Submitted:
16 May 2024
Posted:
16 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Camera-Based SLAM (VSLAM)
2.1. Types of VSLAM
2.1.1. Monocular Camera SLAM
2.1.2. Stereo Camera SLAM
2.1.3. RGB-D Camera SLAM
2.2. Limitations of Frame-Based Cameras in VSLAM
- Ambiguity in feature matching: In feature-based SLAM, feature matching is considered a critical step. However, frame-based cameras face difficulty in capturing scenes with ambiguous features (e.g. plain walls). Moreover, data without depth information (as obtained from standard monocular cameras) makes it even harder for the feature-matching process to distinguish between similar features, which can lead to potential errors in data association.
- Sensitivity to lighting conditions: The sensitivity of traditional cameras to changes in lighting conditions affects the features and makes it more challenging to match features across frames consistently [6]. This can result in errors during the localization and mapping process.
- Limited field of view: The use of frame-based cameras can be limited due to their inherently limited field of view. This limitation becomes more apparent in environments with complex structures or large open spaces. In such cases, having multiple cameras or additional sensor modalities may become necessary to achieve comprehensive scene coverage, but this can lead to greatly increased computational costs as well as other complexities.
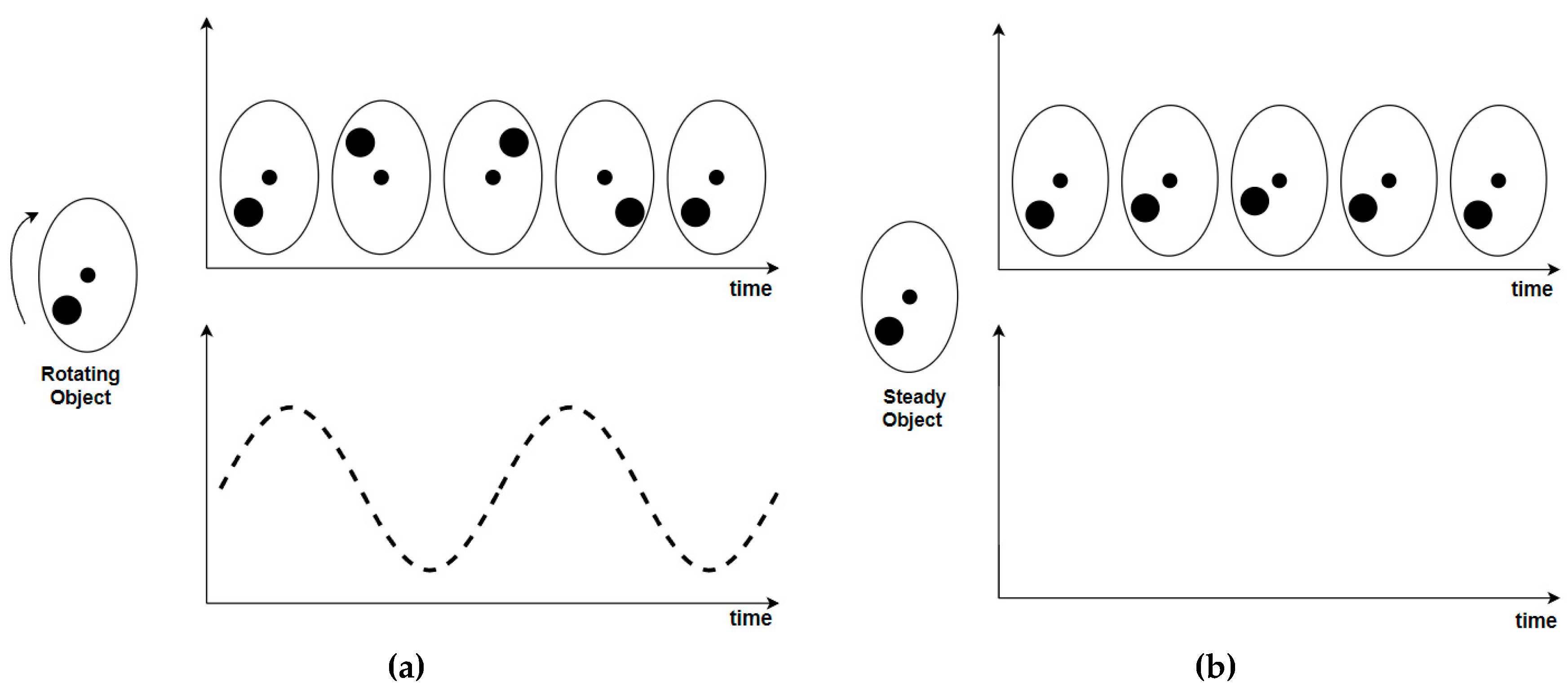
- Challenge in handling dynamic environments: Frame-based cameras face difficulties when it comes to capturing dynamic environments, especially where there is movement of objects or people. It can be challenging to track features consistently in the presence of moving entities, and other sensor types such as depth sensors or Inertial Measurement units (IMUs) must be integrated, or additional strategies must be implemented to mitigate those challenges. Additionally, in situations where objects in a scene are moving rapidly, particularly if the camera itself is on a fast-moving platform (e.g. a drone), then motion blur can significantly degrade the quality of captured frames unless highly specialized cameras are used.
- High computational requirements: Although frame-based cameras are typically less computationally demanding than depth sensors such as LiDAR, feature extraction and matching processes can still necessitate considerable computational resources, particularly for real-time applications.
3. Event Camera-Based SLAM
3.1. Event Camera Operating Principles
3.1.1. Event Generation Model
3.1.2. Event Representation
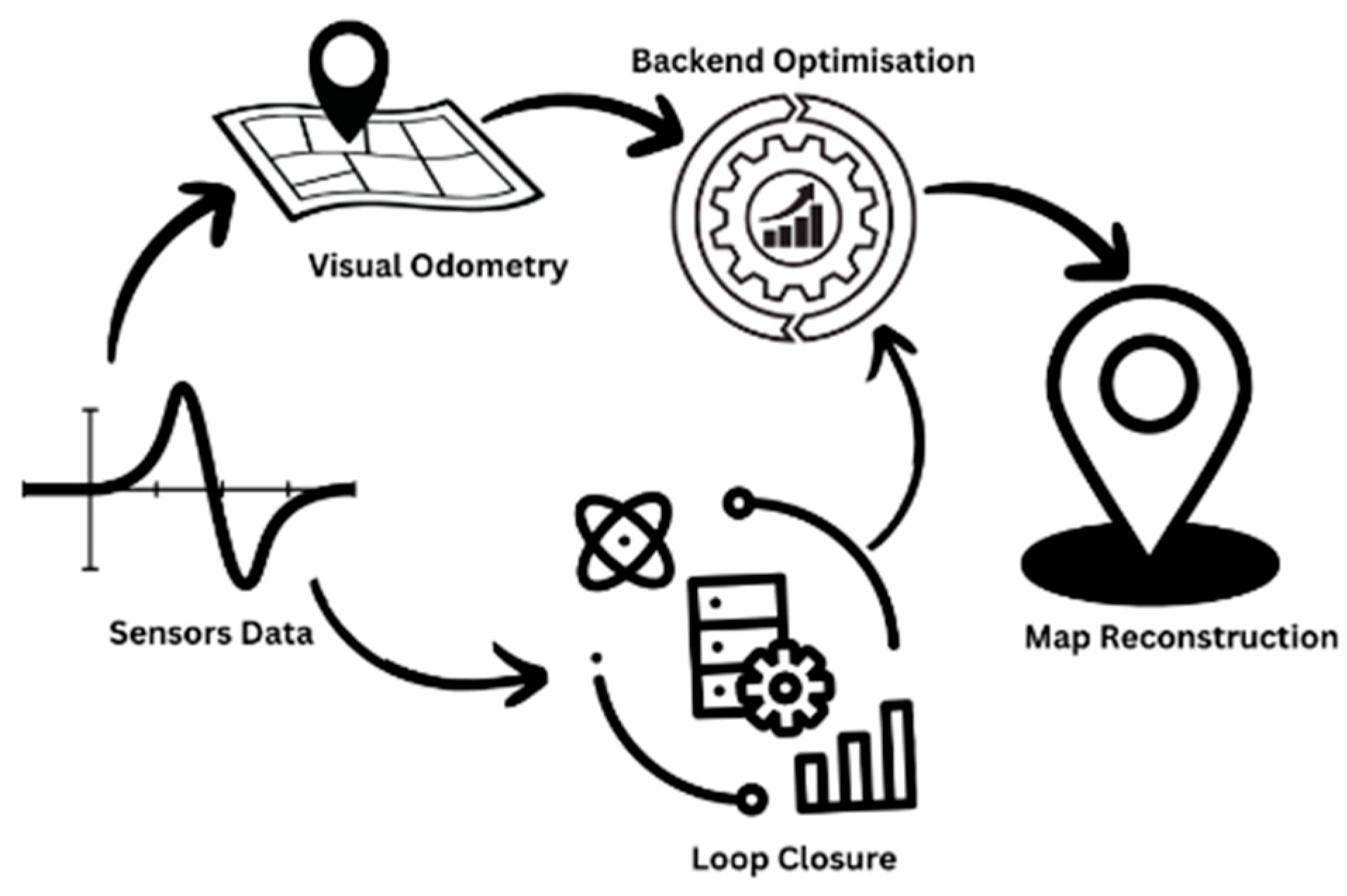
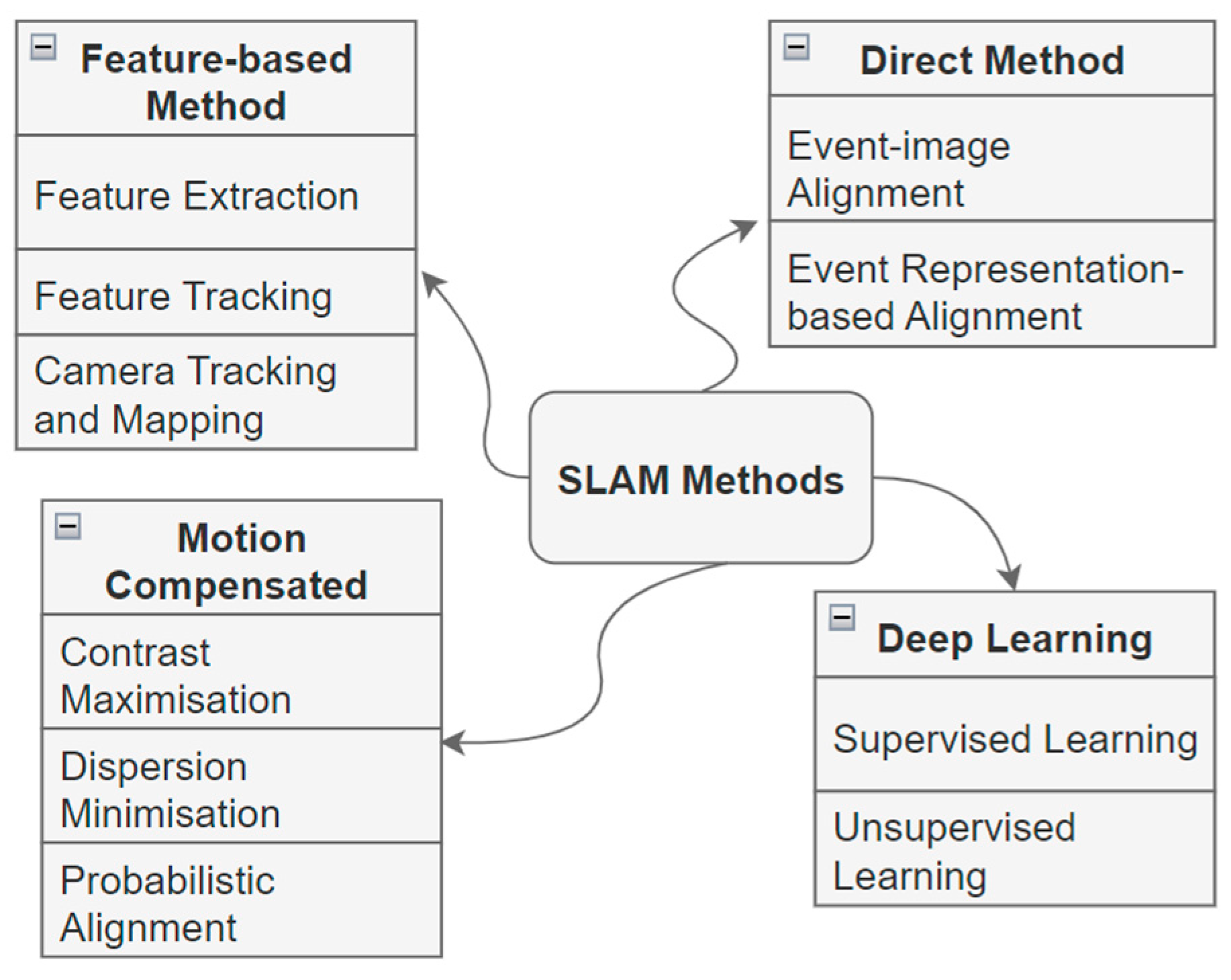
3.2. Method
3.2.1. Feature-Based Methods
3.1.1.1. Feature Extraction
3.1.1.2. Feature Tracking
3.1.1.3. Camera Tracking and Mapping
3.2.2. Direct Method
3.2.3. Motion Compensation Methods
3.2.4. Deep Learning Methods
3.3. Performance Evaluation of SLAM Systems
3.3.1. Event Camera Datasets
3.3.2. Event-Based SLAM Metrics
3.3.3. Performance Comparison of SLAM Methods
3.3.3.1. Depth Estimation
3.3.3.2. Camera Pose Estimation
3.4. Applications of Event Camera-Based SLAM Systems
