Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
15 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. MeHg Chronic Intoxication
2.3. Measuring the Concentration of Hg in Hair, Liver, and Epididymal White Fat
2.4. Body Weight Gain
2.5. Evaluation of Dyslipidemia
2.6. Evaluation of MeHg Liver Toxicity
2.6.1. Liver Function
2.6.2. Oxidative Stress
2.6.3. Hepatic Steatosis Scoring
2.7. MeHg Effects on Epididymal White Fat Structure and Function
2.7.1. Epididymal Adipose Tissue Weight and Morphometry
2.8. Leptin Plasma Levels by ELISA Immunoassay
2.9. Metabolomics Assessment
2.9.1. Sample Preparation
2.9.2. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.9.3. Data Processing
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
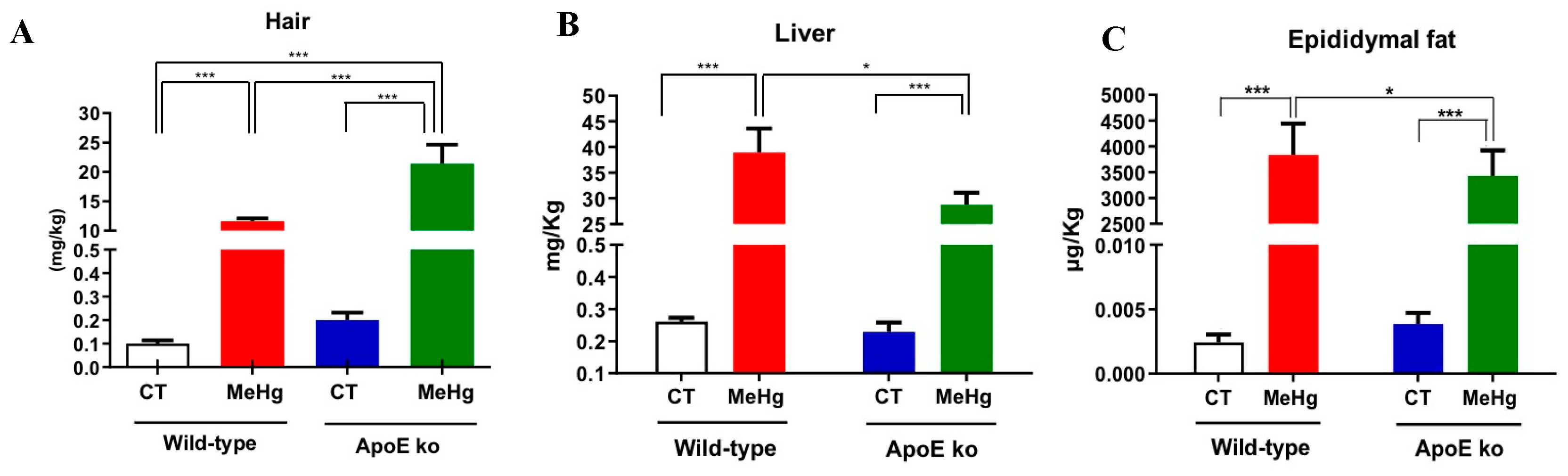
3.1. Hg deposits in Hair, Liver, and EPW Following Chronic MeHg Intoxication
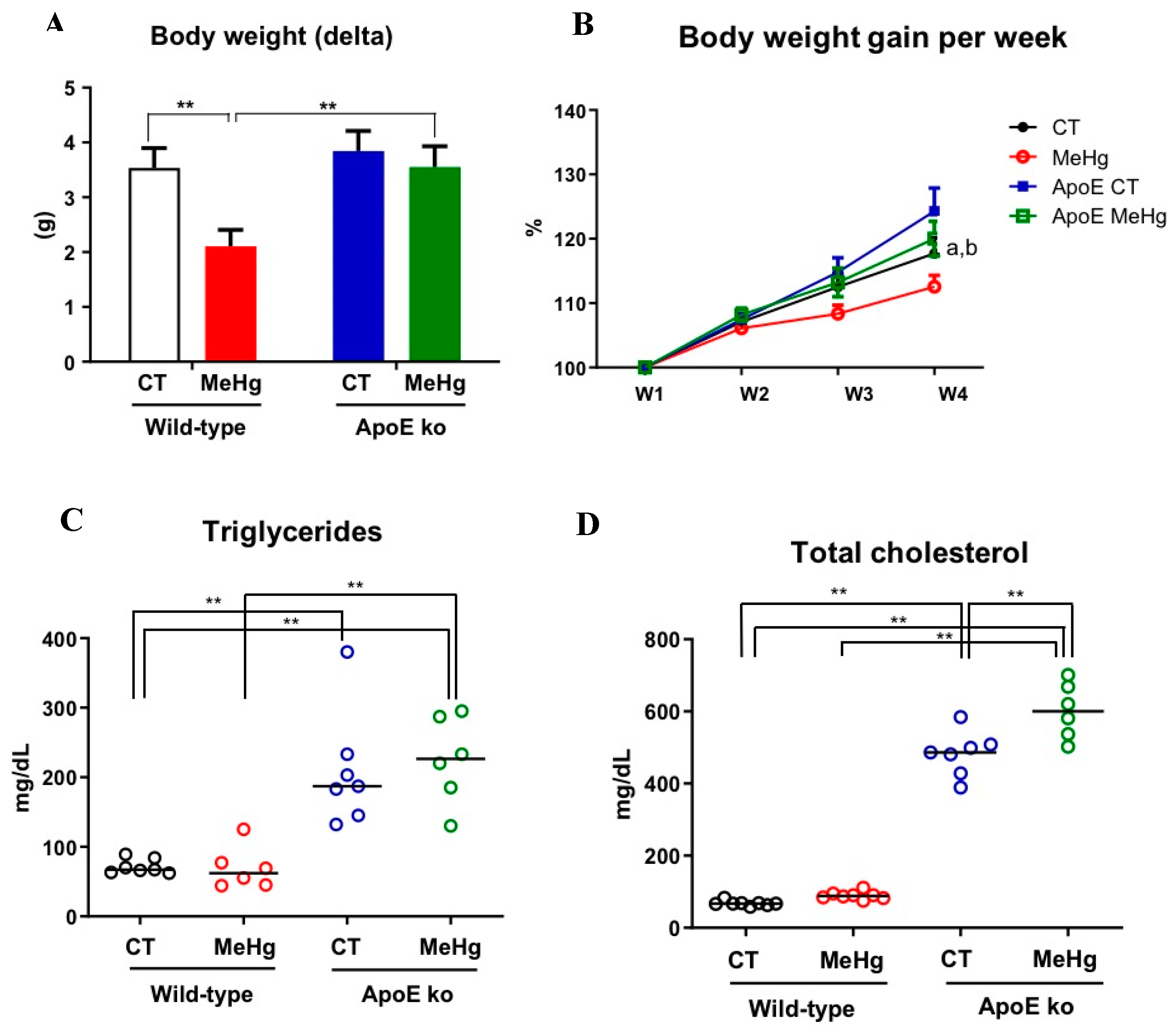
