1. Introduction
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are critical for cellular signal transduction and are major targets in pharmaceutical research [
1,
2]. Structurally, GPCRs have N- and C-terminal regions and seven transmembrane segments [
3]. Upon ligand binding, GPCRs activate G proteins, leading to downstream signaling like cAMP activation, ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and calcium mobilization [
4].
Kisspeptin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that activates the G proteins Gα
q/11 and its natural ligand is Kisspeptin [
5], a family of structurally related peptides derived from the KISS1R gene [
6]. KISS1R encodes a precursor protein of 145 amino acids that is subsequently proteolytically cleaved to produce a series of C-terminal amidated peptides named kisspeptin-54 (KP54), kisspeptin-14 (KP14), kisspeptin-13 (KP13), and kisspeptin-10 (KP10), all of which have biological activity and are endogenous ligands for the kisspeptin receptor [
7].
Currently, the KISS1/kisspeptin receptor system is known to be the main guardian of the reproductive axis in puberty and adulthood and plays a crucial role in the control of endocrine functions [
7]. It serves as a critical regulator of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion, essential for puberty and fertility in both males and females. Kisspeptins stimulates the release of GnRH in the hypothalamus, which in turn triggers the secretion of gonadotropic hormones from the pituitary, thereby regulating reproductive function [
8]. Beyond its reproductive role, the kisspeptin system has been shown to have significant non-canonical roles in various pathological conditions [
9]. Currently, the kisspeptin system, has gained attention in cancer research, kisspeptins and its receptor, have been linked to cancer progression and metastasis in different types of cancer [
10]. Studies have shown kisspeptin receptor role as a metastasis suppressor in prostate cancer[
11], contrasting with its impact in gastric cancer, where low kisspeptin receptor expression is linked to tumor invasion and distant metastasis [
12]. In breast cancer, KISS1R gene upregulation is associated with aggressive tumor phenotypes and increased mortality risk [
13]. In cervical cancer, emerging studies have suggested that kisspeptin may play an inhibitory role in tumor advancement [
14], paving the path for novel targeted treatment strategies. This is a crucial development considering that cancer ranks among the top causes of global mortality [
15], and metastasis stands as a critical determinant of mortality in affected patients [
16]. In this study, we analyzed the modifications in protein phosphorylation triggered by various kisspeptin analogs in cellular models of breast, prostate, cervical, and gastric cancers. Building on this, we specifically aimed to clarify the role of the kisspeptin system in cervical cancer by examining its influence on cellular signaling pathways and kinase phosphorylation dynamics using Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) biosensors and antibody arrays. This comprehensive approach revealed how kisspeptin significantly influences critical signaling pathways involved in the progression of various cancers, offering valuable insights. The emerging evidence underscores the potential of the kisspeptin system as a foundation for novel therapeutic strategies in oncology, highlighting its importance across diverse cancer types.
3. Results
3.1. Design and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry of KP10 Analogs
Earlier studies have shown that the kisspeptin-10 exhibits higher receptor affinity and evokes more potent functional responses than its extended counterparts like kisspeptin-13 and kisspeptin-14 [
30]. To further explore the structural requirements of this core sequence, we have carried out Ala scan of human KP10 to identify important residues for kisspeptin receptor-agonistic activity. To this aim, we synthesized human KP10 Ala-analogs (
Table 1) by standard Fmoc-based solid phase peptide synthesis, and for all synthesized peptides, the experimental molecular weight [M+H]+ observed by MS-MALDI-TOF analysis was in concurrence with the theoretical value calculated using the MS/MS Fragment Ion Calculator program (db system biology) [
31] as shown in
Table 1.
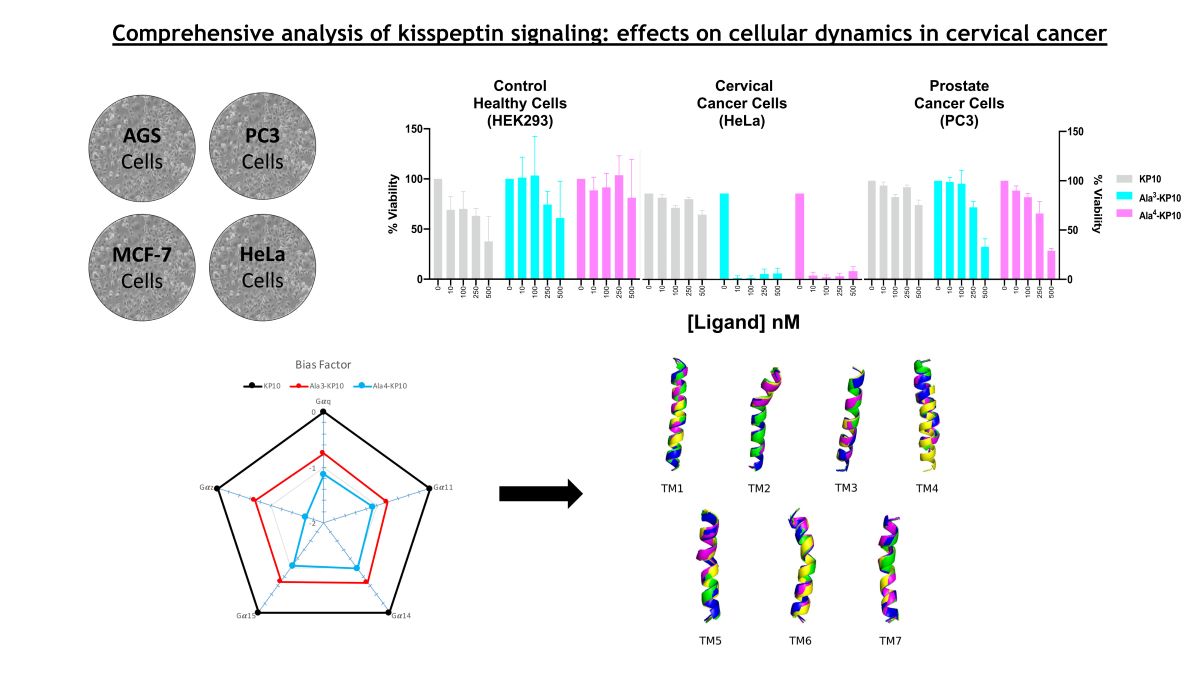
3.2. Effects of KP10 and Ala-Substituted Analogs on Cytotoxicity in Cancer Cells
The cytotoxic profiles of KP10 and its analogs across various cancer cell lines, including HEK293T, MCF7, AGS, HeLa, and PC3, were delineated, revealing notable variances in their biological activities. KP10 displayed differential sensitivity with the HeLa cell line being the most responsive, whereas AGS cells exhibited substantial resistance. Among the analogs, Ala
1-KP10 emerged as consistently more potent across the panel, suggesting an enhanced interaction with the cellular targets. Notably, in HeLa cells, certain analogs, particularly Ala
3-KP10 and Ala
4-KP10, demonstrated heightened cytotoxic efficacy, as indicated by markedly low pIC50 values (
Table 2.). This specificity of response underscores potential selective affinities of the analogs for the molecular components unique to each cell type. These findings propel the rationale for further mechanistic studies to explore the structure-activity relationships governing the efficacy of KP10 analogs and their prospective therapeutic applicability in cancer treatment strategies.