3.4.1. Robotics
3.4.2. Autonomous Vehicles
3.4.3. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
4. Application of Neuromorphic Computing to SLAM
4.1. Neuromorphic Computing Principles
4.1.1. SpiNNaker
4.1.2. TrueNorth
4.1.3. Loihi
4.1.4. BrainScaleS
4.1.5. Dynamic Neuromorphic Asynchronous Processors
4.1.6. Akida
4.2. Spiking Neural Networks
4.3. Neuromorphic Computing in SLAM
- Efficiency: Neuromorphic hardware is designed to mimic the brain's parallel processing capabilities, resulting in efficient computation with low power consumption. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in real-time SLAM applications where rapid low-power processing of sensor data is crucial.
- Adaptability: Neuromorphic systems can adapt and learn from their environment, making them well-suited for SLAM tasks in dynamic or changing environments. They can continuously update their internal models based on new sensory information, leading to improved accuracy and robustness over time.
- Event-based Processing: Event cameras capture data asynchronously in response to changes in the environment. This event-based processing enables SLAM systems to focus computational resources on relevant information, leading to faster and more efficient processing compared to traditional frame-based approaches.
- Sparse Representation: Neuromorphic algorithms can generate sparse representations of the environment, reducing memory and computational requirements. This is advantageous in resource-constrained SLAM applications, such as those deployed on embedded or mobile devices.
5. Conclusion
5.1. Summary of Key Findings
5.2. Current State-of-the-Art and Future Scope
5.3. Neuromorphic SLAM Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Zheng, S.; Lin, X.; Zhu, F. Improving RGB-D SLAM accuracy in dynamic environments based on semantic and geometric constraints. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation 2023, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Hussain, D.; Naveed, K.; Khan, U.S.; Mundial, I.Q.; Aqeel, A.B. Investigation of Widely Used SLAM Sensors Using Analytical Hierarchy Process. In Journal of Sensors, Hindawi Limited: 2022; Vol. 2022.
- Gelen, A.G.; Atasoy, A. An Artificial Neural SLAM Framework for Event-Based Vision. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 58436–58450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Xia, Z.C. SLAM; definition and evolution. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2021, 97, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, J.; Cai, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L. SLAM Back-End Optimization Algorithm Based on Vision Fusion IPS. In Sensors, 2022; Vol. 22.
- Theodorou, C.; Velisavljevic, V.; Dyo, V.; Nonyelu, F. Visual SLAM algorithms and their application for AR, mapping, localization and wayfinding. Array 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Aitken, J.M. HFNet-SLAM: An Accurate and Real-Time Monocular SLAM System with Deep Features. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, T. Introduction to Visual SLAM From Theory to Practice Introduction to Visual SLAM Introduction to Visual SLAM.