3.2. Body Weight Gain and Blood Lipids
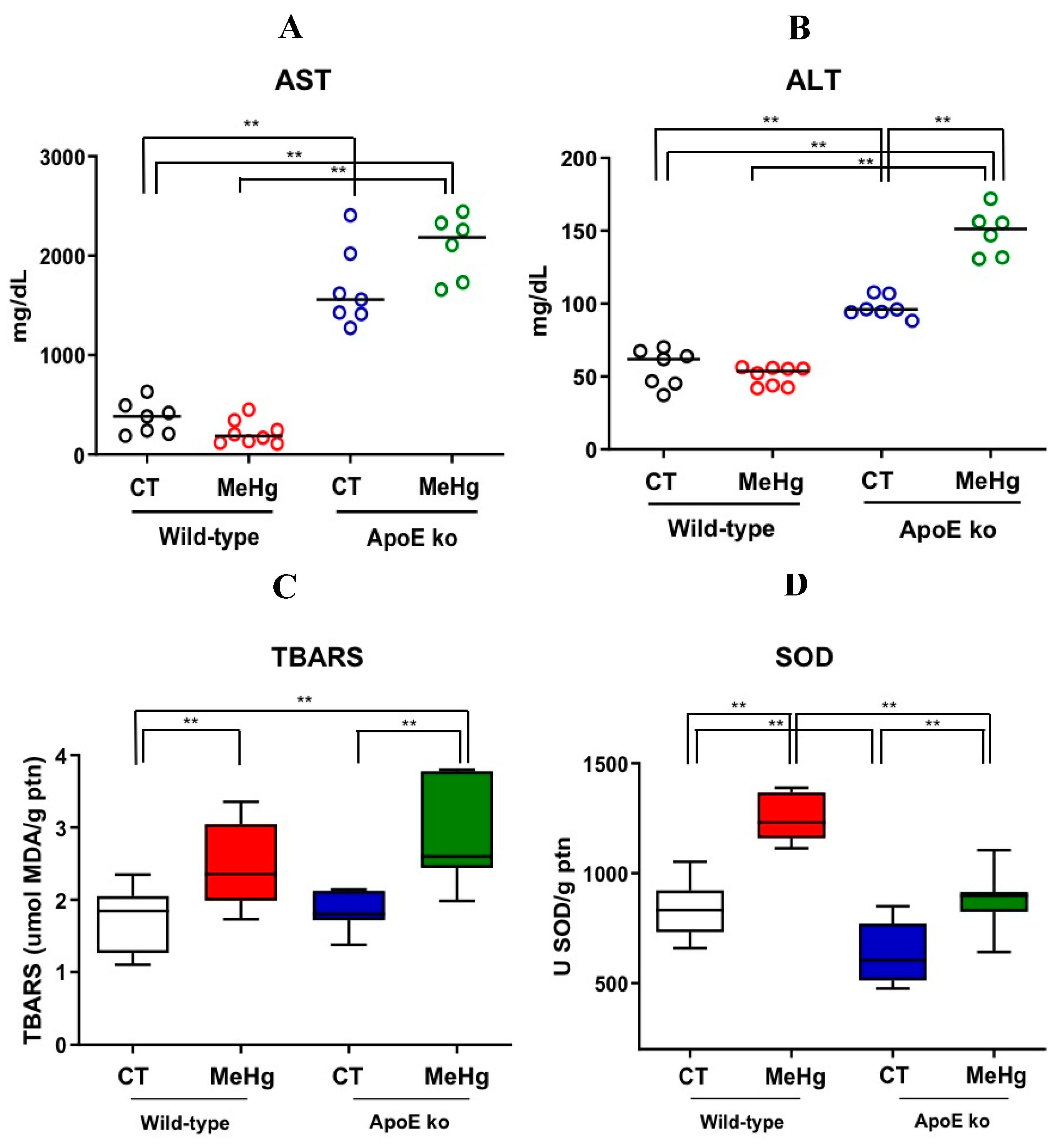
3.3. Liver Enzymes
3.4. Oxidative Stress in Liver Tissue
3.5. Hepatic Steatosis
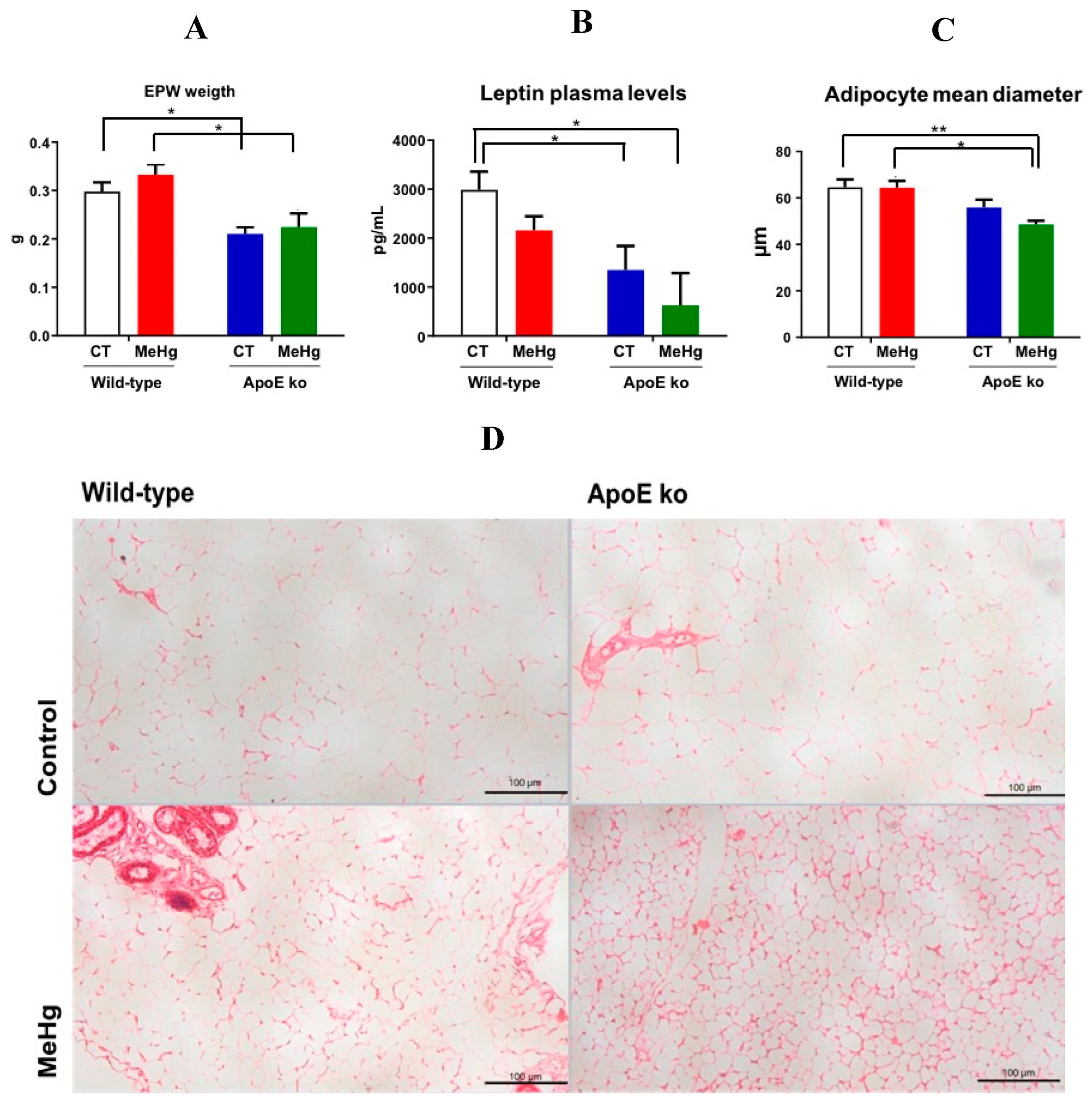
3.6. Weight of EWF
3.7. Plasma Leptin Levels
3.8. Morphometry of EPW Adipocytes
3.9. EPW Metabolomics Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA. United States Evironmental Protection Agency. 2023. Basic Information about Mercury.
