Submitted:
17 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Diversity of the Marine Fish Gut Microbiome
| FISH SPECIES | Sample | Predominant Phyla | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Gadus morhua (Atlantic Cod) |
Intestinal contents |
Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, Bacillota |
[39] |
|
Siganus fuscescens (Mottled spinefoot rabbitfish) |
Intestinal contents |
Pseudomonadota, Bacillota, Bacteroidota, Fusobacteriota, Mycoplasmatota, Cyanobacteriota |
[40] |
| Various White Sea (arctic) fish |
Posterior intestine |
Pseudomonadota, Bacillota, Actinomycetota, Bacteroidota, Mycoplasmatota, Fusobacteriota |
[41] |
| Various Mediterranean fish | Midgut | Pseudomonadota, Bacillota, Bacteroidota, Actinobacteriota, Patescibacteria, Fusobacteriota, Planctomycetota, and Dependentiae |
[42] |
| Coastal fish of Hong Kong | Gastrointestinal contents | Pseudomonadota, Bacillota, Mycoplasmatota | [30] |
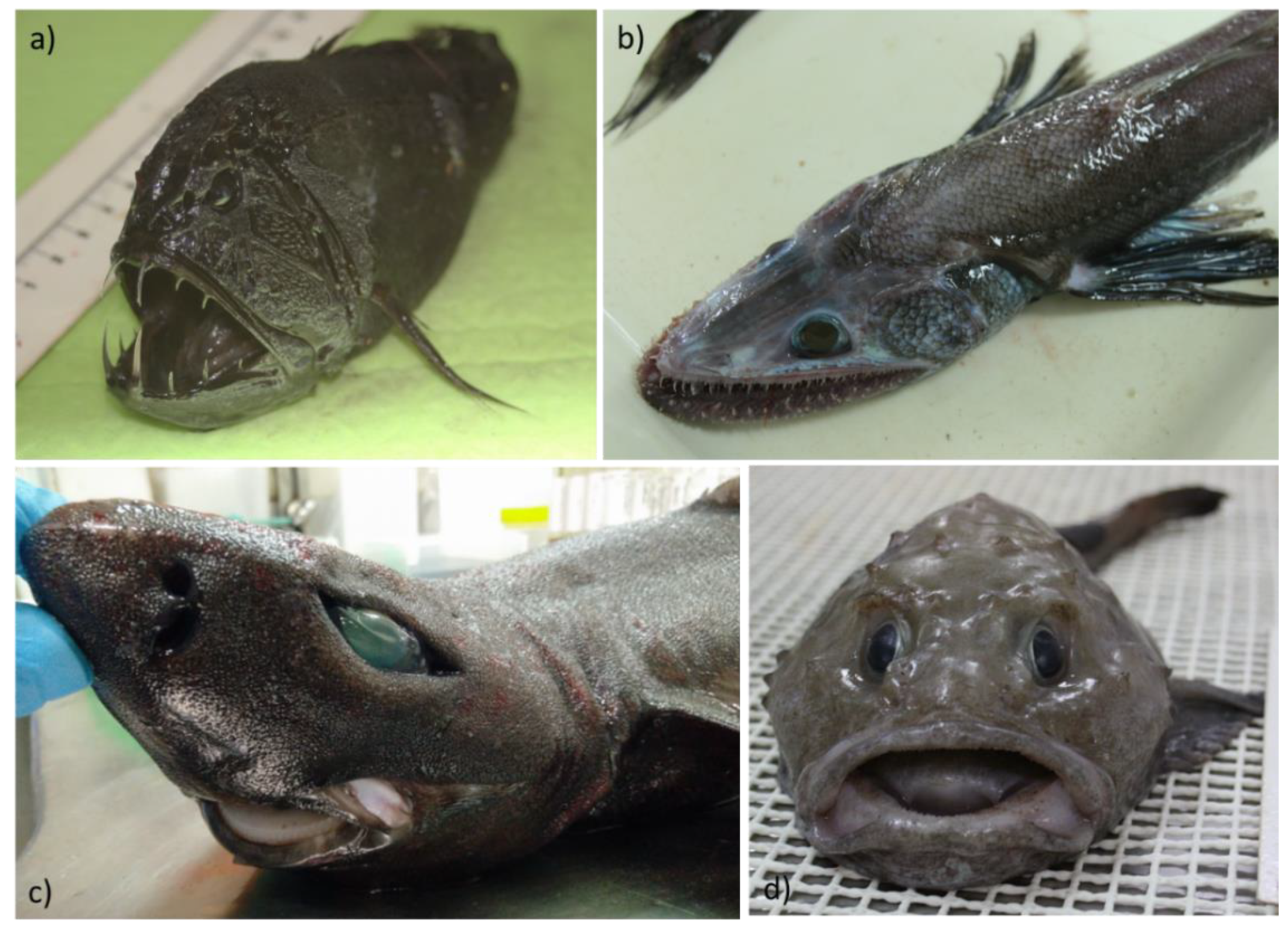
| Various deep-sea fish of Atlantic Ocean | Intestinal contents |
Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, Bacillota, Actinomycetota, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Euryarchaeota, Spirochaetes |
[31] |
| Centroscyllium fabricii (Black dogfish shark) | Gut contents | Actinomycetota, Pseudomonadota, Acidobacteriota (Acidobacteria), Bacillota, Chloroflexota | [43] |
| Benthobatis moresbyi (Dark Blind Ray) | Gut contents | Actinomycetota, Pseudomonadota, Acidobacteriota, Chloroflexota, Bacillota | [38] |
| Fish | Sample | Abundant genera | Abundant Families | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centroscyllium fabricii(Black dogfish shark) | Gut contents | Acinetobacter, Thalassobacillus, Alteromonas, Leeuwenhoekiella, Corynebacterium, Pseudonocardia, Pseudomonas | NR | [43] |
| Benthobatis moresbyi(Dark Blind Ray) | Gut contents | Acinetobacter | Moraxellaceae, Koribacteraceae, Nitrospiraceae | [38] |
| White Sea (arctic) fish | Posterior intestine | Streptococcus, Sphingomonas, Micrococcus, Chthoniobacter, Pseudomonas, Corynebacterium, Staphylococcus, Acinetobacter, Propionibacterium, Vibrio, Photobacterium, Bacillus | Moraxellaceae, Vibrionaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Corynebacteriaceae, Micrococcaceae | [41] |
