Submitted:
10 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
- An open-source preprocessing pipeline (including filtering, segmentation, and feature extraction) for voice data preparation and storage for future applications.
- Model development is on a large longitudinal dataset and validated on a public dataset and locally collected dataset in different environments using SNR as the performance metric.
- Performance comparison of the model with state-of-art Deep Learning based methods.
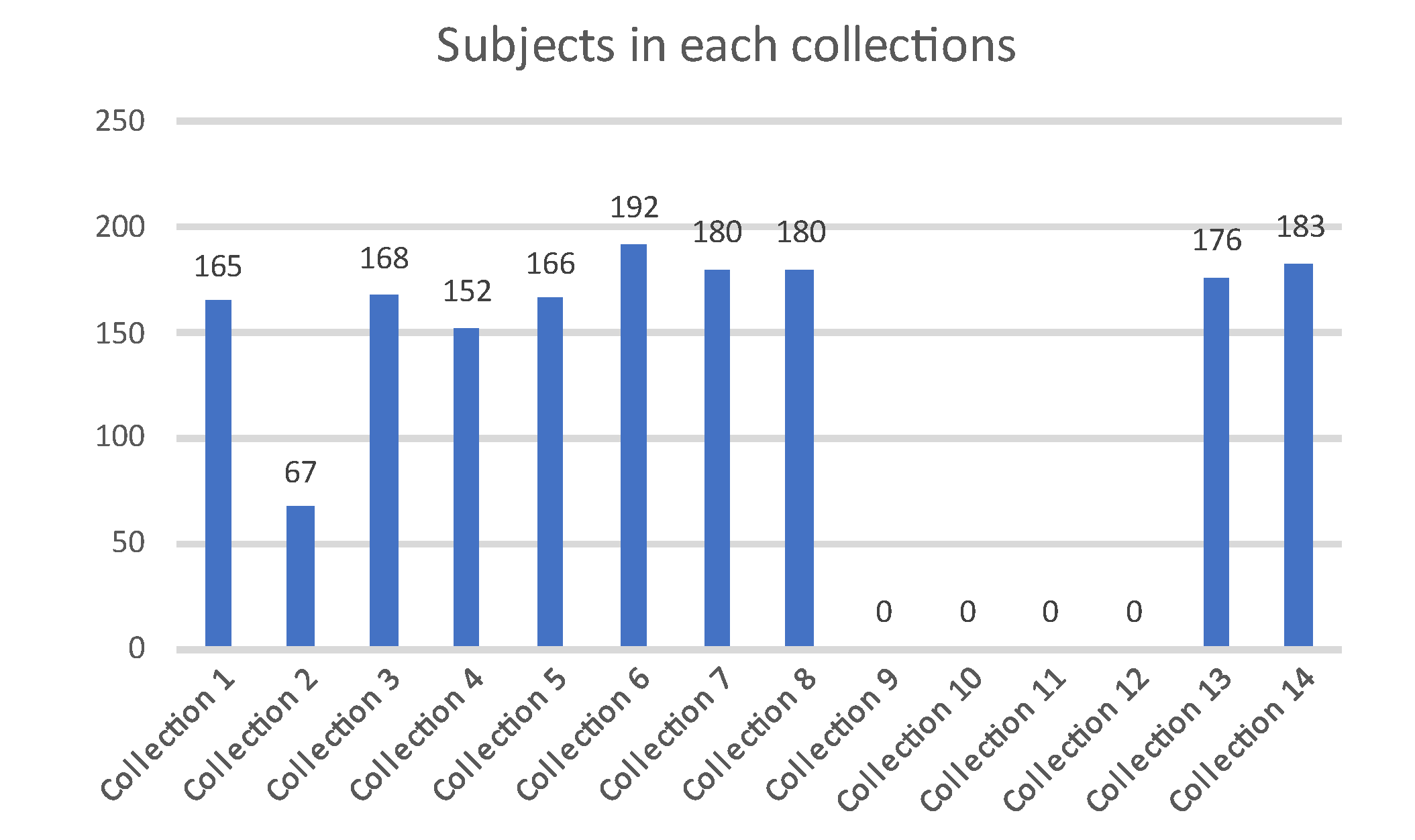
II. Dataset Description
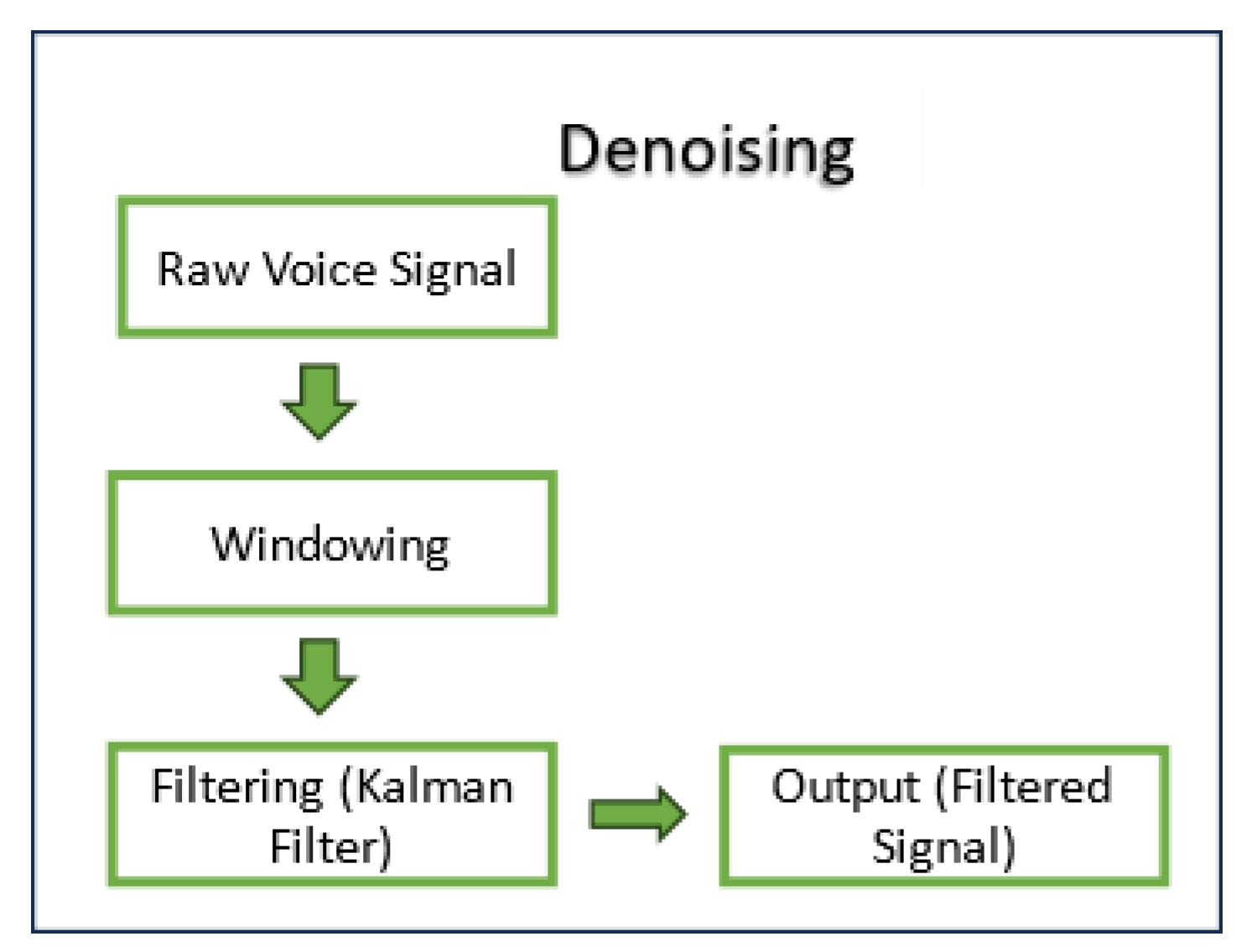
