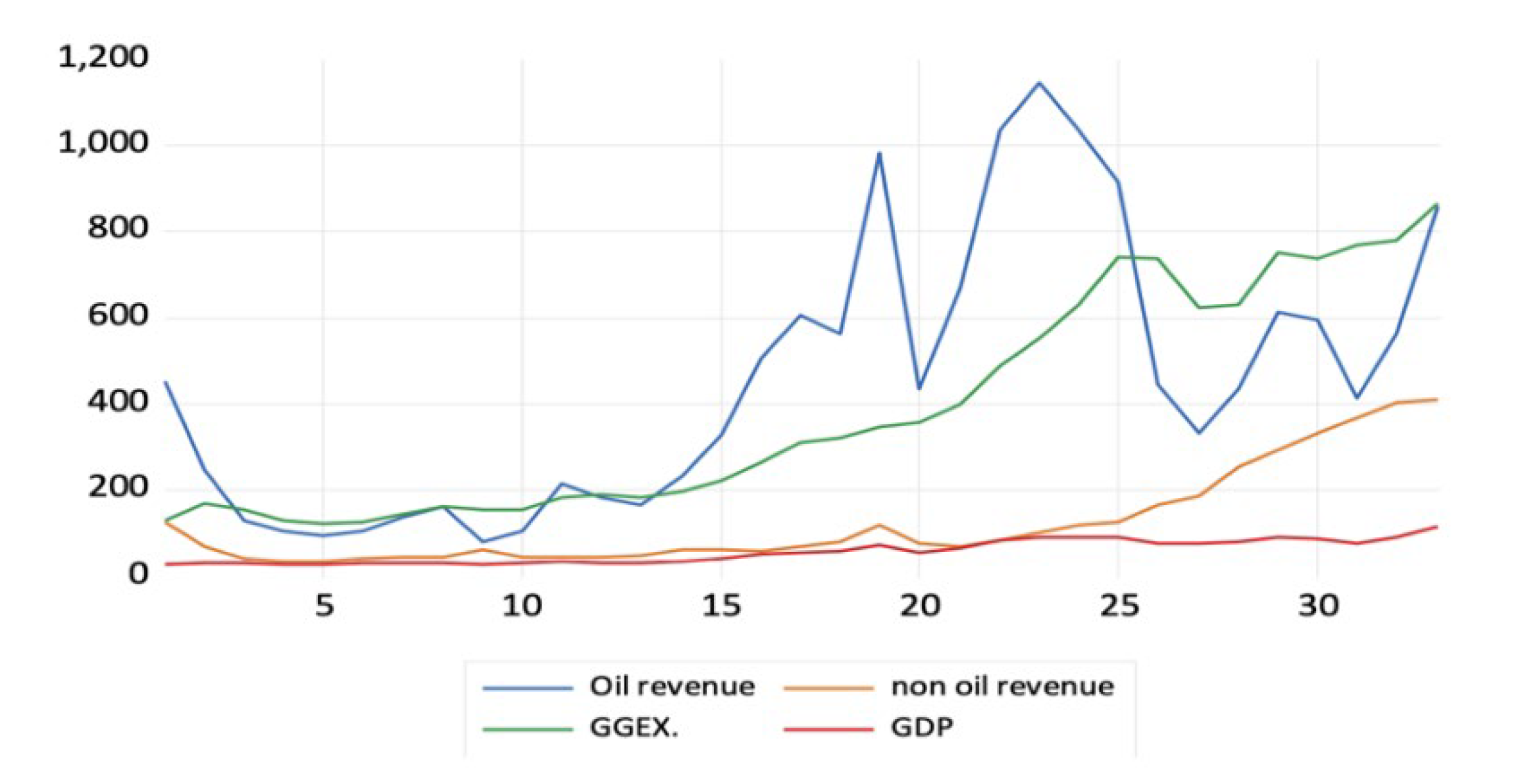
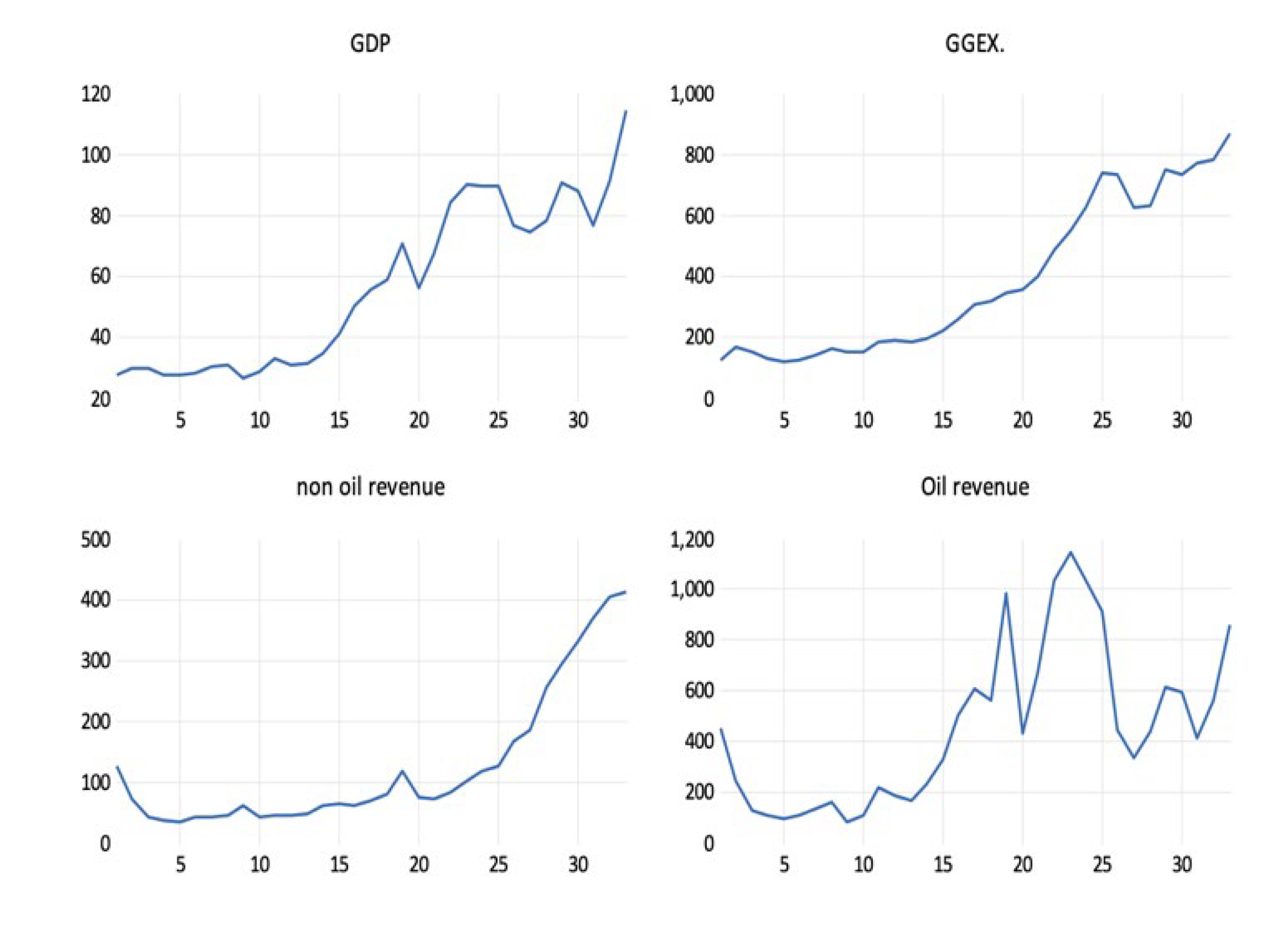
2. Literature Review
Theoretical Backdrop of Counter-Cyclical Fiscal Policies
Counter-cyclical fiscal policies are rooted in Keynesian economic theory, which emphasizes the role of government intervention in stabilizing the economy. These policies are designed to counterbalance the business cycle by adjusting government spending and taxation in a manner that is opposite to the prevailing economic trend. The primary objective is to mitigate the adverse effects of economic fluctuations, thus promoting economic stability and growth (Keynes, 1936).