- Gallego, G.; Delbruck, T.; Orchard, G.; Bartolozzi, C.; Taba, B.; Censi, A.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A.J.; Conradt, J.; Daniilidis, K.; et al. Event-Based Vision: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2022, 44, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shang, G.; Ji, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Hu, K. An Overview on Visual SLAM: From Tradition to Semantic. In Remote Sensing, 2022; Vol. 14.
- Aitsam, M.; Davies, S.; Di Nuovo, A. Neuromorphic Computing for Interactive Robotics: A Systematic Review. In IEEE Access, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: 2022; Vol. 10, pp 122261-122279.
- Cuadrado, J.; Rançon, U.; Cottereau, B.R.; Barranco, F.; Masquelier, T. Optical flow estimation from event-based cameras and spiking neural networks. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.; Milford, M. Event-based visual place recognition with ensembles of temporal windows. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2020, 5, 6924–6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furmonas, J.; Liobe, J.; Barzdenas, V. Analytical Review of Event-Based Camera Depth Estimation Methods and Systems. In Sensors, MDPI: 2022; Vol. 22.
- Zhou, Y.; Gallego, G.; Shen, S. Event-Based Stereo Visual Odometry. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2021, 37, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Gallego, G. Multi-Event-Camera Depth Estimation and Outlier Rejection by Refocused Events Fusion. Advanced Intelligent Systems 2022, 4, 2200221–2200221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S. T-ESVO: Improved Event-Based Stereo Visual Odometry via Adaptive Time-Surface and Truncated Signed Distance Function. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Guan, W.; Lu, P. ESVIO: Event-Based Stereo Visual Inertial Odometry. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2023, 8, 3661–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Event-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: A Comprehensive Survey. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cao, H.; Conradt, J.; Tang, H.; Rohrbein, F.; Knoll, A. Event-Based Neuromorphic Vision for Autonomous Driving: A Paradigm Shift for Bio-Inspired Visual Sensing and Perception. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2020, 37, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Milford, M. How Many Events Do You Need? Event-Based Visual Place Recognition Using Sparse But Varying Pixels. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 12275–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favorskaya, M.N. Deep Learning for Visual SLAM: The State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. In Electronics (Switzerland), MDPI: 2023; Vol. 12.
- Amir, A.; Taba, B.; Berg, D.; Melano, T.; McKinstry, J.; Nolfo, C.D.; Nayak, T.; Andreopoulos, A.; Garreau, G.; Mendoza, M.; et al. A Low Power, Fully Event-Based Gesture Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 21-26 July 2017; pp. 7388–7397. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Shang, J.; Hu, Y.; Milford, M. NeuroSLAM: a brain-inspired SLAM system for 3D environments. Biological Cybernetics 2019, 113, 515–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Bartolozzi, C.; Zhang, H.H.; Nawrocki, R.A. Neuromorphic electronics for robotic perception, navigation and control: A survey. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 126, 106838–106838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, C.D.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Parsa, M.; Mitchell, J.P.; Date, P.; Kay, B. Opportunities for neuromorphic computing algorithms and applications. In Nature Computational Science, Springer Nature: 2022; Vol. 2, pp 10-19.
- Renner, A.; Supic, L.; Danielescu, A.; Indiveri, G.; Frady, E.P.; Sommer, F.T.; Sandamirskaya, Y. Neuromorphic Visual Odometry with Resonator Networks. Robotics 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.; Wild, A.; Orchard, G.; Sandamirskaya, Y.; Guerra, G.A.F.; Joshi, P.; Plank, P.; Risbud, S.R. Advancing Neuromorphic Computing With Loihi: A Survey of Results and Outlook. Proceedings of the the IEEE 2021, 109, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.D.; Carvalho, M.; Carneiro, D.; Cardoso, J.S. Spiking Neural Networks: A Survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60738–60764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewawasam, H.S.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Appuhamillage, G.K. Past, Present and Future of Path-Planning Algorithms for Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society 2022, 3, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furmonas, J.; Liobe, J.; Barzdenas, V. Analytical Review of Event-Based Camera Depth Estimation Methods and Systems. In Sensors, 2022; Vol. 22.
- Schuman, C.D.; Potok, T.E.; Patton, R.M.; Birdwell, J.D.; Dean, M.E.; Rose, G.S.; Plank, J.S. A Survey of Neuromorphic Computing and Neural Networks in Hardware. Neural and Evolutionary Computing, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.D.; D’Angiulli, A.; Dehnavi, M.M.; Chhabra, R. From Brain Models to Robotic Embodied Cognition: How Does Biological Plausibility Inform Neuromorphic Systems? Brain Sciences 2023, 13, 1316–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Malekian, R.; Munir, H. Neural Network-Based Recent Research Developments in SLAM for Autonomous Ground Vehicles: A Review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario Barros, A.; Michel, M.; Moline, Y.; Corre, G.; Carrel, F. A Comprehensive Survey of Visual SLAM Algorithms. In Robotics, MDPI: 2022; Vol. 11.
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tong, K.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y. Review of Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Based on Deep Learning. In Remote Sensing, MDPI: 2023; Vol. 15.
- Tourani, A.; Bavle, H.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Voos, H. Visual SLAM: What Are the Current Trends and What to Expect? In Sensors, 2022; Vol. 22.
- Bavle, H.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Cimarelli, C.; Tourani, A.; Voos, H. From SLAM to Situational Awareness: Challenges and Survey. In Sensors, MDPI: 2023; Vol. 23.
- Dumont, N.S.Y.; Furlong, P.M.; Orchard, J.; Eliasmith, C. Exploiting semantic information in a spiking neural SLAM system. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, A.J.; Reid, I.D.; Molton, N.D.; Stasse, O. MonoSLAM: Real-Time Single Camera SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2007, 29, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.; Murray, D. Parallel Tracking and Mapping for Small AR Workspaces. In Proceedings of the 2007 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, 13-16 Nov. 2007; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Lovegrove, S.J.; Davison, A.J. DTAM: Dense tracking and mapping in real-time. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, 6-13 Nov. 2011; pp. 2320–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Moreno, R.F.; Newcombe, R.A.; Strasdat, H.; Kelly, P.H.J.; Davison, A.J. SLAM++: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping at the Level of Objects. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 23-28 June 2013; pp. 1352–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Y.; Rui, T.; Lu, M.; Fu, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. DDL-SLAM: A Robust RGB-D SLAM in Dynamic Environments Combined With Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 162335–162342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zou, D.; Huang, Y.; Niu, X.; Pei, L.; Yu, W. TextSLAM: Visual SLAM With Semantic Planar Text Features. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2024, 46, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. SO-SLAM: Semantic Object SLAM With Scale Proportional and Symmetrical Texture Constraints. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Mei, K. SDF-SLAM: A Deep Learning Based Highly Accurate SLAM Using Monocular Camera Aiming at Indoor Map Reconstruction With Semantic and Depth Fusion. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10259–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Jeon, J.; Myung, H. UV-SLAM: Unconstrained Line-Based SLAM Using Vanishing Points for Structural Mapping. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, D.; He, L. RS-SLAM: A Robust Semantic SLAM in Dynamic Environments Based on RGB-D Sensor. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 20657–20664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miura, J. RDMO-SLAM: Real-Time Visual SLAM for Dynamic Environments Using Semantic Label Prediction With Optical Flow. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 106981–106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miura, J. RDS-SLAM: Real-Time Dynamic SLAM Using Semantic Segmentation Methods. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23772–23785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodriguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual-Inertial, and Multimap SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Brasch, N.; Wang, Y.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Structure-SLAM: Low-Drift Monocular SLAM in Indoor Environments. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2020, 5, 6583–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavle, H.; Puente, P.D.L.; How, J.P.; Campoy, P. VPS-SLAM: Visual Planar Semantic SLAM for Aerial Robotic Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 60704–60718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ojeda, R.; Moreno, F.A.; Zuñiga-Noël, D.; Scaramuzza, D.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, J. PL-SLAM: A Stereo SLAM System Through the Combination of Points and Line Segments. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2019, 35, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM2: An Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo, and RGB-D Cameras. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Schöps, T.; Cremers, D. LSD-SLAM: Large-Scale Direct Monocular SLAM. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2014, 2014, Springer: Cham; pp. 834–849.
