Submitted:
16 May 2024
Posted:
17 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Study Design, and Ethics
Data Collection
Survey Design and Distribution
Power Calculation
Statistical Analysis
Results
Characteristics of Participants
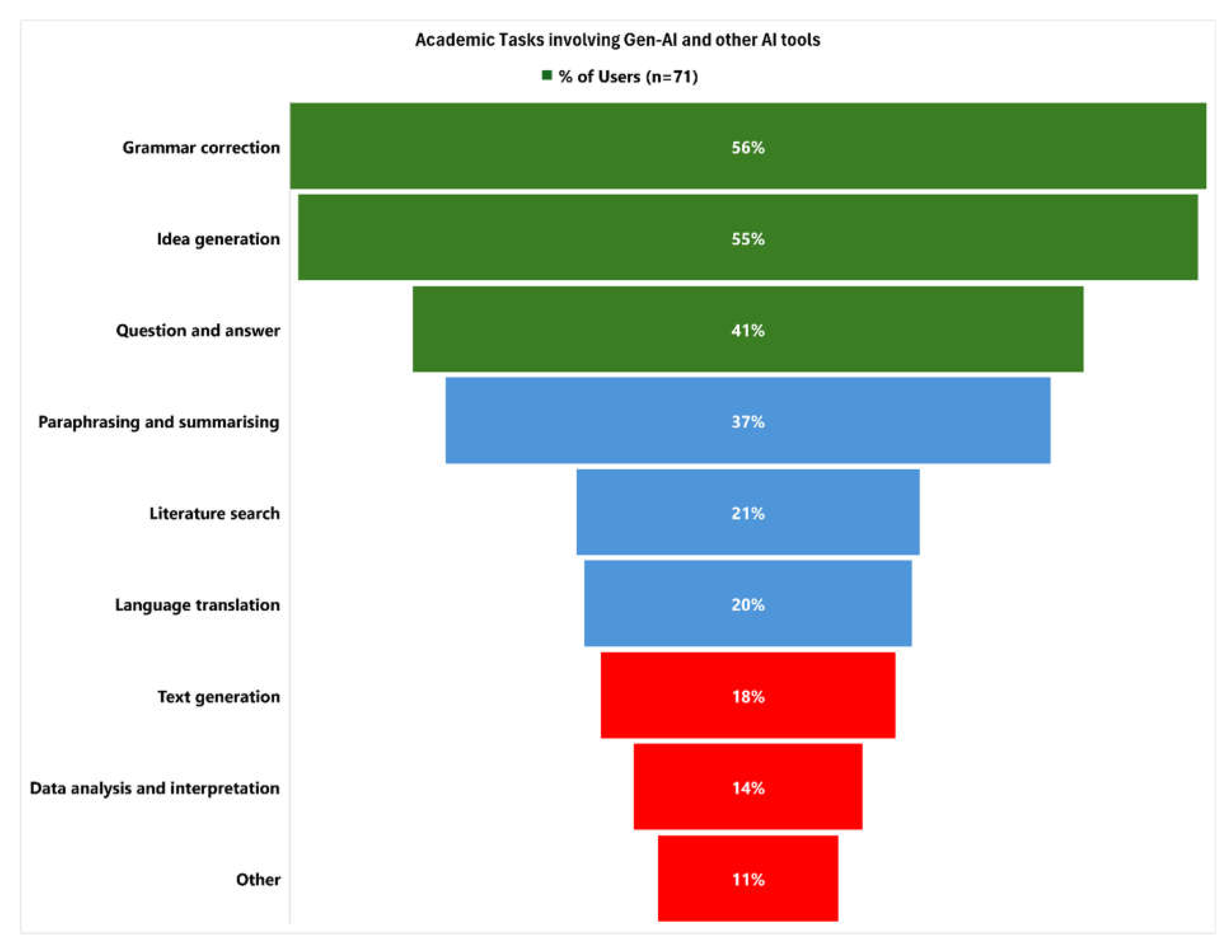
Awareness and Use of Gen-AI