3.3. Impact of Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 on Kinase Activation and Cell Migration Dynamics
The analogs Ala
3-KP10 and Ala
4-KP10 were selected for further analysis based on intriguing cytotoxicity results in cervical cancer cells (
Table 2.), which prompted a more detailed exploration of their effects on kinase phosphorylation and cell migration processes. Although their unique behavior in cervical cancer cells was particularly notable, these analogs were also assessed across other previously mentioned cell lines, including those derived from breast, prostate, gastric, and cervical cancers, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of their potential applications.
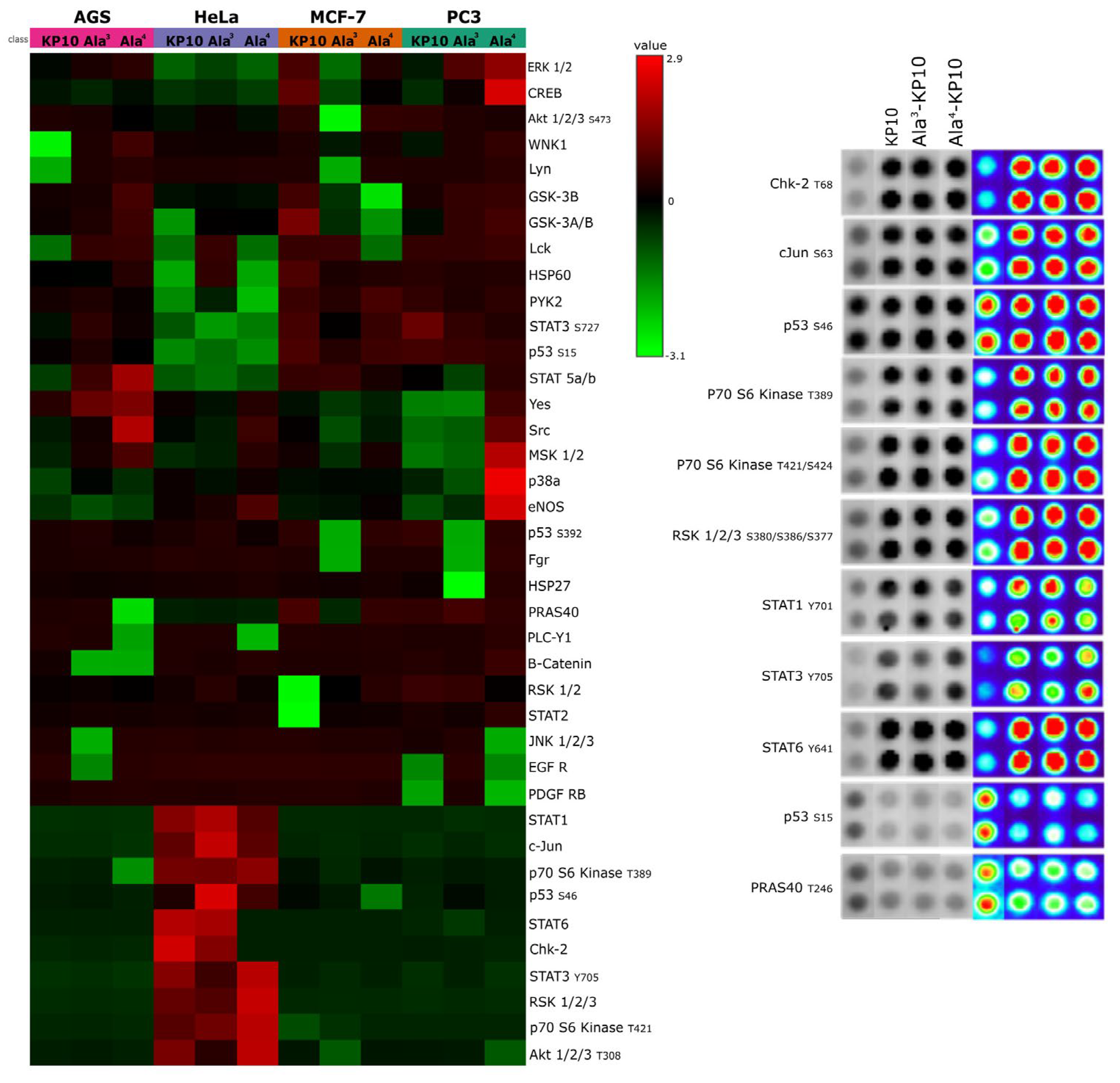
In the analysis of a kinase array (Human Phospho-Kinase Array, Proteome Profiler, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN,USA), when cervical cancer cells were stimulated with KP10 and its analogs, a distinct set of enzymes—Chk2, c-Jun, p53, p70 S6 kinase, RSK 1/2/3, STAT1, STAT3, STAT6, and PRAS40—emerged as key players (
Figure 1.).
Specifically, was observed a decrease in the phosphorylation levels of p53(S15) and PRAS40, suggesting a potential shift towards pathways less reliant on these tumor suppressors. Conversely, kinases such as Chk2, c-Jun, p70 S6 kinase, RSK 1/2/3, and members of the STAT family exhibited increased phosphorylation, indicating an enhanced pro-oncogenic signaling. These findings underscore the dualistic nature of kisspeptin signaling in modulating cancer cell behavior, highlighting its complex role in cervical cancer progression.
