Submitted:
22 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
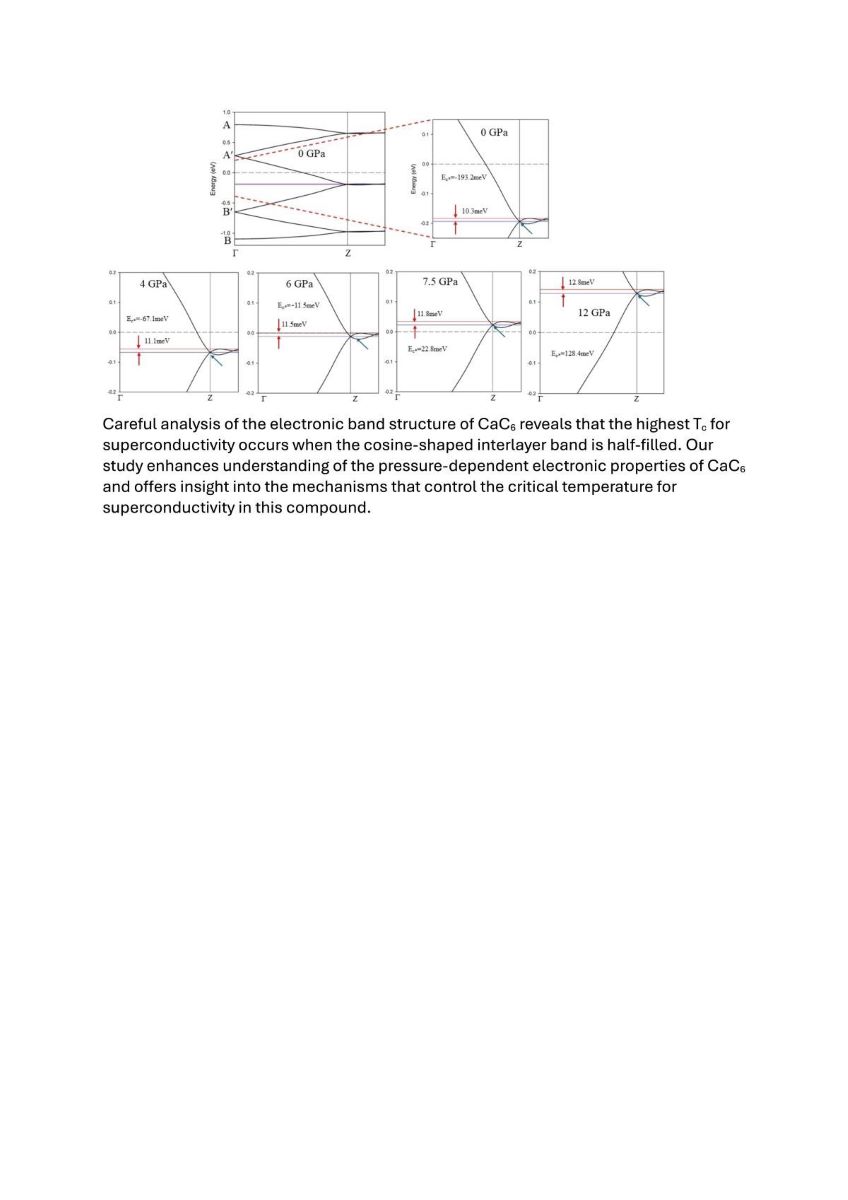
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
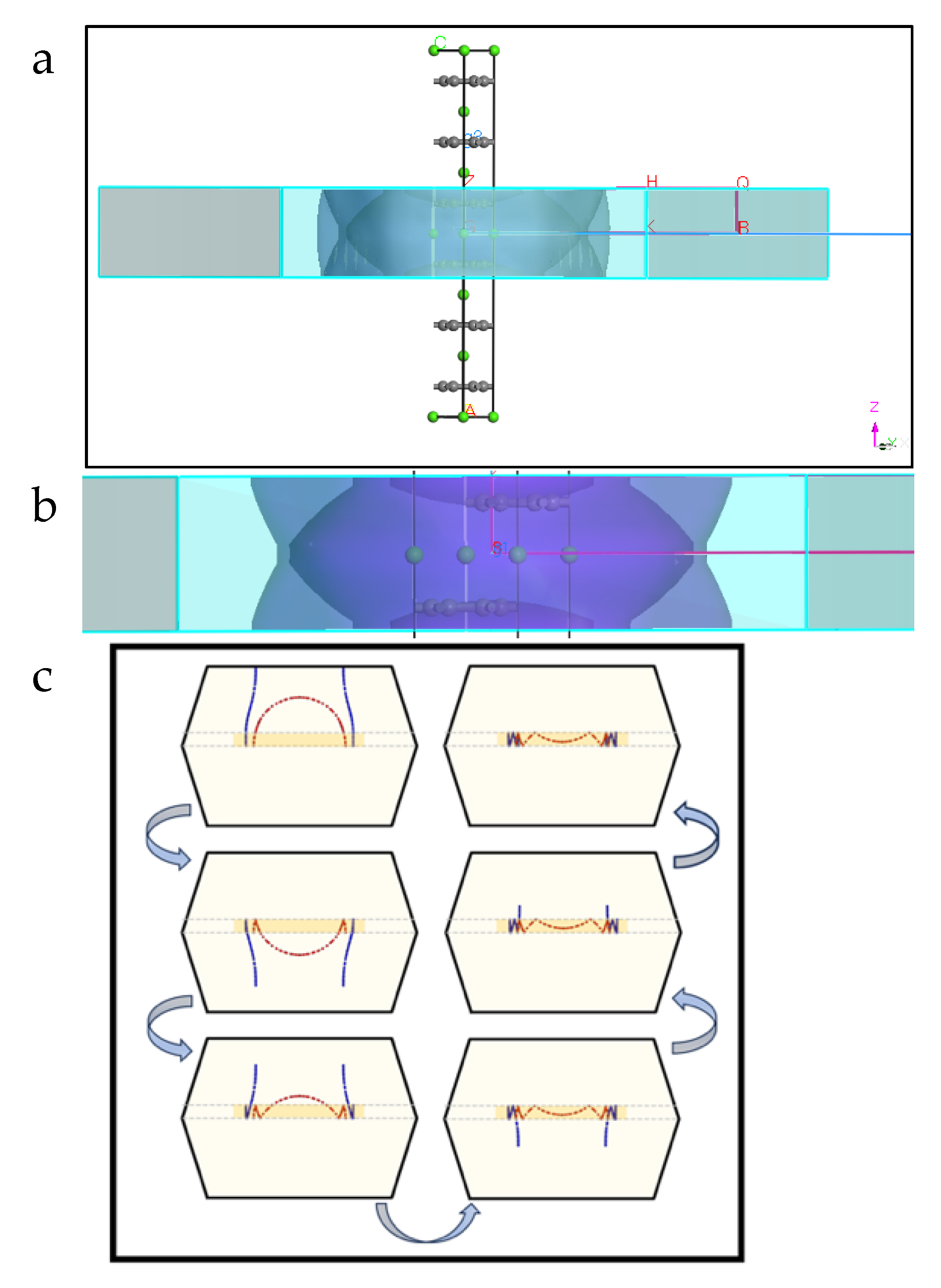
3.1. Electronic Band Structures, Fermi Surfaces and Superlattices
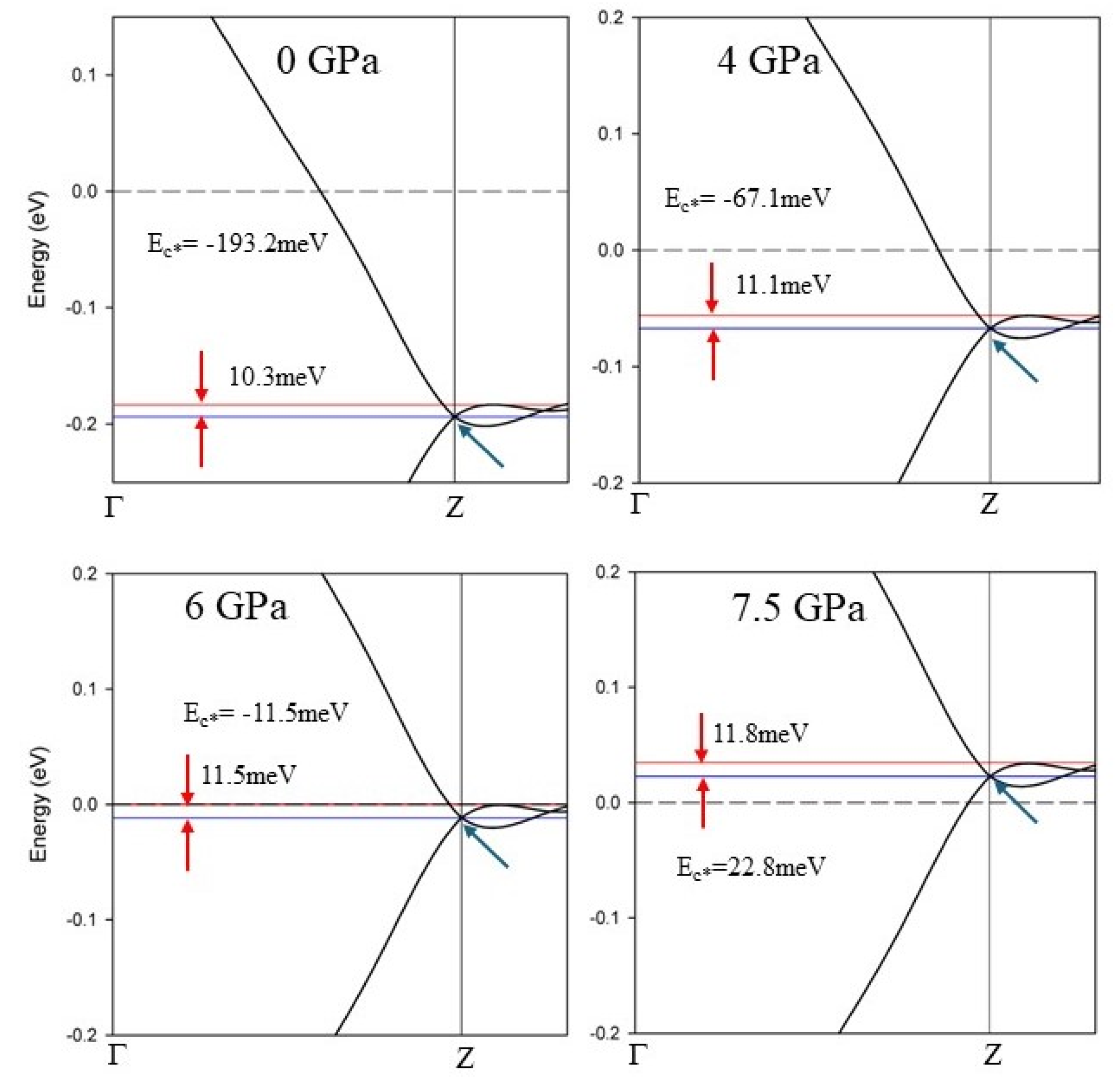
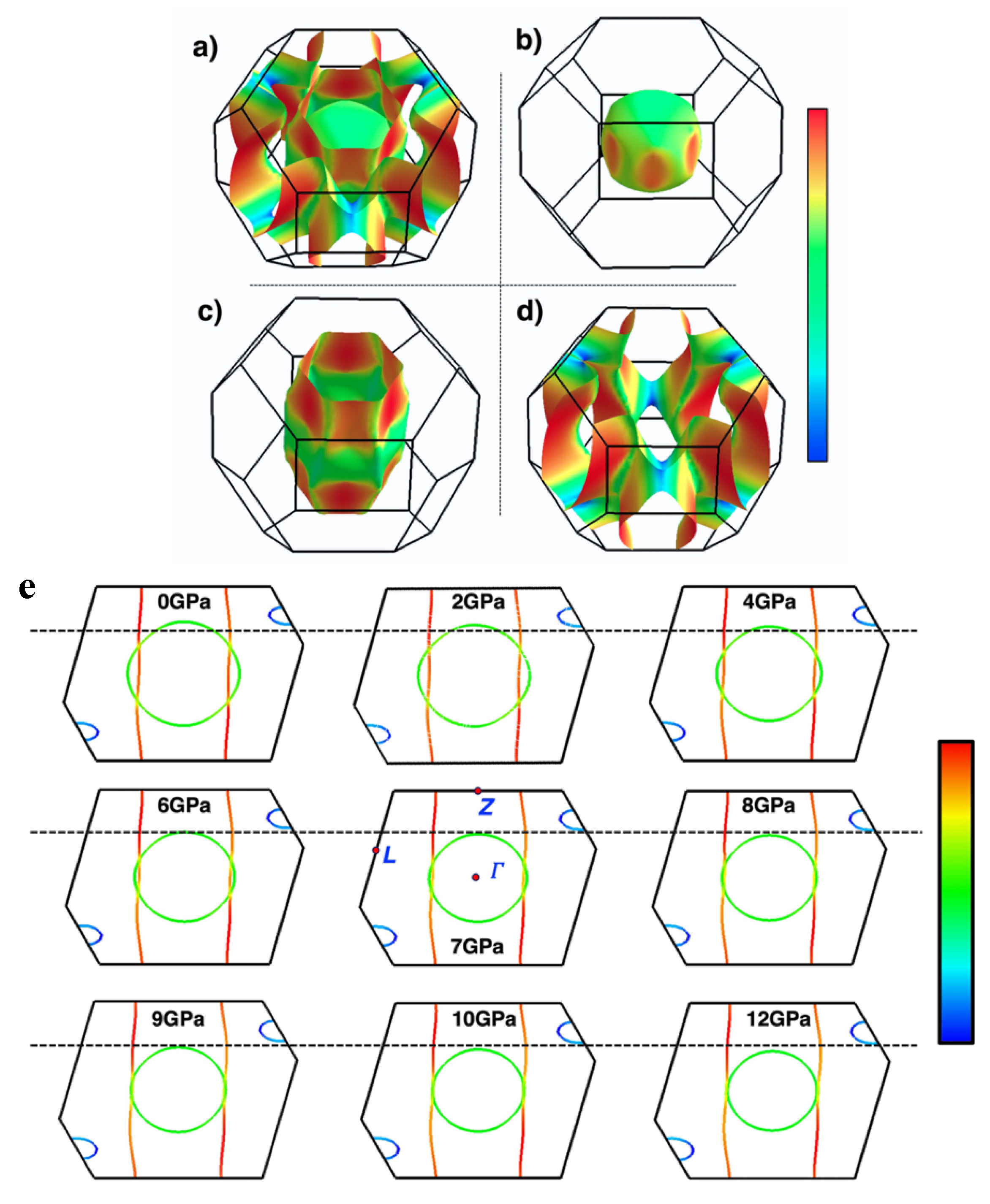
3.2. Electronic Band Structures and Fermi Surfaces with Pressure
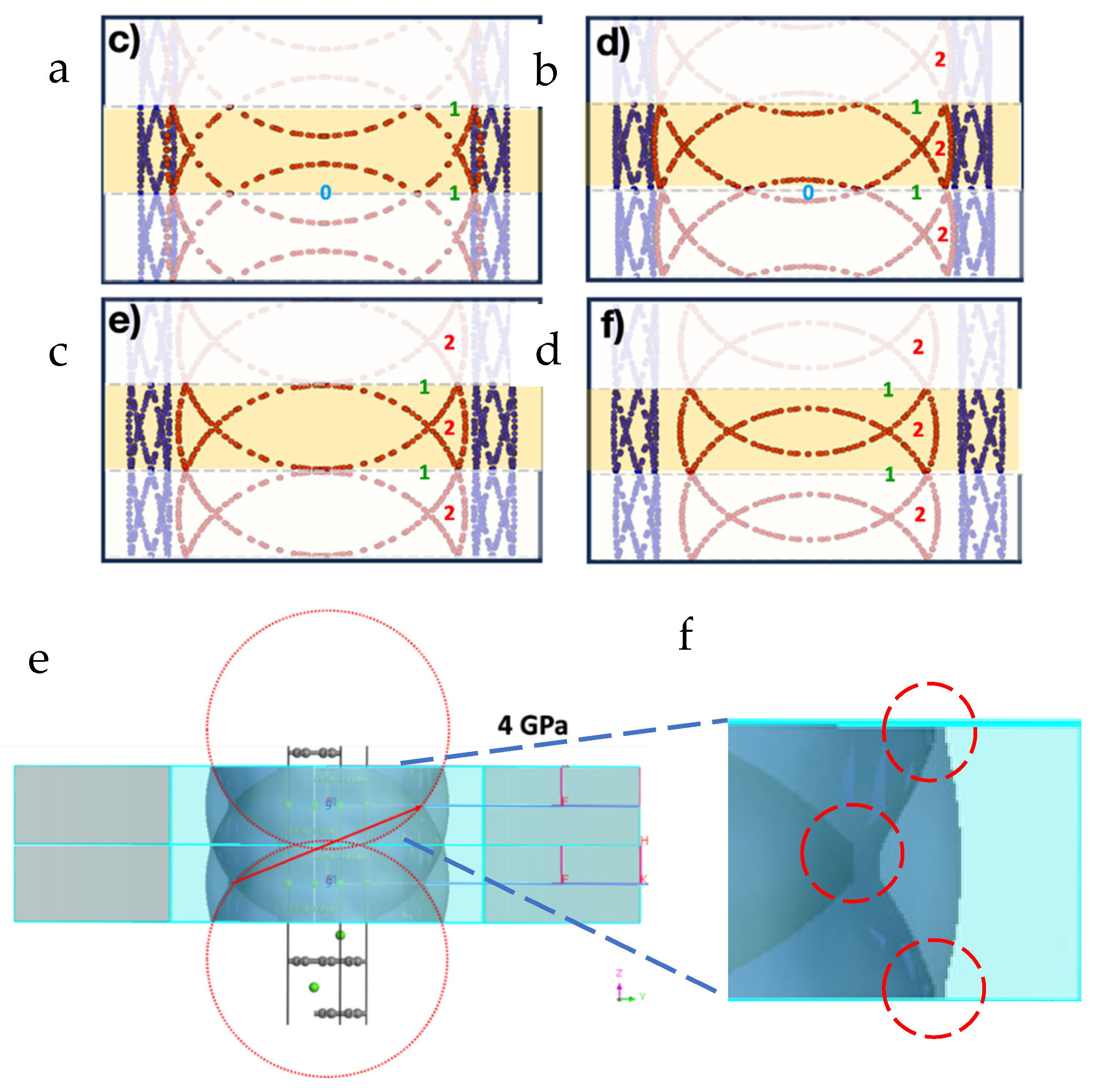
3.3. Bonding/Antibonding, Superlattice and Electronic Topological Transitions
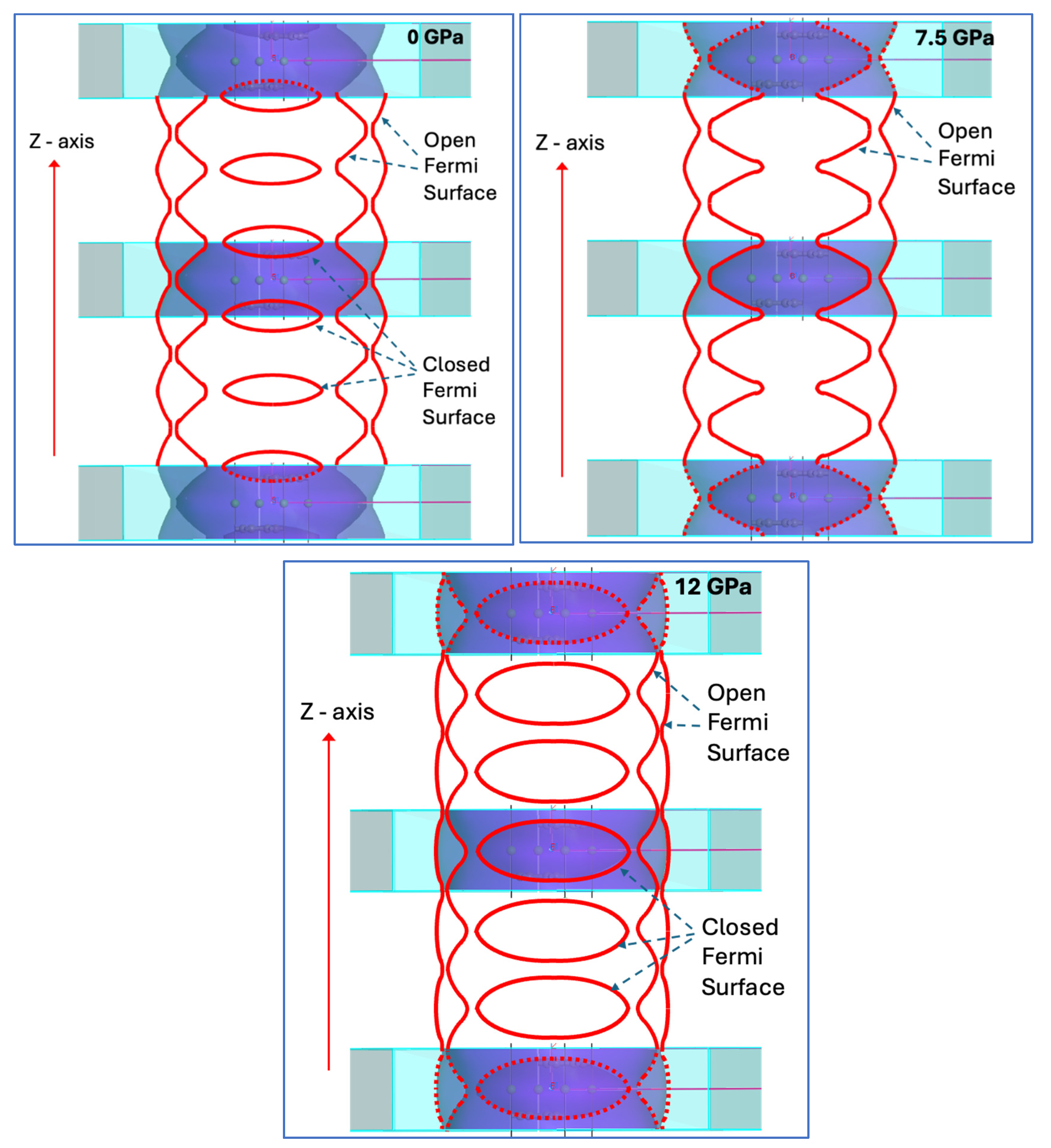
3.3.1. Open and Closed Fermi Surfaces—Topological Transition with Pressure
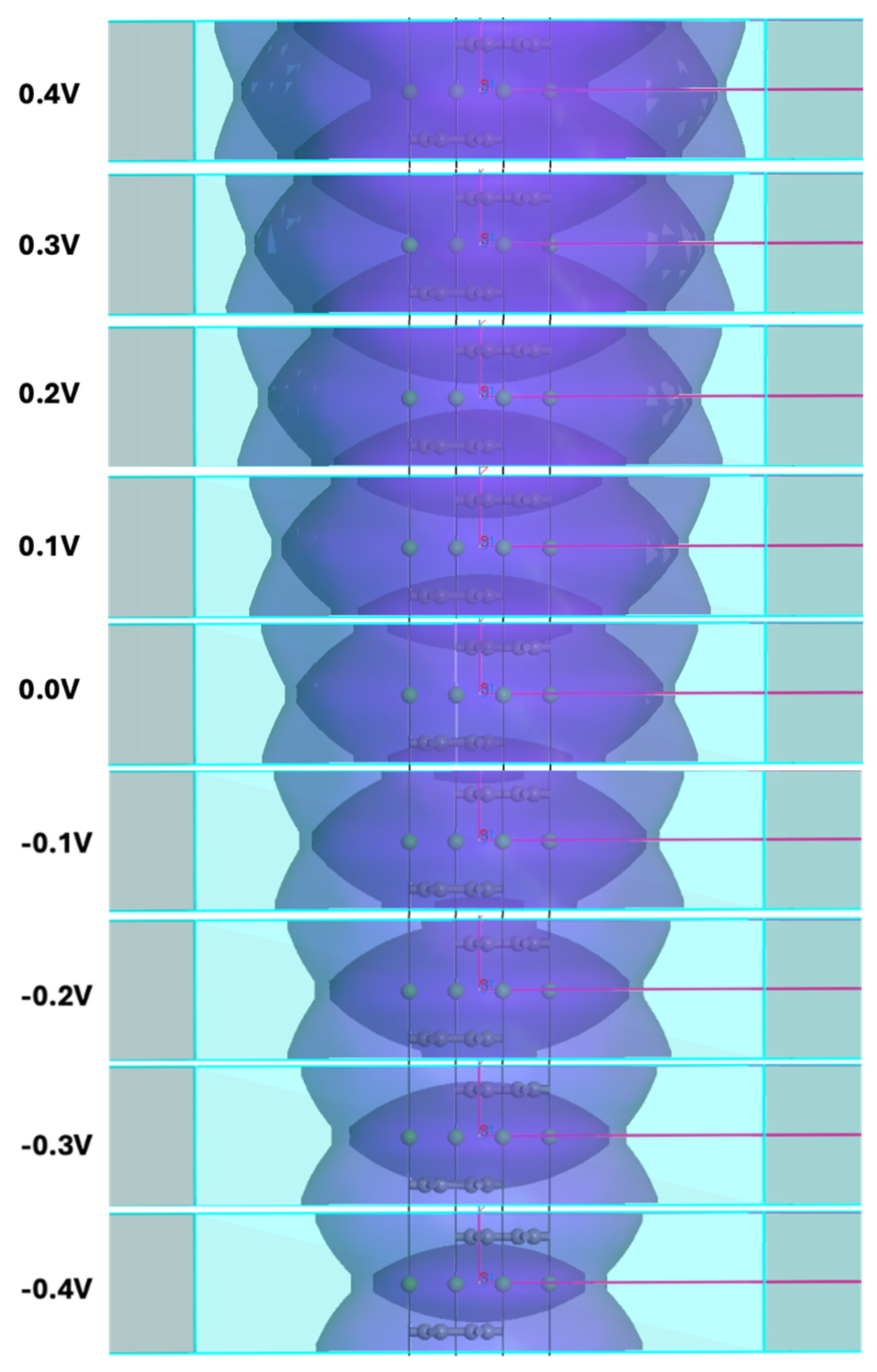
3.3.2. Isoenergetic Fermi Surfaces—Electron Dynamics and Magnetic Fields
3.4. Fermi Velocity and Connection to the Superconducting Gap
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jishi, R.A.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Superconductivity in graphite intercalation compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 12465–12469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannay, N.B.; Geballe, T.H.; Matthias, B.T.; Andres, K.; Schmidt, P.; MacNair, D. Superconductivity