1. Introduction
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has infected more than 704.0 million people and caused more than 7.0 million deaths as of March 11, 2024 [
1]. Currently, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has only approved four COVID-19 treatments: veklury (remdesivir), Olumiant (baricitinib), Actemra (tocilizumab), and Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) [
2]. However, SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, has continuously mutated, leading to variants such as Omicron, which may be able to escape treatments [
3]. For example, monoclonal antibodies, which were previously authorized as COVID-19 treatments, had their approval revoked by the FDA following the emergence of Omicron [
4]. In addition, post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also known as Long COVID, remains an issue for at least 65 million people, yet no treatment has been discovered [
5,
6]. Therefore, increasing the range of therapeutic options is critical as SARS-CoV-2 evolves and continues to cause COVID-19 and PASC.
Host-directed antivirals, which target host proteins and pathways, are a potent strategy for COVID-19 treatments since they have broad-spectrum activity and decreased viral evasion [
7]. One example of host-directed antivirals are interferons (IFN), which are vital components of the innate immune response. They are produced in response to viral infection [
8]. IFN-alpha (α) and -beta (β) are Type I IFN that have previously received approval from the FDA to treat various conditions [
9]. IFN-α has been used to treat hepatitis B and C, melanomas and other cancers, and genital warts [
10]. IFN-β has previously been approved as a treatment for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) to delay the progression of this disease [
11].
Type I IFN have been evaluated for drug repurposing against COVID-19. It has been demonstrated that COVID-19 patients treated with IFN-α, individually or in combination with other therapeutics, had generally improved outcomes [
12,
13,
14]. However, treatments with IFN-β, individually or in combination with other antivirals, in various clinical trials against COVID-19 displayed mixed results, ranging from worsened outcomes to improved outcomes [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. With the lack of conclusive efficacy, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommended in December 2023 against using Type I IFN as COVID-19 treatments except in clinical trials [
9]
However, few published studies have analyzed real-world evidence of Type I IFN treatment in COVID-19 patients with various disparate outcomes. Therefore, this study aims to determine the effect of IFN-α and -β treatment on respiratory, cardiovascular, neurological, and psychiatric outcomes, PASC, and death in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Through our work, we will contribute towards identifying whether IFN-α and -β may serve as effective therapeutics against COVID-19.
2. Materials and Methods
Database Network
This study was conducted with data obtained from TriNetX, LLC (TriNetX), a global federated health research network that furnishes access to electronic medical records (EMRs) from more than 300 million patients. TriNetX is continuously updated with data from healthcare organizations worldwide and includes demographics, diagnoses, procedures, medications, and labs. These data are deidentified, exempting them from Institutional Review Board approval. TriNetX complies with the United States’ Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Study and Cohort Design
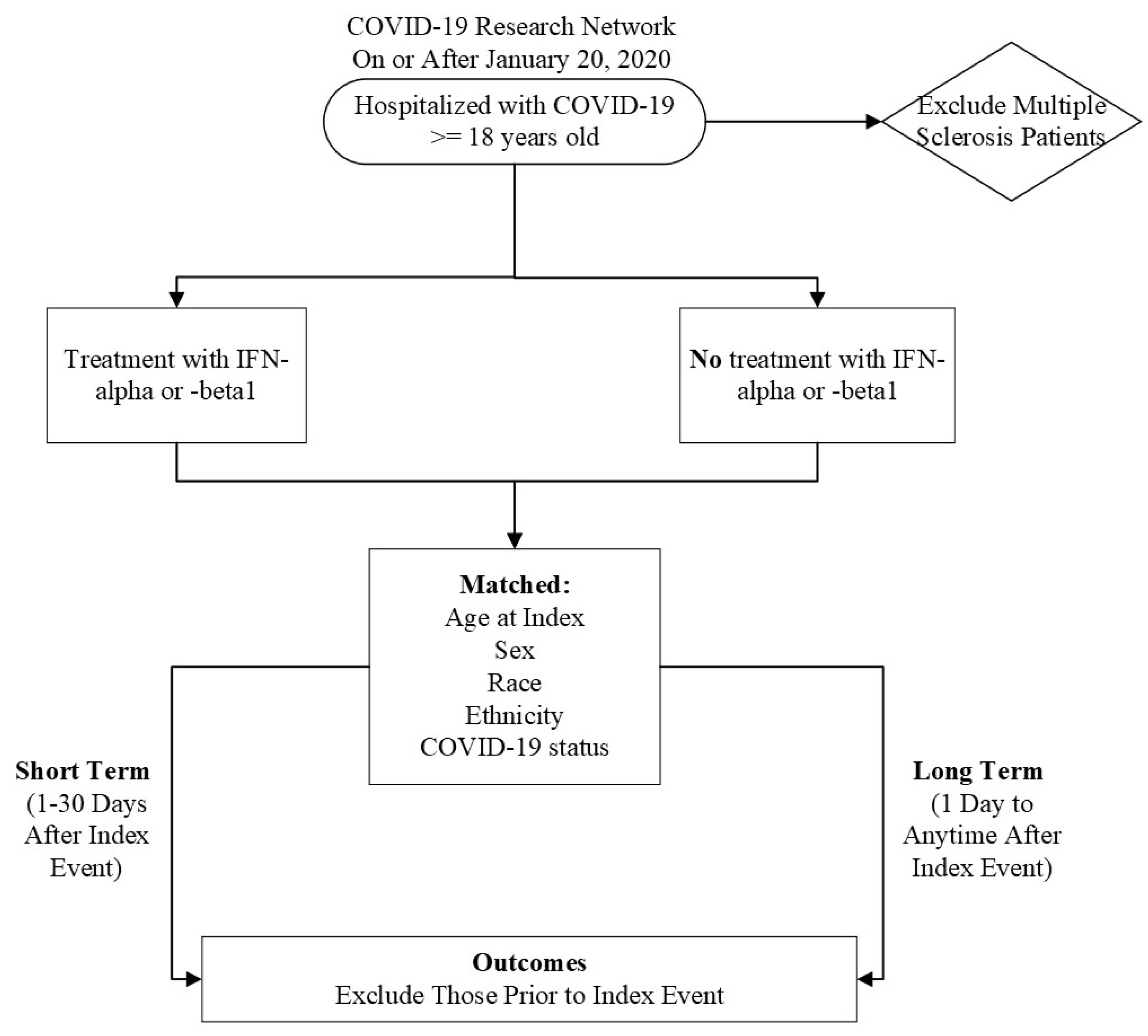
Initially, we characterized our cohort of interest using the TriNetX Research Network. We then performed a retrospective cohort study using the COVID-19 Research Network (
Figure 1). Our study time frame began on January 20, 2020, when COVID-19 was officially diagnosed in the United States, until the date of analysis (October 27, 2023). Our exposed population was patients who were ≥ 18 years old and had a diagnosis of COVID-19 but did not have MS. A patient was considered to have COVID-19 if they had the ICD-10-CM code U07.1 or had a positive result, as compiled and aggregated by TriNetX. A complete list of codes is included in
Supplementary Table S1. These patients received IFN-α or -β treatment after their initial COVID-19 diagnosis. Altogether, these criteria were defined as our “index event,” or the onset of disease and the identified conditions. Our unexposed, or control, cohort were COVID-19 patients who were ≥ 18 years old without multiple sclerosis who did not receive IFN-α or -β treatment after diagnosis. MS patients were excluded because IFN-β is an approved therapy for this autoimmune and chronic disease, creating a likelihood that MS patients may have already been treated with IFN-β prior to contracting COVID-19, which may confound the results [
21].