| Various Mediterranean fish | Midgut | Pseudoalteromonas, Bradyrhizobium, Diaphorobacter, Mycoplasma, Clostridium, Thaumasiovibrio, Microbulbifer | Xanthobacteraceae, Comamonadaceae, Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Clostridiaceae, Vibrionaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Mycoplasmataceae, Flavobacteriaceae, and Peptostreptococcaceae | [42] |
| Various Antarctic fish | Rhodococcus, Thermus, Acinetobacter, Propionibacterium, Streptococcus, and Mycoplasma | NR | [33] | |
| Coastal fish of Hong Kong | Gastrointestinal contents | Clostridium, Photobacterium, Ralstonia, Acinetobacter, Thermus, Ralstonia, | NR | [30] |
3. Bacteriocins from Marine Fish Gut Microbiota
3.1. Bacteriocins from LAB
3.2. Bacteriocins from Bacilli
3.3. Bacteriocins from Actinobacteria
4. ‘Extreme’ Marine Environment Impact on Microbial Products
5. Applications of Marine Fish -Derived Bacteriocins
6. Challenges, Metagenomics and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenaway SF, Sullivan KD, Umfress SH, Beittel AB, Wagner KD. Revised depth of the Challenger Deep from submersible transects; including a general method for precise, pressure-derived depths in the ocean. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 2021;178:103644. [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration USDoC. Layers of the Ocean. https://www.noaa.gov/jetstream/ocean/layers-of-ocean [accessed March 28, 2023.
- Somero GN. Biochemical ecology of deep-sea animals. Experientia, journal article 1992;48(6):537-543. [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou E. Therapeutic properties and uses of marine invertebrates in the ancient Greek world and early Byzantium. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2010;130(2):237-247. [CrossRef]
- 2023. Approved Marine Drugs. https://www.marinepharmacology.org/approved [accessed August 14, 2023.
- Collaborators AR. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. The Lancet; 2022. p. 629-655.
- Frieri M, Kumar K, Boutin A. Antibiotic resistance. Journal of Infection and Public Health 2017;10(4):369-378.
