Submitted:
07 May 2024
Posted:
08 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
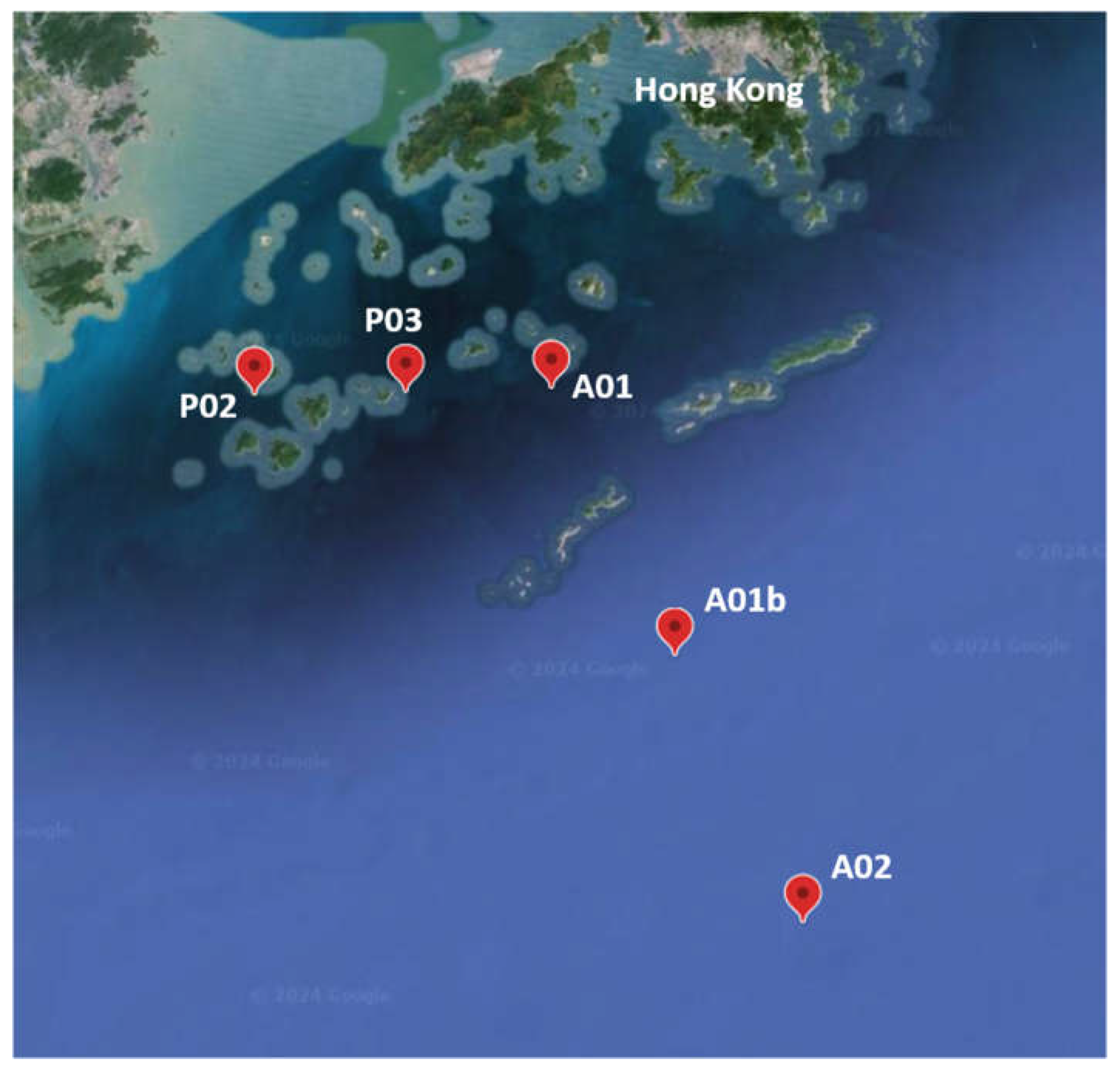
2.1. Study Site and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Environmental Parameters Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Data Processing
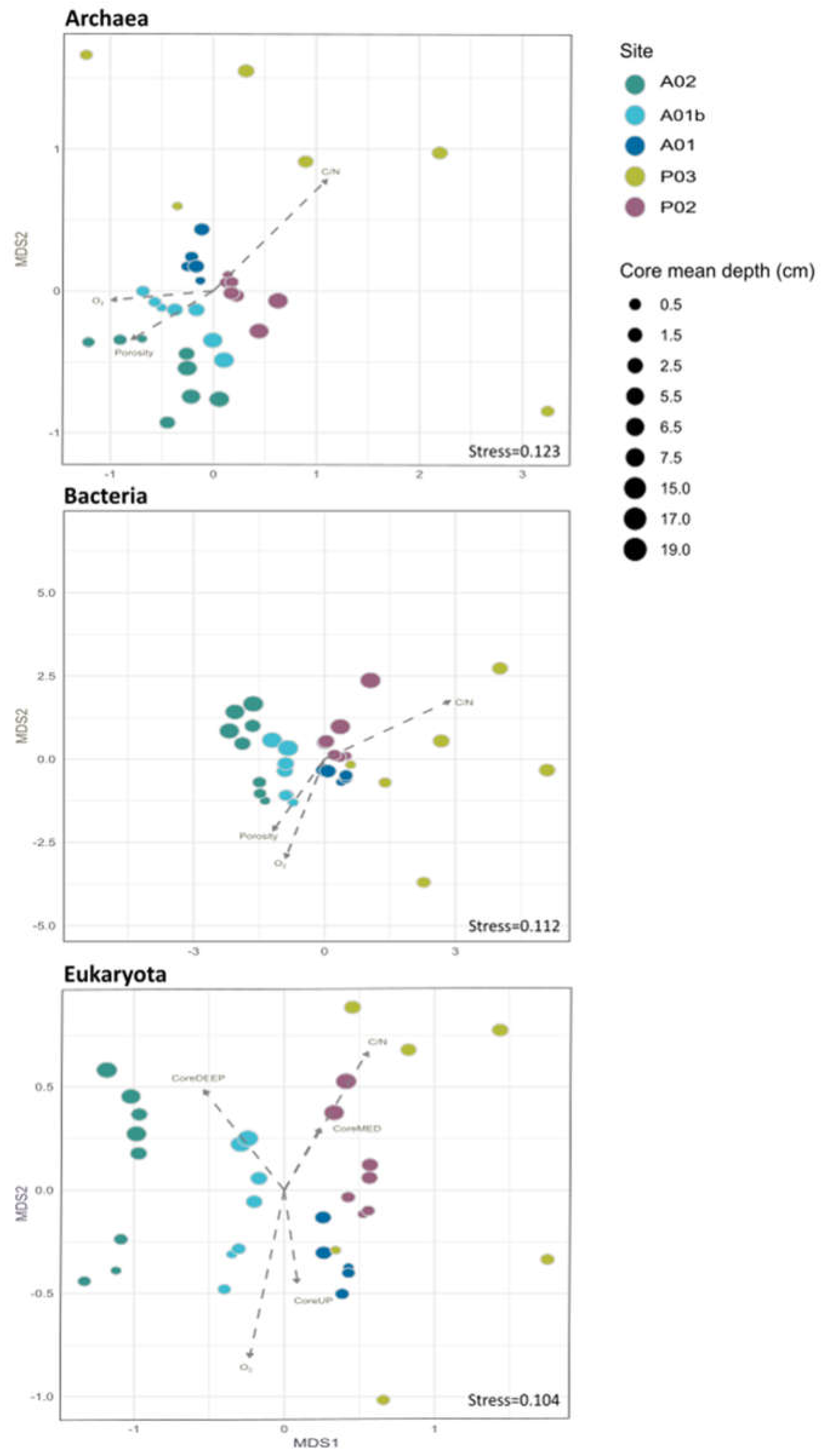
2.5. Community Structure with Environmental Variables (metaNMDS)
2.6. Biomarker Identification (LDA and LDM)
3. Results
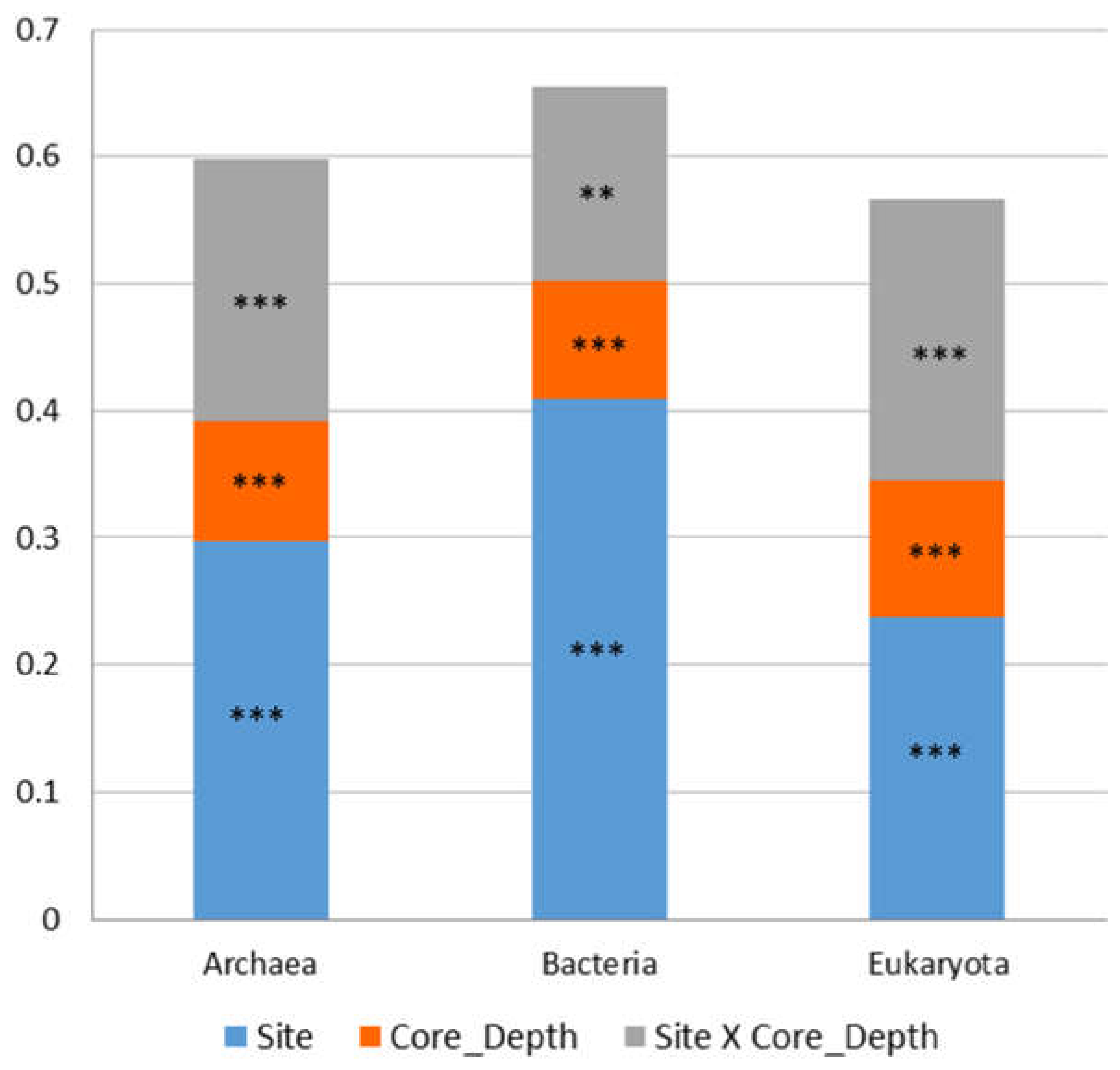
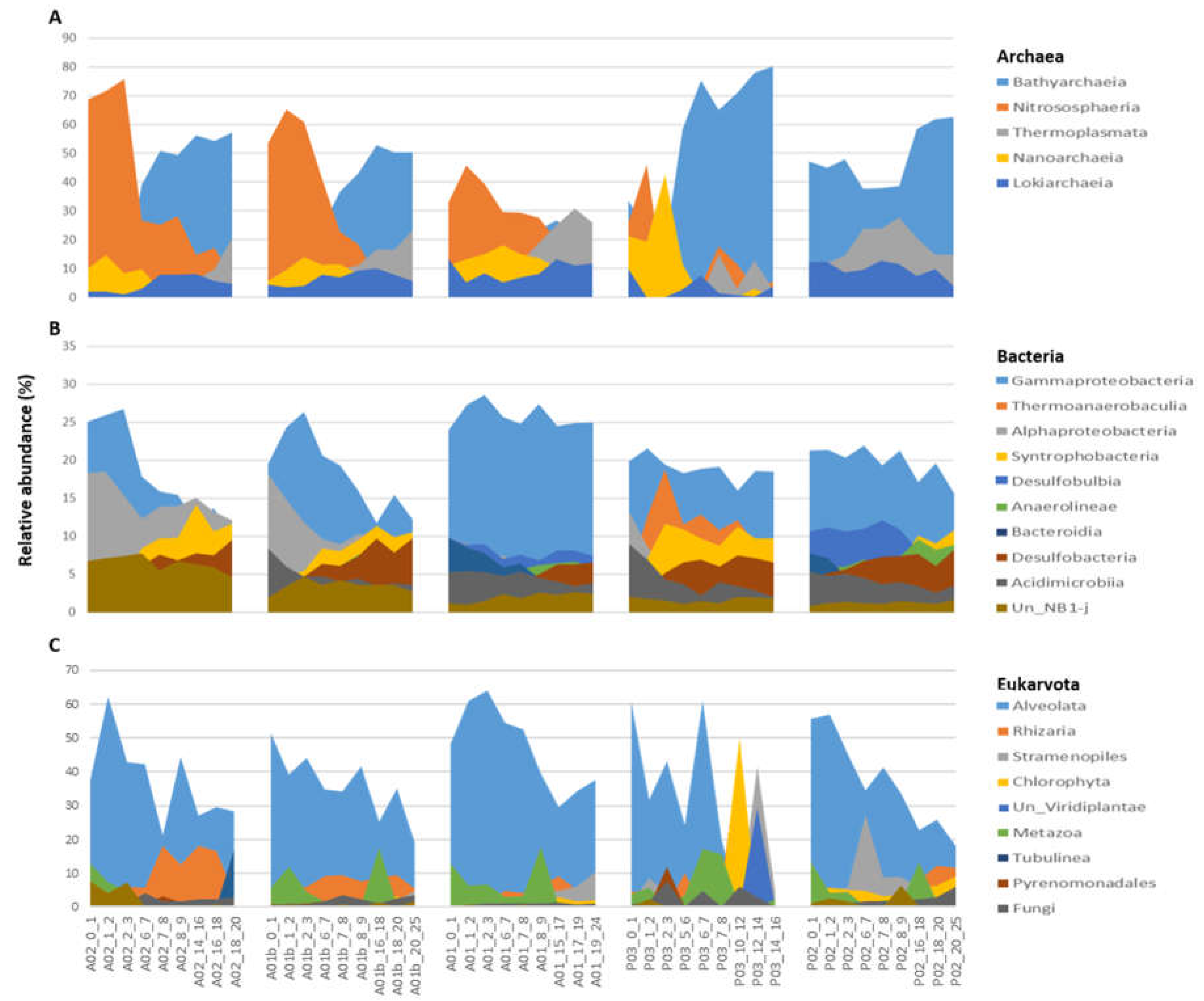
3.1. Microbial Composition and Environmental Drivers
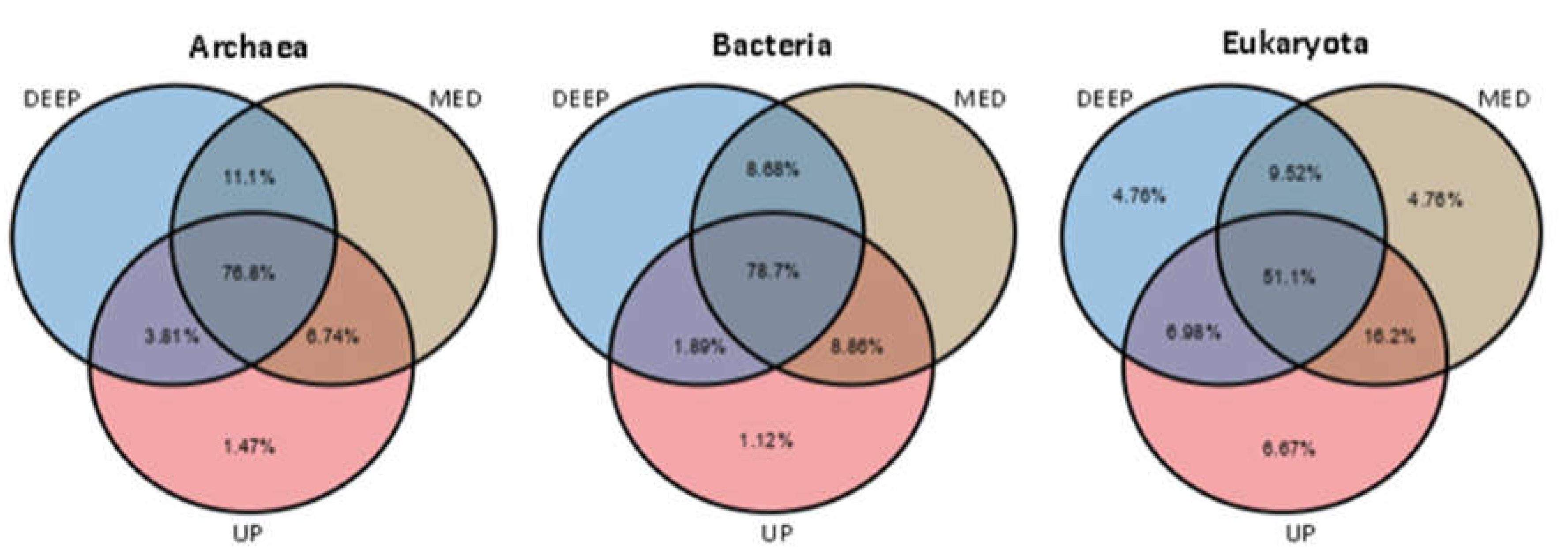
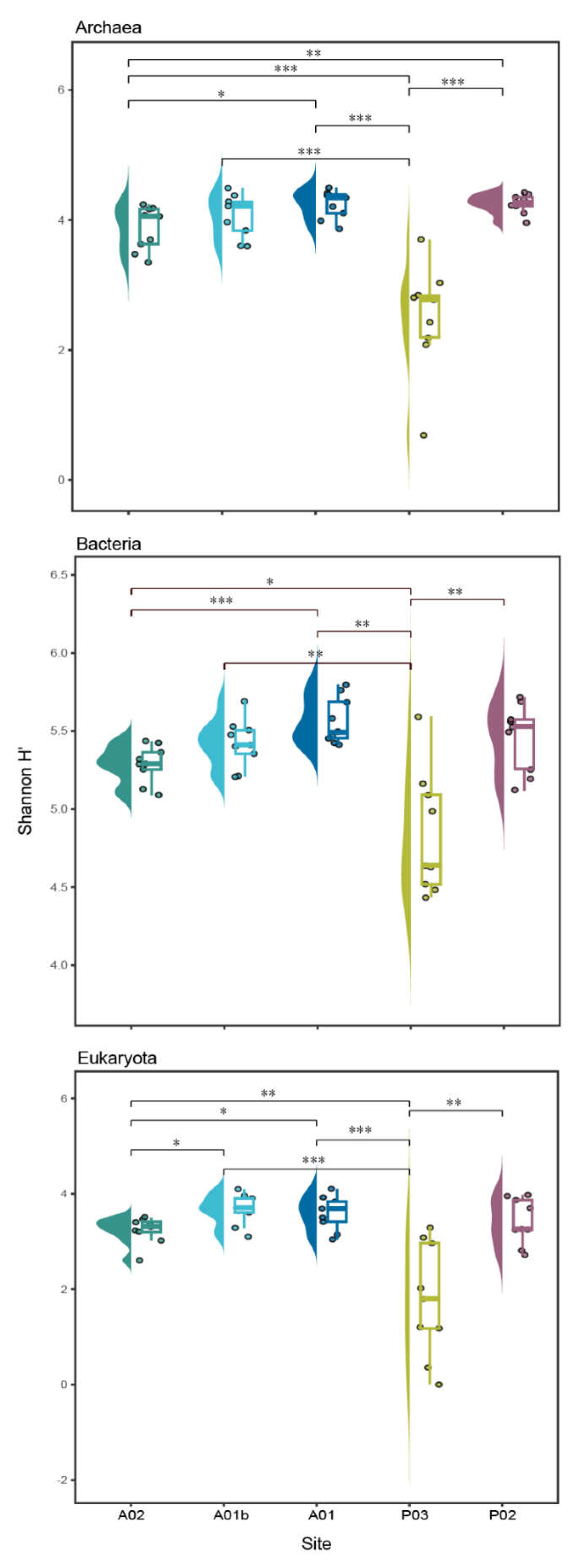
3.2. Sediment Microbial Taxonomy and Diversity
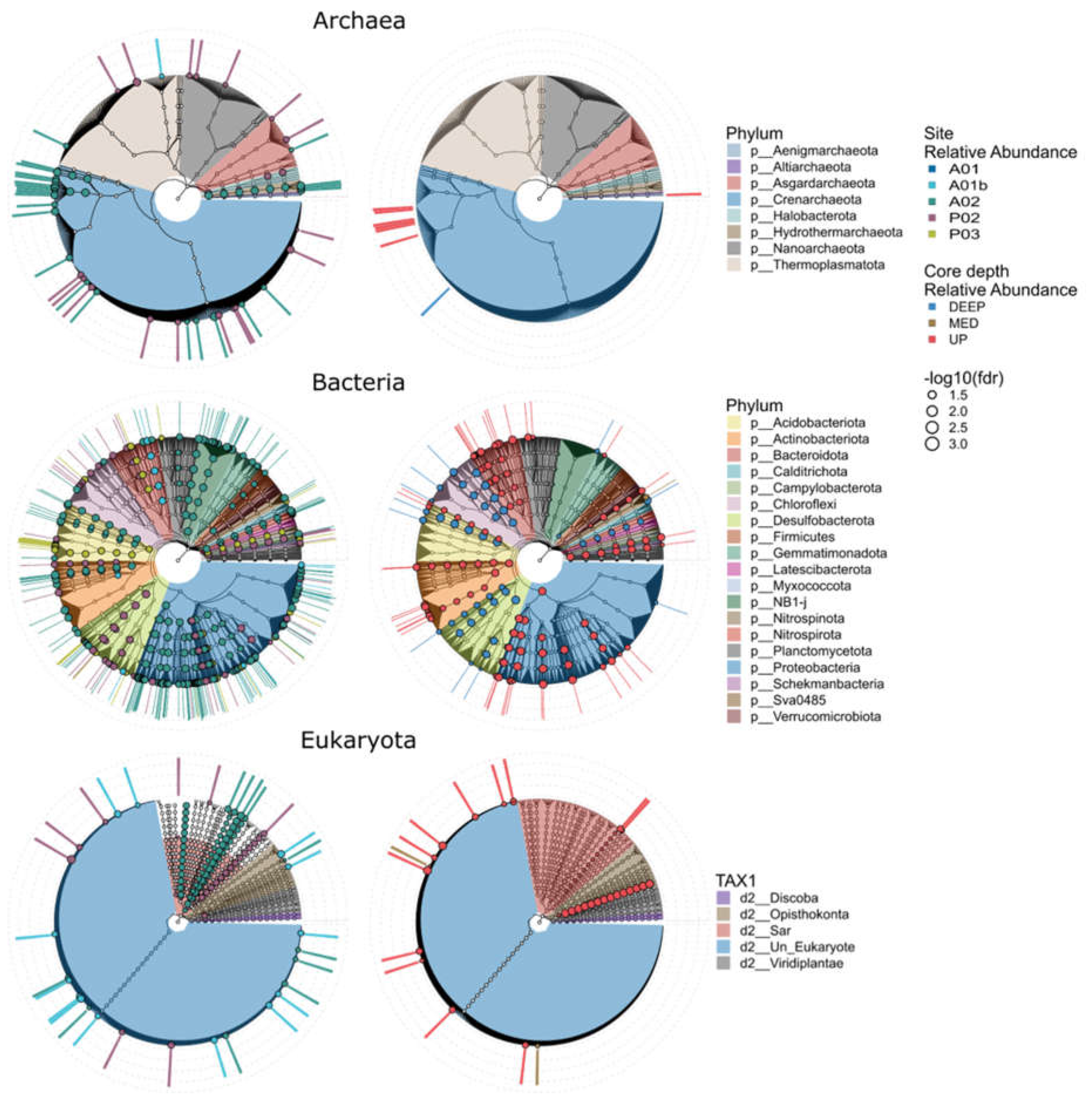