- Hudelson KE, Drevnick PE, Wang F, Armstrong D, Fisk AT. Mercury methylation and demethylation potentials in Arctic lake sediments. Chemosphere. 2020 Jun;248:126001. [CrossRef]
- Raposo R da S, Pinto DV, Moreira R, Dias RP, Fontes Ribeiro CA, Oriá RB, et al. Methylmercury Impact on Adult Neurogenesis: Is the Worst Yet to Come From Recent Brazilian Environmental Disasters? Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Nov 23;12.
- Giang A, Selin NE. Benefits of mercury controls for the United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2016 Jan 12;113(2):286–91. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Mukherjee B, Park SK. Associations of cumulative exposure to heavy metal mixtures with obesity and its comorbidities among U.S. adults in NHANES 2003–2014. Environ Int. 2018 Dec;121:683–94. [CrossRef]
- Novo JP, Martins B, Raposo RS, Pereira FC, Oriá RB, Malva JO, et al. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Methylmercury Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3101. [CrossRef]
- Crespo-López ME, Macêdo GL, Pereira SID, Arrifano GPF, Picanço-Diniz DLW, Nascimento JLM do, et al. Mercury and human genotoxicity: Critical considerations and possible molecular mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 2009 Oct;60(4):212–20. [CrossRef]
- Francis CE, Allee L, Nguyen H, Grindstaff RD, Miller CN, Rayalam S. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Friend or foe to brown and beige adipose tissue? Toxicology. 2021 Nov;463:152972.
- Egger AE, Grabmann G, Gollmann-Tepeköylü C, Pechriggl EJ, Artner C, Türkcan A, et al. Chemical imaging and assessment of cadmium distribution in the human body. Metallomics. 2019;11(12):2010–9. [CrossRef]
- Freire C, Vrhovnik P, Fiket Ž, Salcedo-Bellido I, Echeverría R, Martín-Olmedo P, et al. Adipose tissue concentrations of arsenic, nickel, lead, tin, and titanium in adults from GraMo cohort in Southern Spain: An exploratory study. Science of The Total Environment. 2020 Jun;719:137458. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: Structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Dec;72:3–12. [CrossRef]
- Arrifano G de PF, Oliveira MA de, Souza-Monteiro JR, Paraense RO, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos A, Vieira JRDS, et al. Role for apolipoprotein E in neurodegeneration and mercury intoxication. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2018;10(1):819.
- Pereira LC, Nascimento JCR, Rêgo JMC, Canuto KM, Crespo-Lopez ME, Alvarez-Leite JI, et al. Apolipoprotein E, periodontal disease and the risk for atherosclerosis: a review. Arch Oral Biol. 2019 Feb;98:204–12. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Shi Z, Ji X, Zhang W, Luan J, Zahr T, et al. Adipokines, adiposity, and atherosclerosis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2022 May 3;79(5):272.
- Roque CR, Sampaio LR, Ito MN, Pinto D V., Caminha JSR, Nunes PIG, et al. Methylmercury chronic exposure affects the expression of DNA single-strand break repair genes, induces oxidative stress, and chromosomal abnormalities in young dyslipidemic APOE knockout mice. Toxicology. 2021 Dec;464:152992. [CrossRef]
- Andersen HR, Andersen O. Effects of Dietary α-Tocopherol and β-Carotene on Lipid Peroxidation Induced by Methyl Mercuric Chloride in Mice. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993 Oct 25;73(4):192–201.