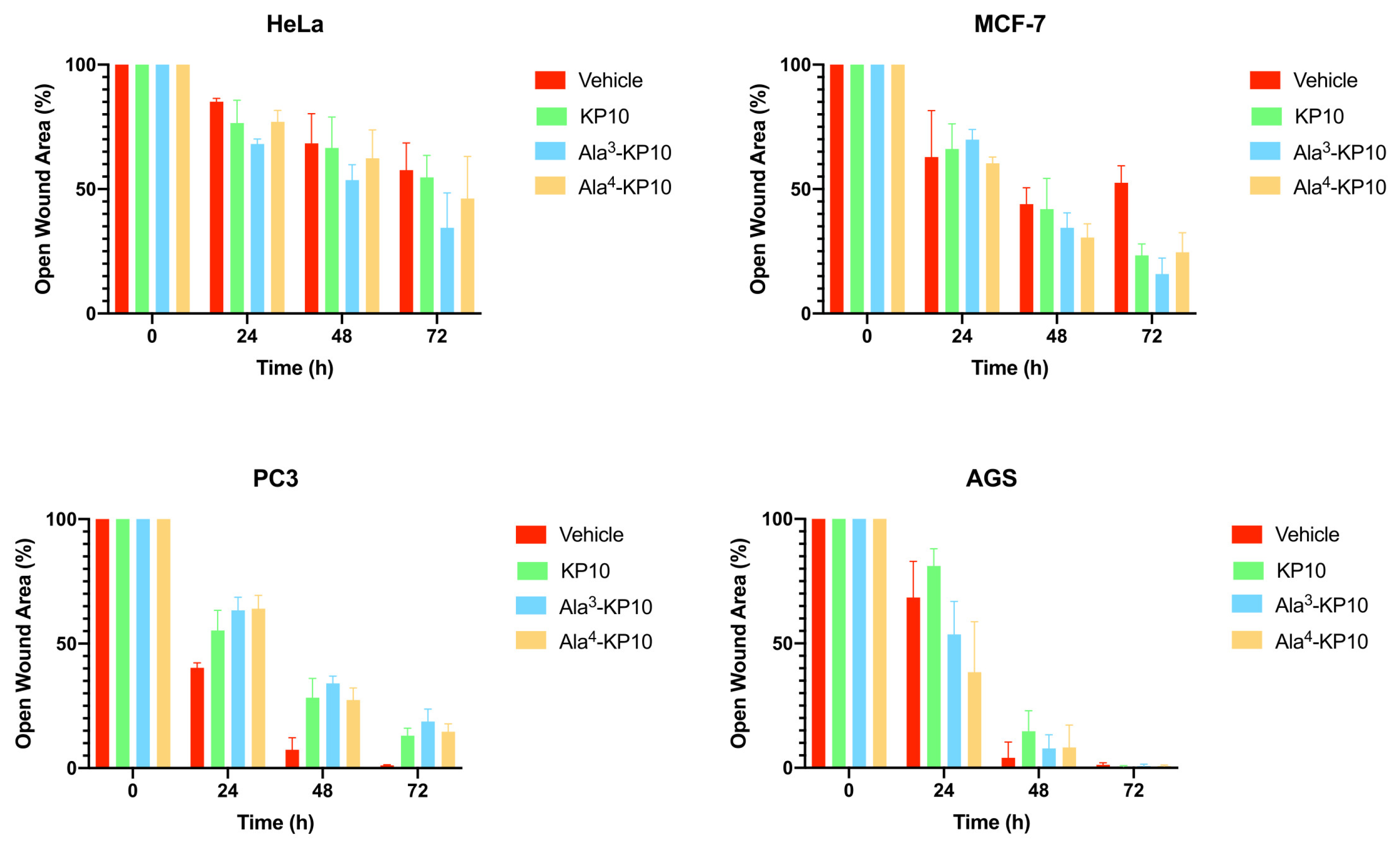
The impact of KP10 and its analogs on cellular migration was explored in all cancer cells through a wound healing assay, incorporating the analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 as illustrated in
Figure 2. In addition, the wound closure dynamics following treatment with KP10 and its analogs displayed intriguing variations in response across different cancer cell lines. HeLa and MCF7 cells exhibited moderate migration inhibition, with the most pronounced effects observed in cells treated with Ala4-KP10, particularly at the 48 and 72-hour marks. This behavior stands in contrast to PC3 and AGS cell lines, where despite Ala4-KP10 remaining the more inhibitory treatment, the difference in the percentage of open wound area compared to the control was less marked. This pattern suggests that the response to KP10 and its analogs might be influenced by the intrinsic cellular characteristics specific to each cancer line, with HeLa and MCF7 showing a higher susceptibility to inhibition of cell migration. These findings highlight the need for further exploration of the underlying molecular interactions that govern these responses in the context of targeted cervical and breast cancer.
