Submitted:
11 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
2. Rotation Motion
-
Shape and Size: Rotation does not alter the shape or size of the object. More Specifically,
- . It means the length of the point will not be changed by rotation motion. Without loss of generality, the rotation motion in this paper is studied with unit norm vectors, i.e., on the unit sphere surface, which represents a unit direction vector in the 3D physical world.
- where are any two unit vectors. It means the angle (structure) of the object is unchanged.
- Axis of Rotation: Rotational motion occurs around a fixed axis. Given a vector , if , it means the after the rotation , the vector direction remains unchanged, and the vector must be parallel to the rotation axis , which is from Euler’s rotation theorem and screw theory [23,24,25,26]. In addition,where is the 3 × 3 identity matrix. Algebraically, Eq.(2) means the rotation axis direction lies in the null space of . Alternatively, let , then the rotation axis direction is an eigenvector of corresponding to the eigenvalue .
3. Linear Expressions for Rotation Motion
4. Special Case I: Great Circle in
- Not all rotations in can rotate to .
- There is more than one rotation that satisfies the given rotation motion.
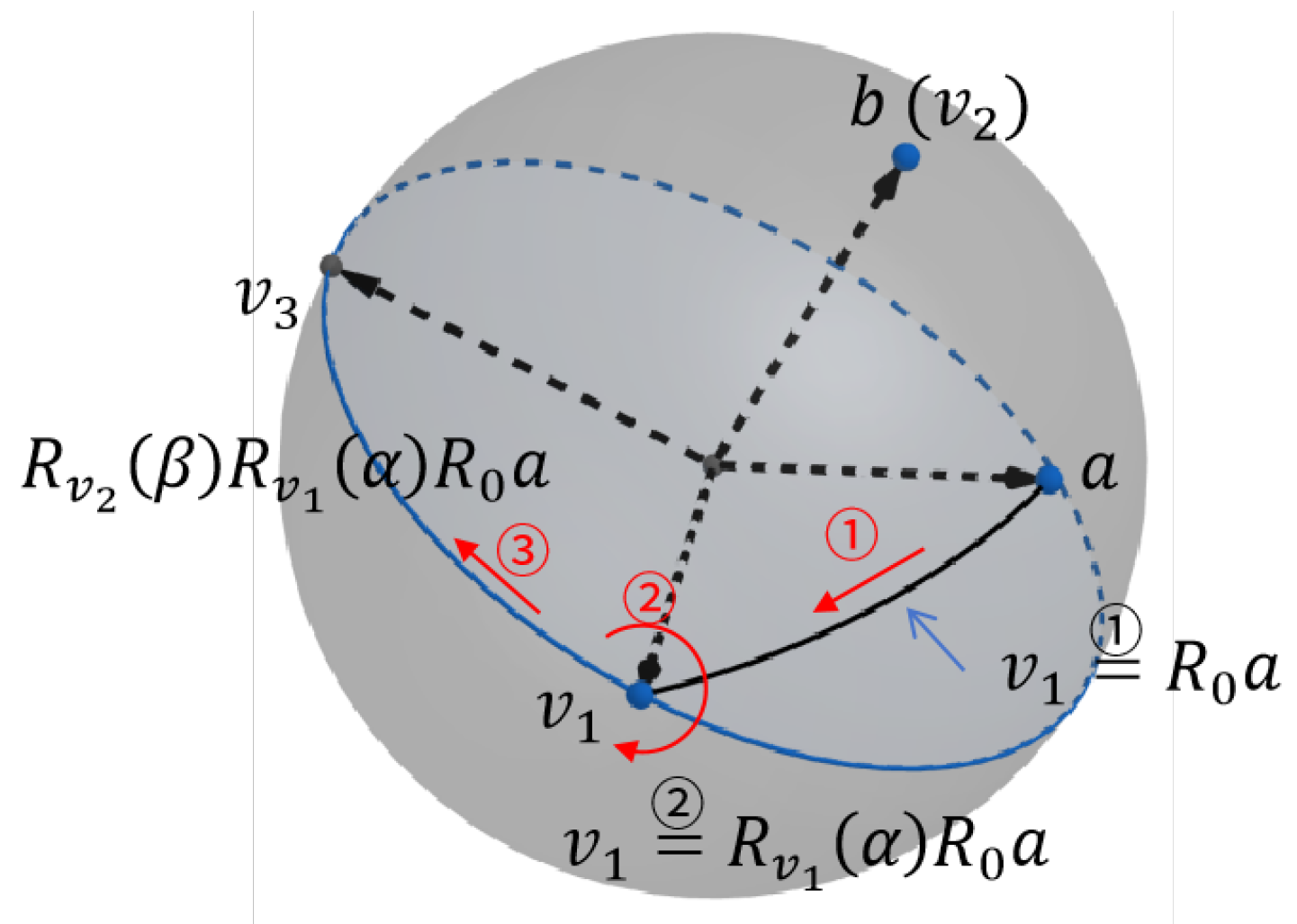
4.1. Alternative Way to Obtain Great Circle in
5. Special Case II: Clifford Torus in
5.1. Alternative Way to Obtain Clifford Torus in
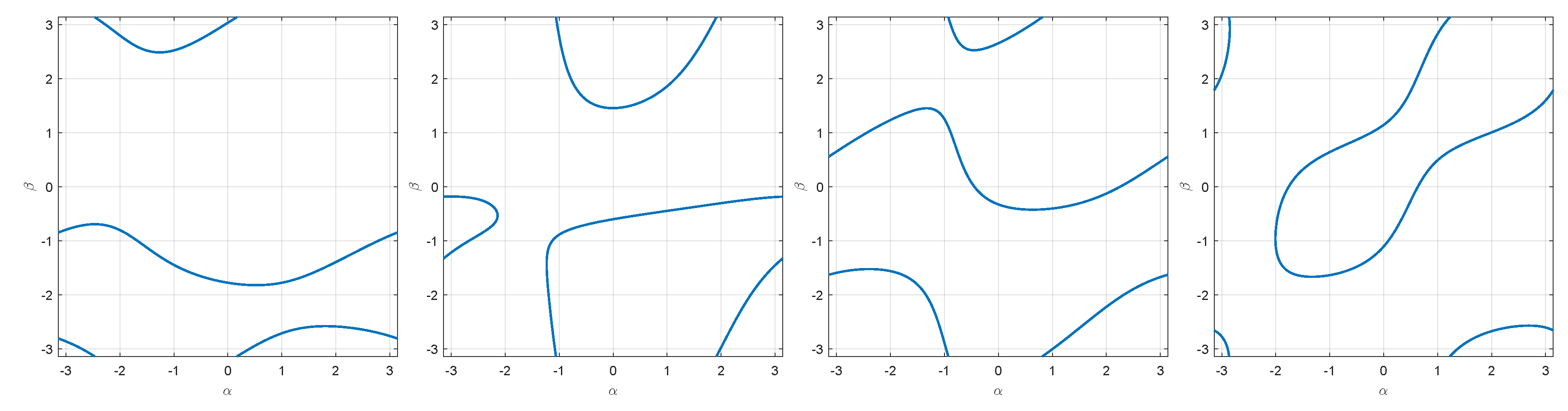