in Graphitic Compounds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1965, 14, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P., T. E. Weller, C.A. Howard, M.P.M. Dean, K.C. Rahnejat, S.S. Saxena, M. Ellerby, Superconductivity in graphite intercalation compounds, Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications 514 2015 50-58.
- Weller, T.E.; Ellerby, M.; Saxena, S.S.; Smith, R.P.; Skipper, N.T. Superconductivity in the intercalated graphite compounds C6Yb and C6Ca. Nat. Phys. 2005, 1, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazin, I.I. , Intercalant-Driven Superconductivity in YbC6 and CaC6, Physical Review Letters 95 2005 227001.
- Emery, N., C. Hérold, M. d’Astuto, V. Garcia, C. Bellin, J.F. Marêché, G. Loupias, Superconductivity of Bulk CaC6, Physical Review Letters 95 2005 087003.
- Kanetani, K., K. Sugawara, T. Sato, R. Shimizu, K. Iwaya, T. Hitosugi, T. Takahashi, Ca intercalated bilayer graphene as a thinnest limit of superconducting C₆Ca, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences - PNAS 109 2012 19610-19613.
- Ichinokura, S.; Sugawara, K.; Takayama, A.; Takahashi, T.; Hasegawa, S. Superconducting Calcium-Intercalated Bilayer Graphene. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Fatemi, V.; Fang, S.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Kaxiras, E.; Jarillo-Herrero, P. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 2018, 556, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csányi, G.; Littlewood, P.B.; Nevidomskyy, A.H.; Pickard, C.J.; Simons, B.D. The role of the interlayer state in the electronic structure of superconducting graphite intercalated compounds. Nat. Phys. 2005, 1, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandra, M., F. Mauri, Theoretical Explanation of Superconductivity in CaC6, Physical Review Letters 95 2005 237002.
- McMillan, W.L. Transition Temperature of Strong-Coupled Superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 1968, 167, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinks, D.G., D. Rosenmann, H. Claus, M.S. Bailey, J.D. Jorgensen, Large Ca isotope effect in the CaC6 superconductor, Physical Review B 75 2007 014509.
- Lamura, G., M. Aurino, G. Cifariello, E. Di Gennaro, A. Andreone, N. Emery, P. Lagrange, Experimental Evidence of s-Wave Superconductivity in Bulk CaC6, Physical Review Letters 96 2006 107008.
