1. Introduction
The sustainable food chain is a major concern of modern agriculture put to the test by the continued adverse impact of climate change and the pressing need for innovative approaches to encourage organic plant breeding. The demands of the world's growing population should be met by maintaining a nutritious and healthy diet with the limited use of pesticides and fertilizers. Several recently introduced policies like the EU “Green Deal” [
1] and the EU “Farm to Fork Strategy” [
2] aim to reduce significantly the use of chemicals in food production. The new approaches implemented in these initiatives often consider the application of natural biostimulants to foster plant growth and development throughout the crop life cycle [
3]. It has been shown that these products could be used also as stress tolerance boosters or abiotic stress recovery promoters, mainly through facilitating nutrient assimilation and translocation or rendering water use efficiency [
4]. Biostimulants exert growth-promoting or stress-protective functions in low concentration through mechanisms that differ from the ones of fertilizers and pesticides. Often their mode of action is linked to the hormonal impacts of the physiologically active levels of auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and jasmonates that are found in the products [
5,
6,
7]. At present, most of the offered formulations labelled as plant growth regulators (PGRs) contain analogues of auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins that are capable of eliciting plant growth, nutrient uptake, and stress-tolerance responses [
8]. The evaluation of their safety and efficiency is necessary to foster the wider application of biostimulants and PGR-based products in “green” agricultural practices.
The present work aimed to elucidate the protective potential of abscisic acid (ABA) and the ethylene precursor 1-aminocyclopropan carboxylic acid (ACC) applied in concentrations corresponding to the naturally observed range in drought-stressed plants [
9,
10]. Based on previously published studies demonstrating the positive effect of exogenous auxin on plant performance under dehydration stress [
11] we included in the pre-treatments the auxin analogue 1-naphthyl acetic acid (NAA). This was motivated also by the fact that lateral root formation, a feature that is crucially important for plant survival under limited water supply, is regulated by the crosstalk of auxins, ethylene and ABA [
12,
13,
14]. Since the growth and formation of roots are shaped by the signaling pathways of both auxin and cytokinins [
15] we considered in the tests also the cytokinin-like acting compound kinetin (KIN). Drought has a significant impact on plant growth and development, leading to a detrimental impact on the yield and quality of food crops, including vegetables [
16,
17]. Plants have evolved multiple defense mechanisms to maintain their growth under water-limited conditions comprising enzyme and non-enzyme antioxidants, as well as metabolites and proteins with protective properties [
18]. Together with particular stress-induced anatomical and physiological changes (like stomata closure and increased root growth), these molecular mechanisms facilitate adaptation and survival under scarce water supply. They are controlled by a complex regulatory network driven by various hormonal interactions.
When challenged by water scarcity, plant cells regulate their osmotic adjustment through the accumulation of compatible solutes (proline, glycine betaine, fructans, etc.) and protective proteins that can maintain the native structure of the enzymatic complexes [
19]. Dehydrins (DHNs) are part of this line of defense and upon reduced water supply their levels in the nucleus and cytoplasm usually increase [
20]. Their unique molecular properties (thermostability and high hydrophilicity) make them a potent element of molecular defense under stress. They can stabilize large-scale hydrophobic interactions in the plant cell that occur among the various membrane structures or hydrophobic protein clusters. The effects of phytohormone-based biostimulants on the accumulation of DHNs are not yet elucidated but several indicative case studies point to the potential protective effect of these products through the activation of certain dehydrin types [
21,
22].
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) that accumulate under dehydration provoke oxidative damage to the cellular components (DNA, proteins, membrane lipids). It has been demonstrated that some phytohormone-based growth regulators support the synthesis of essential antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POX), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) enabling plants to scavenge the harmful free oxygen radicals [
23].
