Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
21 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background and Goals
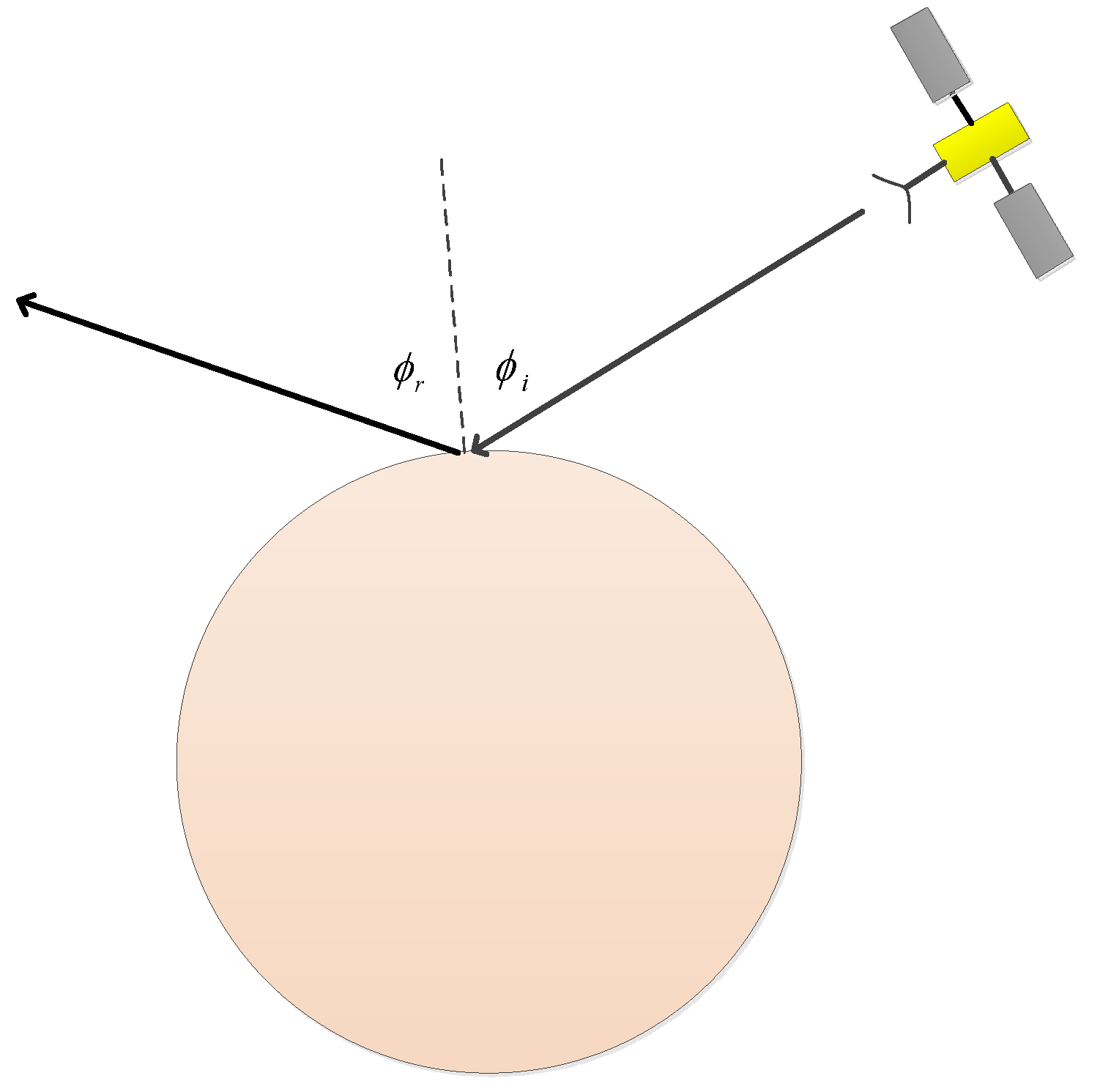
3. Surface Properties from Quasi-Specular Radar Backscatter
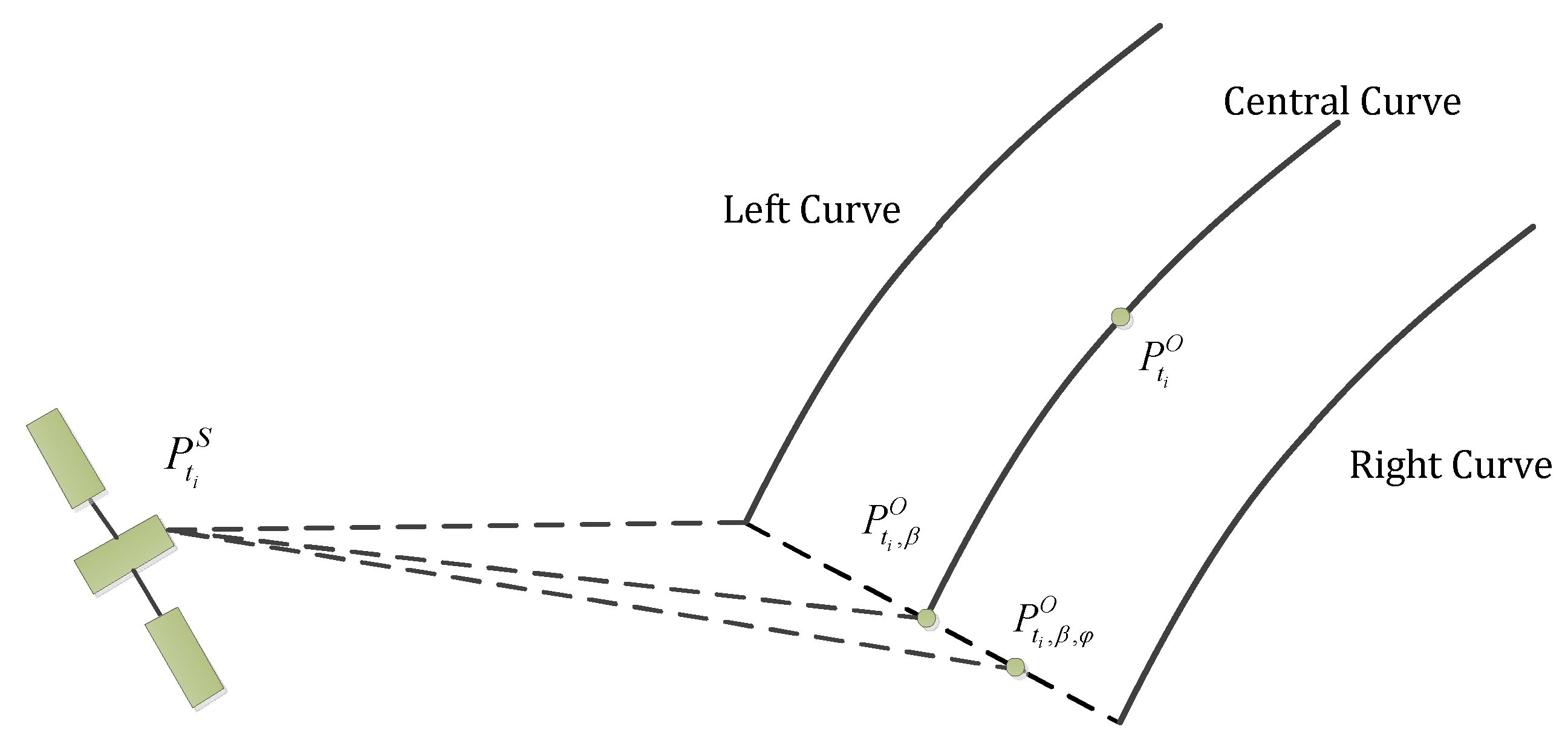
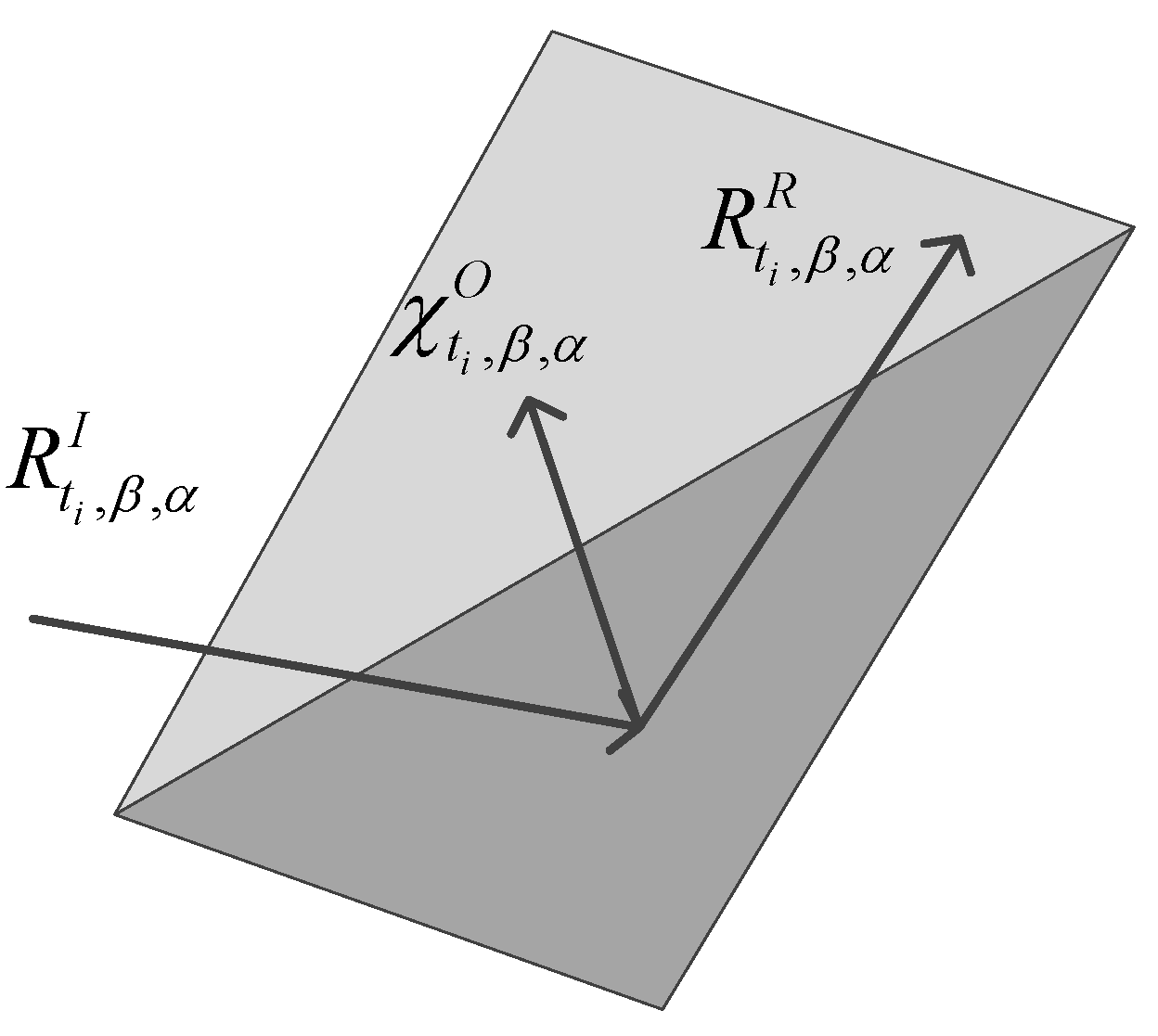
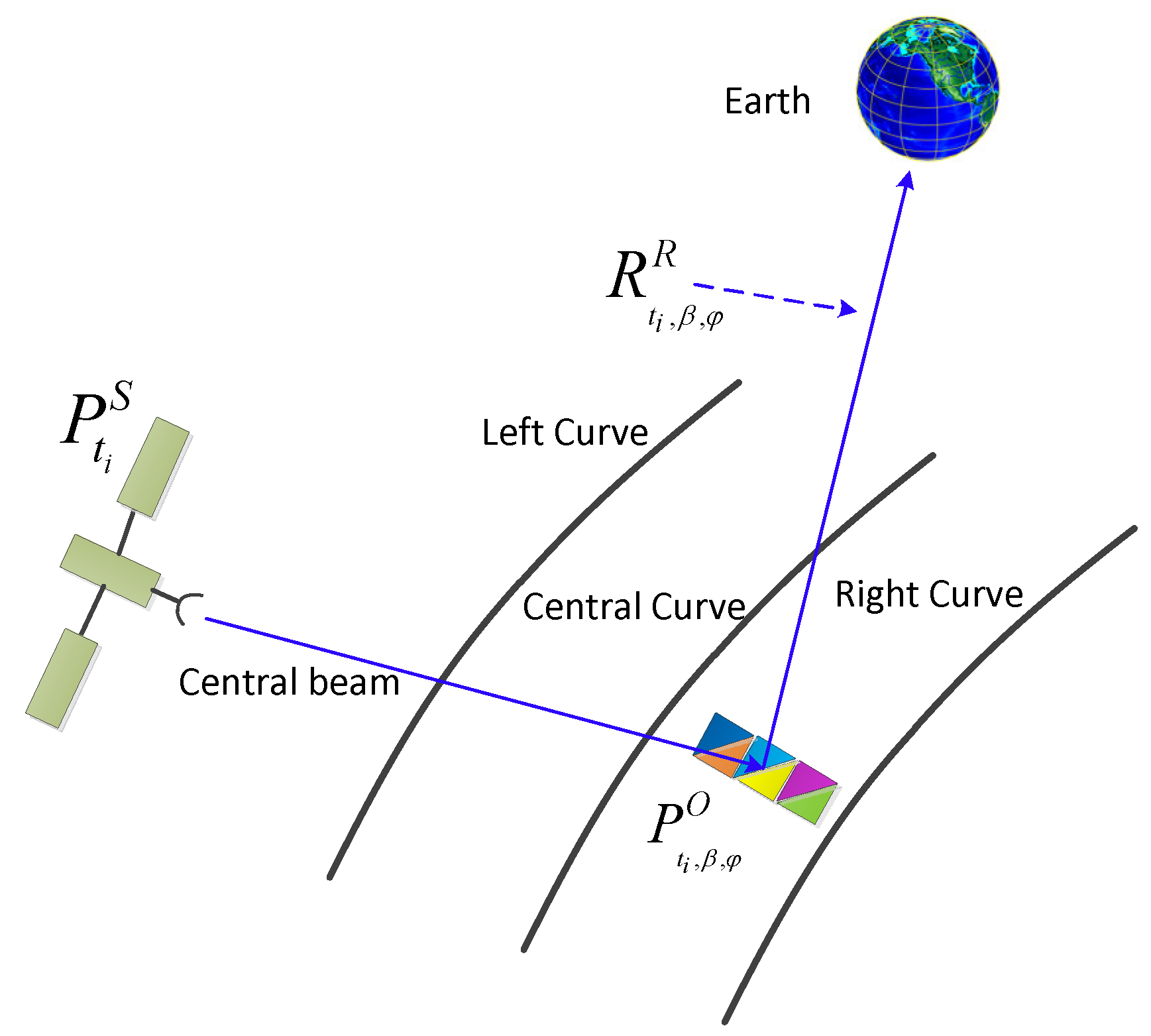
3.1. The Simulation of Reflected Signals
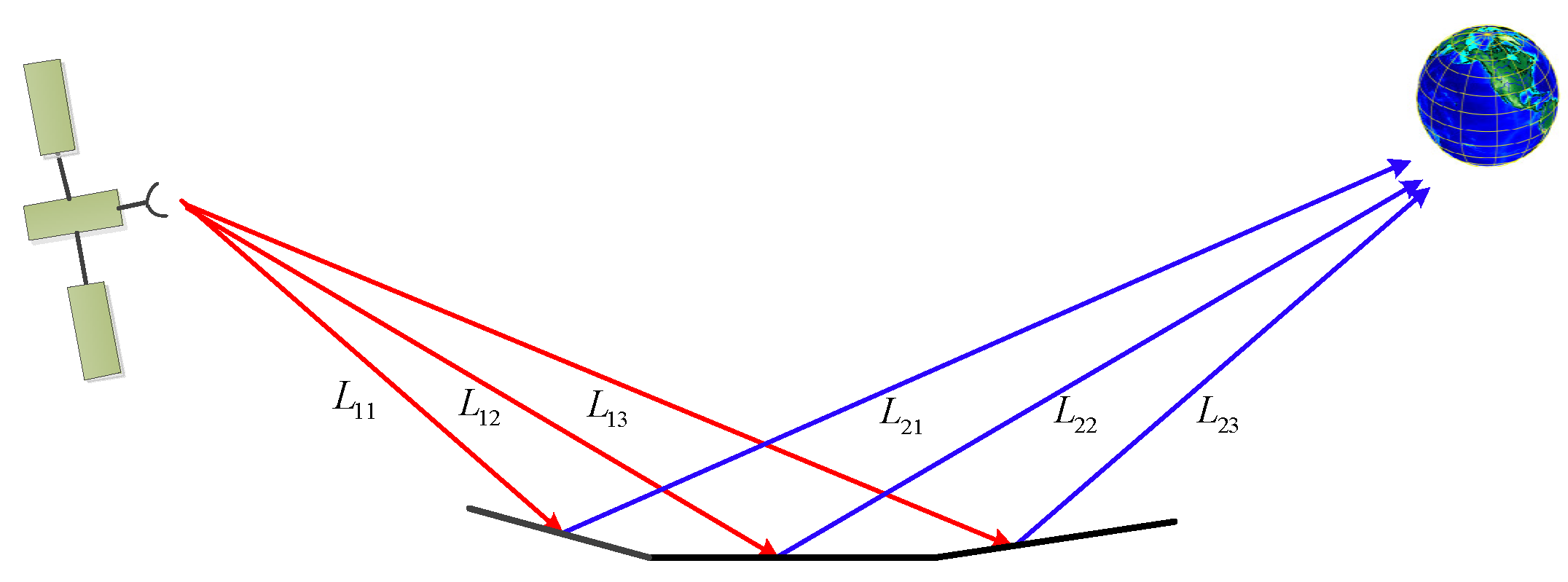