- Mayer AMS, Guerrero AJ, Rodríguez AD, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Nakamura F et al. Marine Pharmacology in 2014–2015: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, Antiviral, and Anthelmintic Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Marine Drugs 2020;18(1):5. [CrossRef]
- Mayer AMS, Guerrero AJ, Rodríguez AD, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Nakamura F et al. Marine Pharmacology in 2016–2017: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Marine Drugs 2021;19(2):49. [CrossRef]
- Mayer AMS, Pierce ML, Howe K, Rodríguez AD, Taglialatela-Scafati O et al. Marine pharmacology in 2018: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Pharmacological Research 2022;183:106391. [CrossRef]
- Halloran K, Underwood MA. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Early Human Development 2019;135:58-65.
- Wang L, Ravichandran V, Yin Y, Yin J, Zhang Y. Natural Products from Mammalian Gut Microbiota. Trends in Biotechnology 2019;37(5):492-504. [CrossRef]
- Wanka KM, Damerau T, Costas B, Krueger A, Schulz C et al. Isolation and characterization of native probiotics for fish farming. BMC microbiology 2018;18(1):119-119. [CrossRef]
- Butt RL, Volkoff H. Gut Microbiota and Energy Homeostasis in Fish. Frontiers in endocrinology 2019;10:9-9. [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Powder Milk and Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. 2001.
- Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2005;3(10):777-788.
- Montalbán-López M, Scott TA, Ramesh S, Rahman IR, van Heel AJ et al. New developments in RiPP discovery, enzymology and engineering. Natural Product Reports, 10.1039/D0NP00027B 2021;38(1):130-239.
- Nissen-Meyer J, Rogne P, Oppegard C, Haugen SH, Kristiansen EP. Structure-Function Relationships of the Non-Lanthionine-Containing Peptide (class II) Bacteriocins Produced by Gram-Positive Bacteria. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 2009;10(1):19-37.
- Cotter PD, Ross RP, Hill C. Bacteriocins — a viable alternative to antibiotics? Nature Reviews Microbiology 2013;11(2):95-105.
- Egerton S, Culloty S, Whooley J, Stanton C, Ross RP. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Frontiers in microbiology 2018;9:873-873.
- Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM et al. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. The ISME journal 2011;5(10):1595-1608.
- Sullam KE, Essinger SD, Lozupone CA, O'Connor MP, Rosen GL et al. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta-analysis. Molecular ecology 2012;21(13):3363-3378.
- Ward NL, Steven B, Penn K, Methé BA, Detrich WH. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota of two Antarctic notothenioid fish species. Extremophiles, journal article 2009;13(4):679-685.
- Troussellier M, Escalas A, Bouvier T, Mouillot D. Sustaining Rare Marine Microorganisms: Macroorganisms As Repositories and Dispersal Agents of Microbial Diversity. Frontiers in microbiology 2017;8:947-947.
- Romero J, Ringø E, Merrifield D. The Gut Microbiota of Fish. 2014.
- Ou W, Yu G, Zhang Y, Mai K. Recent progress in the understanding of the gut microbiota of marine fishes. Marine Life Science & Technology 2021;3(4):434-448.
- Yano Y, Nakayama A, Yoshida K. Population Sizes and Growth Pressure Responses of Intestinal Microfloras of Deep-Sea Fish Retrieved from the Abyssal Zone. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1995;61(12):4480-4483.
- Ohwada K, Tabor PS, Colwell RR. Species composition and barotolerance of gut microflora of deep-sea benthic macrofauna collected at various depths in the atlantic ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 1980;40(4):746-755.
- Ghanbari M, Kneifel W, Domig KJ. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015;448:464-475.
- Huang Q, Sham RC, Deng Y, Mao Y, Wang C et al. Diversity of gut microbiomes in marine fishes is shaped by host-related factors. Molecular ecology 2020;29(24):5019-5034.
- Collins FWJ. An investigation into antimicrobial production in the Lactobacillus genus and the fish microbiome. PhD Thesis Thesis, University College Cork; 2019.
- Andlid T, Juárez R-V, Gustafsson L. Yeast colonizing the intestine of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) and turbot (Scophtalmus maximus). Microbial Ecology, journal article 1995;30(3):321-334.
- Song W, Li L, Huang H, Jiang K, Zhang F et al. The Gut Microbial Community of Antarctic Fish Detected by 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis. BioMed research international 2016;2016:3241529-3241529.