We performed a broad screen of the pretreatment effects of ABA, ACC, NAA, and KIN applied separately or in different combinations. The experiments were performed with hydroponically grown Lactuca sativa plants using 12% polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a dehydrating agent. The evaluation of the different combinations of PGRs revealed that the simultaneous application of the four components had the best dehydration-protective properties. It was linked to the activation of some major components of the antioxidative defence system (SOD, CAT and POX), and the accumulation of free proline and certain dehydrin types in the plants treated with the hormonal mix. The proof of concept experiments with soil-grown plants subjected to moderate drought confirmed the beneficial effect of the hormonal mix.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions and Plant Material
2.1.1. Hydroponic Experiment with 12% PEG
Lactuca sativa L. cv. Lobjoits; Green Cos (purchased from CN seeds Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK) plants were grown for 14 days on Rockwool cubes (Saint-Gobain Cultilene B.V., Rijen, the Netherlands) soaked in ½ Hoaglands-Arnon nutrient solution under controlled conditions (60% air humidity; 200 μmol m−2 s−1 photon flux density, 21/18 °C day/night temperature, and 14/10 h photoperiod). When the seedlings had a fully developed second true leaf (at day 15), they were divided into different groups (consisting of at least 20 individuals). Some of the groups were sprayed with approximately 20 mL/m2 (until full coverage) of one of the following PGR solutions: 2 µM ABA (Carl Roth Karlsruhe, Germany), 5 µM 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany), 4 µM 1-naphthyl acetic acid (NAA, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany), or 0.2 µM kinetin (KIN, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). The same amount of mock solution (containing distilled H2O and 0.05% Tween-20, used as a surfactant) was applied to the control plants. In the treatments were included also the following PGR combinations:
Mix 1 – ABA and KIN
Mix 2 – ABA, KIN, NAA, ACC
Mix 3 – ABA, KIN, ACC
Mix 4 – ABA, NAA, ACC
Mix 5– ABA, NAA
Mix 6 – ABA, and ACC
Mix 7 – KIN and NAA
The final concentration of the components in the mixes was kept the same as the one in the “mono” solutions.
Twenty-four hours after hormonal application (on day 16 of the experiment) half of the plants from each treatment group were transferred to a fresh nutrient solution with 12% PEG. The remaining individuals were transferred to fresh media without PEG. The nutrient solution (+/- PEG) was refreshed every 5 days to ensure the optimal composition of macro and microelements.
After 10 days (at day 25 of the experiment) the plants from the different experimental groups were photographed and the images were used for measurements of the shoot area with the Rosette Tracker plug-in in Image J [
24]. The fresh and dry weights of the differently treated individuals were also registered. Samples derived from the 2nd true leaf were collected and preserved for the subsequent analyses.
2.1.2. Soil Drought Experiment (“Proof-of-Concept”)
Seeds from
Lactuca sativa L. cv. Lobjoits; Green Cos, were sown on 44 mm Jiffy® Peat Pellets (Jiffy Growing Solutions, Zwijndrecht, the Netherlands) saturated with water at 80% of the substrate’s field capacity (FC). The plants were grown under controlled conditions (60% air humidity; 200 μmol m
−2 s
−1 photon flux density, 21/18 °C day/night temperature, and 14/10 h photoperiod) for two weeks. At day 15, the PGR combination (Mix 2) or a “Mock” solution was administered on the plants via foliar spray (20 mL/m
2 ) or through the roots (1 mL per each plant grown separately on a single pellet). After the treatments the plants were split into control (grown under optimal soil humidity) and drought-stressed groups. The dehydration of the “stress” groups (both “Mock” and PGR-treated) followed the protocol described previously [
25]. The humidity of the Jiffy pellets reached 30% FC after 5 days (moderate drought stress). This parameter was maintained for an additional 5-day period. At the end of the experiment (day 25), we measured the fresh and dry weight of individuals from the different treatment groups, as well as their shoot area.
2.2. Biochemical Analyses
2.2.1. Stress Markers and Non-Enzyme Antioxidants
The leaf samples were grinded in 1% cold trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and centrifuged at 15 000 g, for 30 min (at 4° C). The supernatant was used for biochemical analyses of the stress-related biomarkers malondialdehyde (MDA), hydrogen peroxide and free proline. The same extracts were used for the determination of phenolics and free thiol-group-containing compounds.
MDA was analysed according to [
26] with a reagent containing 0.5% thiobarbituric acid (TBA) in 20% trichloroacetic acid. The absorbance of the substances resulting from the TBA-reaction was read at 532 nm and 600 nm. MDA content was calculated using an extinction coefficient of 155 mM cm
−1.