- Boahen, K.A. A burst-mode word-serial address-event link-I: transmitter design. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers 2004, 51, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A.J. Real-Time 3D Reconstruction and 6-DoF Tracking with an Event Camera. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, Cham; 2016//; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrig, M.; Shrestha, S.B.; Mouritzen, D.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-Based Angular Velocity Regression with Spiking Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 31 May-31 Aug. 2020; pp. 4195–4202. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, A.; Scaramuzza, D. Low-latency event-based visual odometry. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 31 May-7 June 2014; pp. 703–710. [Google Scholar]
- Alzugaray, I.; Chli, M. Asynchronous Multi-Hypothesis Tracking of Features with Event Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 16-19 Sept. 2019; pp. 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kueng, B.; Mueggler, E.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. Low-latency visual odometry using event-based feature tracks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 9-14 Oct. 2016; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Mitrokhin, A.; Fermüller, C.; Yorke, J.A.; Aloimonos, Y. Unsupervised Learning of Dense Optical Flow, Depth and Egomotion with Event-Based Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 24 Oct.-24 Jan. 2021; pp. 5831–5838. [Google Scholar]
- Chaney, K.; Zhu, A.Z.; Daniilidis, K. Learning Event-Based Height From Plane and Parallax. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 16-17 June 2019; pp. 1634–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, A.; Do, T.T.; Caldwell, D.G.; Tsagarakis, N.G. Real-Time 6DOF Pose Relocalization for Event Cameras With Stacked Spatial LSTM Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 16-17 June 2019; pp. 1638–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Carrió, J.; Gehrig, D.; Scaramuzza, D. Learning Monocular Dense Depth from Events. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 25-28 Nov. 2020; pp. 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrig, D.; Rüegg, M.; Gehrig, M.; Hidalgo-Carrió, J.; Scaramuzza, D. Combining Events and Frames Using Recurrent Asynchronous Multimodal Networks for Monocular Depth Prediction. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Z.; Thakur, D.; Özaslan, T.; Pfrommer, B.; Kumar, V.; Daniilidis, K. The Multivehicle Stereo Event Camera Dataset: An Event Camera Dataset for 3D Perception. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2018, 3, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Snavely, N. MegaDepth: Learning Single-View Depth Prediction from Internet Photos. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 2041–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Clady, X.; Ieng, S.-H.; Benosman, R. Asynchronous event-based corner detection and matching. Neural Networks 2015, 66, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clady, X.; Maro, J.M.; Barré, S.; Benosman, R.B. A motion-based feature for event-based pattern recognition. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasco, V.; Glover, A.; Bartolozzi, C. Fast event-based Harris corner detection exploiting the advantages of event-driven cameras. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 9-14 Oct. 2016; pp. 4144–4149. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerlinck, C.; Barnes, N.; Mahony, R. Asynchronous Spatial Image Convolutions for Event Cameras. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2019, 4, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueggler, E.; Bartolozzi, C.; Scaramuzza, D. Fast Event-based Corner Detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference.
- Zhu, A.Z.; Atanasov, N.; Daniilidis, K. Event-based feature tracking with probabilistic data association. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 29 May-3 June 2017; pp. 4465–4470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.Z.; Atanasov, N.; Daniilidis, K. Event-Based Visual Inertial Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 21-26 July 2017; pp. 5816–5824. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, A.R.; Rebecq, H.; Horstschaefer, T.; Scaramuzza, D. Ultimate SLAM? Combining Events, Images, and IMU for Robust Visual SLAM in HDR and High-Speed Scenarios. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2018, 3, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderscheid, J.; Sironi, A.; Bourdis, N.; Migliore, D.; Lepetit, V. Speed Invariant Time Surface for Learning to Detect Corner Points With Event-Based Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 15-20 June 2019; pp. 10237–10246. [Google Scholar]
- Chiberre, P.; Perot, E.; Sironi, A.; Lepetit, V. Detecting Stable Keypoints from Events through Image Gradient Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 19-25 June 2021; pp. 1387–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Gioi, R.G.v.; Jakubowicz, J.; Morel, J.M.; Randall, G. LSD: A Fast Line Segment Detector with a False Detection Control. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2010, 32, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everding, L.; Conradt, J. Low-latency line tracking using event-based dynamic vision sensors. Frontiers in Neurorobotics 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzhen, Y.; Ramalingam, S. Fast localization and tracking using event sensors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 16-21 May 2016; pp. 4564–4571. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, J.; Yiğit, A.; Durand, S. Embedded Event-based Visual Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Event-Based Control, Communication, 23-25 Sept. 2020, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP); pp. 1–8.
- Chamorro, W.; Solà, J.; Andrade-Cetto, J. Event-Based Line SLAM in Real-Time. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 8146–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Lu, P. PL-EVIO: Robust Monocular Event-Based Visual Inertial Odometry With Point and Line Features. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brändli, C.; Strubel, J.; Keller, S.; Scaramuzza, D.; Delbruck, T. ELiSeD - An event-based line segment detector. In Proceedings of the 2016 Second International Conference on Event-based Control, Communication, 13-15 June 2016, and Signal Processing (EBCCSP); pp. 1–7.
- Valeiras, D.R.; Clady, X.; Ieng, S.H.; Benosman, R. Event-Based Line Fitting and Segment Detection Using a Neuromorphic Visual Sensor. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2019, 30, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrig, D.; Rebecq, H.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. EKLT: Asynchronous Photometric Feature Tracking Using Events and Frames. International Journal of Computer Vision 2020, 128, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, H.; Lim, J. Robust Feature Tracking in DVS Event Stream using Bézier Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 1-5 March 2020; pp. 1647–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, J.; Klenk, S.; Cremers, D. Event-Based Feature Tracking in Continuous Time with Sliding Window Optimization. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzugaray, I.; Chli, M. HASTE: multi-Hypothesis Asynchronous Speeded-up Tracking of Events. In Proceedings of the 31st British Machine Vision Virtual Conference (BMVC 2020), 7–10.
- Hadviger, A.; Cvišić, I.; Marković, I.; Vražić, S.; Petrović, I. Feature-based Event Stereo Visual Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2021 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), 31 Aug.-3 Sept. 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Kim, Y.; Lim, H.; Lee, A.J.; Myung, H. eCDT: Event Clustering for Simultaneous Feature Detection and Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 23-27 Oct. 2022; pp. 3808–3815. [Google Scholar]
- Messikommer, N.; Fang, C.; Gehrig, M.; Scaramuzza, D. Data-Driven Feature Tracking for Event Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 17-24 June 2023; pp. 5642–5651. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Carrió, J.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-aided Direct Sparse Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 18-24 June 2022; pp. 5771–5780. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Horstschaefer, T.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. EVO: A Geometric Approach to Event-Based 6-DOF Parallel Tracking and Mapping in Real Time. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2017, 2, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecq, H.; Gallego, G.; Mueggler, E.; Scaramuzza, D. EMVS: Event-Based Multi-View Stereo—3D Reconstruction with an Event Camera in Real-Time. International Journal of Computer Vision 2018, 126, 1394–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Kneip, L. DEVO: Depth-Event Camera Visual Odometry in Challenging Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA; pp. 2179–2185.
- Gallego, G.; Rebecq, H.; Scaramuzza, D. A Unifying Contrast Maximization Framework for Event Cameras, with Applications to Motion, Depth, and Optical Flow Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 3867–3876. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Learned-Miller, E.; Sheldon, D.; Gallego, G.; Bideau, P. The Spatio-Temporal Poisson Point Process: A Simple Model for the Alignment of Event Camera Data. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 10-17 Oct. 2021; pp. 13475–13484. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Brown, M.; Snavely, N.; Lowe, D.G. Unsupervised Learning of Depth and Ego-Motion from Video. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 21-26 July 2017; pp. 6612–6619. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Clark, R.; Wen, H.; Trigoni, N. DeepVO: Towards end-to-end visual odometry with deep Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 29 May-3 June 2017; pp. 2043–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Stumberg, L.v.; Wang, R.; Cremers, D. D3VO: Deep Depth, Deep Pose and Deep Uncertainty for Monocular Visual Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 13-19 June 2020; pp. 1278–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Towards Scale Consistent Monocular Visual Odometry by Learning from the Virtual World. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 23-27 May 2022; pp. 5601–5607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Tao, D. JPerceiver: Joint Perception Network for Depth, Pose and Layout Estimation in Driving Scenes. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2022, 2022, Springer: Cham; pp. 708–726.
