Submitted:
09 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction:
Methods:
Subject Enrollment and Clinical Care
Neuropsychological Testing and Clinical Assessment
Image Acquisition
Image Processing & Registration
Functional Image Processing
Diffusion Image Processing
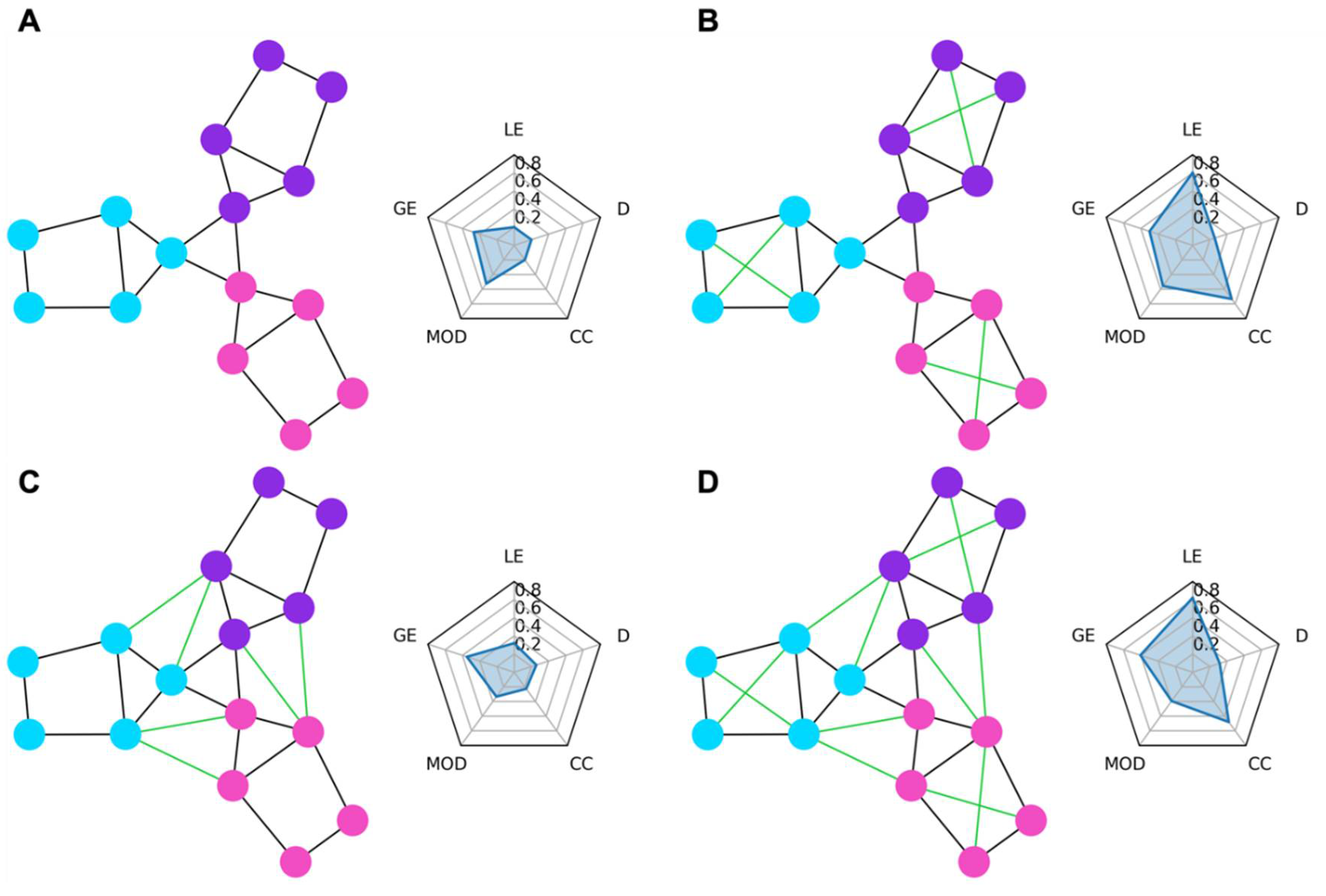
Graph Network Measures
Statistical Analysis
Results
Enrollment
Clinical Assessment
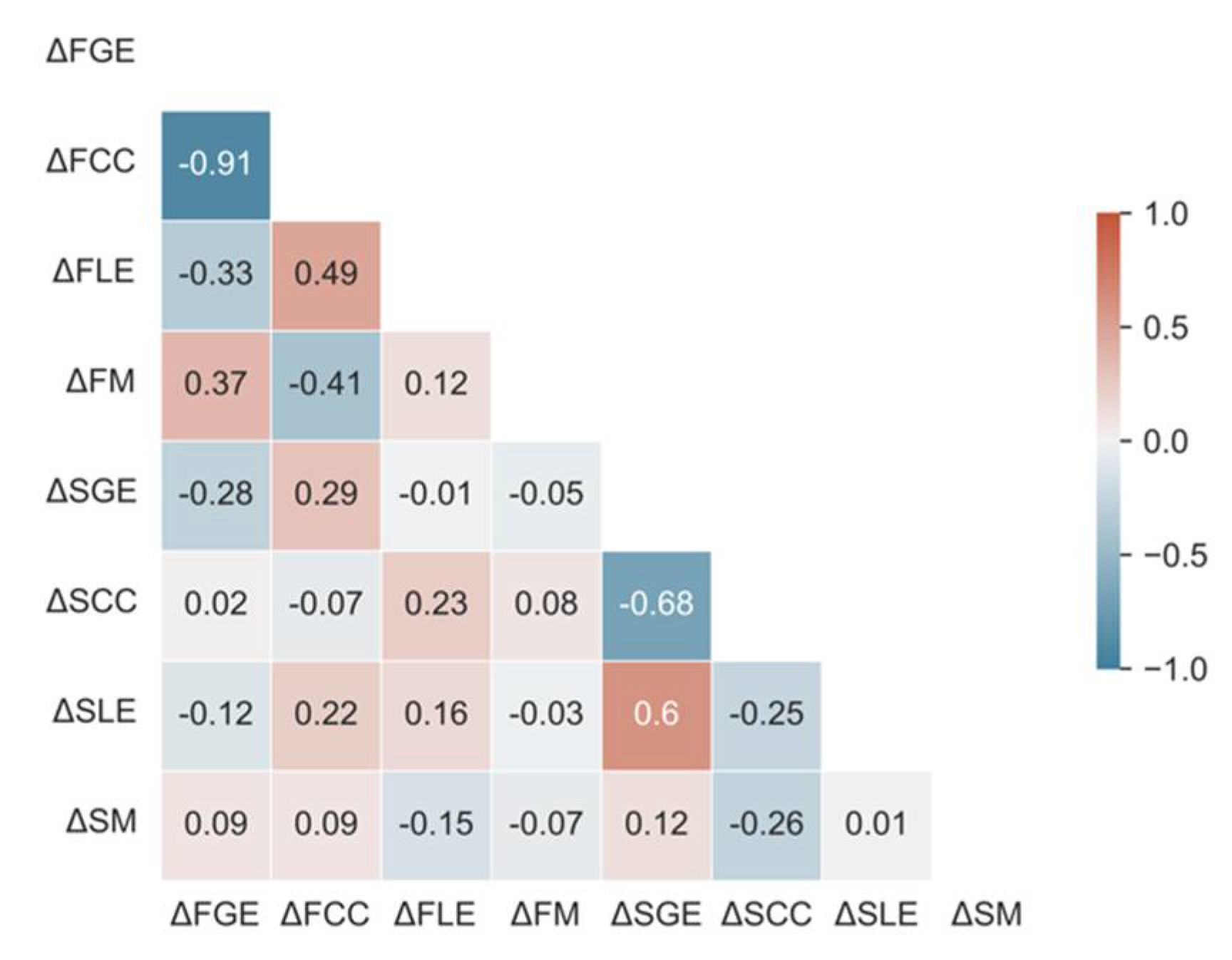
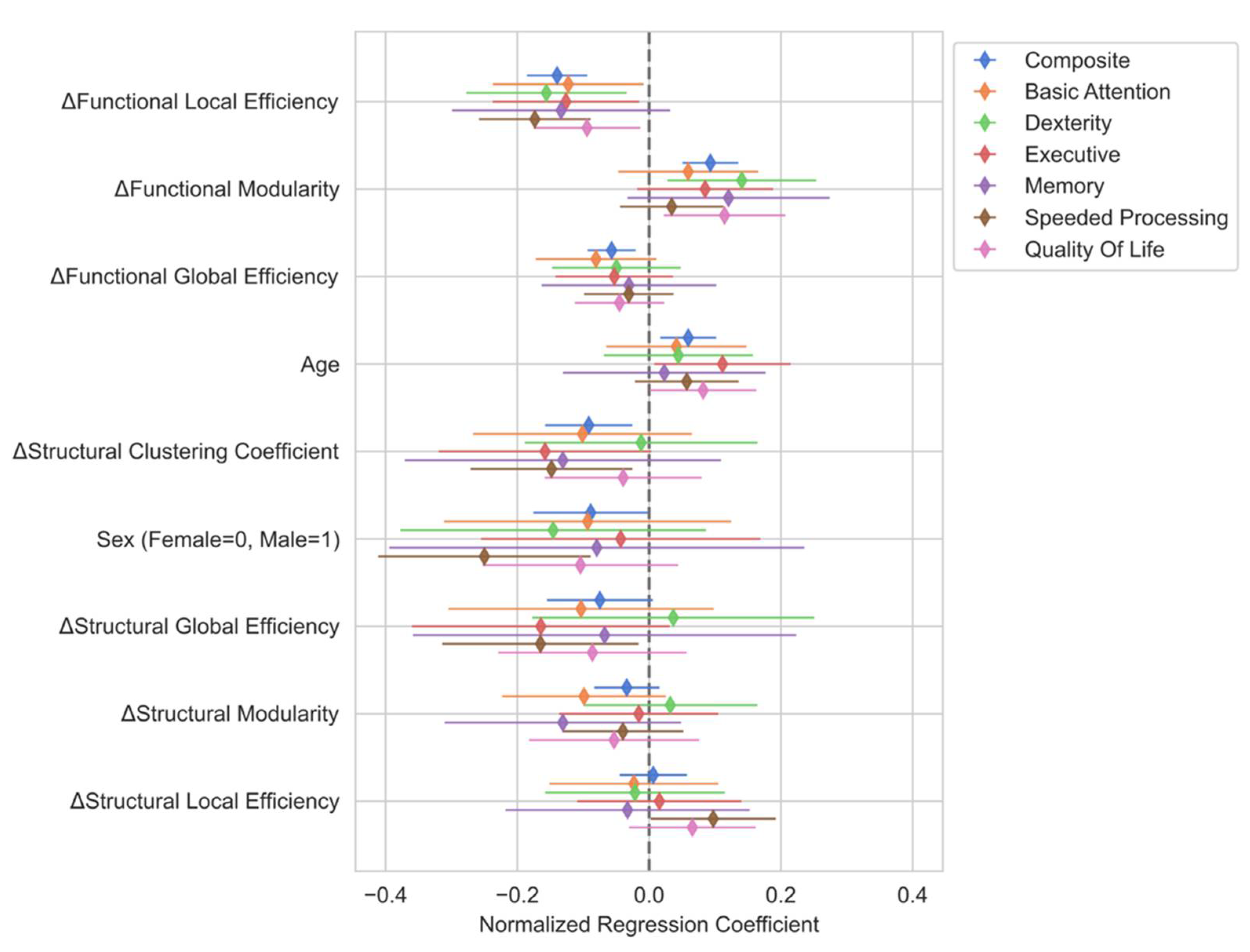
Variable Selection