III. Voice Preprocessing
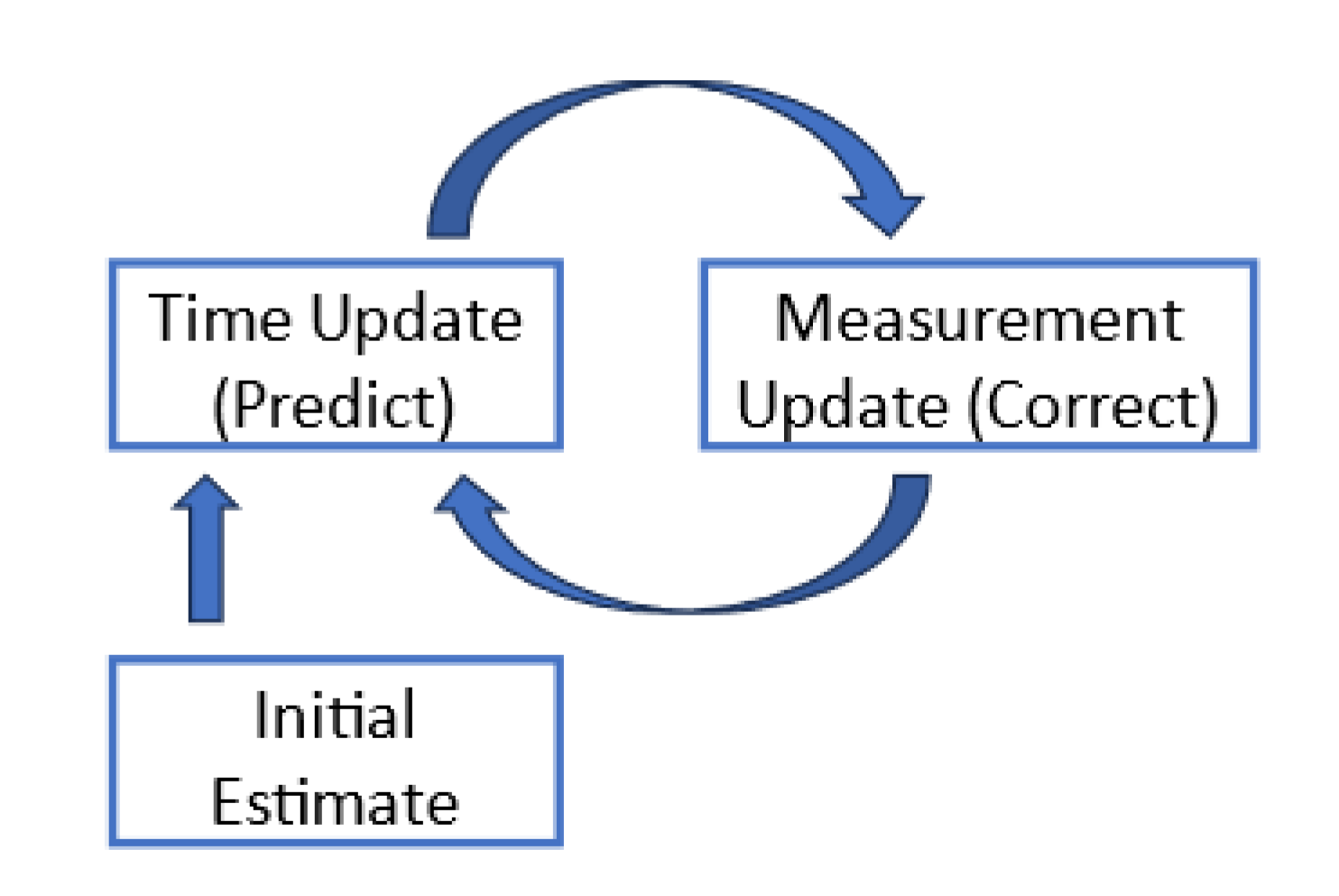
A. Kalman Filter
- Time Update (Prediction equation): Estimate the next step from the previous state.
B. Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
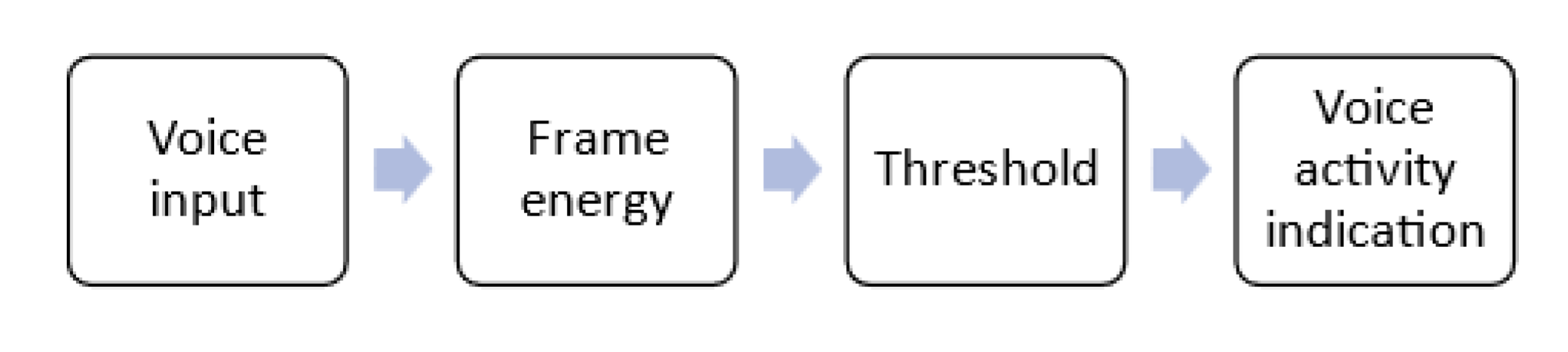
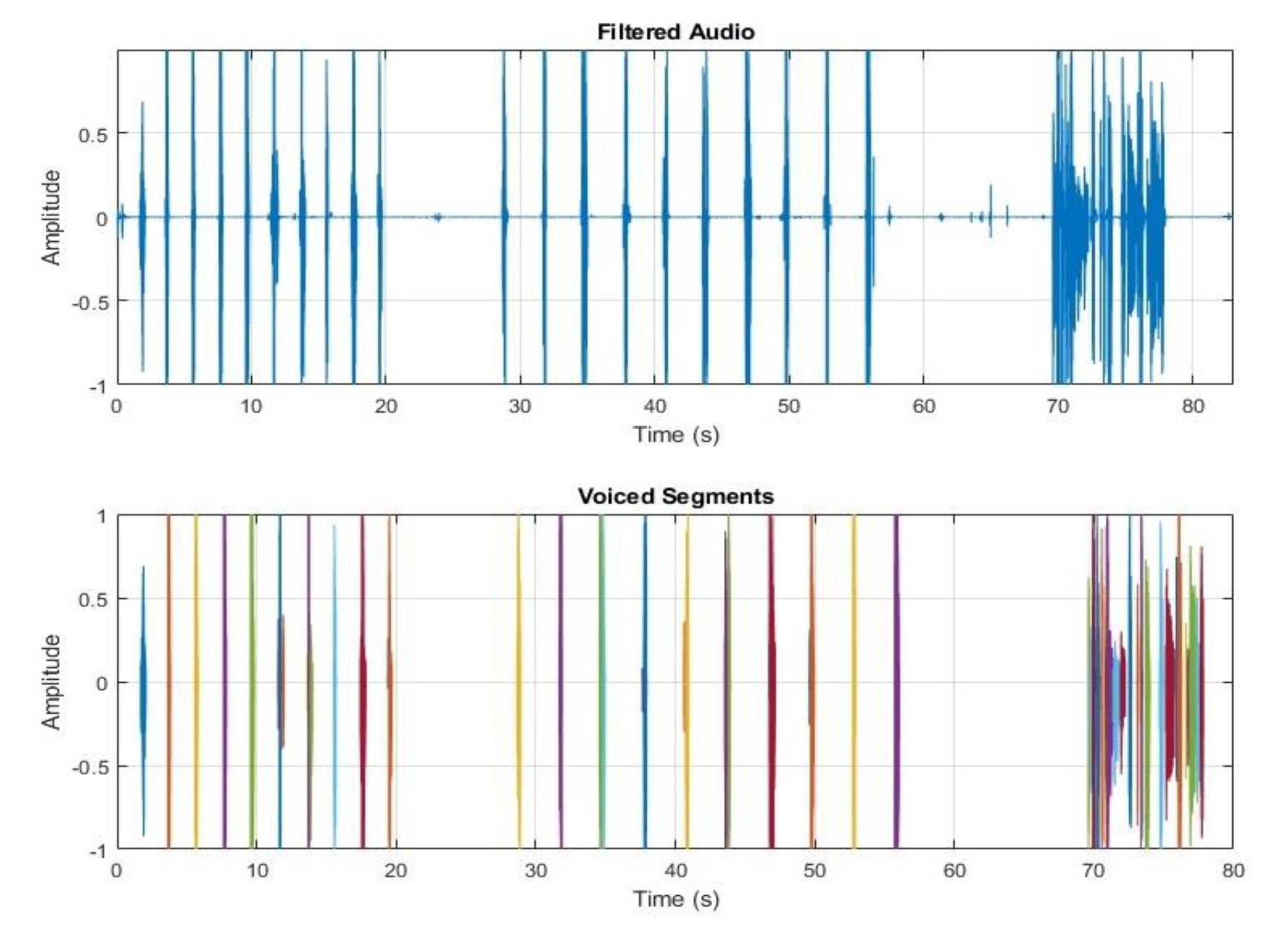
