1. Introduction
Eucalyptus was introduced to East-African countries during the second half of the 19th century to rehabilitate degraded lands [
1,
2]. It has spread throughout the country as an important component of farming systems, because of its great ability to meet increasing demand for construction purposes, fuelwood and higher economic returns [
3,
4,
5,
90]. A substantial portion of productive cropland and grazing land has been converted into Eucalyptus plantation woodlots in the highlands of Ethiopia [
6,
86,
92]. Currently there has been a significant conversion of croplands to the
Eucalyptus globulus plantations in the northern highlands of Ethiopia [
90,
92]. Eucalyptus plantations area coverage was about 148,000 ha in the year of 2000 and about 506,000 ha in 2009 [
7,
8]. Of the total planted area, 58% was covered between 1978 and 1989 as community plantations [
9]. The higher nutritional requirements of the fast-growing
Eucalyptus globulus plantation were most likely an accelerating factor of chemical degradation of the soils [
19,
91]. Eucalyptus reduced markedly the readily available nutrients and water stores in the watersheds, as a result of its greatest water sucking ability due to deep and dense root network [
20]. Furthermore, soil hydrophobicity induced by decomposition of Eucalyptus plantation litter, which reduced infiltration, also reduced water storage [
90]. Litter fall and litter decomposition are the major sources of nutrients in the forest ecosystem, but the litter quality of Eucalyptus plantations is low [
21]. Eucalyptus plantation leaf-litter contains relatively higher phenolic compounds, a low decomposable and mineralization rate by soil microorganisms [
22,
23,
24].
There were concerns about the negative impacts of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations on the soil productivity and environment in Ethiopia and other East African countries as well as all over the world [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. The impacts include soil fertility reduction, high interception, loss of water, and disruption of understory plantations due to allopathic effects that inhibit undergrowth regeneration and fall in the groundwater table. A study by Turner and Lambert [
15] indicated soil organic carbon content to be less in Eucalyptus plantations compared to native vegetation areas. Another study [
16,
86] indicated increased soil acidity and decreased base saturation in the Eucalyptus plantation compared to native vegetation areas and croplands. Moreover, Eucalyptus plantations showed high organic matter (SOM), increased acidification, decreased exchangeable cations, while increased cation exchange capacity (CEC) and nitrogen [
13]. Also, Eucalyptus plantations have been adversely affecting the physicochemical properties of soils [
17,
18,
86]. However, few studies indicating Eucalyptus plantations have a positive influence on soil fertility and crop productivity [
25]. Likewise, soils were found better in soil chemical properties (pH, N, CEC and SOM) under
Eucalyptus globulus plantations compared to cropland [
26]. Farmers perceived that plots under Eucalyptus plantation prior to their conversion to cropland, had better fertility, required less nitrogen fertilizer and better crop yields compared to plots that were under continuous cropping [
44]. In a recent study in Ethiopia [
27], there were no significant differences observed in soil properties such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC) and OM between Eucalyptus plantation and crop land use types. Besides, insignificant variations were observed between
Eucalyptus globulus plantations and the grazing land in available phosphorus (AP), basic cations, as well as CEC [
90,
93].
The impacts of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations on soil properties are still being debated with no total agreement, as the impact would depend mainly on the species, the site characteristics and management practices. Notwithstanding the negative ecological impacts, Eucalyptus continues to be planted by farmers in Ethiopia on their agricultural and grazing lands to meet the increase in the demand for construction materials, economic value and fuelwood [
28,
44,
86]. Nowadays, Ethiopia has the largest area of Eucalyptus plantations in East Africa and is one of the 10 pioneer countries that have introduced Eucalyptus plantations [
2]. It is, indeed, a good source of income for the smallholder farmers of Ethiopia [
90]. Farmers prefer species, namely
Eucalyptus globulus plantations, for their growth performance and yield compared to other exotic and native species in northwestern highlands of Ethiopia [
2,
29,
86,
90]. In the study area, about 33% was covered by
Eucalyptus globulus plantations [
30]. Still, there is limited research evidence on the impact of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations on the soil properties in the study area. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the impacts of
Eucalyptus globulus plantation compared to grazing and cropland use types on soil properties in Wonka
Kebele, Gozamn district, northwestern highlands of Ethiopia. The evidence to create appropriate land use guidelines, manage the valuable soil resources and ensuring the food security for the local community.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Site, Climate and Soil Type
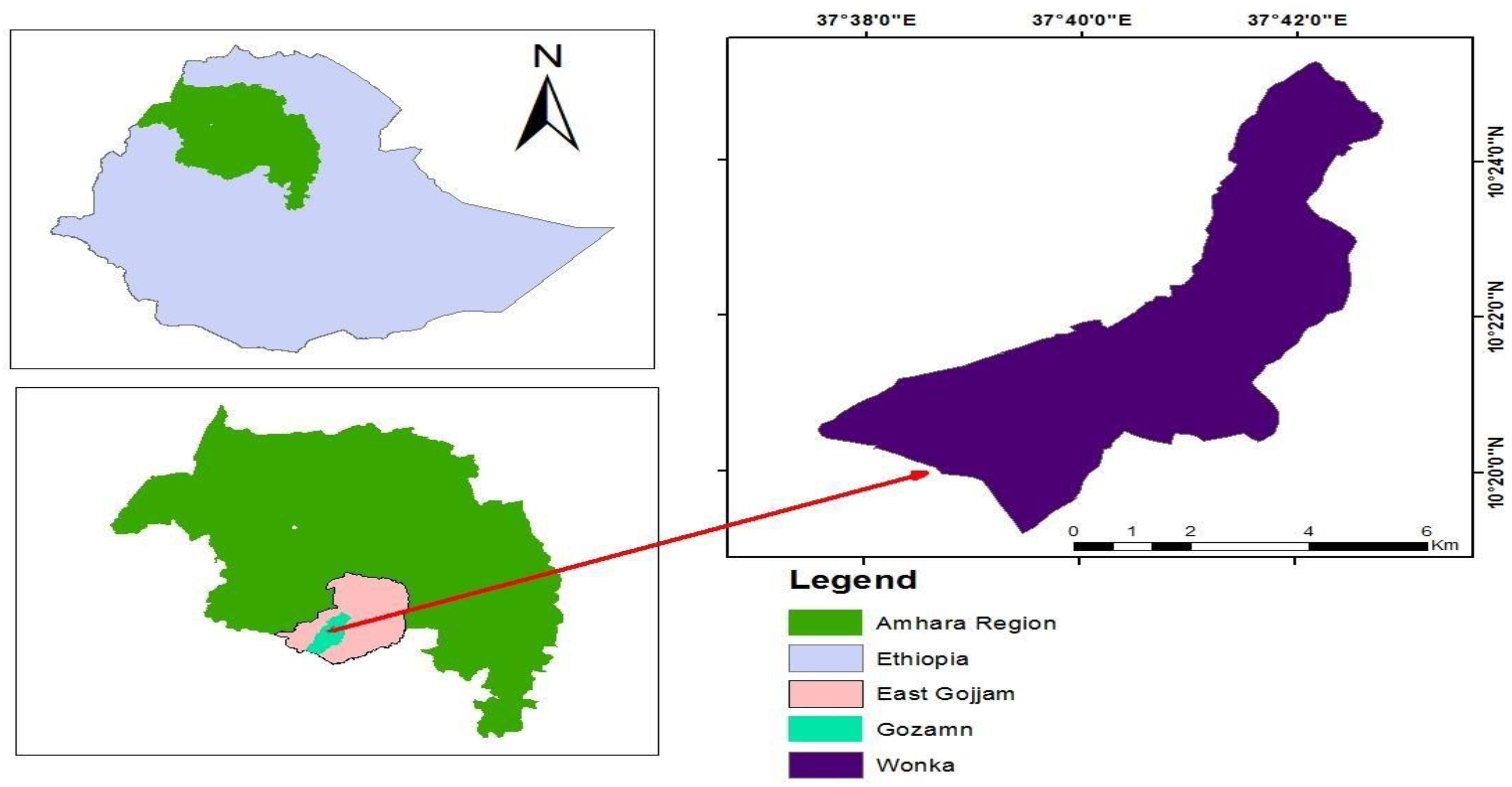
The study was conducted in Wonka
Kebele, the lowest administrative unit of Gozamn district, Amhara region, and northwestern highlands of Ethiopia (
Figure 1). It is situated between 10°1′46″ and 10° 35′ 12″ N latitudes and 37° 23′ 45″ and 37° 55′ 52″ E longitudes (
Figure 1). The altitudes range from 800-3748 m.a.s.l, and it is located 300 km from Addis Ababa. Besides, the study area covers about 2270 ha [
30].