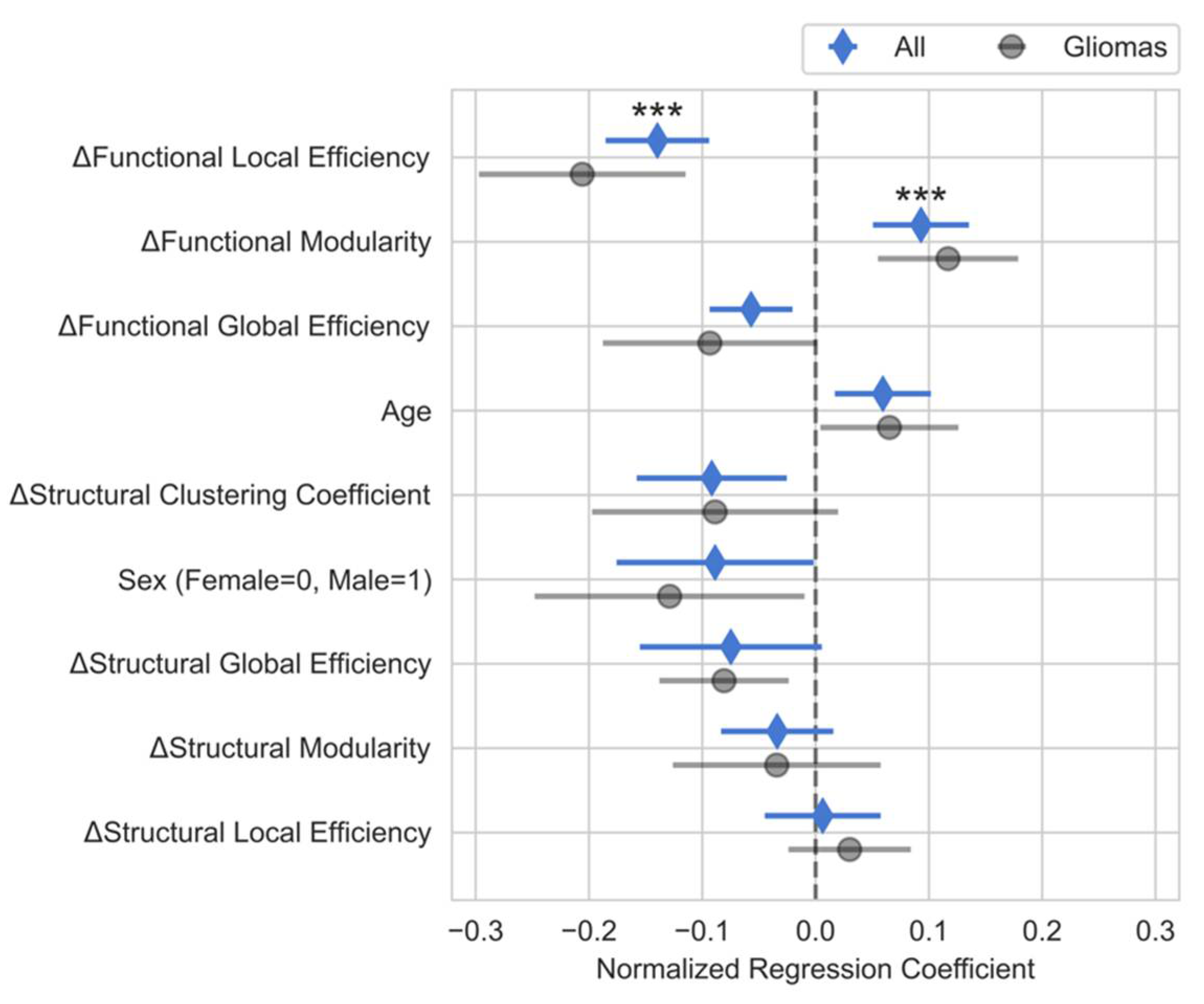
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
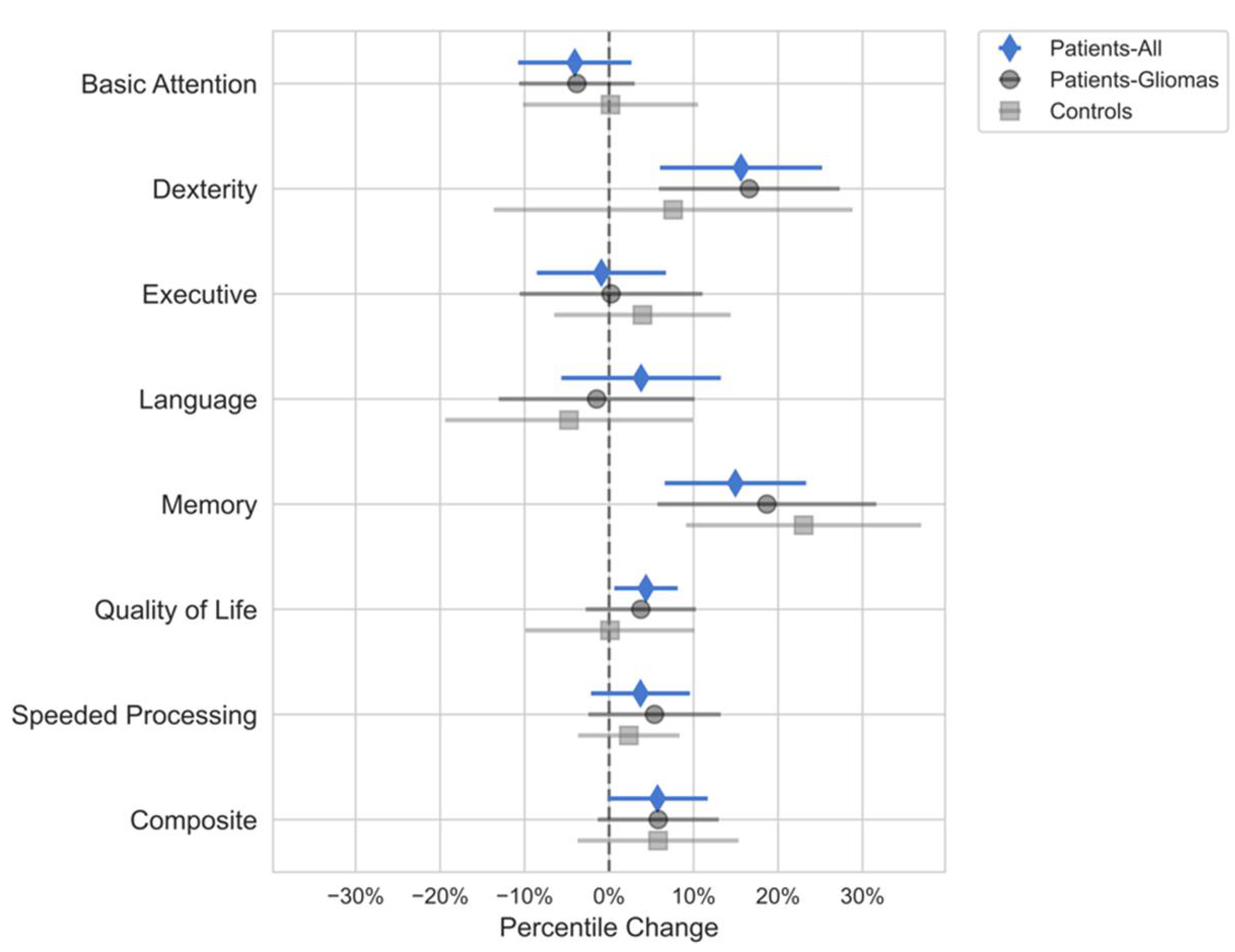
Domain-specific Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
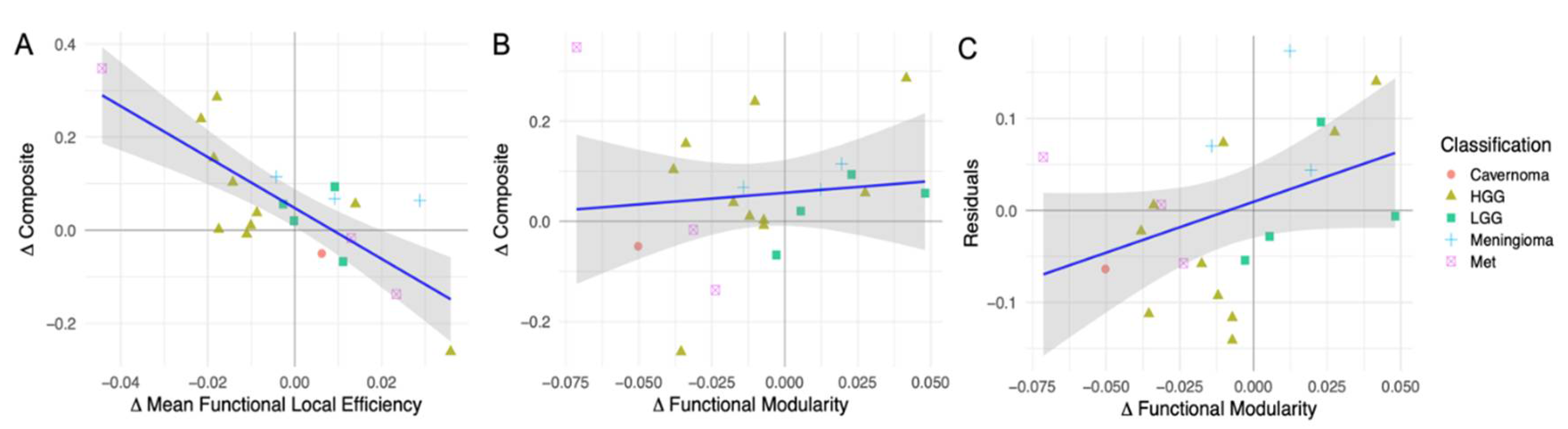
Simple Linear Regression Analysis
Conclusion:
Disclosures
Describe any perceived Conflict(s) of Interest
Acknowledgments
References
- Luna, L.P.; Sherbaf, F.G.; Sair, H.I.; Mukherjee, D.; Oliveira, I.B.; Köhler, C.A. Can Preoperative Mapping with Functional MRI Reduce Morbidity in Brain Tumor Resection? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 68 Observational Studies. Radiology 2021, 300, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, P.D.W.; Robles, S.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Duffau, H.; Berger, M.S. Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.G.; White, M.L.; Hayasaka, S.; Warren, D.E.; Wilson, T.W.; Aizenberg, M.R. Accuracy analysis of fMRI and MEG activations determined by intraoperative mapping. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 48, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, N.; Wang, Y.; da Silva, N.M.; Miserocchi, A.; McEvoy, A.W.; de Tisi, J.; Vos, S.B.; Winston, G.P.; Duncan, J.S.; Taylor, P.N. Structural brain network abnormalities and the probability of seizure recurrence after epilepsy surgery. Neurology 2021, 96, e758–e771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, Z.; Mayrand, R.C.; Zou, J.; Wong, A.L.K.C.; Sinha, R.; Matys, T.; Schönlieb, C.-B.; Price, S.J. Structural connectome quantifies tumour invasion and predicts survival in glioblastoma patients. Brain 2023, 146, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pievani, M.; Filippini, N.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Cappa, S.F.; Frisoni, G.B. Brain connectivity in neurodegenerative diseases—from phenotype to proteinopathy. Nature Reviews Neurology 2014, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrneurol.2014.178#supplementary-information.