To account for potential confounders, the cohorts were propensity-score matched (1:1) within TriNetX on the following variables: Age at index, Race, Ethnicity, Sex, and COVID-19 status. All statistical analyses were performed using TriNetX on October 27, 2023. We utilized odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals to determine the odds of developing an outcome. If a patient had an outcome before the index event, their outcomes were excluded from calculations.
Outcomes
The respiratory outcomes of interest were: assistance with respiratory ventilation at high nasal flow/velocity (ICD-10-PCS: 5A0935A, 5A0945A, and 5A0955A), dependence on respiration (ventilator) (ICD-10-CM: Z99.11), pneumonia (ICD-10-CM: J12.82, J18, and J18.9), dyspnea (ICD-10-CM: R06.00 and R06.02), hypoxemia (ICD-10-CM: R09.02), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ICD-10-CM: J80), acute respiratory failure (ICD-10-CM: J96.0 and J96.00), respiratory ventilation (ICD-10-PCS: 5A1935Z, 5A1945Z, and 5A1955Z), PASC (ICD-10-CM: U09), and death (deceased). They have previously been associated with COVID-19 and are indicators of disease severity [
18].
The cardiovascular outcomes of interest were: essential (primary) hypertension (ICD-10-CM: I10), atrial fibrillation and flutter (ICD-10-CM: I48), acute pericarditis (ICD-10-CM: I30), heart failure (ICD-10-CM: I50), acute myocardial infarction (ICD-10-CM: I21), cardiac arrest (ICD-10-CM: I46), and pulmonary embolism (ICD-10-CM: I26). These outcomes had previously been identified as being elevated in COVID-19 patients [
22].
The neurological and psychiatric outcomes of interest were: nerve, nerve root, and plexus disorders (ICD-10-CM: G50-G59), diseases of myoneural junction and muscle (ICD-10-CM: G70-G73), dementia (ICD-10-CM: F01 or F02), substance use disorders (ICD-10-CM: F10-F19), psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders (ICD-10-CM: F20-F48), and insomnia (ICD-10-CM: F51 or G47.0) [
23].
3. Results
Cohort Characteristics: Research Network
To first characterize hospitalized COVID-19 patients who received Type I IFN, we utilized the TriNetX Research Network. As of October 8, 2023, this network contained data from 111,128,059 patients from 78 HCOs in 4 different countries. The analysis of this data was performed on October 8, 2023, and we had a total of 48 patients who fit the inclusion criteria.
There was an even split between males and females. In the cohort, 64% were non-Hispanic or Latino, while 20% were Hispanic or Latino. Most of the cohort was white (62%), while 20% were Black or African American. These patients were generally unhealthier before contracting COVID-19 and receiving Type I IFN treatment. Approximately 1-30 days prior, 44% of the cohort had circulatory system diseases, and 42% had neoplasms or endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases. Interestingly, 29% of the patients had been previously diagnosed with COVID-19. About 29% of the cohort had diseases of the nervous or respiratory system, while a quarter had acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease.
In terms of medications, 63% of the cohort were using central nervous system medications, with 50% being given analgesics. In addition, 60% were using cardiovascular medications. Interestingly, 58% were using antimicrobials, and 35% were using penicillin and beta-lactam antimicrobials. Related to diabetes, 27% of the cohort used blood glucose regulation agents.
Outcomes: Research Network
To briefly understand the outcomes experienced by this cohort, we examined the percentage of cohort members who developed pneumonia, PASC, or died. When we reviewed outcomes 1-30 days afterward, 96.2% of the cohort had not developed pneumonia, and 91.3% survived. Because PASC is defined as having signs, symptoms, and conditions that are present or develop four or more weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection, our time frame was one day until October 8, 2023 [
5]. We saw that 96.4% of the cohort did not develop PASC. Therefore, these patients generally had positive outcomes after hospitalization, COVID-19 infection, and treatment with a Type I IFN.
Cohort Characteristics: COVID-19 Research Network
We then utilized the TriNetX COVID-19 Research Network, which includes a subset of HCOs that previously indicated a desire to contribute towards COVID-19 research [
24]. It included data from 111,663,882 patients from 87 HCOs in 12 different countries. The analysis of this data was performed on October 27, 2023.