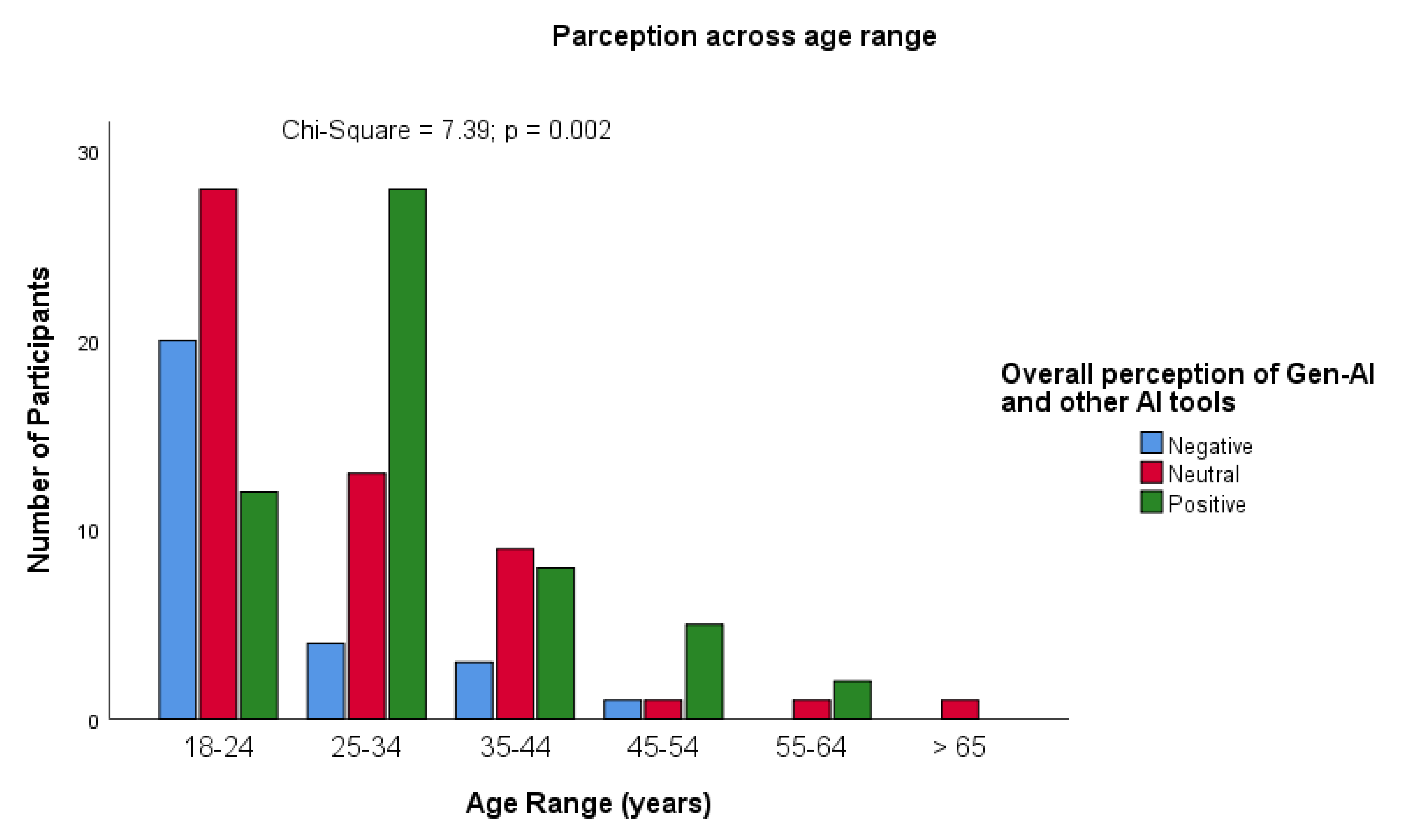
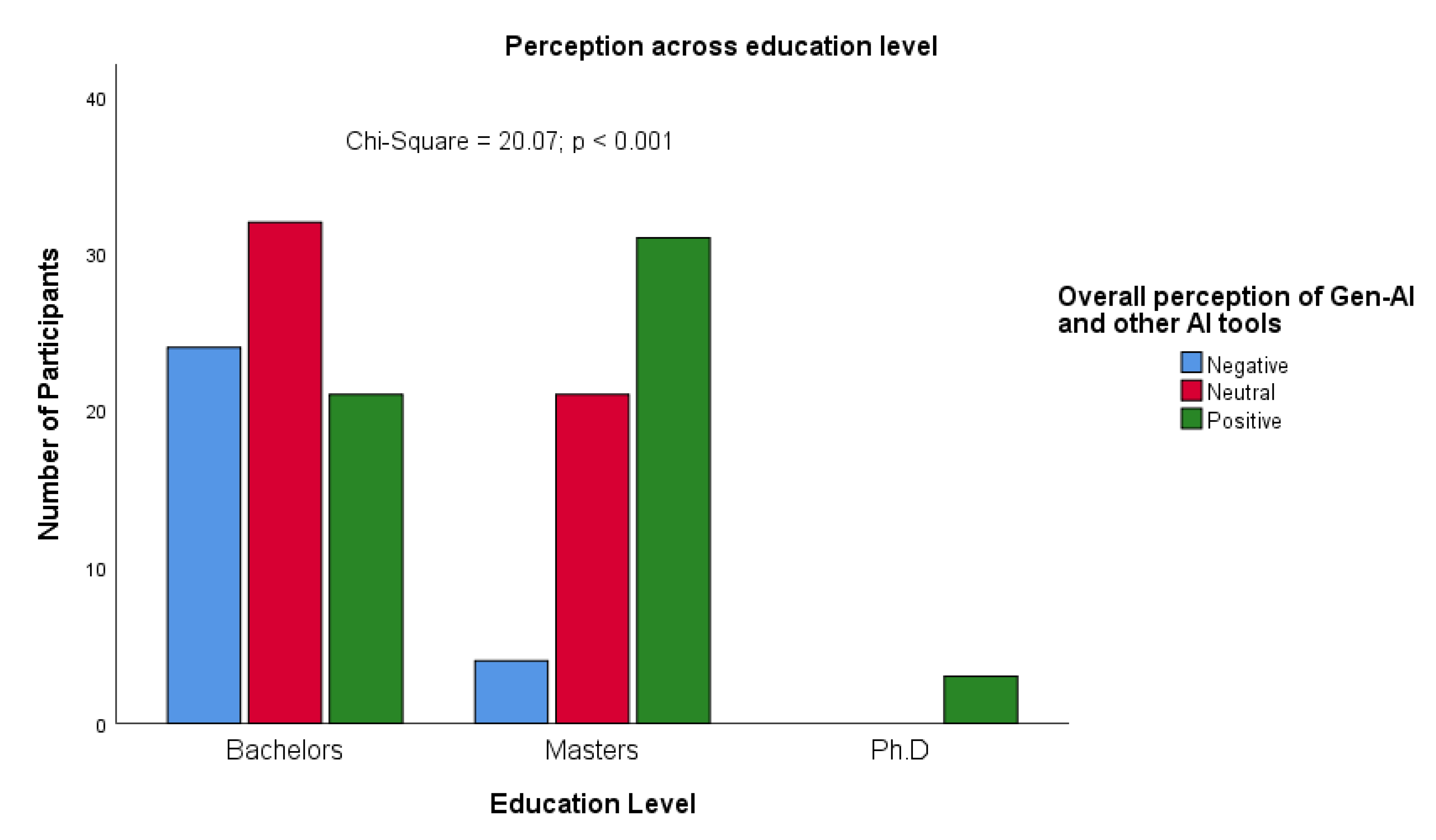
Perception of Gen-AI and Other AI Use for Academic Purposes
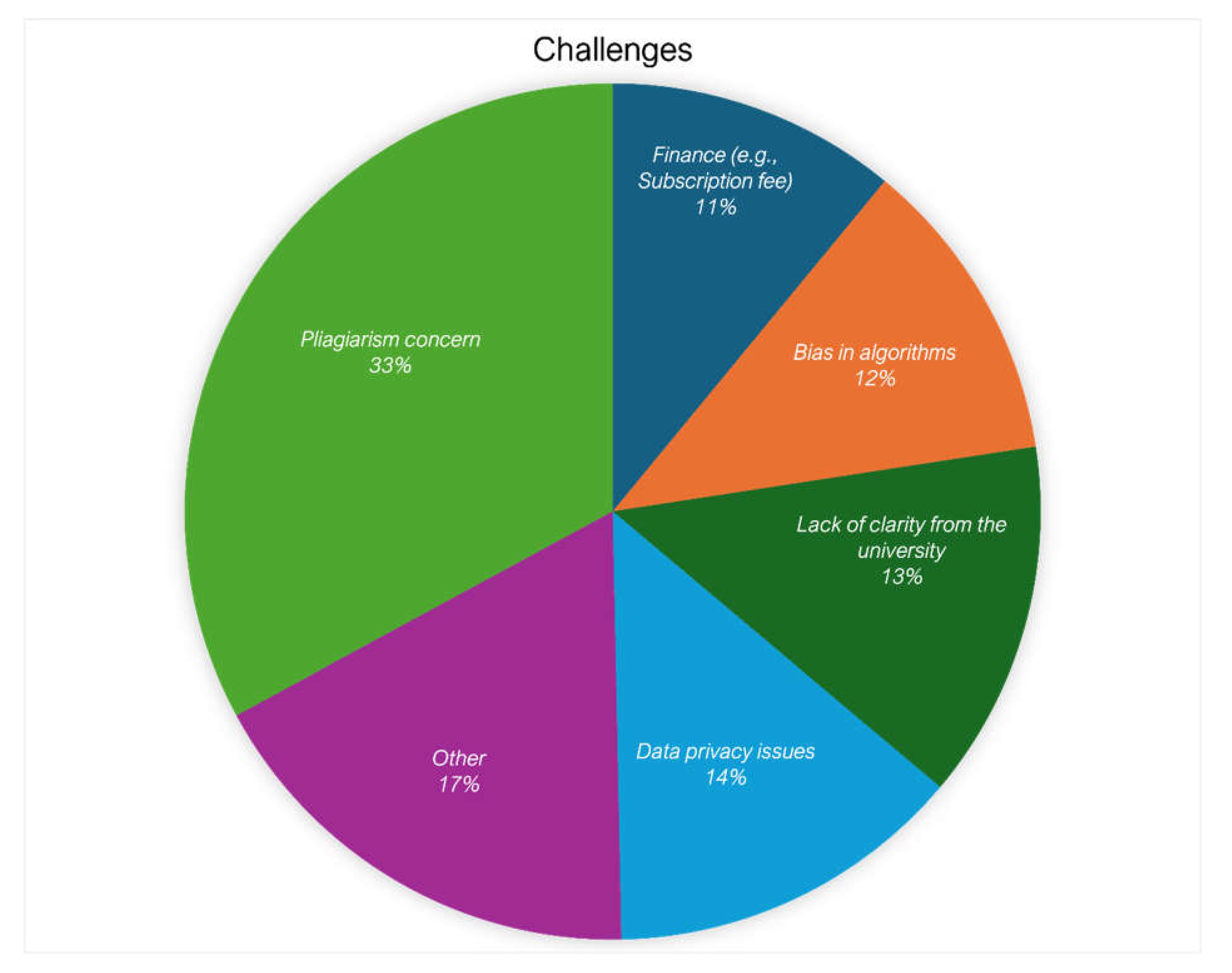
Prospect and Limitation of Gen-AI and Other AI Use for Academic Purposes
| The use of Gen-AI and other AI tools for academic purposes will significantly increase in the future. | |
| Strongly agree | 51 (38) |
| Agree | 61 (45) |
| Neutral | 22 (16) |
| Disagree | 1 (1) |
| Strongly disagree | 1 (1) |
| Gen-AI or other AI tools should be integrated into the university’s curriculum. | |
| Strongly agree | 25 (18) |
| Agree | 40 (29) |
| Neutral | 46 (34) |
| Disagree | 13 (10) |
| Strongly disagree | 12 (9) |
Discussion
Funding statement and conflict of interest disclosure
Data availability
Authors contribution
References
- Education, D.f. Generative AI in education: Educator and expert views; GOV.UK: 2024.
