Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
15 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Unsupervised Models
2.2. Supervised Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Samples
4.2. Analytical Procedures
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Breast cancer statistics. Cancer.Net. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/breast-cancer/statistics. Accessed, April 10, 2024.
- Ma, H.; Lu, Y.; Marchbanks, P.A.; Folger, S.G.; Strom, B.L.; McDonald, J.A.; et al. Quantitative measures of estrogen receptor expression in relation to breast cancer-specific mortality risk among white women and black women. Breast Cancer Res 2013, 15(R90), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Koo, I.; Jung, B.H.; Chung, B.C.; Lee, D. Multivariate classification of urine metabolome profiles for breast cancer diagnosis. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010, 11(Suppl 2) (S4), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X. P.; Elliott, R. L.; Head, J. F. Exogenous normal mammary epithelial mitochondria suppress glycolytic metabolism and glucose uptake of human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2015, 153(3), 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilvo, M.; Matej Orešiè, A. Regulation of lipid metabolism in breast cancer provides diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. Clin Lipidol, 2012, 7(2), 177-188. [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine metabolism and its regulation in the cancer cell. Biochem J. 2012;444(2):335-342. [CrossRef]
- Mikó, E.; Kovács, T.; Sebő, É.; Tóth, J.; Csonka, T.; Ujlaki, G.; et al. Microbiome—microbial metabolome—cancer cell interactions in breast cancer—familiar, but unexplored. Cells, 2019, 8(4), 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, J.; Bailleux, C.; Chardin, D.; Pourcher, T.; Gilhodes, J.; Jing, L.; et al. Comparison of unsupervised machine-learning methods to identify metabolomic signatures in patients with localized breast cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2020, 18, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritas, M. M.; Yasar, A. Performance analysis of ANN and Naive Bayes classification algorithm for data classification. International journal of intelligent systems and applications in engineering, 2019, 7(2), 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H. J.; Li, T. H. S.; Kuo, P. H. Breast cancer–detection system using PCA, multilayer perceptron, transfer learning, and support vector machine. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 204309–204324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Feng, X. A.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; et al. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm enhanced support vector machine for diagnosis of breast cancer based on high-level features. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019, 20(S8), 290. [CrossRef]
- Ozer, M. E.; Sarica, P. O.; Arga, K. Y. New machine learning applications to accelerate personalized medicine in breast cancer: rise of the support vector machines. OMICS, 2020, 24(5), 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosni, M.; Abnane, I.; Idri, A.; de Gea, J. M. C.; Alemán, J. L. F. Reviewing ensemble classification methods in breast cancer. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2019, 177, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murti Rawat, R.; Panchal, S.; Singh, V. K.; Panchal, Y. Breast Cancer detection using K-nearest neighbors, logistic regression, and ensemble learning. In 2020 International conference on electronics and sustainable communication systems (ICESC) Coimbatore, India, 02-04 July 2020 (pp. 534-540).
- Nguyen, Q. H., Do, T. T., Wang, Y., Heng, S. S., Chen, K., Ang, W. H. M.; et al. Breast cancer prediction using feature selection and ensemble voting. In 2019 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE) Dong Hoi, Vietnam, pp. 250-254.
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics and the Multi-Omics View of Cancer. Metabolites 2022, 12(2), 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Systems biology resources arising from the human metabolome project. In Genetics Meets Metabolomics: From Experiment to Systems Biology. Suhre K., ed. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2012. pp. 157–175.