Managing Aggregate Demand
In Keynesian theory, managing aggregate demand is central to stabilizing economic output and employment levels. Counter-cyclical fiscal policies serve as a tool to regulate aggregate demand, ensuring economic stability across business cycles. During recessions, governments can stimulate demand by increasing spending. This boosts economic activity, creates jobs, and offsets the decline in private sector demand. Conversely, during periods of economic expansion, reducing government spending helps prevent overheating and inflation. Additionally, tax policies can be used to manage aggregate demand. Lowering taxes during downturns increases disposable income, stimulating spending and investment. Conversely, raising taxes during economic booms helps reduce excessive demand and control inflationary pressures. By adjusting government spending and tax policies in a counter-cyclical manner, policymakers can effectively manage aggregate demand, contributing to overall economic stability and growth.
Automatic Stabilizers
Automatic stabilizers are fiscal mechanisms that naturally counterbalance economic fluctuations without additional government action. Examples include unemployment insurance, which increases government spending during downturns as more people become eligible for benefits, and progressive taxation, where tax revenues fall during recessions as incomes drop, cushioning disposable incomes.
Smoothing the Business Cycle
Counter-cyclical fiscal policies are designed to smooth the business cycle and promote economic stability. During recessions, these policies aim to mitigate economic downturns by boosting aggregate demand. This helps reduce the depth and duration of recessions, limiting the negative impacts on employment and output. Conversely, during periods of economic expansion, counter-cyclical fiscal policies work to prevent overheating. By curbing demand through measures such as reducing government spending or increasing taxes, these policies help prevent the economy from reaching unsustainable levels of growth that can lead to inflation and asset bubbles. Overall, the goal of counter-cyclical fiscal policies is to maintain a stable economic environment by moderating the extremes of the business cycle and promoting sustainable growth over the long term.
Fiscal Multipliers
The effectiveness of these policies is influenced by fiscal multipliers, which measure the impact of government spending or tax changes on overall economic output. Fiscal multipliers tend to be larger during recessions due to a higher marginal propensity to consume and underutilized resources. Increased demand during downturns can more readily translate into higher output.
Long-term Fiscal Sustainability
While counter-cyclical fiscal policies aim to stabilize the economy in the short term, they must be designed with long-term fiscal sustainability in mind. This involves accumulating surpluses during booms to build a buffer for future downturns and avoiding excessive debt to maintain investor confidence and the ability to respond to future crises.
Influence on Economic Stability and Growth
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation decisions, plays a pivotal role in influencing national economic stability and growth. Foundational economic theories posit that through adept manipulation of these fiscal tools, governments can mitigate the effects of economic downturns and foster conditions conducive to growth during recovery periods. A substantial body of literature has examined the dual role of fiscal policy in both stabilizing economies during recessions and stimulating them during expansions.
Counter-cyclical fiscal policies significantly influence economic stability and growth, particularly in oil-dependent economies like Saudi Arabia. By managing aggregate demand, these policies help mitigate the volatility caused by fluctuations in oil prices. During periods of low oil prices, increased government spending and reduced taxes can sustain economic activity, prevent severe recessions, and promote recovery. Conversely, during periods of high oil prices, reducing spending and increasing taxes can prevent overheating and maintain economic stability.
In the context of Saudi Arabia, where oil revenues form the backbone of government income, counter-cyclical fiscal policies are crucial. Establishing stabilization funds, such as sovereign wealth funds, allows the government to sustain spending during periods of low oil prices without drastic cuts. Implementing counter-cyclical measures ensures that savings are made during boom periods and spent during downturns, helping to stabilize the economy.
The Role of Fiscal Policies in Managing Public Debt
Fiscal policies play a pivotal role in managing public debt, particularly in oil-dependent countries where revenue volatility can significantly affect fiscal stability. Strategic fiscal management involves setting fiscal rules, such as debt ceilings or balanced budget requirements, which constrain excessive borrowing and promote prudent fiscal behavior. For example, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have adopted fiscal rules to manage their debt levels more effectively, enhancing their fiscal resilience and stability. Blanchard and Leigh (2013) suggest that counter-cyclical fiscal policies can mitigate the adverse effects of revenue volatility by smoothing out public spending and avoiding pro-cyclical fiscal behavior that exacerbates economic fluctuations. These policies help stabilize the economy by saving surplus revenues during booms and using these reserves during downturns, ensuring consistent public services and avoiding drastic spending cuts.
