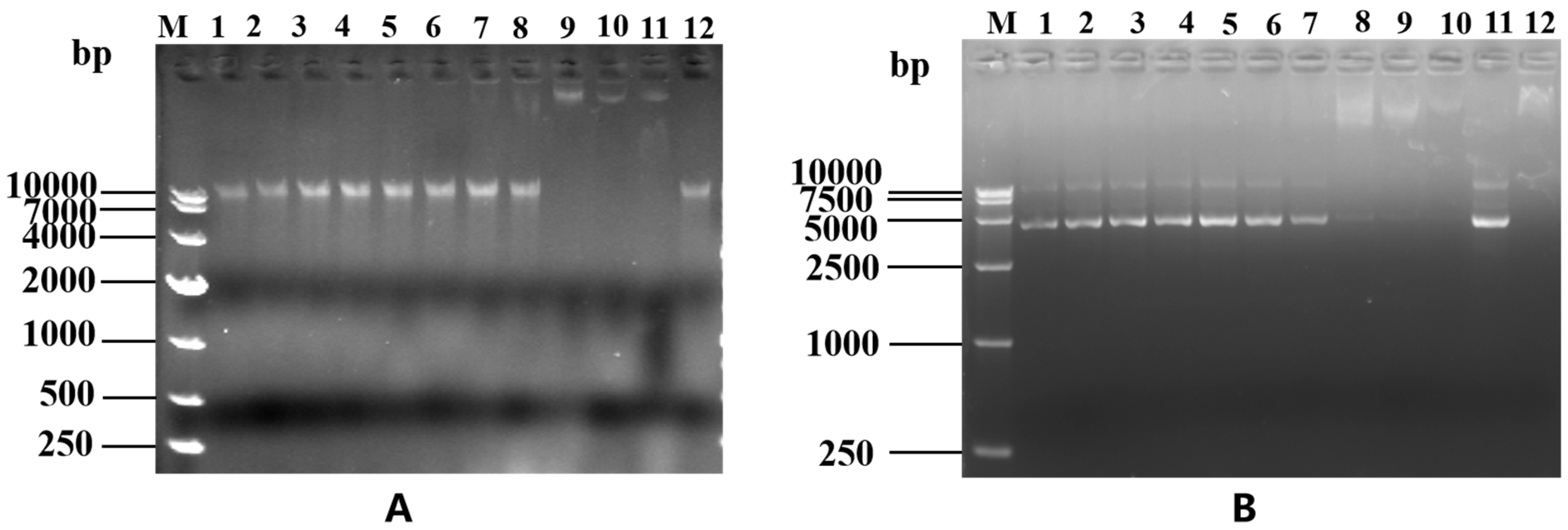
3.10. DNA Gel Retardation Assay
The determination of LR
GG's binding to DNA can be determined through a DNA gel retardation assay, as depicted in
Figure 10A. Through this assay, it was discovered that LR
GG effectively binds to the genomic DNA of
Eschericha coli 25922 and impedes its migration toward the positive pole when the peptide concentration reaches 256 μM. In addition, as shown in
Figure 10B, LR
GG effectively blocked plasmid DNA migration toward the positive pole only when the peptide concentration reached 128 μM.
4. Conclusions
This study has uncovered valuable insights into the antimicrobial functional peptide LRGG, which is expressed through the prokaryotic expression vector pQE-GFP-LRGG. This study demonstrated that the fusion protein of AMP LRGG has a wide range of antibacterial effects on gram-negative bacteria. Additionally, the peptide has shown remarkable stability under various environmental conditions, such as temperature, pH, salt ion, and serum conditions. Moreover, this peptide has been proven to be safe at its Minimal Inhibition Concentration for tested model animals, which is encouraging for prospective antibacterial treatments. The peptide's primary mode of action involves disrupting the Gram-negative bacteria's cell membrane, leading to their death. This ground breaking development in the realm of antibacterial treatments holds great potential.
5. Discussion
Natural AMPs are present at low concentrations in host organisms and are challenging to isolate due to complicated purification procedures. The high cost of chemical synthesis also limits the use of synthetic AMPs, making neither isolation nor chemical synthesis of AMPs good choices for clinical application. Therefore, this study aimed to produce and test the antimicrobial properties of a fully designed AMP that effectively fights against Gram-negative bacteria. Which is the peptide LRGG.