- Bergeal, N., V. Dubost, Y. Noat, W. Sacks, D. Roditchev, N. Emery, G. Loupias, Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy on the Novel Superconductor CaC6, Physical Review Letters 97 2006 077003.
- Sanna, A., G. Profeta, A. Floris, A. Marini, E.K.U. Gross, S. Massidda, Anisotropic gap of superconducting CaC6: A first-principles density functional calculation, Physical Review B 75 2007 020511.
- Gonnelli, R.S., D. Daghero, D. Delaude, M. Tortello, G.A. Ummarino, V.A. Stepanov, S. Massidda, Evidence for Gap Anisotropy in CaC6 from Directional Point-Contact Spectroscopy, Physical Review Letters 100 2008 207004.
- Smith, R.P., A. Kusmartseva, Y.T.C. Ko, S.S. Saxena, A. Akrap, L. Forró, N.T. Skipper, Pressure dependence of the superconducting transition temperature in C6Yb and C6Ca, Physical Review B 74 2006 024505.
- Gauzzi, A., S. Takashima, N. Takeshita, C. Terakura, H. Takagi, N. Emery, G. Loupias, Enhancement of Superconductivity and Evidence of Structural Instability in Intercalated Graphite CaC6 under High Pressure, Physical Review Letters 98 2007 067002.