3.2. Modeling the Reception of Reflected Signals
3.3. The Doppler Shift of the Received Signals
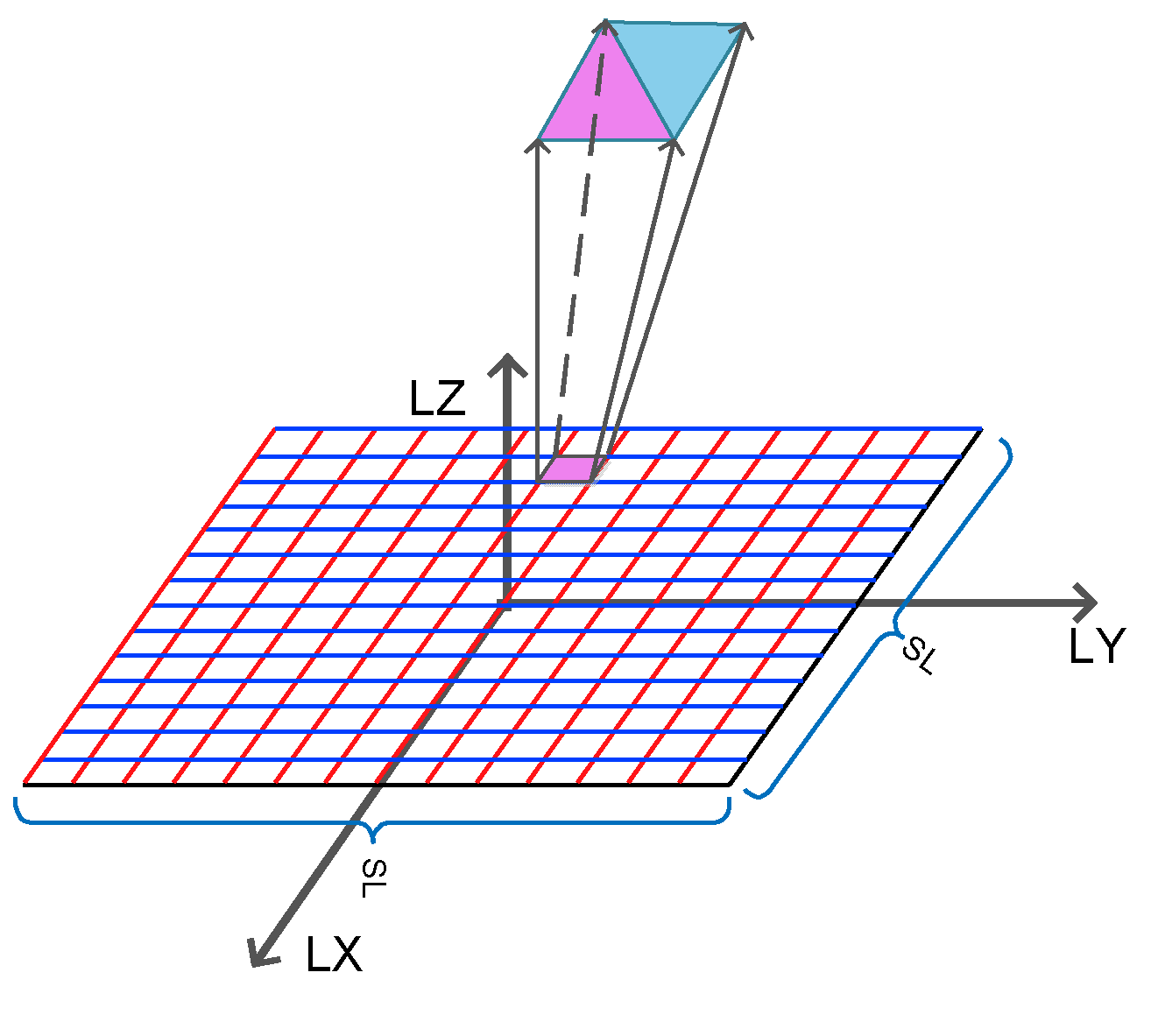
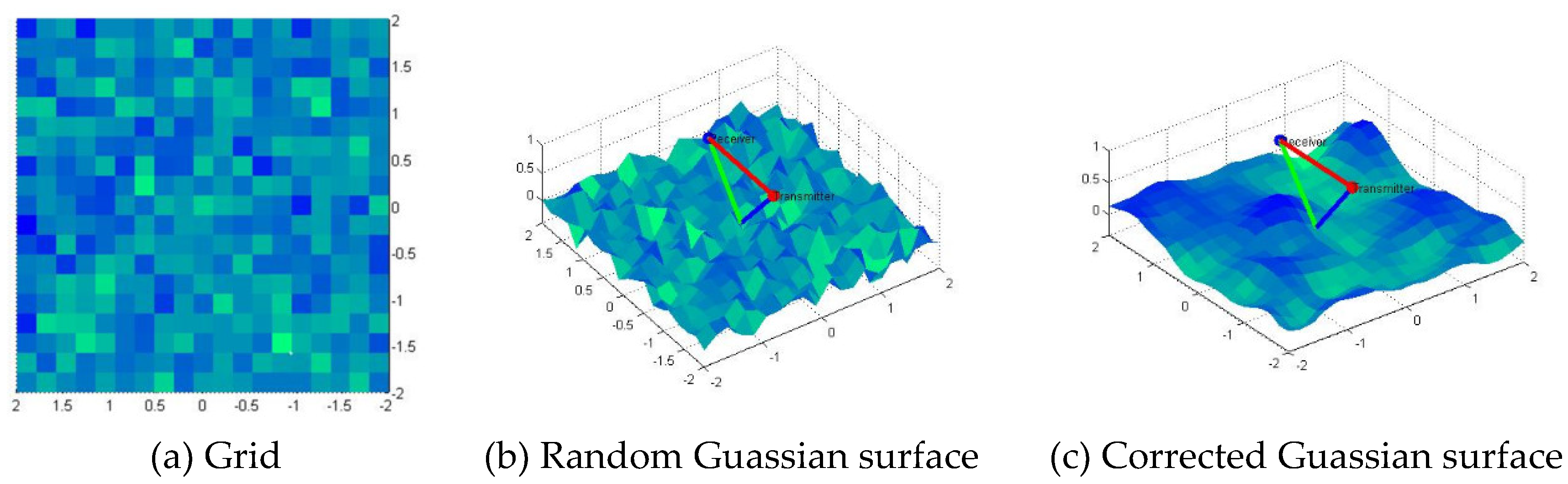
3.4. The Computation of the Rms Slope
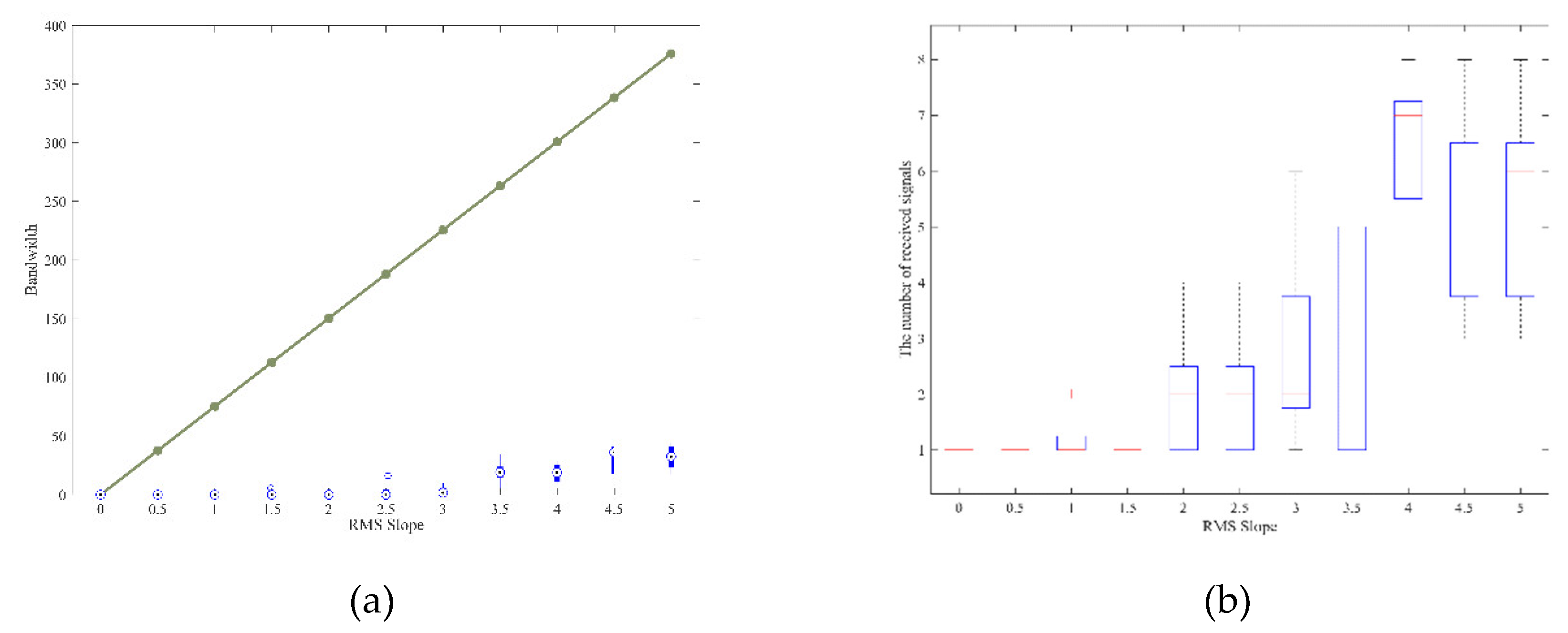
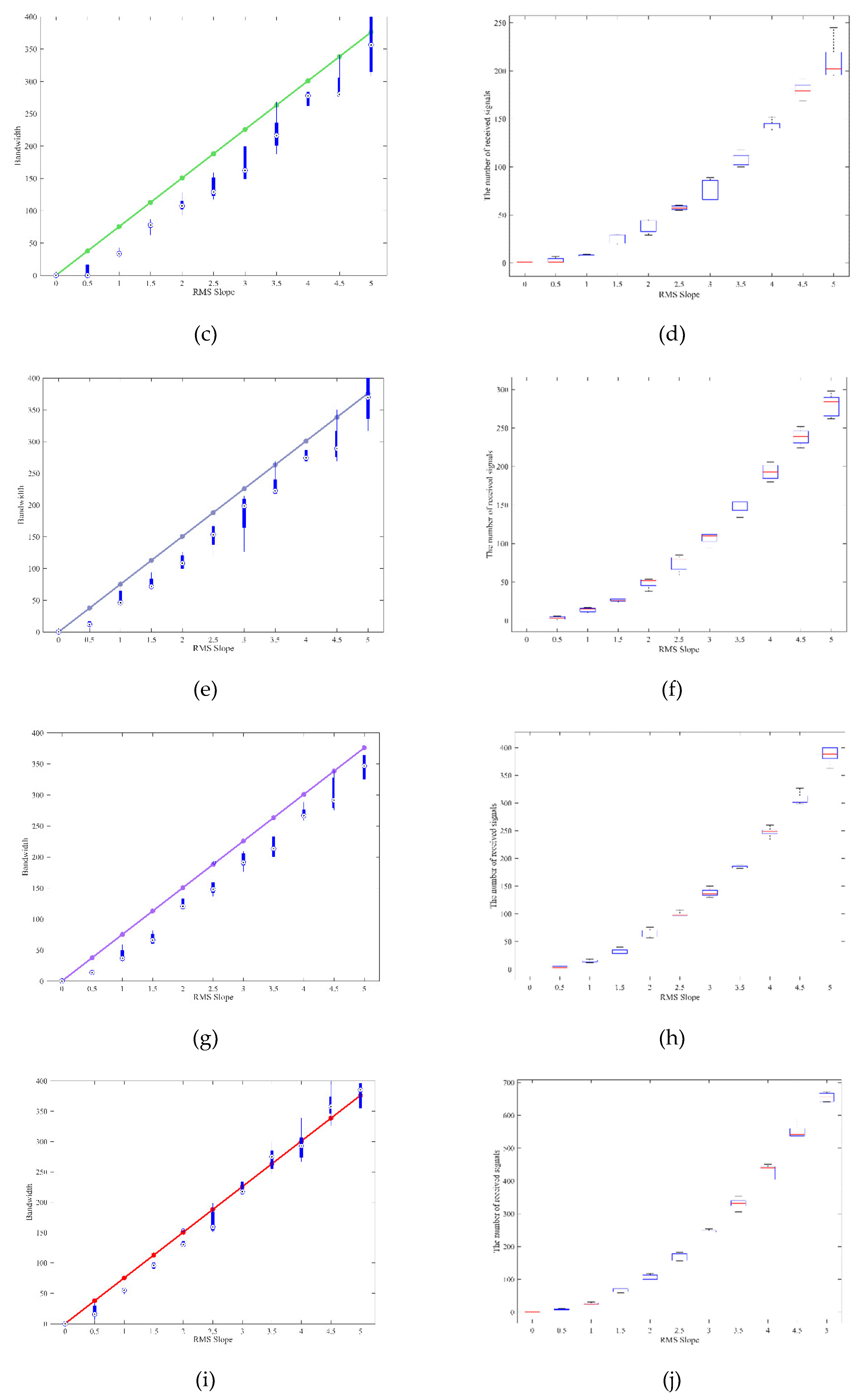
4. Numerical Simulation Experiments
4.1. Case 1: Mars Bistatic Radar Experiments
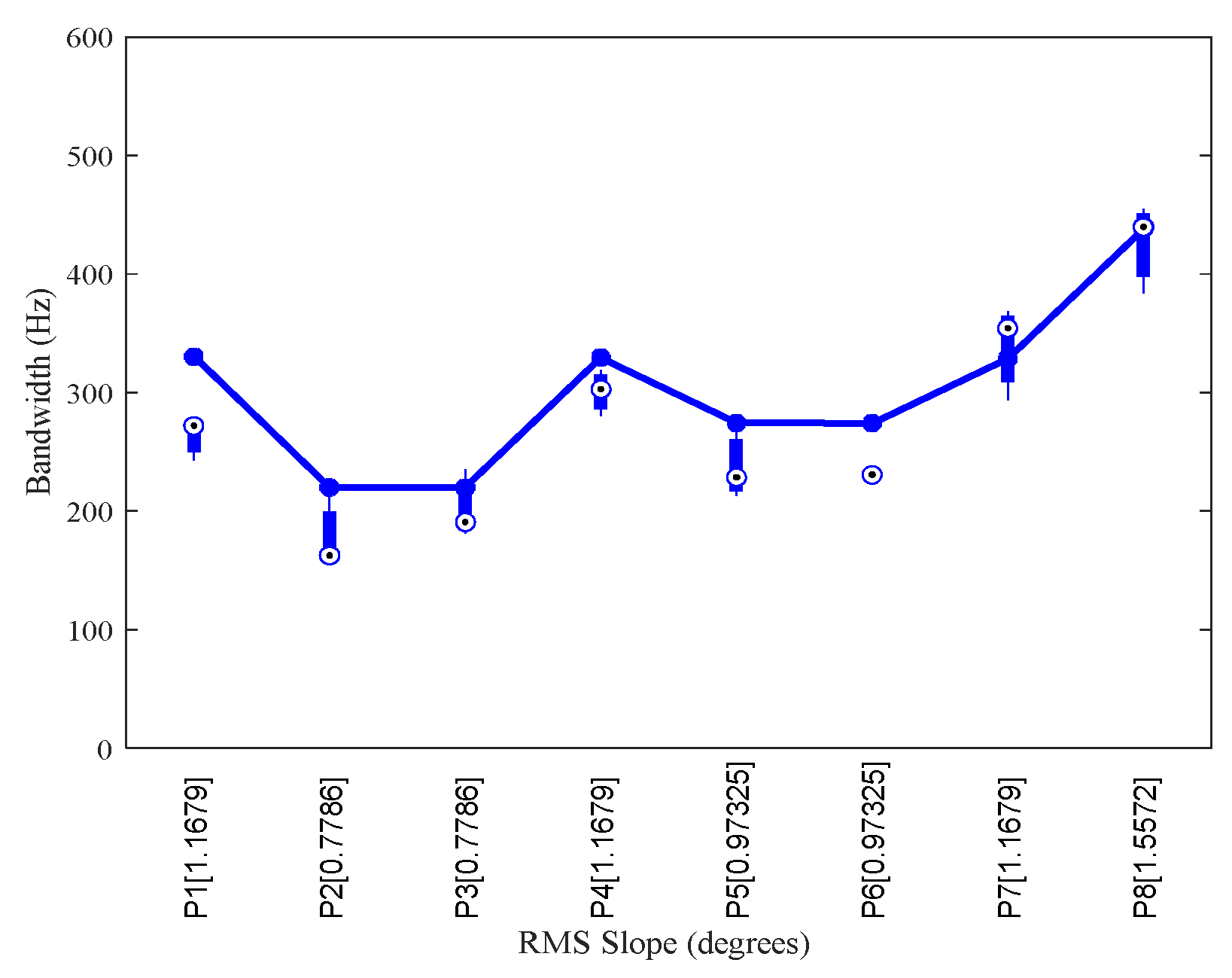
