Submitted:
15 May 2024
Posted:
15 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of Natural Dyes and Preparation of Mordants
2.3. Natural Dyeing and Mordanting
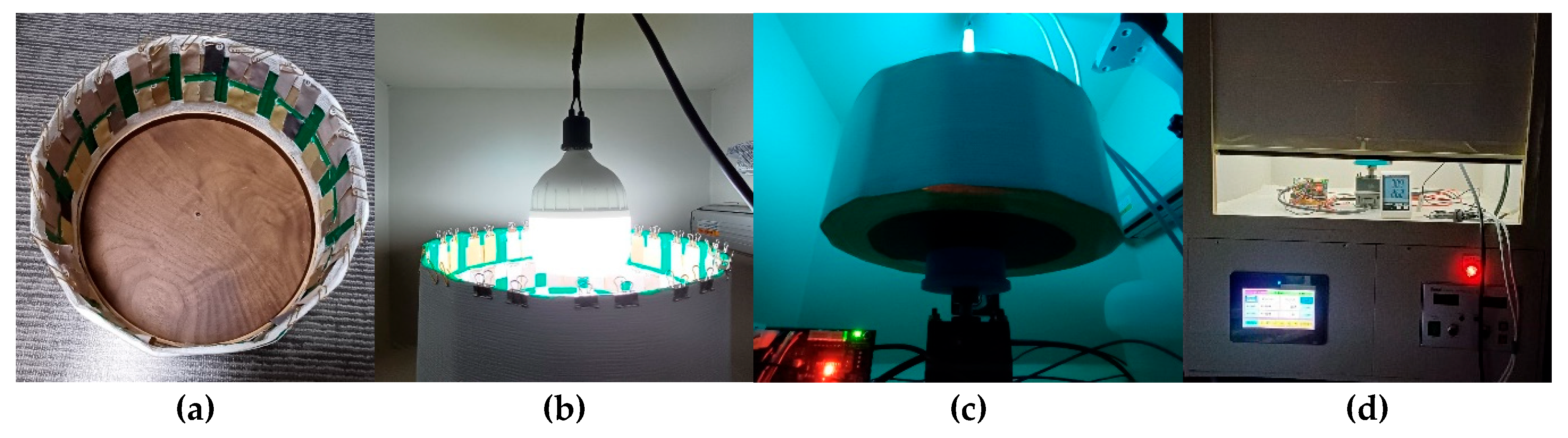
2.4. Exposure to UV-C and D65 Lamps
2.5. Characterization and Chromatic Analyses
3. Results
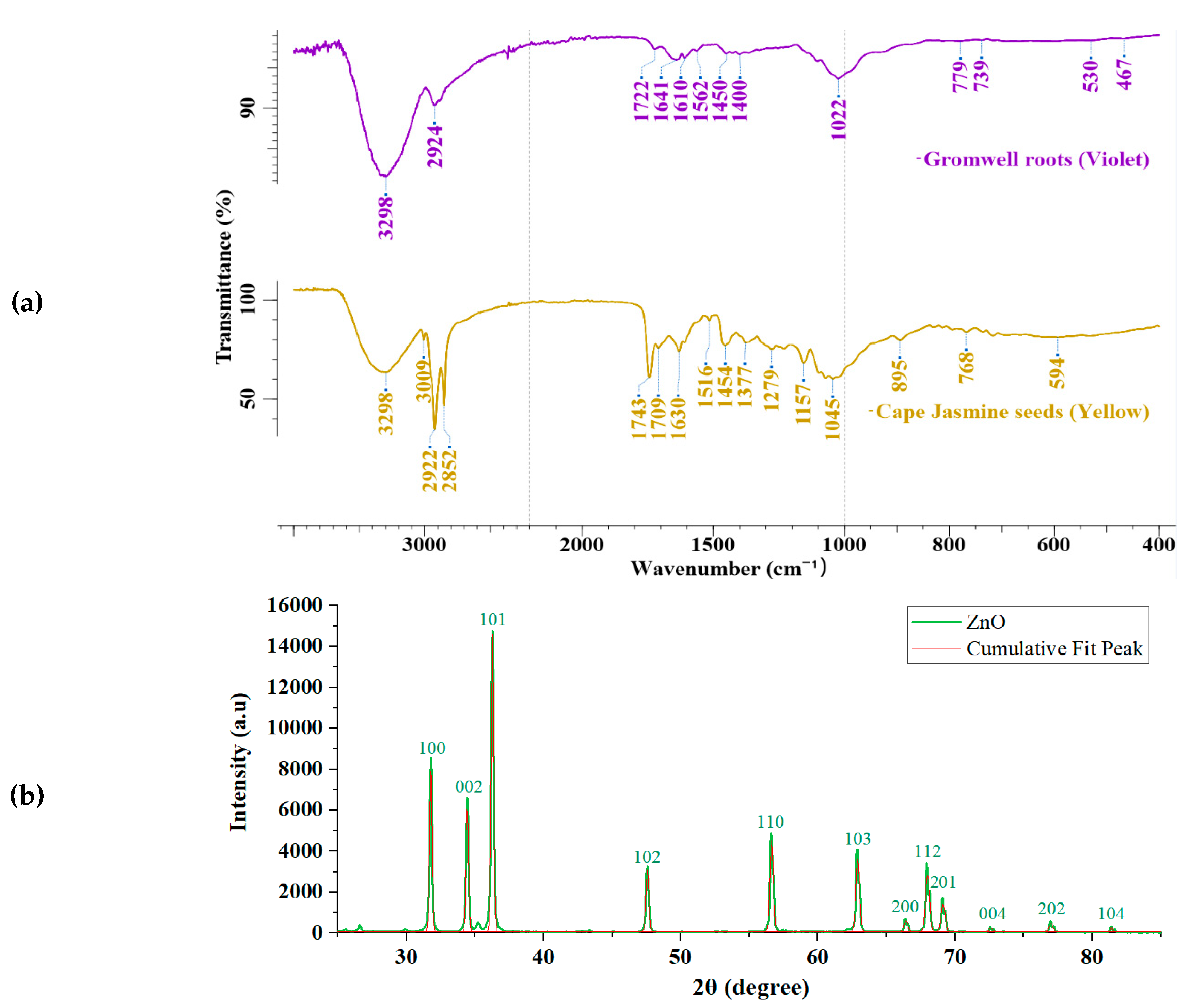
3.1. ATR FTIR Analyses of Natural Dyes and XRD Analyses of Zinc Oxide
3.2. Coloration of Cotton and Polyester Fabrics in Violet and Yellow from Natural Dyes
| Dyes | Gromwell roots (Violet-dyes) [51]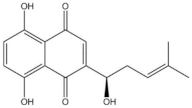
|
||||||
| Fabrics | Cotton-weft twill | Polyester-weft twill | |||||
| Metallic mordants |
UV photo absorber | UV light exposure |
|||||
| Pristine | ZnO | ZnO/phenol | Pristine | ZnO | ZnO/phenol | ||
| KAl(SO4)2 | 11C
|
21C
|
31C
|
12P
|
22P
|
32P
|
Before |
11C_0
|
21C_0
|
31C_0
|
12P_0
|
22P_0
|
32P_0
|
After | |
| Cu(OAc)2 | 15C
|
25C
|
35C
|
15P
|
25P
|
35P
|
Before |
15C_0
|
25C_0
|
35C_0
|
15P_0
|
25P_0
|
35P_0
|
After | |
| SnCl2 | 16C
|
26C
|
36C
|
16P
|
26P
|
36P
|
Before |
16C_0
|
26C_0
|
36C_0
|
16P_0
|
26P_0
|
36P_0
|
After | |
| FeSO4 | 17C
|
27C
|
37C
|
17P
|
27P
|
37P
|
Before |
17C_0
|
27C_0
|
37C_0
|
17P_0
|
27P_0
|
37P_0
|
After | |
| Dyes | Cape Jasmine seeds (Yellow-dyes) [26]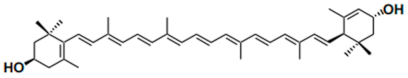
|
||||||
| Fabrics | Cotton-weft satin | Polyester-weft satin | |||||
| Metallic mordants |
UV photo absorbers | UV light exposure |
|||||
| Pristine | ZnO | ZnO/phenol | Pristine | ZnO | ZnO/phenol | ||
| KAl(SO4)2 | 41C
|
51C
|
61C
|
42P
|
52P
|
62P
|
Before |
41C_0
|
51C_0
|
61C_0
|
42P_0
|
52P_0
|
62P_0
|
After | |
| Cu(OAc)2 | 45C
|
55C
|
65C
|
45P
|
55P
|
65P
|
Before |
45C_0
|
55C_0
|
65C_0
|
45P_0
|
55P_0
|
65P_0
|
After | |
| SnCl2 | 46C
|
56C
|
66C
|
46P
|
56P
|
66P
|
Before |
46C_0
|
56C_0
|
66C_0
|
46P_0
|
56P_0
|
66P_0
|
After | |
| FeSO4 | 47C
|
57C
|
67C
|
47P
|
57P
|
67P
|
Before |
47C_0
|
57C_0
|
67C_0
|
47P_0
|
57P_0
|
67P_0
|
After | |
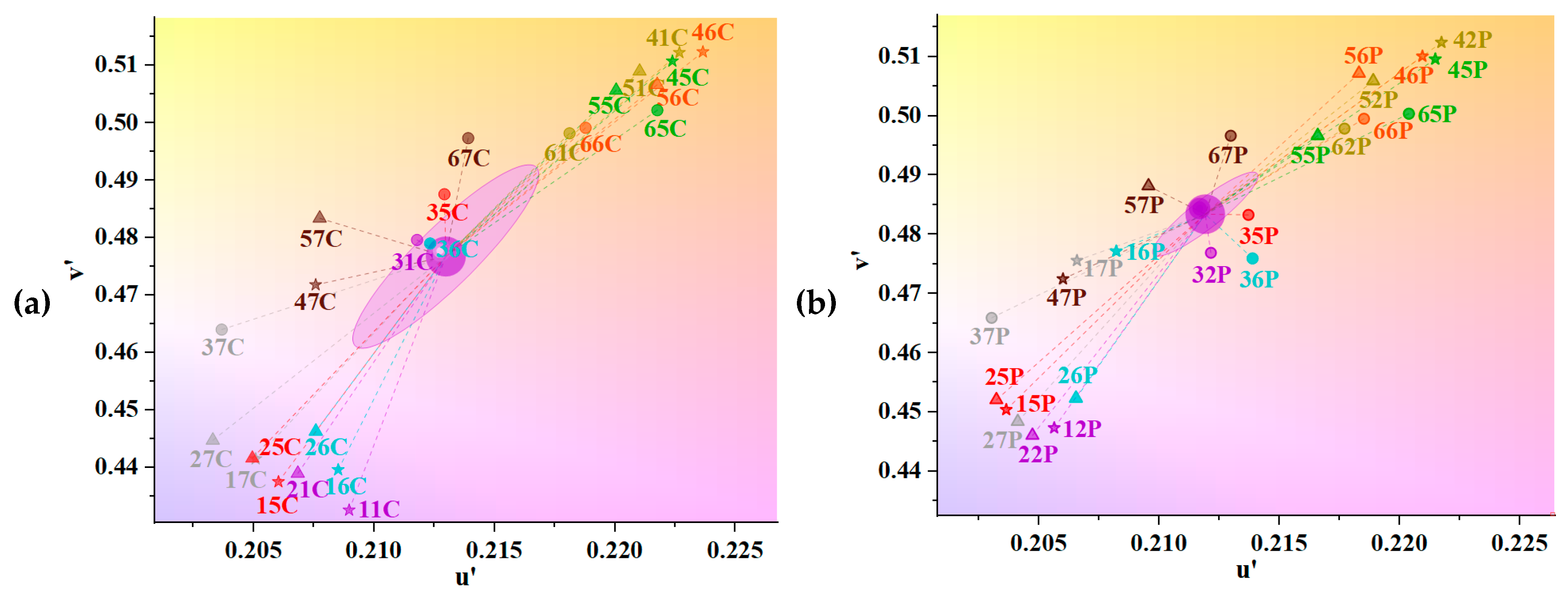
