Submitted:
19 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
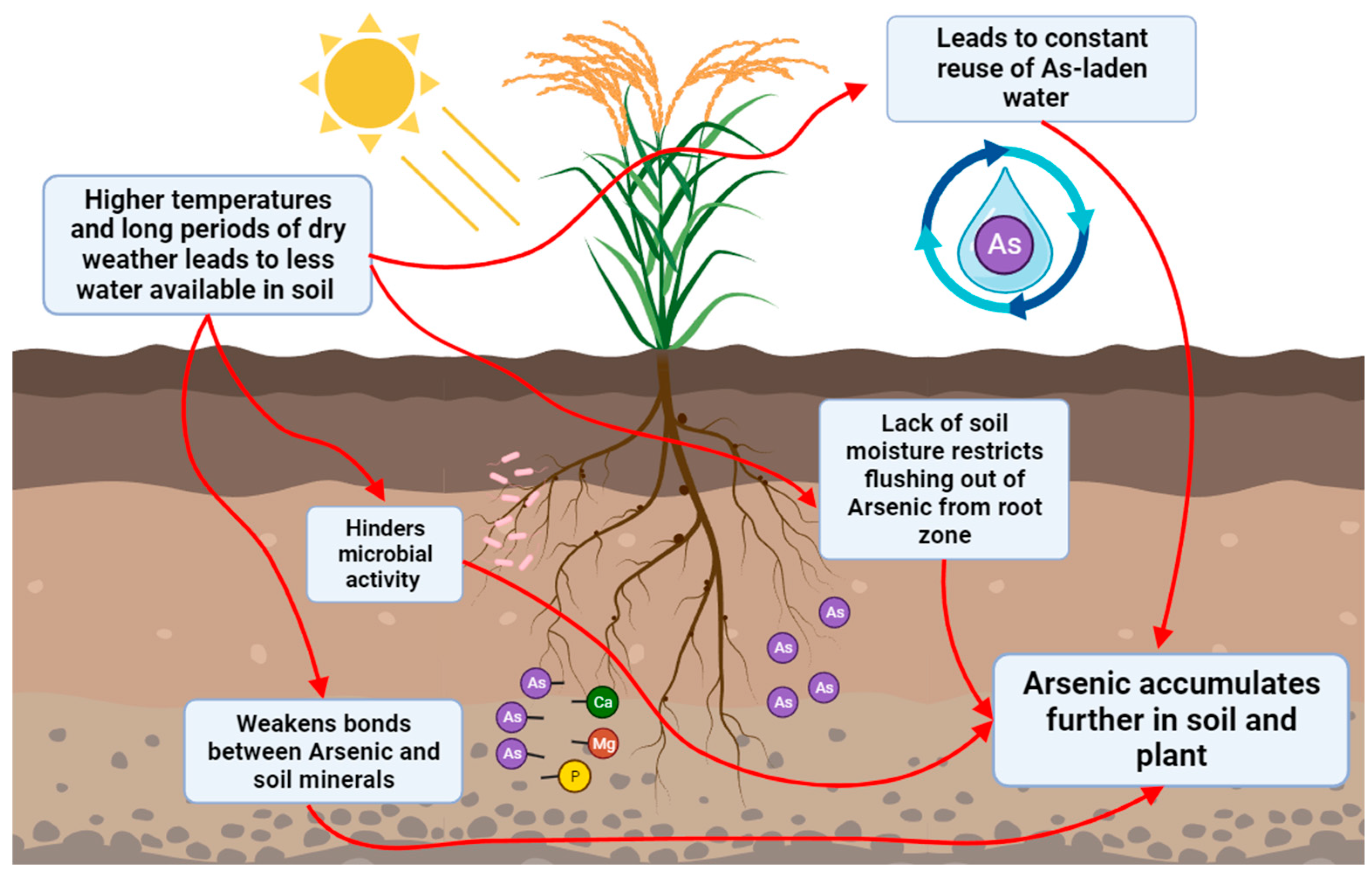
Introduction
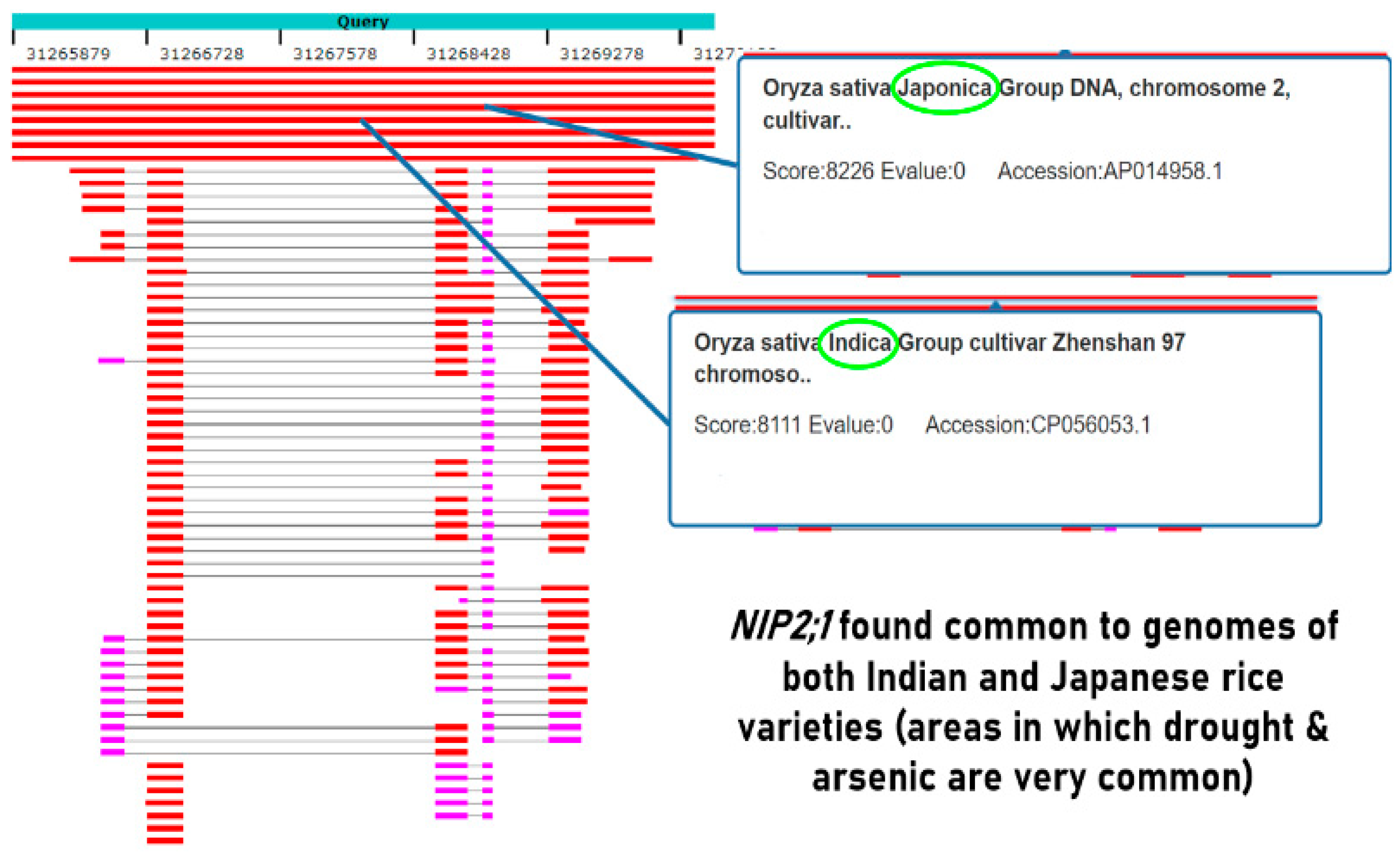
Methods
|
Positive control (P) Soil with arsenic & no plants |
Negative control (N1): No arsenic in soil & non-transgenic plant |
|
Negative control (N2) Soil with arsenic & non-transgenic plant |
Experimental group: Soil with arsenic & transgenic plants with NIP & PIP genes |
Results
Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Muehe, E. M., Wang, T., Kerl, C. F., Planer-Friedrich, B., & Fendorf, S. (2019). Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic. Nature Communications, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Satyapal, G. K., & Kumar, N. (2021). Arsenic: Source, distribution, toxicity and bioremediation. Arsenic Toxicity: Challenges and Solutions, 153-163. [CrossRef]