There was a total of 238 patients who were ≥ 18 years old without MS and were treated with a type I IFN after their first instance of COVID-19 (
Table 1). More than half of the patients were male (62%), with an average age of 61.3 years at the time of analysis. However, 66% of the patients’ race and 64% of their ethnicity were unknown. More than 74% of the patients had already been diagnosed with COVID-19. One month prior to meeting the inclusion criteria, 4% of the cohort were diagnosed with hepatitis B, and 4% of the cohort had hepatitis C. Approximately 4% of the cohort was diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and 4% had malignant melanomas. No one had been diagnosed with hairy cell leukemia, Kaposi’s sarcoma, or genital warts.
Patients in our cohorts were also receiving other medications in addition to Type I IFN. Antivirals were utilized by 48% of the cohort of interest. In addition, 46% of them were using respiratory tract medications alongside Type I IFN. Hydroxychloroquine, which was eventually disproven as a therapy for COVID-19, was used by 42% of the cohort [
25]. Approximately 11% of the cohort of interest were treated with immunological agents as well.
In our control cohort, there was a total of 1,041,910 patients who met the criteria. However, when looking at baseline characteristics, information was only available for 909,529 patients. The average age of the patients was 55.7 years old, and 42% of the patient population were males. Approximately 68% of the patients were non-Hispanic or Latino, and 63% were White. Only 9% of the cohort had been infected with COVID-19 beforehand. A total of 306 patients (0.03%) of the cohort had hepatitis B, and 1,175 (0.13%) of the cohort had hepatitis C. Only 340 patients (0.04%) in the cohort were diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, 572 (0.06%) had malignant melanoma, 25 (0.002%) had hairy cell leukemia, 26 (0.003%) had been diagnosed with Kaposi’s sarcoma, and 174 (0.02%) had genital warts.
In contrast to our cohort of interest, only 3% of the control cohort was using antivirals. However, 20% were using respiratory tract medications such as bronchodilators. Only 1,788 patients, or 0.20% of our control cohort, were using hydroxychloroquine, while 4% of the control cohort were treated with immunological agents. Thus, the control cohort appeared to be taking less medications than the cohort of interest, which may suggest that they were relatively healthier.
After propensity score matching, there were a total of 231 patients in each cohort. Their characteristics were relatively similar, as shown in
Table 2. The average age was 61.4 years in our cohort of interest, while it was 61.5 years in our control cohort. Approximately 61.9% of our cohort of interest was male, which was nearly the same percentage of males in the control cohort (60.6%). In terms of ethnicity, 31.2% of the cohort treated with Type I IFN was non-Hispanic or Latino, while 29.4% of the control cohort was non-Hispanic or Latino. Both cohorts were composed of 26.4% Whites. There was slightly more Blacks or African Americans in the cohort of interest (4.8%) compared to the control cohort (4.3%). In both cohorts, approximately 71.9% of the patients were diagnosed with COVID-19.
Respiratory Outcomes 1-30 Days Afterwards: COVID-19 Research Network
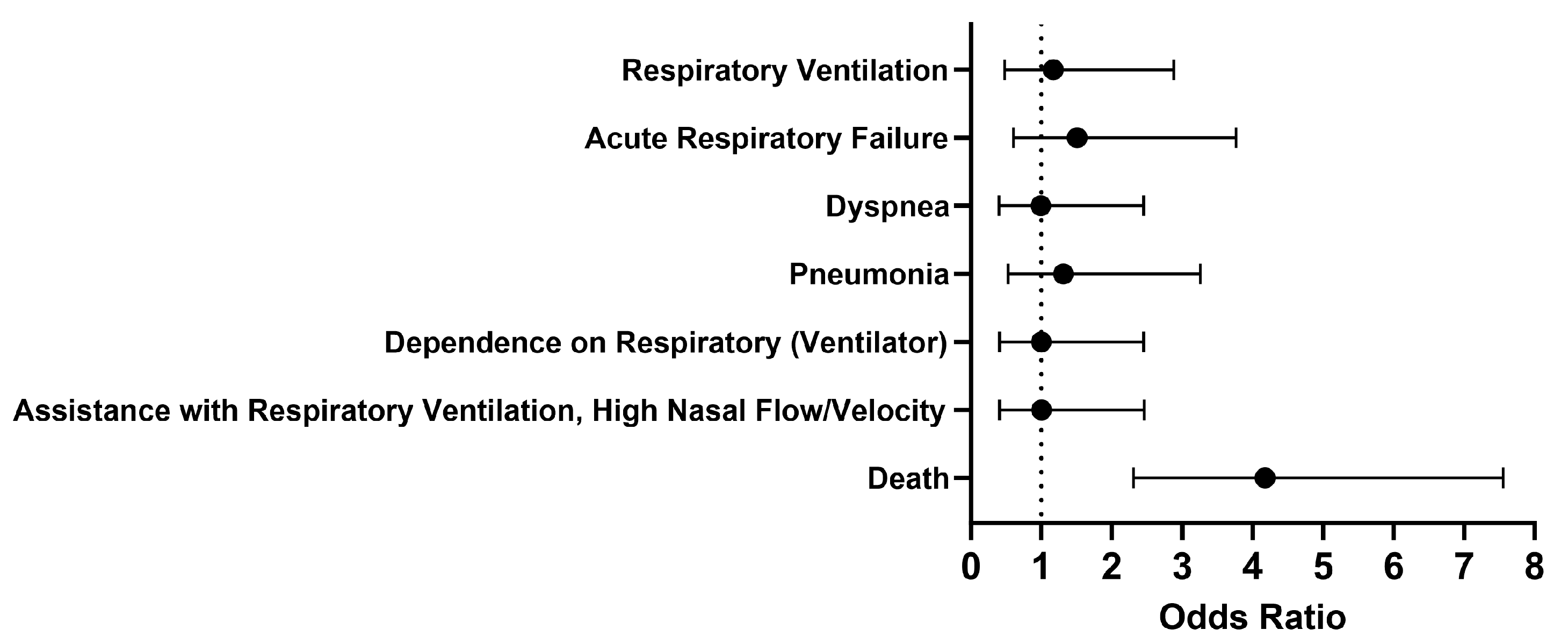
Overall, no significant differences were seen in respiratory outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients without MS who were treated with a Type I IFN compared to those who were untreated (
Figure 2). The odds of the examined outcomes were about the same or slightly higher in the cohort of interest compared to our control cohort. There was no significant difference between the cohorts 1 to 30 days after treatment in terms of respiratory ventilation (OR [95% CI]: 1.2 [0.5-2.9]), acute respiratory failure (OR [95% CI]: 1.5 [0.6-3.8]), dyspnea (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.5]), pneumonia (OR [95% CI]: 1.3 [0.5-3.3]), dependence on the respirator (ventilator) (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.5]), and assistance with respiratory ventilation at high nasal flow/velocity (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.5]). However, the odds of death were 4.2 times higher in COVID-19 patients without MS who received Type I IFN treatment compared to those who did not, with a 95% confidence interval of 2.3-7.5. The probability of survival was 76.0% in our cohort treated with IFN-α or -β.
