Submitted:
17 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and D-Dimer Assay
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Patients
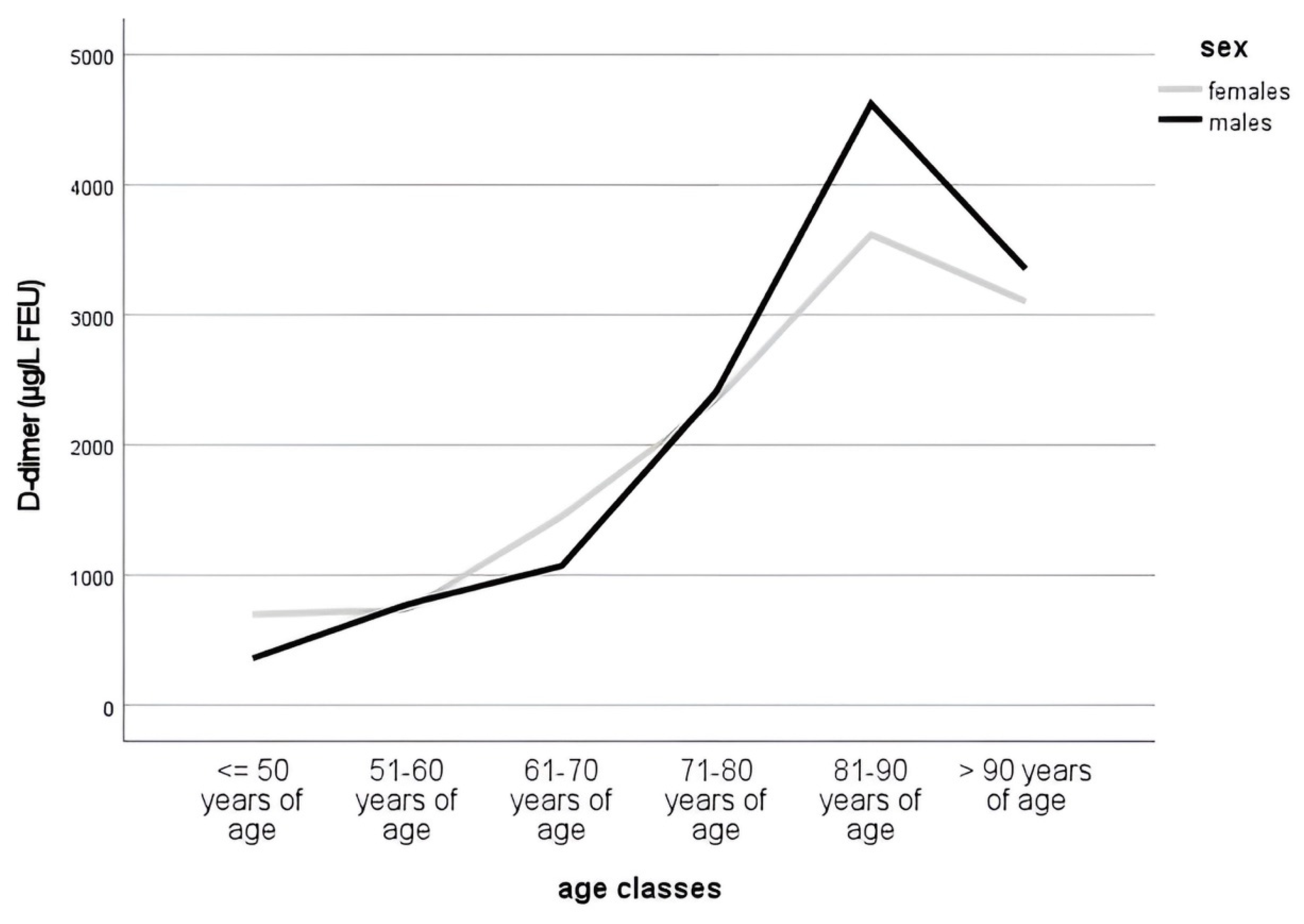
3.2. D-Dimer Levels during Aging
3.3. D-Dimer Levels and Pulmonary Embolism
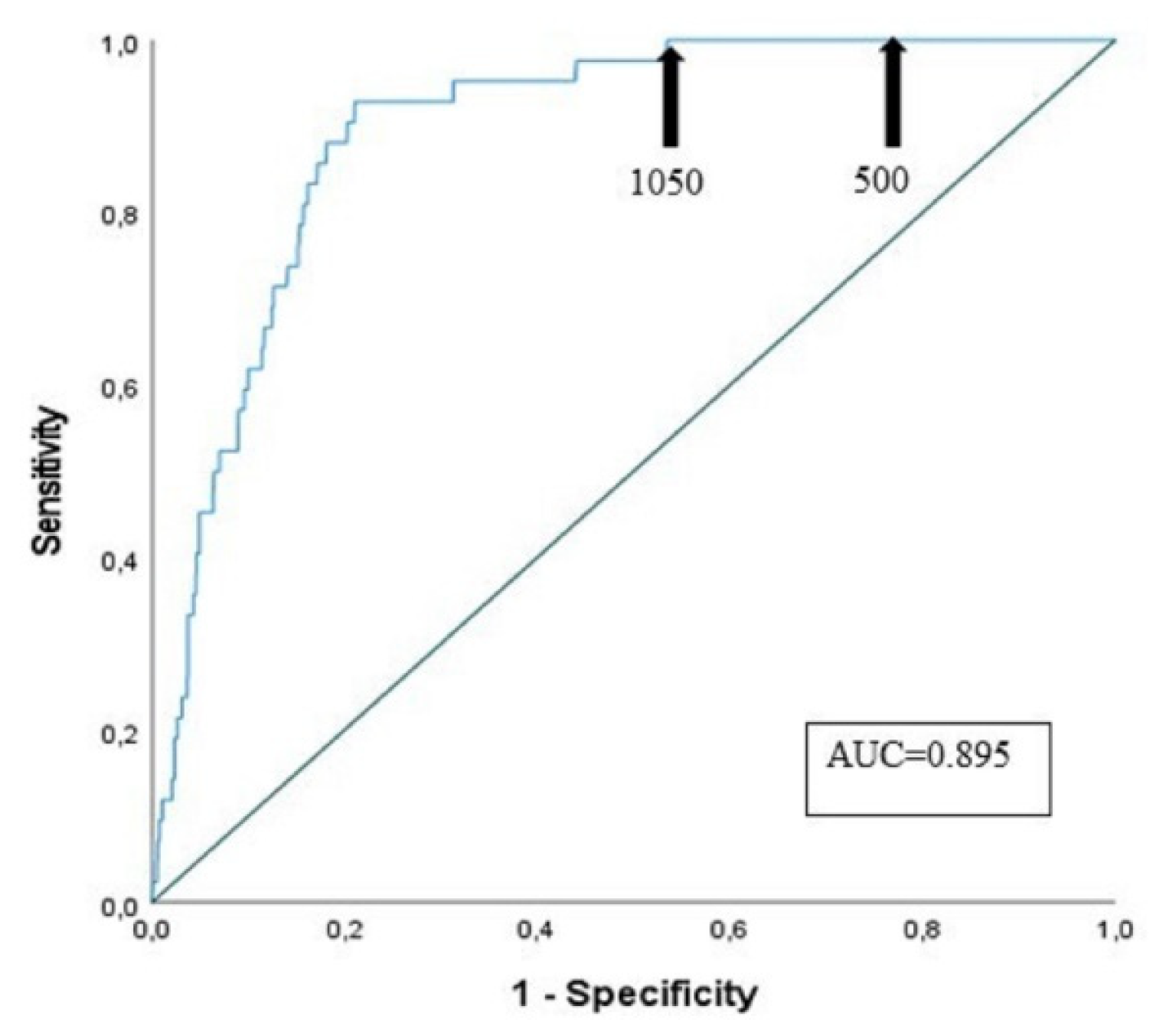
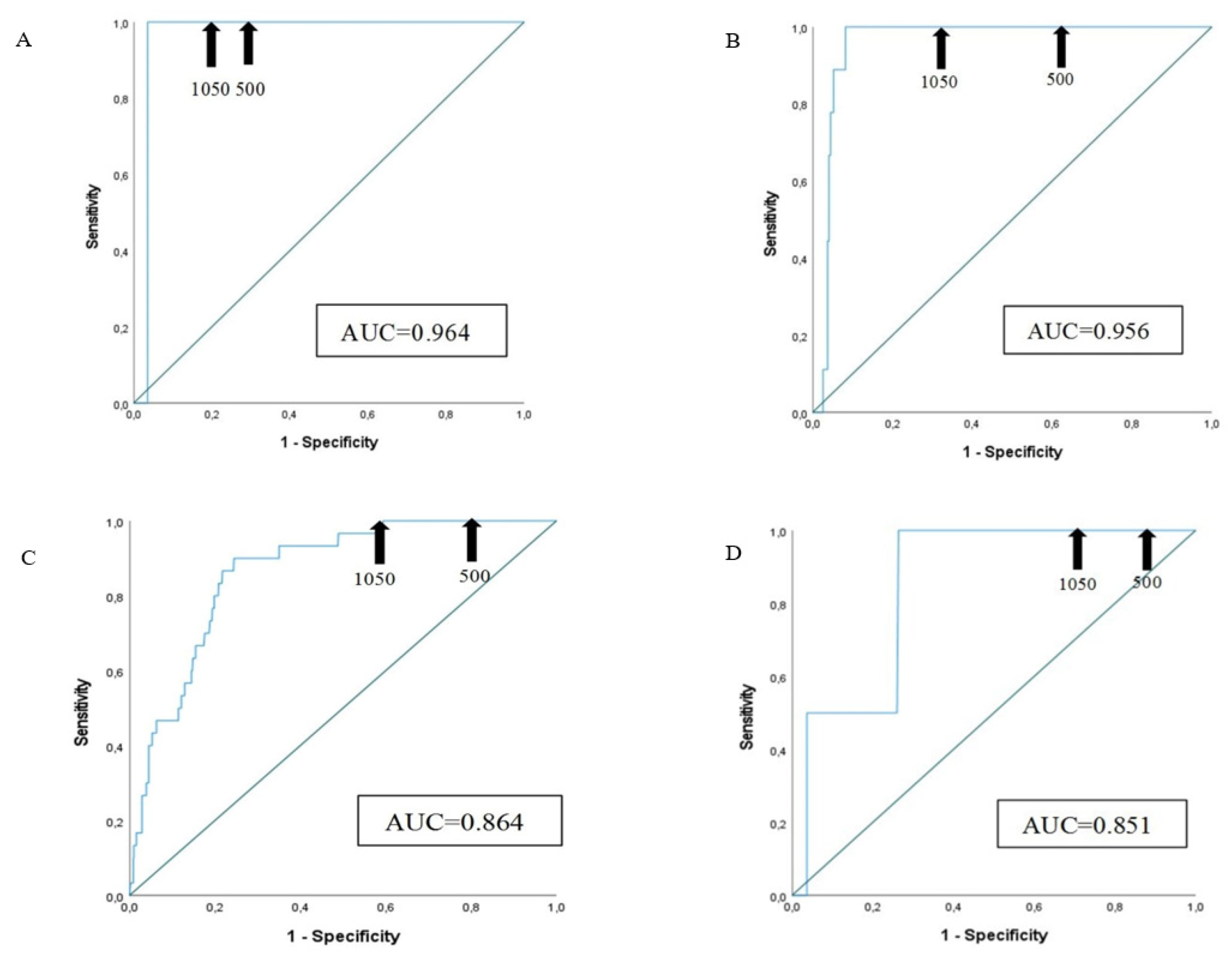
3.4. Sensitivity and Specificity of D-Dimer Assay at Different Cut-Offs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [ADC] | age adjusted DD cut-off level |
| AUC | areas under the curve |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| CHF | Congestive Heart Failure |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| DD | D-dimer |
| DIC | disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| GECD | Geriatric Emergency Care Department |
| HgB | Hemoglobin |
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| PTP | pretest clinical probability |
| RBC | red blood cell |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
| WBC | White blood cell |
References
- Ho, K.M.; Litton, E. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in hospitalized elderly patients: Time to consider a ‘MUST’ strategy. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2011, 8, 114–120f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Wendelboe, A.; Weitz, J.I. ISTH Steering Committee for World Thrombosis Day. Thrombosis: a major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014; 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowska, M.; Thornton, M.; Creese, B.; Velayudhan, L.; Aarsland, D.; Ballard, C.; Tsamakis, K.; Stewart, R.; Mueller, C. Implications of Adverse Outcomes Associated with Antipsychotics in Older Patients with Dementia: A 2011-2022 Update. Drugs Aging 2023, 40, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, A.B.; van Houwelingen, H.C.; Kieft, G.J.; Pattynama, P.M. Prevalence of deep vein thrombosis in suspected and proven pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. Br J Radiol. 