The mode of expression of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and protein tag fusion plays a crucial role in bacterial expression systems. This affects their subsequent purification. In a study by Chen Xin et al., four fusion tags (TrxA, SUMO, protein internal peptides, and GST) were fused with Mycelin and expressed in
Escherichia coli for purification and antimicrobial activity assays [
40]. M. P. Ali et al. fused green fluorescent protein (GFP) with the cell insect toxin Cit1a for expression in silkworms. This finding is consistent with the use of GFP and antimicrobial peptide fusion for expression. This approach effectively prevents the bactericidal effects of antimicrobial peptides on the host bacterium and allows further purification of the antimicrobial peptide [
41]. The 6X His tag added in this study can be used to purify antimicrobial peptides. The construction method used in this study combines the fusion tag GFP with the TEV restriction enzyme and adds the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG, which has been reported in previous research. In this study, the expression vector pQE-GFP-LR
GG was constructed, and the GFP-LR
GG fusion protein was produced by prokaryotic expression. After chromatographic purification and TEV protease cleavage, the purity expressed LR
GG was prepared.
Furthermore, the effects of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and different environmental conditions on the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG were examined. The findings demonstrate that LR
GG exhibits excellent stability under conditions that are typically considered harsh, highlighting its potential as a promising candidate for various applications. However, the results showed that the stability of the peptide LR
GG toward proteases could be improved. This is particularly important because the body contains multiple proteases that can breakdown proteins. The peptide segment of LR
GG is short, consisting of only 16 amino acids, making it highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation. Consequently, the MIC decreased significantly, while the antibacterial activity decreased after protease treatment. Researchers have suggested that modifying the chemical structure of AMPs can enhance the stability of their polypeptides, preventing them from being degraded by proteins [
42]. Additionally, the use of liposome-coated AMPs for delivery can also maintain their stability and reduce their toxicity [
43]. This approach has potential clinical benefits for the application of antimicrobial peptides.
In vitro experiments were conducted to measure the cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity of chemically synthesized and expressed LRGG. The results of safety assessment experiments at the cellular level revealed that LRGG exhibited no hemolytic activity, and no cytotoxicity was detected for either chemically synthesized or expressed LRGG at MIC values of 1-64. Therefore, further research was conducted to determine the toxicity of LRGG to zebrafish embryos. The results showed that the expression of LRGG and chemical synthesis of LRGG at a concentration of 1 × MIC, comparable to the negative control, did not change the morphology of the zebrafish. These results indicate that neither the expressed nor chemically synthesized antimicrobial peptide LRGG had any toxic effects on zebrafish.
The structure of AMPs is crucial to their biological function. The antimicrobial peptide LR
GG examined in this study has an amino acid sequence of (LLRLLRRGGRRLLLLRLL-NH2) and is composed of an α-helix structure [
26]. With arginine as a positively charged amino acid and leucine as a hydrophobic amino acid, it has a tremendous membrane-breaking structure. The positive charge of this antimicrobial peptide and the negative control on the bacterial membrane increase membrane permeability due to electrostatic interactions. This leads to the release of the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG into the cell plasma membrane, eventually causing lysis of the plasma membrane and leading to the death of microbial pathogens. In addition, bacteria can be inhibited by disrupting bacterial cell membranes. In another study, LR
GG was shown to be even more effective when used in combination with ciprofloxacin, colistin, and other antibiotics. LR
GG damages the outer membrane of pathogenic bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and disrupting the ability of the Fe
3+ transport system to permease the FecD protein in the inner membrane (unpublished data). In this study, the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG only bound to DNA at high concentrations, not at the MIC. We suspect that this could be because the DNA double-strand itself is negatively charged, and the antimicrobial peptide is positively charged. As the concentration of antimicrobial peptide increases, it will naturally bind to DNA. Therefore, the exact antibacterial mechanism of the antimicrobial peptide LR
GG after rupture at the lowest inhibitory concentration requires further study.
Author Contributions
C-GH, Y-HH and H-XM conceived and designed the research. Y-HS, S-ZL, Y-HL, S-KW, H-PZ and L-CK conducted the experiments. CG and AF contributed new reagents or analytical tools. L-CK and L-LG analyzed the data. XL and Y-ND wrote the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding and Acknowledgment
This study was funded by the Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program (Grant number: 20230402037GH) and the Open Research Fund of the Engineering Research Center of Bioreactor and Pharmaceutical Development, Ministry of Education. (Grant number: KF202101), which provide by He Yu-Hua of Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University, Animal Science and Technology College, Jilin, China.