- Gauzzi, A., N. Bendiab, M. d’Astuto, B. Canny, M. Calandra, F. Mauri, M. Mezouar, Maximum Tc at the verge of a simultaneous order-disorder and lattice-softening transition in superconducting CaC6, Physical Review B 78 2008 064506.
- Sugawara, K.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, T. Fermi-surface-dependent superconducting gap in C6Ca. Nat. Phys. 2008, 5, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, T., Z. Pan, Superconductivity and Electron-Phonon Coupling in Graphite Intercalation Compunds, Physics and Applications of Graphene-Experiments, IntechOpen London UK 2011.
- Yang, S.-L.; Sobota, J.A.; Howard, C.A.; Pickard, C.J.; Hashimoto, M.; Lu, D.H.; Mo, S.-K.; Kirchmann, P.S.; Shen, Z.-X. Superconducting graphene sheets in CaC6 enabled by phonon-mediated interband interactions. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnejat, K.; Howard, C.; Shuttleworth, N.; Schofield, S.; Iwaya, K.; Hirjibehedin, C.; Renner, C.; Aeppli, G.; Ellerby, M. Charge density waves in the graphene sheets of the superconductor CaC6. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosevich, Topology in the Theory of Metals, in: M.I. Monastyrsky (Ed.), Topology in condensed matter, Springer Science & Business Media2006.