Fiscal policies play a critical role in addressing social and political challenges, particularly in oil-dependent economies like Saudi Arabia. Beyond economic stabilization, these policies can help mitigate social inequities and foster political stability. By allocating resources towards social welfare programs, education, healthcare, and infrastructure, fiscal policies can improve the quality of life for citizens, thereby reducing social unrest and enhancing public trust in government institutions. Additionally, targeted fiscal measures can address regional disparities and promote inclusive growth, ensuring that the benefits of economic development are more evenly distributed across different segments of the population. The implementation of counter-cyclical fiscal policies, such as those supported by the Public Investment Fund (PIF), not only cushions the economy against oil price volatility but also allows the government to maintain essential public services during economic downturns. This approach can prevent the exacerbation of social tensions that often accompany economic hardships. Moreover, transparent and accountable fiscal governance is crucial for maintaining political stability. Effective management of public finances, including anti-corruption measures and fiscal transparency, can strengthen institutional trust and support for government policies. In the context of Saudi Arabia, the strategic use of the PIF to fund diverse economic sectors and social programs aligns with the broader objectives of Vision 2030, aiming to create a more equitable, resilient, and politically stable society. Through these measures, fiscal policies become instrumental in not only driving economic growth but also in fostering social cohesion and political stability.
This theoretical backdrop provides a foundation for understanding the complex interplay between fiscal management and economic performance in oil-dependent countries. By examining these aspects, this study aims to contribute valuable insights into the formulation of more resilient economic strategies for Saudi Arabia, echoing the broader discourse on economic management in similar geopolitical and economic contexts.
According to Keynesian theory, recent studies have highlighted the importance of these policies in mitigating the impacts of economic fluctuations and promoting stability and growth. For instance, Luan, Man, and Zhou (2021) emphasize that fiscal policy can effectively complement monetary policy to stabilize macroeconomic conditions . Similarly, Shaheen (2019) discusses the impact of fiscal policy on private consumption and labor supply, illustrating how government expenditure and tax policies influence economic variables through their effects on aggregate demand .
According to Keynesian theory, aggregate demand plays a crucial role in determining economic output and employment levels. Counter-cyclical fiscal policies manage aggregate demand by increasing government spending and reducing taxes during economic downturns to boost demand and by decreasing spending and increasing taxes during economic expansions to prevent overheating (Bravo & Ayuso, 2021).
Moreover, automatic stabilizers are fiscal mechanisms that naturally counterbalance economic fluctuations without additional government action. Examples include unemployment insurance, which increases government spending during downturns as more people become eligible for benefits, and progressive taxation, where tax revenues fall during recessions as incomes drop, cushioning disposable incomes (Bongers & Díaz-Roldán, 2019). These mechanisms help smooth out the economic cycle, providing a buffer during economic shocks.
Bongers and Díaz-Roldán (2019) as well as Buendía-Martínez, Álvarez-Herranz, & Moreira Menéndez (2020) highlight the significance of counter-cyclical fiscal policies in maintaining economic stability and fostering sustainable growth. These policies, which address economic fluctuations through deliberate fiscal interventions, play a crucial role in smoothing the business cycle, contributing to overall economic resilience and long-term prosperity. By boosting aggregate demand during downturns, they aim to reduce the depth and duration of recessions, while curbing demand during booms helps to prevent inflation and asset bubbles. These fiscal mechanisms include automatic stabilizers such as unemployment insurance and progressive taxation, which operate without additional government action. For instance, unemployment insurance increases government spending automatically during economic downturns as more people become eligible for benefits, while progressive taxation reduces tax revenues during recessions as incomes drop, thereby cushioning disposable incomes and helping to stabilize the economy.