Hydrogen peroxide level was measured following a previously described protocol [
27]. The absorbance was recorded at 390 nm, and the results were calculated using a standard curve.
The free proline content was estimated according to [
28] with some modifications. In brief, 1 mL freshly prepared ninhydrin reagent (1.25 g ninhydrin, 30 mL CH
3COOH, 20 mL 6M H
3PO
4) was combined with 0.5 mL supernatant, 0.5 mL 0.1% TCA, and 1 mL CH
3COOH. The mix was incubated for 1 h in a 100 °C water bath. The reaction was stopped by putting the samples on ice. The absorbance of the reaction mix was measured at 520 nm and the concentration was calculated using a standard curve.
The content of phenolic compounds was estimated according to a modified version of an established protocol [
29]. Aliquots (20 µL) of the supernatant were incubated with 130 µL dH
2O and 50 µL Folin–Ciocalteu reagent at room temperature for 3 minutes. Fifty microliters of 1 M Na
2CO
3 were added to the reaction mix and after that, it was exposed to light for two hours. The absorbance of the samples was measured at 725 nm. The content of the phenolics was calculated using a standard curve prepared with gallic acid as a referent.
The content of free thiol-group-containing compounds (free sulfhydryl groups, –SH groups) was determined according to [
30]. The absorbance of the reaction mixture (comprised of 40 µL supernatant and 150 µL Elman’s reagent) was measured at 412 nm after 10 min incubation at room temperature.
2.2.2. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
For the assessment of the activities of antioxidant enzymes approximately 300 mg fresh leaf material was homogenized in cold potassium phosphate buffer (0.1 M) containing 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.0, and 1% PVP. The homogenate was centrifuged at 15 000 g for 30 min (at 4°C).
Catalase activity (EC 1.11.1.6) was evaluated by monitoring of H
2O
2 degradation for 1 min at 240 nm [
31]. The reaction mixture consisted of 100 µL supernatant, 2.880 mL reaction potassium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0), and 20 µL of freshly prepared 6% hydrogen peroxide.
Guaiacol peroxidase activity (EC 1.11.1.7) was assessed at 470 nm for 1 min by using guaiacol as an electron donor [
32]. The reaction mixture contained 100 µL supernatant, 1.020 mL reaction buffer (50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0), 360 µL 1% guaiacol, and 20 µL 15% H
2O
2.
The inhibition of the photochemical reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium was used to measure the activity of superoxide dismutase (EC 1.15.1.1) at 560 nm [
33]. One unit of SOD corresponds to an enzyme amount capable of 50% substrate inhibition.
The content of total soluble protein was determined according to [
34].
2.3. Immunoblot Analyses
Soluble proteins were extracted from 0.3 g leaf samples with ice-cold 100 mM Tris–HCl buffer, pH 7.4 containing 2 mM phenyl-methane-sulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 12.5% glycerol (v/v), 20 mM β-mercaptho-ethanol and 2% Polyclar® (polyvinyl polypyrrolidone). Equal amounts of total soluble protein (25 µg per lane) were separated by 11% SDS-PAGE in a Mini Protean Dual Slab Cell (BioRad, Hercules, California USA) with PageRuler Prestained Protein Ladder 10-170 kDa (Thermo Scientific, Basel, Switzerland) loaded as a molecular weight reference. The separated proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane using the Trans-Blot system (BioRad, Hercules, California USA). The membrane was blocked in TBS buffer (0.1 M Tris pH 7.9, 0.15 M NaCl) containing 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) at room temperature for 60 min. The antibodies, against K-, S- and Y- segments used to identify dehydrin profiles, and the antibody against Delta-1-Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Synthetase were previously described [
35,
36]. Goat-anti-rabbit-IgG and peroxidase-anti peroxidase soluble complex (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) were used to visualize the immunoblot signals according to previously described protocol [
37]. The peroxidase reaction was developed with 4-chloro-alpha-naphtol (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany).