- Panda, D., Mishra, S. S., & Behera, P. K. (2021). Drought tolerance in rice: Focus on recent mechanisms and approaches. Rice Science, 28(2), 119-132. [CrossRef]
- Selvi, Adikesavan. (2019). Integrated Remediation Processes Toward Heavy Metal Removal/Recovery From Various Environments. Front. Environ. Sci., Volume 7, 22 May 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cai, L., Liu, G., Rensing, C., & Wang, G. (2009). Genes involved in arsenic transformation and resistance associated with different levels of arsenic-contaminated soils. BMC Microbiology,9(1). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jian, and Barry P. Rosen. “Biosensors for Inorganic and Organic Arsenicals.” Biosensors, vol. 4, no. 4, 2014, pp. 494–512. [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, J., Ishikawa, F., Yamaguchi, T., Uemura, M., & Maeshima, M. (2005). Identification of 33 rice Aquaporin genes and analysis of their expression and function. Plant and Cell Physiology, 46(9), 1568-1577. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbinski, L. D., Rosen, B. P., & Chen, J. (2019). Pathways of arsenic uptake and efflux. Environment International, 126, 585-597. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, Tayebeh, and Amin Mojiri. “Arsenic Uptake and Accumulation Mechanisms in Rice Species.” Plants, vol. 9, no. 2, 2020, p. 129. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Han, Y., Cao, Y., Zhu, Y., Rathinasabapathi, B., & Ma, L. Q. (2017). Arsenic transport in rice and biological solutions to reduce arsenic risk from rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8. [CrossRef]