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics for investigating physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99 1819–1875. [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhre, K.; Raffler, J.; Kastenmüller, G. Biochemical insights from population studies with genetics and metabolomics. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 589, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haince, J.F.; Joubert, P.; Bach, H.; Ahmed Bux, R.; Tappia, P.S.; Ramjiawan, B. Metabolomic Fingerprinting for the Detection of Early-Stage Lung Cancer: From the Genome to the Metabolome. Int J Mol Sci 2022, Jan 21;23(3), 1215. [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Hikichi, S.; Takada, M.; Toi, M. Machine learning techniques for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment: a narrative review. Annals of Breast Surgery, 2023, 7, 7–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, C.; Li, A.; Wang, W.; Yang, K.; et al. Predicting ovarian cancer recurrence by plasma metabolic profiles before and after surgery. Metabolomics 2018, 14(5), 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J. Z.; Tsigelny, I. F.; Kesari, S.; Kouznetsova, V. L. Diagnostics of ovarian cancer via metabolite analysis and machine learning. Integr Biol, 2023, 15, zyad005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaul, D. A.; Mezencev, R.; Long, T. Q.; Jones, C.M.; Benigno, B. B.; Gray, A.; et al. Highly-accurate metabolomic detection of early-stage ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5(1), 16351–16357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qiu, M.; Xing, X.; Zhou, J.; Yao, H.; Li, M.; et al. Lung cancer scRNA-seq and lipidomics reveal aberrant lipid metabolism for early-stage diagnosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14 (630), eabk2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.; Yu, J., Kouznetsova, V. L.; Kesari, S.; Tsigelny, I. F. Two-Stage Deep-Learning Classifier for Diagnostics f Lung Cancer Using Metabolites. Metabolites, 2023, 13(10), 1055. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Meng, W. Y.; Li, R. Z.; Wang, Y. W.; Qian, X.; Chan, C.; et al. Early lung cancer diagnostic biomarker discovery by machine learning methods. Transl Oncol 2021, 14(1), 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S-C.; Chen, K.; Chiu, C-Y.; Lu, K-Y.; Lu, H-Y.; Chiang, M-H.; et al. (2019). Metabolomic biomarkers in cervicovaginal fluid for detecting endometrial cancer through nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metabolomics 2019, 15 (11), 146. [CrossRef]
- Bifarin, O. O.; Gaul, D. A.; Sah, S.; Arnold, R. S.; Ogan, K.; Master, V. A.; et al. . Machine learning-enabled renal cell carcinoma status prediction using multiplatform urine-based metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20(7), 3629–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, K.; Su, Z.; et al. Tissue-based metabolomics reveals metabolic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 197, 113937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C-W.; Chen, Y-T.; Hsieh, Y-J.; Chang, K-P.; Hsueh, P-C.; Chen, T-W.; et al. Integrated analyses utilizing metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal perturbation of the polyamine pathway in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 113–122. [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, A.; Czajkowski, M.; Mojsak, P.; Pienkowski, T.; Gosk, W.; Lyson, T.; et al. A comparison of different machine-learning techniques for the selection of a panel of metabolites allowing early detection of brain tumors. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1), 11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G. H. B.; Fernandes, A. A. D. P.; Silva, A. A. R.; Zamora-Obando, H. R.; Amaral, A. G.; Mesquita, A. D. S.; et al. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry untargeted profiling of non-hodgkin’s lymphoma urinary metabolite markers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412 (27), 7469–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneges, C.; Bullinger, D.; Fux, R.; Friese, N.; Seeger, H.; Neubauer, H.; et al. Prediction of breast cancer by profiling of urinary RNA metabolites using support vector machine-based feature selection. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Yanagisawa, T.; Kurihara, T.; Kaneko, M.; Ota, S.; Enomoto, A.; et al. Salivary metabolomics with alternative decision tree-based machine learning methods for breast cancer discrimination. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2019, 177, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasbi, P.; Wang, D.; Cheng, S. L.; Fei, Q.; Cui, J. Y.; Liu, L.; et al. (2019). Breast cancer detection using targeted plasma metabolomics. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2019, 1105, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santaliz-Casiano, A.; Mehta, D.; Danciu, O. C.; Patel, H.; Banks, L.; Zaidi, A.; et al. Identification of metabolic pathways contributing to ER+ breast cancer disparities using a machine-learning pipeline. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, R.; Poudel, S.; Smith, K. D.; Estrada, A.; Lakshmanaswamy, R. Metabolomics of Breast Cancer: A Review. Metabolites 2022, 12(7), 643.