References
- Bruce J, Oyedemi B, Parsons N, Harrison F. Phase 1 safety trial of a natural product cocktail with antibacterial activity in human volunteers. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 16;12(1):19656. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsang J. Bacterial plasmid addiction systems and their implications for antibiotic drug development. Postdoc J. 2017 May;5(5):3-9. [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu L, Wang W, Xu W . Effects of tetracycline antibiotics in chicken manure on soil microbes and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs)[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021:1-12. [CrossRef]
- Wiman E, Zattarin E, Aili D, Bengtsson T, Selegård R, Khalaf H. Development of novel broad-spectrum antimicrobial lipopeptides derived from planta ricin NC8 β. Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 13;13(1):4104. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Topalova Y, Belouhova M, Velkova L, Dolashki A, Zheleva N, Daskalova E, Kaynarov D, Voelter W, Dolashka P. Effect and Mechanisms of Antibacterial Peptide Fraction from Mucus of C. aspersum against Escherichia coli NBIMCC 8785. Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 14;10(3):672. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tallet L, Frisch E, Bornerie M, Medemblik C, Frisch B, Lavalle P, Guichard G, Douat C, Kichler A. Design of Oligourea-Based Foldamers with Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities. Molecules. 2022 Mar 7;27(5):1749. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mardirossian M, Rubini M, Adamo MFA, Scocchi M, Saviano M, Tossi A, Gennaro R, Caporale A. Natural and Synthetic Halogenated Amino Acids-Structural and Bioactive Features in Antimicrobial Peptides and Peptidomimetics. Molecules. 2021 Dec 6;26(23):7401. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hanson MA, Lemaitre B, Unckless RL. Dynamic Evolution of Antimicrobial Peptides Underscores Trade-Offs Between Immunity and Ecological Fitness. Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 8;10:2620. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin Y, Jiang Y, Zhao Z, Lu Y, Xi X, Ma C, Chen X, Zhou M, Chen T, Shaw C, Wang L. Discovery of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide, Temporin-PKE, from the Skin Secretion of Pelophylax kl. esculentus, and Evaluation of Its Structure-Activity Relationships. Biomolecules. 2022 May 29;12(6):759. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tomb RM, Maclean M, Coia JE, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG. Assessment of the potential for resistance to antimicrobial violet‒blue light in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017 Sep 29;6:100. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Czechowicz P, Neubauer D, Nowicka J, Kamysz W, Gościniak G. Antifungal Activity of Linear and Disulfide-Cyclized Ultrashort Cationic Lipopeptides Alone and in Combination with Fluconazole against Vulvovaginal Candida spp. Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 30;13(10):1589. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Popa C, Shi X, Ruiz T, Ferrer P, Coca M. Biotechnological Production of the Cell Penetrating Antifungal PAF102 Peptide in Pichia pastoris. Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 27;10:1472. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vinutha A S , Rajasekaran R .Insight on the mechanism of hexameric Pseudin-4 against bacterial membrane-mimetic environment[J].Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design, 2023, 37(9):419-434. [CrossRef]
- Won TaeJun, Mohid Sk Abdul, Choi JiHye, et al. The role of hydrophobic patches of de novo designed MSI-78 and VG16KRKP antimicrobial peptides on fragmenting model bilayer membranes[J]. Biophysical Chemistry, 2023, 296:106981-106981. [CrossRef]
- Prashant K , Jayachandran K , Suzana S . Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo[J]. Biomolecules, 2018, 8(1):4-17. [CrossRef]
- Mandel S , Michaeli J , Nur N ,et al.OMN6 a novel bioengineered peptide for the treatment of multidrug resistant Gram negative bacteria[J].Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz S, Behera S, Mukhopadhyay K. Lipidated Short Analog of α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Exerts Bactericidal Activity against the Stationary Phase of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Inhibits Biofilm Formation. ACS Omega. 2020 Oct 26;5(44):28425-28440. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panevska A, Hodnik V, Skočaj M, Novak M, Modic Š, Pavlic I, Podržaj S, Zarić M, Resnik N, Maček P, Veranič P, Razinger J, Sepčić K. Pore-forming protein complexes from Pleurotus mushrooms kill western corn rootworm and Colorado potato beetle through targeting membrane ceramide phosphoethanolamine. Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 25;9(1):5073. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panevska A, Čegovnik N, Fortuna K, Vukovič A, Grundner M, Modic Š, Bajc G, Skočaj M, Mravinec Bohte M, Popošek LL, Žigon P, Razinger J, Veranič P, Resnik N, Sepčić K. A single point mutation expands the applicability of ostreolysin A6 in biomedicine. Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 7;13(1):2149. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tomislav Rončević, Jasna Puizina, Alessandro Tossi, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides as Anti-Infective Agents in Pre-Post-Antibiotic Era[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(22):5713-5713. [CrossRef]