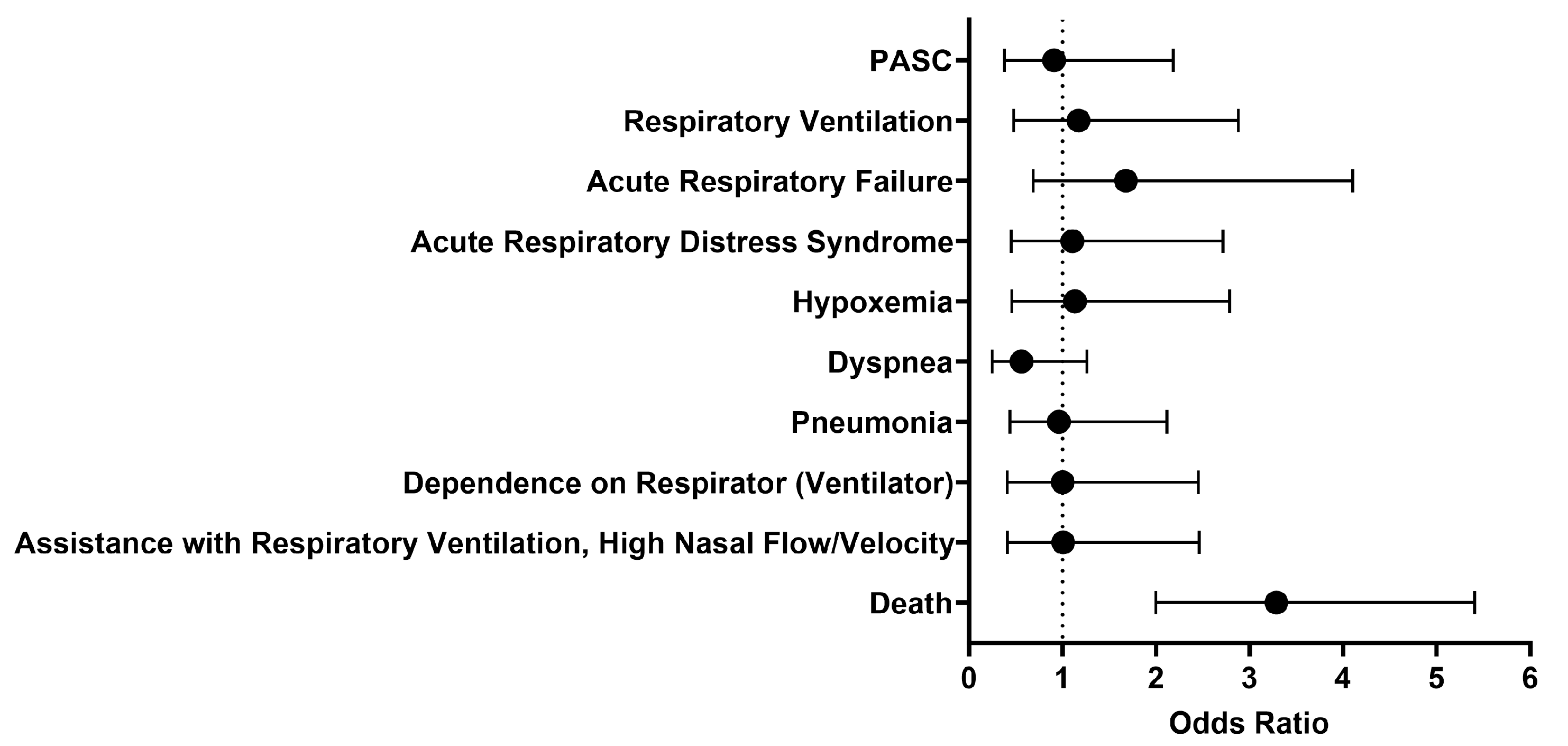
Respiratory Outcomes 1 Day Afterwards – October 27, 2023: COVID-19 Research Network
We then looked at outcomes one day to anytime afterwards, and the analysis was performed on October 27, 2023. The findings were generally similar to what was observed between 1 to 30 days after initial treatment with either IFN-α or -β (
Figure 3). The odds of respiratory ventilation (OR [95% CI]: 1.2 [0.5-2.9]), acute respiratory failure (OR [95% CI]: 1.7 [0.7-4.1]), acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR [95% CI]: 1.1 [0.5-2.7]), hypoxemia (OR [95% CI]: 1.1 [0.5-2.8]), developing pneumonia (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.1]), depending on respirator (ventilator) (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.5]), and needing assistance with respiratory ventilation at high nasal flow/velocity (OR [95% CI]: 1.0 [0.4-2.5]) were all approximately the same. The cohort treated with IFN-α or -β had slightly lower odds for being diagnosed with dyspnea (OR [95% CI]: 0.6 [0.2-1.3]) and PASC (OR [95% CI]: 0.9 [0.4-2.2]). Though there was generally no significant difference in selected outcomes between the two cohorts, the cohort that received Type I IFN treatment had 3.3 times higher odds of dying as compared to the comparison cohort. However, the survival probability was 70.4%, as 160 out of 227 patients survived.