3.3. Microbial Markers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Baker, B. J., Lazar, C. S., Teske, A. P., & Dick, G. J. (2015). Genomic resolution of linkages in carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycling among widespread estuary sediment bacteria. Microbiome, 3, 1-12.
- Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289-300.
- Bolleter, W. T., Bushman, C. J., & Tidwell, P. W. (1961). Spectrophotometric determination of ammonia as indophenol. Analytical Chemistry, 33(4), 592-594.
- Broman, E., Sjöstedt, J., Pinhassi, J., & Dopson, M. (2017). Shifts in coastal sediment oxygenation cause pronounced changes in microbial community composition and associated metabolism. Microbiome, 5(1), 1-18.
- Cai, P., Shi, X., Hong, Q., Li, Q., Liu, L., Guo, X., & Dai, M. (2015). Using 224Ra/228Th disequilibrium to quantify benthic fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon and nutrients into the Pearl River Estuary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 170, 188-203.
- Cai, W. J. (2011). Estuarine and coastal ocean carbon paradox: CO2 sinks or sites of terrestrial carbon incineration?. Annual review of marine science, 3, 123-145.
- Callahan, B. J., McMurdie, P. J., Rosen, M. J., Han, A. W., Johnson, A. J. A., & Holmes, S. P. (2016). DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature methods, 13(7), 581-583.
- Callahan, J., Dai, M., Chen, R. F., Li, X., Lu, Z., & Huang, W. (2004). Distribution of dissolved organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Marine Chemistry, 89(1-4), 211-224.