5.2. Intersections of Two Different Clifford Tori
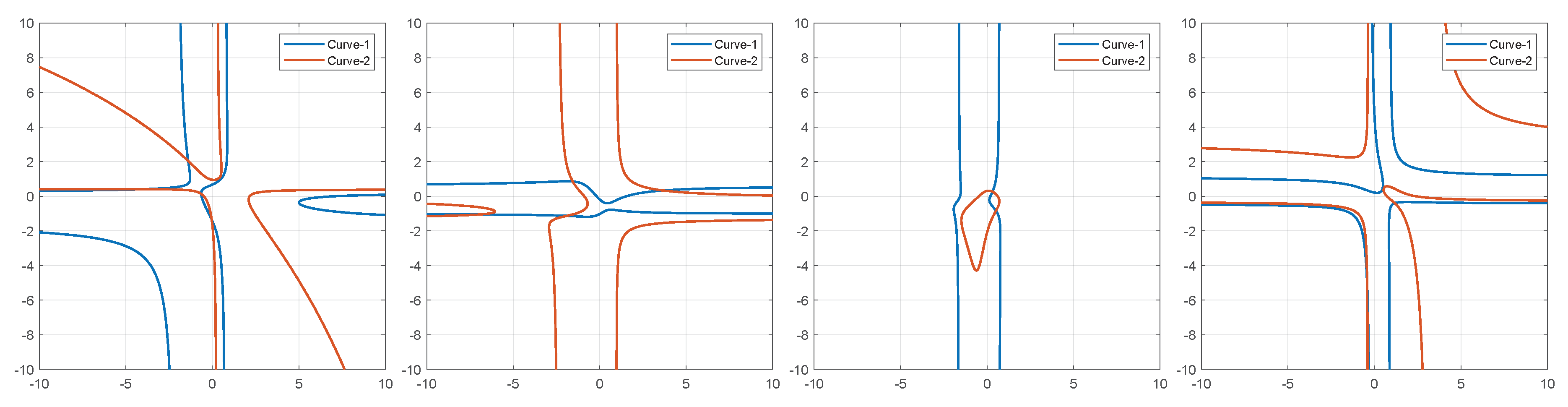
5.3. Intersections of Three Different Clifford Tori
5.3.1. Linear Solution to Solve Intersections of Three Different Clifford Tori
References
- Epp, R.J.; Mann, R.B.; McGrath, P.L. Rigid motion revisited: rigid quasilocal frames. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2009, 26, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, S.L. Rotations, quaternions, and double groups; Courier Corporation, 2005.
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple view geometry in computer vision; Cambridge university press, 2003.
- Goel, R.; Gupta, P. Robotics and industry 4.0. A Roadmap to Industry 4.0: Smart Production, Sharp Business and Sustainable Development 2020, pp. 157–169.
- Teed, Z.; Deng, J. Raft-3d: Scene flow using rigid-motion embeddings. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2021, pp. 8375–8384.
- Kisantal, M.; Sharma, S.; Park, T.H.; Izzo, D.; Märtens, M.; D’Amico, S. Satellite pose estimation challenge: Dataset, competition design, and results. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 2020, 56, 4083–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Rahiman, W.; Nazli Alhady, S.S. A comprehensive study for robot navigation techniques. Cogent Engineering 2019, 6, 1632046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mees, O.; Zeng, A.; Burgard, W. Visual language maps for robot navigation. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2023, pp. 10608–10615.
- Bustos, A.P.; Chin, T.J. Guaranteed Outlier Removal for Point Cloud Registration with Correspondences. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2018, 40, 2868–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, A.; Olsson, C.; Kahl, F.; Chin, T.J. Rotation averaging and strong duality. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 127–135.
- Crassidis, J.L.; Markley, F.L.; Cheng, Y. Survey of nonlinear attitude estimation methods. Journal of guidance, control, and dynamics 2007, 30, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlone, L.; others. Estimation Contracts for Outlier-Robust Geometric Perception. Foundations and Trends® in Robotics 2023, 11, 90–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathavaraj, S.; Butcher, E.A. SE (3)-constrained extended Kalman filtering for rigid body pose estimation. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 2021, 58, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, G.F. Kalman filter. Computer Vision: A Reference Guide 2020, pp. 1–3.
- Trawny, N.; Roumeliotis, S.I. Indirect Kalman filter for 3D attitude estimation. University of Minnesota, Dept. of Comp. Sci. & Eng., Tech. Rep 2005, 2, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, T.J.; Suter, D. The maximum consensus problem: recent algorithmic advances; Springer Nature, 2022.
- Etingof, P. Lie groups and Lie algebras. arXiv arXiv:2201.09397.