- van der Maarel MJEC, Sprenger W, Haanstra R, Forney LJ. Detection of methanogenic archaea in seawater particles and the digestive tract of a marine fish species. FEMS Microbiology Letters 1999;173(1):189-194.
- Vuillemin A, Wankel SD, Coskun ÖK, Magritsch T, Vargas S et al. Archaea dominate oxic subseafloor communities over multimillion-year time scales. Science advances 2019;5(6):eaaw4108-eaaw4108.
- Suttle CA. Viruses in the sea. Nature 2005;437(7057):356-361.
- Geoghegan JL, Di Giallonardo F, Wille M, Ortiz-Baez AS, Costa VA et al. Virome composition in marine fish revealed by meta-transcriptomics. Virus Evolution 2021;7(1):veab005.
- Johny TK, Saidumohamed BE, Sasidharan RS, Bhat SG. Inferences of gut bacterial diversity from next-generation sequencing of 16S rDNA in deep sea blind ray - Benthobatis moresbyi. Ecological Genetics and Genomics 2018;9:1-6.
- Star B, Haverkamp TH, Jentoft S, Jakobsen KS. Next generation sequencing shows high variation of the intestinal microbial species composition in Atlantic cod caught at a single location. BMC Microbiol 2013;13:248.
- Jones J, DiBattista JD, Stat M, Bunce M, Boyce MC et al. The Microbiome of the Gastrointestinal Tract of a Range-Shifting Marine Herbivorous Fish. Frontiers in Microbiology, Original Research 2018;9.
- Burtseva O, Kublanovskaya A, Fedorenko T, Lobakova E, Chekanov K. Gut microbiome of the White Sea fish revealed by 16S rRNA metabarcoding. Aquaculture 2021;533:736175. [CrossRef]
- Kormas K, Nikouli E, Kousteni V, Damalas D. Midgut bacterial microbiota of 12 fish species from a marine protected area in the Aegean Sea (Greece). Microbial Ecology 2023;86(2):1405-1415. [CrossRef]
- Johny TK, Saidumohamed BE, Sasidharan RS, Bhat SG. Metabarcoding data of bacterial diversity of the deep sea shark, Centroscyllium fabricii. Data in Brief 2018;21:1029-1032. [CrossRef]
- Ringø E, Hoseinifar SH, Ghosh K, Doan HV, Beck BR et al. Lactic acid bacteria in finfish—An update. Frontiers in microbiology 2018;9:1818.
- Pilet M-F, Dousset X, Barré R, Novel G, Desmazeaud M et al. Evidence for Two Bacteriocins Produced by Carnobacterium piscicola and Carnobacterium divergens Isolated from Fish and Active Against Listeria monocytogenes. Journal of Food Protection 1995;58(3):256-262. [CrossRef]
- Bhugaloo-Vial P, Dousset X, Metivier A, Sorokine O, Anglade P et al. Purification and amino acid sequences of piscicocins V1a and V1b, two class IIa bacteriocins secreted by Carnobacterium piscicola V1 that display significantly different levels of specific inhibitory activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 1996;62(12):4410-4416. [CrossRef]
- Metivier A, Pilet M-F, Dousset X, Sorokine O, Anglade P et al. Divercin V41, a new bacteriocin with two disulphide bonds produced by Carnobacterium divergens V41: primary structure and genomic organization. Microbiology 1998;144(10):2837-2844. [CrossRef]
- Duffes F, Leroi F, Boyaval P, Dousset X. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by Carnobacterium spp. strains in a simulated cold smoked fish system stored at 4°C. International Journal of Food Microbiology 1999;47(1):33-42.
- Schelegueda LI, Vallejo M, Gliemmo MF, Marguet ER, Campos CA. Synergistic antimicrobial action and potential application for fish preservation of a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus mundtii isolated from Odontesthes platensis. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2015;64(2):794-801.
- Sequeiros C, Garcés ME, Vallejo M, Marguet ER, Olivera NL. Potential aquaculture probiont Lactococcus lactis TW34 produces nisin Z and inhibits the fish pathogen Lactococcus garvieae. Archives of Microbiology 2015;197(3):449-458.
- Heo W-S, Kim E-Y, Kim Y-R, Hossain MT, Kong I-S. Salt effect of nisin Z isolated from a marine fish on the growth inhibition of Streptococcus iniae, a pathogen of streptococcosis. Biotechnology Letters 2012;34(2):315-320.