- Farrelly, T.; Baker, N. Generative artificial intelligence: Implications and considerations for higher education practice. Education Sciences 2023, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Gunasekara, A.; Pallant, J.L.; Pallant, J.I.; Pechenkina, E. Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. The international journal of management education 2023, 21, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.K.; Raghuram, J.N.V. Gen-AI integration in higher education: Predicting intentions using SEM-ANN approach. Education and Information Technologies 2024, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Pervin, N.; Román-González, M. Generative AI and the future of higher education: a threat to academic integrity or reformation? Evidence from multicultural perspectives. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2024, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, Z.H.; Gözüm, A.I.C.; Papadakis, S.; Kallogiannakis, M. Educational Applications of the ChatGPT AI System: A Systematic Review Research. Educational Process: International Journal 2023, 12, 26–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Tambuwal, N.I. Integrating Educational Technology in Teaching: Current Perceptions and Practices in Sokoto State, Nigeri. Arab Journal of Quality in Education 2018, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, J.C. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Education and Its Implications for Assessment. TechTrends 2024, 68, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y. Student Education Management Strategy Based on Artificial Intelligence Information Model under the Support of 5G Wireless Network. Comput Intell Neurosci 2022, 2022, 4709146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z. The application of artificial intelligence assistant to deep learning in teachers’ teaching and students’ learning processes. Front Psychol 2022, 13, 929175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banh, L.; Strobel, G. Generative artificial intelligence. Electronic Markets 2023, 33, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.H.-K.; Lin, C.-H.; Ou, Y.-Y.; Liu, C.-Z.; Wang, W.-K.; Chao, C.-Y. Advantages and constraints of a hybrid model K-12 E-Learning assistant chatbot. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 77788–77801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.Y.; Hu, W. Students’ voices on generative AI: Perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2023, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.C.; Kutar, M. The general data protection regulation (GDPR), emerging technologies and UK organisations: awareness, implementation and readiness. 2018.
- Shrestha, B.; Dunn, L. The declaration of Helsinki on medical research involving human subjects: a review of seventh revision. 2019.
- Ghimire, A.; Prather, J.; Edwards, J. Generative AI in Education: A Study of Educators’ Awareness, Sentiments, and Influencing Factors. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.15586 2024.
- Kelly, A.; Sullivan, M.; Strampel, K. Generative artificial intelligence: University student awareness, experience, and confidence in use across disciplines. 2023.
- Chan, C.K.Y.; Lee, K.K.W. The AI generation gap: Are Gen Z students more interested in adopting generative AI such as ChatGPT in teaching and learning than their Gen X and millennial generation teachers? Smart Learning Environments 2023, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klutka, J.; Ackerly, N.; Magda, A.J. Artificial intelligence in higher education: Current uses and future applications. Louisville: Learning house 2018.