- Caporaso, J. G., Lauber, C. L., Walters, W. A., Berg-Lyons, D., Lozupone, C. A., Turnbaugh, P. J., ... & Knight, R. (2011). Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 108(supplement_1), 4516-4522.
- Chen, F., Koh, X. P., Tang, M. L. Y., Gan, J., & Lau, S. C. (2021). Microbiological assessment of ecological status in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Ecological Indicators, 130, 108084.
- Chen, Y., Mi, T., Liu, Y., Li, S., & Zhen, Y. (2020). Microbial community composition and function in sediments from the Pearl River mouth basin. Journal of Ocean University of China, 19, 941-953.
- Crump, B. C., & Bowen, J. L. (2023). The Microbial Ecology of Estuarine Ecosystems. Annual Review of Marine Science, 16.
- Duarte, C. M., Agustí, S., Wassmann, P., Arrieta, J. M., Alcaraz, M., Coello, A., ... & Vaqué, D. (2012). Tipping elements in the Arctic marine ecosystem. Ambio, 41, 44-55.
- Falkowski, P. G., Fenchel, T., & Delong, E. F. (2008). The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. science, 320(5879), 1034-1039.
- Feng, B. W., Li, X. R., Wang, J. H., Hu, Z. Y., Meng, H., Xiang, L. Y., & Quan, Z. X. (2009). Bacterial diversity of water and sediment in the Changjiang estuary and coastal area of the East China Sea. FEMS microbiology ecology, 70(2), 236-248.
- Froelich, P., Klinkhammer, G. P., Bender, M. A. A., Luedtke, N. A., Heath, G. R., Cullen, D., ... & Maynard, V. (1979). Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 43(7), 1075-1090.