The average annual rainfall of the study area is 1628 mm with the rainy season extending up to six months [
30]. The rainfall, however, is concentrated in the season of May to September [
32]. The maximum and minimum average temperatures were 25°C and 11°C, respectively [
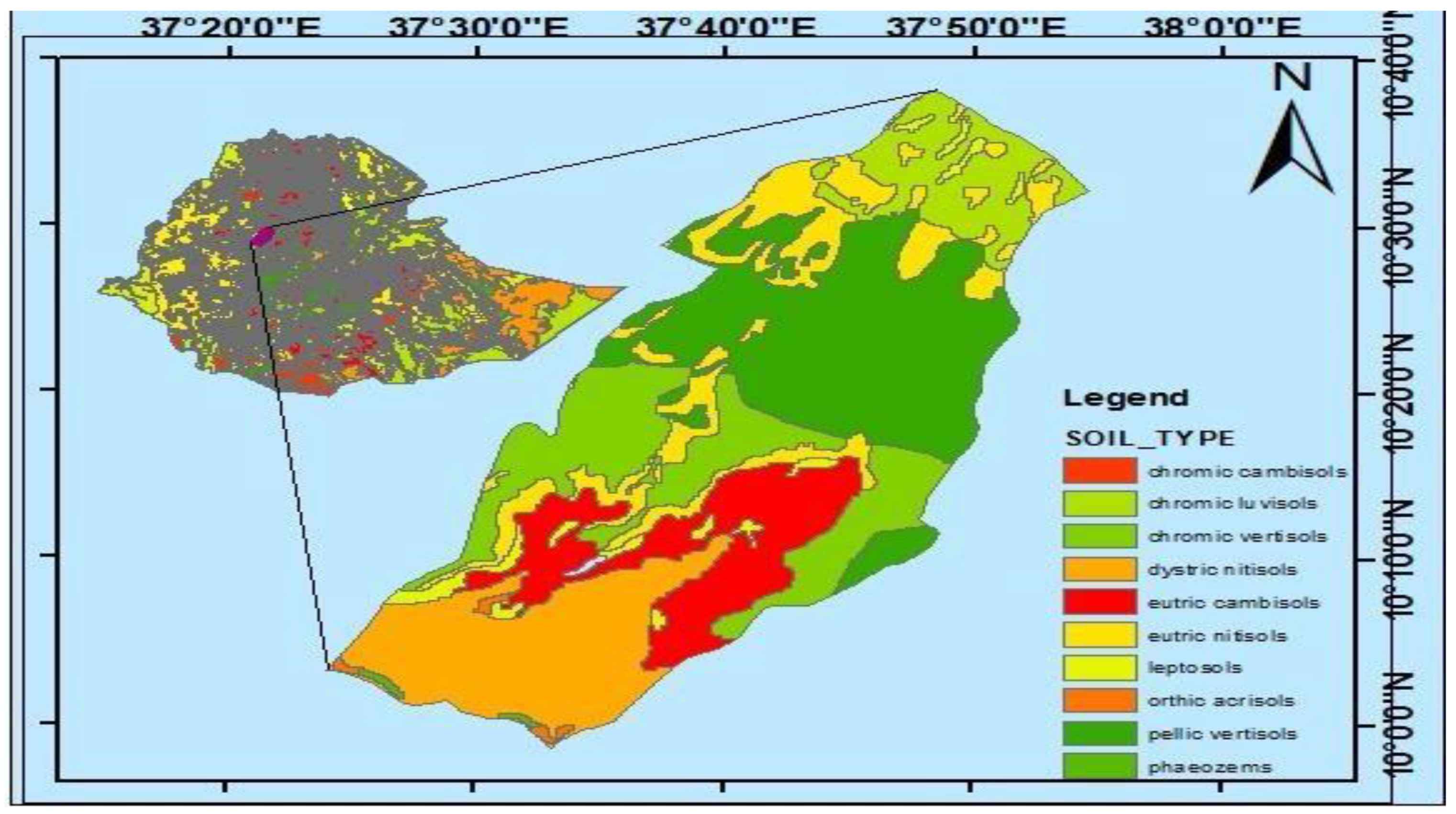
32]. The study area belonged to the midland agro-ecological zone. The dominant soil types are Nitisols, Vertisols and Cambisols, while, Pheazemes, Acrisols and Leptosols are associated to soil types in different parts of the district (
Figure 2). Nitisols are the dominant soil types in the study area [
32].
2.2. Site Selection and Soil Sampling Design
A field survey was conducted in the study area in order to find representative sampling locations that satisfy our objective of looking into how
eucalyptus globulus plantations affect soil properties. Thus, three distinct land use types that are close to one another had soil samples taken from them. The 25-year-old
Eucalyptus globulus plantations, grazing land, and cropland were were selected. The woodlots of the eucalyptus plantation were chosen since they constituted the majority of the plantations in the research area. Grazing areas were chosen to serve as the control group. As a result, three land use options were chosen that had similar agroclimatic zone, soil type, slope and biophysical characteristics. Soil sampling was done by a cluster sampling design given by Thompson [
33], which was later applied by Vagen et al. [
34] and Abegaz et al. [
35]. The same was modified by Adugna and Abegaz [
36] to uniform their small catchment size. Accordingly, three adjacent sites of one-hectare each land use types such as Eucalyptus, grazing and cropland were selected in the study (
Figure 3).
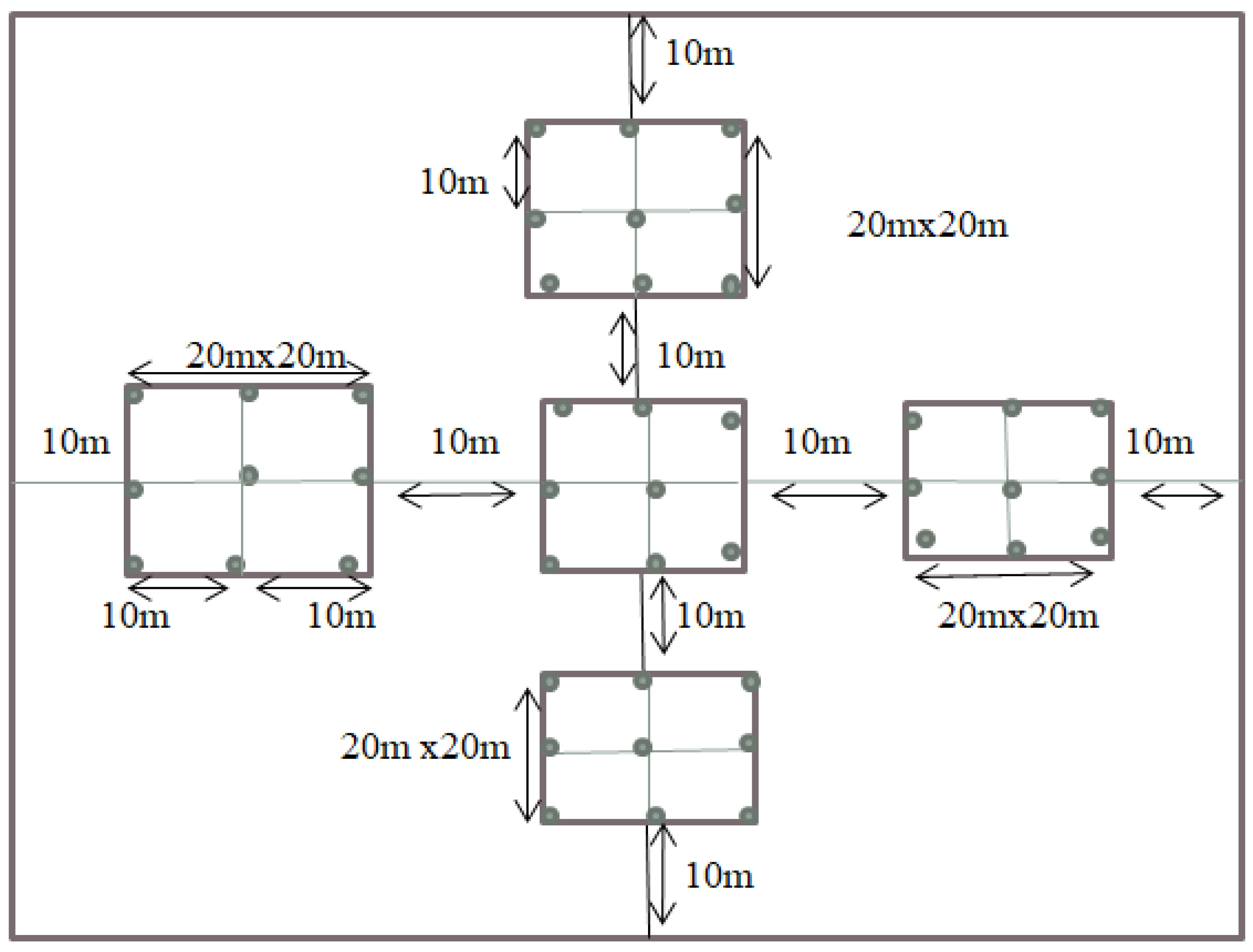
A cluster of 100*100 m and five cluster centroids, each of 20*20m were established (
Figure 4). The first tile (20*20m) was established by fixing its central point at the center of one-hectare area. The area of this sampling plot was marked by using a 10m radius from the cluster center point and four sampling plots were established at a distance of 20m from the center of the sampling plot to the north, south, east and west (
Figure 4). Thus, 1 kg of composite soil samples were collected per plot form three land use types with two soil depths. About 30 composite soil samples (three land use types * two soil depths * five replications) were collected for soil analyses. Likewise, a core sampler was used for collecting 30 undisturbed soil samples (at depths of 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm) from each subplot of the land use types for determining the bulk density. Analyzed soil samples were packed in plastic bags, recorded with a sampling code, and sent to the soil laboratory of Amhara Design and Supervision Works Enterprises (ADSWE). Soil samples were crushed, oven-dried at room temperature, and sieved through a 2 mm sieve.