- Lowry OliverH, Rosebrough NiraJ, Farr AL, Randall RoseJ. PROTEIN MEASUREMENT WITH THE FOLIN PHENOL REAGENT. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–75.
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005 Jun;41(6):1313–21. [CrossRef]
- Rizzetti DA, Corrales P, Piagette JT, Uranga-Ocio JA, Medina-Gomez G, Peçanha FM, et al. Chronic mercury at low doses impairs white adipose tissue plasticity. Toxicology. 2019 Apr;418:41–50. [CrossRef]
- Ferrer B, Peres TV, dos Santos AA, Bornhorst J, Morcillo P, Gonçalves CL, et al. Methylmercury Affects the Expression of Hypothalamic Neuropeptides That Control Body Weight in C57BL/6J Mice. Toxicological Sciences. 2018 Jun 1;163(2):557–68. [CrossRef]
- Tinkov AA, Aschner M, Ke T, Ferrer B, Zhou JC, Chang JS, et al. Adipotropic effects of heavy metals and their potential role in obesity. Fac Rev. 2021 Mar 26;10. [CrossRef]
- Silva JL, Leocádio PCL, Reis JM, Campos GP, Capettini LSA, Foureaux G, et al. Oral methylmercury intoxication aggravates cardiovascular risk factors and accelerates atherosclerosis lesion development in ApoE knockout and C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Res. 2021 Jul 5;37(3):311–21. [CrossRef]
- Rutledge AC, Su Q, Adeli K. Apolipoprotein B100 biogenesis: a complex array of intracellular mechanisms regulating folding, stability, and lipoprotein assembly. This paper is one of a selection of papers published in this special issue entitled “Canadian Society of Biochemistry, Molecular & Cellular Biology 52nd Annual Meeting — Protein Folding: Principles and Diseases” and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process. Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2010 Apr;88(2):251–67.
- Brandão R, Santos FW, Farina M, Zeni G, Bohrer D, Rocha JBT, et al. Antioxidants and metallothionein levels in mercury-treated mice. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2006 Nov 11;22(6):429–38. [CrossRef]
- Bonomini F, Rodella LF, Moghadasian M, Lonati C, Rezzani R. Apolipoprotein E deficiency and a mouse model of accelerated liver aging. Biogerontology. 2013 Apr 18;14(2):209–20. [CrossRef]
- Lacerda Leocádio PC, Dias RP, Pinto DV, Reis JM, Rodrigues Nascimento JC, Anne de Castro Brito G, et al. Pollutants and nutrition: Are methylmercury effects on blood pressure and lipoprotein profile comparable to high-fat diet in mice? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Nov;204:111036.
- Dalla Corte CL, Ramos A, dos Santos CMM, Dressler VL, da Rocha JBT. Selenium and mercury levels in rat liver slices co-treated with diphenyl diselenide and methylmercury. BioMetals. 2016 Jun 2;29(3):543–50. [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Silva HT da, Panzenhagen AC, Schmidtt V, Alves Teixeira A, Espitia-Pérez P, de Oliveira Franco Á, et al. Hepatic and neurobiological effects of foetal and breastfeeding and adulthood exposure to methylmercury in Wistar rats. Chemosphere. 2020 Apr;244:125400. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Khushboo, Pandey R, Sharma B. Modulation of Superoxide Dismutase Activity by Mercury, Lead, and Arsenic. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Aug 10;196(2):654–61. [CrossRef]
- Kawakami T, Hanao N, Nishiyama K, Kadota Y, Inoue M, Sato M, et al. Differential effects of cobalt and mercury on lipid metabolism in the white adipose tissue of high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;258(1):32–42. [CrossRef]
- Ferrer B, Prince LM, Tinkov AA, Santamaria A, Farina M, Rocha JB, et al. Chronic exposure to methylmercury enhances the anorexigenic effects of leptin in C57BL/6J male mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2021 Jan;147:111924. [CrossRef]
- Huang ZH, Gu D, Mazzone T. Role of adipocyte-derived apoE in modulating adipocyte size, lipid metabolism, and gene expression in vivo. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2009 May;296(5):E1110–9. [CrossRef]
- Li Y hong, Liu L. Apolipoprotein E synthesized by adipocyte and apolipoprotein E carried on lipoproteins modulate adipocyte triglyceride content. Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Dec 23;13(1):136.
