Submitted:
21 May 2024
Posted:
21 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
An Introduction to Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) and Phosphodiesterase Type 6 (PDE6)
Background on Currently Available PDE5 Inhibitors and Their Action Mechanisms
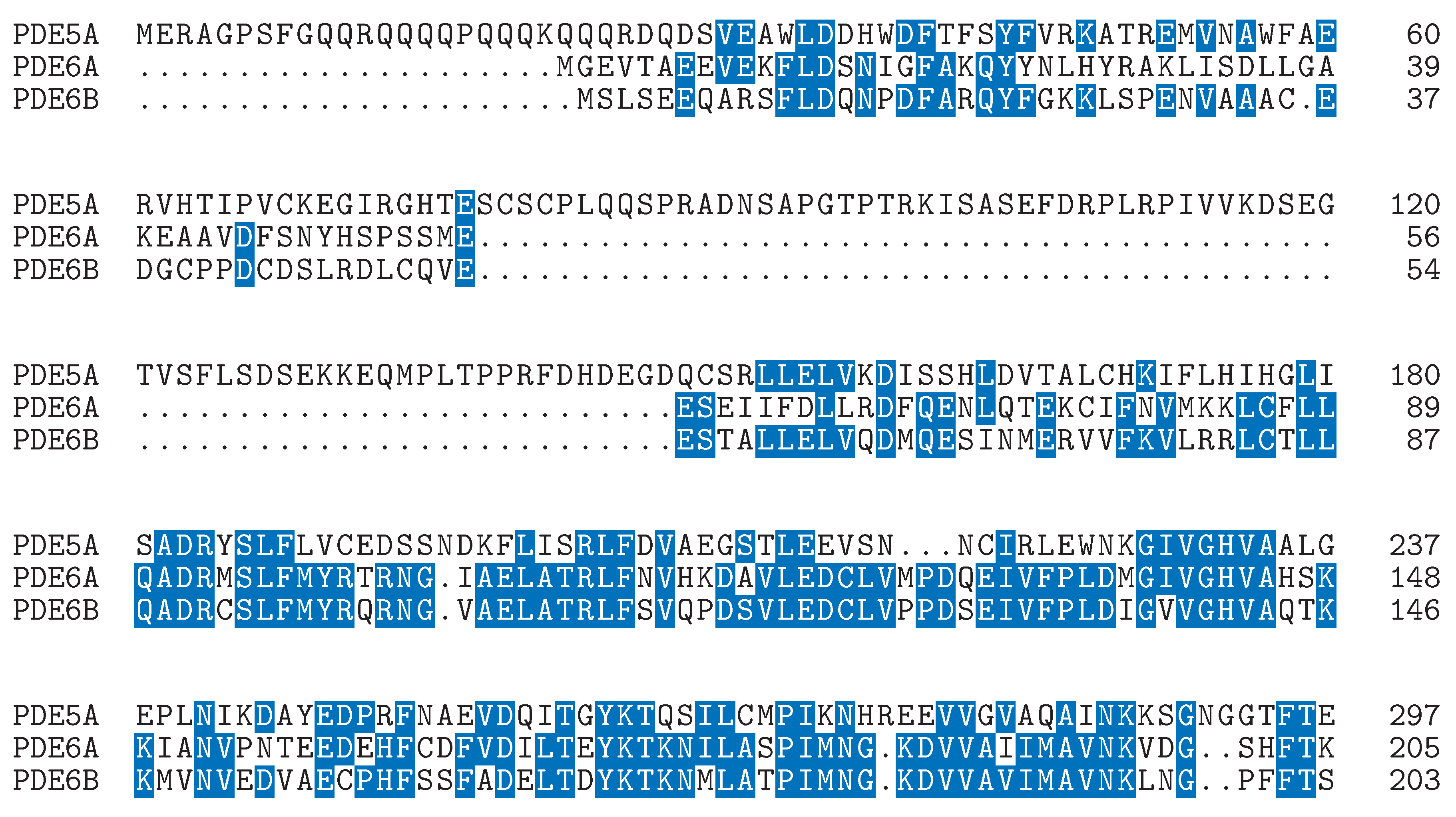