2.3. Soil Laboratory Analysis
Soil particle size distribution was done by the hydrometer method [
37]. The soil bulk density (BD) was determined by using the core sampler [
38]. The porosity of the samples was calculated from the values of BD and particle density (PD) (2.65g/cm
3). Soil moisture content (MC) was determined by gravimetric method [
38]. The pH of the soil was determined by a glass electrode pH meter using a 1:2.5 soil: water ratio [
87]. Exchangeable acidity (H+ and Al3+) in extracts titrated with 0.01 M NaOH at 1 M KCl was measured [
39]. The soil organic carbon (OC) content was determined following a wet digestion method [
40] and soil organic matter (OM) was obtained by multiplying organic carbon content by 1.724. The total nitrogen (TN) content in soil was evaluated by the Kjeldahl digestion and distillation method [
41]. Available phosphorus (AP) was determined using the Olsen method [
42]. The exchangeable bases were extracted employing 1N ammonium acetate solution at pH 7.0. Calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) were determined on the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer, while potassium (K) and sodium (Na) were estimated by Flame Photometer [
88]. The Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was determined by employing ammonium-saturated soil samples, which were leached with NaCl and displaced ammonium was distilled and titrated [
43]. The electrical conductivity (EC) was measured using a 1:5 soil: water ratio [
89]. Percent changes in the soil properties under eucalyptus compared to cropland and grazing land were computed as given by Adugna and Abegaz [
36]
Where, is the percentage change in soil property under Eucalyptus plantation compared to cropland and grazing land, and are the mean values of the soil properties under Eucalyptus globulus plantation, crop and grazing lands, respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The data of soil properties under Eucalyptus globulus plantation and other land uses were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance using SAS software. The treatments were arranged in a factorial randomized complete block design format with land use and soil depth. Comparison of means was done using list significant difference (LSD) at (0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Eucalyptus Globulus Plantation on Soil Properties
3.1.1. Soil Texture
The Eucalyptus globulus plantation had statistically comparable in sand particles (18.2%) to cropland (16.0%), but significantly lower than grazing land (21.0%) (
Table 1). However, there is an insignificant difference between the interaction effects of land use types and soil depths (
Table 3). The silt content was significantly higher in Eucalyptus plantations (17.0%) than in cropland (12.1%) and grazing land (15.6%). Clay content under eucalyptus (64.7%) was statistically insignificant for grazing land (63.4%), but lower than cropland (71.9%). Silt and clay under Eucalyptus relative to cropland was 14, 41 and -10% and relative to grazing land it was -13, 9 and 2%, respectively (
Table 7). A higher proportion of coarser fraction and lower proportion of fine fraction under Eucalyptus than on cropland, suggests the soil under Eucalyptus has been relatively degraded compared to cultivated land.
Soil depth was insignificant effect on sand, but it was in silt and clay (
Table 1). Silt was significantly higher under 0-20 cm depth (20.2%) than 20-40 cm depth (16.6%), the clay was significantly higher under 20-40 cm depth (73.0%) than 0-20 cm depth (67.1%) (
Table 1). The higher clay content in the subsurface soil compared to surface soil could be due to illuviation process, i.e. migration of clay from surface soil and its deposition in the subsurface soil. Similar findings have been reported by Eyayu et al. [
45] who found overall mean values of silt to be higher on the surface than in the subsurface, and that of clay to be higher in the subsurface than in the surface layer in northwest Ethiopia. Likewise, Gebeyaw [
46] reported that clay content was higher in the subsurface layer than in the surface layer of soils in Ethiopia. Furthermore, Sonaimuthu et al. [
47,
86] stated that clay content was increased with soil depth and silt content was decreased with increased soil depth under different land uses due to translocation of clay and its accumulation in the subsurface layer.
3.1.2. Bulk Density (BD) and Total Porosity (TP)
The BD was varied from 1.09 Mg m-3 to 1.11 Mg m-3 under Eucalyptus globulus plantation and cultivated and grazing lands but not significant variation (p <0.05) the interaction effects (
Table 1 and 2). Percent change of Eucalyptus vs. cropland and grazing lands was low i.e. -1.8 % (
Table 7). Similarly, Yitaferu et al. [
26] found no difference in BD values among the Eucalyptus and cropland use types. The 0-20 cm depth had significantly lower value of BD (1.08 Mgm-3) compared to 20-40 cm soil depth (1.34 Mgm-3). This was due to high pore space as a result of higher OM content and biological activity. The lower BD in the surface soils under diverse land uses has also been reported by Fikadu et al. [
48] and Sonaimuthu et al. [
47]. The BD of the soils under the three land uses at both depths is considered as low according to Hazelton and Murphy [
49]. The findings are similar to Chanie et al. [
50] who found low soil BD (1.0 to 1.1 Mg m-3) at all depths under Eucalyptus plantation. The lower BD implies greater pore space and improved aeration, creating a choice environment for biological activity. Moreover, TP varied from 58.9% for Eucalyptus globulus plantations and 58.1% for cropland and grazing land types (
Table 1). Accordingly, the soils under Eucalyptus globulus plantations were supposed to be structurally better than cropland and grazing lands. The TP was significantly affected by soil depth (
Table 1). The surface soil had a significantly higher TP (59.2%) than the subsurface soil (49.4%). This might be due to the presence of organic matter in the Eucalyptus globulus plantations. Similar findings on TP have been reported by Sonaimuthu et al. [
47].
3.1.3. Soil Moisture Content (MC)
The MC showed significantly (p<0.05) affected by land use, soil depth and interaction effects (
Table 1 and 2). The higher soil MC (23.6%) was recorded under Eucalyptus globulus plantation than grazing land (18.7%) and cropland (20.3%) (
Table 1). The MC under Eucalyptus increased by 16 and 26% compared to cropland and grazing lands, respectively (
Table 7). Relatively higher MC under the Eucalyptus globulus plantation might be due to relatively good ground cover that could decrease soil temperature and increase water retention in the soil. As reported by Karim et al. [
51] MC of soil under canopy cover was higher as compared to bare land, which indicated that canopy cover decreased the rate of evaporation of water in dry weather from soil and increased the water holding capacity of soil. The higher OM content of Eucalyptus plantations might also be the reason for increased MC in soil. Besides, the consumption was a significantly lower amount of water to produce a high amount of dry biomass by Eucalyptus as compared to croplands [
52]. According to Kumar [
53], Eucalyptus has a low transpiration rate and it controls stomata for water retention. The capability of Eucalyptus in adjusting their consumption to the availability of water helped keep better MC in the study area.
Table 1 showed that the subsurface (20-40 cm) soil had significantly higher MC (22.7%) than the surface soil (19.8%). The more exposure of upper soil to high temperatures and more evaporation could be the reasons for relatively drier soil conditions on the surface. Besides, the lowest value (15.44%) and the highest value (25.13%) were found in the surface soil (0-20 cm) and subsurface (20-40 cm) soil of cropland, respectively (
Table 1). The marked difference in the MC at the surface and subsurface of cropland was due to more withdrawal of moisture from the surface soil by the crops, as the root system of most of the cereal crops is concentrated in the surface soil.
Table 2.
Soil physical properties as affected by interaction between land use and soil depth.
Table 2.