3.4. Analysis of KP10 and Relevant Analogs in Kisspeptin Receptor Signaling Transduction Pathways
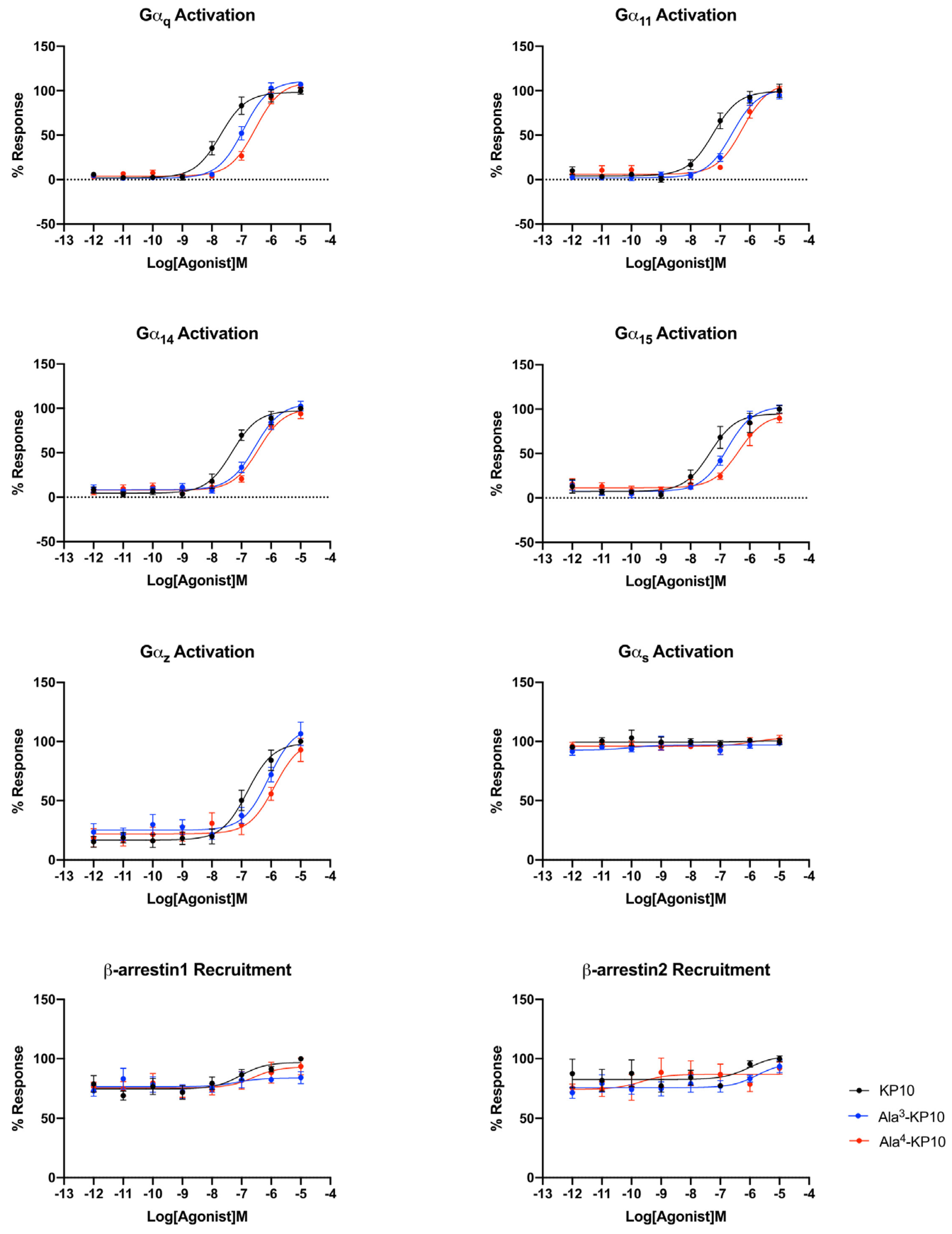
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) was employed to study the signaling profiles of the kisspeptin receptor upon stimulation with KP10 and analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10. This technique allowed for real-time monitoring of receptor activation and subsequent intracellular signaling events, providing a detailed understanding of the receptor dynamics and interactions triggered by these peptides. Signaling profiles of KP10 and its analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 were developed in HeLa cells, chosen for their relevance to cervical cancer results. Given that KP10 is the endogenous ligand, the comparison of EC50 values across different G protein signaling pathways for Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 (Supplementary Mat 1.) offers an understanding of their pharmacological profile in the context of HeLa cells.
The endogenous ligand, KP10, exhibits the lowest EC50 values, indicating it has the highest potency and serves as a benchmark for efficacy in activating Gαq, Gα11, Gα14, and Gα15 pathways. This high affinity of the natural agonist highlights its critical role in physiological signaling processes and sets a standard for evaluating the potency of synthetic or external compounds. In contrast, Ala3-KP10, with EC50 values one order of magnitude higher than KP10, demonstrates reduced potency across all pathways. While capable of activating the signaling pathways, the increased EC50 suggests a lesser efficiency compared to the endogenous control. This indicates that while Ala3-KP10 can elicit responses through these G protein pathways, it may require higher concentrations to achieve effects comparable to the endogenous ligand, potentially affecting its therapeutic window and specificity. Ala4-KP10 exhibits the highest EC50 values, significantly surpassing both the natural ligand and Ala3-KP10, which denotes the lowest relative potency among the tested compounds. The substantial increase in EC50 values for Ala4-KP10, particularly in pathways mediated by Gα11 and Gα15, suggests markedly diminished efficacy in activating these signaling mechanisms. This reduced potency underscores the challenge in designing synthetic analogs that match the efficacy of endogenous ligands, emphasizing the need for further optimization to enhance their pharmacological activity. Also, the substitution of Trp with Ala and Asn with Ala in the KP10 peptide significantly reduces its potency in activating Gαq protein-dependent signaling pathways, likely due to alterations in peptide-receptor interaction and conformational changes. The smaller, less polar alanine residues disrupt essential hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding, crucial for the peptide proper folding and affinity towards its receptor. This modification impairs the peptide ability to induce necessary receptor conformational changes, leading to attenuated signal transduction. These findings underscore the critical role of specific amino acid residues in the structural and functional integrity of signaling peptides.
In the analysis of E
max values across Gα
q family signaling pathways, no significant differences were observed between the analogs and the KP10 (Supplementary Mat 1). This suggests that while the analogs may vary in potency as indicated by their EC
50 values, their maximum achievable effect (E
max) in activating Gα
q-mediated signaling remains comparable to that of the endogenous control (
Figure 3). This uniformity in Emax underscores the analog’s ability to fully engage the receptor and elicit a maximal response, highlighting their functional similarity to the natural ligand in terms of the ceiling effect on Gα
q pathway activation.