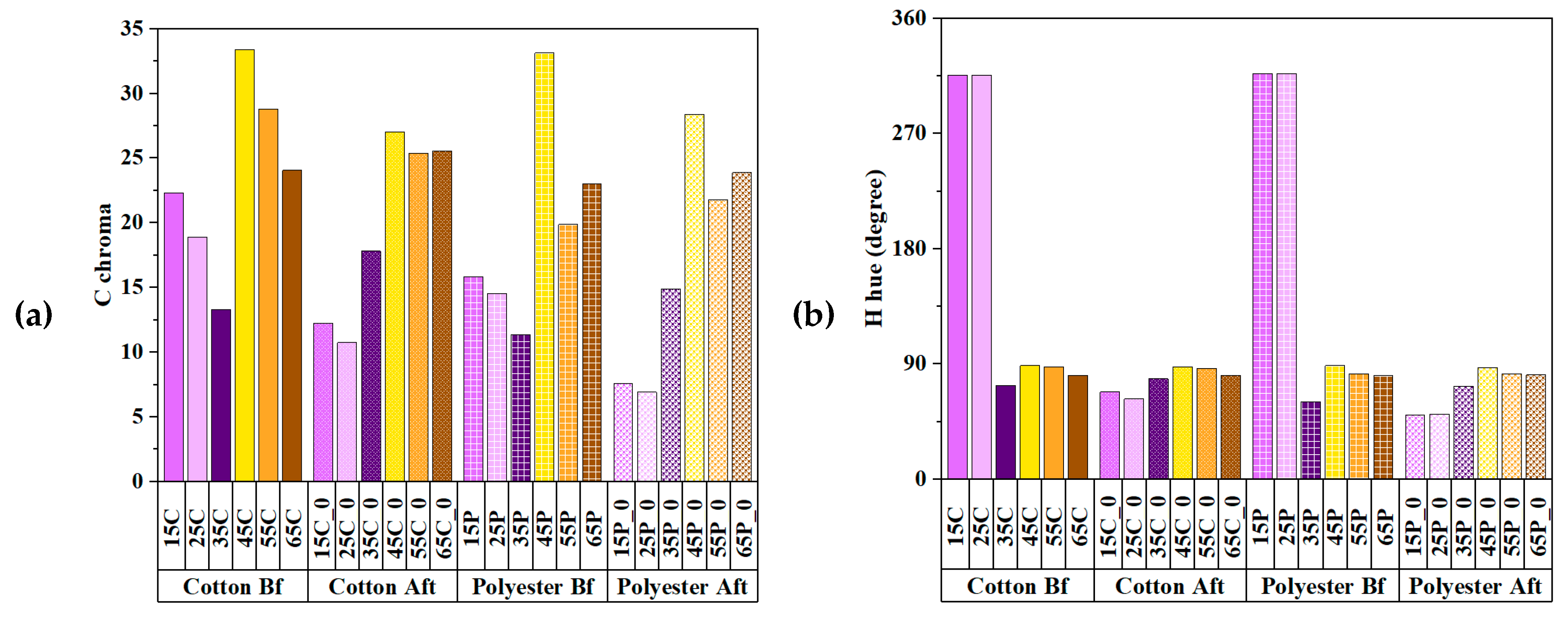
3.3. Chromaticity of UV Absorbers and Metallic Mordants
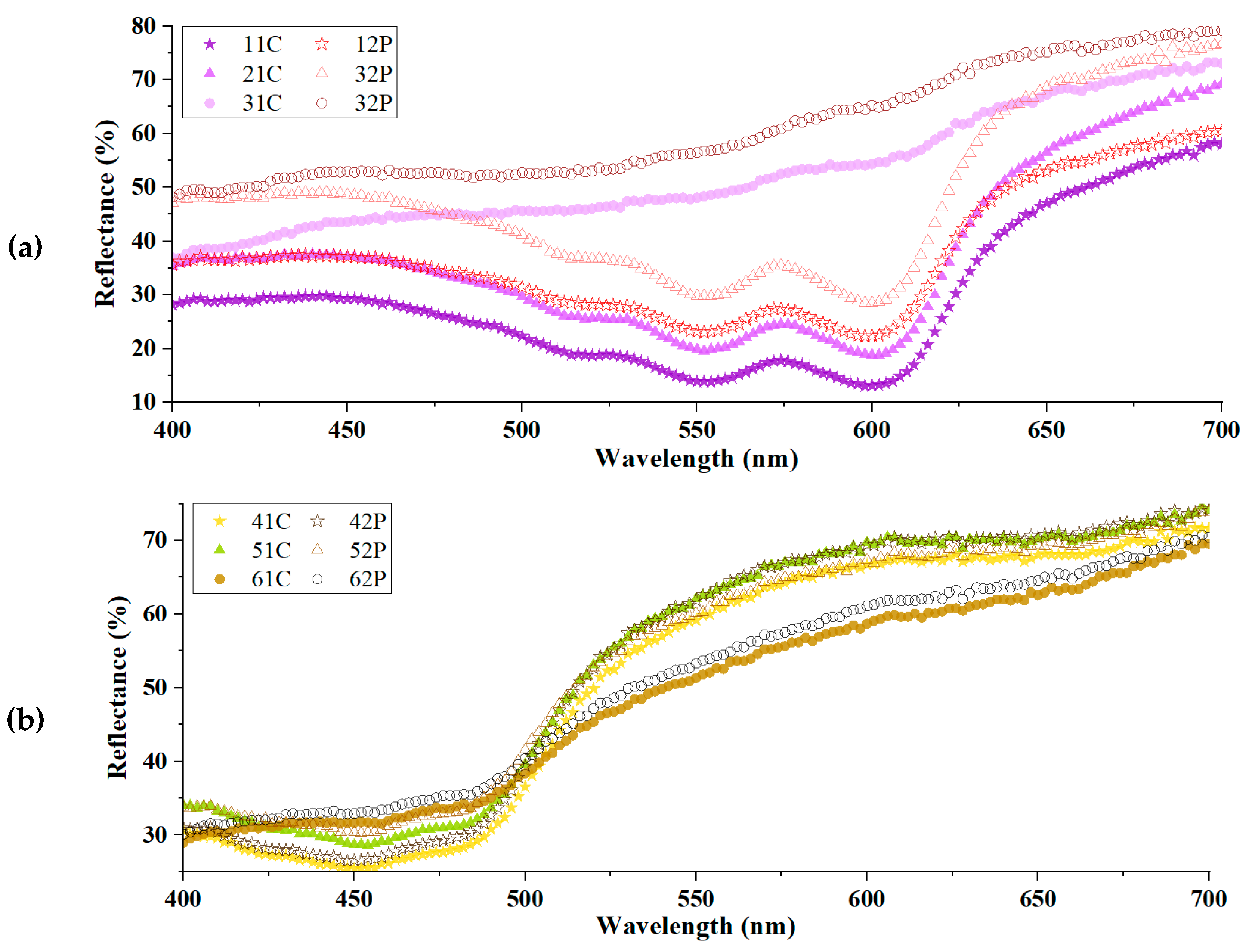
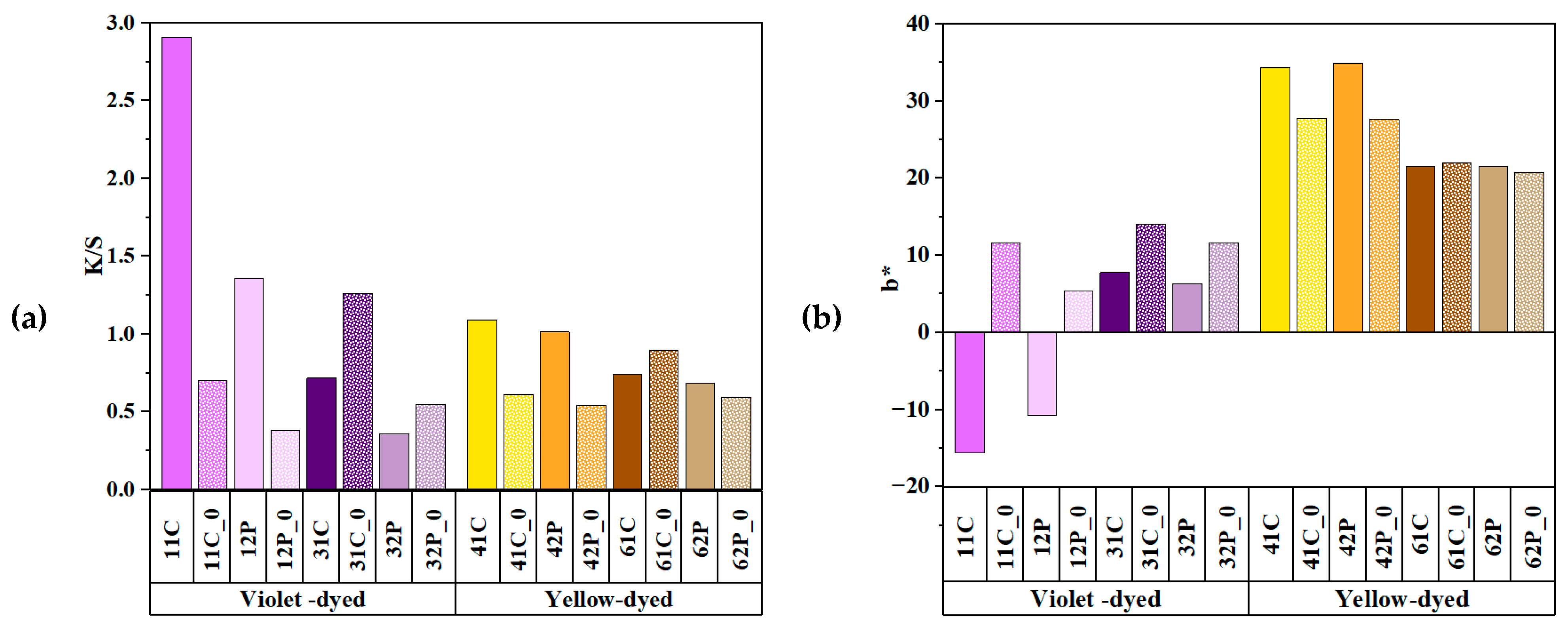
3.4. Comparison of Colorimetric Parameters with ZnO/Polyphenol Treatment after UV Exposure
3.5. Effects of Copper Acetate Mordants on UV Protection and Chromaticity
4. Discussion
4.1. Strategies to Improve Chromaticity for UV Shielding
4.2. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghazi, S. Do the polyphenolic compounds from natural products can protect the skin from ultraviolet rays? Results Chem, 2022, 4, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, M. C.; Grisel, M.; Gore, E. Multifunctional active ingredient-based delivery systems for skincare formulations: A review. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2022, 112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Guo, N.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Recent Advances of Metal–Polyphenol Coordination Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Biosensors, 2023, 13(8), 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, D.E.; Gangemi, S.; Genovese, C.; Cicero, N.; Casciaro, M. Polyphenols from Mediterranean Plants: Biological Activities for Skin Photoprotection in Atopic Dermatitis, Psoriasis, and Chronic Urticaria. Plants 2023, 12(20), 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yue, M.; Huang, X.; Duan, G.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; Yin, X. Preparation, application and enhancement dyeing properties of ZnO nanoparticles in silk fabrics dyed with natural dyes. Nanomater. 2022, 12(22), 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Theoretical and experimental investigations of the thermoelectric properties of Al-, Bi-and Sn-doped ZnO. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 66, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Rehman, U.; Mahmood, K.; Ali, A.; Mehboob, K.; Ashfaq, A.; Ashraf, F. Improved thermoelectric performance of Al and Sn doped ZnO nano particles by the engineering of secondary phases. Ceram. Int, 2020, 46(10), 15013–15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaviano, B. T. H.; Sannomiya, M.; de Lima, F. S.; Tangerina, M. M. P.; Tamayose, C. I.; Ferreira, M. J. P.; da Costa, S. M. Pomegranate peel extract and zinc oxide as a source of natural dye and functional material for textile fibers aiming for photoprotective properties. Mater. Chem. Phys, 2023; 293, 126766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, R.; Ho, K. C. Zinc oxide based dye-sensitized solar cells: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Mekuria, M.; Adam, G. Incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in cotton textiles for ultraviolet light protection and antibacterial activities. Nanomater. Nanotechnolo. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rise, M. S.; Ranjbar, A. H.; Noori, H.; Saheb, V. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorods-Zn2SiO4 nanoparticles-PMMA nanocomposites for UV-C protection. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranei, M.; Taheri, R. A.; Tirgar, M.; Saeidi, A.; Oroojalian, F.; Uzun, L.; Goodarzi, V. Anticancer effect of green tea extract (GTE)-Loaded pH-responsive niosome Coated with PEG against different cell lines. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brza, M.A.; Shujahadeen B.; Aziz, H.; Anuar, Fathilah Ali, Elham M.A.; Dannoun, Salah R.; Saeed, Sewara J.; Mohammed, Rebar T. Abdulwahid. Green coordination chemistry as a novel approach to fabricate polymer:Cd(II)-complex composites: Structural and optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2021, 116, 111062. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, P.; Wei, J. Engineering functional mesoporous materials from plant polyphenol based coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 468, 214649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S. C.; Alonso-Varona, A.; Palomares, T.; Zubillaga, V.; Labidi, J.; Bulone, V. Exploiting