- Mulders JW, Boerrigter IJ, ROLLEMA HS, SIEZEN RJ, de VOS WM. Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. European Journal of Biochemistry 1991;201(3):581-584.
- Breukink E, van Kraaij C, Demel RA, Siezen RJ, Kuipers OP et al. The C-Terminal Region of Nisin Is Responsible for the Initial Interaction of Nisin with the Target Membrane. Biochemistry 1997;36(23):6968-6976.
- Li Q, Chen Q, Wu Y, Chen Z, Liu Y et al. Purification, characterization and structural identification of a novel bacteriocin produced by marine original Enterococcus durans YQ-6, and its inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes. LWT 2023;173:114329.
- Bindiya ES, Tina KJ, Raghul SS, Bhat SG. Characterization of Deep Sea Fish Gut Bacteria with Antagonistic Potential, from Centroscyllium fabricii (Deep Sea Shark). Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2015;7(2):157-163.
- Bindiya ES, Tina KJ, Sasidharan RS, Bhat SG. BaCf3: highly thermostable bacteriocin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BTSS3 antagonistic on food-borne pathogens. 3 Biotech 2019;9(4):136. [CrossRef]
- Saidumohamed BE, Johny TK, Raveendran AT, Sheela UB, Sreeranganathan M et al. 3D Structure Elucidation and Appraisal of Mode of Action of a Bacteriocin BaCf3 with Anticancer Potential Produced by Marine Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BTSS3. Re:GEN Open 2022;2(1):45-56. [CrossRef]
- Singh PK, Chittpurna, Ashish, Sharma V, Patil PB et al. Identification, purification and characterization of laterosporulin, a novel bacteriocin produced by Brevibacillus sp. strain GI-9. PLoS One 2012;7(3):e31498. [CrossRef]
- Collins FWJ, O'Connor PM, O'Sullivan O, Rea MC, Hill C et al. Formicin - a novel broad-spectrum two-component lantibiotic produced by Bacillus paralicheniformis APC 1576. Microbiology 2016;162(9):1662-1671.
- An J, Zhu W, Liu Y, Zhang X, Sun L et al. Purification and characterization of a novel bacteriocin CAMT2 produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolated from marine fish Epinephelus areolatus. Food Control 2015;51:278-282.
- Saidumohamed BE, Baburaj AP, Johny TK, Sheela UB, Sreeranganathan M et al. A magainin-2 like bacteriocin BpSl14 with anticancer action from fish gut Bacillus safensis SDG14. Analytical Biochemistry 2021;627:114261.
- Emam AM, Dunlap CA. Genomic and phenotypic characterization of Bacillus velezensis AMB-y1; a potential probiotic to control pathogens in aquaculture. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2020;113(12):2041-2052.
- Yi Y, Zhang Z, Zhao F, Liu H, Yu L et al. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis JW: Antimicrobial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria and immune enhancement effects on Carassius auratus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2018;78:322-330.
- Wu J, Xu G, Jin Y, Sun C, Zhou L et al. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus sp. GFP-2, a novel Bacillus strain with antimicrobial activities, from Whitespotted bamboo shark intestine. AMB Express 2018;8(1):84.
- Valliappan K, Sun W, Li Z. Marine actinobacteria associated with marine organisms and their potentials in producing pharmaceutical natural products. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014;98(17):7365-7377. [CrossRef]
- Jang KH, Nam S-J, Locke JB, Kauffman CA, Beatty DS et al. Anthracimycin, a Potent Anthrax Antibiotic from a Marine-Derived Actinomycete. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2013;52(30):7822-7824. [CrossRef]
- Vignesh A, Ayswarya S, Gopikrishnan V, Radhakrishnan M. Bioactive potential of actinobacteria isolated from the gut of marine fishes. 2019.
- Vadivel M, Venugopal G, Angamuthu V, Manikkam R, Joseph J et al., editors. Exploration of Fish Gut Associated Actinobacteria for its Anti-Microbial and Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties. International Seminar on Promoting Local Resources for Sustainable Agriculture and Development (ISPLRSAD 2020); 2021: Atlantis Press.
- Subramani R, Sipkema D. Marine Rare Actinomycetes: A Promising Source of Structurally Diverse and Unique Novel Natural Products. Marine Drugs 2019;17(5):249.