2.4. RT-qPCR Analysis
GeneJET Plant RNA Purification Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to extract total RNA. The synthesis of cDNA was performed with 100 ng total RNA using RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific™, Vilnius, Lithuania) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The gene transcript abundance was evaluated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) using 2X GreenMasterMix No ROXTM (GENAXXON Bioscience, Ulm, Germany) with ‘PikoReal’ Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Scientific, Basel, Switzerland). The PCR program settings were: 95° C for 15 min and 45 cycles of 95° C for 15 s followed by 60° C for 30 s, and melting curve analysis with a temperature range of 60° C–95° C in 0.2° C increment for 60 s.
The relative expression of the target genes was calculated by the ΔΔCq method [
38] using actin (Gene Bank ID: XM_023878805) and 18S ribosomal RNA (Gene Bank ID: AH001680) as references.
Lactuca sativa genes coding for different antioxidant enzymes that were analyzed and the used respective primers are listed in
Table 1.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
A completely randomized experimental design was implied. The presented results are based on three independent experiments and the graphs reflect a representative dataset. The error bars depict the calculated Standard Error (SE). The statistical significance of the results was evaluated by one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test and Students’s t-test at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
Exogenous application of plant growth regulating substances is a common practice for improving plant productivity and resilience, including facilitating drought survival (reviewed in [
39]). The PGR products that are offered on the market include mainly growth-stimulating compounds like gibberelic acid or cytokinin and auxin analogues (Ascend® SL, Planofix ®, CytoGro®, etc.). ABA and ethylene-like acting compounds, such as Ethrel ®, are mainly used for pre-and postharvest management. This is based on their ability to stimulate the maturation and ripening of non-climacteric (mainly ABA) and climacteric fruits (ethylene and ABA). ABA also provokes abscission and seed dormancy which is particularly important for post-harvest management in grain crops. A recent study reports that when treated with ethylene in darkness and subsequently exposed to light, plants exhibited enhanced root growth, denser lateral roots, and increased fresh weight of aerial tissues, a phenomenon observed both in the model species
Arabidopsis thaliana, as well as in various crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and wheat [
40]. This newly identified property of the gaseous hormone opens new perspectives for its use in agricultural practice as a growth-boosting compound that fortifies plant vigour and resilience.
The results obtained in the present study suggest that combining stress hormones (ABA, ethylene or its precursor ACC) with growth-stimulating substances (auxins and cytokinins) in bioequivalent amounts and applying them before dehydration, could subsequently improve plant performance under water limitation. The strategy is based on the understanding that drought response engages multiple physiological, biochemical and morphological changes driven by a complex network of hormonal inputs.
3.1. The Combined Pretreatment with Bioequivalent Amounts of ABA, ACC, NAA, and KIN Ameliorates the Negative Effect of Dehydration Stress Provoked by 12% PEG in Hydroponically Grown Lactuca sativa
3.1.1. Growth Parameters
We screened the effect of exogenous ABA, ACC, NAA and kinetin applied in the intrinsic concentration range of the respective phytohormones via spraying. ABA and ACC doses were chosen based on previous studies of drought stress response in which the endogenous levels of these hormones were estimated [
9,
10]. The applied growth-stimulating cytokinin and auxin analogues also reflected the naturally observed endogenous levels (micromolar and submicromolar concentrations). In parallel, varying combinations of the PGRs, consistently applied in the same final concentration, were tested for any potential stress-mitigating properties.