Challenges in the Design of PDE5 Inhibitors: Balancing Efficacy and Safety
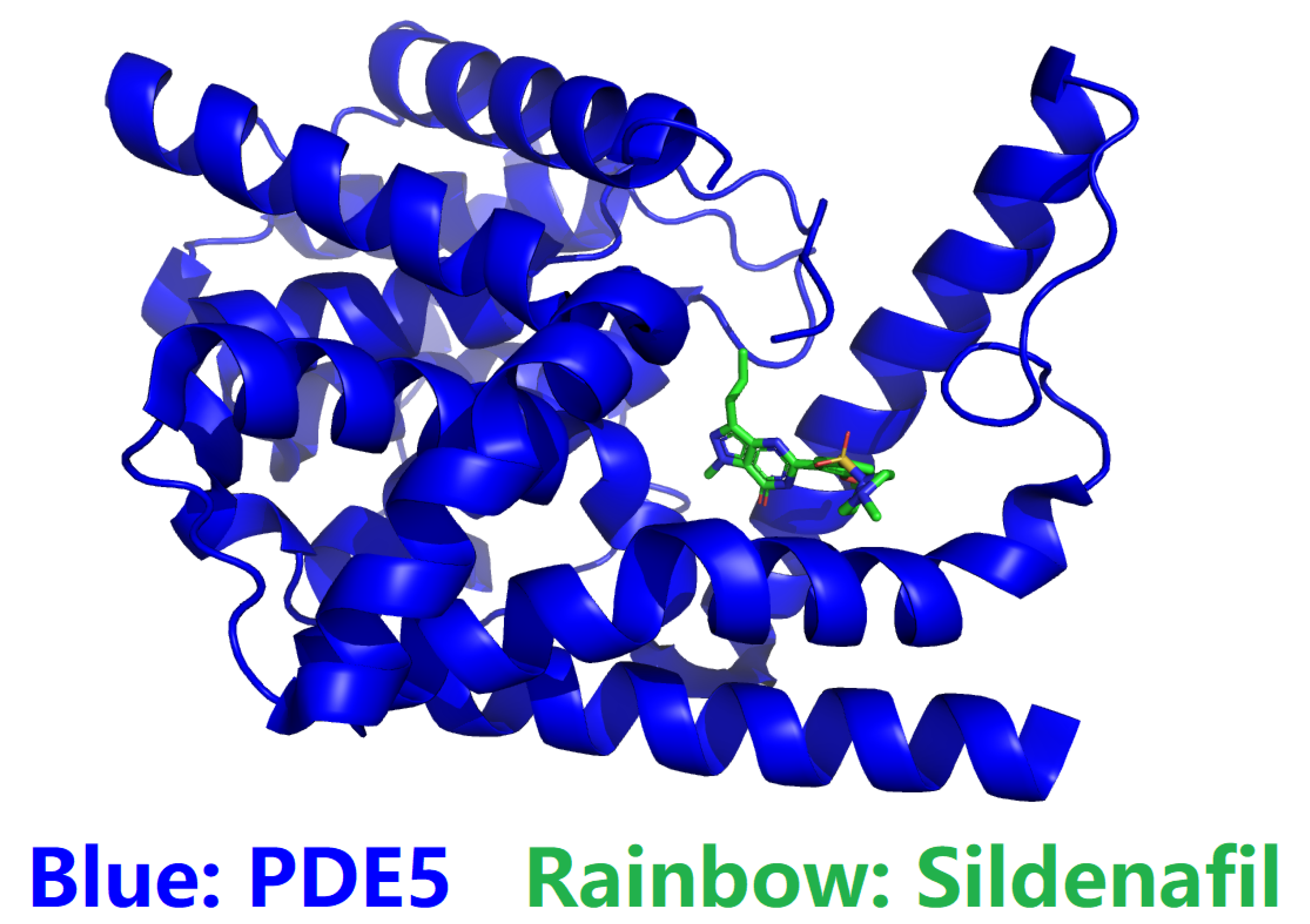
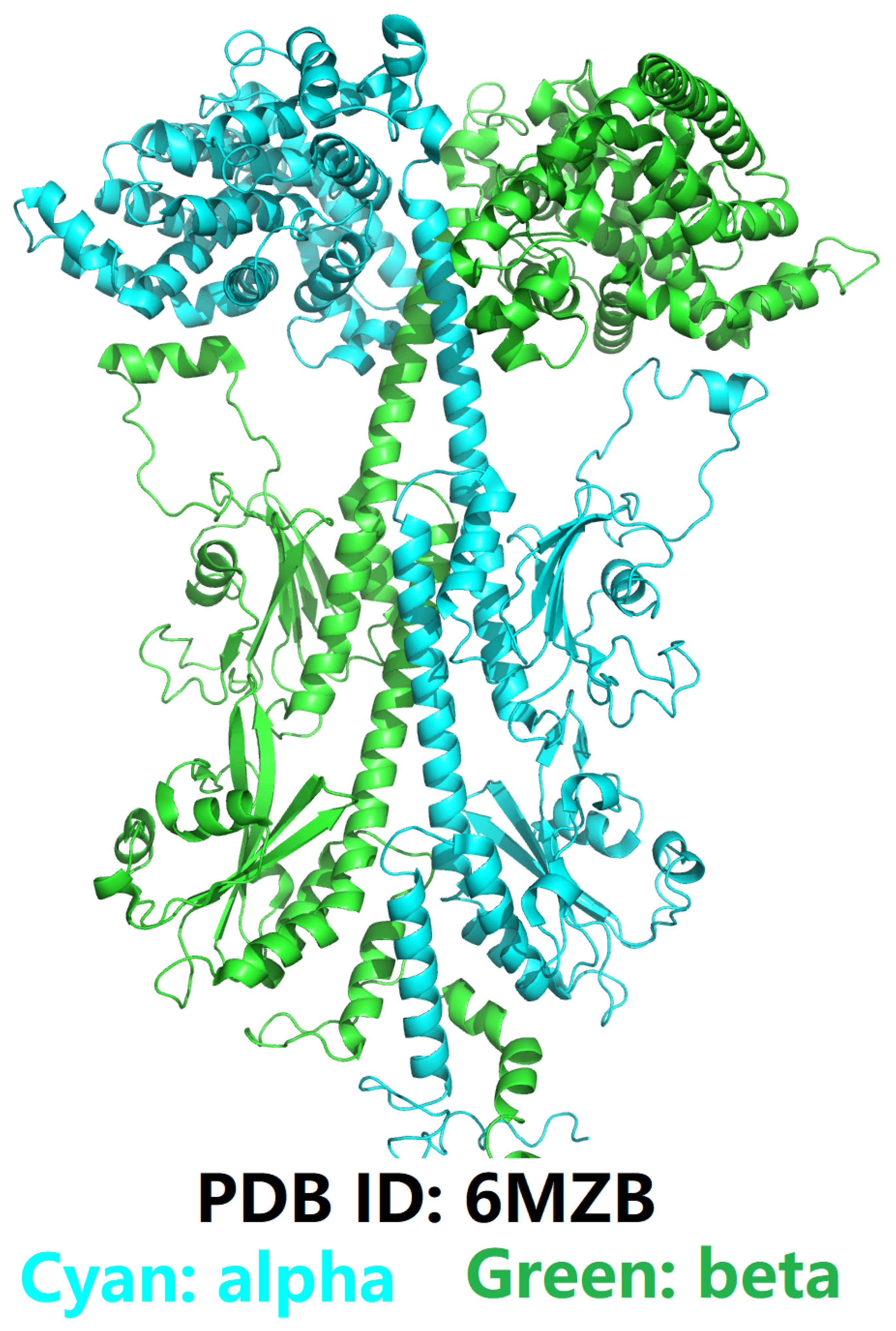
Defining the Challenge in PDE5 Inhibitor Design with a Structural and Biophysical Perspective
- molecule X does bind to PDE5, i.e., ∆G (kcal/mol) ; and
- molecule X does not bind to PDE6, i.e., ∆G (kcal/mol) or ∆G (kcal/mol) ; and
- in the presence of molecule X, cGMP does not bind to PDE5 (i.e., ∆G (kcal/mol) or ∆G (kcal/mol) ), such that PDE5 is unable, or at least not as able as in the absence of molecule X, to catalyze cGMP.