Recent studies have emphasized the critical importance of designing fiscal policies with long-term sustainability in mind, complementing short-term counter-cyclical measures. Piroli and Calderón (2021) underscored this point in their analysis of fiscal sustainability in Central and Eastern European countries, highlighting the need to accumulate surpluses during economic booms to prepare for future downturns.
Studies such as those by Auerbach and Gorodnichenko (2012) have demonstrated the variability of fiscal multipliers, showing that government spending can have different impacts on the economy depending on the state of the economic cycle. During recessions, fiscal multipliers are typically larger due to increased idle capacity and higher marginal propensities to consume among households. Conversely, in boom times, the impact of fiscal expansion might be more subdued or even counterproductive, leading to overheating of the economy.
These insights reinforce the foundational principles of Keynesian economics and the practical importance of counter-cyclical fiscal measures in achieving economic stability.
However, the effectiveness of these fiscal tools often depends on the economic context, the structural characteristics of the economy, and the initial fiscal position of the government. For example, high levels of public debt can constrain a government’s ability to implement expansive fiscal policies due to the increased cost of borrowing and potential impacts on investor confidence. Thus, while the theoretical benefits of fiscal policy are widely recognized, its practical implementation and outcomes can vary significantly across different economic environments.
Fiscal policy in oil dependent economies
Fiscal policy in oil dependent economies is characterized by its heavy reliance on oil revenues to fund government expenditures and stimulate economic growth. These economies often face unique challenges and vulnerabilities due to the volatility of oil prices, which can lead to fluctuations in government revenues and budget deficits.
In such economies, fiscal policy plays a crucial role in managing the impacts of oil price volatility. Governments typically use fiscal policy to stabilize their economies, especially during periods of low oil prices. This can involve adjusting government spending and taxation to maintain fiscal sustainability and economic stability.
However, the effectiveness of fiscal policy in oil-dependent economies can be limited by several factors. These include a lack of economic diversification, which makes these economies overly reliant on oil revenues, as well as institutional weaknesses, such as poor governance and corruption, which can undermine the efficiency and effectiveness of fiscal policy measures.
To address these challenges, policymakers in oil-dependent economies often seek to diversify their economies away from oil, strengthen fiscal institutions, and improve the transparency and accountability of fiscal policy decisions. By doing so, they aim to reduce their economies’ vulnerability to oil price volatility and promote sustainable economic growth.
Venezuela presents a stark example of the risks associated with high oil dependency. As detailed by Su et al. (2020), Venezuela’s economic crises have been exacerbated by fiscal mismanagement and an inability to stabilize or diversify the economy away from oil. The result has been hyperinflation, soaring public debt, and severe social and economic dislocations, illustrating the consequences of not adhering to counter-cyclical fiscal policies. The situation in Venezuela illustrates a compelling case of how heavy reliance on oil revenues, combined with fiscal mismanagement, can lead to significant economic instability. Venezuela possesses one of the world’s largest oil reserves, and historically, the country’s economy has been highly dependent on oil revenues. This dependency meant that the government’s spending was closely tied to the fluctuations of global oil prices. When prices were high, the country experienced substantial government spending and economic growth. However, the lack of diversification in its economy made it highly vulnerable to oil price shocks. The Venezuelan government, under various administrations, increased public expenditures significantly during periods of high oil prices without sufficient savings for future downturns. This fiscal policy was not sustainable and was compounded by a lack of transparency and accountability in managing public funds. Investments in other sectors of the economy were neglected, and over time, the non-oil economic infrastructure deteriorated. As oil prices began to fall after 2014, Venezuela’s government faced enormous fiscal deficits. In response, rather than implementing counter-cyclical fiscal policies, which would involve cutting expenditures or increasing savings, the government financed the deficit by printing money, leading to hyperinflation. According to Su et al. (2020), these actions were a primary driver behind the economic instability that followed.
Contrasting with the previous study on Venezuela, where fiscal mismanagement amidst resource dependency precipitated severe economic disruptions, the case of Russia presents a different scenario. A study conducted by Antonio Spilimbergo (2007) analyzed the performance of fiscal policy in Russia, particularly its role in stabilizing the economy post-1998 crisis. This analysis highlighted effective fiscal management as crucial during this period. Unlike Venezuela, the subsequent oil price boom enabled the Russian government to maintain a sustainable fiscal balance. However, significant oil revenues since 2003 have raised concerns regarding the underdevelopment of non-oil sectors, capable of absorbing this increased fiscal capacity. The study also credited the Oil Stabilization Fund (OSF) with successfully managing the surge in oil revenues in 2004, mitigating the potential for fiscal imbalances.