Soil physical properties as affected by interaction between land use and soil depth.
| Land use types |
Depth
(cm) |
Sand
(%) |
Silt (%) |
Clay
(%) |
BD (Mg m-3) |
TP (%) |
MC (%) |
| Eucalyptus |
0-20 |
17.9a
|
20.5 |
61.4 |
1.10 |
58.1 |
24.1a`
|
| |
20-40 |
16.1b
|
16.0 |
68.0 |
1.08 |
59.2 |
23.0ab
|
| Cropland |
0-20 |
12.0c
|
18.3 |
69.7 |
1.15 |
56.6 |
15.4d
|
| |
20-40 |
12.2c
|
13.7 |
74.1 |
1.07 |
59.6 |
25.1a
|
| Grazing Land |
0-20 |
16.0b
|
20.0 |
63.9 |
1.15 |
56.6 |
17.4cd
|
| |
20-40 |
16.0b
|
20.0 |
63.9 |
1.06 |
59.8 |
20.0bc
|
| LSD0.05
|
|
0.2 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
3.6 |
| SEM (±) |
|
0.5 |
1.2 |
1.6 |
0.05 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
| CV (%) |
|
5.1 |
10.0 |
3.8 |
33 |
4.78 |
13.11 |
3.1.4. Soil pH
The lower soil pH was recorded under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation (5.07) than cropland (5.08) and grazing land (5.39) (
Table 3). Accordingly, the percent change in soil pH under Eucalyptus compared to cropland and grazing land was decreased by -0.2 and -0.6 %, respectively (
Table 7). Through their root systems, eucalyptus trees have been shown to release specific organic acids into the soil. The pH of the soil may be lowered by organic acids' contribution to soil acidification [
90,
93]. Moreover, the lower soil pH in the Eucalyptus plantation was associated with the depletion of the soil base cations in the Eucalyptus tree [
86]. However, as per the rating of Tekalign [
54], the soil under Eucalyptus and cropland was strongly acidic and moderately acidic under grazing land. The lower soil pH under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation compared to grazing and croplands in the central and highlands of Ethiopia [
55,
56,
86]. Also, Hailu [
3] found low pH on
Eucalyptus globulus plantations compared to cultivated land. Relatively lower content of pH under Eucalyptus could lead to more bioavailability of iron, aluminum, or manganese that could reach toxic levels in plants [
57,
58,
59].
Table 3.
Effect of land use and soil depth on chemical properties of soils.
Table 3.
Effect of land use and soil depth on chemical properties of soils.
| Land use types |
pH |
Ex. acidity EC (dS m-1) |
OM (%) |
TN (%) |
AP (mg kg-1) |
| Eucalyptus |
5.07 |
1.47a 0.02b
|
4.87a
|
0.24a
|
1.24b
|
| Cropland |
5.08 |
1.26a 0.03a
|
2.80b
|
0.14b
|
2.49a
|
| Grazing land |
5.39 |
0.95b 0.03a
|
4.41a
|
0.20a
|
2.80a
|
| LSD0.05
|
NS |
0.30 0.005 |
0.97 |
0.05 |
0.70 |
| SEM (±) |
0.19 |
0.10 0.001 |
0.25 |
0.01 |
0.18 |
| Depth (cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0-20 |
5.05 |
0.95a 0.02b
|
4.17 |
0.20 |
2.65 |
| 20-40 |
5.31 |
1.51a 0.03a
|
3.89 |
0.18 |
1.71 |
| LSD0.05
|
NS |
0.26 0.004 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
| SEM (±) |
0.04 |
0.10 0.001 |
0.37 |
0.01 |
0.23 |
| CV (%) |
20.60 |
12.11 16.09 |
24.89 |
26.00 |
22.35 |
3.1.5. Exchangeable Acidity
Soil pH was significantly higher under Eucalyptus plantation (1.47 cmol kg-1) compared to grazing land (0.95 cmol kg-1) and cropland (1.26 cmol kg-1). The increase under Eucalyptus compared to grazing land was by about 33% (
Table 7). The results are corroborated by the findings of [
60] who found more acidic soil under Eucalyptus plantation after conversion from grazing land. Also, Yitaferu et al. [
26] found relatively higher exchangeable acidity under Eucalyptus plantation compared to cropland land. Alemie [
20] was found a very acidic soil condition under Eucalyptus plantation. The higher soil acidity under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation might have resulted from the cumulative effect of hydrogen (H+) ion released by its roots leading to soil acidification [
14,
61]. High soil acidity under Eucalyptus plantation could be higher uptake of basic cations and their removal from the soil. As stated by Nsabimana [
62], the high nutrient consumption by Eucalyptus plantations and removal of biomass is the major reason for the acidity of soil under the Eucalyptus plantation. The frequent harvesting of high nutrient content aboveground biomass can lower the availability of basic soil nutrients and intensify soil acidification [
13,
63]. The higher exchange acidity under Eucalyptus could also be attributed to the decomposition of OM, which releases organic acids including humic, nitric and sulfuric acids in the soil [
64,
65].
3.1.6. Electrical conductivity (EC)
The electrical conductivity showed significant variation (p < 0.05) across land use types and soil depth but no interaction effects (
Table 3 and 4). It was significantly lower under the
Eucalyptus globulus plantation (0.02dSm-1) than grazing land (0.03dSm-1) and cropland (0.03dSm-1) (
Table 3). The result agrees with the findings of Jaleta [
93], who found higher EC in grazing land soils as compared to the soils in cultivated land and
Eucalyptus globulus plantations. The effect could be due to less accumulation of basic cations due to high rainfall in the study area. The higher EC with soil depth could be explained by more accumulation of base cations due to leaching from upper to lower depths. Similar results by Jaleta [
93] who stated that the EC was increased with increases soil depth. The EC values were, however, below the critical level of <4 dS m-1 [
49] and did not pose any salinity problem in the three land use types.
Table 4.
Soil chemical properties as affected by the interaction between land use and soil depth.
Table 4.
Soil chemical properties as affected by the interaction between land use and soil depth.
| Land use types |
Depth (cm) |
pH |
Ex. acidity
(cmol kg-1) |
EC (dSm-1) |
OM (%) |
TN (%) |
AP (mg kg-1) |
| Eucalyptus |
0-20 |
5.13 |
1.01 |
0.02b
|
5.32 |
0.26 |
1.38c
|
| |
20-40 |
5.01 |
1.52 |
0.02b
|
4.42 |
0.20 |
1.11c
|
| Cropland |
0-20 |
5.22 |
1.25 |
0.03a
|
3.07 |
0.15 |
3.44a
|
| |
20-40 |
4.95 |
1.70 |
0.025b
|
2.54 |
0.12 |
1.54c
|
| Grazing land |
0-20 |
5.59 |
0.60 |
0.03a
|
5.02 |
0.23 |
3.12a
|
| |
20-40 |
5.19 |
1.31 |
0.02b
|
3.81 |
0.17 |
2.48b
|
| LSD0.05
|
|
NS |
NS |
0.005 |
NS |
NS |
0.63 |
| SEM (±) |
|
0.20 |
0.22 |
0.01 |
0.25 |
0.01 |
0.18 |
| CV (%) |
|
20.60 |
12.10 |
16.09 |
24.90 |
26.00 |
22.30 |
3.1.7. Organic Matter (OM)
The
Eucalyptus globulus plantation had significantly higher soil OM content (4.87 %) than cropland use (2.80 %), while statistically similar to grazing land use (4.41%) (
Table 3). The increase in OM content under eucalyptus compared to cropland and grazing lands was 74 and 10%, respectively (
Table 7). The Eucalyptus plantation, therefore, offered more biomass for decomposing into the soil. The results are corroborated by the findings of Liang et al. [
66], who found significantly higher OM content in Eucalyptus plantations (7.71%) compared to cropland (4.83%). Yitaferu et al. [
26] also found significantly high OM was recorded in the Eucalyptus plantation/woodlots (3.21%) compared to croplands (2.86%) in Koga irrigation area, Ethiopia. The continuous leaf litter fall and its decomposition, lack of tillage as well as reduced soil erosion are the factors contributing towards the build-up of OM in the soils under Eucalyptus plantations. On the contrary, the continuous tillage of cropland enhanced depletion of OM in the soil. Also, the practice of complete removal of crop residues from the cropland for animal feed and fuelwood might have resulted in minimal turnover of organic residues into the cropland soils. Lower soil temperatures under Eucalyptus plantations decreasing the rate of decomposition could also be a factor in increasing OM input under Eucalyptus plantations [
67]. The OM content was increased from the surface (0-20cm) soil to subsurface (20-40 cm) (
Table 5). Organic matter was higher on surface soil depth than subsurface soil due to the source of organic matter that have found on the surface of the soil [
68].
Table 5.
Effect of land use and soil depth on exchangeable bases, cation exchange capacity and percent base saturation.
Table 5.