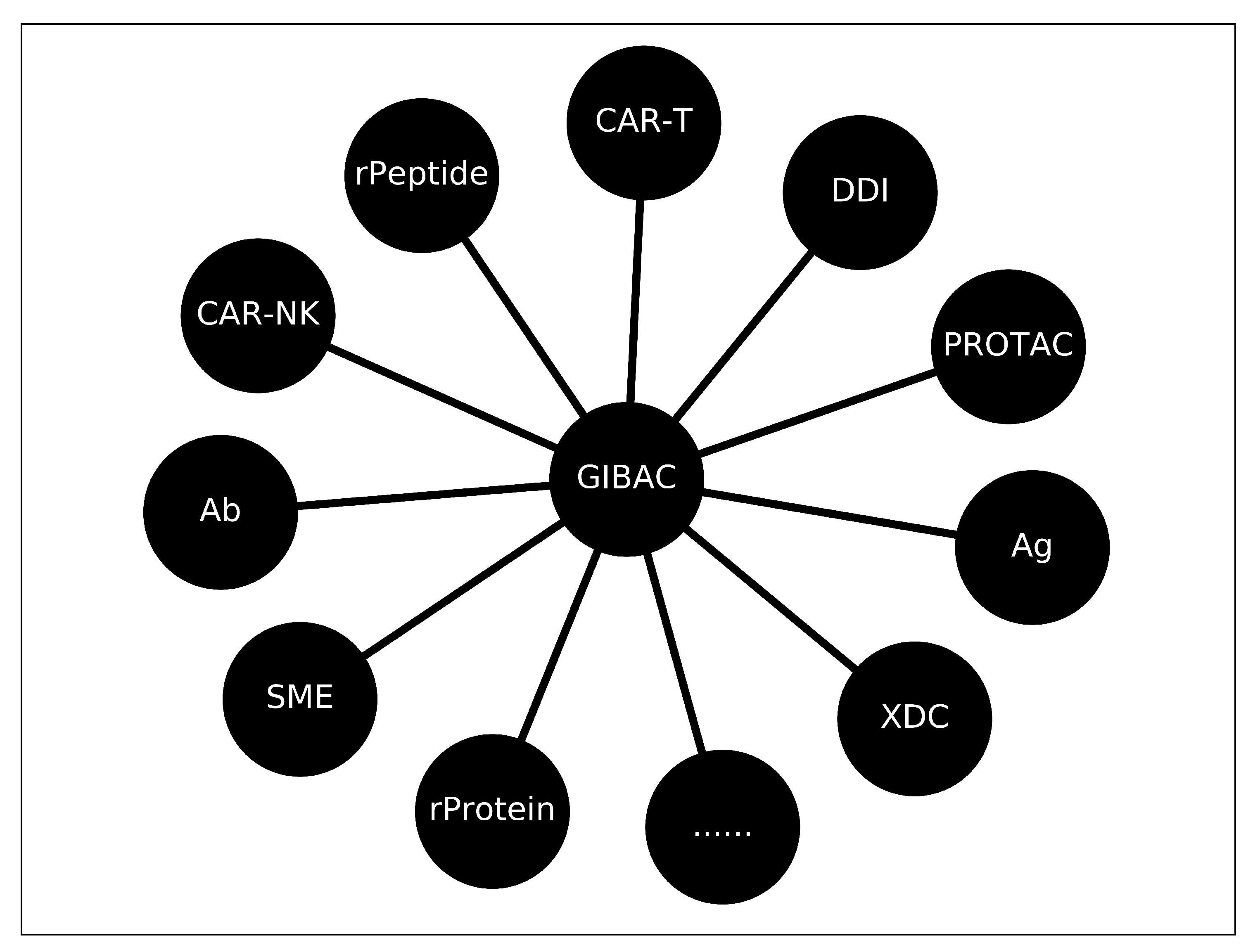
A GIBAC-Based Selectivity Strategy for the Design of Non-PDE6-Binding PDE5 Inhibitors
- a real GIBAC needs to take genetic variations into account; and
- a real GIBAC needs to work even without structural information; and
- for a real GIBAC, a variety of factors need to be taken into account, such as temperature, pH [45,46], site-specific protonation states (e.g., side chain pKa of protein) [47,48], post-translational modifications (PTMs) [49,50,51], post-expression modifications (PEMs) [52,53], buffer conditions [54], et cetera; and
- a real GIBAC requires a general forcefield for all types of molecules [55]; and
- a real GIBAC is able to be used the other way around, i.e., to be used as a search engine for therapeutic candidate(s). With such a GIBAC-based search engine, a list of therapeutic candidates can be retrieved and ranked according to drug-target Kd value(s), with input parameters including drug target(s) and a desired drug-target Kd value or a range of it.
- experimental structures of PDE5 and its inhibitor(s);
- experimental structures of PDE6 and its inhibitor(s);
- PDE5-related computational structural data from AlphaFold database [?];
- PDE6-related computational structural data from AlphaFold database [?];
- synthetic (both apo and complex) PDE5-related structural data generators [?];
- synthetic (both apo and complex) PDE6-related structural data generators [?];
- molecular docking & dynamics simulation tools [??].
- synthetic Kd data generators [36];
Future Direction of GIBAC’s Practical Application in Drug Discovery and Design
- can you generate a Kd-ranked list of therapeutic candidates which targets X but not Y or Z?
Towards a GIBAC-Based Paradigm Shift in Computational Drug Discovery and Design
- the crucial roles of Kd and ∆G in drug discovery & design; and
- the availability of a substantial amount of structural and biophysical data, experimental and synthetic; and
- the availability of a variety of AI algorithms [37] for drug discovery & design; and
Ethical Statement
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, A.; Durrant, D.; Salloum, F.N.; Xi, L.; Kukreja, R.C. PDE5 inhibitors as therapeutics for heart disease, diabetes and cancer. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2015, 147, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.S.; Geethakumari, A.M.; Biswas, K.H. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5): Structure-function regulation and therapeutic applications of inhibitors. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 134, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemnes, A.R.; Champion, H.C. Sildenafil, a PDE5 inhibitor, in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy 2006, 4, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samidurai, A.; Xi, L.; Das, A.; Kukreja, R.C. Beyond Erectile Dysfunction: cGMP-Specific Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors for Other Clinical Disorders. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2023, 63, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, K. PDE5 inhibitors – pharmacology and clinical applications 20 years after sildenafil discovery. British Journal of Pharmacology 2018, 175, 2554–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, M.; Vergelli, C.; Graziano, A.; Dal Piaz, V. PDE5 Inhibitors and their Applications. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2010, 17, 2564–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayık, G.; Tüzün, N.S.; Durdagi, S. Investigation of PDE5/PDE6 and PDE5/PDE11 selective potent tadalafil-like PDE5 inhibitors using combination of molecular modeling approaches, molecular fingerprint-based virtual screening protocols and structure-based pharmacophore development. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 32, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, E. Potency, selectivity, and consequences of nonselectivity of PDE inhibition. International Journal of Impotence Research 2004, 16, S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, R.H. Characteristics of Photoreceptor PDE (PDE6): similarities and differences to PDE5. International Journal of Impotence Research 2004, 16, S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, B.J.; Yeon Hwang, K.; Ho Jeon, Y.; Lee, J.I.; Heo, Y.S.; Hwan Kim, J.; Moon, J.; Min Yoon, J.; Hyun, Y.L.; Kim, E.; Jin Eum, S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.O.; Gyu Lee, T.; Ro, S.; Myung Cho, J. Structure of the catalytic domain of human phosphodiesterase 5 with bound drug molecules. Nature 2003, 425, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, B.J.; Lee, J.; Heo, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Moon, J.; Yoon, J.; Hyun, Y.L.; Kim, E.; Eum, S.; Lee, T.; Cho, J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.O.; Jeon, Y.; Hwang, K.; Ro, S. Crystal structure of Human Phosphodiesterase 5 complexed with Sildenafil(Viagra). 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsletter On Protein Crystallography 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, S.; Palczewski, K.; Engel, A.; Stahlberg, H.; Kovacik, L. Cryo-EM structure of phosphodiesterase 6 reveals insights into the allosteric regulation of type I phosphodiesterases. Science Advances 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, S.; Palczewski, K. Cryo-EM structure of phosphodiesterase 6, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, I.C.; Cho, H.J.; Je, N.; Kwon, O.M.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Sohn, D.W. PDE 5 inhibition with udenafil improves left ventricular systolic/diastolic functions and exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. American Heart Journal 2015, 169, 813–822.