- Rogers, B.P.; Morgan, V.L.; Newton, A.T.; Gore, J.C. Assessing functional connectivity in the human brain by fMRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K.M.; Potter, G.G.; Boyd, B.D.; Kang, H.; Taylor, W.D. Brain network functional connectivity and cognitive performance in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 110, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.; Schirner, M.; Jeurissen, B.; Van Roost, D.; Achten, E.; Ritter, P.; Marinazzo, D. Modeling Brain Dynamics in Brain Tumor Patients Using the Virtual Brain. eNeuro 2018, 5, ENEURO.0083-0018.2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Sawyer, A.M.; Meyers, C.A.; O’Neill, B.P.; Wefel, J.S. Early measures of cognitive function predict survival in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, K.R.; Sullaway, C.; Ziu, M.; Weinberg, J.S.; Wefel, J.S. Relationships between tumor grade and neurocognitive functioning in patients with glioma of the left temporal lobe prior to surgical resection. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefel, J.S.; Noll, K.R.; Rao, G.; Cahill, D.P. Neurocognitive function varies by IDH1 genetic mutation status in patients with malignant glioma prior to surgical resection. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, T.; Mendoza, T.; Gring, I.; Coco, C.; Cohen, M.; Eriksen, L.; Hsu, M.-A.; Gilbert, M.R.; Cleeland, C. Validation of the MD Anderson symptom inventory brain tumor module (MDASI-BT). J. Neurooncol. 2006, 80, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzner, M.A.; Meyers, C.A.; Gelke, C.K.; Byrne, K.S.; Levin, V.A.; Cella, D.F. The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) scale. Development of a brain subscale and revalidation of the general version (FACT-G) in patients with primary brain tumors. Cancer 1995, 75, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, J.; Malloy, P.H. Frontal systems behavior scale (FrSBe): Professional manual; Psychological Assessment Resources (PAR): 2001.
- Iverson, G.L.; Brooks, B.L.; White, T.; Stern, R.A. Neuropsychological Assessment Battery: Introduction and advanced interpretation. 2008.
- Scale, W.D.W.M. WMS-III. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation 1997.
- Meyers, J.E.; Volbrecht, M.; Axelrod, B.N.; Reinsch-Boothby, L. Embedded symptom validity tests and overall neuropsychological test performance. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2011, 26, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, C.; Freshwater, S. Stroop Color and Word Test Adult Version. A manual for clinical and experimental uses.(2a ed.). Wood Dale, Illinois: Stoelting 2002.
- Armstrong, T.; Wefel, J.; Wang, M.; Won, M.; Bottomley, A.; Mendoza, T.; Coens, C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Brachman, D.; Choucair, A. Clinical utility of neurocognitive function (NCF), quality of life (QOL), and symptom assessment as prognostic factors for survival and measures of treatment effects on RTOG 0525. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2016–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wefel, J.S.; Cloughesy, T.; Zazzali, J.L.; Zheng, M.; Prados, M.; Wen, P.Y.; Mikkelsen, T.; Schiff, D.; Abrey, L.E.; Yung, W.A. Neurocognitive function in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.P.; Somerville, L.H.; Ances, B.M.; Andersson, J.; Barch, D.M.; Bastiani, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Brown, T.B.; Buckner, R.L.; Burgess, G.C.; et al. Extending the Human Connectome Project across ages: Imaging protocols for the Lifespan Development and Aging projects. Neuroimage 2018, 183, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, E.S.; Shen, X.; Scheinost, D.; Rosenberg, M.D.; Huang, J.; Chun, M.M.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T. Functional connectome fingerprinting: identifying individuals using patterns of brain connectivity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nn.4135#supplementary-information.