Within the Gαi/o family of G protein-coupled signaling pathways, widespread activation was not observed across the board, with the notable exception of the Gαz protein pathway. Although Gαz exhibits significantly stronger activation, it is important to note that some Gαi proteins, such as Gαi3, may show minor activation. Additionally, the activation of proteins like GαoA and GαoB may be masked due to constitutive activity, as indicated by elevated basal levels. Thus, while the focus should primarily be on Gαz due to its robust activation, it is noteworthy that other Gαi/o proteins may still exhibit activation, underscoring the importance of comprehensive assessment in future investigations. (The activation curves of the Gαi/o family can be found in the supplementary information section of the manuscript.). Here, differential EC50 values were recorded for KP10 and its analogs, Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10, with KP10 showing an EC50 of 1.63x10-7 M, Ala3-KP10 with 6.46x10-7 M, and Ala4-KP10 with 1.10x10-6 M. Here, it can be seen that the substitution of Trp and Asn with Ala at positions 3 and 4 in KP10 crucially diminishes its potency in activating the Gαz protein, reducing effectiveness approximately by a factor of ten. This alteration underscores the significant role of the Trp and Asn residues in facilitating the optimal interaction necessary for Gαz pathway engagement. The considerable loss in activation potency due to these amino acid replacements highlights the specificity of KP10 interaction with Gαz, demonstrating how precise molecular configurations are essential for maintaining functional activity.
This distinct activation profile of the Gαz pathway, in contrast to the lack of activation in other Gαi/o family pathways, underscores the specificity of KP10 and its analogs interactions with G protein-coupled receptors. This selective activation of the Gαz pathway by KP10 and its analogs, among the broader inactivity within the Gαi/o protein family, highlights the unique pharmacological profile of these compounds. It raises intriguing questions about the role of Gαz-mediated signaling in the biological processes influenced by KP10 and its analogs. Further research into the downstream effects of Gαz activation could unveil novel insights into the mechanisms by which KP10 and its analogs exert their effects, offering potential avenues for therapeutic intervention based on the modulation of this specific pathway.
The KP10 analogs also showed no activation of the Gαs signaling pathway, as well as Gα12 and Gα13 proteins. This finding underscores the specificity of these compounds interactions with G protein-coupled receptors, highlighting their selective influence on certain pathways while leaving others, such as the Gαs, Gα12 and Gα13 pathways, unaffected. This selective activation pattern may have implications for understanding the biological roles of KP10 and its analogs and could guide the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Analyzing the EC
50 values for β-arrestin1 and β-arrestin2 recruitment by KP10 and its analogs reveals insightful trends regarding their efficacy and selectivity in engaging these important signaling intermediates (
Figure 3.). Ala
3-KP10, with EC
50 values of 1.19x10
-6 M for β-arrestin1 and 1.43x10
-6 M for β-arrestin2, demonstrates a generally lower potency in recruiting both β-arrestins compared to KP10. The relatively close EC
50 values for β-arrestin1 and β-arrestin2 suggest a more balanced interaction with both β-arrestins, albeit at a reduced efficacy. Ala
4-KP10 presents the least potency in recruiting β-arrestins, with a markedly high EC
50 value of 1.30x10
-5 M for β-arrestin1 and 2.58x10
-6 M for β-arrestin2. The significant disparity in the recruitment efficiency between β-arrestin1 and β-arrestin2, especially the pronounced reduction in β-arrestin1 recruitment, indicates a distinct signaling profile that could impact its biological and therapeutic utility.
On the other hand, each transmembrane of the kisspeptin receptor reported in the study of Kotani et. Al [
32] was analyzed to check their possible structural changes between the inactive and the active form of the receptor, and also the possible structural changes when Ala
3-KP10 and Ala
4-KP10 peptides interact with the kisspeptin receptor (see
Figure 4). For these analysis, molecular dynamics simulations were conducted and the final structure (after 200 ns) for each transmembrane in each simulation were extracted and RMSD values were calculated between them (see
Table 3). Notably, significant conformational changes were observed only in the TM4 region of the receptor-Ala
4-KP10 complex. These findings suggest that the substitution of tryptophan residues at position 4 with alanine in the KP10 sequence induces unique structural rearrangements within the receptor's TM4 region, which could have implications for the receptor's activation and signaling mechanisms.
4. Discussion
The study on the pharmacological properties of KP10 and its analogs illuminates the contextual variability in the efficacy of kisspeptins across different cancer types, revealing metastasis-suppressing effects in various models but also contradictory roles, such as in hepatocellular carcinoma [
33]. This contradiction highlights the diversity of intracellular networks triggered by kisspeptin signaling, involving pathways like MAPK, Akt, Wnt/β-catenin, and CXCR4, which regulate proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, and other pro-metastatic behaviors. Our findings indicate that activation of the kisspeptin system leads to a reduction in the phosphorylation of p53(S15) and PRAS40, suggesting an alternative signaling mechanism in cancer biology that might prioritize cell survival over apoptosis. This demonstrates that kisspeptin activation modulates tumor progression pathways by reducing the activity of the tumor suppressor p53 and PRAS40, which are crucial for inhibiting tumor growth and promoting cell death. Furthermore, an observed increase in the phosphorylation of kinases such as Chk2, c-Jun, p70 S6 kinase, RSK 1/2/3, and members of the STAT family upon kisspeptin system activation highlights its multifaceted role in cancer biology. This elevation in kinase activity indicates a potential pro-oncogenic influence of kisspeptin signaling, promoting pathways associated with cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis, and underscores the need for targeted research to fully understand its therapeutic implications and risks in cancer treatment.
The interaction between Chk2, c-Jun, p53, p70 S6 kinase, RSK 1/2/3, STAT1, STAT3, STAT6, and PRAS40 underlines a complex signaling network in cancer biology. p53 and Chk2 emerge as guardians against oncogenesis, with p53 halting cell proliferation through apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, while Chk2 enhances this defense through both p53-dependent and independent pathways to counter DNA damage [
34]. Conversely, c-Jun promotes cellular proliferation and oncogenic progression, regulated by AP-1 pathway activation [
35]. Within the mTOR pathway, p70 S6 kinase and PRAS40 act as key modulators of cancer progression, influenced by their phosphorylation status [
36]. RSK supports this network by promoting growth and survival downstream of the Ras-MAPK pathway [
37], while the STAT family, particularly STAT3 and STAT5, play a crucial role in cell proliferation and immune evasion, marking them as potential therapeutic targets [
38]. Together, these elements comprise a complex signaling mosaic, offering multiple targets for cancer therapy.