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Towards Scale-Aware, Robust, and Generalizable Unsupervised Monocular Depth Estimation by Integrating IMU Motion Dynamics. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2022, 2022, Springer: Cham; pp. 143–160.
- Zhu, A.Z.; Yuan, L.; Chaney, K.; Daniilidis, K. Unsupervised Event-Based Learning of Optical Flow, Depth, and Egomotion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 15-20 June 2019; pp. 989–997. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Wu, Y.J.; Deng, L.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y. Comparing SNNs and RNNs on neuromorphic vision datasets: Similarities and differences. Neural Networks 2020, 132, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Liang, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, G.; Li, P.; Xie, Y. Rethinking the performance comparison between SNNS and ANNS. Neural Networks 2020, 121, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, L.R.; Chua, Y.; Li, H. Is Neuromorphic MNIST neuromorphic? Analyzing the discriminative power of neuromorphic datasets in the time domain. 2018, 10.3389/fnins.2021.608567. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Panda, P. Optimizing Deeper Spiking Neural Networks for Dynamic Vision Sensing. Neural Networks 2021, 144, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Cao, G.; Li, G. Sparser spiking activity can be better: Feature Refine-and-Mask spiking neural network for event-based visual recognition. Neural Networks 2023, 166, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueggler, E.; Rebecq, H.; Gallego, G.; Delbruck, T.; Scaramuzza, D. The event-camera dataset and simulator: Event-based data for pose estimation, visual odometry, and SLAM. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2017, 36, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gallego, G.; Rebecq, H.; Kneip, L.; Li, H.; Scaramuzza, D. Semi-dense 3D Reconstruction with a Stereo Event Camera. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2018, 2018, Springer: Cham; pp. 242–258.
- Guan, W.; Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Lu, P. PL-EVIO: Robust Monocular Event-based Visual Inertial Odometry with Point and Line Features.
- Delmerico, J.; Cieslewski, T.; Rebecq, H.; Faessler, M.; Scaramuzza, D. Are We Ready for Autonomous Drone Racing? In The UZH-FPV Drone Racing Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 20-24 May 2019; pp. 6713–6719. [Google Scholar]
- Klenk, S.; Chui, J.; Demmel, N.; Cremers, D. TUM-VIE: The TUM Stereo Visual-Inertial Event Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 27 Sept.-1 Oct. 2021; pp. 8601–8608. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Kneip, L. VECtor: A Versatile Event-Centric Benchmark for Multi-Sensor SLAM. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 8217–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, A.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Zou, D. M2DGR: A Multi-Sensor and Multi-Scenario SLAM Dataset for Ground Robots. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, J.; Engelhard, N.; Endres, F.; Burgard, W.; Cremers, D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 7-12 Oct. 2012; pp. 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, G.; Lund, J.E.A.; Mueggler, E.; Rebecq, H.; Delbruck, T.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-Based, 6-DOF Camera Tracking from Photometric Depth Maps. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, U.M.; Demiris, Y. Entropy Minimisation Framework for Event-Based Vision Model Estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2020, 2020, Springer: Cham; pp. 161–176.
- Nunes, U.M.; Demiris, Y. Robust Event-Based Vision Model Estimation by Dispersion Minimisation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2022, 44, 9561–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryner, S.; Gallego, G.; Rebecq, H.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-based, Direct Camera Tracking from a Photometric 3D Map using Nonlinear Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 20-24 May 2019; pp. 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Koltun, V.; Cremers, D. Direct Sparse Odometry. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecq, H.; Ranftl, R.; Koltun, V.; Scaramuzza, D. High Speed and High Dynamic Range Video with an Event Camera. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 43, 1964–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Lu, P. Monocular Event Visual Inertial Odometry based on Event-corner using Sliding Windows Graph-based Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 23-27 Oct. 2022; pp. 2438–2445. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falotico, E.; Vannucci, L.; Ambrosano, A.; Albanese, U.; Ulbrich, S.; Vasquez Tieck, J.C.; Hinkel, G.; Kaiser, J.; Peric, I.; Denninger, O.; et al. Connecting Artificial Brains to Robots in a Comprehensive Simulation Framework: The Neurorobotics Platform. Frontiers in Neurorobotics 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Jaiswal, A.; Panda, P. Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing. Nature 2019, 575, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furber, S. Large-scale neuromorphic computing systems. Journal of Neural Engineering 2016, 13, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, S.R.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Babu, A.V.; Rajendran, B. Building Brain-Inspired Computing Systems: Examining the Role of Nanoscale Devices. IEEE Nanotechnology Magazine 2018, 12, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolozzi, C.; Indiveri, G.; Donati, E. Embodied neuromorphic intelligence. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Srinivasa, N.; Lin, T.H.; Chinya, G.; Cao, Y.; Choday, S.H.; Dimou, G.; Joshi, P.; Imam, N.; Jain, S.; et al. Loihi: A Neuromorphic Manycore Processor with On-Chip Learning. IEEE Micro 2018, 38, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.D.; Aimone, J.B.; Miner, N.E.; Vineyard, C.M.; Rothganger, F.H.; Carlson, K.D.; Mulder, S.A.; Draelos, T.J.; Faust, A.; Marinella, M.J.; et al. A historical survey of algorithms and hardware architectures for neural-inspired and neuromorphic computing applications. In Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures, Elsevier B.V.: 2017; Vol. 19, pp 49-64.
- Strukov, D.; Indiveri, G.; Grollier, J.; Fusi, S. Building brain-inspired computing. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, C.S.; Molin, J.L.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Indiveri, G.; Kumar, K.; Qiao, N.; Schemmel, J.; Wang, R.; Chicca, E.; Olson Hasler, J.; et al. Large-Scale Neuromorphic Spiking Array Processors: A Quest to Mimic the Brain. In Frontiers in Neuroscience, Frontiers Media S.A.: 2018; Vol. 12.
- Furber, S.B.; Galluppi, F.; Temple, S.; Plana, L.A. The SpiNNaker project. Proceedings of the the IEEE 2014, 102, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furber, S. Large-scale neuromorphic computing systems. In Journal of Neural Engineering, Institute of Physics Publishing: 2016; Vol. 13.
- Schemmel, J.; Brüderle, D.; Grübl, A.; Hock, M.; Meier, K.; Millner, S. A wafer-scale neuromorphic hardware system for large-scale neural modeling. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 30 May-2 June 2010; pp. 1947–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, S.; Klähn, J.; Bellec, G.; Grübl, A.; Güttler, M.; Hartel, A.; Hartmann, S.; Husmann, D.; Husmann, K.; Jeltsch, S.; et al. Neuromorphic hardware in the loop: Training a deep spiking network on the BrainScaleS wafer-scale system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 14-19 May 2017; pp. 2227–2234. [Google Scholar]
- DeBole, M.V.; Taba, B.; Amir, A.; Akopyan, F.; Andreopoulos, A.; Risk, W.P.; Kusnitz, J.; Otero, C.O.; Nayak, T.K.; Appuswamy, R.; et al. TrueNorth: Accelerating From Zero to 64 Million Neurons in 10 Years. Computer 2019, 52, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainchip. Availabe online: https://brainchip.com/akida-generations/ (accessed on 4/10/2023).