1998, 71, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, L.; Zuin, M.; Mahmoudpour, S.H.; Zuliani, G.; Zonzin, P.; Barco, S.; Roncon, L. Aggiornamento sui dati relativi alla mortalità da embolia polmonare in Italia (2003-2015). [An update on pulmonary embolism-related mortality in Italy (2003-2015)]. G Ital Cardiol. (Rome), 2020; 21, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageno, W.; Squizzato, A.; Garcia, D.; Imberti, D. Epidemiology and risk factors of venous thromboembolism. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006, 32, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, A.S.; Greenberg, J.O.; Qaseem, A.; Denberg, T.D.; Fitterman, N.; Schuur, J.D. Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Evaluation of Patients With Suspected Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Best Practice Advice From the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 163, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedullo, P.F.; Tapson, V.F. Clinical practice. The evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2003, 349, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.M. D-dimer assays in diagnosis and management of thrombotic and bleeding disorders. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012, 38, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Cervellin, G.; Casagranda, I.; Morelli, B.; Testa, S.; Tripodi, A. D-dimer testing for suspected venous thromboembolism in the emergency department. Consensus document of AcEMC, CISMEL, SIBioC, and SIMeL. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014; 52, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, F.; Andras, A.; Welch, K.; Sheares, K.; Keeling, D.; Chappell, F.M. D-dimer test for excluding the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 2016, CD010864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; Kucher, N.; Lang, I.M.; Lankeit, M.; Lorusso, R.; Mazzolai, L.; Meneveau, N.; Ní Áinle, F.; Prandoni, P.; Pruszczyk, P.; Righini, M.; Torbicki, A.; Van Belle, E.; Zamorano, J.L. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020; 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tacey, M.; Ho, P. Retrospective review of D-dimer testing for venous thrombosis recurrence risk stratification: is this a useful test in the real world? J Thromb Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douketis, J.; Tosetto, A.; Marcucci, M.; Baglin, T.; Cushman, M.; Eichinger, S.; Palareti, G.; Poli, D.; Tait, R.C.; Iorio, A. Patient-level meta-analysis: effect of measurement timing, threshold, and patient age on ability of D-dimer testing to assess recurrence risk after unprovoked venous thromboembolism. Ann Intern Med. 2010, 153, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.S.; Anderson, D.R.; Rodger, M.; Stiell, I.; Dreyer, J.F.; Barnes, D.; Forgie, M.; Kovacs, G.; Ward, J.; Kovacs, M.J. Excluding pulmonary embolism at the bedside without diagnostic imaging: management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism presenting to the emergency department by using a simple clinical model and D-dimer. Ann Int Med. 2001, 135, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, J.R.; Xing, J.L.; Gu, P.; Zhu, B.F. Comparison of the Wells score with the revised Geneva score for assessing suspected pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2016; 41, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Lippi, G.; Roy, P.M.; Chatelain, B.; Jacqmin, H.; Ten Cate, H.; Mullier, F. D-dimer: Preanalytical, analytical, postanalytical variables, and clinical applications. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2018, 55, 548–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talon, L.; Fourneyron, V.; Trapani, A.; Pereira, B.; Sinegre, T.; Lebreton, A. Analytical performance of a new immunoturbidimetric D-dimer assay and comparison with available assays. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022, 6, e12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Franchini, M. Pathogenesis of venous thromboembolism: When the cup runneth over. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008, 34, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, M. Epidemiology and risk factors for venous thrombosis. Semin Hematol. 2007, 44, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righini, M.; Van Es, J.; Den Exter, P.L.; Roy, P.M.; Verschuren, F.; Ghuysen, A.; Rutschmann, O.T.; Sanchez, O.; Jaffrelot, M.; Trinh-Duc, A.; Le Gall, C.; Moustafa, F.; Principe, A.; Van Houten, A.A.; Ten Wolde, M.; Douma, R.A.; Hazelaar, G.; Erkens, P.M.; Van Kralingen, K.W.; Grootenboers, M.J.; Durian, M.F.; Cheung, Y.W.; Meyer, G.; Bounameaux, H.; Huisman, M.V.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Le Gal, G. Age-adjusted D-dimer cutoff levels to rule out pulmonary embolism: the ADJUST-PE study. JAMA. 2014, 311, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douma, R.A.; Tan, M.; Schutgens, R.E.; Bates, S.M.; Perrier, A.; Legnani, C.; Biesma, D.H.; Ginsberg, J.S.; Bounameaux, H.; Palareti, G.; Carrier, M.; Mol, G.C.; Le Gal, G.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Righini, M. Using an age-dependent D-dimer cut-off value increases the number of older patients in whom deep vein thrombosis can be safely excluded. Haematologica. 2012, 97, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, F.J.; Schutgens, R.E.; Biesma, D.H. An age-adapted approach for the use of D-dimers in the exclusion of deep venous thrombosis. Am J Hematol. 2009, 84, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, P.L.; Theakston, E.; Ahmed, J.; Ockelford, P. D-dimer concentration increases with age reducing the clinical value of the D-dimer assay in the elderly. Intern Med J. 2007, 37, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, L.; Valente, M.J.; Rocha, S.; Coimbra, S.; Catarino, C.; Lousa, I.; Bronze-da-Rocha, E.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Sameiro-Faria, M.D.; Oliveira, J.G.; Madureira, J.; Fernandes, J.C.; Miranda, V.; Nunes, J.P.L.; Santos-Silva, A. Age-Related Changes in Clinical and Analytical Variables in Chronic Hemodialyzed Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candore, G.; Balistreri, C.R.; Listì, F.; Grimaldi, M.P.; Vasto, S.