In concordance with the observed inhibitory effects on HeLa cell migration by KP10 and its analogs, an inverse relationship was identified between cellular motility and the phosphorylation status of STAT1, STAT3, and STAT6. Notably, treatment with KP10 analogs resulted in heightened levels of phosphorylated STAT1 which is commonly associated with anti-proliferative and anti-migratory responses [
39], potentially elucidating the mechanism behind the reduced migration rates. Conversely, although STAT3 phosphorylation was also observed, its expected pro-migratory action was not realized, suggesting a non-canonical role of STAT3 in this context or the predominance of STAT1 and STAT6 signaling pathways in mediating the cellular response to these treatments. These findings indicate a complex interplay between STAT family members in governing cell migration, where the activation of STAT1 and STAT6 may override the promigratory signals of phosphorylated STAT3, thereby aligning with the overall diminished migratory capacity of HeLa cells upon exposure to KP10 analogs. Also, treatment with both analogs led to a significant increase in the phosphorylation of key regulatory proteins Chk-2, p70 S6 kinase, cJun, and RSK. The elevated phosphorylation levels of Chk-2 and p70 S6 kinase are indicative of enhanced DNA damage response and protein synthesis regulation [
40], potentially contributing to cellular stabilization and reduced migratory activity. Concurrently, the activation of cJun and RSK, through phosphorylation, may suppress migration by modulating gene expression related to cellular adhesion and cytoskeletal dynamics [
37,
41]. Collectively, these phosphorylation events present a molecular signature that correlates with the observed inhibition of cellular migration, suggesting a multifaceted inhibitory mechanism exerted by the KP10 analogs on the migratory capacity of cancer cells.
This study also delves into the efficacy of KP10 and its analogs across diverse G protein signaling pathways, with a focus on cervical cancer cells, to elucidate their pharmacological profiles and potential therapeutic implications. The determination of EC
50 values for KP10 and its analogs across pathways such as Gα
q, Gα
11, Gα
14, Gα
15, and notably, the Gα
z pathway, along with their recruitment of β-arrestin1 and β-arrestin2, provides a foundational understanding of their interactions with the kisspeptin receptor (
Figure 3.). KP10 is shown to possess remarkable potency in activating the Gα
q pathway, highlighting its significant role in modulating cellular processes pertinent to cancer progression. This potent activation suggests the influence of KP10 on critical pathways involved in cell proliferation, survival, and potentially metastasis [
42].
The analysis extends to the comparison of KP10 analogs, revealing a reduced ability to activate the Gα
q pathway, suggesting a diminished impact on tumorigenesis and metastasis signaling cascades in cervical cancer. Furthermore, KP10 selective activation of the Gα
z pathway, with significantly lower EC
50 values compared to its analogs, underscores a unique interaction with kisspeptin receptor, highlighting the need for further exploration into Gα
z role in cancer biology (
Figure 3.). The study also examines the differential recruitment of β-arrestins by KP10 and its analogs, indicating a potential preference for β-arrestin2-mediated pathways by KP10. This preference could implicate receptor desensitization, internalization, and the initiation of distinct downstream signaling events, shedding light on the complex balance of activating versus inhibitory signals that dictate cellular outcomes in their presence (
Figure 3).
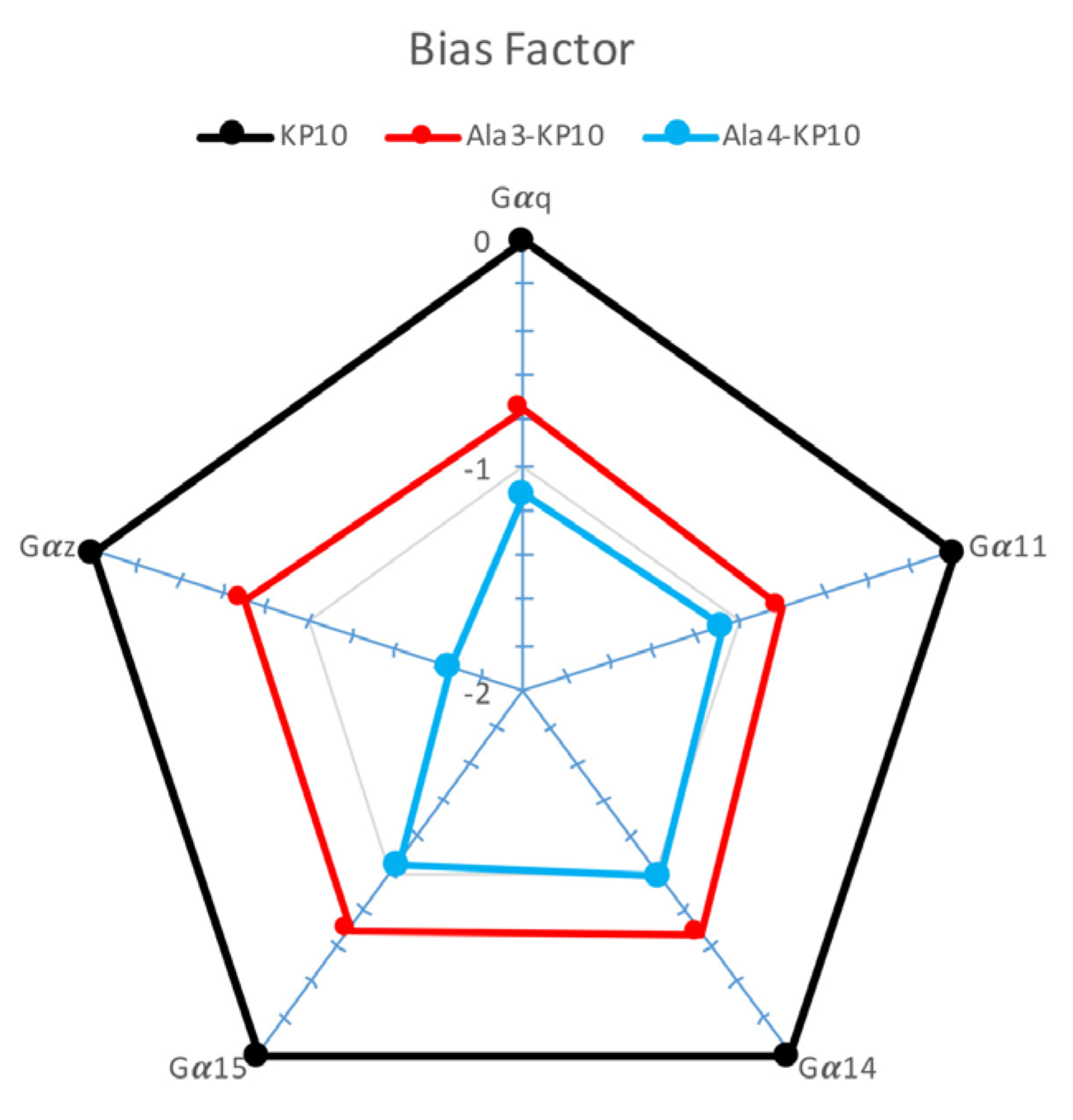
To gain a clearer visualization of the signaling profiles across various analogs, we decided to calculate the bias factor [
43] for Ala
3-KP10 and Ala
4-KP10 in different signaling pathways (
Figure 4). Based on the provided Δ(logτ/KA) values for KP10 and its analogs, a comparative analysis reveals insights into their signaling bias across Gα
q, Gα
11, Gα
14, Gα
15 and Gα
z pathways. KP10, serving as the reference with a Δ(logτ/KA) of 0 across all pathways, establishes a baseline for evaluating the signaling bias of its analogs. In β-arrestin recruitment the bias factor was not considered due to the very low values obtained, which did not yield usable data. The negative values observed for both Ala
3-KP10 and Ala
4-KP10 indicate a relative decrease in affinity or efficacy compared to KP10, reflecting a negative signaling bias. Notably, Ala
4-KP10 exhibits a more pronounced negative bias than Ala
3-KP10 across the board, except for Gα
14, where Ala
3-KP10 shows slightly greater bias. This trend is especially noticeable in Gα
z pathway, where Ala
4-KP10 demonstrates a substantial decrease in preference (Δ(logτ/KA) of -1.66) compared to Ala
3-KP10 Δ(logτ/KA) of -0.7. These findings suggest that specific modifications in KP10 analogs significantly impact their signaling through various G protein pathways relative to native KP10. The pronounced decrease in Ala