- Pannunzi, M.; Hindriks, R.; Bettinardi, R.G.; Wenger, E.; Lisofsky, N.; Martensson, J.; Butler, O.; Filevich, E.; Becker, M.; Lochstet, M.; et al. Resting-state fMRI correlations: From link-wise unreliability to whole brain stability. Neuroimage 2017, 157, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, O.; Markiewicz, C.; Burns, C.; Johnson, H.; Ziegler, E.; Manhães-Savio, A.; Jarecka, D.; Ellis, D.; Yvernault, B.; Hamalainen, C. nipy/nipype: 1.5. 0. Zenodo https://doi. org/10.5281/zenodo 2020, 596855. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, O.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Blair, R.W.; Moodie, C.A.; Isik, A.I.; Erramuzpe, A.; Kent, J.D.; Goncalves, M.; DuPre, E.; Snyder, M. fMRIPrep: a robust preprocessing pipeline for functional MRI. Nature methods 2019, 16, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, O.; Wright, J.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Thompson, W.H.; Goncalves, M.; Ciric, R.; Blair, R.W.; Feingold, F.; Rokem, A.; Ghosh, S. NiPreps: enabling the division of labor in neuroimaging beyond fMRIPrep. 2019.
- Schaefer, A.; Kong, R.; Gordon, E.M.; Laumann, T.O.; Zuo, X.-N.; Holmes, A.J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Yeo, B.T. Local-global parcellation of the human cerebral cortex from intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3095–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.C.; Janke, A.L.; Collins, D.L.; Baillet, S. Brain templates and atlases. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciric, R.; Thompson, W.H.; Lorenz, R.; Goncalves, M.; MacNicol, E.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Halchenko, Y.O.; Ghosh, S.S.; Gorgolewski, K.J.; Poldrack, R.A.; et al. TemplateFlow: FAIR-sharing of multi-scale, multi-species brain models. bioRxiv 2022, 2021.2002.2010.430678. [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.; Song, G. Advanced normalization tools (ANTS). Insight j 2009, 2, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Skare, S.; Ashburner, J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 870–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolrich, M.W.; Jbabdi, S.; Patenaude, B.; Chappell, M.; Makni, S.; Behrens, T.; Beckmann, C.; Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S.M. Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in FSL. Neuroimage 2009, 45, S173–186. [Google Scholar]
- 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.055.
- Greve, D.N.; Fischl, B. Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. Neuroimage 2009, 48, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.D.; Mitra, A.; Laumann, T.O.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Pedregosa, F.; Eickenberg, M.; Gervais, P.; Mueller, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Gramfort, A.; Thirion, B.; Varoquaux, G. Machine learning for neuroimaging with scikit-learn. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Palaniyappan, L.; Li, M.; Kendrick, K.M.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yu, R.; Deng, W.; Wang, Q.; et al. Voxel-based, brain-wide association study of aberrant functional connectivity in schizophrenia implicates thalamocortical circuitry. Npj Schizophrenia 2015, 1, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://www.nature.com/articles/npjschz201516#supplementary-information.
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeurissen, B.; Tournier, J.-D.; Dhollander, T.; Connelly, A.; Sijbers, J. Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 2014, 103, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Tournier, J.-D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Anatomically-constrained tractography: Improved diffusion MRI streamlines tractography through effective use of anatomical information. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Tournier, J.-D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. SIFT: Spherical-deconvolution informed filtering of tractograms. Neuroimage 2013, 67, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T.; Joliot, M.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Implementation of a new parcellation of the orbitofrontal cortex in the automated anatomical labeling atlas. Neuroimage 2015, 122, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, B.; Descoteaux, M.; Mori, S.; Leemans, A. Diffusion MRI fiber tractography of the brain. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yin, Q.; Fang, R.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Bezerianos, A.; Tang, H.; Miao, F.; Sun, J. Disrupted Functional Brain Connectivity and Its Association to Structural Connectivity in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS One 2014, 9, e96505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamboa, O.L.; Tagliazucchi, E.; von Wegner, F.; Jurcoane, A.; Wahl, M.; Laufs, H.; Ziemann, U. Working memory performance of early MS patients correlates inversely with modularity increases in resting state functional connectivity networks. Neuroimage 2014, 94, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Simon, E.; Maron-Katz, A.; Lahav, N.; Shamir, R.; Hendler, T. Tired and misconnected: A breakdown of brain modularity following sleep deprivation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 3300–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, B.T.T.; Krienen, F.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Lashkari, D.; Hollinshead, M.; Roffman, J.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Zöllei, L.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1125–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A language and environment for statistical computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022.