- Rima Mariam, Rima Mohamad, Fajloun Ziad, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: A Potent Alternative to Antibiotics[J]. Antibiotics, 2021, 10(9):1095-1095. [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Sun, L.C.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, P.; He, J.; Mackey, V.; Coy, D.H.; He, Q.Y. The antimicrobial peptides and their potentialclinical applications. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3919–3931. [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Håkansson, J.; Ringstad, L.; Björn, C. Antimicrobial peptides: An emerging category of therapeutic agents. Front.Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 194-208. [CrossRef]
- Bin Hafeez Ahmer, Jiang Xukai, Bergen Phillip J., et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Update on Classifications and Databases[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(21):11691-11691. [CrossRef]
- Upton M , Cotter P , Tagg J . Antimicrobial Peptides as Therapeutic Agents[J]. International Journal of Microbiology, 2012, 2012:326503-326512. [CrossRef]
- Boyan Jia, Yiming Wang,y, Ying Zhang, Zi Wang, Xue Wang, Inam Muhammad, Lingcong Kong, Zhihua Pei, Hongxia Ma, and Xiuyun Jiang. High Cell Selectivity and Bactericidal Mechanism of Symmetric Peptides Centered on d-Pro–Gly Pairs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1140. [CrossRef]
- Sampaio de Oliveira Kamila Botelho, Leite Michel Lopes, Rodrigues Gisele Regina, et al. Strategies for recombinant production of antimicrobial peptides with pharmacological potential.[J]. Expert review of clinical pharmacology, 2020, 13(4):367-390. [CrossRef]
- MejíaPitta Adriana, Broset Esther, de la FuenteNunez Cesar, et al. Probiotic engineering strategies for heterologous production of antimicrobial peptides.[J]. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2021, 176:113863-113863. [CrossRef]
- Bartolo-Aguilar Y, Chávez-Cabrera C, Flores-Cotera LB, Badillo-Corona JA, Oliver-Salvador C, Marsch R. The potential of cold-shock promoters for the expression of recombinant proteins in microbes and mammalian cells. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 29;20(1):173. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmadi Z, Farajnia S, Farajzadeh D, Pouladi N, Pourvatan N, Karbalaeimahdi M, Shayegh F, Arya M. Optimized Signal Peptide for Secretory Expression of Human Recombinant Somatropin in Eschericha coli. Adv Pharm Bull. 2023 Mar;13(2):339-349. Epub 2022 Apr 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Starr CG, Wimley WC. Antimicrobial peptides are degraded by the cytosolic proteases of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017 Dec;1859(12):2319-2326. Epub 2017 Sep 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deo Soumya, Turton Kristi L, Kainth Tajinder, et al. Strategies for improving antimicrobial peptide production.[J]. Biotechnology advances, 2022, 59:107968-107968. [CrossRef]
- Lee Tek-Hyung, Carpenter Timothy S, D'haeseleer Patrik, et al. Encapsulin carrier proteins for enhanced expression of antimicrobial peptides.[J]. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 2020, 117(3):603-613. [CrossRef]
- Chalfie M . Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression[J]. Trends in Genetics, 1994, 10(5):151-151. [CrossRef]
- Müller, Hagen, Salzig D, Czermak P. Considerations for the process development of insect-derived antimicrobial peptide production[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2015, 31(1):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Blommel P G, Fox B G. A combined approach to improving large-scale production of tobacco etch virus protease.[J]. Protein Expression & Purification, 2007, 55(1):53-68. [CrossRef]
- Kurussi S R, Cherry S, Zhang D, and S Waugh. Removal of Affinity Tags with TEV Protease. Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1586: 221–230. [CrossRef]
- Dong N, Zhu X, Chou S, et al. Antimicrobial potency and selectivity of simplified symmetricend peptides[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(27): 8028-8039. [CrossRef]
- Chou S L, Shao C X, Wang J J, et al. Short, multiple-stranded β-hairpin peptides have antimicrobial potency with high selectivity and salt resistance[J]. Acta Biomater, 2016, 30: 78-93. [CrossRef]
- Chen Xin, Shi Jiawei, Chen Rui, et al. Molecular chaperones (TrxA, SUMO, Intein, and GST) mediating expression, purification, and antimicrobial activity assays of plectasin in Escherichia coli.[J]. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry, 2015, 62(5):606-14. [CrossRef]
- Ali M P, Yoshimatsu Katsuhiko, Suzuki Tomohiro, et al. Expression and purification of cyto-insectotoxin (Cit1a) using silkworm larvae targeting for an antimicrobial therapeutic agent.[J]. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 2014, 98(16):6973-82. [CrossRef]
- Dale Beverly A, Fredericks L Page.Antimicrobial peptides in the oral environment: expression and function in health and disease.[J]. Current issues in molecular biology, 2005, 7(2):119-33. [CrossRef]
- F.L. Brancatisano, G. Maisetta, F. Barsotti, et al. Reduced Human Beta Defensin 3 in Individuals with Periodontal Disease[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 2011, 90(2):241-245. [CrossRef]
Figure 2.