4-KP10 affinity or efficacy, particularly towards the Gα
z pathway, warrants further investigation into the molecular interactions or receptor-ligand conformations driving these differences. In summary, KP10 analogs exhibit distinct signaling bias profiles compared to KP10, with Ala
4-KP10 showing a more marked tendency towards negative bias in the activation of examined signaling pathways, providing an intriguing foundation for future research on peptide modifications in GPCR signaling modulation and therapeutic potential.
The differential responses observed in cervical and breast cancer compared to gastric and prostate cancers may reflect the physiological role of kisspeptin in the reproductive system, suggesting a nuanced influence based on sex-determined factors. Given kisspeptin's integral role in reproductive hormone regulation, it is conceivable that its signaling pathways might exert antitumoral effects in female-associated cancers such as cervical and breast, by influencing pathways that restrict proliferation and metastasis. Conversely, in male-associated cancers such as prostate cancer, the same signaling pathways could potentially have protumoral effects, perhaps by aligning with the mechanisms that promote cell growth and survival. This hypothesis underscores the complex interplay between the physiological roles of peptides and their influence on cancer pathophysiology, which can differ markedly between sexes and cancer types. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the sex-specific oncological roles of kisspeptin and its potential as a differential target in cancer therapy.
Figure 5.
Bias factor of KP10 and analogs across Gαq, Gα11, Gα14, Gα15, and Gαz Pathways. This plot presents the bias factor of KP10 and its analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 toward activating Gαq, Gα11, Gα14, Gα15, and Gαz signaling pathways in cervical cancer cells. ∆Log(τ/KA) ratios for Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 were plotted in “ratial graphs” using a logarithmic scale to represent normalized transduction coefficients obtained in each pathway.
Figure 5.
Bias factor of KP10 and analogs across Gαq, Gα11, Gα14, Gα15, and Gαz Pathways. This plot presents the bias factor of KP10 and its analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 toward activating Gαq, Gα11, Gα14, Gα15, and Gαz signaling pathways in cervical cancer cells. ∆Log(τ/KA) ratios for Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10 were plotted in “ratial graphs” using a logarithmic scale to represent normalized transduction coefficients obtained in each pathway.
Figure 1.
Kinase Activity Profiles Across Cell Lines. A)This heatmap displays the kinase activity profiles in AGS, HeLa, MCF7, and PC3 cell lines following stimulation with KP10 and its analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10. Each row represents a different kinase, while columns correspond to the various treatment conditions across the four cell lines. Color intensity indicates the level of kinase activation or inhibition, providing a comparative visualization of the cellular responses to KP10 and its analogs. B) Examination of phosphorylation levels in 11 human kinase substrates, which exhibited changes in their phosphorylation status following stimulation with KP10, Ala3-KP10, or Ala4-KP10 in HeLa cells. The analysis captures the phosphorylation dynamics of these substrates, where spot intensities have been transformed into a color-coded scale to underscore the observed variations.
Figure 1.
Kinase Activity Profiles Across Cell Lines. A)This heatmap displays the kinase activity profiles in AGS, HeLa, MCF7, and PC3 cell lines following stimulation with KP10 and its analogs Ala3-KP10 and Ala4-KP10. Each row represents a different kinase, while columns correspond to the various treatment conditions across the four cell lines. Color intensity indicates the level of kinase activation or inhibition, providing a comparative visualization of the cellular responses to KP10 and its analogs. B) Examination of phosphorylation levels in 11 human kinase substrates, which exhibited changes in their phosphorylation status following stimulation with KP10, Ala3-KP10, or Ala4-KP10 in HeLa cells. The analysis captures the phosphorylation dynamics of these substrates, where spot intensities have been transformed into a color-coded scale to underscore the observed variations.
Figure 2.
Temporal evolution of wound closure in HeLa, MCF7, PC3 and AGS cells subjected to KP10, Ala3-KP10, and Ala4-KP10. The graph displays the percentage of open wound area over time, with significant differences in healing efficacy among the treatments highlighted by bars in different colors corresponding to each peptide. This combined visual analysis demonstrates the distinct impact of each peptide on the healing process, providing a clear comparison of their effectiveness at various time intervals.
Figure 2.