Cardiovascular Outcomes 1 Day – Anytime Afterwards: COVID-19 Research Network
Since SARS-CoV-2 not only affects the respiratory tract, we decided to explore other systems such as the cardiovascular system. COVID-19 has previously been shown to increase the risk of cardiovascular issues such as heart attack and stroke up to a year post-infection [
22]. Therefore, we decided to investigate whether treatment with Type I IFN would affects cardiovascular outcomes. The analysis was performed on March 10, 2024, and there were 275 patients in each cohort.
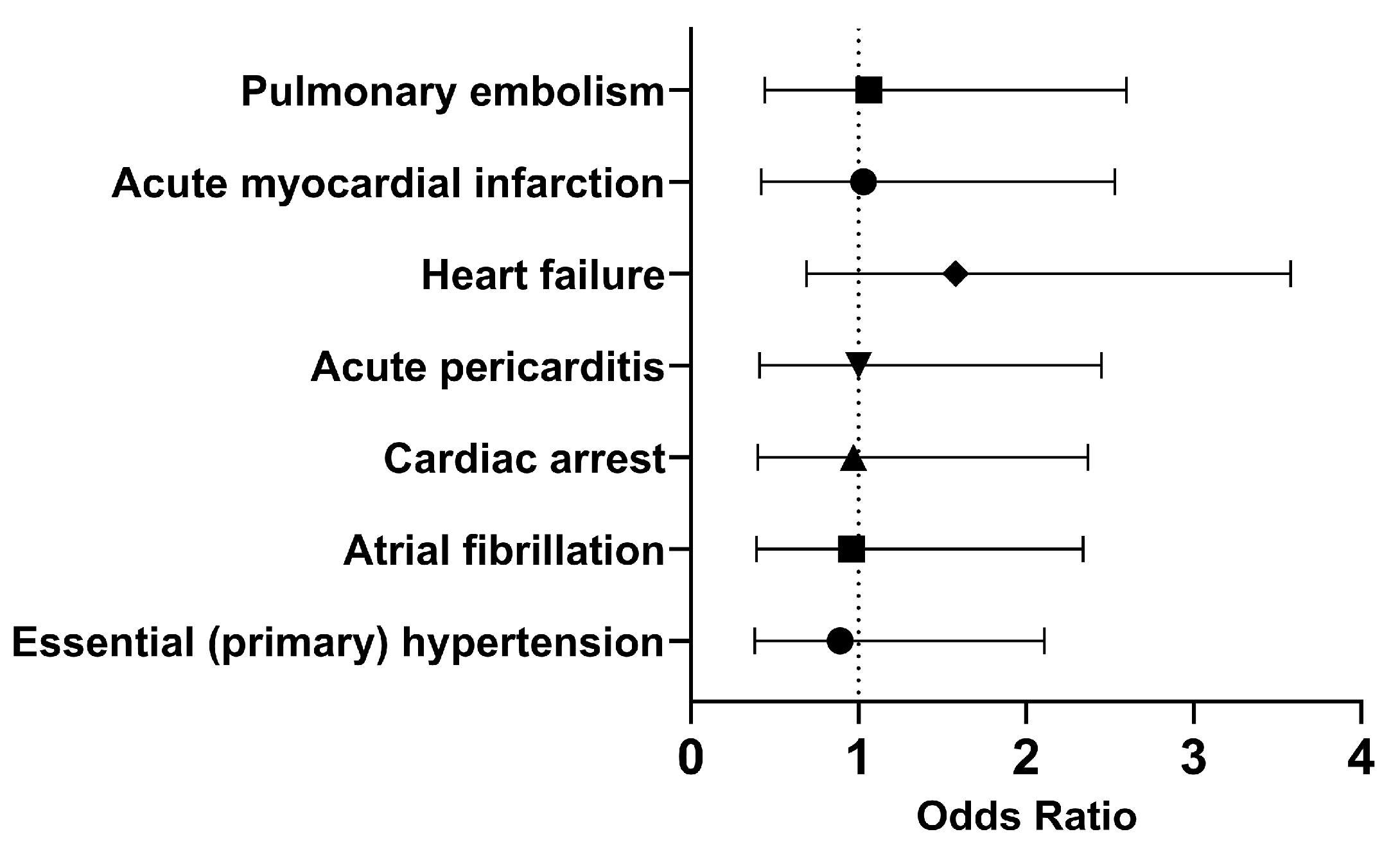
In both cohorts, most of the patients did not develop the selected outcomes within 30 days. Therefore, we investigated the long-term outcomes. The odds of having essential (primary) hypertension (OR [95% CI]: 0.89 [0.38, 2.11]), atrial fibrillation (OR [95% CI]: 0.96 [0.39, 2.34]), cardiac arrest (OR [95% CI]: 0.97 [0.40, 2.37]) were slightly lower in the cohort of interest compared to the control cohort. However, COVID-19 patients who had been treated with Type I IFN had approximately the same or slightly higher odds of developing acute pericarditis (OR [95% CI]: 1.00 [0.41, 2.45]), heart failure (OR [95% CI]: 1.58 [0.69, 3.58]), acute myocardial infarction (OR [95% CI]: 1.03 [0.42, 2.53]), and pulmonary embolism (OR [95% CI]: 1.06 [0.44, 2.60]). Overall, it appears that the odds of developing cardiovascular issues were approximately the same in both cohorts in the long term.