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltez, N.; Maxwell, L.J.; Rirash, F.; Tanjong Ghogomu, E.; Harding, S.E.; Tingey, P.C.; Wells, G.A.; Tugwell, P.; Pope, J. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE5i) for the treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chen, T.; Xu, Y. Crystal structure of the PDE5A1 catalytic domain in complex with novel inhibitors. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Tian, G.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, W. Utilization of Halogen Bond in Lead Optimization: A Case Study of Rational Design of Potent Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2011, 54, 5607–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouni, F.; Abu samra, K. Are Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors Associated with Vision-Threatening Adverse Events? A Critical Analysis and Review of the Literature. The Journal of Sexual Medicine 2011, 8, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliferis, K.; Petropoulos, I.; Farpour, B.; Matter, M.; Safran, A. Should Central Serous Chorioretinopathy Be Added to the List of Ocular Side Effects of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors? Ophthalmologica 2011, 227, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laties, A.; Sharlip, I. Ocular Safety in Patients Using Sildenafil Citrate Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction. The Journal of Sexual Medicine 2006, 3, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, Q.; Hazarika, A.; Mishra, R. A Review on the Pharmacological Importance of PDE5 and Its Inhibition to Manage Biomedical Conditions. Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics 2022, 13, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, H.; Qi, F.; Qu, L.; Takaesu, Y.; Hoshino, T. Prediction of Ligand Binding Affinity to Target Proteins by Molecular Mechanics Theoretical Calculation. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2017, 65, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2003, 10, 980–980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Half-a-century Burial of ρ, θ and φ in PDB 2021. φ. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Visualising the Experimentally Uncharted Territories of Membrane Protein Structures inside Protein Data Bank 2020.
- Li, W. A Local Spherical Coordinate System Approach to Protein 3D Structure Description 2020.
- Li, W. Structurally Observed Electrostatic Features of the COVID-19 Coronavirus-Related Experimental Structures inside Protein Data Bank: A Brief Update 2020.
- Li, W. How do SMA-linked mutations of SMN1 lead to structural/functional deficiency of the SMA protein? PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0178519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Extracting the Interfacial Electrostatic Features from Experimentally Determined Antigen and/or Antibody-Related Structures inside Protein Data Bank for Machine Learning-Based Antibody Design 2020.