- Nieto-Castanon, A. Handbook of functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging methods in CONN; Hilbert Press: 2020.
- Stanley, M.L.; Simpson, S.L.; Dagenbach, D.; Lyday, R.G.; Burdette, J.H.; Laurienti, P.J. Changes in brain network efficiency and working memory performance in aging. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagoe, T.; Onoda, K.; Yamaguchi, S. Associations among executive function, cardiorespiratory fitness, and brain network properties in older adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Bloch, A.; Gogtay, N.; Meunier, D.; Birn, R.; Clasen, L.; Lalonde, F.; Lenroot, R.; Giedd, J.; Bullmore, E. Disrupted Modularity and Local Connectivity of Brain Functional Networks in Childhood-Onset Schizophrenia. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallen, C.L.; D’Esposito, M. Brain Modularity: A Biomarker of Intervention-related Plasticity. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M. Graph theoretical analysis of Alzheimer’s disease: Discrimination of AD patients from healthy subjects. Information Sciences 2017, 384, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.S.; Seitzman, B.A.; Ramsey, L.E.; Ortega, M.; Gordon, E.M.; Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Petersen, S.E.; Shulman, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Re-emergence of modular brain networks in stroke recovery. Cortex 2018, 101, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, S.L.; Hu, T.; Naseh, M.; Fava, N.M.; O’Driscoll, J.; Alvarez, D.; Cottler, L.B.; Duara, R. Factors influencing attrition in 35 Alzheimer’s Disease Centers across the USA: a longitudinal examination of the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center’s Uniform Data Set. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Domain | Neuropsychological Assessment |
|---|---|
| Basic Attention | NAB Digits Forward [16] |
| NAB Orientation [16] | |
| WMS-III Spatial Span Forward [17] | |
| Dexterity | Grooved Pegboard [18] |
| Executive | HRB Trails B [18] |
| Stroop Inference [19] | |
| NAB Digits Backward [16] | |
| WMS-III Spatial Span Backward [17] | |
| Language | Controlled Oral Word Association [18] |
| Boston Naming Test [18] | |
| Memory | Auditory Verbal Learning Test [18] |
| Rey Complex Figure Test [18] | |
| Speeded processing | HRB Trails A [18] |
| Stroop Color and Word [19] | |
| Quality of life (QOL) | MDASI-BT [13] |
| FACT-Br [14] | |
| FrSBe [15] |
| Patients (n=37) |
Controls (n=7) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| Mean (±SD) | 50.1 (±11.8) | 32.8 (±3.8) |
| Range | 26 – 71 | 27 – 37 |
| Handedness | ||
| R (%) | 33 (89%) | 6 (100%) |
| L (%) | 4 (11%) | 0 (0%) |
| Education (years) | ||
| Mean (±SD) | 13.8 (±2.3) | 19.2 (±1.8) |
| Range | 11 – 18 | 16 – 21 |
| Sex | ||
| M (%) | 24 (65%) | 3 (50%) |
| F (%) | 13 (35%) | 3 (50%) |
| Count (%) | |
|---|---|
| Classification | |
| LGG | 5 (14%) |
| HGG | 14 (38%) |
| Met | 11 (30%) |
| Meningioma | 4 (11%) |
| Cavernoma | 3 (8%) |
| Hemisphere | |
| R | 18 (49%) |
| L | 19 (51%) |
| Location | |
| Frontal | 10 (27%) |
| Frontoparietal | 1 (3%) |
| Occipital | 4 (11%) |
| Parietal | 9 (24%) |
| Temporal | 11 (30%) |
| Frontal/Cingulate | 1 (3%) |
| Insula | 1 (3%) |
| Preop | Postop | Both | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI | 37 | 34 | 34 |
| Neuropsych | 31 | 30 | 30 |
| Complete Neuropsych | 24 | 24 | 22 |
| Complete Neuropsych + QOL | 20 | 19 | 17 |
| Complete MRI + Neuropsych | 22 | 23 | 21 |
| Complete MRI + Neuropsych + QOL | 19 | 18 | 16 |
| Pre-existing (% of all patients) |
Resolved | Improved | No change | Worsened | Unknown | New Deficits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | 4 (11%) | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Language | 5 (14%) | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Sensory | 3 (8%) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cognitive | 5 (14%) | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Visual | 5 (14%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