Figure 4.
Odds ratio of cardiovascular outcomes in COVID-19 patients with Type I IFN treatment compared to COVID-19 patients without Type I IFN treatment, 1 day to anytime afterwards.
Figure 4.
Odds ratio of cardiovascular outcomes in COVID-19 patients with Type I IFN treatment compared to COVID-19 patients without Type I IFN treatment, 1 day to anytime afterwards.
Neurological and Psychiatric Outcomes 1 Day – Anytime Afterwards: COVID-19 Research Network
Lastly, we decided to explore neurological and psychiatric sequelae in our cohorts. A side effect of Type I IFN treatment includes development or worsening mental illness [
10,
11]. In addition, six months following SARS-CoV-2 infection, neurological and psychiatric sequelae may occur, though these outcomes may be transient [
23,
26]. Therefore, it was important to understand what neurological and psychiatric outcomes patients treated with Type I IFN might experience. The analysis was performed on March 10, 2024, and each cohort had 275 patients following propensity score matching.
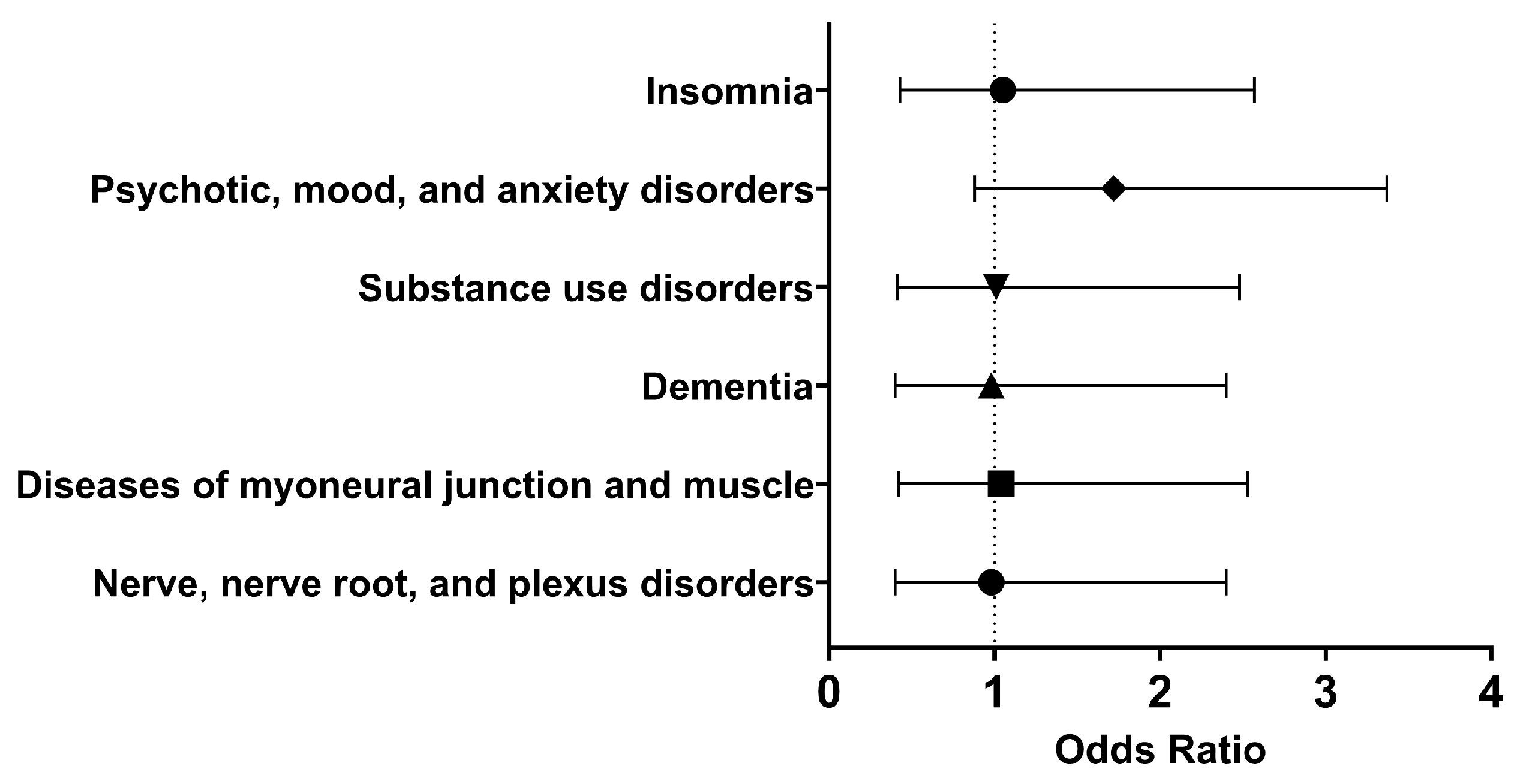
Within thirty days of hospitalization with COVID-19 and Type I IFN treatment, the cohort of interest had approximately the same odds as the control cohort of having nerve, nerve root, and plexus disorders (OR [95% CI]: 0.98 [0.40, 2.40]), substance use disorders (OR [95% CI]: 1.01 [0.41, 2.48]), psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders (OR [95% CI]: 0.94 [0.38, 2.30]), and insomnia (OR [95% CI]: 1.05 [0.43, 2.57]). Therefore, in the short term, using Type I IFN neither alleviated nor increased the odds of these neurological and psychiatric disorders.
In the long term, there were similar odds of developing nerve, nerve root, and plexus disorders (OR [95% CI]: 0.98 [0.40, 2.40]), diseases of myoneural junction and muscle (OR [95% CI]: 1.04 [0.42, 2.53]), dementia (OR [95% CI]: 0.98, 0.40, 2.40), substance use disorders (OR [95% CI]: 1.01 [0.41, 2.48]), psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders (OR [95% CI]: 1.72 [0.88, 3.37]), and insomnia (OR [95% CI]: 1.05 [0.43, 2.57]). Therefore, it appeared that Type I IFN treatment did not significantly affect selected neurological and psychiatric sequelae.