mycosporines as natural molecular sunscreens for the fabrication of UV-absorbing green materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7(30), 16558–16564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Flourat, A. L.; Allais, F.; Han, K. Ultrafast barrierless photoisomerization and strong ultraviolet absorption of photoproducts in plant sunscreens. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8(5), 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Mallick, N. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Algal metabolites shaping the safety and sustainability profiles of commercial sunscreens. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, N.; Xiang, Z.; Rong, Y.; Zhu, L.; Huang, X. Natural polyphenol as radical inhibitors used for DLP-based 3D printing of photosensitive gels. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, I.; Kanelli, M.; Ariese, F.; van Bommel, M. R. Parameters that affect the photodegradation of dyes and pigments in solution and on substrate–An overview. Dyes Pigm. 2023, 210, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader Bowers LM; Schmidtke Sobeck SJ. Impact of medium and ambient environment on the photodegradation of carmine in solution and paints. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 127:18–24. [CrossRef]
- Michelin, C.; Hoffmann, N. Photosensitization and photocatalysis—Perspectives in organic synthesis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8(12), 12046–12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiola, T. T.; Whittock, A. L.; Stavros, V. G. Unravelling the photoprotective mechanisms of nature-inspired ultraviolet filters using ultrafast spectroscopy. Mol. 2020, 25(17), 3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, N. G.; Iscan, A.; Sayil, C.; Avinc, O.; Kalayci, E. Naphthoquinone disperse dyes and their dyeing application to polyethylene terephthalate fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulo, B.; Phan, K.; Githaiga, J. Natural Quinone Dyes: A