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Franceschi, C.; Lio, D.; Caselli, G.; Caruso, C. Immunogenetics, gender, and longevity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006, 1089, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.S.; Yende, S. Effects of Aging on Inflammation and Hemostasis through the Continuum of Critical Illness. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dutton, J.; Dachsel, M.; Crane, R. Can the use of an age-adjusted D-dimer cut-off value help in our diagnosis of suspected pulmonary embolism? Clin Med (Lond). 2018, 18, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobes, J.; Messow, C.M.; Khan, M.; Hrobar, P.; Isles, C. Age-adjusted D-dimer excludes pulmonary embolism and reduces unnecessary radiation exposure in older adults: retrospective study. Postgrad Med J. 2017, 93, 93,420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righini, M.; Nendaz, M.; Le Gal, G.; Bounameaux, H.; Perrier, A. Influence of age on the cost-effectiveness of diagnostic strategies for suspected pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2007, 5, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All n=1617 |
Males n=655 |
Females n=962 |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 85 [80-89] | 84 [80-88] | 85 [81-90] | ≤0.01 |
| D-dimer (µg/L FEU) | 1200 [550-2990] | 1180 [510-3160] | 1205 [580-2870] | 0.765 |
| Pulmonary embolism (Yes/No) | 42/1575 | 14/641 | 28/934 | 0.337 |
| WBC x 103/µL | 8.4 [6.6-11.2] | 8.4 [6.6-11.2] | 8.40 [6.60-11.29] | 0.677 |
| RBC x 106/µL | 4.21 [3.76-4.60] | 4.21 [3.74-4.65] | 4.20 [3.77-4.57] | 0.559 |
| HgB (g/dL) | 12.5 [11.1-13.7] | 12.9 [11.2-14.1] | 12.3 [11.1-13.4] | ≤0.01 |