- Sanchez LM, Wong WR, Riener RM, Schulze CJ, Linington RG. Examining the Fish Microbiome: Vertebrate-Derived Bacteria as an Environmental Niche for the Discovery of Unique Marine Natural Products. PLOS ONE 2012;7(5):e35398.
- Gerday C, Aittaleb M, Arpigny JL, Baise E, Chessa J-P et al. Psychrophilic enzymes: a thermodynamic challenge. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1997;1342(2):119-131.
- Mykytczuk NCS, Wilhelm RC, Whyte LG. Planococcus halocryophilus sp. nov., an extreme sub-zero species from high Arctic permafrost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2012;62(Pt 8):1937-1944. [CrossRef]
- Martin D, Bartlett DH, Roberts MF. Solute accumulation in the deep-sea bacterium Photobacterium profundum. Extremophiles, journal article 2002;6(6):507-514. [CrossRef]
- Brindley AA, Pickersgill RW, Partridge JC, Dunstan DJ, Hunt DM et al. Enzyme sequence and its relationship to hyperbaric stability of artificial and natural fish lactate dehydrogenases. PloS one 2008;3(4):e2042-e2042. [CrossRef]
- Porter ML, Roberts NW, Partridge JC. Evolution under pressure and the adaptation of visual pigment compressibility in deep-sea environments. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 2016;105:160-165.
- Morita T. Structure-based analysis of high pressure adaptation of α-actin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, Article 2003;278(30):28060-28066.
- Lemaire B, Karchner SI, Goldstone JV, Lamb DC, Drazen JC et al. Molecular adaptation to high pressure in cytochrome P450 1A and aryl hydrocarbon receptor systems of the deep-sea fish Coryphaenoides armatus. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 2018;1866(1):155-165.
- Yancey PH, Blake WR, Conley J. Unusual organic osmolytes in deep-sea animals: adaptations to hydrostatic pressure and other perturbants. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2002;133(3):667-676.
- Somero GN. Protein adaptations to temperature and pressure: complementary roles of adaptive changes in amino acid sequence and internal milieu. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2003;136(4):577-591.
- Desriac F, Defer D, Bourgougnon N, Brillet B, Le Chevalier P et al. Bacteriocin as Weapons in the Marine Animal-Associated Bacteria Warfare: Inventory and Potential Applications as an Aquaculture Probiotic. Marine Drugs 2010;8(4):1153-1177.
- Sahoo TK, Jena PK, Patel AK, Seshadri S. Bacteriocins and their applications for the treatment of bacterial diseases in aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture Research 2016;47(4):1013-1027.
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020 . Sustainability in action. Rome, Italy2020. Report No.: 978-92-5-132692-3 Contract No.: 63.
- Shastry RP, Arunrenganathan RR, Rai VR. Characterization of probiotic Enterococcus lactis RS5 and purification of antibiofilm enterocin. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2021;31:101897. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen TL, Park C-I, Kim D-H. Improved growth rate and disease resistance in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, by probiotic Lactococcus lactis WFLU12 isolated from wild marine fish. Aquaculture 2017;471:113-120. [CrossRef]
- Deming JW, Baross JA. Survival, Dormancy, and Nonculturable Cells in Extreme Deep-Sea Environments. In: Colwell RR, Grimes DJ (editors). Nonculturable Microorganisms in the Environment. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2000. pp. 147-197.
- Choi Eun J, Nam S-J, Paul L, Beatty D, Kauffman Christopher A et al. Previously Uncultured Marine Bacteria Linked to Novel Alkaloid Production. Chemistry & Biology 2015;22(9):1270-1279.
- López R, Monteón V, Chan E, Montejo R, Chan M. Oxygen limitation favors the production of protein with antimicrobial activity in Pseudoalteromonas sp. Brazilian journal of microbiology : [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology] 2012;43(3):1206-1212.
- Nakayama A, Yano Y, Yoshida K. New Method for Isolating Barophiles from Intestinal Contents of Deep-Sea Fishes Retrieved from the Abyssal Zone. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1994;60(11):4210-4212. [CrossRef]
- Zeng X, Xiao X, Wang P, Wang FP. Screening and characterization of psychrotrophic, lipolytic bacteria from deep-sea sediments. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2004;14:952-958.
- Nichols D, Lewis K, Orjala J, Mo S, Ortenberg R et al. Short Peptide Induces an “Uncultivable” Microorganism To Grow In Vitro. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2008;74(15):4889.
