Submitted:
21 May 2024
Posted:
22 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
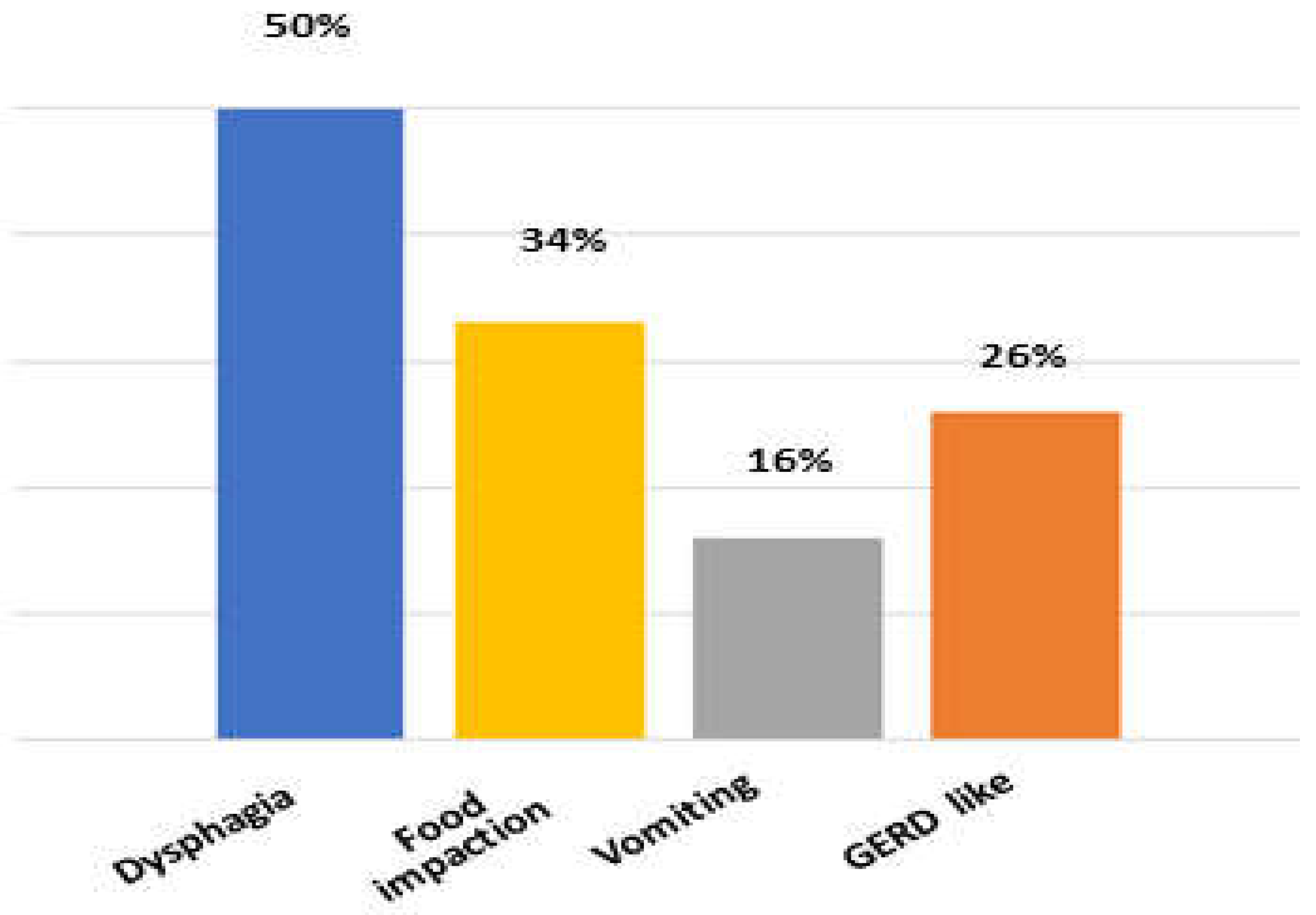
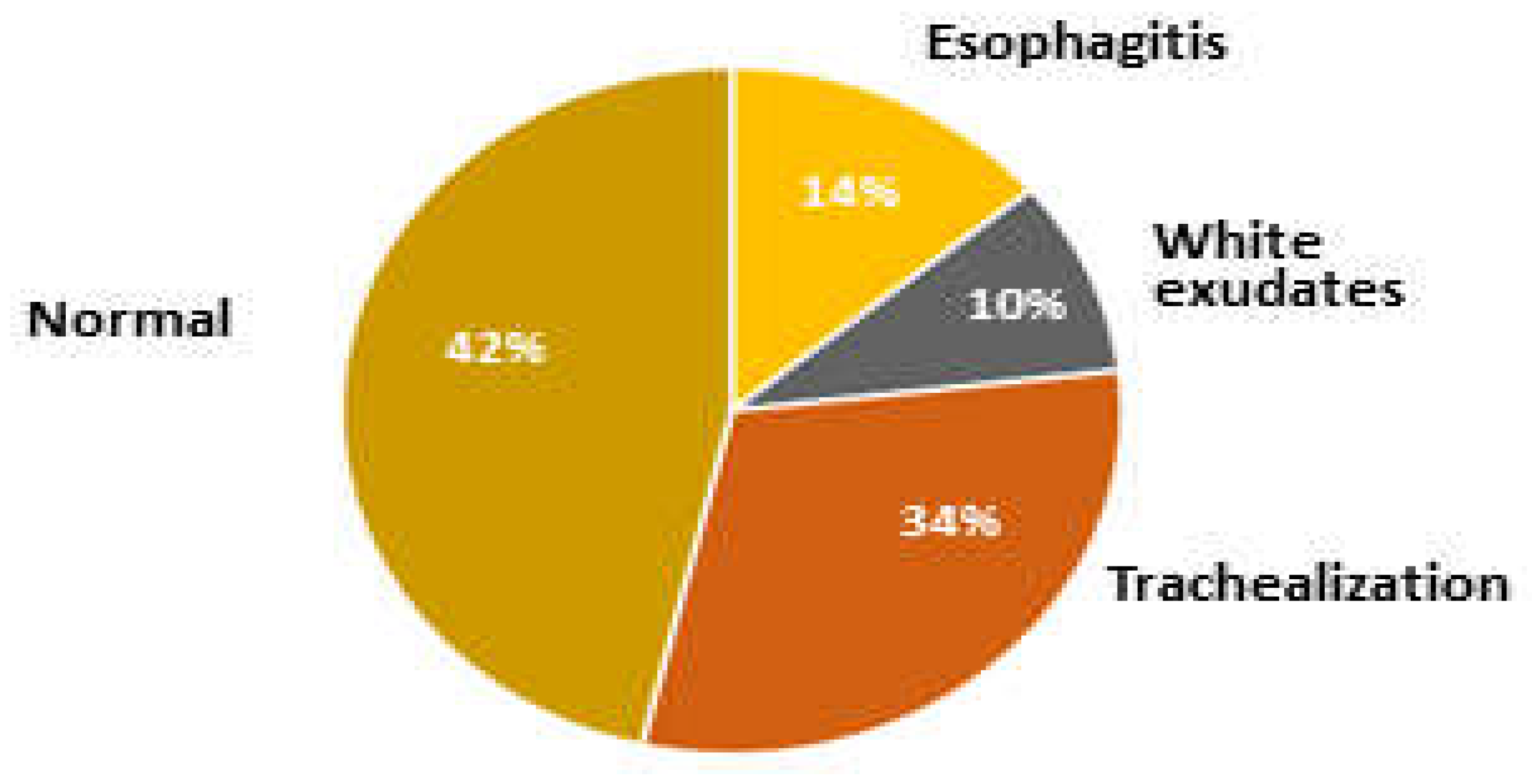
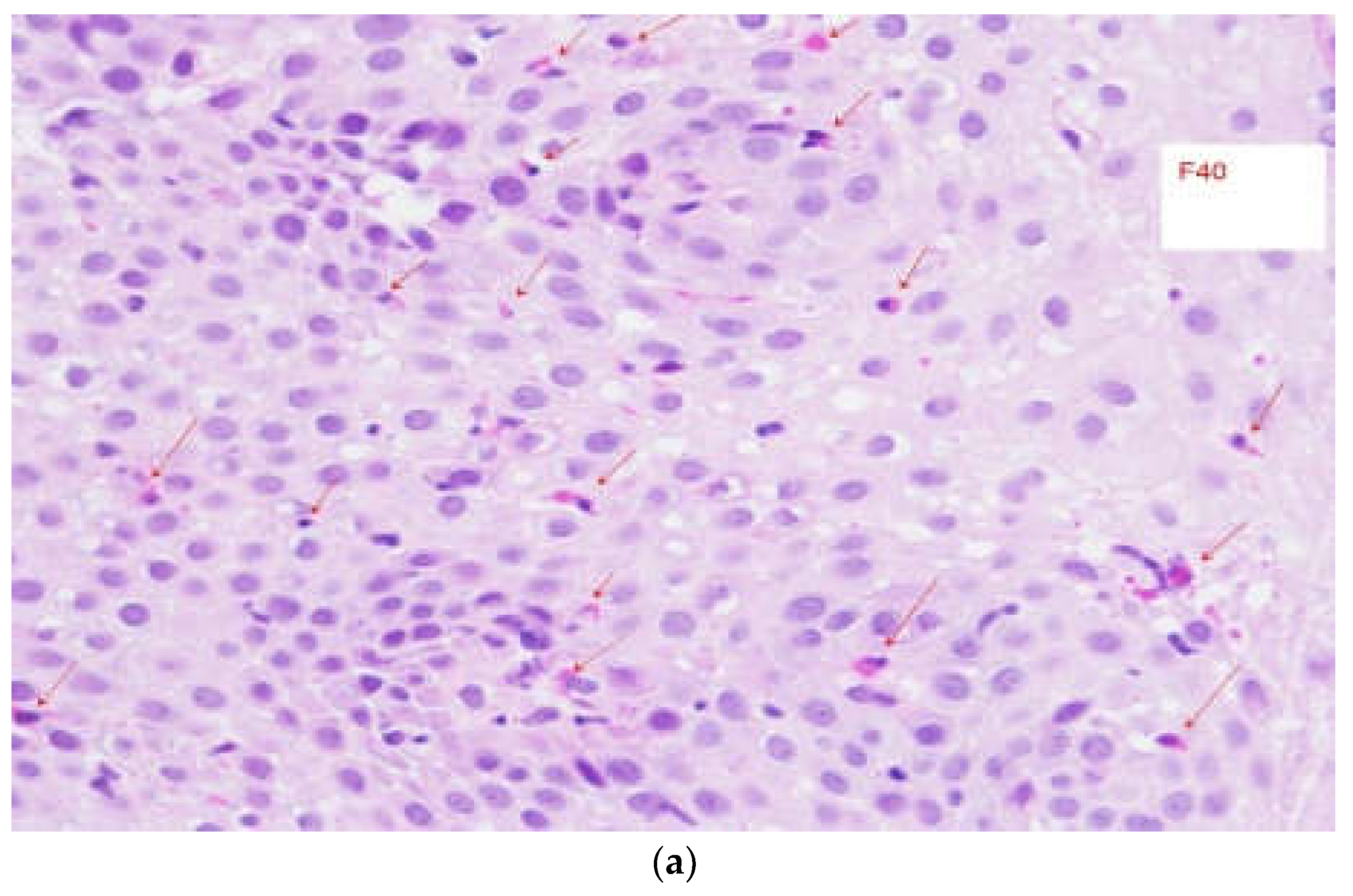
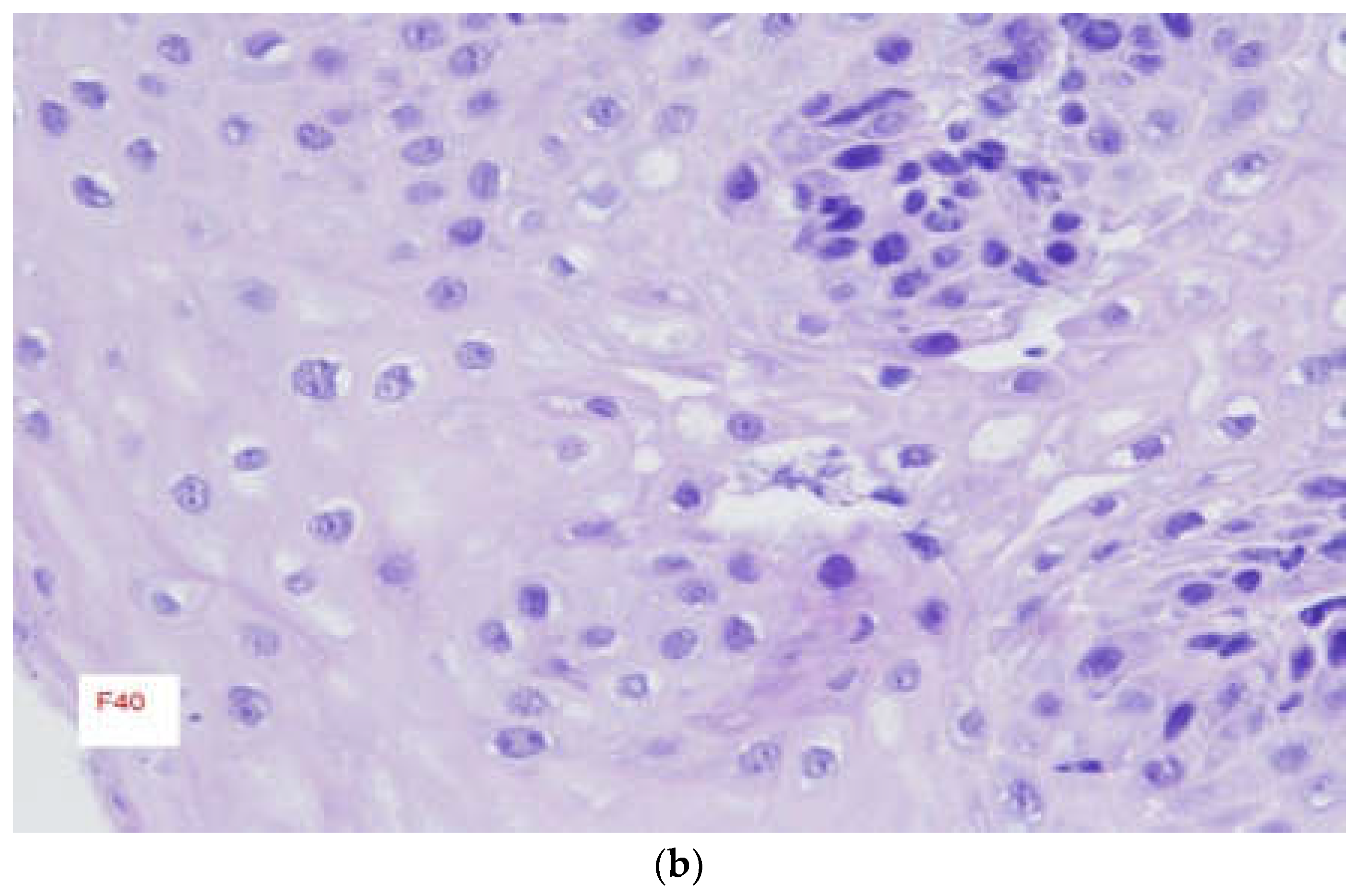
3.2. Endoscopic Findings
3.3. Initial Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liacouras, C.A.; Furuta, G.T.; Hirano, I.; Atkins, D.; Attwood, S.E.; Bonis, P.A.; Burks, A.W.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Dellon, E.S.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 3–20.e6. [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Hirano, I. Epidemiology and Natural History of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 319–+. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Iorio, N.; Schey, R. Esophageal motility in eosinophilic esophagitis. 2015, 80, 205–213. [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; Perezmartinez, I.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 3–15. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.S.; Martin, L.J.; Collins, M.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Sucharew, H.; He, H.; Mukkada, V.A.; Succop, P.