- Li, W. Structural Identification of the Electrostatic Hot Spots for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein to Be Complexed with Its Receptor ACE2 and Its Neutralizing Antibodies 2020.
- Li, W. Calcium Channel Trafficking Blocker Gabapentin Bound to the α-2-δ-1 Subunit of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel: A Computational Structural Investigation 2020.
- Li, W. Inter-Molecular Electrostatic Interactions Stabilizing the Structure of the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis: A Structural Evolutionary Perspective 2020.
- Li, W. Structural and Functional Consequences of the SMA-Linked Missense Mutations of the Survival Motor Neuron Protein: A Brief Update. In Novel Aspects on Motor Neuron Disease; IntechOpen, 2019.
- Li, W. Designing Nerve Growth Factor Analogues to Suppress Pain Signal Transduction Mediated by the p75NTR-NGF-TrkA Complex: A Structural and Biophysical Perspective 2024. [CrossRef]
- Vangone, A.; Bonvin, A.M. Contacts-based prediction of binding affinity in protein-protein complexes. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Vottevor, G. Towards a Truly General Intermolecular Binding Affinity Calculator for Drug Discovery & Design 2023.
- Li, W. Towards a General Intermolecular Binding Affinity Calculator 2022.
- Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. The insulin receptor: structure, function and signaling. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 1994, 266, C319–C334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahuel-Clermont, S.; French, C.A.; Kaarsholm, N.C.; Dunn, M.F. Mechanisms of Stabilization of the Insulin Hexamer through Allosteric Ligand Interactions. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 5837–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, E.; Pridal, L.; Glendorf, T.; Hansen, B.F.; Hubálek, F.; Kjeldsen, T.; Kristensen, N.R.; Lützen, A.; Lyby, K.; Madsen, P.; Pedersen, T.Å.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Stidsen, C.E.; Haahr, H. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of insulin icodec: a new basal insulin analog designed for once-weekly dosing. BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care 2021, 9, e002301. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Designing Insulin Analogues with Lower Binding Affinity to Insulin Receptor than That of Insulin Icodec 2024. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. How Structural Modifications of Insulin Icodec Contributes to Its Prolonged Duration of Action: A Structural and Biophysical Perspective 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Siah, K.W.; Lo, A.W. Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters. Biostatistics 2018, 20, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.S.; Honig, B. On the pH Dependence of Protein Stability. Journal of Molecular Biology 1993, 231, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.K.; Turner, G.J. Structural Basis of Perturbed pKa Values of Catalytic Groups in Enzyme Active Sites. IUBMB Life (International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: Life) 2002, 53, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Gravity-driven pH adjustment for site-specific protein pKa measurement by solution-state NMR. Measurement Science and Technology 2017, 28, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.L.; Kay, L.E. Measurement of histidine pKa values and tautomer populations in invisible protein states. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, E1705–E1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herget, S.; Ranzinger, R.; Maass, K.; Lieth, C.W. GlycoCT—a unifying sequence format for carbohydrates. Carbohydrate Research 2008, 343, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.M.; Moreno, P.; Fabregat, A.; Hermjakob, H.; Steinbeck, C.; Apweiler, R.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Vizcaíno, J.A. LipidHome: A Database of Theoretical Lipids Optimized for High Throughput Mass Spectrometry Lipidomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S. Template-based combinatorial enumeration of virtual compound libraries for lipids. Journal of Cheminformatics 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Strengthening Semaglutide-GLP-1R Binding Affinity via a Val27-Arg28 Exchange in the Peptide Backbone of Semaglutide: A Computational Structural Approach. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry 2021, 20, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M. Design of ultra-stable insulin analogues for the developing world. Journal of Health Specialties 2013, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent Treatment of Internal and Surface Residues in Empirical pKa Predictions. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.W.M.; Kuleshova, L.N. A general force field by machine learning on experimental crystal structures. Calculations of intermolecular Gibbs energy with iFlexCryst. Acta Crystallographica Section A Foundations and Advances 2023, 79, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, X.; Li, M.; Shao, B.; Liu, T.Y. AIMD-Chig: Exploring the conformational space of a 166-atom protein Chignolin with ab initio molecular dynamics. Scientific Data 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Hansen, F.K.; Gütschow, M.; Lindsley, C.W.; Liotta, D. New Drug Modalities in Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Translational Science. ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science 2021, 4, 1712–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. A Reversible Spherical Geometric Conversion of Protein Backbone Structure Coordinate Matrix to Three Independent Vectors of ρ, θ and φ 2024. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. An Exhaustive Exploration of the Semaglutide-GLP-1R Sequence Space towards the Design of Semaglutide Analogues with Elevated Binding Affinity to GLP-1R 2024. [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Pozzo, E.D.; Giacomelli, C.; Barresi, E.; Taliani, S.; Settimo, F.D.; Martini, C. TSPO ligand residence time: a new parameter to predict compound neurosteroidogenic efficacy. Scientific Reports 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. The drug-target residence time model: a 10-year retrospective. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2015, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, R.; Kizerwetter, M.; Yang, H.; Christodoulou, I.; Fearnow, A.; Vorri, S.; Spangler, J.; Bonifant, C. Poster: AML-496 Study of Affinity Tuning in AML-Targeted CAR-NK Cells. Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia 2022, 22, S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Sutter, A.; Shooter, E.M. Monoclonal antibodies against beta nerve growth factor and their effects on receptor binding and biological activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1981, 78, 4611–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Mantyh, P.W.; Murrell, J.; Innes, J.F.; Lascelles, B.D.X. Anti-nerve growth factor monoclonal antibodies for the control of pain in dogs and cats. Veterinary Record 2019, 184, 23–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnins, G. mature recombinant horse NGF, 2020.
- Sheng, X.; Ye, D.; Zhou, A.; Yao, X.; Luo, H.; He, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zou, Q.; He, C.; Guo, J.; Tu, X.; Liu, Z.; Shi, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, P.; Wei, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, F.; Wu, D.; Fu, C.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Wang, L.; Qin, S.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, G.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Guo, J. Efficacy and safety of vorolanib plus everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A three-arm, randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase III study (CONCEPT). European Journal of Cancer 2023, 178, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urva, S.; O’Farrell, L.; Du, Y.; Loh, M.T.; Hemmingway, A.; Qu, H.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Coskun, T. The novel GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist retatrutide delays gastric emptying. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2023, 25, 2784–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrai-Rad, H. Insulin-degrading enzyme identified as a candidate diabetes susceptibility gene in GK rats. Human Molecular Genetics 2000, 9, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Delving deep into the structural aspects of a furin cleavage site inserted into the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2: A structural biophysical perspective. Biophysical Chemistry 2020, 264, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Peng, H.; Voyer, J.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Cao, H.; Mayer, M.L.; Song, K.; Xu, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B. Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 postfusion spike in membrane. Nature 2023, 619, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, L.; Feig, M. Modeling of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Proteins by Machine Learning and Physics-Based Refinement 2020.
- Noble, D.; Blundell, T.L.; Kohl, P. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology: A brief history of the journal. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology 2018, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, O.M.; MacKerell Jr, A.D.; Roux, B.; Watanabe, M. Computational biochemistry and biophysics; CRC Press,, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kendon, V. Quantum computing using continuous-time evolution. Interface Focus 2020, 10, 20190143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cookson, C. Taking bold bets: new UK agency prepares to fund breakthrough technologies, 2023. Accessed: (August 30, 2023).
- Zhou, S.F.; Zhong, W.Z. Drug Design and Discovery: Principles and Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output |
|---|---|---|
| , , ... | Kd, Kon, Koff, RT, pKa | |
| , , ... | Kd, Kon, Koff, RT, pKa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