- Zhong Z, He B, Li J, Li Y-X. Challenges and advances in genome mining of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology 2020;5(3):155-172. [CrossRef]
- Johny TK, Puthusseri RM, Bhat SG. Metagenomic landscape of taxonomy, metabolic potential and resistome of Sardinella longiceps gut microbiome. Archives of Microbiology 2021;204(1):87. [CrossRef]
- Collins FWJ, Walsh CJ, Gomez-Sala B, Guijarro-García E, Stokes D et al. The microbiome of deep-sea fish reveals new microbial species and a sparsity of antibiotic resistance genes. Gut Microbes 2021;13(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Stevenson SJ, Lee KC, Handley KM, Angert ER, White WL et al. Substrate degradation pathways, conserved functions and community composition of the hindgut microbiota in the herbivorous marine fish Kyphosus sydneyanus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2022;272:111283. [CrossRef]
- Yi Y, Liang L, Wang Z, Ai P, You X et al. A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals. Animals 2019;9(9):660. [CrossRef]
- Collins FWJ, Mesa-Pereira B, O'Connor PM, Rea MC, Hill C et al. Reincarnation of Bacteriocins From the Lactobacillus Pangenomic Graveyard. Front Microbiol 2018;9:1298. [CrossRef]
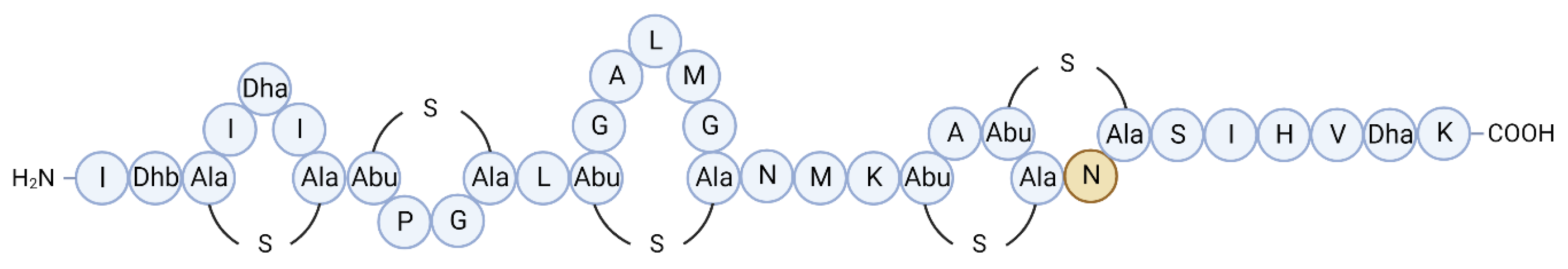
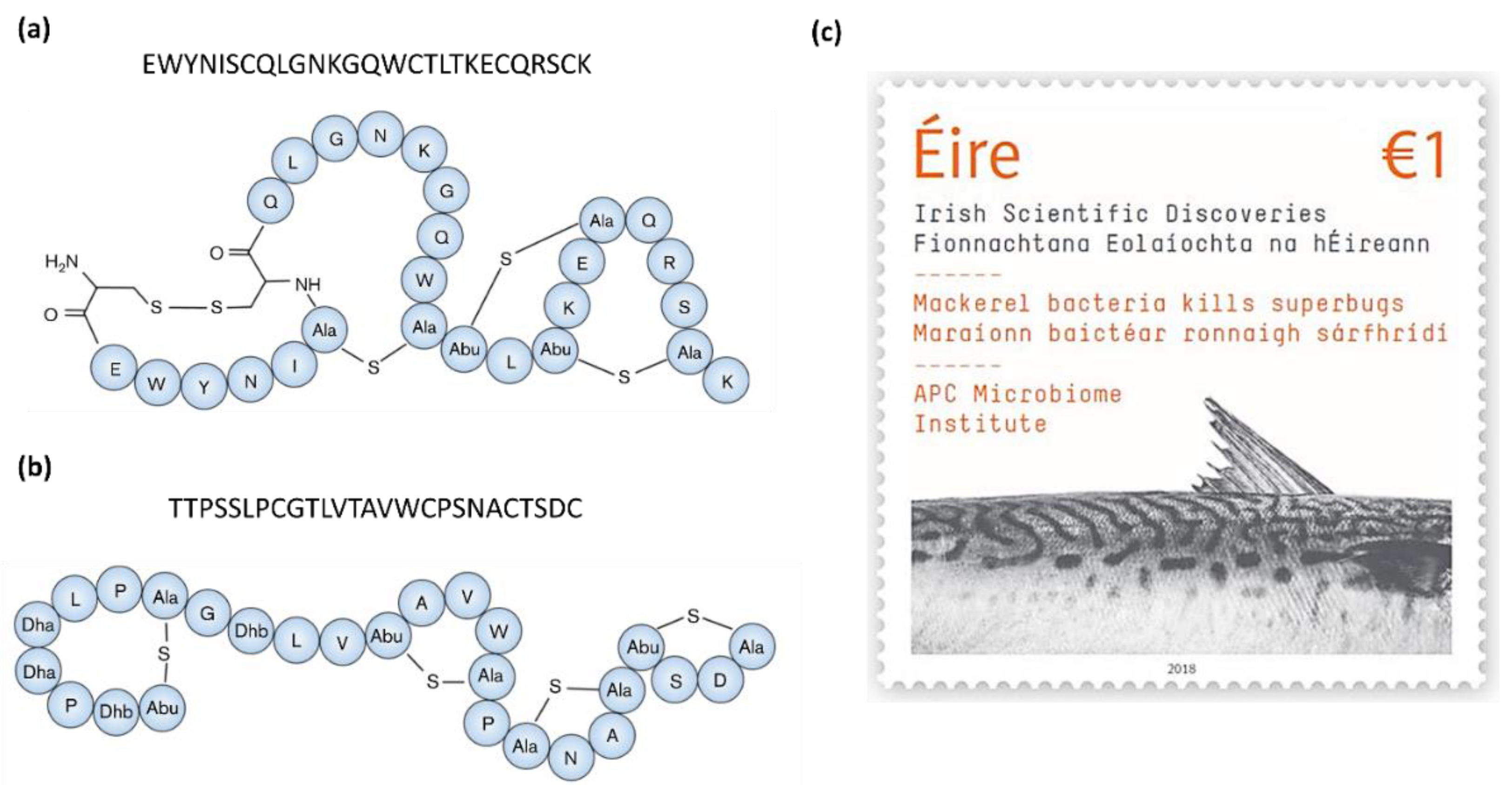
| Molecule | Producer | Host, source | Susceptible organism(s) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I bacteriocins (lanthipeptide subclass II) | ||||
| Formicin | Bacillus paralicheniformis APC 1576 | Scomber scombrus, intestine | Clostridia spp., Bacillus spp., Listeria spp., Enterococcus spp., Streptococcus mutans, M. luteus | [52] |