- Gao, Y., Fu, J., Meng, M., Wang, Y., Chen, B., & Jiang, G. (2015). Spatial distribution and fate of perfluoroalkyl substances in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96(1-2), 226-234.
- Garvine, R. W. (1975). The distribution of salinity and temperature in the Connecticut River estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research, 80(9), 1176-1183.
- Ghosh, A., & Bhadury, P. (2019). Exploring biogeographic patterns of bacterioplankton communities across global estuaries. MicrobiologyOpen, 8(5), e00741.
- Gray, J. S., & Elliott, M. (2009). Ecology of marine sediments: from science to management. Oxford University Press.
- Gu, Y. G., Li, Q. S., Fang, J. H., He, B. Y., Fu, H. B., & Tong, Z. J. (2014). Identification of heavy metal sources in the reclaimed farmland soils of the pearl river estuary in China using a multivariate geostatistical approach. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 105, 7-12.
- Guo, X., Song, G., Li, Y., Zhao, L., & Wang, J. (2022). Switch of bacteria community under oxygen depletion in sediment of Bohai Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 833513.
- Hampel, J. J., Moseley, R. D., Mugge, R. L., Ray, A., Damour, M., Jones, D., & Hamdan, L. J. (2022). Deep-sea wooden shipwrecks influence sediment microbiome diversity. Limnology and Oceanography, 67(2), 482-497.
- Harrison, P. J., Yin, K., Lee, J. H. W., Gan, J., & Liu, H. (2008). Physical–biological coupling in the Pearl River Estuary. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12), 1405-1415.
- Hoch, M. P., & Kirchman, D. L. (1993). Seasonal and inter-annual variability in bacterial production and biomass in a temperate estuary. Marine ecology progress series. Oldendorf, 98(3), 283-295.
- Howland, R. J. M., Tappin, A. D., Uncles, R. J., Plummer, D. H., & Bloomer, N. J. (2000). Distributions and seasonal variability of pH and alkalinity in the Tweed Estuary, UK. Science of the total environment, 251, 125-138.
- Hu, J., & Chivas, A. R. (2009). Molecular biomarker evidence of origins and transport of organic matter in sediments of the Pearl River estuary and adjacent South China Sea. Applied Geochemistry, 24(9), 1666-1676.
- Hu, J., & Zhang, H. (2006). Fatty acid composition of surface sediments in the subtropical Pearl River estuary and adjacent shelf, Southern China. Estuarine, coastal and shelf science, 66(1-2), 346-356.
- Hu, X., & Burdige, D. J. (2007). Enriched stable carbon isotopes in the pore waters of carbonate sediments dominated by seagrasses: Evidence for coupled carbonate dissolution and reprecipitation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(1), 129-144.
- Hu, Y. J., & Satten, G. A. (2020). Testing hypotheses about the microbiome using the linear decomposition model (LDM). Bioinformatics, 36(14), 4106-4115.
- Hu, Y., Hong, Y., Ye, J., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Ye, F., ... & Long, A. (2021). Shift of DNRA bacterial community composition in sediment cores of the Pearl River Estuary and the impact of environmental factors. Ecotoxicology, 1-15.
- Huang, J., Hu, J., Li, S., Wang, B., Xu, Y., Liang, B., & Liu, D. (2019). Effects of physical forcing on summertime hypoxia and oxygen dynamics in the Pearl River Estuary. Water, 11(10), 2080.
- Huang, X. P., Huang, L. M., & Yue, W. Z. (2003). The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River estuary, South China. Marine pollution bulletin, 47(1-6), 30-36.
- Huang, F., Lin, X., Hu, W., Zeng, F., He, L., & Yin, K. (2021). Nitrogen cycling processes in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: Spatial variations, controlling factors, and environmental implications. Catena, 206, 105545.
- Jiang, L., Zheng, Y., Peng, X., Zhou, H., Zhang, C., Xiao, X., & Wang, F. (2009). Vertical distribution and diversity of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the Pearl River estuarine sediments, Southern China. FEMS microbiology ecology, 70(2), 249-262.
- Kallmeyer, J., Pockalny, R., Adhikari, R. R., Smith, D. C., & D’Hondt, S. (2012). Global distribution of microbial abundance and biomass in subseafloor sediment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(40), 16213-16216.
- Lalzar, M., Zvi-Kedem, T., Kroin, Y., Martinez, S., Tchernov, D., & Meron, D. (2023). Sediment Microbiota as a Proxy of Environmental Health: Discovering Inter-and Intrakingdom Dynamics along the Eastern Mediterranean Continental Shelf. Microbiology Spectrum, 11(1), e02242-22.
- Lamb, A. L., Wilson, G. P., & Leng, M. J. (2006). A review of coastal palaeoclimate and relative sea-level reconstructions using δ13C and C/N ratios in organic material. Earth-Science Reviews, 75(1-4), 29-57.
- Li, K. Z., Yin, J. Q., Huang, L. M., & Tan, Y. H. (2006). Spatial and temporal variations of mesozooplankton in the Pearl River estuary, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 67(4), 543-552.
- Li, D., Gan, J., Hui, R., Liu, Z., Yu, L., Lu, Z., & Dai, M. (2020). Vortex and biogeochemical dynamics for the hypoxia formation within the coastal transition zone off the Pearl River Estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(8), e2020JC016178.
- Li, J., & Katsev, S. (2014). Nitrogen cycling in deeply oxygenated sediments: Results in Lake Superior and implications for marine sediments. Limnology and oceanography, 59(2), 465-481.
- Li, J., Brown, E. T., Crowe, S. A., & Katsev, S. (2018a). Sediment geochemistry and contributions to carbon and nutrient cycling in a deep meromictic tropical lake: Lake Malawi (East Africa). Journal of Great Lakes Research, 44(6), 1221-1234.