Effect of land use and soil depth on exchangeable bases, cation exchange capacity and percent base saturation.
| Land use types |
Ca
(cmol kg-1) |
Mg
(cmol kg-1) |
Na
(cmol kg-1) |
K
(cmolkg-1) |
CEC
(cmol kg-1) |
PBS
(%) |
| Eucalyptus |
3.29c
|
1.14c
|
0.58b
|
0.17c |
27.6a |
18.89c
|
| Cropland |
5.35b
|
1.77b
|
0.70a
|
0.30b |
23.95c |
34.26b
|
| Grazing land |
7.47a
|
2.82a
|
0.60b
|
0.69a
|
25.04b
|
46.97a
|
| LSD0.05
|
1.13 |
0.44 |
0.08 |
0.11 |
1.44 |
2.21 |
| SEM (±) |
0.38 |
0.15 |
0.02 |
0.05 |
0.53 |
0.97 |
| Depth(cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0-20 |
4.31b |
1.61 |
0.60 |
0.29 |
25.14b
|
27.10b
|
| 20-40 |
6.43a
|
2.21 |
0.66 |
0.49 |
25.90a
|
37.80a
|
| LSD0.05
|
0.95 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
1.17 |
1.81 |
| SEM ± |
0.54 |
0.21 |
0.01 |
0.05 |
0.75 |
1.54 |
| CV (%) |
9.86 |
18.51 |
11.86 |
15.01 |
2.51 |
6.83 |
3.1.8. Total Nitrogen
The total nitrogen (TN) in soils was significantly (p<0.05) affected by the land use types, but the interaction effects not significant (
Table 3 and 4). The soil under the Eucalyptus plantation had a significantly higher content of TN (0.24%) than cropland (0.14%) and grazing land (0.20%) (
Table 3). The higher TN under Eucalyptus vs. cropland and grazing lands was 71 and 20 %, respectively (
Table 7). This might be associated with
Eucalyptus globulus plantations having high litter fall and biomass that decomposes into the soil, which results in increased TN and OM content. As per the ratings by Hazelton and Murphy [
49], the TN status under Eucalyptus and grazing lands was medium, while it was low under cropland. The higher TN content of soil was recorded under Eucalyptus plantations shown by Mengist [
13]. Likewise, soils of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations/woodlots were high TN was recorded as compared to croplands [
26]. Lalisa et al. [
55] also indicated that TN was higher on the soils of Eucalyptus woodlots than grazing land and cropland soils in the central highlands of Ethiopia. The low TN content under cropland could be expected due to considerable amounts of N lost through soil erosion and runoff from croplands [
69]. The TN level in soils was similar to the level of OM, which influences the amount of N in soil [
51]. The OM is the main pool of N in the soil [
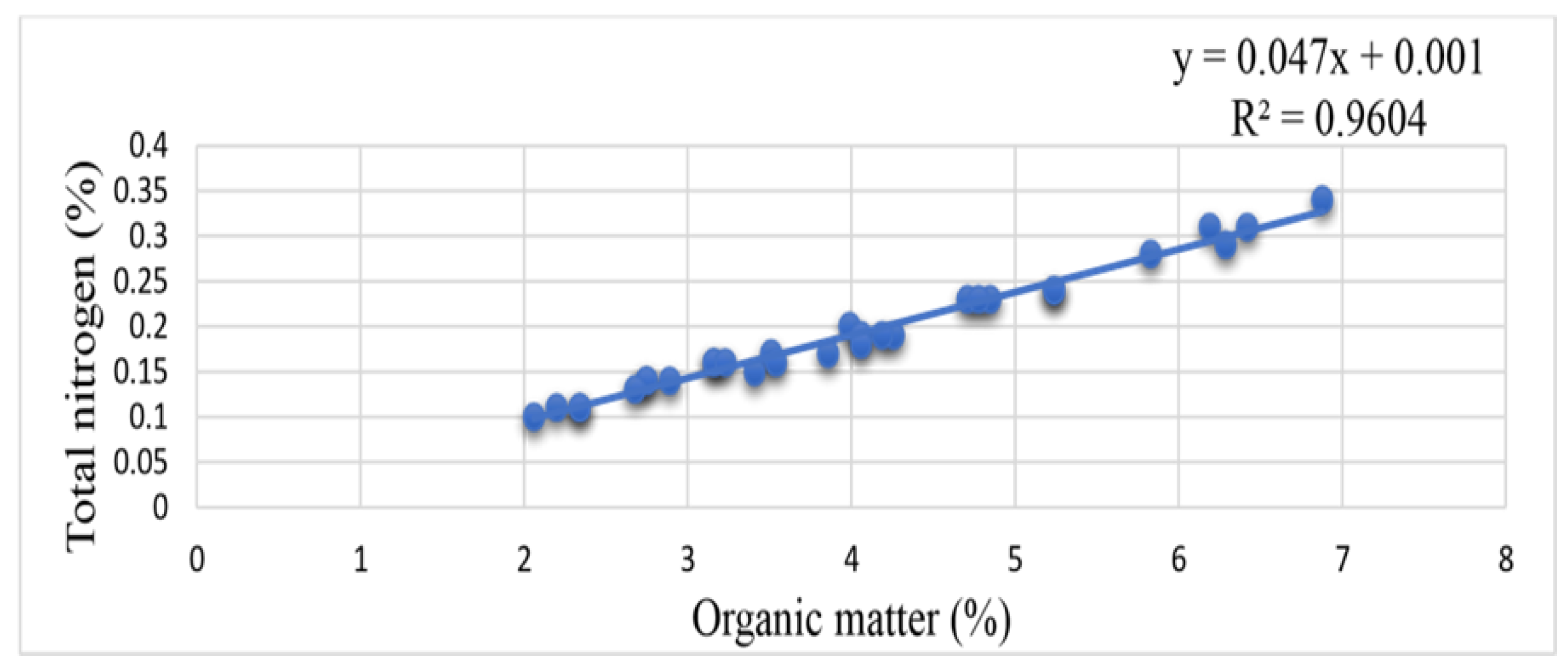
70], largely governing the relative distribution of TN in three land use types. The dependence of TN on OM is well evidenced by a highly significant relationship (r = 0.98**) between OM and TN content of soils (
Figure 5). Which was the higher content of TN in the soil of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations was a higher amount of OM through litter fall and its decomposition, the factors governing nutrient supply in forest soils [
26,
71,
72]. The organic pools, including microbial biomass, contributed more than half of the mineralizing the nitrogen in Eucalyptus plantations [
73]. The capacity of Eucalyptus species to extend the nutrient cycle deep to the ground soil, where other trees and crop species could not access, might also increase the contents of TN [
74]. Eucalyptus trees increase nutrients from deeper parts of the soil through their roots to the litter, which after decomposition would have an additive effect on the nutrient increments in the soil [
26]. Also, the large canopy cover under Eucalyptus, lowering the soil temperature and volatilization loss of N, could also contribute to high nitrogen under Eucalyptus [
13,
26]. Thus, considering TN levels from three land use systems, the
Eucalyptus globulus plantation exerted a positive influence on the soil of TN.
3.1.9. Available Phosphorus (AP)
Soil AP was significantly (p < 0.05) affected by land use and interaction effects but not soil depth (
Table 3 and 4).
Eucalyptus globulus plantation indicated significantly lower AP (1.24 mg kg-1) than grazing land (2.8 mg kg-1) and cropland (2.49 mg kg-1) (
Table 3). The percent changes of AP under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation compared to cropland and grazing lands were -50 and -55.7%, respectively (
Table 7). The interaction of land use and soil depth (
Table 7) indicated AP under Eucalyptus at 0-20 cm depth was significantly lower than cropland and grazing lands, whereas at 20-40 cm depth the significant reduction was recorded only compared to grazing land. The lower AP content in the
Eucalyptus globulus plantation relative to grazing and croplands might be due to more fixation of AP by acidic in
Eucalyptus globulus plantations. This was closely evidenced by the higher values of exchange acidity (1.47 cmol kg-1) in the
Eucalyptus globulus plantations than grazing land (0.95 cmol kg-1) (
Table 3). According to [
75], highly acidic soils which have a pH value less than 5.5 contain high concentrations of acidic cations such as aluminum (Al) and iron (Fe) on the exchange sites of soil colloids, which precipitate AP in soil. The bond of phosphorus with Al and Fe becomes stronger over time, limiting the availability of AP in the soils [
76]. The finding of the study is confirmed by Chanie et al. [
50], who found a very low range of AP was recorded in the Eucalyptus woodlot. Moreover, Yechale and Solomon [
77,
78] found the amount of AP in Eucalyptus woodlots much lower than croplands. The AP also showed lower Eucalyptus woodlot (14.94 mg kg-1) compared to cropland (17.96 mg kg-1) in Ethiopia [
26].
3.1.10. Exchangeable Bases
The mean values of exchangeable cations (Ca, Mg, K, Na) were significantly (p<0.05) affected by land use and soil depth (
Table 5). Eucalyptus plantations indicated significantly lower concentrations of exchangeable cations than on cropland and grazing land (
Table 5). The decreases under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation compared to cropland and grazing lands were 38 and 56 % for Ca, 36 & 60 % for Mg and 43 and 75 % for K, respectively (
Table 7). The interaction between land use and soil depth (
Table 5) also indicated decreased concentrations of Ca, Mg and K under
Eucalyptus globulus plantations than on cropland and grazing lands in respect of 0-20 and 20-40 cm soil depths (
Table 5). The mineral elements Ca2+ and K+ seem to be, particularly, limited under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation due to removal of biomass and immobilization of Ca, Mg and K into woody biomass might be the reason for such a reduction of basic cations. Besides, the fast-growing nature of
Eucalyptus globulus plantation which was largely absorbs basic cation and releases hydrogen ions [
86]. The results are verified by the findings of [
19,
86], who found lower concentrations of Ca, Mg and K in the soils of
Eucalyptus globulus plantations than on grazing land. Likewise, the soil plantation of Eucalyptus showed low levels of exchangeable cations (Ca, K and Mg) compared to their concentrations prior to plantation [
13,
90,
93]. Similarly, Chen et al. [
79] showed the content of basic cations was lower in the Eucalyptus plantations. Soil fertility may suffer a notable decrease, particularly if nutrients in tree crowns are lost through short harvest cycles [
80,
81,
82]. Berthrong et al. [
83] indicated a decrease in mineral soil cations by redistribution from soil of eucalyptus plantations. The status of basic cations such as Ca, Mg and K as per the ratings of Hazelton and Murphy [
49] was, in general, low to moderate under Eucalyptus and moderate to high under grazing and croplands.