- Sayers EW, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Canese K, Chan J, Comeau DC, Connor R, Funk K, Kelly C, Kim S, Madej T, Marchler-Bauer A, Lanczycki C, Lathrop S, Lu Z, Thibaud-Nissen F, Murphy T, Phan L, Skripchenko Y, Tse T, Wang J, Williams R, Trawick BW, Pruitt KD, Sherry ST. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D20-D26. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- 1Shackel, K. (2011). A plant-based approach to deficit irrigation in trees and vines. HortScience, 46(2), 173-177. [CrossRef]

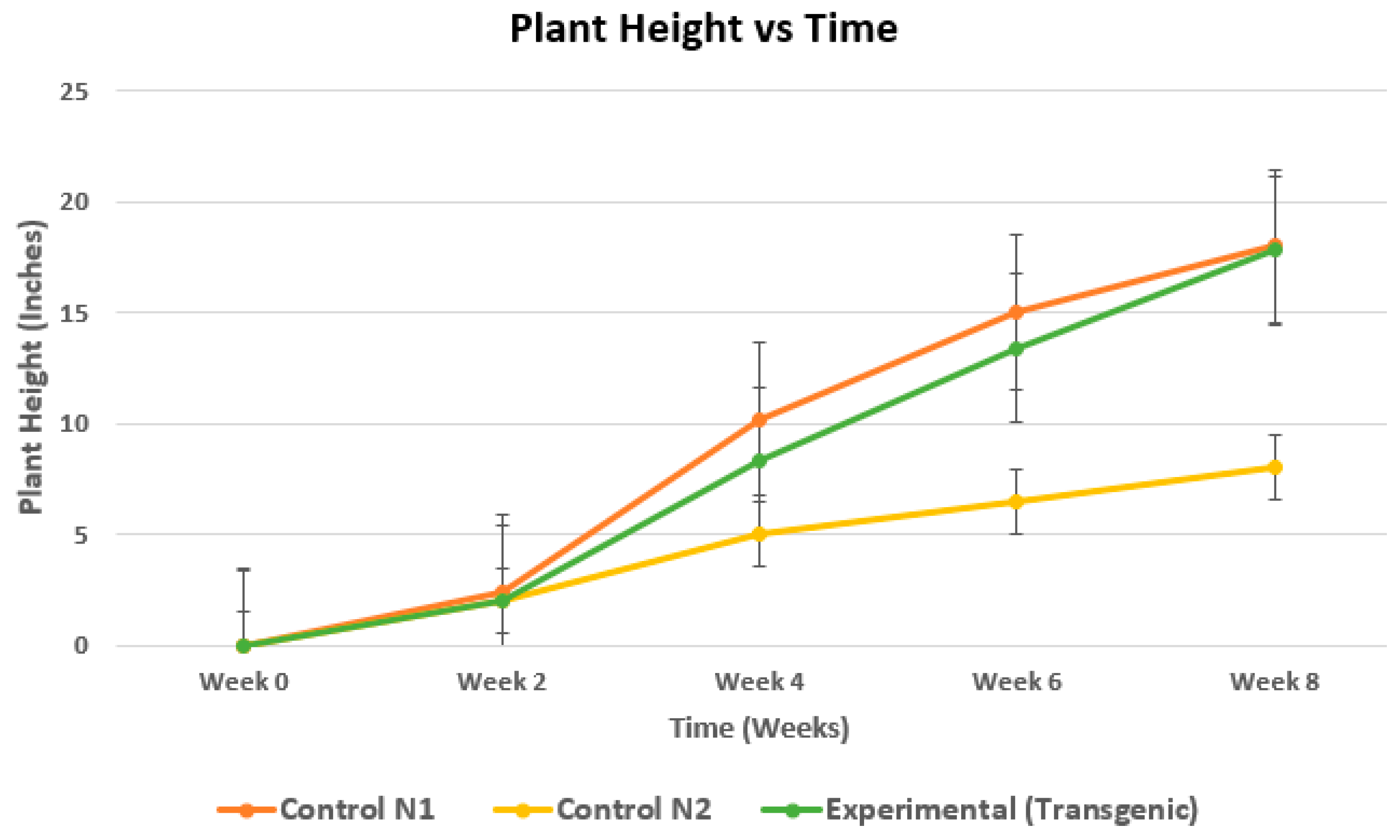
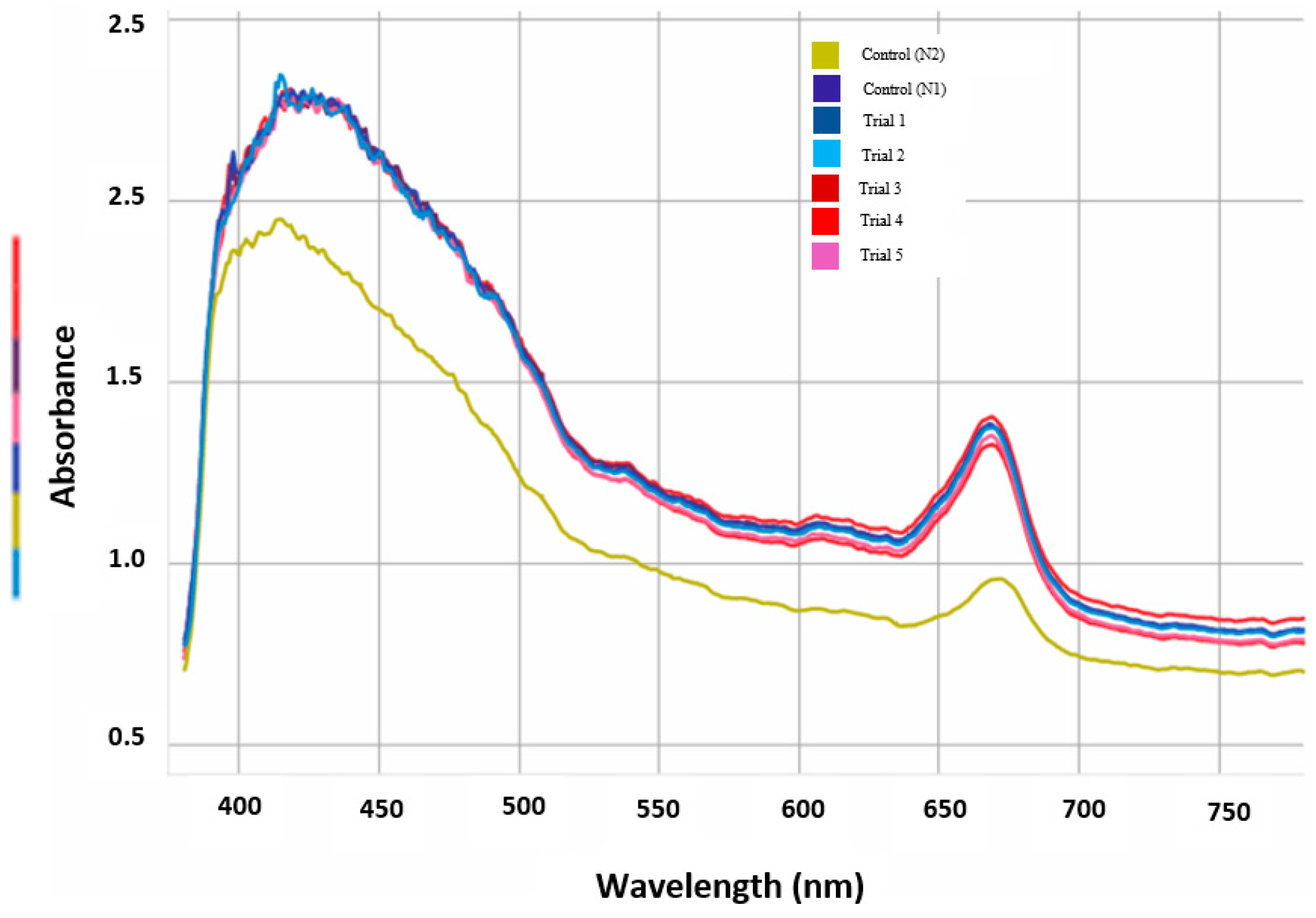
| Week 0 | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (P) | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 25 ppm |
| Control N2 | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 20 ppm | 15 ppm |
| Transgenic | 25 ppm | 25 ppm | 15 ppm | 15 ppm | 5 ppm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