4.2. Case 2: JUICE
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- G. Fjeldbo, Bistatic-radar methods for studying planetary ionospheres and surfaces scientific report no. 2/final. No. NASA-CR-62823. 1964.
- R.A. Simpson, “Spacecraft studies of planetary surfaces using bistatic radar.” IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 31, no. 2 (1993): 465-482. [CrossRef]
- R.A. Simpson, G. L. Tyler, M. Pätzold, and B. Häusler. “Inference of Electrical and Physical Surface Properties from Mars Express Bistatic Radar.” In Seventh International Conference on Mars, vol. 1353, p. 3044. 2007.
- M. Brozovic, B. Butler, J.-L. Margot, S. P. Naidu, T. J. W. Lazio, Planetary bistatic radar, ASPC 517 (2018) 113.
- B.A. Campbell, D. B. Campbell, J. F. Chandler, A. A. Hine, M. C. Nolan, and P. J. Perillat. “Radar imaging of the lunar poles.” Nature 426, no. 6963 (2003): 137-138. [CrossRef]
- M. Pérez-Ayúcar, R. D. Lorenz, N. Floury, R. Prieto-Cerdeira, and J-P. Lebreton. “Bistatic observations of Titan’s surface with the Huygens probe radio signal.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 111, no. E7 (2006). [CrossRef]
- W. Kofman, A. Herique, V. Ciarletti, J. Lasue, A. C. Levasseur-Regourd, S. Zine, and D. Plettemeier. “The interior of 67P/CG comet as seen by CONSERT bistatic radar on ROSETTA, key results and implications.” In European Planetary Science Congress 2017, vol. 11, pp. EPSC2017-203. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Nozette, C. Lichtenberg, P. Spudis, R. Bonner, W. Ort, E. Malaret, M. Robinson, E. Shoemaker, The clementine bistatic radar experiment, Science 274 (5292) (1996) 1495-1498.