3.1.11. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
The result indicated that the CEC was significantly affected by land use, soil depth and the interaction between land use and depth (
Table 5 and 6). It was significantly higher under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation (27.6 cmol kg-1) compared to cropland (23.95 cmol kg-1) and grazing (25.4 cmol kg-1) lands (
Table 5). The higher CEC under soils of eucalyptus plantations might be related to high organic matter content in eucalyptus plantation that increases CEC. The interaction between land use and depth also indicated significantly higher values of CEC under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation than cropland and grazing lands for both 0-20 and 20-40 cm depths (
Table 5). This could be due to the clay soil's composition and OM was more in eucalyptus plantations, which raise CEC. As per ratings by Hazelton and Murphy [
49], the CEC value was high under Eucalyptus, whereas moderate under cropland and grazing lands. The prevalence of acidic cations (Al
3+, Fe
3+, and H
+) in the soil exchange complex, which is supported by a significantly more acidic as shown by higher exchangeable acidity and low amount of basic cations, might be the cause of the higher CEC under eucalyptus [
84]. The higher CEC under
Eucalyptus globulus plantation compared with the soil from cropland and grazing land might be explained by the tree's comparatively higher OM content, which offers more cation exchange sites. Higher CEC in soils with higher OM levels [
26,
82,
85].
Table 6.
Interaction effects between land use types and soil depths on soil properties.
Table 6.
Interaction effects between land use types and soil depths on soil properties.
| Land use types |
Depth (cm) |
Ca |
Mg |
Na |
K |
CEC |
PBS |
| Eucalyptus |
0-20 |
2.42d
|
1.01c
|
0.57 |
0.08d
|
28.1a
|
14.5d
|
| |
20-40 |
4.17c
|
1.28c
|
0.59 |
0.27c
|
27.1b
|
23.3c
|
| Cropland |
0-20 |
4.36c
|
1.45c
|
0.60 |
0.27c
|
22.25d
|
30.1b
|
| |
20-40 |
6.34b
|
2.08b
|
0.80 |
0.34c
|
25.64c
|
37.2c
|
| Grazing land |
0-20 |
6.16b
|
2.37a
|
0.60 |
0.53b
|
25.1c
|
38.5b
|
| |
20-40 |
8.79a
|
3.26b
|
0.60 |
0.85a
|
24.99c
|
54.02a
|
| LSD0.05
|
|
0.69 |
0.46 |
NS |
0.08 |
0.8 |
2.38 |
| SEM± |
|
0.38 |
0.15 |
0.02 |
0.005 |
0.3 |
0.89 |
| CV (%) |
|
9.85 |
18.5 |
11.9 |
15.01 |
2.51 |
6.83 |
3.1.12. Percent Base Saturation
The results of the analysis of variance showed that soil depth, land use, and their interactions all had a significant impact on the percent base saturation (PBS) (
Table 5 and 6). Compared to cropland (34.26%) and grazing land (46.97%), it was much lower than
Eucalyptus globulus plantations (18.89%) (
Table 5).
Table 7, showed the difference the PBS between cultivated and grazing areas and eucalyptus fields was -45 and -60%, respectively (
Table 7). The lowest PBS could result from high and prolonged uptake of basic cations by plant roots and a poor source of biomass available to the soil and the fast-growing eucalyptus plantations largely absorb basic cations. The study conducted in Ethiopia [
16,
56] that PBS was decreased in the Eucalyptus was grown compared to native vegetation sites and adjacent croplands. Such a reduction in PBS under Eucalyptus compared to cultivated and grazing lands could be uptake basic cations by the woody biomass of Eucalyptus as indicated earlier. As per the rating of Hazelton and Murphy [
49], the PBS was very low under Eucalyptus, moderate under grazing land and low under cultivated land in the study area.
Table 7.
Percentage change of land use types on some selected soil properties .
Table 7.
Percentage change of land use types on some selected soil properties .
| Land use types |
Sand |
Silt |
Clay |
BD |
Porosity MC |
pH |
Acidity EC |
| Eucalyptus Vs. Cropland |
14% |
41% |
-10% |
-1.8% |
1.4 % 16% |
-0.2 |
-14% -33% |
| Eucalyptus Vs. Grazing land |
-13% |
9% |
2 % |
-1.8% |
1.4% 26% |
-0.6 |
33% -33% |
| |
OM |
TN |
AP Ca |
Mg K CEC |
PBS |
| Eucalyptus Vs. Cropland |
74% |
71% |
-50% -38.5% |
-35.6% 15.1% -43.3% |
-45% |
| Eucalyptus Vs. Grazing land |
10% |
20% |
-56% -55.9% |
-60% 10.1% -75.4% |
-60% |
4. Conclusions
The studies evaluate the effects of Eucalyptus globulus plantations compared to cropland and grazing land on soil properties. According to the findings, soil properties found in Eucalyptus globulus plantations had substantially greater contents of silt particles, moisture content (MC), organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN), and cation exchange capacity (CEC) than in cropland and grazing land. In contrast to grazing and cropland, Eucalyptus globulus plantations were found to have lower levels of bulk density (BD), soil pH, available phosphorus (AP), electrical conductivity (EC), and exchangeable bases (Ca, Mg, K, and Na). Besides, sand, silt, and clay, as well as pH, EC, CEC, BD, MC, and PBS, were higher while decreasing soil depth. Soil properties such as AP, pH, EC, and basic cations were decreasing in Eucalyptus globulus plantations. Nevertheless, the effects of Eucalyptus globulus plantations on the soil were soil acidity and a decrease of basic cations, AP and PBS. Therefore, appropriate and effective land use management models should be applied on the study site in order to manage the soil properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Design methodology, Writing-original draft preparation (K. G.), Investigation, Software, conceptualization and formal analysis (R. Z.), Edit the paper (F. A.), Supervision (P. D. S. and T. A).
Funding
The research was supported by Ministry of Science and higher Education, Ethiopia.
Informed Consent Statement
Each participant in the study offered their informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The second author expresses her sincere gratitude to the Ministry of Higher Education, Ethiopia, for granting the financial assistance to carry out this research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding publication of this paper.
References
- M. Zewdie, Temporal changes of biomass production, soil properties and ground flora in Eucalyptus globulus plantations in the central highlands of Ethiopia, Doctoral thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala, 74 p, 2008.
- FAO, Eucalyptus in East Africa: Socio-economic and environmental issues by Gessesse Dessie, Teklu Erkossa. FAO, Rome: Planted Forests and Trees Working Paper 46/E, Forest Management Team, Forest Management Division, 2011.
- Z. Hailu, Ecological impact evaluation of Eucalyptus plantation in comparison with agricultural and grazing land use types in the highlands of Ethiopia, Ph. D Thesis, University of Agricultural Science, Vienna, 2002.
- M. Lemenih, Growing Eucalyptus by smallholder farmers in Ethiopia. In Eucalyptus Species Management, History, Status and Trends in Ethiopia (Gil, L., Wubalem, T., Tolosana, E and López, R., Eds.). Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, pp. 91-103, 2010.
- Z. Mekonnen, H. Kassa, M. Lemenh & B. Campbell, The role and management of eucalyptus in Lode Hetosa district, central Ethiopia, Forests, Trees and Livelihoods, 17:4, pp. 309-323, 2012. [CrossRef]
- D. Jenbere, M. Lemenih & H. Kassa, , Expansion of eucalypt farm forestry and its determinants in Arsi Negelle District, south central Ethiopia. Small-scale Forestry, 11(3): 389-405, 2012. [CrossRef]
- FAO, Global forest resources assessment (FRA). Forestry paper 139, Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, Italy, 2000.
- FAO, Eucalyptus in East Africa: The Socio-economic and environmental issues. Food and Agriculture Organization, Subregional Office Eastern Africa, March 2009, Addis Ababa, 46 p, 2009.
- M. Yitebitu, Eucalyptus trees and the environment: A new perspective in times of climate change. In L. Gil, W. Tadesse, E. Tolosana, & R. López (Eds.), Eucalyptus species management, history, status and trends in Ethiopia. Proceedings from the congress held in Addis Ababa (pp. 104–113). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2010.
- P. Jagger & J. Pender. 2003. The role of trees for sustainable management of less-favored lands: The case of Eucalyptus in Ethiopia. Forest Policy and Economics, 5: 83-95. [CrossRef]
- P. Oballa, , E. Chagala-Odera, , L. Wamalwa, , V. Oeba, , E. Mutitu, , and L. Mwangi, The Performance of Eucalyptus Hybrid Clones and Locallandraces in Various Agro ecological Zones in Kenya.13p. 2005.