Construction of PQE-GFP-LRGG expression vector. A: lane M:Trans5K DNA Marker;lane 1: Linearized pQE80-KAN vector, lane 2: gfp gene, lane 3: TEV site - LRGG fragmen. B: lane M: Trans2K DNA Marker lane 1: GFP + TEV sites restriction + LRGG .
Figure 2.
Construction of PQE-GFP-LRGG expression vector. A: lane M:Trans5K DNA Marker;lane 1: Linearized pQE80-KAN vector, lane 2: gfp gene, lane 3: TEV site - LRGG fragmen. B: lane M: Trans2K DNA Marker lane 1: GFP + TEV sites restriction + LRGG .
Figure 3.
Induced expression and purification of GFP-LRGG fusion protein. Fusion protein GFP-LRGG purification resulte by Ni-NTA column, lane 1: Before purify, lane 2: Flow through, M: Molecular weight standard, lane 3-7: elution of 300 mM Imidazole.
Figure 3.
Induced expression and purification of GFP-LRGG fusion protein. Fusion protein GFP-LRGG purification resulte by Ni-NTA column, lane 1: Before purify, lane 2: Flow through, M: Molecular weight standard, lane 3-7: elution of 300 mM Imidazole.
Figure 4.
Tricine-SDS‒PAGE results after the TEV enzyme cutting the label protein. 1: Before cutting; 2: After TEV enzyme cutting; 3: Purified LRGG of TEV enzyme cutting; 4: Chemical synthesis of LRGG.
Figure 4.
Tricine-SDS‒PAGE results after the TEV enzyme cutting the label protein. 1: Before cutting; 2: After TEV enzyme cutting; 3: Purified LRGG of TEV enzyme cutting; 4: Chemical synthesis of LRGG.
Figure 5.
Cytotoxicity of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG to RAW264.7 (A) and Vero (B) cells. Note: * * * P< 0.001 indicates a very significant difference, * * P< 0.01 indicates a very significant difference, * P< 0.05 indicates a significant difference.
Figure 5.
Cytotoxicity of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG to RAW264.7 (A) and Vero (B) cells. Note: * * * P< 0.001 indicates a very significant difference, * * P< 0.01 indicates a very significant difference, * P< 0.05 indicates a significant difference.
Figure 6.
Hemolytic activity of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG on sheep red blood cells. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 6.
Hemolytic activity of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG on sheep red blood cells. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 7.
Embryonic safety of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG in zebrafish. A.Negative control containing culture medium; B. Containing 1 × Expression peptide LRGG at MIC concentration; C. Containing 200 μg/mL sodium dehydroacetate; D. Containing 1 ×MIC of the Chemical Synthesis Peptide LRGG.
Figure 7.
Embryonic safety of the expressed peptide LRGG and the synthetic peptide LRGG in zebrafish. A.Negative control containing culture medium; B. Containing 1 × Expression peptide LRGG at MIC concentration; C. Containing 200 μg/mL sodium dehydroacetate; D. Containing 1 ×MIC of the Chemical Synthesis Peptide LRGG.
Figure 8.
Pairs E. expressing peptide LRGG Inner (A) and Outer (B) Membrane Permeability of E. coli ATCC25922. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 8.
Pairs E. expressing peptide LRGG Inner (A) and Outer (B) Membrane Permeability of E. coli ATCC25922. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 9.
Effect of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG on the plasma membrane potential of E. coli ATCC25922. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 9.