IV. Segmentation
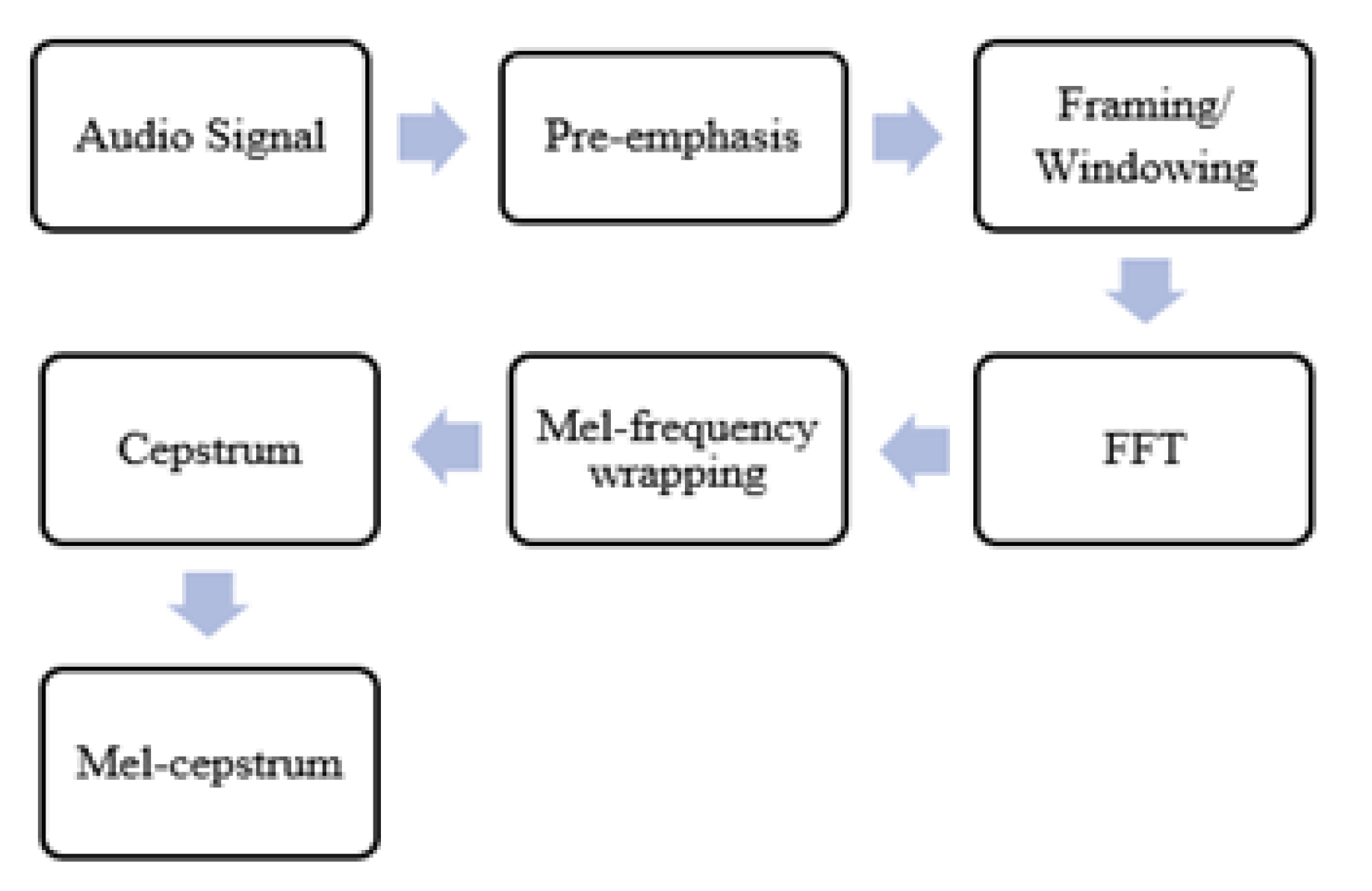
V. Feature Extraction
VI. Performance Evaluation
A. Validation Using Different Microphones
B. Comparison with the Traditional High-Pass Filter
C. Validation Using Local Dataset
D. Validation Using a Public Dataset
E. Comparison with Deep Learning Model