- Lichtenberg, Christopher L. Bistatic radar observations of the moon using the Clementine spacecraft and Deep Space Network. The Johns Hopkins University, 2000.
- J.W. Head III, A. R. Peterfreund, J. B. Garvin, and S. H. Zisk. “Surface characteristics of Venus derived from Pioneer Venus altimetry, roughness, and reflectivity measurements.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 90, no. B8 (1985): 6873-6885.
- R.A. Simpson, G. Leonard Tyler, Bernd Häusler, Riccardo Mattei, and Martin Pätzold. “Venus Express bistatic radar: High-elevation anomalous reflectivity.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 114, no. E9 (2009). [CrossRef]
- R.A. Simpson, G. L. Tyler, M. Pätzold, and B. Häusler. “Determination of local surface properties using Mars Express bistatic radar.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 111, no. E6 (2006). [CrossRef]
- R.A. Simpson, G. L. Tyler, M. Pätzold, B. Häusler, S. W. Asmar, and A. K. Sultan-Salem. “Polarization in bistatic radar probing of planetary surfaces: application to Mars Express data.” Proceedings of the IEEE 99, no. 5 (2011): 858-874. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Y. Ying, and K. S. Chen. “Martian topographic roughness spectra and its influence on bistatic radar scattering.” IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 18, no. 11 (2020): 1951-1955. [CrossRef]
- Brighi, G. “Cassini Bistatic Radar Experiments: Preliminary Results on Titan’s Polar Regions” Aerotec. Missili Spaz. 102, 59–76 (2023).
- Poggiali, V., Brighi, G., Hayes, A. G., Nicholson, P. D., MacKenzie, S., Lalich, D. E., Bonnefoy, L. E., Oudrhiri, K., Lorenz, R. D., Soderblom, J. M., Tortora, P., Zannoni, M. “Surface properties of Titan’s seas as revealed by Cassini RSS bistatic radar experiments.”, Nature Communications, accepted, in press. 2024.
- I, Linscott, S. Asmar, M. Bird, C. DeBoy, R. Sepan, A. Stern, M. Vincent et al. “Pluto’s Surface Properties from the New Horizons Uplink Bistatic Radar Experiment.” In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, vol. 2019, pp. P34A-01. 2019.
- E.M. Palmer, E. Heggy, and W. Kofman. “Orbital bistatic radar observations of asteroid Vesta by the Dawn mission.” Nature communications 8, no. 1 (2017): 409. [CrossRef]
- M. Pätzold, B. Häusler, K. Aksnes, J. D. Anderson, S. W. Asmar, J.P. Barriot, M. K. Bird et al. “Rosetta radio science investigations (RSI).” Space science reviews 128 (2007): 599-627. [CrossRef]
- G.G. Peytavi, T. Andert, M. Paetzold, B. Häusler, S. Remus, S. Tellmann, M. K. Bird, and S.W. Asmar. “Processing bistatic radar observations of comet 67P/CG by the RSI experiment aboard Rosetta.” In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, vol. 2018, pp. P51G-2953. 2018.
- Brighi, G., Probing the surface of Ganymede by means of bistatic radar with the JUICE mission, Materials Research Proceedings, Vol. 33, pp 110-117, 2023.
- S.W. Asmar, J. Lazio, D. H. Atkinson, D. J. Bell, J. S. Border, I. S. Grudinin, A. J. Mannucci R. A. Preston, and H. Elliott. “Small spacecraft for planetary atmospheric, surface, and interior structure using radio links.” In 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, pp. 1-8. IEEE, 2018.
- D.J. Bell, A. Fraeman, J. Lazio, and D. C. Nunes. “Opportunistic Bistatic Radar for Mars Helicopter.” In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, vol. 2018, pp. P51D-2918. 2018.
- K. Oudrhiri, N. Rodriguez-Alvarez, Y.M. Yang, N. E. Lay, D. Buccino, D. Shin, E. Podest, and R. Brockers. “Bistatic Radar Experiments with UAV: Qualification and Performance of a Miniaturized Instrument.” In 2021 IEEE Aerospace Conference (50100), pp. 1-12. IEEE, 2021.
- J. Balaram, M. Aung, and M. P. Golombek. “The ingenuity helicopter on the perseverance rover.” Space Science Reviews 217, no. 4 (2021): 56. [CrossRef]
- I, Linscott, S. Asmar, M. Bird, C. DeBoy, R. Sepan, A. Stern, M. Vincent et al. “Pluto’s Surface Properties from the New Horizons Uplink Bistatic Radar Experiment.” In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, vol. 2019, pp. P34A-01. 2019.
- Hagfors, T. Backscattering from an undulating surface with applications to radar returns from the Moon[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(18): 3779-3784.
- J.A. Ogilvy, and H. M. Merklinger. “Theory of wave scattering from random rough surfaces.” (1991): 3382-3382.
- R. Simpson, and G. Tyler. “Radar scattering laws for the lunar surface.” IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 30, no. 3 (1982): 438-449.
- F.T. Ulaby, R. K. Moore, and A. K. Fung. “Microwave remote sensing: Active and passive. Volume 2-Radar remote sensing and surface scattering and emission theory.” (1982).
- G. Rees, The remote sensing data book. Cambridge university press, 1999.
- G.L. Tyler, and D. H. Ingalls. “Functional dependences of bistatic-radar frequency spectra and cross sections on surface scattering laws.” Journal of Geophysical Research 76, no. 20 (1971): 4775-4785. [CrossRef]
- R.A. Simpson, “Highly oblique bistatic radar observations using Mars Global Surveyor.” In Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, p. 1987. 2002.