- Hannan, E.; Liu, S. AI: New source of competitiveness in higher education. Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal 2023, 33, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-H.; Im, K.; Yoo, M.; Roll, I.; Seo, K. Supporting students’ self-regulated learning in online learning using artificial intelligence applications. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2023, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, J.S.; Aldhahir, A.M.; Al Ghamdi, S.S.; Aldakhil, A.M.; Al-Otaibi, H.M.; AlRabeeah, S.M.; Alzahrani, E.M.; Elsafi, S.H.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Al-maqati, T.N. Teaching faculty perceptions, attitudes, challenges, and satisfaction of online teaching during COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A national survey. 2022.
- Kim, J.; Merrill, K.; Xu, K.; Sellnow, D.D. My teacher is a machine: Understanding students’ perceptions of AI teaching assistants in online education. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction 2020, 36, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, K. Designing real-time teacher augmentation to combine strengths of human and AI instruction. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Carnegie Mellon University 2019.
- Diwan, C.; Srinivasa, S.; Suri, G.; Agarwal, S.; Ram, P. AI-based learning content generation and learning pathway augmentation to increase learner engagement. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 2023, 4, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.; Cobo, C.; Mariño, O.; Wheeler, S. Can artificial intelligence transform higher education? Springer: 2020; Vol. 17, pp 1-12.
- Althubaiti, A. Information bias in health research: definition, pitfalls, and adjustment methods. J Multidiscip Healthc 2016, 9, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solem, R.C. Limitation of a cross-sectional study. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2015, 148, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgwick, P.; Greenwood, N. Understanding the Hawthorne effect. Bmj 2015, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, J.G. The Hawthorne effect: a reconsideration of the methodological artifact. Journal of applied psychology 1984, 69, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, F. How can we be inclusive of diverse cultural perspectives in international higher education? exploring interculturality. In Intersectionality and Creative Business Education: Inclusive and Diverse Cultures in Pedagogy, Springer: 2023; pp. 93-108.
| Characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age range (years), n (%) | |
| 18 – 24 | 60 (44%) |
| 24 – 34 | 45 (33%) |
| 35 – 44 | 20 (15%) |
| ≥ 45 | 11 (8%) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 80 (59%) |
| Female | 47 (35%) |
| Non-Binary | 6 (4%) |
| Level of Study, n (%) | |
| Undergraduate | 77 (57%) |
| Post-graduate | 57 (42%) |
| Doctoral | 2 (1%) |
| Field of Study | |
| Arts and Design | 34 (25%) |
| Education | 3 (2%) |
| Engineering and Technology | 57 (42%) |
| Health and Medicine | 6 (4%) |
| Humanities and Social Sciences | 3 (2%) |
| Physical Sciences | 1 (1%) |
| Others | 32 (24%) |
| Statement | N (%) |
|---|---|
| How familiar are you with Gen-AI? | |
| Extremely familiar | 26 (19) |
| Moderately familiar | 57 (42) |
| Somewhat familiar | 30 (22) |
| Slightly familiar | 19 (14) |
| Not at all familiar | 4 (3) |
| How aware are you of Gen-AI use for academic purposes? | |
| Extremely aware | 27 (20) |
| Moderately aware | 54 (40) |
| Somewhat aware | 26 (19) |
| Slightly aware | 21 (15) |
| Not at all aware | 8 (66) |
| Have you ever used Gen-AI for academic purposes? | |
| Yes | 71 (52%) |
| No | 65 (48%) |
| How frequently do you use Gen-AI and other AI tools for your academic tasks? (71/136) | |
| Always | 4 (6) |
| Often | 22 (31) |
| Sometimes | 24 (34) |
| Rarely | 19 (27) |
| Never | 2 (3) |
| Statement | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Gen-AI and other AI tools provide academic advantage. | |
| Strongly agree | 29 (21) |
| Agree | 47 (35) |
| Neutral | (40 (29) |
| Disagree | 17 (13) |
| Strongly disagree | 3 (2) |
| What is your overall perception about the use of Gen-AI and other AI tools? | |
| Positive | 55 (40) |
| Neutral | 53 (39) |
| Negative | 28 (21) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