VII. Result
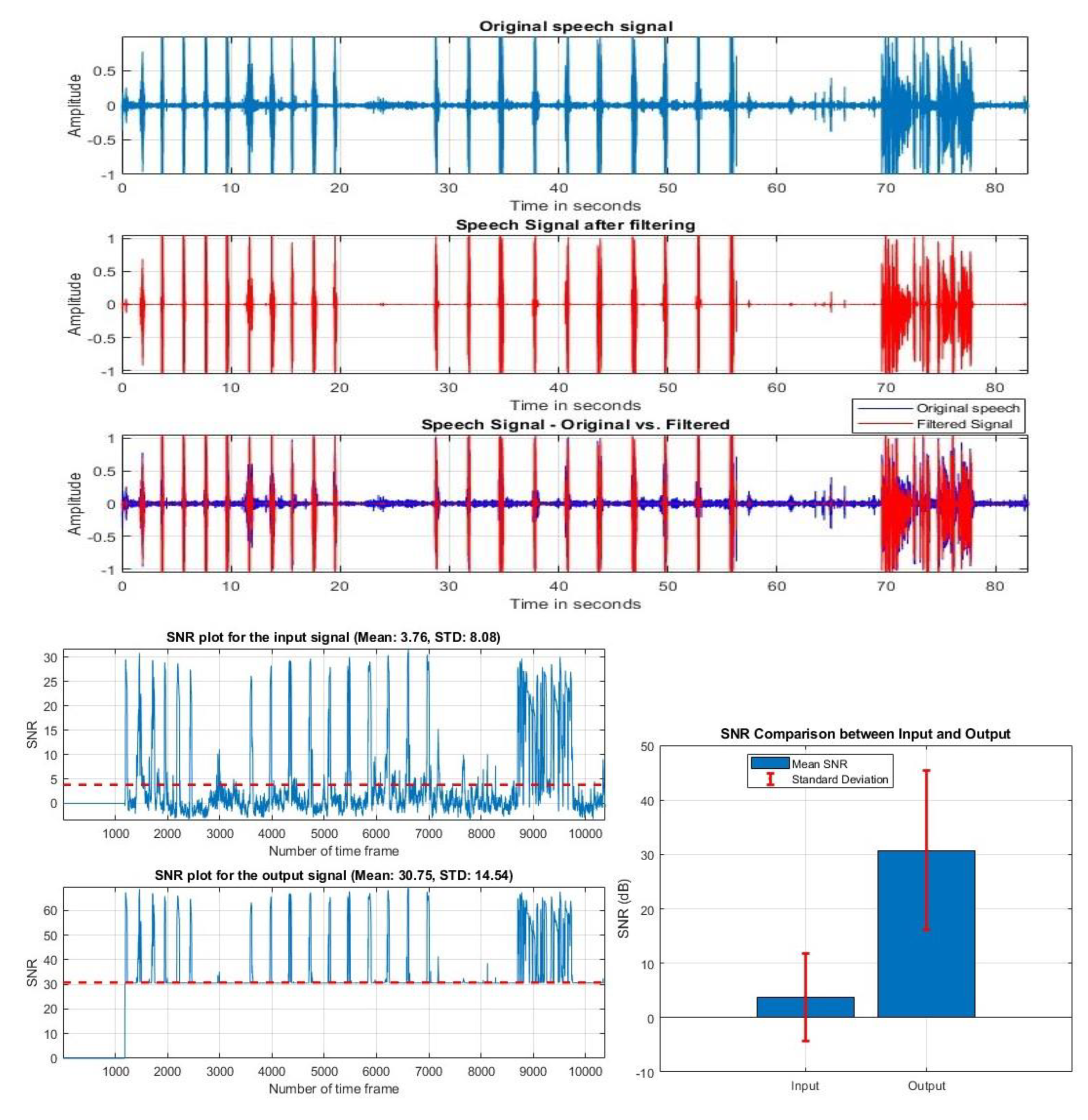
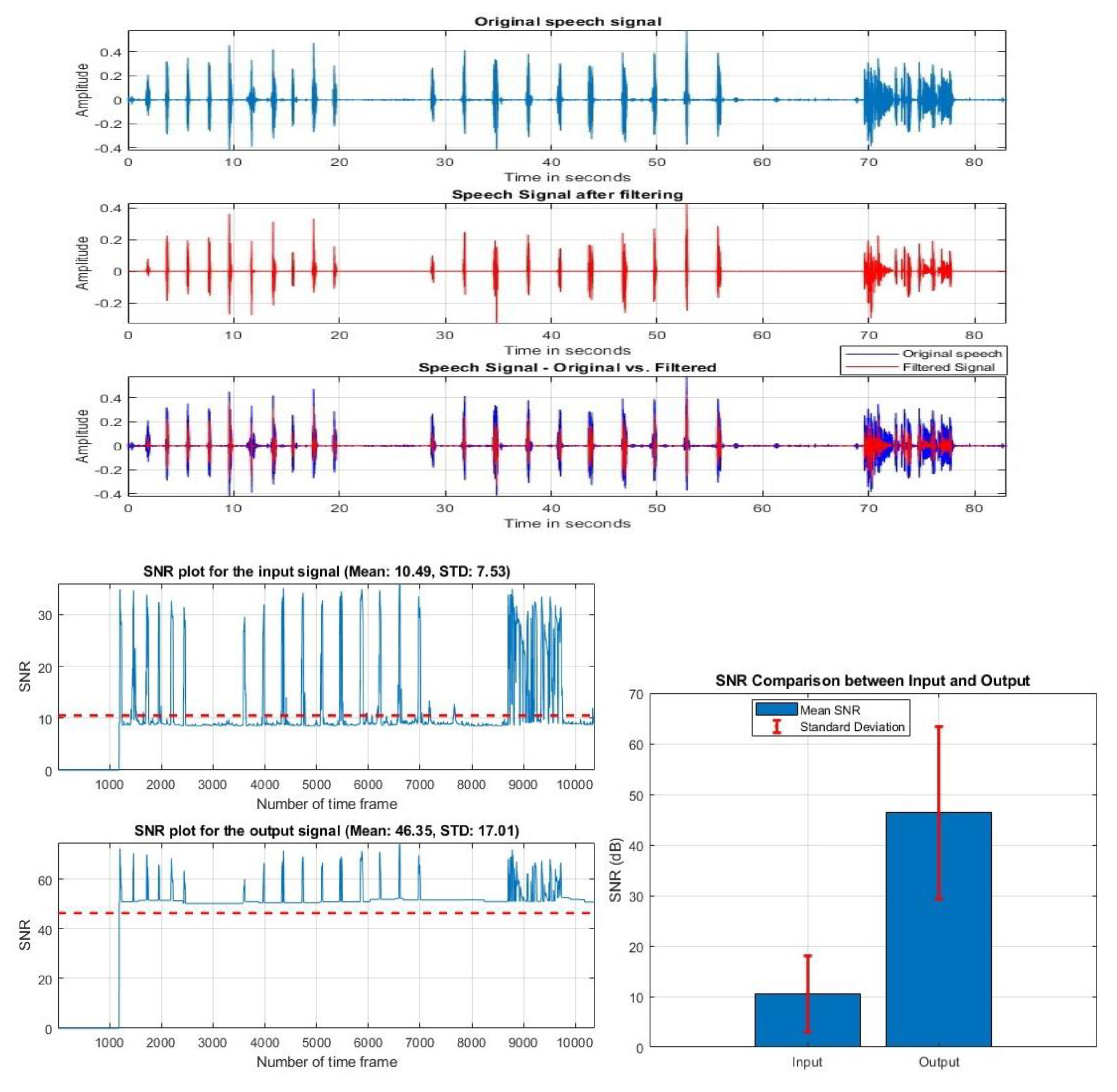
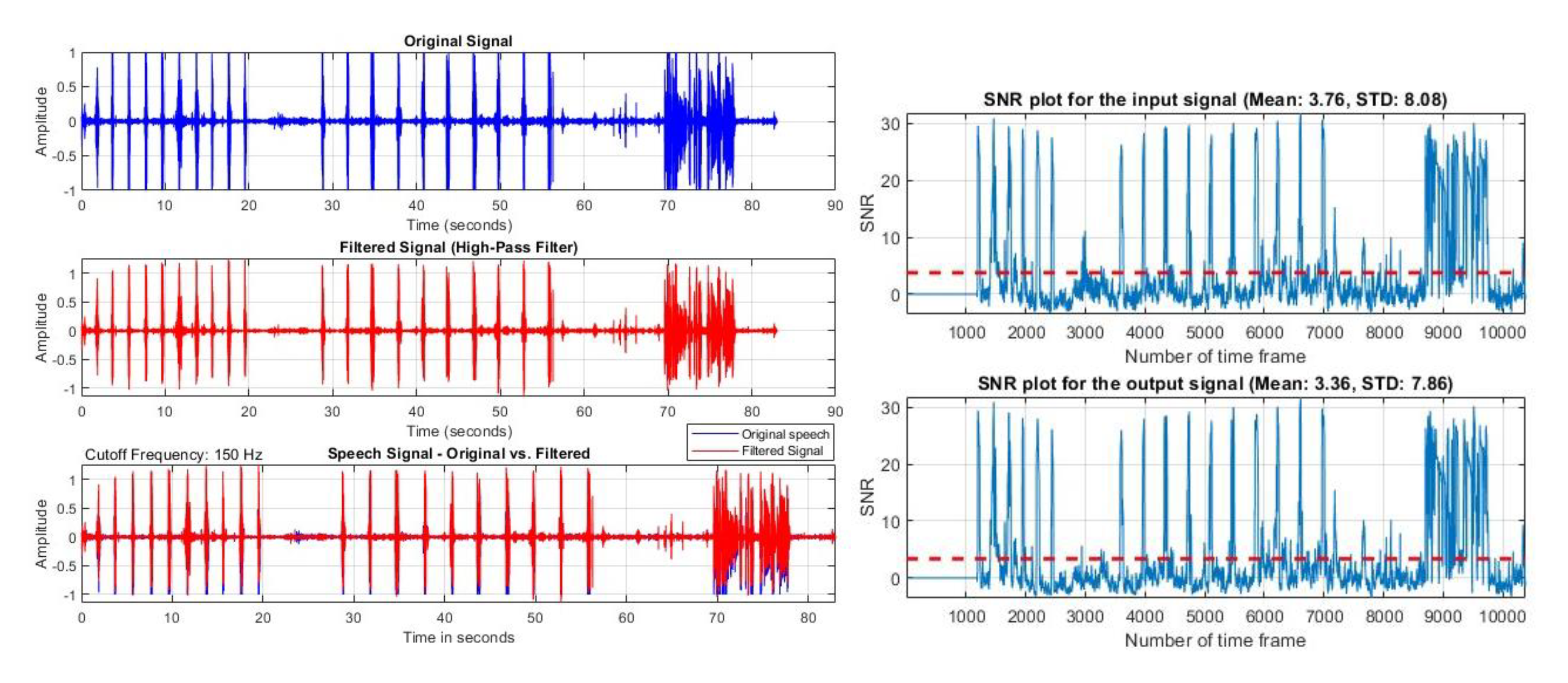
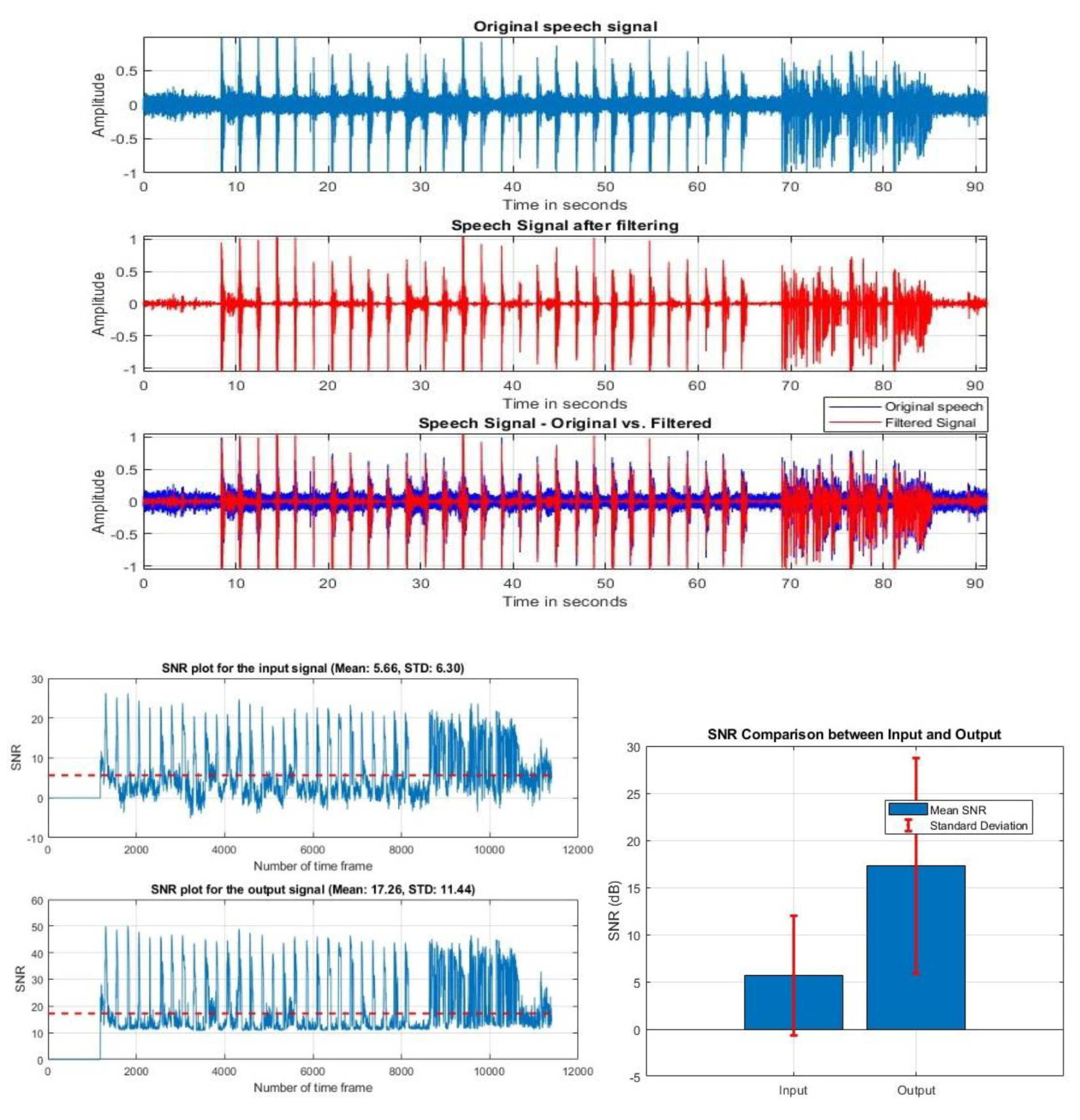
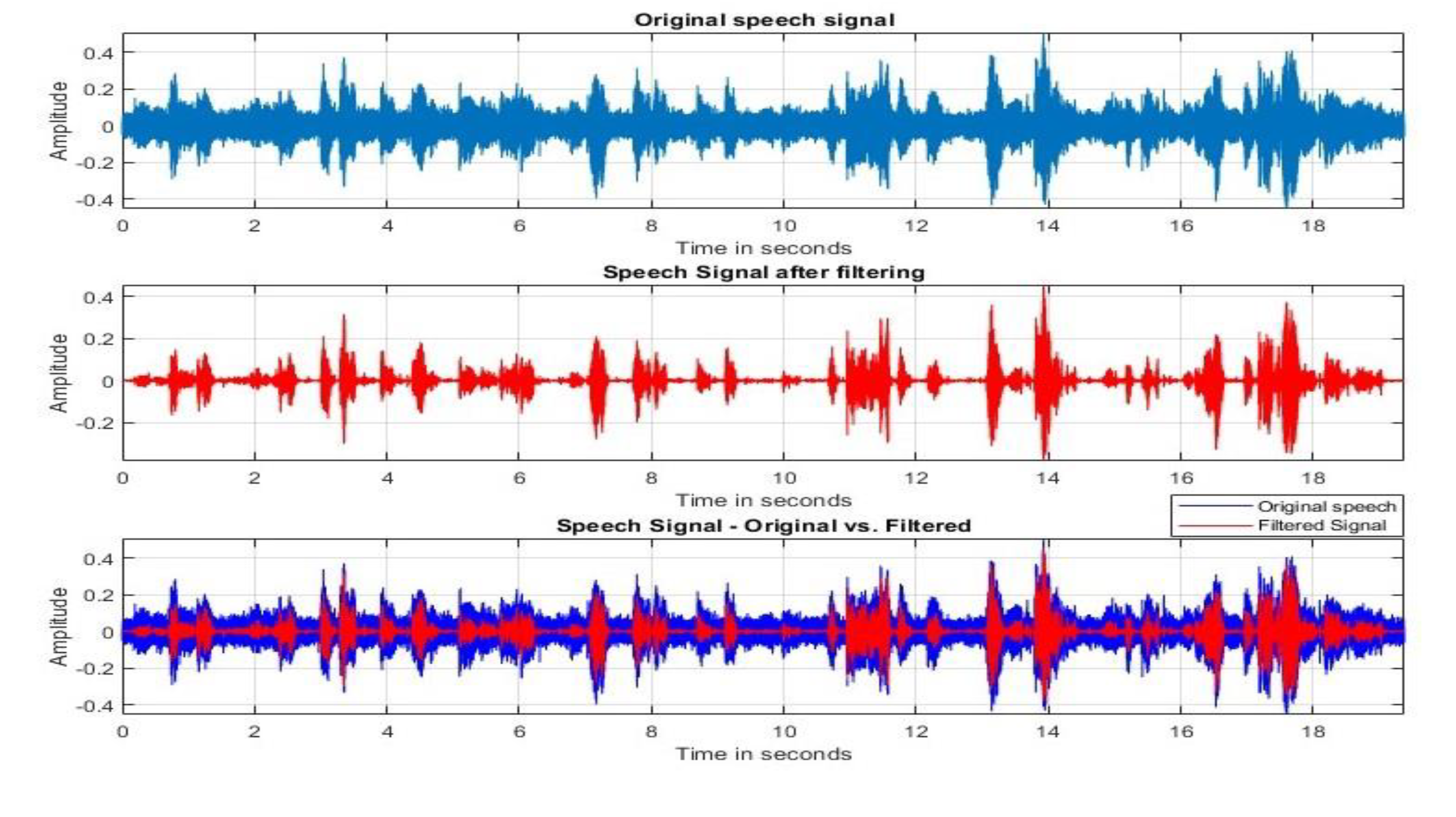
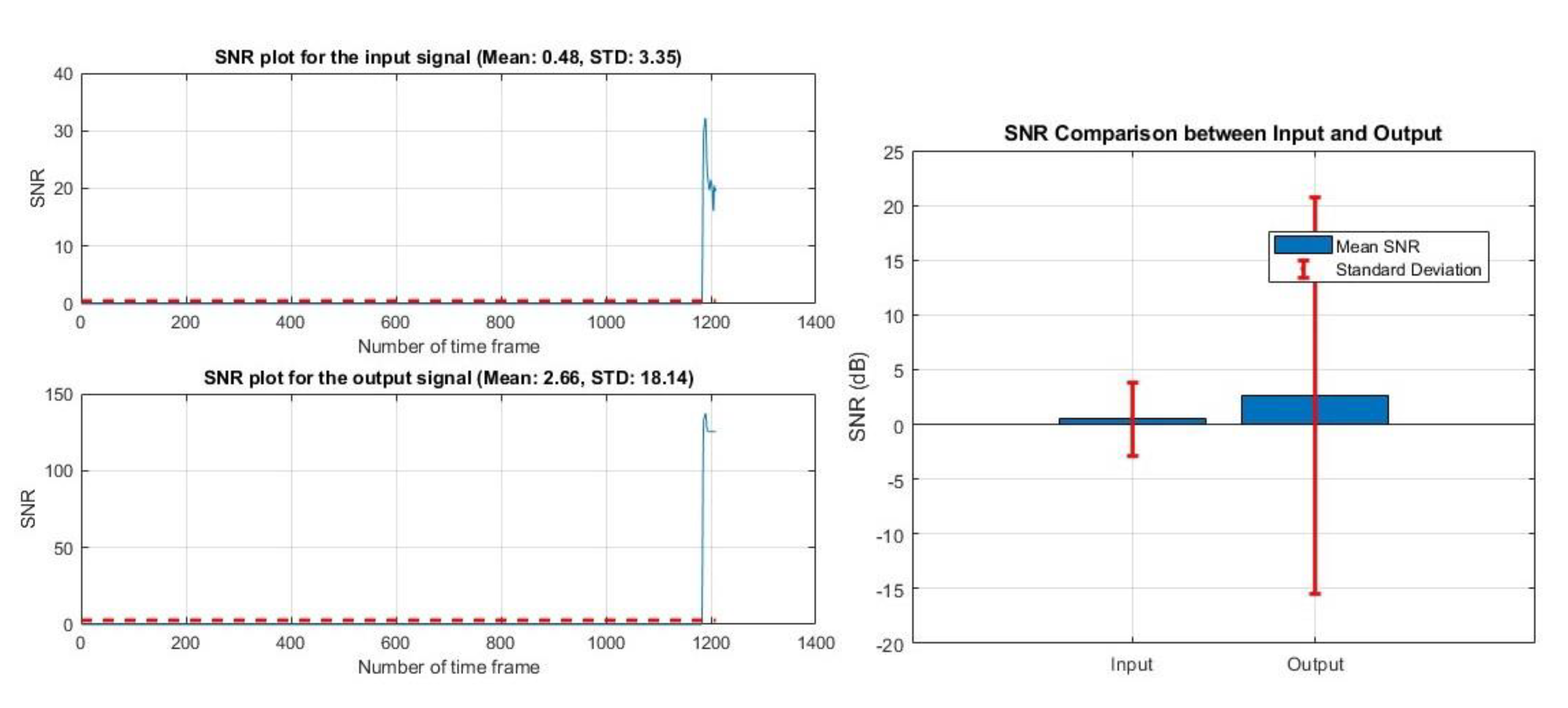
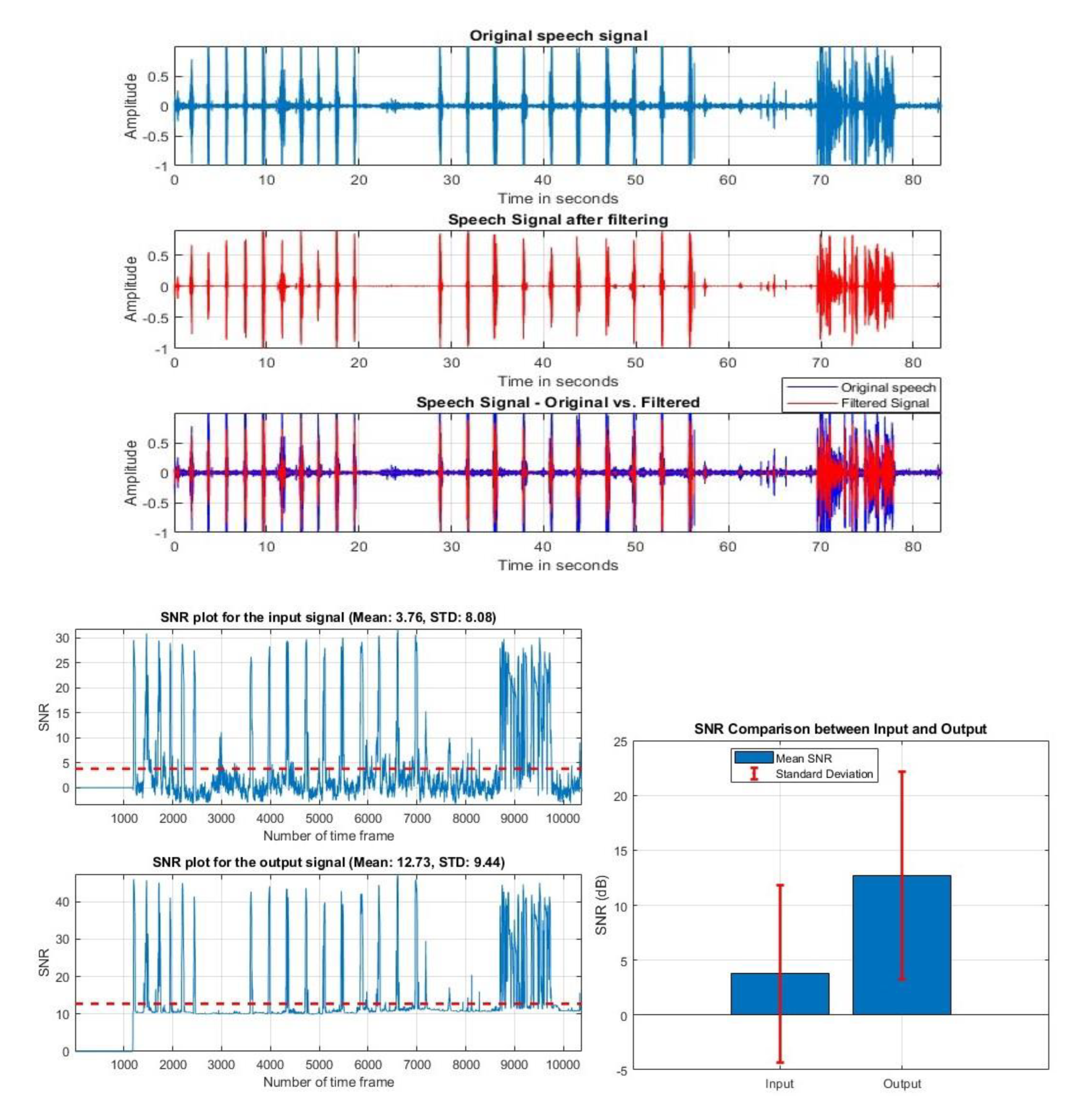
VIII. Discussion
IX. Conclusion
References
- R. Singh, “A Step-by-Step Guide to Speech Recognition and Audio Signal Processing in Python,” Medium. Accessed: Dec. 05, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-step-by-step-guide-to-speech-recognition-and-audio-signal-processing-in-python-136e37236c24.