- Li, J., Crowe, S. A., Miklesh, D., Kistner, M., Canfield, D. E., & Katsev, S. (2012). Carbon mineralization and oxygen dynamics in sediments with deep oxygen penetration, Lake Superior. Limnology and Oceanography, 57(6), 1634-1650.
- Li, J., Zhang, Y., & Katsev, S. (2018b). Phosphorus recycling in deeply oxygenated sediments in Lake Superior controlled by organic matter mineralization. Limnology and Oceanography, 63(3), 1372-1385.
- Li, S., Fang, J., Zhu, X., Spencer, R. G., Álvarez-Salgado, X. A., Deng, Y., ... & Huang, C. (2022). Properties of sediment dissolved organic matter respond to eutrophication and interact with bacterial communities in a plateau lake. Environmental Pollution, 301, 118996.
- Liu, J., Yang, H., Zhao, M., & Zhang, X. H. (2014). Spatial distribution patterns of benthic microbial communities along the Pearl Estuary, China. Systematic and applied microbiology, 37(8), 578-589.
- Liu, W., Jiang, L., Yang, S., Wang, Z., Tian, R., Peng, Z., ... & Liu, L. (2020). Critical transition of soil bacterial diversity and composition triggered by nitrogen enrichment. Ecology, 101(8), e03053.
- Lu, Z., Gan, J., Dai, M., Liu, H., & Zhao, X. (2018). Joint effects of extrinsic biophysical fluxes and intrinsic hydrodynamics on the formation of hypoxia west off the Pearl River Estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(9), 6241-6259.
- Moffett, B. F., Nicholson, F. A., Uwakwe, N. C., Chambers, B. J., Harris, J. A., & Hill, T. C. (2003). Zinc contamination decreases the bacterial diversity of agricultural soil. FEMS microbiology ecology, 43(1), 13-19.
- Naqib, A., Poggi, S., Wang, W., Hyde, M., Kunstman, K., & Green, S. J. (2018). Making and sequencing heavily multiplexed, high-throughput 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicon libraries using a flexible, two-stage PCR protocol. Gene expression analysis: Methods and protocols, 149-169.
- Nealson, K. H. (1997). Sediment bacteria: who’s there, what are they doing, and what’s new?. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 25(1), 403-434.
- Ohore, O. E., Wei, Y., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Ifon, B. E., Liu, W., & Wang, Z. (2022). Vertical characterisation of phylogenetic divergence of microbial community structures, interaction, and sustainability in estuary and marine ecosystems. Science of The Total Environment, 851, 158369.
- Oksanen, J., Simpson, G., Blanchet, F., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., Minchin, P., ... & Weedon, J. (2022). Vegan: Community Ecology Package (R Package Version 2.6-2). 2022. Google Scholar There is no corresponding record for this reference.
- Owen, R. B. (2005). Modern fine-grained sedimentation—spatial variability and environmental controls on an inner pericontinental shelf, Hong Kong. Marine Geology, 214(1-3), 1-26.
- Parida, P. K., Behera, B. K., Dehury, B., Rout, A. K., Sarkar, D. J., Rai, A., ... & Mohapatra, T. (2022). Community structure and function of microbiomes in polluted stretches of river Yamuna in New Delhi, India, using shotgun metagenomics. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(47), 71311-71325.
- PD, N. (1986). Determination of monounsaturated fatty acid double bonds and geometry for microbial cultures and complex consortia by capillary GC-MS and their dimethyl disulphide adducts. J Microbiol Methods, 5, 49-55. Jiang.
- Petro, C., Starnawski, P., Schramm, A., & Kjeldsen, K. U. (2017). Microbial community assembly in marine sediments. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 79(3), 177-195.
- Rasmussen, H., & Jørgensen, B. B. (1992). Microelectrode studies of seasonal oxygen uptake in a coastal sediment: Role of molecular diffusion. Marine ecology progress series. Oldendorf, 81(3), 289-303.
- Rout, A. K., Tripathy, P. S., Dixit, S., Behera, D. U., Behera, B., Das, B. K., & Behera, B. K. (2024). Metagenomics analysis of sediments of river Ganga, India for bacterial diversity, functional genomics, antibiotic resistant genes and virulence factors. Current Research in Biotechnology, 100187.
- Rubin-Blum, M., Sisma-Ventura, G., Yudkovski, Y., Belkin, N., Kanari, M., Herut, B., & Rahav, E. (2022). Diversity, activity, and abundance of benthic microbes in the Southeastern Mediterranean Sea. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 98(2), fiac009.
- Segata, N., Izard, J., Waldron, L., Gevers, D., Miropolsky, L., Garrett, W. S., & Huttenhower, C. (2011). Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome biology, 12, 1-18.
- Southwell, M. W., Kieber, R. J., Mead, R. N., Brooks Avery, G., & Skrabal, S. A. (2010). Effects of sunlight on the production of dissolved organic and inorganic nutrients from resuspended sediments. Biogeochemistry, 98, 115-126.
- Southwell, M. W., Mead, R. N., Luquire, C. M., Barbera, A., Avery, G. B., Kieber, R. J., & Skrabal, S. A. (2011). Influence of organic matter source and diagenetic state on photochemical release of dissolved organic matter and nutrients from resuspendable estuarine sediments. Marine Chemistry, 126(1-4), 114-119.
- Spietz, R. L., Williams, C. M., Rocap, G., & Horner-Devine, M. C. (2015). A dissolved oxygen threshold for shifts in bacterial community structure in a seasonally hypoxic estuary. PloS one, 10(8), e0135731.
- Stahl, D. A., & De La Torre, J. R. (2012). Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Annual review of microbiology, 66, 83-101.