Byiabani and Mohseni (2014) explored the impact of fiscal policy on Iran’s economic growth from 1974 to 2007. Utilizing co-integration techniques and a vector error correction model, their empirical analysis indicated that Iran’s long-term economic performance was influenced by various factors, including labor force and physical capital, alongside proactive fiscal measures such as tax reductions and increased government spending on development. This approach starkly contrasts with the Venezuelan experience, highlighting the significance of strategic fiscal management in avoiding economic volatility.
Aghilifar, H., Zare, H., Piraei, K., & Ebrahimi, M. (2023) demonstrated that although Iran heavily relies on oil for its revenue, making it susceptible to global price fluctuations, effective fiscal policies have been crucial in mitigating the impact of these external shocks and maintaining macroeconomic stability.
Similarly, in a study conducted by Khosravi and Karimi (2010), the relationship between fiscal and monetary policy and economic growth in Iran was examined. The bounds testing (ARDL) approach to cointegration was used to analyse the long-term and short-term relationships between fiscal policy, monetary policy, and economic growth. Their findings revealed that while government expenditure, as a fiscal policy, had a significant positive impact on GDP growth, inflation, and exchange rates, as components of monetary policy, had a negative impact.
These case studies underscore the critical importance of strategic fiscal management and the necessity for oil-dependent economies to diversify their revenue bases. Implementing counter-cyclical fiscal policies could potentially mitigate the adverse effects of revenue volatility. Moreover, research by Schmidt-Hebbel and Marshall (2007) demonstrates how effectively integrating oil and non-oil revenue streams into the fiscal policy framework can help stabilize the economy and reduce dependence on oil.
The comprehensive review underscores the necessity for oil-dependent economies to pursue diversified economic strategies, enhancing non-oil exports and developing industrial and service sectors to foster economic resilience. These integrated studies enrich the context of fiscal policy effectiveness, particularly in economies undergoing significant structural transformations.
Economic Diversification as a Necessity for Fiscal Resilience in Oil Dependent Countries
Economic diversification stands as a crucial imperative for nations heavily reliant on oil revenues. The vulnerability of oil-dependent economies to price volatility has been starkly demonstrated in recent years, emphasizing the urgent need for these countries to broaden their economic bases. This section explores the concept of economic diversification as a fundamental strategy for enhancing fiscal resilience in oil-dependent countries. By reducing dependence on oil revenues and fostering a more diversified economic structure, these nations can mitigate the risks associated with volatile oil markets and build a more sustainable foundation for economic growth and stability. The following discussion examines the key principles and benefits of economic diversification, highlighting its importance in the context of fiscal policy and long-term economic development.
Diversifying revenue sources is also crucial for managing public debt in oil-dependent economies. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 aims to develop sectors such as tourism, entertainment, and renewable energy, reducing dependence on oil revenues and creating a more balanced economic structure. By broadening the tax base and developing non-oil sectors, governments can achieve more stable and predictable fiscal outcomes. Maintaining fiscal discipline and managing public expenditures effectively are fundamental to controlling public debt. Cavallo (2005) and Tulsidharan (2006) highlight the importance of efficient government spending in maintaining economic stability and growth. Prioritizing essential expenditures and avoiding wasteful spending improve fiscal balance and reduce debt levels.
Structural reforms and institutional strengthening are vital for effective public debt management. Fatai et al. (2017) emphasize that institutional quality, including effective governance and anti-corruption measures, significantly influences fiscal outcomes. Strong fiscal institutions provide a stable framework for policy implementation, ensuring sustainable debt management. Empirical studies, such as those by Aslam and Shastri (2019) and Hamdi & Sbia (2013), demonstrate the long-term benefits of strategic fiscal planning and diversification in countries like Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Bahrain. These studies show that well-managed fiscal policies can help stabilize economies and reduce debt burdens, even in the face of oil revenue volatility.