- Jobard, E.; Dossus, L.; Baglietto, L.; Fornili, M.; Lécuyer, L.; Mancini, F.R.; et al. Investigation of circulating metabolites associated with breast cancer risk by untargeted metabolomics: a case–control study nested within the French E3N cohort. Br J Cancer, 2021, 124(10), 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Yang, Y.S.; Yang, F.; Ding, J.H.; Gong, Y.; et al. Comprehensive metabolomics expands precision medicine for triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Res 2022, 32, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistyakov, D. V.; Guryleva, M. V.; Stepanova, E. S.; Makarenkova, L. M.; Ptitsyna, E. V.; Goriainov, S. V.; et al. Multi-omics approach points to the importance of oxylipins metabolism in early-stage breast cancer. Cancers, 2022, 14(8), 2041. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Du, S., Liu, J., Huang, W., Liu, W., Zhang, M.; et al. Diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer by high-performance serum metabolic fingerprints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(12), e2122245119. [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, K.M.; Im, Y.; Seok, S.H.; Chung, H.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Nicotinamide (niacin) supplement increases lipid metabolism and ROS-induced energy disruption in triple-negative breast cancer: potential for drug repositioning as an anti-tumor agent. Mol Oncol. 2022, 16(9):1795-1815. [CrossRef]
- Lécuyer, L.; Dalle, C.; Lyan, B.; Demidem, A.; Rossary, A.; Vasson, M. P.; et al. Plasma metabolomic signatures associated with long-term breast cancer risk in the SU. VI. MAX prospective cohort. Cancer Epidemiol, Biomarkers & Prev, 2019, 28(8), 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, S.; Song, X. Screening and diagnosis of triple negative breast cancer based on rapid metabolic fingerprinting by conductive polymer spray ionization mass spectrometry and machine learning. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10, 1075810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, X. Mass spectrometry imaging-based metabolomics to visualize the spatially resolved reprogramming of carnitine metabolism in breast cancer. Theranostics, 2020, 10(16), 7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B. , Schafferer, S., Tang, Q., Scheffler, M., Nees, J., Heil, J., Schott, S., Golatta, M., Wallwiener, M., Sohn, C., Koal, T., Wolf, B.; Schneeweiß, A.; Burwinkel, B. A plasma metabolite panel as biomarkers for early primary breast cancer detection. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144(11), 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetikova, S. A.; Koshel, E. I. Microbiota and cancer: host cellular mechanisms activated by gut microbial metabolites. Int J Med Microbiol, 2020, 310(4), 151425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girithar, H. N.; Staats Pires, A.; Ahn, S. B.; Guillemin, G. J.; Gluch, L.; Heng, B. Involvement of the kynurenine pathway in breast cancer: updates on clinical research and trials. Br J Cancer, 2023, 129(2), 185-203. [CrossRef]
- Dougan, M. M.; Li, Y.; Chu, L. W.; Haile, R. W.; Whittemore, A. S.; Han, S. S.; et al. Metabolomic profiles in breast cancer: A pilot case-control study in the breast cancer family registry. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Sinha, S.; Aldape, K.; Hannenhalli, S.; Sahinalp, C.; Ruppin, E. Big data in basic and translational cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer 2022, 22(11), 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, C. Comparative study of deep learning models on the images of biopsy specimens for diagnosis of lung cancer treatment. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 2023, 16(2), 10055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales Martinez, R.; van Dongen, D. M. Deep learning algorithms for the early detection of breast cancer: A comparative study with traditional machine learning. Inform Med Unlocked, 2023, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, J.; Jilani, A. K. Predicting Breast Cancer Using Logistic Regression and Multi-Class Classifiers. International Journal of Engineering & Technology 2018, (7), 22-26. [CrossRef]
- Alakwaa, F.M.; Chaudhary, K.; Garmire, L.X. Deep Learning Accurately Predicts Estrogen Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Metabolomics Data. J Proteome Res, 2018, 17(1), 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Rolfo, C.; Maksymiuk, A.W.; Tappia, P.S.; Sitar, D.S.; Russo, A.; et al. Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer Screening: The Contribution of Metabolomics. Results of A Pilot Study. Cancers 2019, 11(8):1069. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Ahmed, R.; Huang, G.; Reid, J.; Mandal, R.; et al. A High-Performing Plasma Metabolite Panel for Early-Stage Lung Cancer Detection. Cancers 2020, 12(3):622. [CrossRef]
- Rosato, A.; Tenori, L.; Cascante, M.; De Atauri Carulla, P.R.; Martins Dos Santos, V.A.P.; Saccenti, E. From correlation to causation: analysis of metabolomics data using systems biology approaches. Metabolomics. 2018, 14(4), 37. [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Computational approaches to metabolomics. In Methods in Molecular Biology, Clifton, N.J.; Humana Press Inc: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; 593, pp. 283–313. editor.