- D. I. Forrester, J. Bauhus,, A. L Cowie, & J. K.Vanclay, Mixed-species plantations of Eucalyptus with nitrogen-fixing trees: A review. Forest Ecol. and Management, 233: 211–230, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Mengist, Eucalyptus plantations in the highlands of Ethiopia revisited: A comparison of soil nutrient status after the first coppicing. Master’s Thesis, University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences, Department of Forest- and Soil, Vienna, 2011.
- K. Albert, Effects of Eucalyptus on soil Physico-Chemical properties in Thiririka Sub-Catchment, Kiambu County, Kenya. M.Sc. thesis, Kenyatta University, Kenya. 76p. (2016).
- J.W.Turner and M.P. Lambert, Changing in organic carbon in forest plantations in eastern Australia. Forest Ecology and Management 133: 231-247, 2000. [CrossRef]
- M. Lemenih, T. Gidyelew and D. Teketay, Effect of canopy cover and under story environment of tree plantations on richness, density and size of colonizing woody species in southern Ethiopia. Forest Ecology and Management 194: 1-10, 2004.
- Y. G. Wen, X. Zheng, M. C. Li, H. G. Xu, H. W. Liang, C. B. Huang, H. G. Zhu, and B. B. He, Effects of Eucalyptus replacing Masson pine forest on soil physicochemical properties in Guangxi, Southern China. 31 (6), 149-153, 2009.
- H. G. Zhu, Y. G. Wen, H. W. Liang, H. G. Xu, Y. Q. Yang, M. C. Li, Z. H. Huang, and R.Y. Deng, Effects of Eucalyptus replacing Masson pine forest on plant species diversity in Guangxi, Southern China. Journal of Beijing Forest University,31(6),149–153, 2009.
- F. Leite, I. Silva, R. Novais, R. Barros, & C.L.M. Júlio, Alterations of soil chemical properties by Eucalyptus cultivation in five regions in the Rio Doce Valley. 34, 821-831. 2010. [CrossRef]
- T. Alemie, The Effect of Eucalyptus on Crop Productivity, and Soil Properties in the Koga Watershed, Western Amhara Region, Ethiopia. M.Sc. thesis, Cornell University, USA, 48p, 2009.
- W. Xiao, X. Ge, L. Zeng, Z. Huang, J. Lei, B. Zhou, and M. Li, Rates of Litter Decomposition and Soil Respiration in Relation to Soil Temperature and Water in Different Aged Pinus massoniana Forests in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Journal of PLoS ONE, 9 (7), 2014. [CrossRef]
- F. Bernhard-Reversat, I. Mboukou-Kimbatsa, and J.J. Loumeto, Eucalyptus litters quality and sandy soils: Addressing two cumulative effects on top soil organic-matter and signal activity in African plantations. 23-29 p. 50, 2001.
- P.G. Waterman, and S. Mole, Analysis of phenolics plant metabolites, Methods in Ecology. London. 238 pp: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1994.
- J. Harborne, Role of phenolics secondary metabolites in plants and their degradation in nature. In: Driven by Nature: Plant litter quality and decomposition, (Cadisch, G. & Giller, K.E., Ed.) Oxon: CAB International, 1997.
- E. A. El-Amin, I. E. Diab, S. I. Ibrahim, Influence of Eucalyptus cover on some physical and chemical properties of a soil in Sudan, Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 32(13-14):2267-2278, September 2001. [CrossRef]
- Y. Birru, A. Anteneh, and A. Tadele, Expansion of Eucalyptus Woodlots in the Fertile Soils of the Highlands of Ethiopia: Could It Be a Treat on Future Cropland Use? Journal of Agricultural Science, 5 (8), 97-107, 2013. [CrossRef]
- B. Mengistu, F. Amayu, W. Bekele & Z. Dibaba, Effects of Eucalyptus species plantations and cropland on selected soil properties, Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes, 2020:. [CrossRef]
- H. Zerfu, Glatzel, and S, Monika, Community Needs, Management and the Environment Pertinent to Eucalyptus. In W. T. Luis Gil ( Ed.), Edition: UPM (Technical University of Madrid), EIAR (Ethiopian Institute of Agronomical research) and ENCE, 2010. ISBN: 978-84-693-8769-6.
- S. Kidanu, T. Mamo and L. Stroosnijder, Biomass production of Eucalyptus boundary plantations and their effects on crop productivity on Ethiopia highland vertisol. Agroforestry Forum 63: 281-290, 2004.
- 2017; 30. GDARDO, Gozamn District Agricultural and Rural Development Office, Debre Markos, Personal communication, 2017.
- FAO/UNESCO, Soil map of the world, 1:5,000,000 (Vol. 2), Retrieved from http://www.fao.org, 1984.
- Mekonnen, Response and uptake of Barley (Hordeum irregulare L.) to different rates of organic-P and Nitrogen fertilizers on Nitosols of Gozamin District,Ethiopia. MSc thesis Alemaya University, Alemaya, 2005.
- S. K. Thompson, Adaptive clusters sampling: Designs with primary and secondary units. Journal of the international Biometric society, 47 (3), 1103–1115, 1991. [CrossRef]
- T. G. Vågen, L. A. Winowiecki, A. Abegaz, and K. M. Hadgu, Landsat-based approaches for mapping of land degradation prevalence and soil functional properties in Ethiopia, Remote Sens. Environ., 134, 266–275, 2013.
- Abegaz, A. A. Winowiecki, T. G. Vågen, S. Langan, and J. U. Smith, Spatial and temporal dynamics of soil organic carbon in landscape of the upper Blue Nile basin of the Ethiopian Highlands. Journal of Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 218, 190 -208, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Adugna, and A. Abegaz, Effects of land use changes on the dynamics of selected soil properties in northeast Wellega, Ethiopia. SOIL, 2, 63-70, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Klute, and C. Dirksen, Hydraulic conductivity and diffusivity: Laboratory methods. In: Klute, A. Ed., Methods of Soil Analysis Part 1-Physical and Mineralogical Methods. American Society of Agronomy, USA. 687-734, 1986.
- K. Kolay, Basic Concepts of Soil Science (2nd edition). New Delhi, India: New Age International Publishers, 2000.
- J. M. Anderson, and J. S. Ingram, Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility. Wallington ford, Oxon, UK: C.A.B. International, 221p, 1993.
- Walkley, and I. Black, An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Journal of soil Science, 37 (1), 29-38, 1934. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Bremner and C. S. Mulvaney, “Total nitrogen,”“Total nitrogen,” in Methods of Soil Analysis. II. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, and D. R. Keeney, Eds., pp. 595–624, American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, 1982.
- S. R. Olsen, C. V. Cole, F. S. Watanabe, and L. A. Dean, Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate, Allen Institute for AI, Seattle, WA, USA, 1954.
- H. D. Chapman, “Cation exchange capacity”, in Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, C. A. Black, Ed., American Society Agronomy, Madison, WI., USA, 1965.
- S. Kidanu, T. Mamo, and L. Stroosnijder, “Biomass production of Eucalyptus boundary plantations and their effect on crop productivity on Ethiopian highland Vertisols,” Agroforestry Systems, vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 281–290, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Eyayu, H. Gebrekidan, T. Mamo, and M. Assen, Effects of land use change on selected soil properties in the Tera Gedam Catchment and adjacent agro-ecosystems, north-west Ethiopia, Ethiopian Journal of Natural Resources, 11, pp.35-62, 2009.
- T. Y. Gebeyaw, Assessment of soil fertility variation in different land uses and management practices in Maybar watershed, south Wollo zone, north Ethiopia, International Journal of Environmental Bioremediation and Biodegradation, 3, 15-22, 2015.
- M. Sonaimuthu, K. Sivakumar, K. Rajan, M.Tilak, R.J. Sudhagar, P.Raja, and D. Dinesh. Effect of land uses on soil physical qualities in mountainous ecosystem of Western Ghats, India, Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, Vol 66, No.3, pp 249-257, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Fekadu, A. Abdu, L. Mulugeta, & F. Aramde, Effects of different land uses on soil physical and chemical properties in Wondo Genet area, Ethiopia. New York Science Journal, 5(11), 110-118, 2012, 2012.
- P. Hazelton, and B. Murphy, Interpreting soil test results: What do all the numbers mean? 2nd Edition. CSIRO Publishing. 152p, 2007.
- T. Chanie, A. S. Collick, E. Adgo, C. J. Lehmann, & T. S. Steenhuis, Ecohydrological impacts of Eucalyptus in the semi-humid Ethiopian Highlands: The Lake Tana Plain. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 61(1): 21–29, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Karim, A. Mukhtar, H. Mukhtar, and M. Athar, Effect of the canopy cover on the organic and inorganic content of soil in cholistan desert. Pak. J. Bot, 41 (5), 2387-2395, 2009.