Figure 5.
Odds ratio of neurological and psychiatric outcomes in COVID-19 patients with Type I IFN treatment compared to COVID-19 patients without Type I IFN treatment, 1 day to anytime afterwards.
Figure 5.
Odds ratio of neurological and psychiatric outcomes in COVID-19 patients with Type I IFN treatment compared to COVID-19 patients without Type I IFN treatment, 1 day to anytime afterwards.
4. Discussion
Overall, hospitalized COVID-19 patients without MS who were or were not treated with a Type I IFN had similar odds of selected respiratory, cardiovascular, neurological, and psychiatric outcomes. This is important in terms of neurological and psychiatric sequelae because Type I IFN treatment can lead to severe side effects, such as depression, mood and behavior problems, and suicidal ideation [
10,
11]. Therefore, our study suggests that Type I IFN treatment may not significantly affect long-term neurological and psychiatric outcomes.
The most significant difference between cohorts was mortality in the short- and long-term. The odds of death decreased from 4.2 (1-30 days after treatment) to 3.3 (1 day to anytime afterwards), suggesting that death occurred soon after treatment was initiated (data not shown). Though the odds of mortality are higher in our treated cohort in the short- and long-term, the cause of death may not be related to the respiratory, cardiovascular, neurological, and psychiatric sequelae we examined. Therefore, it would be interesting to further determine what may have contributed to mortality to better prevent it from occurring.
An important consideration is that patients in our cohort of interest were generally unhealthier than our control cohort. When looking at the Research Network, nearly a third or a half of the patients had pre-existing health conditions and were taking medications. In the COVID-19 Research Network, nearly 75% of the cohort had already been diagnosed with COVID-19. In addition, our cohort was composed of older adults (average age: 61.2 years), so they may have been at higher risk of severe disease [
27]. Thus, IFN treatment may not have been as effective in this cohort as it might be in other populations.
In addition, treatment with Type I IFN may not directly affect the respiratory, cardiovascular, or neurological systems. IFN-α was given either subcutaneously, intramuscularly, intravenously, or intralesionally, while IFN-β was given subcutaneously [
10,
11]. Mechanistically, Type I IFN induce an antiviral state in the host by activating the innate immune response. However, this resistance to viral infection is nonspecific [
28,
29]. Timing is also important in IFN production, as SARS-CoV-2 is able to delay the Type I IFN response. As the IFN response may have already been induced by the time the COVID-19 patient was hospitalized and treated with Type I IFN, this timing may have affected our results.
Another point is whether SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern affected the effectiveness of IFN treatment. In cell culture models, SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern appeared to have greater resistance to IFN treatment [
30]. Although it is not possible to know exactly which variant patients were infected with, as these data were not available, we could potentially correspond time of infection with the variant circulating in the future. Briefly, in our data (not shown), we saw that the greatest number of patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020 and 2022, and during these years, the original SARS-CoV-2 and the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant were spreading worldwide.
A potential bias is the inability to follow up participants, as some patients may have experienced outcomes that were not reported. In addition, the patients in both cohorts were hospitalized, which may lead to selection bias. The number of patients experiencing outcomes was often ≤ 10, which may affect the odds ratios. This also suggests that these outcomes were relatively rare in the cohorts. Though we tried to include as many potential confounders as possible, others may remain unaccounted for. Patients younger than 18 years old were excluded from the study, and as older adults are at higher risk of severe disease, this may have affected our outcomes. However, we attempted to account for this important risk factor through propensity score matching.
Our work lends support to the NIH’s position on Type I IFN as treatment options for COVID-19. However, patients treated with Type I IFN were generally unhealthier than the comparison cohort, meaning that these results should be taken with some caution. These findings may not apply to patients with MS, as they were excluded from this comparison. The patients in our cohort were also derived from multiple countries, so there might be different treatment strategies and other underlying factors that cannot be reflected in the data. Generally, though, Type I IFN did not appear to protect against mortality, though we observed similar odds of morbidity in the short- and long-term.
A potential future direction is to examine whether patients who received Type I IFN treatment prior to diagnosis with COVID-19 had improved outcomes, as earlier treatment with Type I IFN may improve outcomes. In addition, it would be interesting to include patients with MS and see if the results differed than what was found here. Another possibility would be to select different outcomes related to the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, or reproductive tract, as SARS-CoV-2 has demonstrated the ability to affect these systems as well [
5]. Lastly, we are interested in utilizing causal inference to determine the effectiveness of Type I IFN amongst the hospitalized COVID-19 patients who received treatment.
As COVID-19 continues to plague our society, discovering effective therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses remains a priority. Though type I IFN may not be a recommended treatment option for COVID-19, our work has broader underlying implications. As our study demonstrates, it is difficult to identify novel treatments for COVID-19. Traditionally, it takes 10 years and between 1.2-2.5 billion dollars for a drug to reach the clinic [
31]. However, the COVID-19 pandemic, the mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) outbreak, and other pathogens have demonstrated the ability to emerge and rapidly spread worldwide. Thus, we need to find treatments against potential pandemic pathogens to prevent future pandemics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Code for creation of cohorts; Table S2: Baseline characteristics of the cohort of interest in the COVID-19 Research Network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.Y.T., P.H., and G.G.; methodology, V.Y.T., G.G.; investigation, V.Y.T., G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, V.Y.T.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, C-T.K.T, G.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted with the support of the Institute for Translational Sciences at The University of Texas Medical Branch, supported in part by a Clinical and Translational Science Award (UL1TR001439) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to deidentification of data by TriNetX, LLC (TriNetX). TriNetX complies with the United States’ Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Leslie Stalnaker and Dr. Shannan Rossi for their helpful suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- COVID - Coronavirus Statistics - Worldometer [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
- Commissioner O of the. Know Your Treatment Options for COVID-19. FDA [Internet]. 2023 Dec 18 [cited 2024 Mar 11]; Available from: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19.