- Xia J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for comprehensive metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016;55:14. [CrossRef]
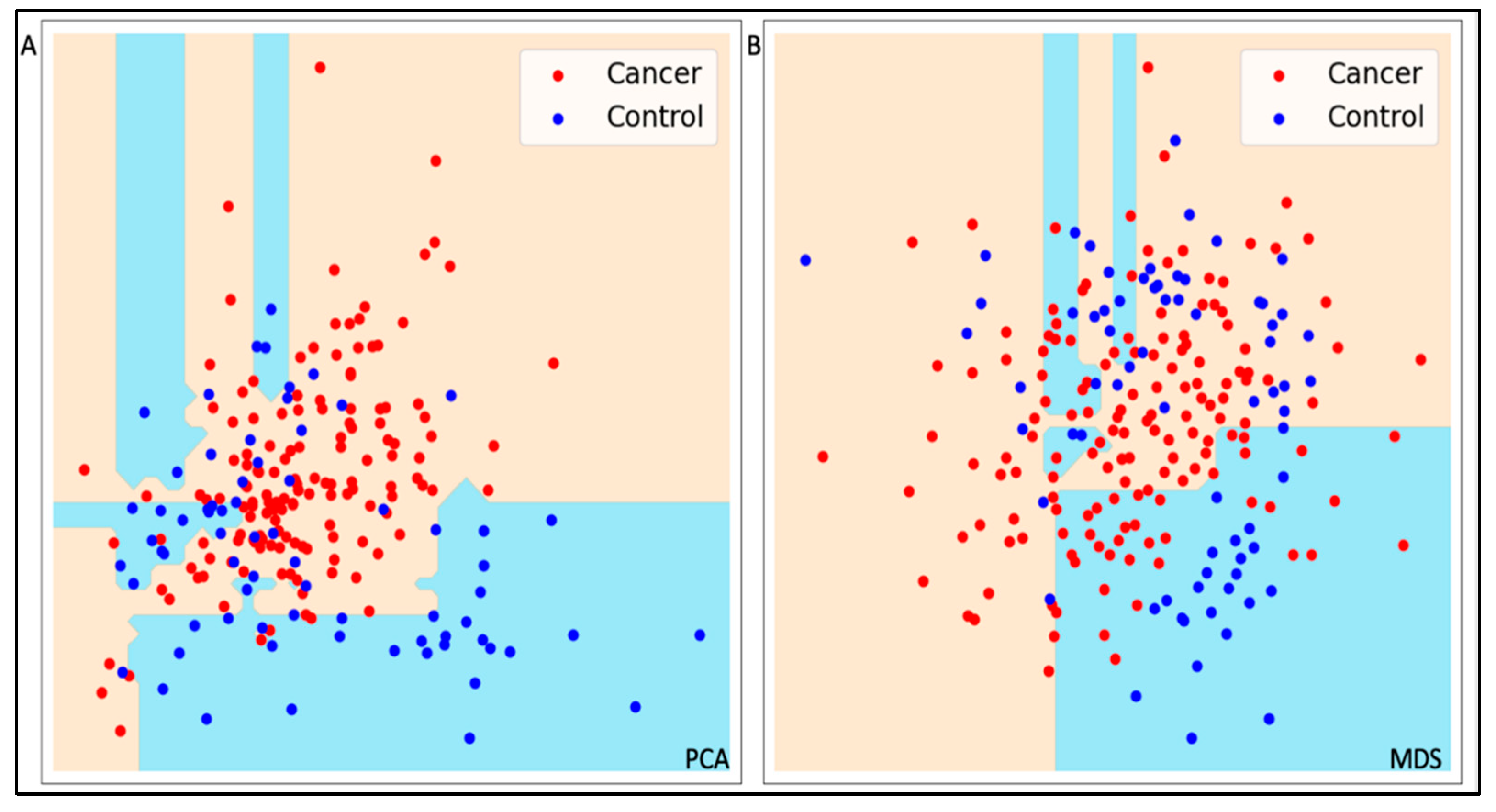