Building on the discussion of fiscal responsiveness, the literature also delves into the significant impact of oil revenue volatility on the fiscal policies of oil-dependent countries. A pivotal study by Sohag, Kalina, and Samargandi (2024) explores this dynamic interplay between oil price fluctuations and fiscal policies in OPEC+ member countries. The authors employ advanced econometric tools such as Hodrick-Prescott and Hamilton filters to isolate cyclical components of oil prices, enhancing the analysis through a Panel VAR approach under a system GMM framework. This methodology addresses potential issues of endogeneity, heterogeneity, and cross-sectional biases.
Their findings reveal that cyclical oil price shocks have an immediate, positive impact on the fiscal stances of these countries, though the effects tend to diminish over the medium to long term. Interestingly, gradual oil price trends show an insignificant impact on fiscal policies, suggesting that OPEC+ countries’ fiscal strategies are more responsive to abrupt changes rather than gradual shifts in the oil market. The study highlights the disparate capabilities among OPEC+ countries, such as Gabon, Iraq, Russia, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Kazakhstan, to leverage these shocks for economic advantage. This differentiation is critical as it illustrates the varied economic resilience within the alliance, informing tailored policy formulations aimed at enhancing fiscal stability and growth.
Further contributing to our understanding of the fiscal dynamics in oil-dependent economies, Fatai, Liu, Adeniyi, and Kabir (2017) utilize a panel dataset from 2000 to 2015 to empirically examine the relationship between crude oil rents and fiscal balance, controlling for various covariates. Employing several econometric techniques, including pooled OLS, LSDV fixed effects, and instrumental variable approaches like IV/2SLS, their analysis underscores the limitations of the General Method of Moments (GMM) due to the small sample size. Their findings suggest that in countries with fiscal rules, the reaction of fiscal balance to oil rent shocks is weak and statistically insignificant. They also highlight thoes factors such as welfare spending, the debt-to-GDP ratio, and the government’s effectiveness in curbing corruption and mismanagement significantly influence fiscal balance. These insights are invaluable for policymakers within the OPEC+ alliance, providing empirical evidence that can guide strategic fiscal planning in the face of oil market volatility.
Economic diversification has been widely advocated in the literature as a crucial strategy for oil-dependent economies to mitigate the risks associated with volatile oil markets. This approach involves expanding the economic base to include a broader array of sectors beyond the dominant oil and gas industry, thereby reducing the economy’s vulnerability to global oil price fluctuations. In exploring the trajectories of economic development and diversification, Gelb (2010) highlights the significant shift from primary commodity exports to industrial products in developing countries. Originally, these countries exported primarily commodities, but now, industries such as manufacturing have come to dominate their export structures. This evolution has been crucial to their transformation into major industrial economies, with nations like China, India, and Brazil becoming central players in global production networks. The diversification into various industrial sectors not only stabilized their national incomes but also reduced economic volatility, contributing substantially to sustainable growth. This shift, according to Gelb, is indicative of successful integration into South–South trade and continuous enhancement of export sophistication.
Parallel to Gelb’s findings on economic diversification, Richard M. Auty (2001) has extensively explored the role of resource abundance in enhancing economic performance. Auty’s work emphasizes that while resource wealth can lead to economic advantages, strategic diversification is crucial to harness these benefits effectively and sustainably. His analysis suggests that countries with abundant resources can leverage this advantage to fuel broader economic development, but this requires deliberate policy efforts aimed at diversification into non-resource sectors to avoid the pitfalls of over-reliance on volatile resource markets. This perspective is crucial for understanding the complex dynamics between natural resource wealth and long-term economic stability.
Fiscal policies play a fundamental role in supporting diversification efforts, as noted by the World Bank (2019). Strategic government spending and tax incentives can encourage investments in non-oil sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and services, thus broadening the economic landscape. Countries such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE have utilized fiscal initiatives like the development of economic cities, investment in renewable energy projects, and labor law reforms to promote economic diversification. These policies aim to attract foreign direct investment, stimulate private sector growth, and create a more resilient economic environment.