Review on Structure, Extraction Techniques, Analysis and Application Potential. Waste Biomass Valor, 2021, 12, 6339–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, E. H.; Giusti, M. M. Ultraviolet–Visible Excitation of cis-and trans-pC oumaric Acylated Delphinidins and Their Resulting Photochromic Characteristics. ACS Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 2(5), 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoka, T. Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. J Nat Med. 2020, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, A.; Ikram, M.; Ali, S.; Niaz, F.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2021, 97, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canopoli, L.; Coulon, F.; Wagland, S. T. Degradation of excavated polyethylene and polypropylene waste from landfill. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Guan, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Tannic interfacial linkage within ZnO-loaded fabrics for durable UV-blocking applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 568, 150960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, B.; Jabeen, U.; Naeem, A.; Kasi, P.; Malghani, M. N. K.; Khan, S. U.; Aamir, M. Synthesis of zinc stannate nanoparticles by sol-gel method for photocatalysis of commercial dyes. Results Chem. 2020, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Du, J.; Xu, C. Establishment of a color tolerance for yarn-dyed fabrics from different color-depth yarns. Color Res. Appl., 2022, 47(1), 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Xiao, K.; Pointer, M.; Melgosa, M.; Bressler, Y. Optimizing Parametric Factors in CIELAB and CIEDE2000 Color-Difference Formulas for 3D-Printed Spherical Objects. Mater. 2022, 15, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repon, M. R.; Dev, B.; Rahman, M. A.; Jurkonienė, S.; Haji, A.; Alim, M. A.; Kumpikaitė, E. Textile dyeing using natural mordants and dyes: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Hu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X. Ionic liquid treated cellulose-based intelligent pH-responsive color indicator film, with excellent anti-ultraviolet function. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30(9), 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soosairaj, A.; Pabba, D.P.; Gunasekaran, A.; et al. Synergetic impact of natural light harvesting materials to reduce the recombination rate and improve the device performance of dye sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gong, T.; Liu, M.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Zeng, S.; Xu, H. Shikonin, a naphthalene ingredient: Therapeutic actions, pharmacokinetics, toxicology, clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytomedicine, 2022, 94, 153805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaram, S. Spectral, third-order nonlinear optical and optical switching behavior of β-carotenoid extracted from phyllanthus niruri. Ind. J. Phys. 2022, 96(6), 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Xiao, F.; Fu, L.; Jing, D.; Wu, Y. Structural characteristics of polysaccharide GP2a in Gardenia jasminoides and Its Immunomodulatory Effect on Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(19), 11279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedokun, O.; Adedeji, O. L.; Bello, I. T.; Awodele, M. K.; Awodugba, A. O. Fruit peels pigment extracts as a photosensitizer in ZnO-based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Phys. 2021, 3, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, M. H.; Lee, K. B.; Lee, Y. Characterization of natural dyes and traditional Korean silk fabric by surface analytical techniques. Mater. 2013, 6(5), 2007–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P. M. D. S.; Fiaschitello, T. R.; Queiroz, R. S. D.; Freeman, H. S.; Costa, S. A. D.; Leo, P.; Costa, S. M. D. Natural dye from Croton urucurana Baill. bark: extraction, physicochemical characterization, textile dyeing and color fastness properties. Dyes Pigm. 2020, 