| Class IIa bacteriocins | ||||
| Divercin V41 | Carnobacterium divergens V41 | salmon or trout, intestine | Carnobacterium piscicola, Listeria spp. | [42] |
| Mundticin KS | Enterococcus mundtii Tw56 | Odontesthes platensis, intestine | Enterococcus spp., Listeria spp., M. luteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shewanella putrefaciens | [44] |
| Enterocin R5 |
Enterococcus lactis RS5 |
Sillago indica, gut | E. coli, S. enterica Typhimurium, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa. B. subtilis, B. cereus, Proteus vulgaris | [76] |
| Nisin Z | Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | Paralichthys olivaceus, intestine | Streptococcus iniae | [46] |
| Nisin Z | Lactococcus lactis TW34 | Odontesthes platensis, intestine | Lactococcus garvieae | [45] |
| Piscidins Vla, Vlb | Carnobacterium piscola V1 | salmon/trout, intestine | Listeria spp. | [41] |
| Class IId bacteriocins | ||||
| CAMT6 |
Enterococcus durans YQ-6 |
Larimichthys polyactis, NR |
S. aureus, Bacillus spp., S. haemolyticus, P. acnes, Salmonella paratyphi, V. parahaemolyticus, P. foulis, E. aerogenes, Fusarium sylvaticum, Aspergillus fumigatus |
[49] |
| Other AMPs /bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances | ||||
| BaCf3 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BTSS3 | Centroscyllium fabricii, intestine |
Bacillus spp., Clostridium perfringens, Salmonella Typhimurium, Proteus vulgaris |
[50,51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