| Platelets x 103/µL | 215.0 [171.0-268.7] | 198.0 [159.5-242.0] | 228 [182-281] | ≤0.01 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137 [134-139] | 136 [134-139] | 137 [133-139] | 0.750 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.0 [3.7-4.4] | 4.1 [3.8-4.4] | 4.0 [3.7-4.4] | 0.056 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 2.91 [0.59-8.39] | 3.61 [0.81-8.77] | 2.05 [0.50-8.13] | 0.047 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 48 [36-75] | 53 [38-80] | 46 [35-71] | ≤0.01 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 [0.8-1.5] | 1.2 [0.9-1.7] | 1.0 [0.8-1.3] | ≤0.01 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 54 [36-75] | 55 [36-76] | 53 [35-73] | 0.423 |
| Age classes | All n=1617 |
Males n=655 |
Females n=962 |
|---|---|---|---|
| <= 50 years n (%) | 30 (1.9) | 14 (2.1) | 16 (1.7) |
| 51-60 years n (%) | 29 (1.8) | 12 (1.8) | 17 (1.8) |
| 61-70 years n (%) | 85 (5.3) | 47 (7.2) | 38 (4.0) |
| 71-80 years n (%) | 277 (17.1) | 128 (19.5) | 149 (15.5) |
| 81-90 years n (%) | 921 (57) | 374 (57.1) | 547 (56.9) |
| >= 91 years n (%) | 275 (17) | 80 (12.2)* | 195 (20.3)* |
|
All median [IQR] |
Males median [IQR] |
Females median [IQR] |
|
| Pulmonary embolism (yes) |
8910 [4195-15817.5] | 14970 [6440-21612.5] | 5830 [4142.5-13202.5] |
| Pulmonary embolism (no) |
1160 [550-2740] | 1160 [505-2975] | 1180 [560-2615] |
| P | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 |
|
D-dimer levels median [IQR] |
P |
|
| WBC<= 9 | 950 [450-2110] | ≤0.01 |
| WBC> 9 | 1700 [740-4050] | |
| PCR<= 0.5 | 800 [460-1990] | ≤0.01 |
| PCR> 0.5 | 2030 [950-4592.5] | |
| eGFR<= 30 | 2030 [930-4300] | ≤0.01 |
| eGFR> 30 | 1090 [510-2550] |
| Age classes | Patients (n of PE) |
Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) Cut-off 500 µg/L FEU |
Specificity (%) Cut-off ADC= (patient’s agex0.01) µg/L FEU |
Specificity (%) Cut-off (1050 µg/L FEU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <= 50 years | 30 (0) | - | - |
- | - |
| 51-60 years | 29 (0) | - | - |
- | - |
| 61-70 years | 85 (1) | 100.0 | 65.5 | 72.6 | 76.2 |
| 71-80 years | 277 (9) | 100.0 | 33.6 | 51.5 | 64.2 |
| 81-90 years | 921 (30) | 100.0 | 16.3 | 34.0 | 40.6 |
| >= 91 years | 275 (2) | 100.0 | 9.9 | 28.2 | 30.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