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Foote, H.; et al. Twin and family studies reveal strong environmental and weaker genetic cues explaining heritability of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1084–1092.e1. [CrossRef]
- Mahesh VN, Holloway RH, Nguyen NQ. Changing epidemiology offood bolus impaction: is eosinophilic esophagitis to blame? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.2013;28: 963–6.8.
- Dellon ES. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis.Gastroenterol.Clin. North Am.2014;43: 201–18.9.
- Ali MA, Lam-Himlin D, Voltaggio L. Eosinophilic esophagitis: aclinical, endoscopic, and histopathologic review.Gastrointest. Endosc.2012;76: 1224–37.
- Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Grize L, Bucher KA, Beglinger C, Simon HU. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years.Gastroenterology2003;125:1660–9.11.
- Giriens B, Yan P, Safroneeva E, Zwahlen M et al Escalating incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis in Canton of Vaud, Switzerland, 1993-2013: a population-based study. Allergy. 2015 Dec;70(12):1633-9.
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Dias, J.A.; Bove, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.P. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 19–42. [CrossRef]
- Varadarajulu S, Eloubeidi MA, Patel RS et al (2005) The yield and the predictors of esophageal pathology when upper endoscopy is used for the initial evaluation of dysphagia. Gastrointest Endosc 61:804–808.
- Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones DM, Kerlin P (2006) Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to treatment with fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc 63:3–12.
- Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, Furuta GT. Et al Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology. 2018 Oct;155(4):1022-1033.e10.
- Lucendo, AJ, Molina-Infante, J, Arias, A, et al Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J 2017; 5: 335–358.
- Dellon ES, Rothenberg ME, Collins MH, et al Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 22;387(25):2317-2330.
- Van Rhijn, BD, Weijenborg, PW, Verheij, J, et al Proton pump inhibitors partially restore mucosal integrity in patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia but not eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12: 1815–1823.e2.
- Cheng, E, Zhang, X, Huo, X, et al Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD. Gut 2013; 62: 824–832.
- Laserna-Mendieta, EJ, Casabona, S, Savarino, E, et al Efficacy of therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in real-world practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 18: 2903-2911.e4.
- Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Schlag, C.; Vieth, M.; von Arnim, U.; Molina-Infante, J.; Hartmann, D.; Bredenoord, A.J.; de Los Rios, C.C.; Schubert, S.; et al. Efficacy of Budesonide Orodispersible Tablets as Induction Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 74–86.e15. [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Vieth, M.; Schlag, C.; Biedermann, L.; Vaquero, C.S.; de Los Rios, C.C.; Schmoecker, C.; Madisch, A.; et al. Budesonide Orodispersible Tablets Maintain Remission in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1672–1685.e5. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