- K. B. Bhangale and K. Mohanaprasad, “A review on speech processing using machine learning paradigm,” Int J Speech Technol, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 367–388, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Aggarwal, S. P. G. Aggarwal, S. P. Gochhayat, and L. Singh, “Chapter 10 - Parameterization techniques for automatic speech recognition system,” in Machine Learning and the Internet of Medical Things in Healthcare, K. K. Singh, M. Elhoseny, A. Singh, and A. A. Elngar, Eds., Academic Press, 2021, pp. 209–250. [CrossRef]
- “How speech occurs,” Mayo Clinic. Accessed: Dec. 05, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vocal-cord-paralysis/multimedia/how-speech-occurs/img-20005645.
- S. Safavi, “Comparison of Speaker Verification Performance for Adult and Child Speech,” WOCCI 2014, Jan. 2014, Accessed: Dec. 05, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/7894241/Comparison_of_Speaker_Verification_Performance_for_Adult_and_Child_Speech.
- F. Ye and J. Yang, “A Deep Neural Network Model for Speaker Identification,” Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 8, Art. no. 8, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Kabir, M. F. M. M. Kabir, M. F. Mridha, J. Shin, I. Jahan, and A. Q. Ohi, “A Survey of Speaker Recognition: Fundamental Theories, Recognition Methods and Opportunities,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 79236–79263, 2021. [CrossRef]
- “How Voice Analysis Can Help Solve Crimes,” Frontiers for Young Minds. Accessed: Nov. 01, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2022.702664.
- “A brief history of speech recognition,” Sonix. Accessed: Nov. 07, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://sonix.ai/history-of-speech-recognition.
- M. Minsky, “Steps toward Artificial Intelligence,” Proceedings of the IRE, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 8–30, Jan. 1961. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Jordan and T. M. Mitchell, “Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects,” Science, vol. 349, no. 6245, pp. 255–260, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Purnapatra, P. Das, L. Holsopple, and S. Schuckers, “Longitudinal study of voice recognition in children,” in 2020 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Sep. 2020, pp. 1–8. Accessed: Oct. 01, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9211067.
- “What is Speech Recognition? | IBM.” Accessed: Dec. 06, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/topics/speech-recognition.
- “What is Speech Recognition?,” Customer Experience. Accessed: Dec. 06, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcustomerexperience/definition/speech-recognition.
- S. Mohanlal, “Applications of Speech Recognition,” GetSmarter Blog. Accessed: Dec. 06, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.getsmarter.com/blog/market-trends/applications-of-speech-recognition/.
- L. Zhang, F. Schlaghecken, J. Harte, and K. L. Roberts, “The Influence of the Type of Background Noise on Perceptual Learning of Speech in Noise,” Front Neurosci, vol. 15, p. 646137, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- “How to Design Voice Assistants for Noisy Environments,” SoundHound. Accessed: Nov. 24, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.soundhound.com/blog/how-to-design-voice-assistants-for-noisyenvironments/.
- N. Murugendrappa, A. G. N. Murugendrappa, A. G. Ananth, and K. M. Mohanesh, “Adaptive Noise Cancellation Using Kalman Filter for Non-Stationary Signals,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 925, no. 1, p. 012061, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y.-H. Goh, Y.-L. Goh, Y.-K. Lee, and Y.-H. Ko, “Robust speech recognition system using multi-parameter bidirectional Kalman filter,” Int J Speech Technol, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 455–463, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- “What is a Condenser Microphone?,” PreSonus. Accessed: Nov. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://legacy.presonus.com/learn/technical-articles/What-Is-a-Condenser-Microphone.
- P. B. Music, “Dynamic vs Condenser Mics: A Basic Introduction,” Bothners | Musical instrument stores. Accessed: Nov. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://bothners.co.za/dynamic-vs-condenser-mics-a-basicintroduction/.
- R. Microphones, “What is a Condenser Microphone and When to Use One | RØDE.” Accessed: Nov. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://rode.com/en/about/news-info/what-is-a-condenser-microphone-andwhen-to-use-one.
- “What Is a Condenser Microphone? How Condenser Mics Work - 2023,” MasterClass. Accessed: Nov. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.masterclass.com/articles/what-is-a-condenser-microphone.
- “What Is a Condenser Microphone: Behind the Audio,” KommandoTech. Accessed: Oct. 16, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://kommandotech.com/guides/what-is-a-condenser-microphone/.
- “Mono vs Stereo Microphone: Is There Any Difference?,” KommandoTech. Accessed: Oct. 17, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://kommandotech.com/guides/mono-vs-stereo-microphone/.
- A.Crampton, “Audio For Film 101: Mono vs Stereo - Which VideoMic Do I Need?” Accessed: Nov. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://rode.com/en/about/news-info/audio-for-film-101-mono-vs-stereo-whichvideomic-do-i-need.
- David, “Answer to ‘What is the Hamming window for?,’” Stack Overflow. Accessed: Oct. 12, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://stackoverflow.com/a/21641171.
- “Kalman Filter Applications.” Accessed: Oct. 19, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:6R4JtEbywewJ:https://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4758/2012sp/materials/MI63slides.pdf&hl=en&gl=us.
- B. V. Martínez, “SpeechEnhancementUsingKalmanFiltering”.
- A.Becker (www.kalmanfilter.net), “Online Kalman Filter Tutorial.” Accessed: May 03, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.kalmanfilter.net/.
- X. R. Li and V. P. Jilkov, “Survey of maneuvering target tracking: dynamic models,” presented at the AeroSense 2000, O. E. Drummond, Ed., Orlando, FL, Jul. 2000, pp. 212–235. [CrossRef]
- “Kalman filter,” Wikipedia. Apr. 17, 2023. Accessed: May 03, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Kalman_filter&oldid=1150297514.
- Movo, “What Is Signal to Noise Ratio? | Why SNR Matters in Audio,” Movo. Accessed: Oct. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.movophoto.com/blogs/movo-photo-blog/what-is-signal-to-noise-ratio.
- “What is Signal to Noise Ratio and How to calculate it?” Accessed: Oct. 27, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://resources.pcb.cadence.com/blog/2020-what-is-signal-to-noise-ratio-and-how-to-calculate-it.
- “Signal-to-Noise Ratio | Definition, Calculation & Formula - Video & Lesson Transcript,” study.com. Accessed: Oct. 27, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://study.com/WEB-INF/views/jsp/redesign/academy/lesson/seoLessonPage.jsp.
- S. Aggarwal et al., “Audio Segmentation Techniques and Applications Based on Deep Learning,” Scientific Programming, vol. 2022, p. e7994191, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Venkatesh, D. S. Venkatesh, D. Moffat, and E. R. Miranda, “You Only Hear Once: A YOLO-like Algorithm for Audio Segmentation and Sound Event Detection,” Applied Sciences, vol. 12, no. 7, p. 3293, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Theodorou, I. T. Theodorou, I. Mporas, and N. Fakotakis, “An Overview of Automatic Audio Segmentation,” IJITCS, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 1–9, Oct. 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. S. Jat, A. S. D. S. Jat, A. S. Limbo, and C. Singh, “Chapter 6 - Voice Activity Detection-Based Home Automation System for People With Special Needs,” in Intelligent Speech Signal Processing, N. Dey, Ed., Academic Press, 2019, pp. 101–111. [CrossRef]
- X.-K. Yang, L. X.-K. Yang, L. He, D. Qu, and W.-Q. Zhang, “Voice activity detection algorithm based on long-term pitch information,” EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, vol. 2016, no. 1, p. 14, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- “Naive voice activity detection using short time energy.” Accessed: Nov. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://superkogito.github.io/blog/2020/02/09/naive_vad.html.
- “Voice activity detection (VAD) - Introduction to Speech Processing - Aalto University Wiki.” Accessed: Nov. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://wiki.aalto.fi/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=151500905.html.