- H.M. Gunnarsdottir, I. R. Linscott, J. L. Callas, M. D. Cousins, R. A. Simpson, and G. L. Tyler. “Root-mean-square surface slopes of Phoenix landing sites with 75-cm bistatic radar received by Mars Odyssey.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 113, no. E3 (2008).
- A.K. Sultan-Salem, and G. Leonard Tyler. “Hagfors’ law revisited.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 111, no. E6 (2006).
- Grasset, M. K. Dougherty, A. Coustenis, E. J. Bunce, C. Erd, D. Titov, M. Blanc et al. “JUpiter ICy moons Explorer (JUICE): An ESA mission to orbit Ganymede and to characterise the Jupiter system.” Planetary and Space Science 78 (2013): 1-21. [CrossRef]
- JUICE - Jupiter Icy moons Explorer Consolidated Report on Mission Analysis (CReMA) v.5, ESA Document.
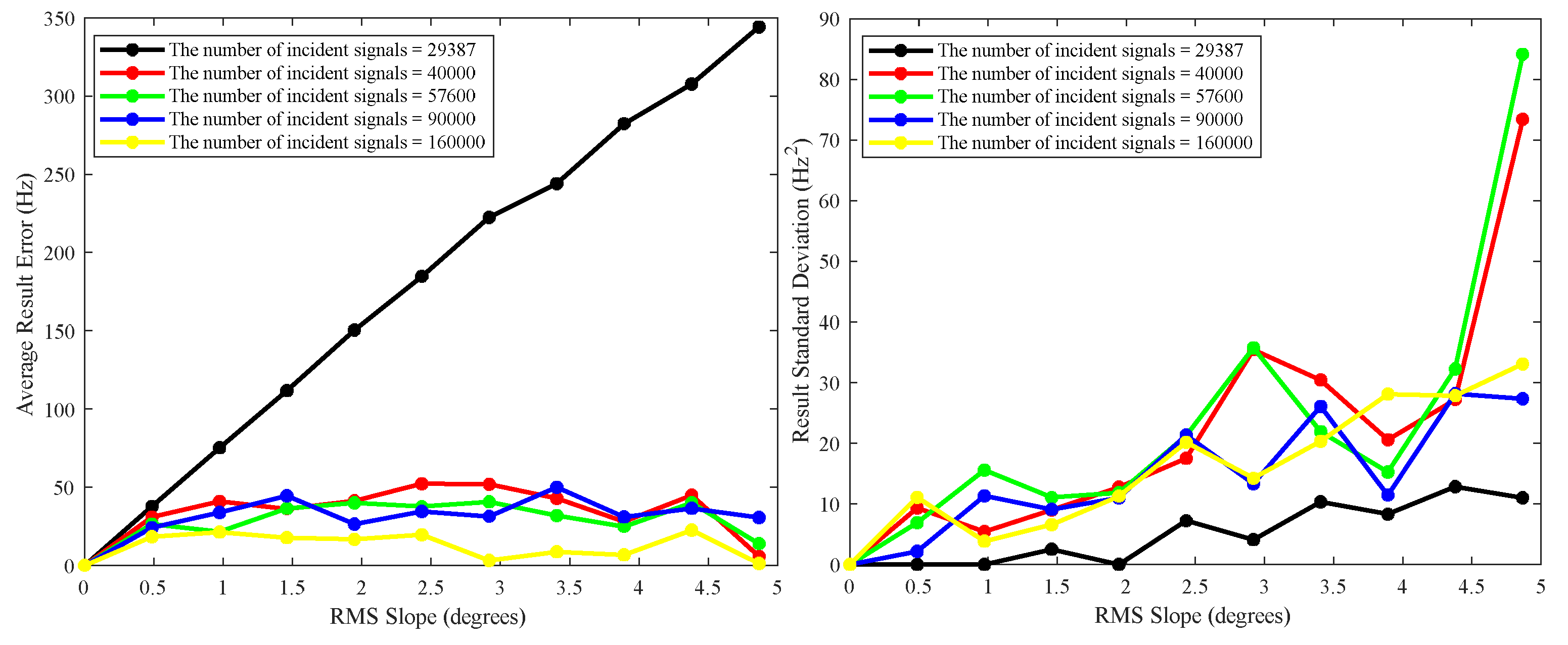
| rms H (km) | ζ with 29387 grid points | ζ with 40000 grid points | ζ with 57600 grid points | ζ with 90000 grid points | ζ with 160000 grid points (degrees) | ζ computed by Eq. (3) |
| 0 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| 0.02 | 0.11136(77.12%) | 0.5632(15.73%) | 0.52963(8.84%) | 0.49545(1.81%) | 0.48783(0.25%) | 0.48663 |
| 0.04 | 0.22181(77.21%) | 1.1308(16.19%) | 1.0739(10.34%) | 0.99048(1.77%) | 0.97412(0.09%) | 0.97325 |
| 0.06 | 0.33319(77.18%) | 1.694(15.62%) | 1.5954(9.28%) | 1.4849(1.71%) | 1.4594(0.03%) | 1.4599 |
| 0.08 | 0.44457(77.16%) | 2.2535(15.77%) | 2.1339(9.63%) | 1.9785(1.64%) | 1.9483(0.09%) | 1.9465 |
| 0.1 | 0.54651(77.54%) | 2.8279(16.21%) | 2.6648(9.51%) | 2.4807(1.96%) | 2.4376(0.18%) | 2.4331 |
| 0.12 | 0.66127(77.35%) | 3.4209(17.16%) | 3.1748(8.73%) | 2.9608(1.40%) | 2.8965(0.80%) | 2.9198 |
| 0.14 | 0.77938(77.12%) | 3.9271(15.29%) | 3.7156(9.08%) | 3.4624(1.64%) | 3.4036(0.08%) | 3.4064 |
| 0.16 | 0.89038(77.15%) | 4.4841(15.18%) | 4.2575(9.36%) | 3.9631(1.80%) | 3.8912(0.20%) | 3.893 |
| 0.18 | 1.0112(76.91%) | 5.0768(15.92%) | 4.7752(9.03%) | 4.4374(1.32%) | 4.3644(0.35%) | 4.3796 |
| 0.2 | 1.1042(77.31%) | 5.6252(15.60%) | 5.3022(8.96%) | 4.9312(1.33%) | 4.8398(0.54%) | 4.8663 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