- Dehmamy, N.; Walters, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, R. Automatic symmetry discovery with lie algebra convolutional network. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, P.E.; Murray, W.; Wright, M.H. Numerical linear algebra and optimization; SIAM, 2021.
- Farin, G.; Hansford, D. Practical linear algebra: a geometry toolbox; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2021.
- Horn, R.A.; Johnson, C.R. Matrix analysis; Cambridge university press, 2012.
- Taubin, G. 3D Rotations. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 2011, 31, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, R.S. The theory of screws: A study in the dynamics of a rigid body. Mathematische Annalen 1876, 9, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palais, B.; Palais, R. Euler’s fixed point theorem: The axis of a rotation. Journal of fixed point theory and applications 2007, 2, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. The Theorems of Euler and Chasles. University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science, I-Net, USA 2000.
- Joseph, T. An alternative proof of Euler’s rotation theorem. The Mathematical Intelligencer 2020, 42, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiture, L. A history of the description of the three-dimensional finite rotation. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences 2009, 57, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.I.; Kahl, F. Global optimization through rotation space search. International Journal of Computer Vision 2009, 82, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.B. Quaternions and rotations. Com S 2008, 477, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Quaternions and Spatial Rotation. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quaternions_and_spatial_rotation.
- Hartley, R.; Trumpf, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, H. Rotation averaging. International journal of computer vision 2013, 103, 267–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, M. Rotation representations and their conversions. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 6682–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, M.D. A survey of attitude representation. Journal of The Astronautical Sciences 1993, 41, 439–517. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Globally Optimal Solutions for Unit-Norm Constrained Computer Vision Problems. PhD thesis, Technische Universität München, 2022.
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, M. 2d-3d point set registration based on global rotation search. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2018, 28, 2599–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Campbell, D.; Jia, Y. Go-ICP: A globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2015, 38, 2241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HORN, B.P. Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions. Journal of the Optical Society of America. A, Optics and image science 1987, 4, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Tsakiris, M.C.; Vidal, R. Arcs: Accurate rotation and correspondence search. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 11153–11163.
- McClintock, P. Relating plane transformations with stereographic projection. PhD thesis, 2022.
- Wilkins, D.R. Möbius transformations and stereographic projection, 2017.
- Gluck, H. Great circle fibrations and contact structures on the 3-sphere. Geometriae Dedicata 2022, 216, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flat torus. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torus.
- Ayzenberg, A. Torus action on quaternionic projective plane and related spaces. Arnold Mathematical Journal 2021, 7, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsan, R.A.; Rosen, G.T.; Mohamed, D.F.N.; Choset, H. Estimating SE (3) elements using a dual quaternion based linear Kalman filter. Robotics: Science and systems, 2016.
- Arun Srivatsan, R.; Zevallos, N.; Vagdargi, P.; Choset, H. Registration with a small number of sparse measurements. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019, 38, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, O.; Bengtsson, I. Clifford tori and unbiased vectors. Reports on mathematical physics 2017, 79, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukelova, Z.; Heller, J.; Fitzgibbon, A. Efficient intersection of three quadrics and applications in computer vision. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, pp. 1799–1808.
- Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Koch, R. Pose estimation from line correspondences: A complete analysis and a series of solutions. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2016, 39, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y. An efficient and globally optimal method for camera pose estimation using line features. Machine Vision and Applications 2020, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, Q. Camera pose estimation from lines: a fast, robust and general method. Machine Vision and Applications 2019, 30, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K. A simple mathematical approach for determining intersection of quadratic surfaces. In Multiscale optimization methods and applications; Springer, 2006; pp. 271–298.
- Sarraga, R.F. Algebraic methods for intersections of quadric surfaces in GMSOLID. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing 1983, 22, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturmfels, B. Introduction to resultants. Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics. American Mathematical Society, 1998, Vol. 53, pp. 25–40.
- Woody, H. Polynomial resultants. GNU operating system 2016. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks. Resultant of two polynomials. [Online]. Available: https://www.mathworks.com/help/symbolic/sym.resultant.html.