- Y. Moges, Eucalyptus Trees and the Environment: A new perspective in times of climate change. (Wubalem. T. Luis ,G.,Eduardo, T. and Rosana, L. Ed.) 104-113, 2010.
- Kumar, Place of Eucalyptus in Indian Agro-forestry Systems, In Proceedings (edited by J. K. Sharma, C.T.S. Nair, S. Kedharnath, and K. S. Peechi) National Seminar on Eucalypts in Indian Forestry: Past, Present and Future, 30-31 January 1984. KFRI. pp. 257-260, 1984.
- T. Tekalign, Soil, Plant, Water, Fertilizer, Animal Manure and Compost AnalysisInternational Livestock Research Center for Africa, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1991.
- Lalisa, H. Herbert, & S. Monika, Effects of land use types on soil chemical properties in smallholder farmers of central highland Ethiopia. Ekologia (Bratislava), 29(1), 1–14, 2010. Retrieved from www.http//dx.doi.10.4149/ekol_2010_01_1.pdf.
- G. S. Yihenew, & A. Getachew, Effects of different land use systems on selected physico-chemical properties of soils in Northwestern Ethiopia. Journal of agricultural science, 5(4), 112-120, 2013. [CrossRef]
- G. Liu, R. Mylavarapu, E. Hanlon, and C.W. Lee, Soil pH Management for Optimum Commercial Fruit Production in Florida, 2014. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu. [CrossRef]
- K. A. Frimpong, E. K. A. Afrifa, E. A. Ampofo, and P. K. Kwakye, Plant litter turnover, soil chemical and physical properties in a Ghanaian gold-mined soil re-vegetated with Acacia species. International Journal of Environmental Sciences, 4 (5), 987-1005, 2015.
- M, I. Onwuka, U. V. Ozurumba, and O. S. Nkwocha, Changes in Soil pH and Exchangeable Acidity of Selected Parent Materials as Influenced by Amendments in South East of Nigeria. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 4, 80-88, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, J. Gonzalo, and M. B. Turrion, Effects of short-rotation Eucalyptus on soil quality attributes in highly acidic soils of the central highlands of Ethiopia. Journal of Soil Use and Management, 32 (2), 210–219, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Lauchli, and S. R. Grattan, Soil pH extremes. In: Plant stress physiology. (S. Shabala, Ed.), 194-209 pp, (2012). [CrossRef]
- L. K. Nasabimana, Soil carbon and nutrient accumulation under forest plantations in southern Rwanda. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology .2 (6), 142-149, 2008.
- Binkley, A. M. Connell, and K.V. Sankaran, Management of Soil, Nutrients and Water in Tropical Plantation Forests. (B. A. E.K.S., Ed.) Nambiar, Australia, 1997.
- K, K. Bhardwaj, R. S. Dhillon, K. Sushil, J. Vishal, V. Dalal, and S. B. Chavan, Effect of Eucalyptus Bund Plantation on Yield of Agricultural Crops and Soil Properties in Semi-Arid Region of India. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 6 (10), 2059-2065, 2017.
- M. C. Nierves, and F. M. Salas, Assessment of Soil Phosphorus and Phosphorus Fixing Capacity of Three Vegetable Farms at Cabintan, Ormoc City, Leyte. World Journal of Agricultural Research, 3 (2), 70-73, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Liang, R. Travis, W. Alemayehu, C. Cathy, and W. Atalel, Effects of exotic Eucalyptus on soil properties in and around sacred natural sites in the northern Ethiopian Highlands. Journal of agriculture and food, 1 (2), 175-193, 2018.
- L. Mann, and V. Tolbert, Soil Sustainability in Renewable Biomass Plantings. Journal of the Human Environment, 29 (8), 492-498, 2000. [CrossRef]
- P. Charman, and M. Roper, Soil Organic Matter in soils: Their Properties and Management. (Vol. 3). (PEV. Charman and BW Murphy Ed.) Melbourne: Pp 260-270. Oxford University Press. 51, 2007.
- Fabian, Fernandez, E. Daniel, and Kaiser. Understanding nitrogen in soils. University of Minnesota extension. Retrieved from https://extension.umn. Edu /nitrogen /understanding nitrogen-soils, 2018.
- K. C. Cameron, and R. J. Haynes, Retention and movement of nitrogen in soils. (R.Haynes, Ed.) London: Academic Press , 166–241, 1986.
- Araujo, E. Silva, L. Nunes, and R. Carneiro, The effect of converting tropical native savanna to Eucalyptus grandis forest on soil microbial biomass. Journal of land degradation and development, 21, 540-545, 2010. [CrossRef]
- T. O., G. Ndibe, G. B. Onwumere, and T. Bulus, Litter decomposition and release of nutrients form Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf on Eucalypt plantation soils. Kaduna State University, Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, Kaduna, Nigeria. 62, 24-45, 2017.
- P. Barreto, A. Gama - Rodrigues, E. Gama-Rodrigues, and N. Barros, Nitrogen Balance in soil under Eucalyptus. R. Bras. Ci. Solo, 36, 1239-1248, 2012.
- D. Jaleta, M. Lemenih, and P. Boniface, Eucalyptus Expansion as Relieving and Provocative Tree in Ethiopia. Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research, 6 (3), 1-12, 2016.
- Birhanu, A. Enyew, and A. Mekuria, Impact of land use types on soil acidity in the highlands of Ethiopia: The case of Fageta lekoma district. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2 (8), 124-132, 2014. [CrossRef]
- N. J. McKenzie, D. J. Jacquier, R. F Isbell, and K. L. Brown, Australian Soils and Landscapes: An Illustrated Compendium. Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO publishing.416p, 2004.
- K. Yechale, and A. J. Solomon Raju, Effect of land use/land cover change on soil properties in the Hare river watershed, Ethiopia. The Ecoscan, 5 (1&2), 69-74, 2011.
- B. Guedes, Effects of 34-year-old Pinus taeda and Eucalyptus grandis plantations on soil carbon and nutrient status in former miombo forest soils. Journal of Global Ecology and Conservation , 8, 190-202, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Chen, Z. H. Xu and N. J. Mathers, Soil carbon pools in adjacent natural and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. Soil Science Society of America Journal 68: 282-291, 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Jorgensen, and C. G. Wells, Tree nutrition and fast-growing plantations in developing countries. International Journal of Tree crops. 3 (4), 1986. [CrossRef]
- Folster, P. K. Khanna, Dynamics of nutrient supply in plantation soils.In Management of soil, nutrients and water in tropical plantation forests. (E. K. Sadanandan, E.K.S. Nambiar, A. G. Brown(Ed.) 43, 339-378. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, 1997.
- Demessie, B, R. Singh, R. Lal, and T. Borresen, Effects of Eucalyptus and coniferous plantations on soil properties in Gambo District, Southern Ethiopia. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica,Section B Soil & Plant Science, 62 (5), 455-466, 2012.
- S. T. Berthrong, E. G. Jobbagy, and R. B. Jackson, A global meta-analysis of soil exchangeable cations, pH, carbon, and nitrogen with afforestation. (Treseder, K.K, Ed.) Journal of Ecological Applications, 19 (8), 2228–2241, 2009.
- D. S. Ross, and Q. Ketterings, Recommended Methods for Determining Soil Cation Exchange Capacity. Cooperative Bulletin No. 493, 2011.
- Z. Eshetu, R. Giesler, and P. Hogberg, Historical land use pattern affects the chemistry of forest soils in the Ethiopian highlands. Geoderma, 118 (3-4), 149-165, 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. Molla, K. Getnet, and M. Mekonnen, “Land use change and its effect on selected soil properties in the northwest highlands of Ethiopia,” Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 8, p. e10157, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Carter and E. G. Gregorich, Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, US, 2007.
- A: Methods of Soil, Plant, and Water Analysis, 2013; 88. Estefan, Methods of Soil, Plant, and Water Analysis: A Manual for the West Asia and North Africa Region, International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), Beirut, Lebanon, 2013.
- He, Y., DeSutter, T., Prunty, L., Hopkins, D., Jia, X. and Wysocki, D.A., 2012. Evaluation of 1: 5 soil to water extract electrical conductivity methods. Geoderma, 185, pp.12-17. [CrossRef]
- Yimam, A. Mekuriaw, D. Assefa & W. Bewket (2024). Effect of Eucalyptus globulus Plantations on Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2024. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhu, X. Wang, F. Chen, C. Li, and L. Wu, “Efects of the successive planting of Eucalyptus urophylla on soil bacterial and fungal community structure, diversity, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity,” Land Degradation & Development, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 636–646, 2019.
- Abate, J. G., Borges, J. G., S. Marques, & V. Bushenkov (2022). An Ecological-Economic Approach to Assess Impacts of the Expansion of Eucalyptus Plantations in Agroforest Landscapes of Northern Ethiopia. Forests, 13(5), 686. [CrossRef]
- Jaleta Negasa (2020). Effects of land use types on selected soil properties in central highlands of Ethiopia. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 2020, 1-9.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).