- “8.4. Speaker Recognition and Verification — Introduction to Speech Processing.” Accessed: Nov. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://speechprocessingbook.aalto.fi/Recognition/Speaker_Recognition_and_Verification.html.
- T. B. Mokgonyane, T. J. Sefara, T. I. Modipa, M. M. Mogale, M. J. Manamela, and P. J. Manamela, “Automatic Speaker Recognition System based on Machine Learning Algorithms,” in 2019 Southern African Universities Power Engineering Conference/Robotics and Mechatronics/Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa (SAUPEC/RobMech/PRASA), Jan. 2019, pp. 141–146. [CrossRef]
- T. Singh, “MFCC’s Made Easy,” Medium. Accessed: Nov. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@tanveer9812/mfccs-made-easy-7ef383006040.
- U. Kiran, “MFCC Technique for Speech Recognition,” Analytics Vidhya. Accessed: Nov. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/06/mfcc-technique-for-speech-recognition/.
- R. Ranjan and A. Thakur, “Analysis of feature extraction techniques for speech recognition system,” International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, vol. 8, no. 7C2, pp. 197–200, 2019.
- A.Pervaiz et al., “Incorporating Noise Robustness in Speech Command Recognition by Noise Augmentation of Training Data,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 8, Art. no. 8, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Giannakopoulos and A. Pikrakis, “Chapter 4 - Audio Features,” in Introduction to Audio Analysis, T. Giannakopoulos and A. Pikrakis, Eds., Oxford: Academic Press, 2014, pp. 59–103. [CrossRef]
- J. Jogy, “How I Understood: What features to consider while training audio files?,” Medium. Accessed: Nov. 01, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-i-understood-what-features-to-consider-while-training-audio-files-eedfb6e9002b.
- Department Of Electronics Engineering, J.J. Magdum College of Engg.,Jaysingpur, Shivaji University Kolhapur,India, D. S. Shete, Prof. S.B. Patil, and Prof. S.B. Patil, “Zero crossing rate and Energy of the Speech Signal of Devanagari Script,” IOSRJVSP, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 01–05, 2014. [CrossRef]
- R. G. Bachu, S. R. G. Bachu, S. Kopparthi, B. Adapa, and B. D. Barkana, “Voiced/Unvoiced Decision for Speech Signals Based on Zero-Crossing Rate and Energy,” in Advanced Techniques in Computing Sciences and Software Engineering, K. Elleithy, Ed., Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2010, pp. 279–282. [CrossRef]
- M. Jalil, F. Butt, and A. Malik, “Short-time energy, magnitude, zero crossing rate and autocorrelation measurement for discriminating voiced and unvoiced segments of speech signals,” presented at the Technol. Adv. Electric. Electron. Comp. Eng. (TAEECE), May 2013, pp. 208–212. [CrossRef]
- OpenAI, “ChatGPT Response.” Accessed: Nov. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://chat.openai.com/c/0179a39f-93d5-413d-8b24-2ec8044d3244.
- “SpEAR Database.” Accessed: Dec. 16, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://web.archive.org/web/20060831010952/http://cslu.ece.ogi.edu/nsel/data/SpEAR_database.html.
- D. Stoller, S. D. Stoller, S. Ewert, and S. Dixon, “Wave-U-Net: A Multi-Scale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation.” arXiv, Jun. 08, 2018. [CrossRef]
- “GitHub - f90/Wave-U-Net: Implementation of the Wave-U-Net for audio source separation.” Accessed: Dec. 22, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://githubcom/f90/Wave-U-Net.
- Z. Rafii, A. Z. Rafii, A. Liutkus, F.-R. Stöter, S. I. Mimilakis, and R. Bittner, “MUSDB18 - a corpus for music separation.” Zenodo, Dec. 17, 2017. [CrossRef]
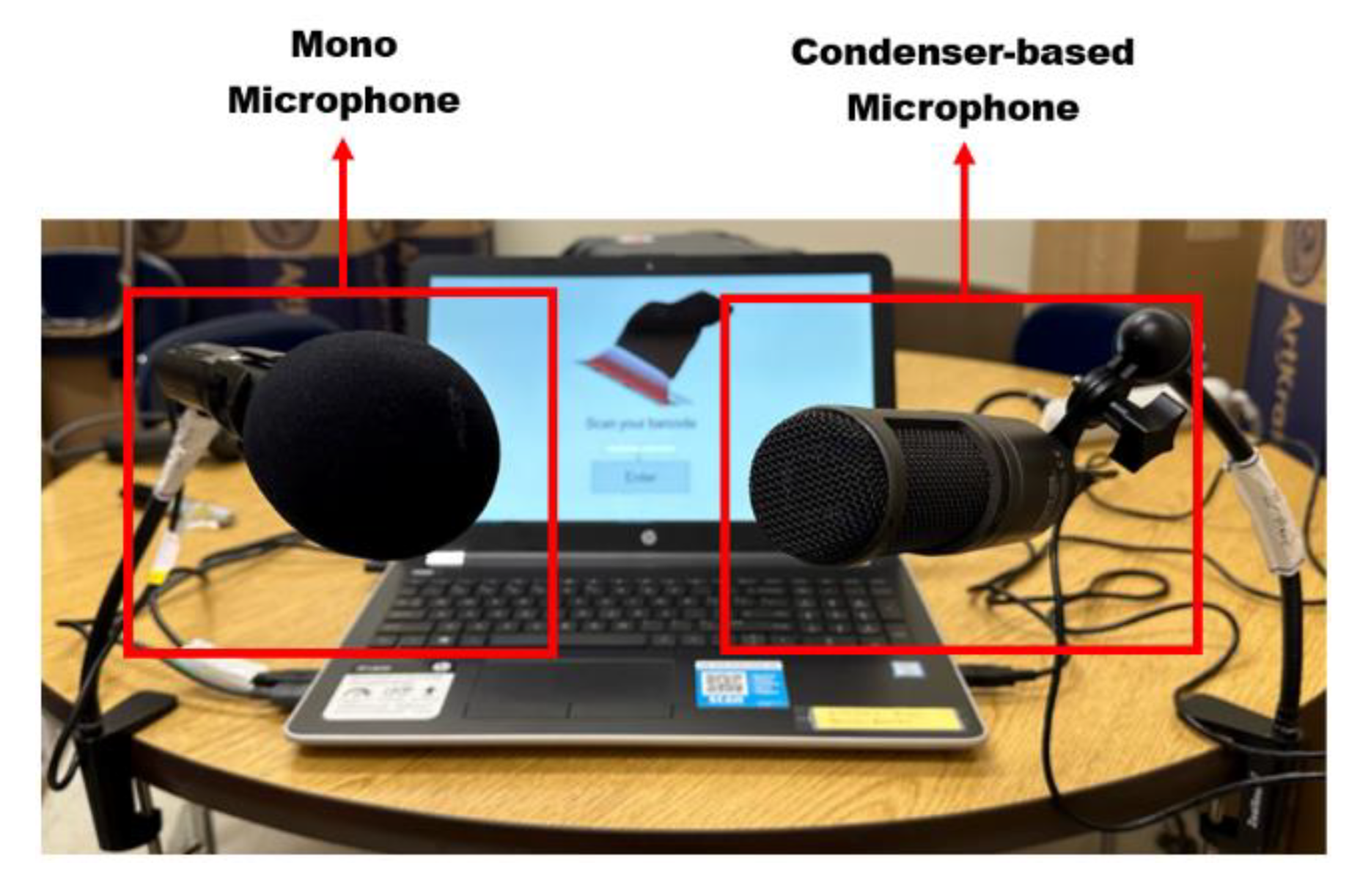

| Collection 14 | Collection 13 | |||
| Enroll and Probe | Original | Filtered | Original | Filtered |
| Sam1 | 83 | 78.5 | 57.5 | 61.5 |
| Sam2 | 80.5 | 80.5 | 117.5 | 127 |
| Sam3 | 106.5 | 206.5 | 121.5 | 112 |
| Sam4 | 72 | 77.5 | 114.5 | 110.5 |
| Sam5 | 85.5 | 78.5 | 89.5 | 135 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).