- Vanarse, A.; Osseiran, A.; Rassau, A. Neuromorphic engineering — A paradigm shift for future IM technologies. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine 2019, 22, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppner, S.; Yan, Y.; Dixius, A.; Scholze, S.; Partzsch, J.; Stolba, M.; Kelber, F.; Vogginger, B.; Neumärker, F.; Ellguth, G.; et al. The SpiNNaker 2 Processing Element Architecture for Hybrid Digital Neuromorphic Computing. Hardware Architecture, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Chezhegov, A.; Kiselev, M.; Grunin, A.; Larionov, D. Neuromorphic artificial intelligence systems. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C.; Hoeppner, S.; Furber, S.B. SpiNNaker 2: A 10 Million Core Processor System for Brain Simulation and Machine Learning. Emerging Technologies, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Albada, S.J.; Rowley, A.G.; Senk, J.; Hopkins, M.; Schmidt, M.; Stokes, A.B.; Lester, D.R.; Diesmann, M.; Furber, S.B. Performance Comparison of the Digital Neuromorphic Hardware SpiNNaker and the Neural Network Simulation Software NEST for a Full-Scale Cortical Microcircuit Model. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merolla, P.A.; Arthur, J.V.; Alvarez-Icaza, R.; Cassidy, A.S.; Sawada, J.; Akopyan, F.; Jackson, B.L.; Imam, N.; Guo, C.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Artificial brains. A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 2014, 345, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreopoulos, A.; Kashyap, H.J.; Nayak, T.K.; Amir, A.; Flickner, M.D. A Low Power, High Throughput, Fully Event-Based Stereo System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 7532–7542. [Google Scholar]
- DeWolf, T.; Jaworski, P.; Eliasmith, C. Nengo and Low-Power AI Hardware for Robust, Embedded Neurorobotics. Frontiers in Neurorobotics 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagsted, R.K.; Vitale, A.; Renner, A.; Larsen, L.B.; Christensen, A.L.; Sandamirskaya, Y. Event-based PID controller fully realized in neuromorphic hardware: A one DoF study. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems; 2020/10//; pp. 10939–10944. [Google Scholar]
- Lava software framework. Availabe online: https://lava-nc.org/ (accessed on 30/4).
- Grübl, A.; Billaudelle, S.; Cramer, B.; Karasenko, V.; Schemmel, J. Verification and Design Methods for the BrainScaleS Neuromorphic Hardware System. Journal of Signal Processing Systems 2020, 92, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, T.; Kungl, A.F.; Müller, E.; Hartel, A.; Stradmann, Y.; Aamir, S.A.; Grübl, A.; Heimbrecht, A.; Schreiber, K.; Stöckel, D.; et al. Demonstrating Advantages of Neuromorphic Computation: A Pilot Study. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolla, P.; Arthur, J.; Akopyan, F.; Imam, N.; Manohar, R.; Modha, D.S. A digital neurosynaptic core using embedded crossbar memory with 45pJ per spike in 45nm. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), 19-21 Sept. 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Stromatias, E.; Neil, D.; Galluppi, F.; Pfeiffer, M.; Liu, S.C.; Furber, S. Scalable energy-efficient, low-latency implementations of trained spiking Deep Belief Networks on SpiNNaker. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 12-17 July 2015; Volume 2324, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Querlioz, D.; Bichler, O.; Gamrat, C. Simulation of a memristor-based spiking neural network immune to device variations. In Proceedings of the The 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 31 July-5 Aug 2011; Volume 375, pp. 1775–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, B.; Billaudelle, S.; Kanya, S.; Leibfried, A.; Grübl, A.; Karasenko, V.; Pehle, C.; Schreiber, K.; Stradmann, Y.; Weis, J.; et al. Surrogate gradients for analog neuromorphic computing. Proceedings of the the National Academy of Sciences 2022, 119, e2109194119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.; Wunderlich, T.C.; Pehle, C.; Petrovici, M.A.; Schemmel, J.; Meier, K. Closed-loop experiments on the BrainScaleS-2 architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 Annual Neuro-Inspired Computational Elements Workshop, 2020, Association for Computing Machinery: Heidelberg, Germany; p. 17.
- Moradi, S.; Qiao, N.; Stefanini, F.; Indiveri, G. A Scalable Multicore Architecture With Heterogeneous Memory Structures for Dynamic Neuromorphic Asynchronous Processors (DYNAPs). IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems 2017, 12, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanarse, A.; Osseiran, A.; Rassau, A.; van der Made, P. A Hardware-Deployable Neuromorphic Solution for Encoding and Classification of Electronic Nose Data. In Sensors, 2019; Vol. 19.
- Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Dang, X. Supervised learning in spiking neural networks: A review of algorithms and evaluations. Neural Networks 2020, 125, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. The bulletin of mathematical biophysics 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fouda, M.E.; Eltawil, A.M.; Salama, K.N. Neural Coding in Spiking Neural Networks: A Comparative Study for Robust Neuromorphic Systems. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jia, S.; Cheng, X.; Xu, B. Tuning Convolutional Spiking Neural Network With Biologically Plausible Reward Propagation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2022, 33, 7621–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordone, L. Performance of spiking neural networks on event data for embedded automotive applications; Université Côte d’Azur: 2022.
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Luo, T.; Qu, C.; Aung, M.T.L.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wong, M.M.; Pu, J.; Do, A.T.; et al. Coreset: Hierarchical neuromorphic computing supporting large-scale neural networks with improved resource efficiency. Neurocomputing 2022, 474, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Shah, A.; Michmizos, K.P. Spiking Neural Network on Neuromorphic Hardware for Energy-Efficient Unidimensional SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 3-8 Nov. 2019; pp. 4176–4181. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, A.; Fang, H.; Mei, Z.; Rider, D.P.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Q. A Survey on Neuromorphic Computing: Models and Hardware. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine 2022, 22, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiser, R.; Cartiglia, M.; Martel, J.N.P.; Conradt, J.; Sandamirskaya, Y. A Neuromorphic Approach to Path Integration: A Head-Direction Spiking Neural Network with Vision-driven Reset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 27-30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiser, R.; Renner, A.; Sandamirskaya, Y.; Pienroj, P. Pose Estimation and Map Formation with Spiking Neural Networks: towards Neuromorphic SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 1-5 Oct. 2018; pp. 2159–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiser, R.; Waibel, G.; Armengol, N.; Renner, A.; Sandamirskaya, Y. Error estimation and correction in a spiking neural network for map formation in neuromorphic hardware. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 31 May-31 Aug. 2020; pp. 6134–6140. [Google Scholar]
- Aboumerhi, K.; Güemes, A.; Liu, H.; Tenore, F.; Etienne-Cummings, R. Neuromorphic applications in medicine. Journal of Neural Engineering 2023, 20, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.; Preyer, A.; Babalola, K.; Butera, R.J.; Hasler, P. An artificial synapse for interfacing to biological neurons. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 21-24 May 2006; pp. 4–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Boi, F.; Moraitis, T.; De Feo, V.; Diotalevi, F.; Bartolozzi, C.; Indiveri, G.; Vato, A. A Bidirectional Brain-Machine Interface Featuring a Neuromorphic Hardware Decoder. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurse, E.; Mashford, B.S.; Yepes, A.J.; Kiral-Kornek, I.; Harrer, S.; Freestone, D.R. Decoding EEG and LFP signals using deep learning: heading TrueNorth. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers, 2016, Association for Computing Machinery: Como, Italy; pp. 259–266.
- Jung, R.; Brauer, E.J.; Abbas, J.J. Real-time interaction between a neuromorphic electronic circuit and the spinal cord. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2001, 9, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, F.; Bontrager, D.; Indiveri, G. Toward neuromorphic intelligent brain-machine interfaces: An event-based neural recording and processing system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, 22-24 Oct. 2014; pp. 584–587. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, F.; Indiveri, G. A Neuromorphic Event-Based Neural Recording System for Smart Brain-Machine-Interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems 2015, 9, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Suh, J.; Bakkaloglu, B.; Cao, Y. A workload-aware neuromorphic controller for dynamic power and thermal management. In Proceedings of the 2011 NASA/ESA Conference on Adaptive Hardware and Systems (AHS), 6-9 June 2011; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Brooke, M. A fully parallel learning neural network chip for real-time control. In Proceedings of the IJCNN'99. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Proceedings (Cat. No.99CH36339), 10-16 July 1999; pp. 2323–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Brooke, M. Fully parallel on-chip learning hardware neural network for real-time control. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 30 May-2 June 1999; pp. 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H. A novel memristive multilayer feedforward small-world neural network with its applications in PID control. ScientificWorldJournal 2014, 2014, 394828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocke, P.; McGinley, B.; Maher, J.; Morgan, F.; Harkin, J. Investigating the Suitability of FPAAs for Evolved Hardware Spiking Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Evolvable Systems: From Biology to Hardware, Berlin, Heidelberg; 2008//; pp. 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, M.E.; Chan, J.; Daffron, C.; Disney, A.; Reynolds, J.; Rose, G.; Plank, J.S.; Birdwell, J.D.; Schuman, C.D. An Application Development Platform for neuromorphic computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 24-29 July 2016; pp. 1347–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Schuman, C.D.; Disney, A.; Singh, S.P.; Bruer, G.; Mitchell, J.P.; Klibisz, A.; Plank, J.S. Parallel Evolutionary Optimization for Neuromorphic Network Training. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd Workshop on Machine Learning in HPC Environments (MLHPC), 14-14 Nov. 2016; pp. 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Galluppi, F.; Davies, S.; Rast, A.; Sharp, T.; Plana, L.A.; Furber, S. A hierachical configuration system for a massively parallel neural hardware platform. In Proceedings of the 9th conference on Computing Frontiers, 2012, Association for Computing Machinery: Cagliari, Italy; Plana, L.A.; pp. 183–192.