Temporal evolution of wound closure in HeLa, MCF7, PC3 and AGS cells subjected to KP10, Ala3-KP10, and Ala4-KP10. The graph displays the percentage of open wound area over time, with significant differences in healing efficacy among the treatments highlighted by bars in different colors corresponding to each peptide. This combined visual analysis demonstrates the distinct impact of each peptide on the healing process, providing a clear comparison of their effectiveness at various time intervals.
Figure 3.
Comparative activation of the kisspeptin receptor through different signaling pathways in cervical cancer cells by KP10, Ala3-KP10, and Ala4-KP10. Activation levels for each pathway are quantified to illustrate the specific and differential impacts of KP10 and its analogs on these signaling routes. Data were generated from 4 independent experiments.
Figure 3.
Comparative activation of the kisspeptin receptor through different signaling pathways in cervical cancer cells by KP10, Ala3-KP10, and Ala4-KP10. Activation levels for each pathway are quantified to illustrate the specific and differential impacts of KP10 and its analogs on these signaling routes. Data were generated from 4 independent experiments.
Figure 4.
Comparative of the final structures for each transmembrane in the 4 systems, i.e., inactive form (magenta), with KP10 (green), with Ala3-KP10 (blue), and with Ala4-KP10 (yellow).
Figure 4.
Comparative of the final structures for each transmembrane in the 4 systems, i.e., inactive form (magenta), with KP10 (green), with Ala3-KP10 (blue), and with Ala4-KP10 (yellow).
Table 1.
Amino Acid sequences and Mass Spectrometry values of synthesized KP10 analogs. This table lists the amino acid sequences of peptides utilized in our research, detailing their composition and modifications. Calculated indicates the theoretical monoisotopic MH+ value. Observed values were assessed by MALDI-TOF in the reflector mode unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Amino Acid sequences and Mass Spectrometry values of synthesized KP10 analogs. This table lists the amino acid sequences of peptides utilized in our research, detailing their composition and modifications. Calculated indicates the theoretical monoisotopic MH+ value. Observed values were assessed by MALDI-TOF in the reflector mode unless otherwise noted.
| |
Peptide |
Sequence |
Mass Spectrometry (Da) |
| |
Calculated |
Observed |
| |
KP-10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1304 |
1303,537 |
| |
Ala1-KP10 |
Ala |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1211 |
1211,234 |
| |
Ala2-KP10 |
Tyr |
Ala |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1261 |
1261,461 |
| |
Ala3-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Ala |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1188 |
1188,489 |
| |
Ala4-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Ala |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1260 |
1260,589 |
| |
Ala5-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ala |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1288 |
1288,241 |
| |
Ala6-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Ala |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1228 |
1228,284 |
| |
Ala7-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Ala |
Leu |
Arg |
Phe |
1318 |
1318,354 |
| |
Ala8-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Ala |
Arg |
Phe |
1262 |
1262,203 |
| |
Ala9-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Ala |
Phe |
1218 |
1218,613 |
| Ala10-KP10 |
Tyr |
Asn |
Trp |
Asn |
Ser |
Phe |
Gly |
Leu |
Arg |
Ala |
1227 |
1226,697 |
Table 2.
pIC50 Values from Cytotoxicity Assays Across Cell Lines. This table compiles the pIC50 values derived from cytotoxicity assays performed with KP10 and its analogs on several cancer cell lines, including HEK293T, MCF7, AGS, HeLa, and PC3. Each cell line response to the treatment is quantified to reflect the inverse logarithmic concentration of the compound required to inhibit cell viability by 50% (pIC50), providing a comparative measure of the analogs' cytotoxic potency.
Table 2.
pIC50 Values from Cytotoxicity Assays Across Cell Lines. This table compiles the pIC50 values derived from cytotoxicity assays performed with KP10 and its analogs on several cancer cell lines, including HEK293T, MCF7, AGS, HeLa, and PC3. Each cell line response to the treatment is quantified to reflect the inverse logarithmic concentration of the compound required to inhibit cell viability by 50% (pIC50), providing a comparative measure of the analogs' cytotoxic potency.
| Peptide |
pIC50 |
| HEK293T |
HeLa |
MCF7 |
PC3 |
AGS |
| KP-10 |
2,489 |
3,209 |
3,106 |
2,678 |
43,88 |
| Ala1-KP10 |
2,311 |
2,483 |
2,947 |
2,475 |
50,33 |
| Ala2-KP10 |
2,918 |
0,5728 |
2,756 |
2,67 |
38,71 |
| Ala3-KP10 |
2,959 |
-0,6081 |
2,624 |
2,737 |
51,7 |
| Ala4-KP10 |
3,489 |
-0,2705 |
3,132 |
2,541 |
43,25 |
| Ala5-KP10 |
3,335 |
2,61 |
3,327 |
2,203 |
43,42 |
| Ala6-KP10 |
3,518 |
2,523 |
3,168 |
2,461 |
38,05 |
| Ala7-KP10 |
3,027 |
2,554 |
3,009 |
2,42 |
49,16 |
| Ala8-KP10 |
4,017 |
2,564 |
3,15 |
2,151 |
34,5 |
| Ala9-KP10 |
4,197 |
2,429 |
3,183 |
2,295 |
36,86 |
| Ala10-KP10 |
3,292 |
2,493 |
2,826 |
1,739 |
34,56 |
Table 3.
RMSD (Å) distances for each transmembrane of the kisspeptin receptor in its inactive form in comparison with the active form with the kisspeptin, with Ala3-KP10 peptide, and with Ala4-KP10 peptide.
Table 3.
RMSD (Å) distances for each transmembrane of the kisspeptin receptor in its inactive form in comparison with the active form with the kisspeptin, with Ala3-KP10 peptide, and with Ala4-KP10 peptide.
| Inactive |
KP10 |
Ala3-KP10 |
Ala4-KP10 |
| TM1 |
0,868 |
0,937 |
0,529 |
| TM2 |
1,254 |
0,510 |
0,803 |
| TM3 |
0,525 |
0,665 |
0,495 |
| TM4 |
0,711 |
0,568 |
1,880 |
| TM5 |
0,770 |
0,849 |
0,604 |
| TM6 |
1,046 |
1,096 |
1,118 |
| TM7 |
1,045 |
0,751 |
0,941 |