The literature also suggests that while the immediate benefits of diversification may be gradual, the long-term effects are significantly positive. Diversified economies tend to exhibit more stable economic conditions during oil downturns. However, the effectiveness of these strategies often relies on the consistent implementation of supportive fiscal policies and the overall political and economic stability of the country. Therefore, policymakers are encouraged to consider comprehensive fiscal reforms that align with broader economic diversification goals to ensure sustainable development and economic stability.
Case studies highlight the importance of strategic fiscal management and the necessity for oil-dependent economies to diversify their revenue bases. Implementing counter-cyclical fiscal policies, such as those proposed by Blanchard and Leigh (2013), could potentially mitigate the adverse effects of revenue volatility. Additionally, integrating oil and non-oil revenue streams effectively into the fiscal policy framework, as shown in VAR models by Schmidt-Hebbel and Marshall (2007), can help stabilize the economy and reduce dependence on oil.
The interplay between fiscal policies and their economic impacts is critical, with government expenditures significantly shaping economic outcomes. Foundational studies by Cavallo (2005) and Tulsidharan (2006) examine the effects of government expenditure on economic stability and growth, particularly in India, setting the stage for a detailed exploration of General Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GC) and its role during financial crises. Similarly, Kira (2013) highlights the significant role of government and household consumption in influencing GDP in developing countries like Tanzania, underscoring the importance of fiscal measures in driving economic output.
Empirical studies illustrate that General Consumption (GC) acts as a stabilizer during downturns by buffering cyclical fluctuations and supporting demand. For instance, Auerbach and Gorodnichenko (2012) demonstrate the variability of fiscal multipliers of GC across business cycles, highlighting increased effectiveness during recessions. This is particularly notable in sectors directly linked to government spending, such as healthcare and infrastructure, where Blanchard & Leigh (2013) observed enhanced benefits.
Drawing on historical crises, the literature suggests prioritizing GC in fiscal strategies for rapid and effective economic recovery, supported by empirical evidence from past events like the 2008 financial crisis (Bernanke, 2015).
This section synthesizes findings from countries like Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Bahrain, focusing on the long-term and short-term impacts of oil revenues on GDP, demonstrated through studies by Aslam and Shastri (2019) and Hamdi & Sbia (2013). The need for strategic economic planning and diversification away from oil-dependence is emphasized. Khayati (2019) provides insights into the differential impacts of oil and non-oil exports on Bahrain’s economic growth, advocating for economic diversification to reduce volatility and promote sustainable development. Azmi (2013) supports this view by demonstrating the significant impact of government spending on economic metrics like GDP, interest rates, and unemployment in Malaysia, further reinforcing the multifaceted role of fiscal policies in economic management.
Building on this discussion, the literature further explores the relationship between national oil revenues and economic growth across various countries. A pivotal study conducted by Al Rasasi, Qualls, and Alghamdi in 2019 illustrates a strong link between oil revenues and both the short- and long-term growth in Saudi Arabia, emphasizing the promotion of the private sector outside the traditional oil industry. This study highlights the importance of effectively harnessing oil wealth to foster economic growth and development, particularly in the non-oil private sector.
Similarly, in 2017, Nwoba and Abah examined the impact of oil revenues and the presence of multinational oil companies on economic growth in Nigeria. Their findings suggest that these factors play a vital role in driving economic growth, particularly through job creation. Furthermore, a study by Hassan and Abdullah in 2015 investigated the impact of oil revenues on the output of the service sector in Sudan between 2000 and 2010, finding that oil revenues positively affected the sector’s output.
These studies collectively provide robust evidence of the diverse effects of oil revenues on economic growth in regions like Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, and Sudan. They underscore the nuanced ways in which oil-dependent economies can leverage their natural resources to achieve broader economic objectives, highlighting the need for carefully crafted fiscal policies that support sustainable development and diversification.
In conclusion, while oil revenues can provide substantial funding for government budgets, their volatility demands a sophisticated approach to fiscal policy that emphasizes stability, diversification, and long-term economic planning. The experiences of Saudi Arabia, Russia, and Venezuela offer valuable lessons on the potential pitfalls and strategic necessities in managing economies with significant oil revenues.