- Rezende, S.M. Introduction to Electronic Materials and Devices; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Moessner, R., J. E. Moore, Topological phases of matter, Cambridge University Press2021.
- Wang, B.; Bianconi, A.; Mackinnon, I.D.R.; Alarco, J.A. Superlattice Delineated Fermi Surface Nesting and Electron-Phonon Coupling in CaC6. Crystals 2024, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarco, J.A., I. D.R. Mackinnon, Superlattices, Bonding-Antibonding, Fermi Surface Nesting, and Superconductivity, Condensed Matter, 2023, pp. 1-13.
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.J.; Segall, M.D.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Probert, M.I.J.; Refson, K.; Payne, M.C. First Principles Methods Using CASTEP. Z. Kristallogr./Cryst. Mater. 2005, 220, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, I.D.R., A. Almutairi, J.A. Alarco, Insights from Systematic DFT Calculations on Superconductors, in: J.M.V. Arcos (Ed.), Real Perspective of Fourier Transforms and Current Developments in Superconductivity, IntechOpen, London UK, 2021, pp. 1-29.
- Alarco, J.A.; Almutairi, A.; Mackinnon, I.D.R. Progress Towards a Universal Approach for Prediction of the Superconducting Transition Temperature. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 33, 2287–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Alarco, J.; Talbot, P.C.; Mackinnon, I.D.R. Identification of superconductivity mechanisms and prediction of new materials using Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations. J. Physics: Conf. Ser. 2018, 1143, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, R.; Küçükbenli, E.; Pham, C.H.; de Gironcoli, S. Phonons in nonlocal van der Waals density functional theory. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 235120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berland, K.; Londero, E.; Schröder, E.; Hyldgaard, P. Harris-type van der Waals density functional scheme. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, P.; Jiao, Y.; Shukla, V. Screening nature of the van der Waals density functional method: a review and analysis of the many-body physics foundation. J. Physics: Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 393001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Murray, É.D.; Kong, L.; Lundqvist, B.I.; Langreth, D.C. Higher-accuracy van der Waals density functional. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 081101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D., K. Berland, T. Thonhauser, Next-Generation Nonlocal van der Waals Density Functional, Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 16 2020 5893-5911.
- Berland, K., D. Chakraborty, T. Thonhauser, van der Waals density functional with corrected C6 coefficients, Physical Review B 99 2019 195418.
- Kawaguchi, N.; Shibata, K.; Mizoguchi, T. Possible New Graphite Intercalation Compounds for Superconductors and Charge Density Wave Materials: Systematic Simulations with Various Intercalants Using a van der Waals Density Functional Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 9833–9843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarco, J.A.; Talbot, P.C.; Mackinnon, I.D.R. Comparison of Functionals for Metal Hexaboride Band Structure Calculations. Model. Numer. Simul. Mater. Sci. 2014, 04, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarco, J.A.; Chou, A.; Talbot, P.C.; Mackinnon, I.D.R. Phonon modes of MgB2: super-lattice structures and spectral response. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 24443–24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarco, J.A.; Talbot, P.C.; Mackinnon, I.D.R. Coherent phonon decay and the boron isotope effect for MgB2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25386–25392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartók, A.P.; Yates, J.R. Ultrasoft pseudopotentials with kinetic energy density support: Implementing the Tran-Blaha potential. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 235103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Chevary, J.A.; Vosko, S.H.; Jackson, K.A.; Pederson, M.R.; Singh, D.J.; Fiolhais, C. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 46, 6671–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzari, N.; Vanderbilt, D.; De Vita, A.; Payne, M.C. Thermal Contraction and Disordering of the Al(110) Surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 3296–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawan, W.; Curtarolo, S. High-throughput electronic band structure calculations: Challenges and tools. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 49, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Harrison, W. Applied Quantum Mechanics; World Scientific Pub Co Pte Ltd: Singapore, Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, M. FermiSurfer: Fermi-surface viewer providing multiple representation schemes. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2019, 239, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanville, E.; Kenny, S.D.; Smith, R.; Henkelman, G. Improved grid-based algorithm for Bader charge allocation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 084204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Trinkle, D.R. Accurate and efficient algorithm for Bader charge integration. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 064111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelman, G.; Arnaldsson, A.; Jónsson, H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2005, 36, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarco, J.A., B. Gupta, M. Shahbazi, D. Appadoo, I.D.R. Mackinnon, THz/Far infrared synchrotron observations of superlattice frequencies in MgB2, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 23 2021 23922-23932.
- Mazziotti, M.V.; Raimondi, R.; Valletta, A.; Campi, G.; Bianconi, A. Resonant multi-gap superconductivity at room temperature near a Lifshitz topological transition in sulfur hydrides. arXiv, 2106. [Google Scholar]
- Blanter, Y.; Kaganov, M.; Pantsulaya, A.; Varlamov, A. The theory of electronic topological transitions. Phys. Rep. 1994, 245, 159–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, I.M., M. I. Kaganov, Geometrical concepts in the Electron Theory of Metals, in: M. Springford (Ed.), Electrons at the Fermi Surface, Cambridge University Press Cambridge UK, 2011.
- Bianconi, A. Lifshitz Transitions In Multi-band Hubbard Models for Topological Superconductivity in Complex Quantum Matter. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotti, M.V.; Bianconi, A.; Raimondi, R.; Campi, G.; Valletta, A. Spin–orbit coupling controlling the superconducting dome of artificial superlattices of quantum wells. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 193908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angilella, G.G.N.; Bianconi, A.; Pucci, R. Multiband Superconductors Close to a 3D–2D Electronic Topological Transition. J. Supercond. 2005, 18, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlborg, T.; Bianconi, A. Breakdown of the Migdal approximation at Lifshitz transitions with giant zero-point motion in the H3S superconductor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24816–24816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, L., V. Palmisano, M. Fratini, M. Filippi, P. Parisiades, D. Lampakis, A. Bianconi, Isotope effect on the E2g phonon and mesoscopic phase separation near the electronic topological transition in Mg1-xAlxB2, Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics 80 2009 14520.