- Hartley, R.; Li, H. An efficient hidden variable approach to minimal-case camera motion estimation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2012, 34, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukelova, Z.; Bujnak, M.; Pajdla, T. Polynomial eigenvalue solutions to minimal problems in computer vision. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2011, 34, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, V.Y. Good News for Polynomial Root-finding. arXiv arXiv:1805.12042.
- Kalantari, B. Polynomial root-finding and polynomiography; World Scientific, 2008.
- Tisseur, F.; Meerbergen, K. The quadratic eigenvalue problem. SIAM review 2001, 43, 235–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghojogh, B.; Karray, F.; Crowley, M. Eigenvalue and Generalized Eigenvalue Problems: Tutorial, 2023, [arXiv:stat.ML/1903.11240].
- Williams, M.P. Solving polynomial equations using linear algebra. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest 2010, 28, 354–363. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, P.; Zaballa, I. Diagonalizable quadratic eigenvalue problems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2009, 23, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 |
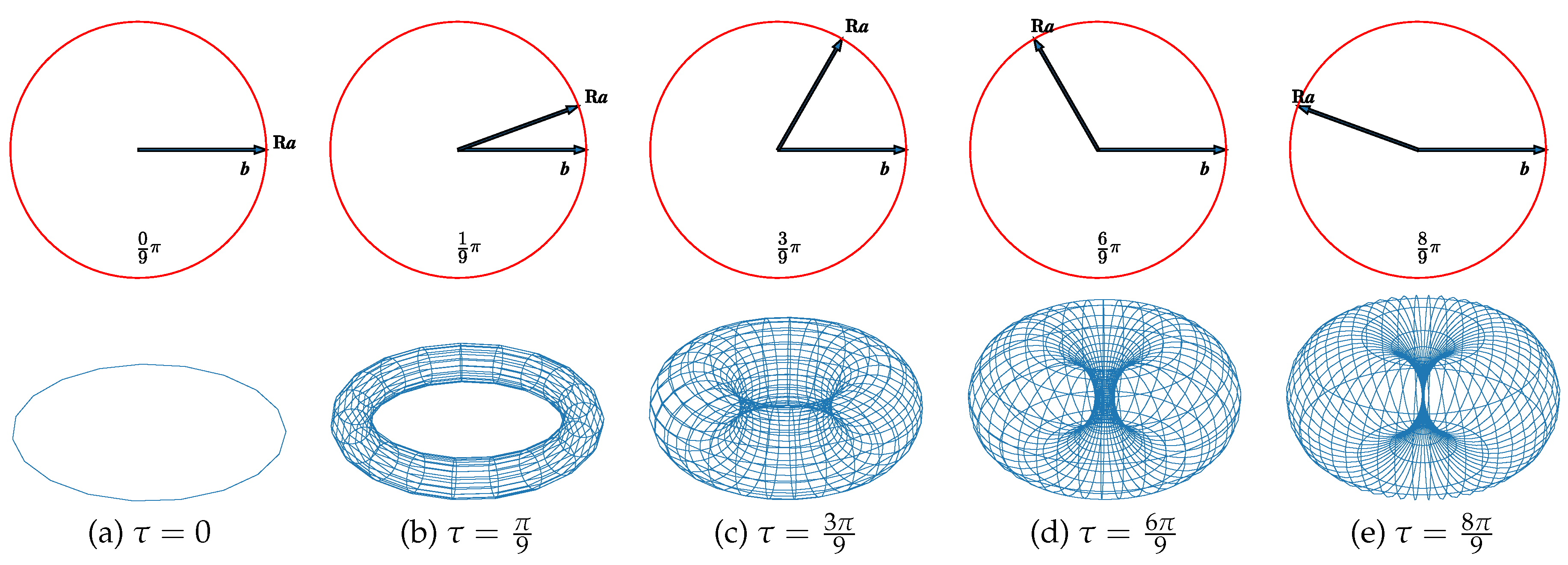
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) |

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