- VanBlargan LA, Errico JM, Halfmann PJ, Zost SJ, Crowe JE, Purcell LA, et al. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat Med [Internet]. 2022 Mar [cited 2024 Mar 11];28(3):490–5. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01678-y.
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/antivirals-including-antibody-products/anti-sars-cov-2-monoclonal-antibodies/.
- Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM, Topol EJ. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol [Internet]. 2023 Mar [cited 2024 Mar 11];21(3):133–46. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41579-022-00846-2.
- Long COVID | NIH COVID-19 Research [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Available from: https://covid19.nih.gov/covid-19-topics/long-covid.
- Chitalia VC, Munawar AH. A painful lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic: the need for broad-spectrum, host-directed antivirals. J Transl Med [Internet]. 2020 Oct 15 [cited 2024 Mar 11];18(1):390. [CrossRef]
- Galbraith MD, Kinning KT, Sullivan KD, Araya P, Smith KP, Granrath RE, et al. Specialized interferon action in COVID-19. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2022 Mar 15 [cited 2024 Mar 11];119(11):e2116730119. Available from: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2116730119.
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Interferons. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/antivirals-including-antibody-products/interferons/.
- Interferon Alfa-2b Injection: MedlinePlus Drug Information [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a690006.html.
- Interferon Beta-1b Injection: MedlinePlus Drug Information [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 11]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601151.html.
- Wang B, Li D, Liu T, Wang H, Luo F, Liu Y. Subcutaneous injection of IFN alpha-2b for COVID-19: an observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):723.
- Pandit A, Bhalani N, Bhushan BLS, Koradia P, Gargiya S, Bhomia V, et al. Efficacy and safety of pegylated interferon alfa-2b in moderate COVID-19: A phase II, randomized, controlled, open-label study. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;105:516–21.
- Yu J, Lu X, Tong L, Shi X, Ma J, Lv F, et al. Interferon-α-2b aerosol inhalation is associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease-2019. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;87(12):4737–46.
- Hung IFN, Lung KC, Tso EYK, Liu R, Chung TWH, Chu MY, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. The Lancet [Internet]. 2020 May 30 [cited 2024 Mar 11];395(10238):1695–704. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)31042-4/fulltext.
- Hassaniazad M, Farshidi H, Gharibzadeh A, Bazram A, Khalili E, Noormandi A, et al. Efficacy and safety of favipiravir plus interferon-beta versus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-beta in moderately ill patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. J Med Virol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2024 Mar 11];94(7):3184–91. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jmv.27724.
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium, Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo AM, Preziosi MP, Sathiyamoorthy V, et al. Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 - Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 11;384(6):497–511.
- Sosa JP, Ferreira Caceres MM, Ross Comptis J, Quiros J, Príncipe-Meneses FS, Riva-Moscoso A, et al. Effects of Interferon Beta in COVID-19 adult patients: Systematic Review. Infect Chemother. 2021 Jun;53(2):247–60.
- Tam AR, Zhang RR, Lung KC, Liu R, Leung KY, Liu D, et al. Early Treatment of High-Risk Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients With a Combination of Interferon Beta-1b and Remdesivir: A Phase 2 Open-label Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Infect Dis [Internet]. 2023 Feb 1 [cited 2024 Mar 11];76(3):e216–26. [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan P, Chew KW, Giganti MJ, Hughes MD, Moser C, Main MJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of inhaled interferon-β1a (SNG001) in adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomized, controlled, phase II trial. eClinicalMedicine [Internet]. 2023 Nov 1 [cited 2024 Mar 11];65. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(23)00427-3/fulltext.
- Multiple Sclerosis | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 12]. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/multiple-sclerosis.
- Xie Y, Xu E, Bowe B, Al-Aly Z. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Med [Internet]. 2022 Mar [cited 2024 Mar 12];28(3):583–90. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-01689-3.
- Taquet M, Geddes JR, Husain M, Luciano S, Harrison PJ. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry [Internet]. 2021 May 1 [cited 2024 Mar 12];8(5):416–27. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpsy/article/PIIS2215-0366(21)00084-5/fulltext#seccestitle80.
- TriNetX [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 12]. TriNetX. Available from: https://trinetx.com/real-world-resources/coronavirus/.
- World Health Organization [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Mar 12]. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Hydroxychloroquine. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-hydroxychloroquine.
- Taquet M, Sillett R, Zhu L, Mendel J, Camplisson I, Dercon Q, et al. Neurological and psychiatric risk trajectories after SARS-CoV-2 infection: an analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies including 1 284 437 patients. Lancet Psychiatry [Internet]. 2022 Oct 1 [cited 2024 Mar 12];9(10):815–27. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpsy/article/PIIS2215-0366(22)00260-7/fulltext#seccestitle10.
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023 [cited 2024 Mar 12]. Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19: Information for Healthcare Professionals. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html.
- McNab F, Mayer-Barber K, Sher A, Wack A, O’Garra A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol [Internet]. 2015 Feb [cited 2024 Mar 12];15(2):87–103. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nri3787.
- Houglum JE. Interferon: mechanisms of action and clinical value. Clin Pharm. 1983;2(1):20–8.
- Guo K, Barrett BS, Morrison JH, Mickens KL, Vladar EK, Hasenkrug KJ, et al. Interferon resistance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 2022 Aug 9 [cited 2024 Mar 12];119(32):e2203760119. Available from: https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2203760119.
- Subbiah V. The next generation of evidence-based medicine. Nat Med [Internet]. 2023 Jan [cited 2024 Mar 12];29(1):49–58. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-02160-z.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).