- Agrestini, S., C. Metallo, M. Filippi, L. Simonelli, G. Campi, C. Sanipoli, A. Bianconi, Substitution of Sc for Mg in MgB2: Effects on transition temperature and Kohn anomaly, Phys. Rev. B 70 2004 134514.
- Brandt, N.B., S. M. Chudinov, Electronic Structure of Metals, Revised from the 1973 Russian ed., Mir, Moscow, 1975.
- Lifshitz, I.M. , Anomalies of Electron Characteristics in the High Pressure Region, 1960.
- Tinkham, M. , Introduction to superconductivity, 2nd ed., Dover Publications, Mineola, N.Y, 2004.
- Alarco, J.A., M. Shahbazi, I.D.R. Mackinnon, Experimental control of Tc in AlB2-type compounds using an applied voltage Cornell University Library / arXiv, 2022.
- Bianconi, A. Feshbach Shape Resonance in Multiband Superconductivity in Heterostructures. J. Supercond. 2005, 18, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, H.; Aoki, H.; Perali, A.; Bianconi, A. Emergent Fano-Feshbach resonance in two-band superconductors with an incipient quasiflat band: Enhanced critical temperature evading particle-hole fluctuations. Phys. Rev. B 2024, 109, L140504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
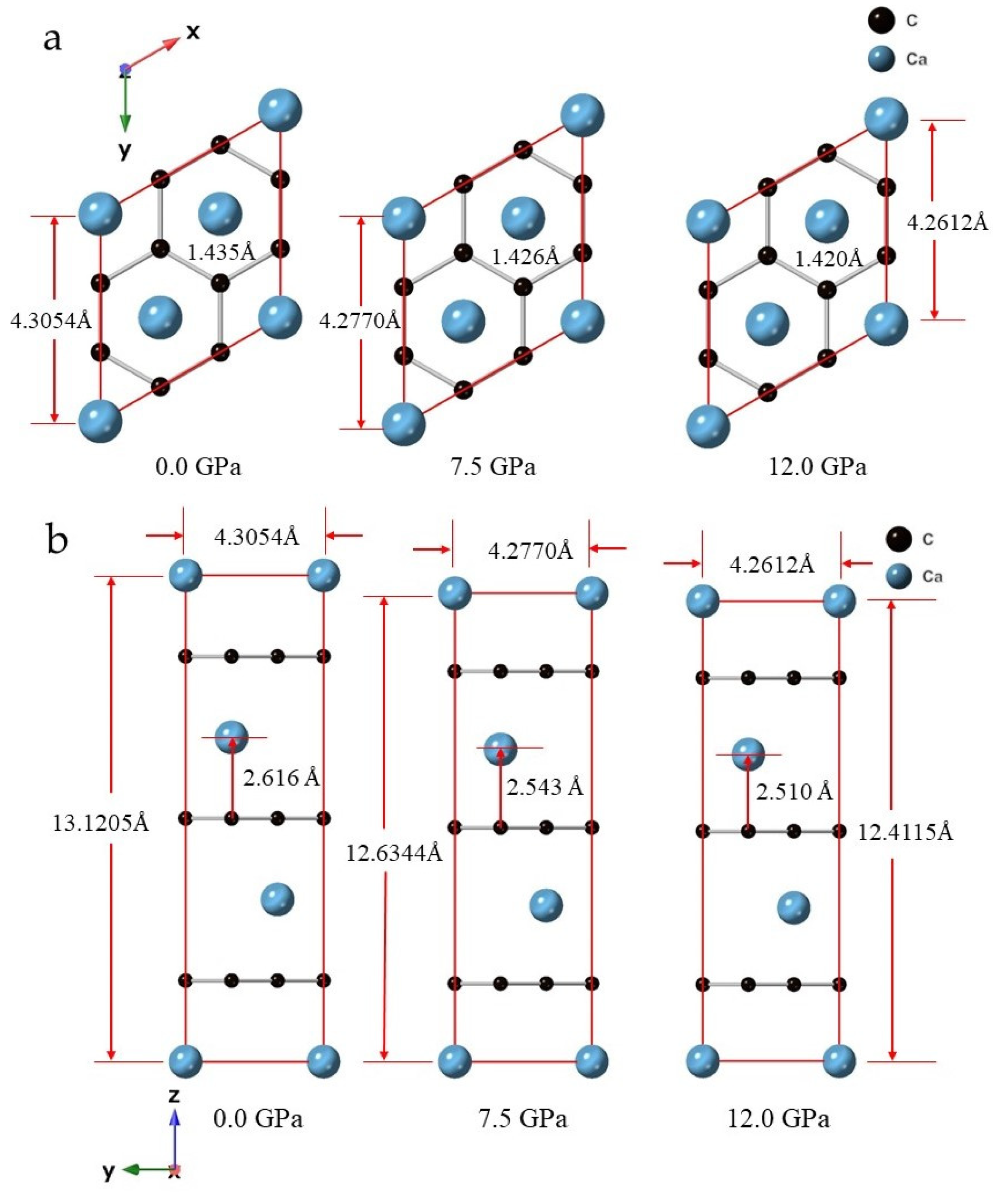
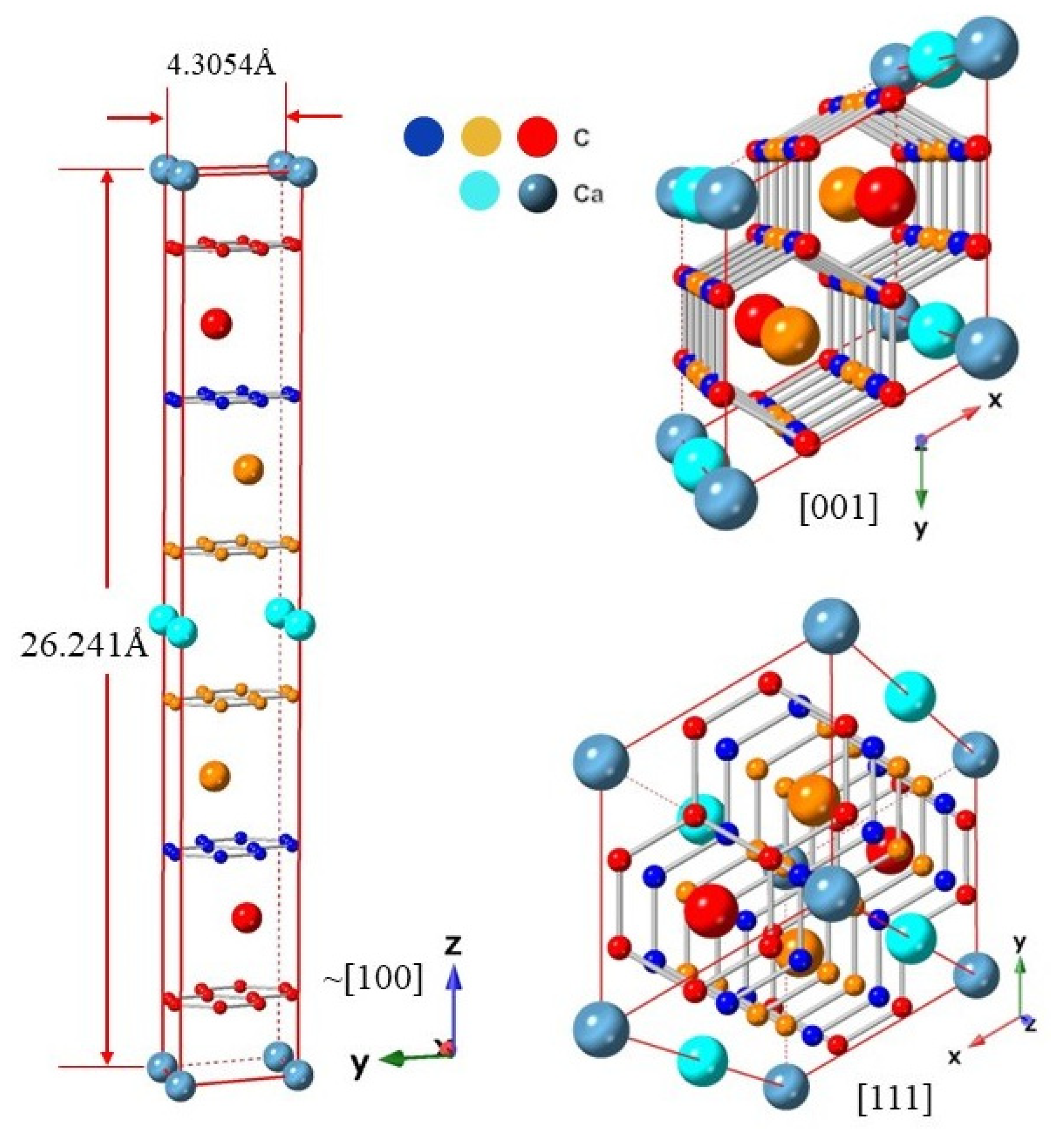
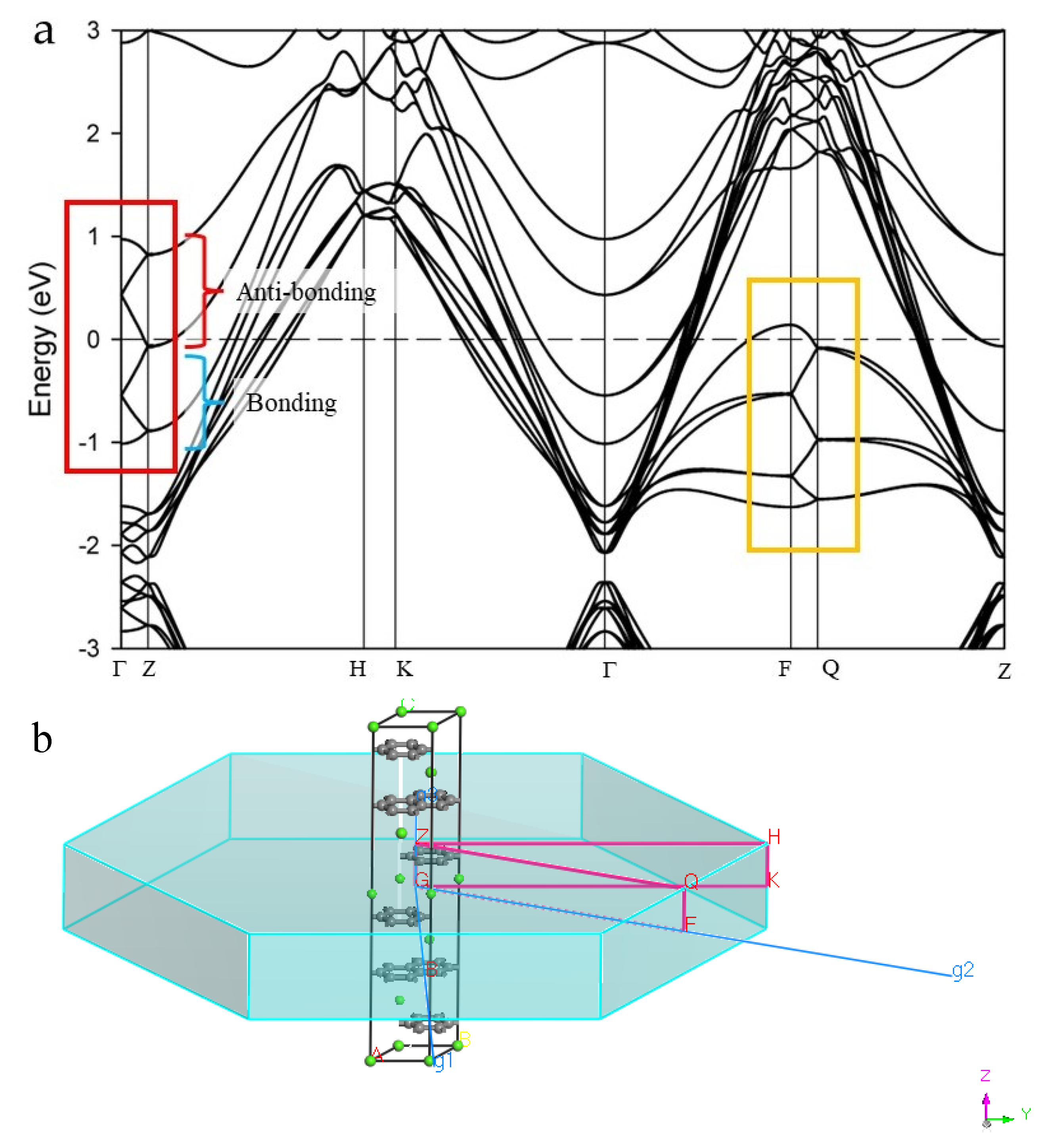
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