- Stoeck, T., Bass, D., Nebel, M., Christen, R., Jones, M. D., Breiner, H. W., & Richards, T. A. (2010). Multiple marker parallel tag environmental DNA sequencing reveals a highly complex eukaryotic community in marine anoxic water. Molecular ecology, 19, 21-31.
- Stoeck, T., Frühe, L., Forster, D., Cordier, T., Martins, C. I., & Pawlowski, J. (2018). Environmental DNA metabarcoding of benthic bacterial communities indicates the benthic footprint of salmon aquaculture. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 127, 139-149.
- Suh, S. S., Park, M., Hwang, J., Kil, E. J., Jung, S. W., Lee, S., & Lee, T. K. (2015). Seasonal dynamics of marine microbial community in the South Sea of Korea. PLoS One, 10(6), e0131633.
- Takahashi, S., Tomita, J., Nishioka, K., Hisada, T., & Nishijima, M. (2014). Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PloS one, 9(8), e105592.
- Tang, D., Kester, D. R., Ni, I. H., Qi, Y., & Kawamura, H. (2003). In situ and satellite observations of a harmful algal bloom and water condition at the Pearl River estuary in late autumn 1998. Harmful Algae, 2(2), 89-99.
- Tourna, M., Stieglmeier, M., Spang, A., Könneke, M., Schintlmeister, A., Urich, T., ... & Schleper, C. (2011). Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(20), 8420-8425.
- Urakawa, H., Yoshida, T., Nishimura, M., & Ohwada, K. (2000). Characterization of depth-related population variation in microbial communities of a coastal marine sediment using 16S rDNA-based approaches and quinone profiling. Environmental Microbiology, 2(5), 542-554.
- Viollier, E., Inglett, P. W., Hunter, K., Roychoudhury, A. N., & Van Cappellen, P. (2000). The ferrozine method revisited: Fe (II)/Fe (III) determination in natural waters. Applied geochemistry, 15(6), 785-790.
- Vipindas, P. V., Jabir, T., Rahiman, K. M., Rehitha, T. V., Sudheesh, V., Jesmi, Y., & Hatha, A. M. (2022). Impact of anthropogenic organic matter on bacterial community distribution in the continental shelf sediments of southeastern Arabian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 174, 113227.
- Waidner, L. A., & Kirchman, D. L. (2005). Aerobic anoxygenic photosynthesis genes and operons in uncultured bacteria in the Delaware River. Environmental Microbiology, 7(12), 1896-1908.
- Wang, Y., Sheng, H. F., He, Y., Wu, J. Y., Jiang, Y. X., Tam, N. F. Y., & Zhou, H. W. (2012). Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags. Applied and environmental microbiology, 78(23), 8264-8271.
- Wen, W.Y., Zhang, G.X., & Du, W.C., (1995). A study on water pollution in the Zhujing (Pearl River) estuary. In: Wong, C.K., Chu, K.H., Chen, Q.C., Ma, X.L. (Eds.), Environmental Research in Pearl River and Coastal Area. Guangdong Higher Education Press, Guangzhou, China, pp. 99–108.
- Wu, Z., Zhou, H., Peng, X., & Chen, G. (2006). Anaerobic oxidation of methane: geochemical evidence from pore-water in coastal sediments of Qi’ao Island (Pearl River Estuary), southern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 2006-2015.
- Xie, W., Zhang, C., Zhou, X., & Wang, P. (2014). Salinity-dominated change in community structure and ecological function of Archaea from the lower Pearl River to coastal South China Sea. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 98, 7971-7982.
- Xie, Y., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Ren, C., Song, C., Yang, J., ... & Zhang, X. (2016). Using in situ bacterial communities to monitor contaminants in river sediments. Environmental Pollution, 212, 348-357.
- Xu, B., Li, F., Cai, L., Zhang, R., Fan, L., & Zhang, C. (2022). A holistic genome dataset of bacteria, archaea and viruses of the Pearl River estuary. Scientific Data, 9(1), 49.
- Xu, J., Yin, K., Lee, J. H., Liu, H., Ho, A. Y., Yuan, X., & Harrison, P. J. (2010). Long-term and seasonal changes in nutrients, phytoplankton biomass, and dissolved oxygen in Deep Bay, Hong Kong. Estuaries and coasts, 33, 399-416.
- Xu, S., Zhan, L., Tang, W., Wang, Q., Dai, Z., Zhou, L., ... & Yu, G. (2023). MicrobiotaProcess: A comprehensive R package for deep mining microbiome. The Innovation, 4(2).
- Yu, L., Gan, J., Dai, M., Hui, C. R., Lu, Z., & Li, D. (2021). Modeling the role of riverine organic matter in hypoxia formation within the coastal transition zone off the Pearl River Estuary. Limnology and Oceanography, 66(2), 452-468.
- Yuan, D., Chen, L., Luan, L., Wang, Q., & Yang, Y. (2020). Effect of salinity on the zooplankton community in the Pearl River estuary. Journal of Ocean University of China, 19, 1389-1398.
- Zhang, L., Wang, L., Yin, K., Lü, Y., Zhang, D., Yang, Y., & Huang, X. (2013). Pore water nutrient characteristics and the fluxes across the sediment in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent waters, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 133, 182-192.
- Zhang, X., Cui, L., Liu, S., Li, J., Wu, Y., Ren, Y., & Huang, X. (2023). Seasonal dynamics of bacterial community and co-occurrence with eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Pearl River Estuary. Marine Environmental Research, 106193.
- Zhou, L. (2022). Sediment Oxygen Uptake and Carbon Mineralization in the Pearl River Estuary and Adjacent Coastal Waters (Doctoral dissertation, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology).
- Zou, D., Pan, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, C., Liu, H., & Li, M. (2020). The distribution of Bathyarchaeota in surface sediments of the Pearl river estuary along salinity gradient. Frontiers in microbiology, 11, 285.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