173, 01–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liman, M. L. R; Islam, M. T; Repon, M. R; Hossain, M. M; Sarker, P. Comparative dyeing behavior and UV protective characteristics of cotton fabric treated with polyphenols enriched banana and watermelon biowaste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, U. O.; Ač, A.; Klem, K.; Urban, O.; Jansen, M. A. A meta-analysis of the effects of UV radiation on the plant carotenoid pool. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022, 183, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, E. H; Giusti, M. M. Ultraviolet–Visible Excitation of cis- and trans-pCoumaric Acylated Delphinidins and Their Resulting Photochromic Characteristics. ACS Food Science & Technology, 2022, 2(5), 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, X.; Khan, A.; Yao, J.; Tahir Hussain, M. Dyeing mechanism and photodegradation kinetics of gardenia yellow natural colorant. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91(7-8), 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J. Color inconstancy in CIELAB: A red herring? Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47(4), 900–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulansari, A. D.; Hayati, D.; Long, D. X.; Choi, K.; Hong, J. Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives for UV-selective and visibly transparent dye-sensitized solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13(1), 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.; and Booth, B. W. Biomedical applications of tannic acid. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36(8), 1503–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; Ahmed, K.; Hasany, S. F.; Butt, R. A. Non-Covalent Bonding of Green Synthesized Copper Nanoparticles to enhance Physicochemical behavior of Sulfur-Dyed Cotton Fabric. AATCC J. Res. 2023, 10(5), 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed K, Khan I, Gul T, Sadiq M. Efficient photodegradation of methyl violet dye using TiO2/Pt and TiO2/Pd photocatalysts. Appl Water Sci 2017; 7:3841–8. [CrossRef]