- Arthur, J.V.; Merolla, P.A.; Akopyan, F.; Alvarez, R.; Cassidy, A.; Chandra, S.; Esser, S.K.; Imam, N.; Risk, W.; Rubin, D.B.D.; et al. Building block of a programmable neuromorphic substrate: A digital neurosynaptic core. In Proceedings of the The 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 10-15 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shrestha, A.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q. System Design for In-Hardware STDP Learning and Spiking Based Probablistic Inference. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), 11-13 July 2016; pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, J.; Andreou, A.G.; Pouliquen, P.O. A mixed analog/digital asynchronous processor for cortical computations in 3D SOI-CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 21-24 May 2006; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Shih-Chii, L.; Oster, M. Feature competition in a spike-based winner-take-all VLSI network. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 21-24 May 2006; pp. 4–3637. [Google Scholar]
- Glackin, B.; Harkin, J.; McGinnity, T.M.; Maguire, L.P.; Wu, Q. Emulating Spiking Neural Networks for edge detection on FPGA hardware. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, 31 Aug.-2 Sept. 2009; pp. 670–673. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.H.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Andreou, A.G. Probabilistic synaptic weighting in a reconfigurable network of VLSI integrate-and-fire neurons. Neural Networks 2001, 14, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Han, W.H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.B.; Yang, F.H. An analog CMOS pulse coupled neural network for image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, 1-4 Nov. 2010; pp. 1883–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Secco, J.; Farina, M.; Demarchi, D.; Corinto, F. Memristor cellular automata through belief propagation inspired algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), 2-5 Nov. 2015; pp. 211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bohrn, M.; Fujcik, L.; Vrba, R. Field Programmable Neural Array for feed-forward neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 36th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), 2-4 July 2013; pp. 727–731. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.C.; Sheu, B.J.; Chen, O.T.C.; Choi, J. A VLSI neural processor for image data compression using self-organization networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 1992, 3, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.J.; Toledo, F.J.; Ferrández, J.M. New emulated discrete model of CNN architecture for FPGA and DSP applications. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Nets Problem Solving Methods, Heidelberg, 2003, Springer: Berlin; pp. 33–40.
- Shi, B.E.; Tsang, E.K.S.; Lam, S.Y.M.; Yicong, M. Expandable hardware for computing cortical feature maps. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 21-24 May 2006; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ielmini, D.; Ambrogio, S.; Milo, V.; Balatti, S.; Wang, Z.Q. Neuromorphic computing with hybrid memristive/CMOS synapses for real-time learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 22-25 May 2016; pp. 1386–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R.; Kyrmanidis, A.; Hellweg, W.L.; Ponce, P.M.; Saleh, L.A.; Schroeder, D.; Krautschneider, W.H. Integrated circuit with memristor emulator array and neuron circuits for neuromorphic pattern recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 39th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), 27-29 June 2016; pp. 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Rose, G.S. Hardware realization of BSB recall function using memristor crossbar arrays. In Proceedings of the DAC Design Automation Conference 2012, 3-7 June 2012; pp. 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Tarkov, M.S. Hopfield Network with Interneuronal Connections Based on Memristor Bridges. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2016, 2016, Springer: Cham; pp. 196–203.
- Soltiz, M.; Kudithipudi, D.; Merkel, C.; Rose, G.S.; Pino, R.E. Memristor-Based Neural Logic Blocks for Nonlinearly Separable Functions. IEEE Transactions on Computers 2013, 62, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Forgetting memristor based neuromorphic system for pattern training and recognition. Neurocomputing 2017, 222, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.; Calayir, V.; Pileggi, L.; Weldon, J.A. Ultracompact Graphene Multigate Variable Resistor for Neuromorphic Computing. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology 2016, 15, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.B.Q.W.W.; Rajendran, J. Security of neuromorphic computing: Thwarting learning attacks using memristor's obsolescence effect. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Austin, TX, USA; pp. 1–6.
- Vitabile, S.; Conti, V.; Gennaro, F.; Sorbello, F. Efficient MLP digital implementation on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 8th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD'05), 30 Aug.-3 Sept. 2005; pp. 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Garbin, D.; Vianello, E.; Bichler, O.; Azzaz, M.; Rafhay, Q.; Candelier, P.; Gamrat, C.; Ghibaudo, G.; DeSalvo, B.; Perniola, L. On the impact of OxRAM-based synapses variability on convolutional neural networks performance. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures (NANOARCH´15), 8-10 July 2015; pp. 193–198.
- Fieres, J.; Schemmel, J.; Meier, K. Training convolutional networks of threshold neurons suited for low-power hardware implementation. In Proceedings of the The 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Network Proceedings, 16-21 July 2006; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, K.; R, S.P.; R. K, N. Identification of traffic signs for advanced driving assistance systems in smart cities using deep learning. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2023, 82, 26465–26480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrayev, T.; James, A.P.; Merkel, C.; Kudithipudi, D. A design of HTM spatial pooler for face recognition using memristor-CMOS hybrid circuits. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 22-25 May 2016; pp. 1254–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Knag, P.; Chester, L.; Zhengya, Z. A 1. In 40mm2 141mW 898GOPS sparse neuromorphic processor in 40nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI-Circuits), 15-17 June 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Farabet, C.; Poulet, C.; Han, J.Y.; LeCun, Y. CNP: An FPGA-based processor for Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, 31 Aug.-2 Sept. 2009; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.H. Applying Artificial Neural Networks for Face Recognition. Advances in Artificial Neural Systems 2011, 2011, 673016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, Á.-S.; Jesús, A.Á.-C.; Roberto, H.-C. Detection of facial emotions using neuromorphic computation. In Proceedings of the Proc.SPIE; p. 122260.
- Manakitsa, N.; Maraslidis, G.S.; Moysis, L.; Fragulis, G.F. A Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, and Human Action Recognition in Machine and Robotic Vision. In Technologies, 2024; Vol. 12.
- Adhikari, S.P.; Yang, C.; Kim, H.; Chua, L.O. Memristor Bridge Synapse-Based Neural Network and Its Learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2012, 23, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Bao, W.; Tao, L.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, D.; Xiong, J.; Shang, D. High-Speed Object Recognition Based on a Neuromorphic System. In Electronics, 2022; Vol. 11.
- Yang, B. Research on Vehicle Detection and Recognition Technology Based on Artificial Intelligence. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2023, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Gao, L.; Su, M.; You, Q.; Qu, H.; Sun, Q. A Novel Neural Network Model for Traffic Sign Detection and Recognition under Extreme Conditions. Journal of Sensors 2021, 2021, 9984787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, A.; Huang, C.-C.; Men, T.-C.; Lin, F.-C.; Wang, H.-C. Air Pollution Detection Using a Novel Snap-Shot Hyperspectral Imaging Technique. In Sensors, 2022; Vol. 22.
- Kow, P.-Y.; Hsia, I.W.; Chang, L.-C.; Chang, F.-J. Real-time image-based air quality estimation by deep learning neural networks. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 307, 114560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorato, M.; Valle, M.; Caviglia, D.D.; Bisio, G.M. Non-linear circuit effects on analog VLSI neural network implementations. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Microelectronics for Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems, 26-28 Sept 1994; pp. 430–438.
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, S. Using Deep Learning to Detect Defects in Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Survey and Current Challenges. In Materials, 2020; Vol. 13.