Effect of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG on the plasma membrane potential of E. coli ATCC25922. Note: * * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * * P<0.01, there is a very significant difference, * P<0.05, there is a significant difference.
Figure 10.
EMSA of genomic DNA (A) and plasmid DNA (B). A. The effect of LRGG on the genomic DNA of E. coli 25922 EMSA test. M: DL10000 DNA Marker;1-10 Gradually increasing concentrations of LRGG peptide(1-512μM);11: positive control;12: Negtive control. In addition, all 1-12 wills additional with E. coli 25922 genome (300 ng/μL). B. Effects of different concentrations of LRGG on the pkk3535 plasmid EMSA test. M: DL10000 DNA Marker;1-10 Gradually increasing concentrations of LRGG peptide(1-512μM);11: positive control;12: Negtive control. In addition, all 1-12 wills additional with pKK3535 plasmid (300 ng/μL).
Figure 10.
EMSA of genomic DNA (A) and plasmid DNA (B). A. The effect of LRGG on the genomic DNA of E. coli 25922 EMSA test. M: DL10000 DNA Marker;1-10 Gradually increasing concentrations of LRGG peptide(1-512μM);11: positive control;12: Negtive control. In addition, all 1-12 wills additional with E. coli 25922 genome (300 ng/μL). B. Effects of different concentrations of LRGG on the pkk3535 plasmid EMSA test. M: DL10000 DNA Marker;1-10 Gradually increasing concentrations of LRGG peptide(1-512μM);11: positive control;12: Negtive control. In addition, all 1-12 wills additional with pKK3535 plasmid (300 ng/μL).
Table 3.
MICs of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against bacteria (μM).
Table 3.
MICs of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against bacteria (μM).
| Test Strains |
MICs (μg/mL) |
| Chem. syn. LRGG
|
Expressed LRGG
|
Fusion protein
GFP-LRGG
|
| Gram-negative |
|
|
|
|
E.coli ATCC25922 |
2 |
2 |
›512 |
|
S. pullorum NCTC5776 |
4 |
4 |
›512 |
|
K. pneumoniae ATCC46117 |
8 |
16 |
›512 |
|
P.aeruginosaATCC27853 |
8 |
8 |
›512 |
|
S.flexneri CMCC51572 |
8 |
8 |
›512 |
| Gram-positive bacteria |
|
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 |
32 |
32 |
›512 |
|
S. aureus ATCC29213 |
16 |
16 |
›512 |
|
Enterococcus faecalis ATCC29212 |
32 |
32 |
›512 |
| MRSA |
256 |
128 |
›512 |
Table 4.
MIC value of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 at different temperature and pH value.
Table 4.
MIC value of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 at different temperature and pH value.
| AMPs |
Control
(pH 7) |
temperature |
pH |
| 0℃ |
37℃ |
100℃ |
pH 4 |
pH 6 |
pH 8 |
pH 10 |
| Chem. syn. LRGG
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
8 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
4 |
| Expressed LRGG
|
2 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
16 |
| Melittin |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
Table 5.
MIC values of the antibacterial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 under the action of different enzymes.
Table 5.
MIC values of the antibacterial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 under the action of different enzymes.
| Peptide |
control |
Proteinase (1 mg/mL) |
| Trypsin |
pepsin |
papain |
protease K |
| Chem. syn. LRGG
|
2 |
>128 |
>128 |
>64 |
>64 |
| Exprssed LRGG
|
4 |
>128 |
>128 |
>64 |
>64 |
| Melittin |
2 |
4 |
4 |
2 |
4 |
Table 6.
MIC value of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 under different salt ion environments.
Table 6.
MIC value of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 under different salt ion environments.
| Peptide |
Control |
Physical salt concentration |
| CaCl2
|
NaCl |
KCl |
NH4Cl |
MgCl2
|
| Chem. Syn. LRGG
|
2 |
4 |
8 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
| Expressed LRGG
|
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
4 |
8 |
| Melittin |
2 |
4 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Table 7.
MIC values of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 at different serum concentrations.
Table 7.
MIC values of the antimicrobial peptide LRGG against Eschericha coli ATCC25922 at different serum concentrations.
| peptide |
control |
Serum |
| 5% |
10% |
20% |
40% |
50% |
| Chem. syn. LRGG
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
8 |
16 |
16 |
| Expressed LRGG
|
2 |
2 |
4 |
32 |
32 |
32 |
| Melittin |
2 |
32 |
128 |
128 |
128 |
128 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).