- Hofmann SM, Perez-Tilve D, Greer TM, Coburn BA, Grant E, Basford JE, et al. Defective Lipid Delivery Modulates Glucose Tolerance and Metabolic Response to Diet in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Diabetes. 2008 Jan 1;57(1):5–12. [CrossRef]
- Kazak L, Chouchani ET, Jedrychowski MP, Erickson BK, Shinoda K, Cohen P, et al. A Creatine-Driven Substrate Cycle Enhances Energy Expenditure and Thermogenesis in Beige Fat. Cell. 2015 Oct;163(3):643–55. [CrossRef]
- Shi R, Zhang J, Fang B, Tian X, Feng Y, Cheng Z, et al. Runners’ metabolomic changes following marathon. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Dec 13;17(1):19. [CrossRef]
- Yu Y, Zeng F, Han P, Zhang L, Yang L, Zhou F, et al. Dietary chlorogenic acid alleviates high-fat diet-induced steatotic liver disease by regulating metabolites and gut microbiota. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Feb 22;1–16. [CrossRef]
- Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of l-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 2013 May 7;19(5):576–85. [CrossRef]
- McCann MR, George De la Rosa MV, Rosania GR, Stringer KA. L-Carnitine and Acylcarnitines: Mitochondrial Biomarkers for Precision Medicine. Metabolites. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):51. [CrossRef]
- Park TS, Panek RL, Mueller SB, Hanselman JC, Rosebury WS, Robertson AW, et al. Inhibition of Sphingomyelin Synthesis Reduces Atherogenesis in Apolipoprotein E–Knockout Mice. Circulation. 2004 Nov 30;110(22):3465–71. [CrossRef]