- Aibe, N.; Mizuno, R.; Nakamura, M.; Yasunaga, M.; Yoshihara, I. Performance evaluation system for probabilistic neural network hardware. Artificial Life and Robotics 2004, 8, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceolini, E.; Frenkel, C.; Shrestha, S.B.; Taverni, G.; Khacef, L.; Payvand, M.; Donati, E. Hand-Gesture Recognition Based on EMG and Event-Based Camera Sensor Fusion: A Benchmark in Neuromorphic Computing. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Aldrich, C. Deep Learning Approaches to Image Texture Analysis in Material Processing. In Metals, 2022; Vol. 12.
- Dixit, U.; Mishra, A.; Shukla, A.; Tiwari, R. Texture classification using convolutional neural network optimized with whale optimization algorithm. SN Applied Sciences 2019, 1, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roska, T.; Horvath, A.; Stubendek, A.; Corinto, F.; Csaba, G.; Porod, W.; Shibata, T.; Bourianoff, G. An Associative Memory with oscillatory CNN arrays using spin torque oscillator cells and spin-wave interactions architecture and End-to-end Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2012 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, 29-31 Aug. 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, D.; Chen, Y.; Kim, K. A neuromorphic system for video object recognition. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salih, A.A.M.; Ahson, S.I. Object detection and features extraction in video frames using direct thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies, 14-16 March 2009; pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Liao, B.; Huang, L.; Gong, Y.; Huang, C. Real-time and accurate object detection in compressed video by long short-term feature aggregation. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 2021, 206, 103188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wei, H.; Li, B.; Yuan, X.; Kehtarnavaz, N. A Review of Video Object Detection: Datasets, Metrics and Methods. In Applied Sciences, 2020; Vol. 10.
- Koh, T.C.; Yeo, C.K.; Jing, X.; Sivadas, S. Towards efficient video-based action recognition: context-aware memory attention network. SN Applied Sciences 2023, 5, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Caballero, A.; Fuentes-Jiménez, D.; Losada-Gutiérrez, C. Real-time human action recognition using raw depth video-based recurrent neural networks. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2023, 82, 16213–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-K.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wang, W.-Y.; Huang, S.-K. Deep Learning-Based Real-Time Multiple-Person Action Recognition System. In Sensors, 2020; Vol. 20.
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.-W.; Lee, J.; Bae, O.; Hong, C.-P. An Effective Motion-Tracking Scheme for Machine-Learning Applications in Noisy Videos. In Applied Sciences, 2023; Vol. 13.
- Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Yang, Y. Moving scene object tracking method based on deep convolutional neural network. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2024, 86, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypkowiak, S.S.; Jain, V.K. Video motion estimation using a neural network. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems - ISCAS '94, 30 May-2 June 1994; pp. 217–220213.
- Botella, G.; García, C. Real-time motion estimation for image and video processing applications. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing 2016, 11, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kong, K.; Bae, G.; Song, W.-J. BlockNet: A Deep Neural Network for Block-Based Motion Estimation Using Representative Matching. In Symmetry, 2020; Vol. 12.
- Yoon, J.H.; Raychowdhury, A. NeuroSLAM: A 65-nm 7.25-to-8.79-TOPS/W Mixed-Signal Oscillator-Based SLAM Accelerator for Edge Robotics. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Rush, A.; Merkel, C.; Herrmann, E.; Jacob, A.P.; Thiem, C.; Jha, R. A neuromorphic SLAM architecture using gated-memristive synapses. Neurocomputing 2020, 381, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, J.H. A Neuromorphic SLAM Accelerator Supporting Multi-Agent Error Correction in Swarm Robotics. In Proceedings of the Proceedings - International SoC Design Conference 2022, ISOCC 2022; pp. 241–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.H.; Raychowdhury, A. 31. In 1 A 65nm 8.79TOPS/W 23.82mW Mixed-Signal Oscillator-Based NeuroSLAM Accelerator for Applications in Edge Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), 16-20 Feb. 2020; pp. 478–480. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Yu, F.; Gu, F.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, X. ORB-NeuroSLAM: A Brain-Inspired 3-D SLAM System Based on ORB Features. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024, 11, 12408–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Name | Sensors | Descriptions (Key Points) | Strength (Achievements) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | TextSLAM [45] |
RGB-D | Text objects in the environment are used to extract semantic features |
More accurate and robust even under challenging conditions |
| 2023 | HFNet-SLAM [7] |
Monocular | Extension of ORB-SLAM3 (incorporates CNNs) | Performs better than ORB-SLAM3 (higher accuracy) |
| 2022 | SO-SLAM [46] |
Monocular | Introduced object spatial constraints (object level map) |
Proposed two new methods for object SLAM |
| 2022 | SDF-SLAM [47] |
Monocular | Semantic deep fusion model with deep learning | Less absolute error than the state-of-the-art SLAM framework |
| 2022 | UV-SLAM [48] |
Monocular | Vanishing points (line features) are used for structural mapping |
Localization accuracy and mapping quality have improved |
| 2021 | RS-SLAM [49] |
RGB-D | Employed semantic segmentation model |
Both static and dynamic objects are detected |
| 2021 | RDMO-SLAM [50] |
RGB-D | Semantic label prediction using dense optical flow | Reduce the influence of dynamic objects in tracking |
| 2021 | RDS-SLAM [51] |
RGB-D | Extends ORB-SLAM3; Added semantic thread and a semantic-based optimization thread | Tracking thread is not required to wait for semantic information as novel threads run in parallel |
| 2021 | ORB-SLAM3 [52] |
Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D |
Perform visual, visual-inertial and multimap SLAM |
Effectively exploits the data associations and boosts the system accuracy level |
| 2020 | Structure-SLAM [53] |
Monocular | Decoupled rotation and translation estimation |
Outperforms the state of the art on common SLAM benchmarks |
| 2020 | VPS-SLAM [54] |
RGB-D | Combined low-level VO/VIO with planar surfaces |
Provides better results than the state-of-the-art VO/VIO algorithms |
| 2020 | DDL-SLAM [44] |
RGB-D | Dynamic object segmentation and background painting added to ORB-SLAM2 | Dynamic objects detected utilizing semantic segmentation and multi-view geometry |
| 2019 | PL-SLAM [55] |
Stereo | Combines point and line segments | The first open-source SLAM system with points and line segment features |
| 2017 | ORB-SLAM2 [56] |
Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D |
Complete SLAM system including map reuse, loop closing, and re-localization capabilities | Achieved state-of-the-art accuracy while evaluating 29 popular public sequences |
| 2015 | ORB-SLAM [57] |
Monocular | Feature-based monocular SLAM system |
Robust to motion clutter, allows wide baseline loop closing and re-localization |
| 2014 | LSD-SLAM [58] |
Monocular | Direct monocular SLAM system | Achieved post-estimation accuracy and 3D environment reconstructions |
| 2011 | DTAM [42] |
Monocular | Camera tracking and reconstruction based on a dense feature | Achieved real-time performance using the commodity GPU hardware |
| 2007 | PTAM [41] |
Monocular | Estimate camera pose in an unknown scene | Accuracy and robustness have surpassed the state-of-the-art system |
| 2007 | MonoSLAM [40] |
Monocular | Real-Time Single Camera SLAM | Recovered the 3D trajectory of a monocular camera |
| Year | Processor/ Chips |
I/O | On-device Training |
Event-based | Feature Size (nm) | Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | SpiNNaker | Real Numbers, Spikes | STDP | No | 22 | 20 nj/operation |
| 2014 | TrueNorth | Spikes | No | Yes | 28 | 0.18W |
| 2018 | Loihi | Spikes | STDP | Yes | 14 | 80 pj /operation |
| 2020 | BrainScaleS | Real Numbers, Spikes |
STDP, Surrogate Gradient | Yes | 65 | 0.2W |
| 2021 | Loihi2 | Real Numbers, Spikes |
STDP, Surrogate, Backpropagation | Yes | 7 | - |
| 2021 | DYNAP SE2, SEL, CNN | Spikes | STDP (SEL) | Yes | 22 | 10mW |
| 2021 | Akida | Spikes | STDP (Last Layer) |
Yes | 28 | 100 µW– 300 mW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