- Guo, C; He, J; Song, X; Tan, L; Wang, M; Jiang, P; Peng, C. Pharmacological properties and derivatives of shikonin—A review in recent years. Pharmacol. Res. Commun, 2019, 149, 104463. [CrossRef]
- Bruce Lindbloom. Available online: www.brucelindbloom.com (accessed on 19 February 2024).

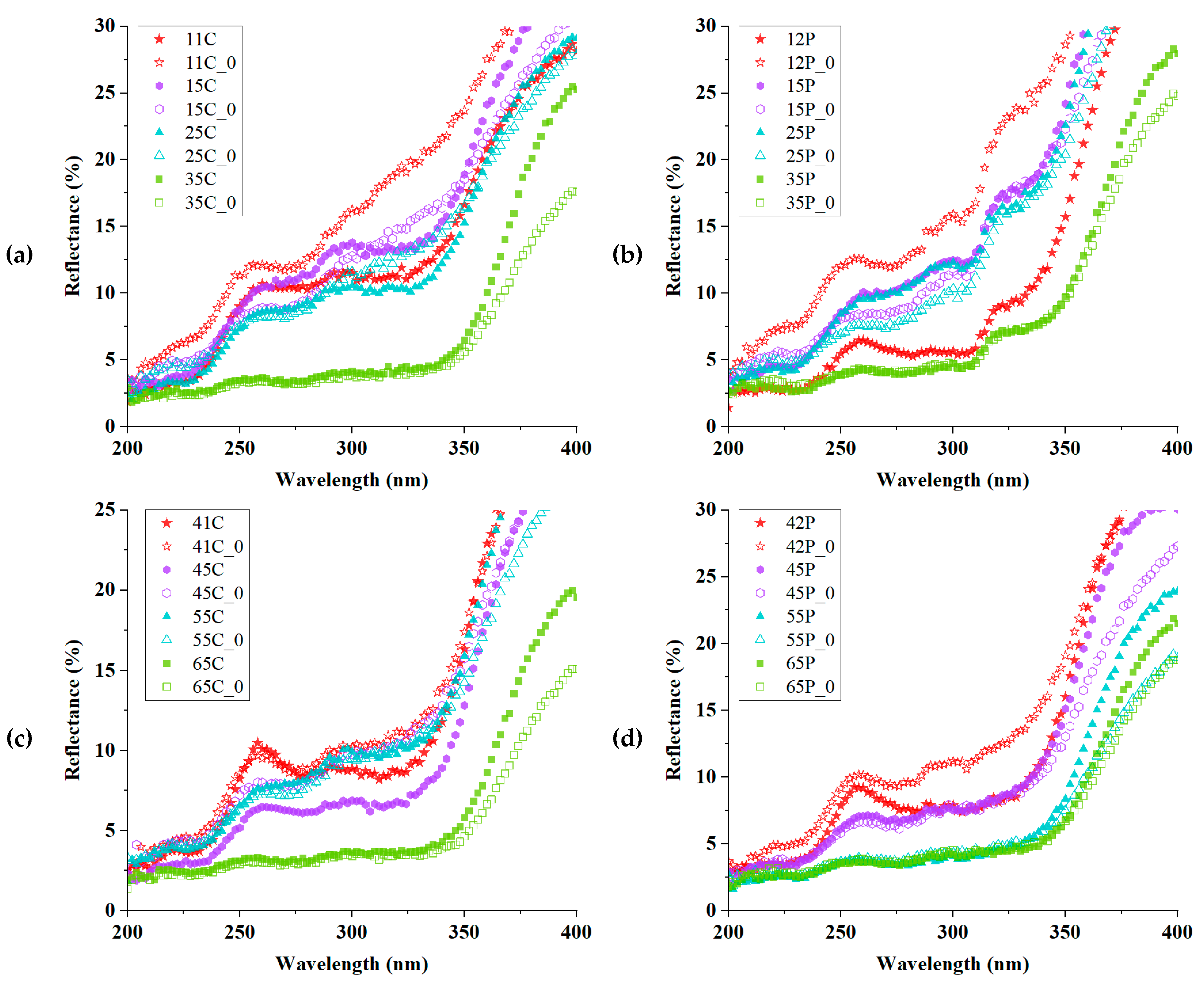
| Sample | CIE1976 ΔEab | CMC ΔEcmc (2:1) | CIEDE2000 ΔE00 | Mean ΔE±Std. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11C, 11C_0 | 37.03 | 27.51 | 25.00 | 29.85±6.35 |
| 21C, 21C_0 | 32.64 | 26.15 | 21.46 | 26.75±5.61 |
| 31C, 31C_0 | 6.60 | 8.70 | 22.57 | 12.62±8.68 |
| 12P, 12P_0 | 24.82 | 18.65 | 21.59 | 21.69±3.09 |
| 22P, 22P_0 | 22.26 | 18.26 | 21.61 | 20.71±2.15 |
| 32P, 32P_0 | 6.22 | 7.92 | 18.65 | 10.93±6.74 |
| 41C, 41C_0 | 7.49 | 3.35 | 18.01 | 9.62±7.56 |
| 51C, 51C_0 | 7.98 | 3.74 | 4.79 | 5.50±2.21 |
| 61C, 61C_0 | 2.60 | 1.13 | 5.95 | 3.23±2.47 |
| 42P, 42P_0 | 8.16 | 3.63 | 18.66 | 10.15±7.71 |
| 52P, 52P_0 | 4.46 | 2.22 | 2.90 | 3.19±1.15 |
| 62P, 62P_0 | 1.60 | 1.06 | 2.44 | 1.70±0.70 |
| Violet-Dyed Sample | Reflectance (%) | Yellow-Dyed Sample | Reflectance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11C | 11.14 | 41C | 8.81 |
| 21C | 13.60 | 51C | 10.94 |
| 31C | 3.84 | 61C | 3.70 |
| 12P | 5.57 | 42P | 7.43 |
| 22P | 13.01 | 52P | 7.57 |
| 32P | 5.28 | 62P | 3.69 |
| Sample | CIE1976 ΔEab | CMC ΔEcmc (2:1) | CIEDE2000 ΔE00 | Mean ΔE±Std. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15C, 15C_0 | 30.27 | 25.83 | 21.59 | 25.90±4.34 |
| 15P, 15P_0 | 17.58 | 17.63 | 12.89 | 16.03 ± 2.72 |
| 35C, 35C_0 | 6.15 | 2.77 | 2.90 | 4.42±1.64 |
| 35P, 35P_0 | 4.55 | 2.26 | 3.13 | 4.43±1.24 |
| 45C, 45C_0 | 6.74 | 2.05 | 1.98 | 3.94±2.49 |
| 45P, 45P_0 | 4.45 | 1.07 | 1.12 | 2.58±1.70 |
| 65C, 65C_0 | 3.28 | 1.43 | 1.57 | 2.09±1.03 |
| 65P, 65P_0 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 0.69±0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