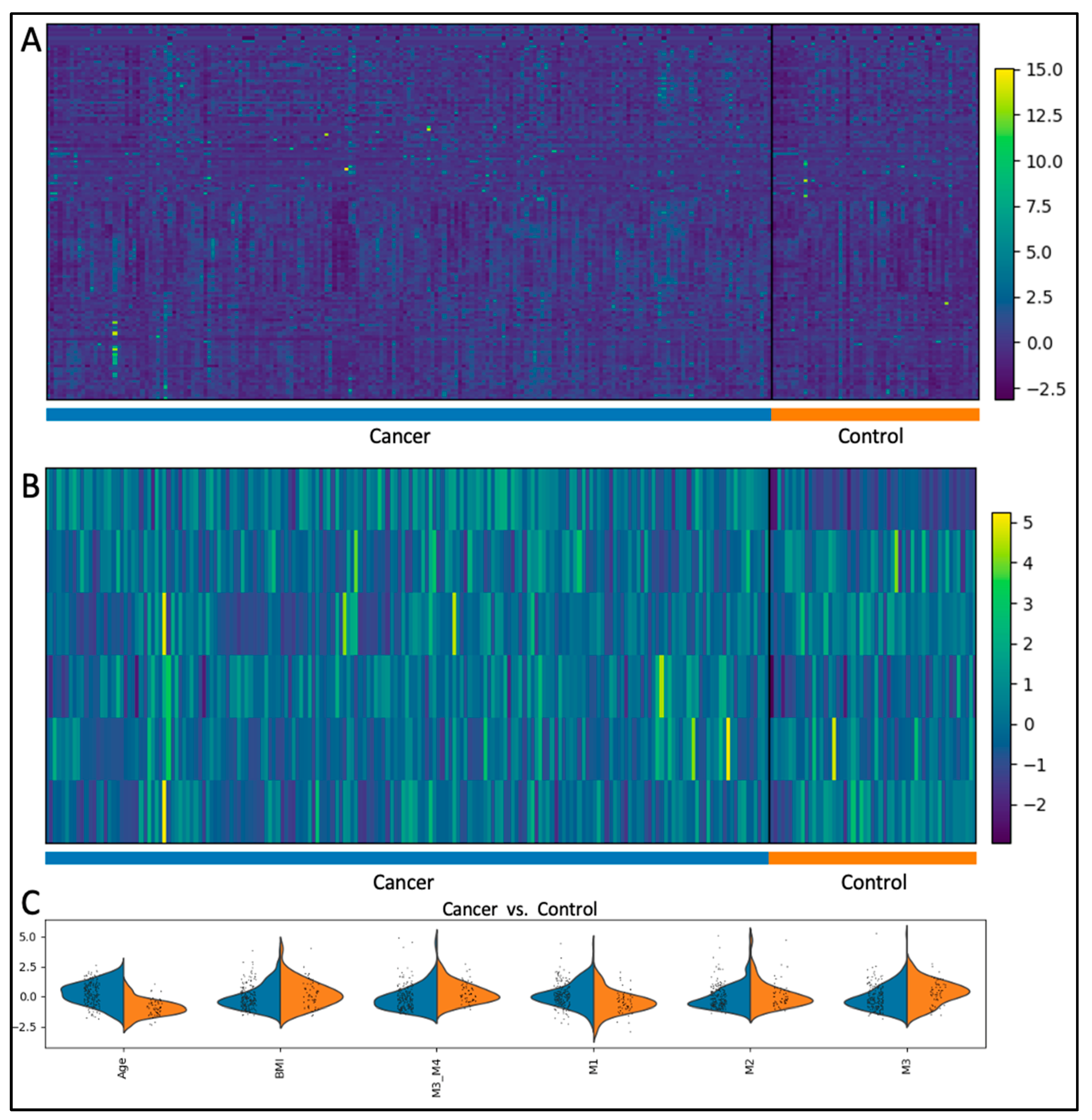
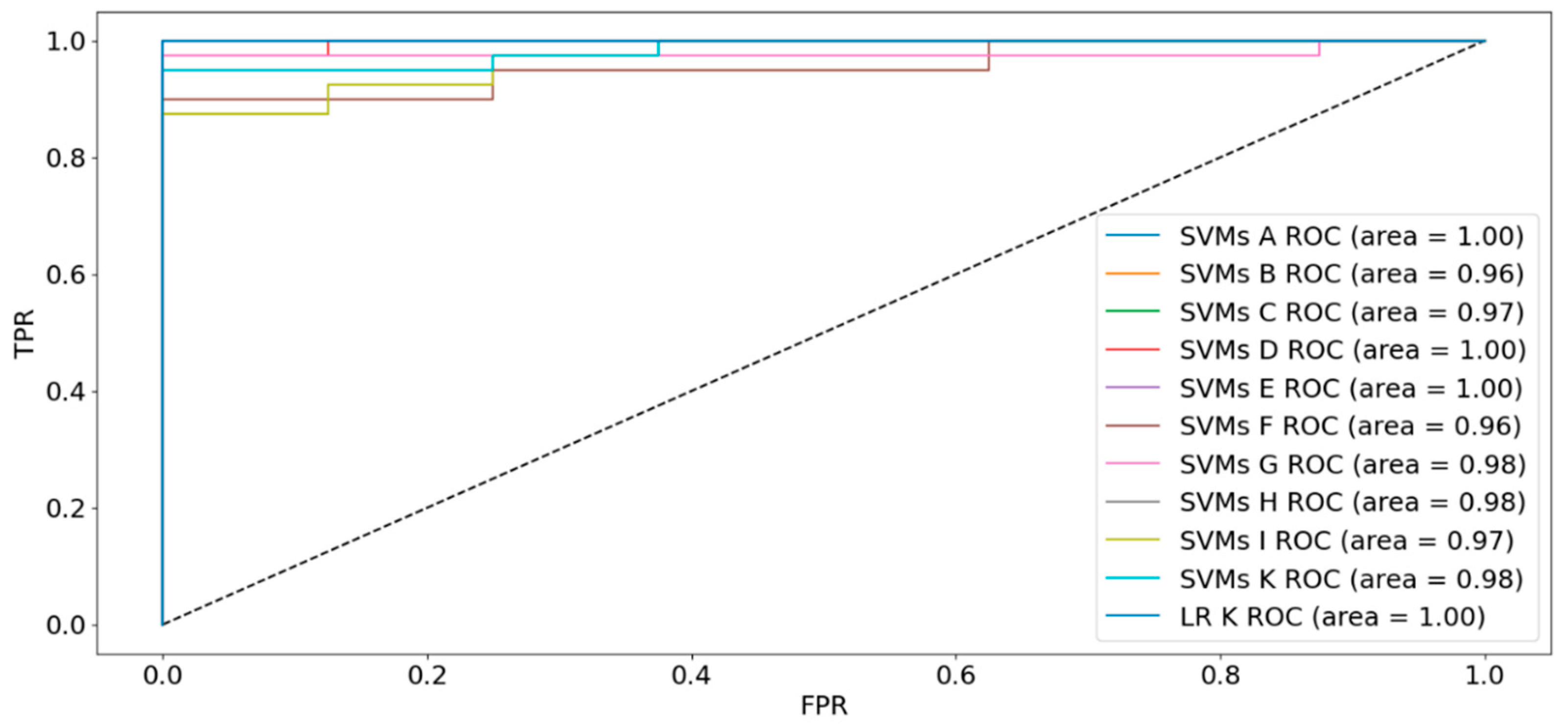

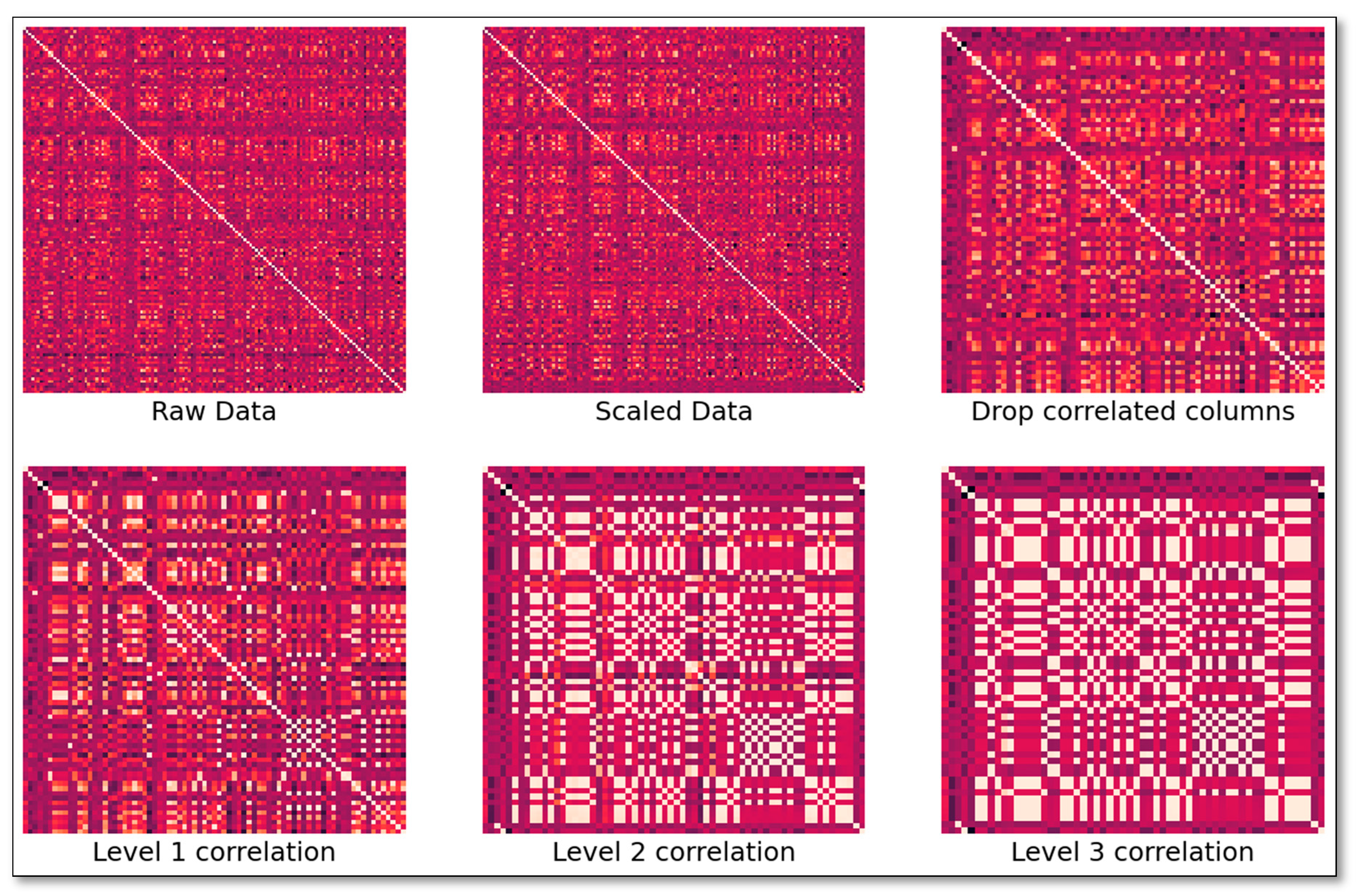
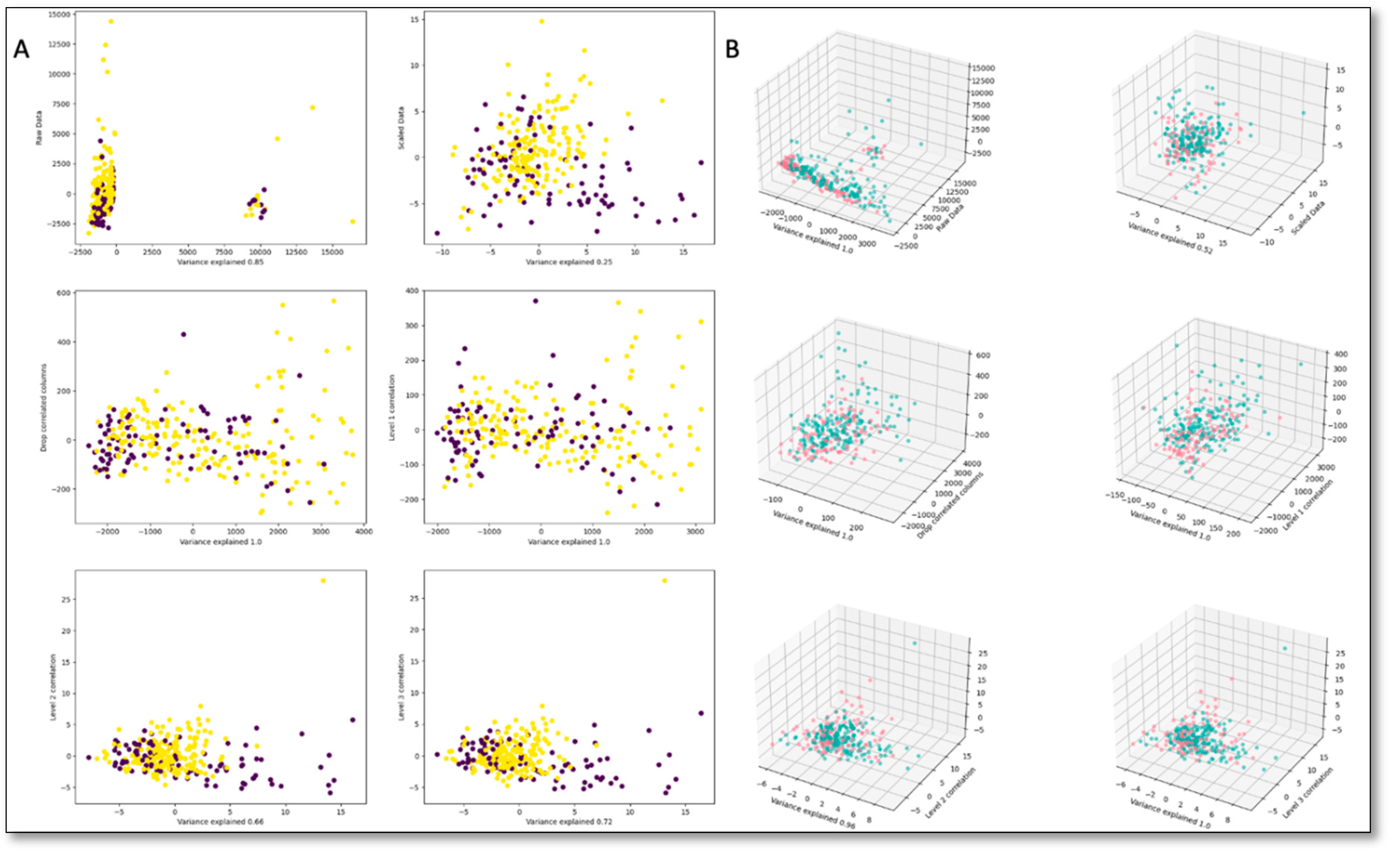
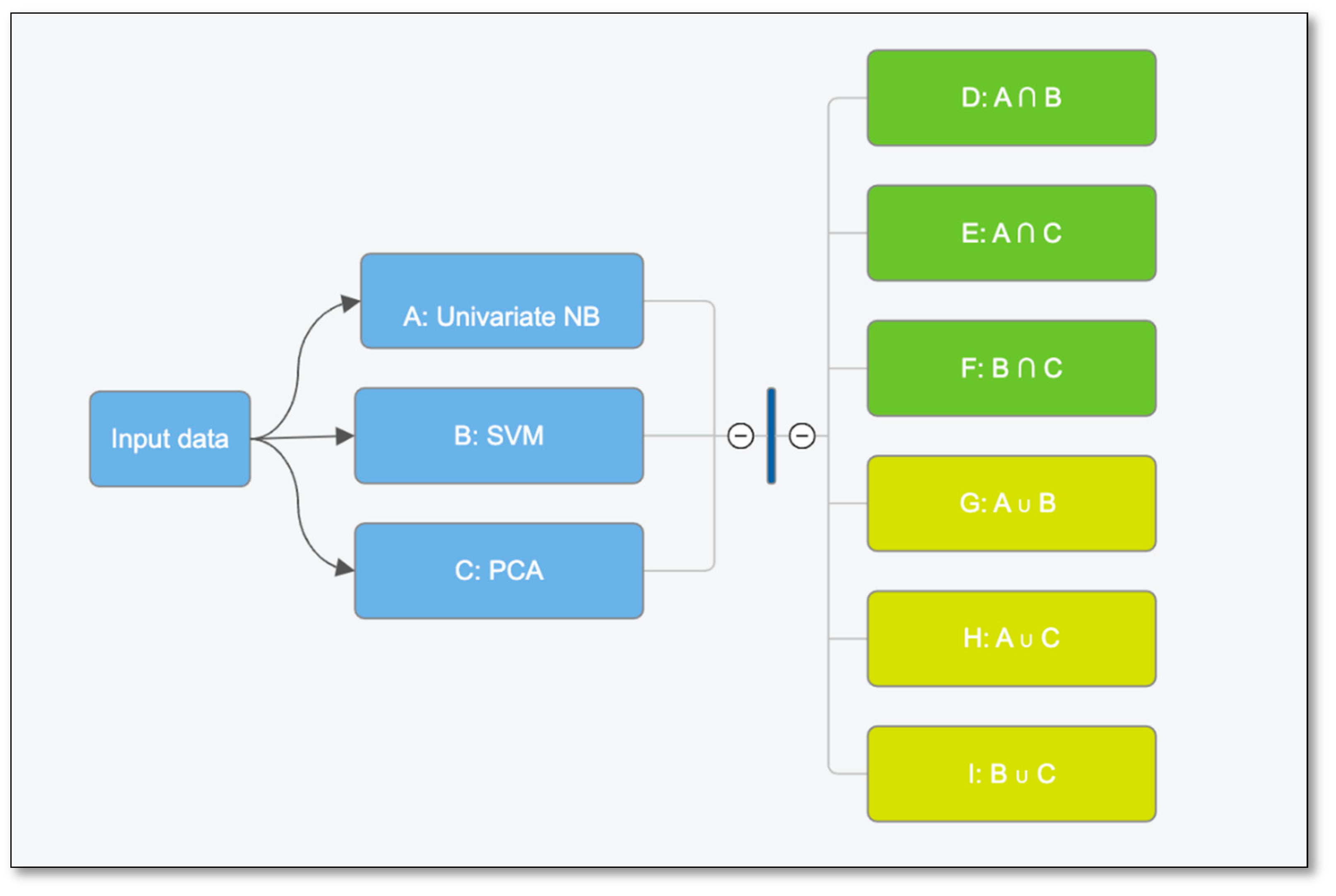
| Dataset | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | FI Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: 59 features | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| B: 50 features | 100% | 25% | 88% | 67% | 96% |
| C: 15 features | 95% | 75% | 92% | 85% | 97% |
| D: 92 features | 100% | 88% | 98% | 96% | 100% |
| E: 67 features | 100% | 88% | 98% | 96% | 100% |
| F: 50 features | 100% | 25% | 88% | 67% | 96% |
| G: 17 features | 97% | 62% | 92% | 83% | 98% |
| H: 7 features | 95% | 100% | 96% | 93% | 98% |
| I: 15 features | 95% | 75% | 92% | 85% | 97% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