- Piña-Zentella G, de la Rosa-Cuevas G, Vázquez-Meza H, Piña E, de Piña MZ. Taurine in adipocytes prevents insulin-mediated H2o2 generation and activates Pka and lipolysis. Amino Acids. 2012 May 3;42(5):1927–35. [CrossRef]
- Putta MR, Yu D, Bhagat L, Wang D, Zhu FG, Kandimalla ER. Impact of Nature and Length of Linker Incorporated in Agonists on Toll-Like Receptor 9-Mediated Immune Responses. J Med Chem. 2010 May 13;53(9):3730–8. [CrossRef]
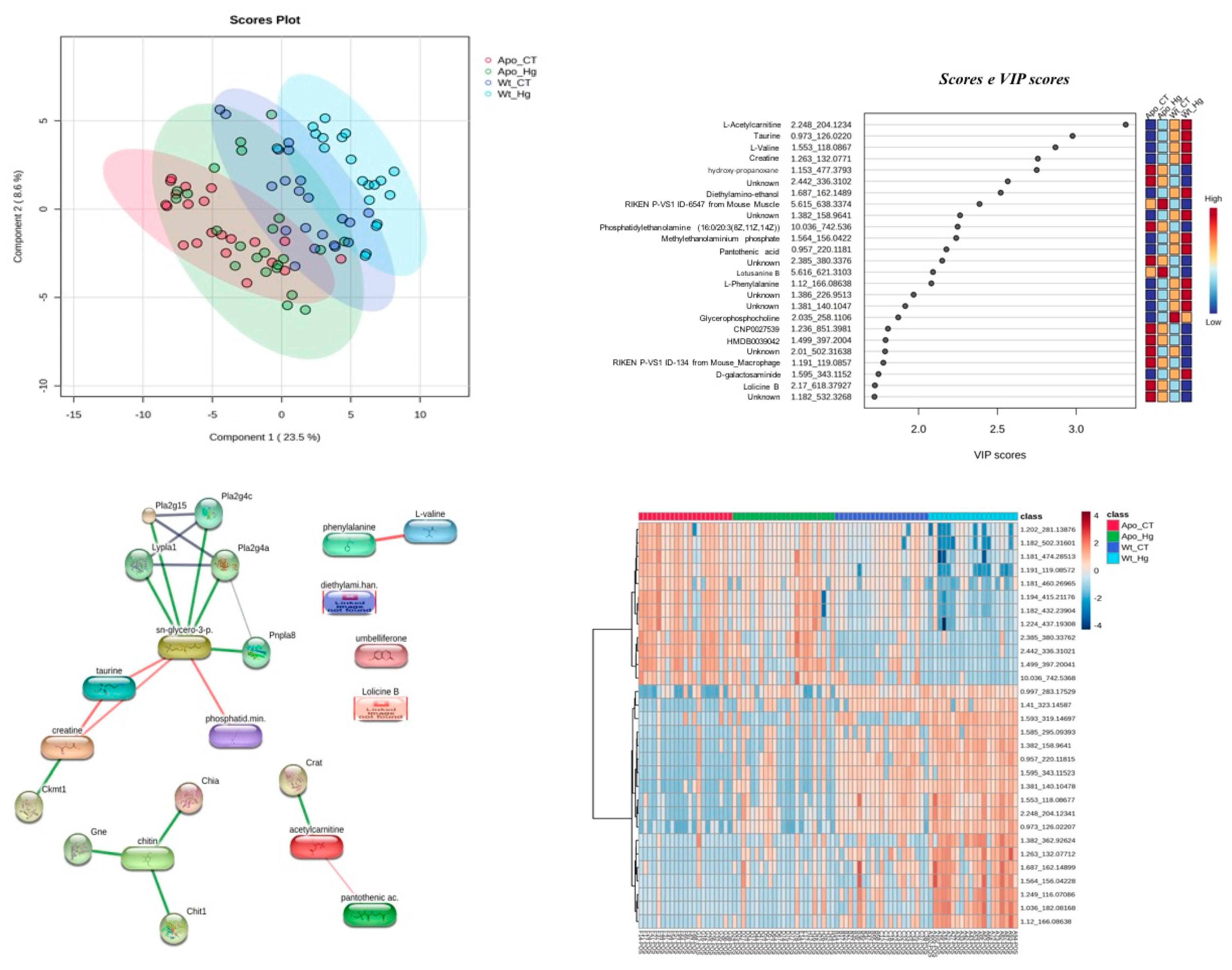
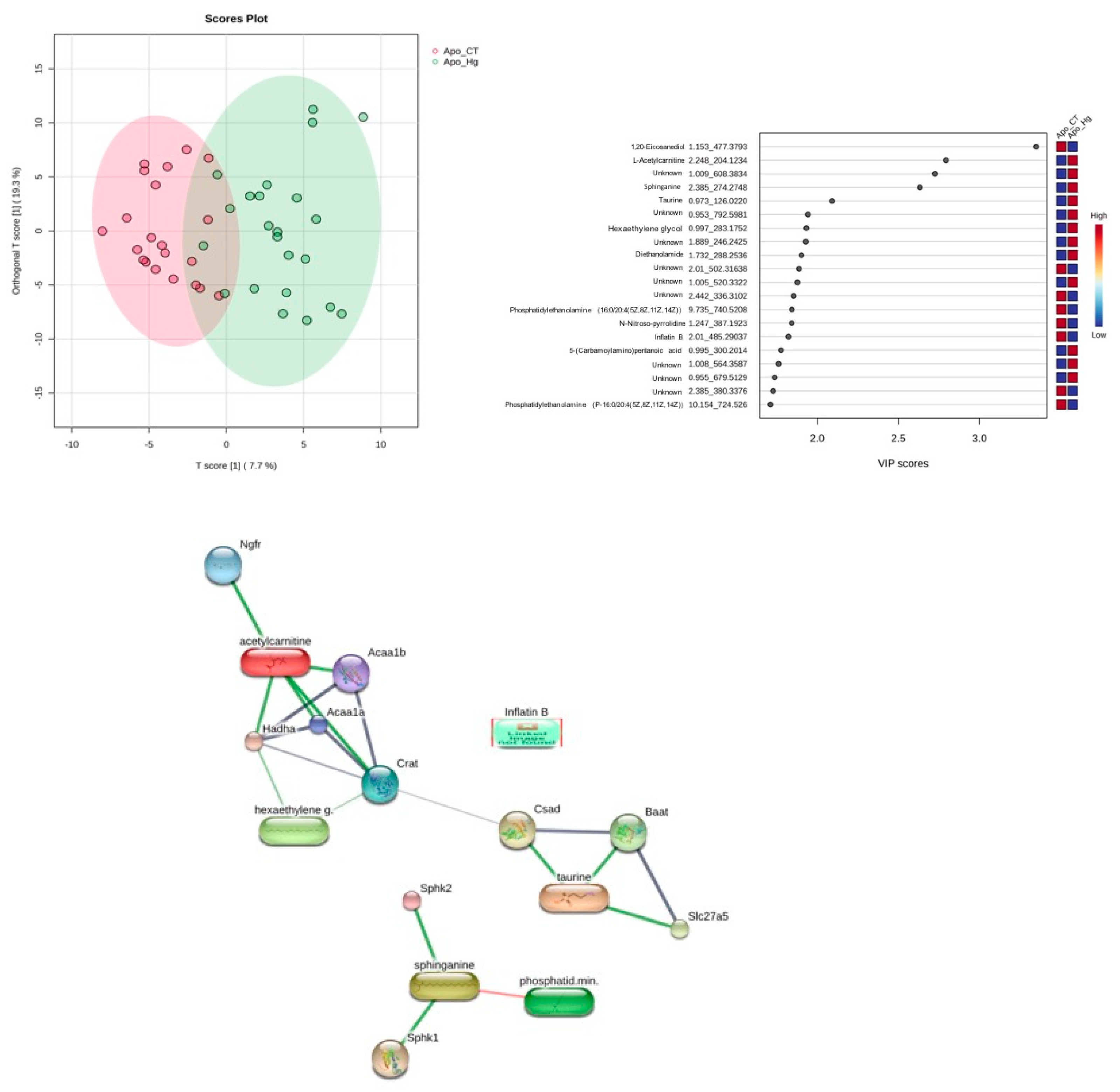
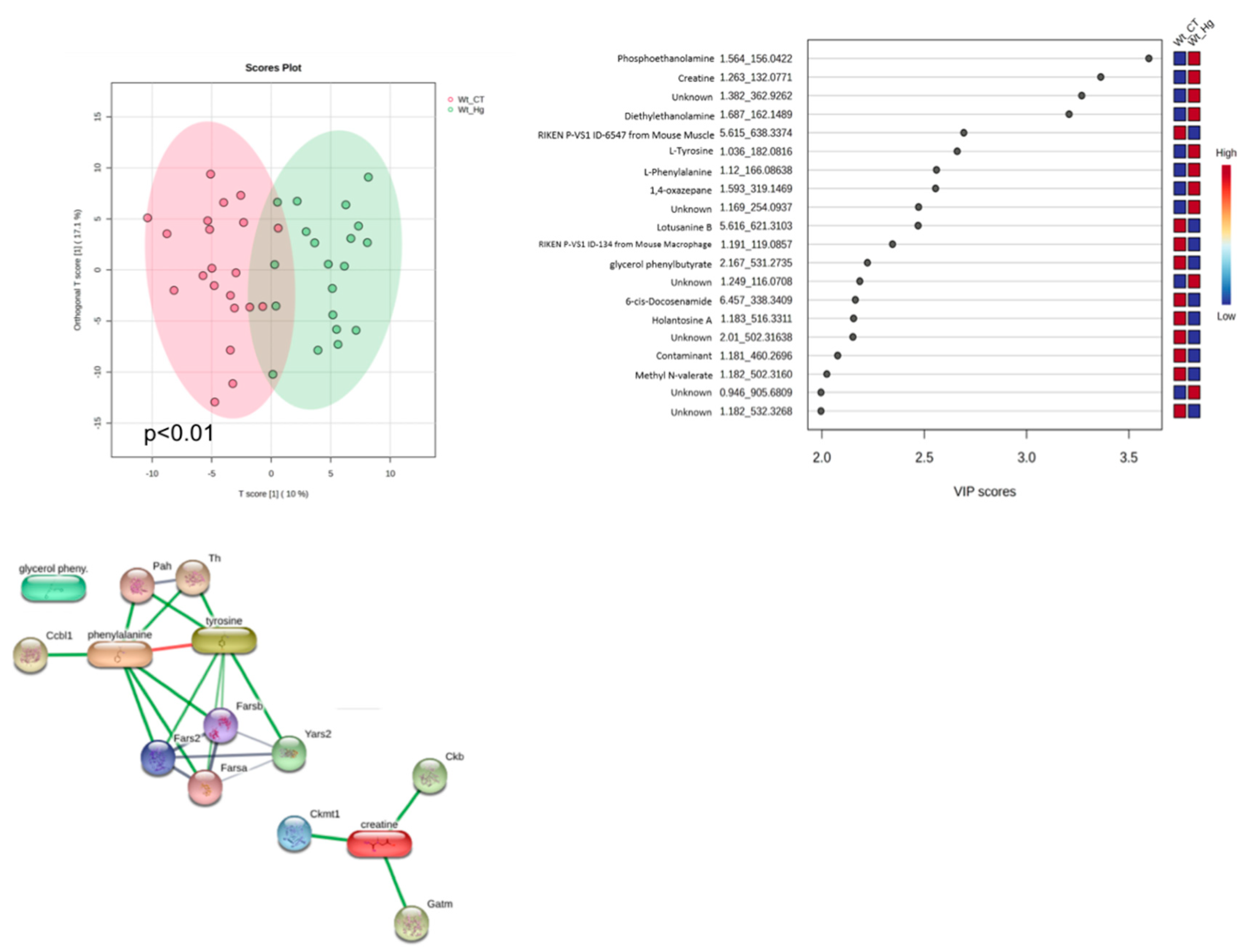
| Groups | Steatosis | Ballooning |
| CT | 0 (0-0) | 0 (0-1) |
| MeHg | 0 (0-0) | 0 (0-2) |
| ApoE ko CT | 0 (0-1) | 1 (0-2) |
| ApoE ko MeHg | 0 (0-1)a,b | 1 (0-2)b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