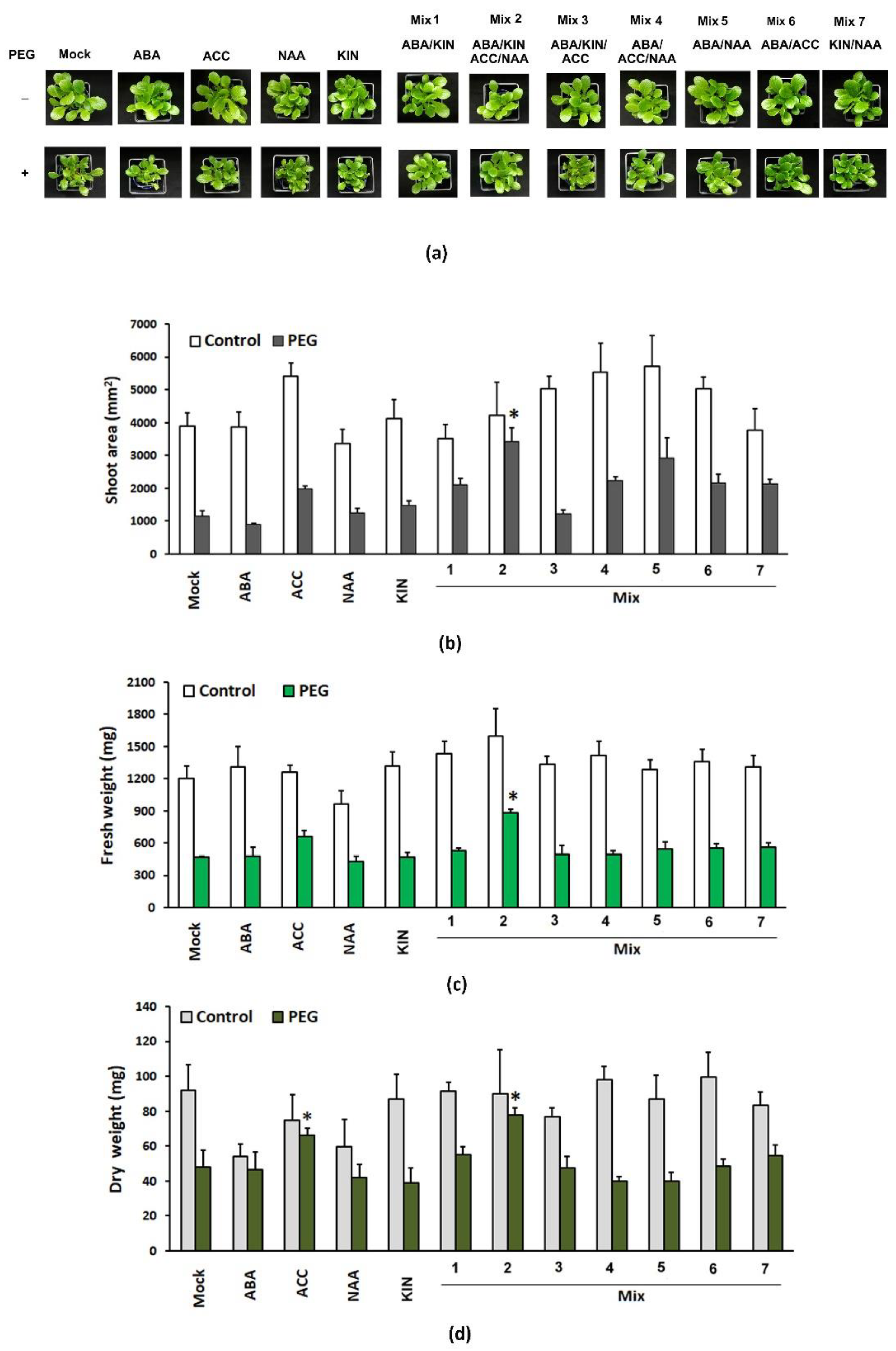
The phenotypes of the different control and PEG-stressed groups are presented in
Figure 1a. We did not observe any significant differences in shoot area, or fresh and dry weights of the control groups subjected to hormonal treatments. This means that the applied exogenous PGRs have not interfered with the intrinsic mechanisms controlling the growth and development under normal conditions. However, in the PEG-stressed variants, the hormonal combination comprising the full spectrum of the tested compounds (Mix 2) significantly affected the three growth parameters with a well-sustained shoot growth indicated by the relatively bigger shoot area (
Figure 1b). The pretreated group had up to 20% higher fresh weight and around 30% higher dry weight than the PEG-stressed non-primed plants (
Figure 1c,d). We also observed a weaker positive effect of the ACC application on the growth parameters of the pre-treated PEG-stressed plants which exhibited statistically significant higher dry weight compared to the “mock” PEG-grown variant (
Figure 1d). The observed fluctuations of the growth indexes in the other treatment groups were not found to be statistically significant.
3.1.2. Malondialdehyde (MDA), Free Sulfhydryl Groups (SH-groups), and Total Phenolic Compounds
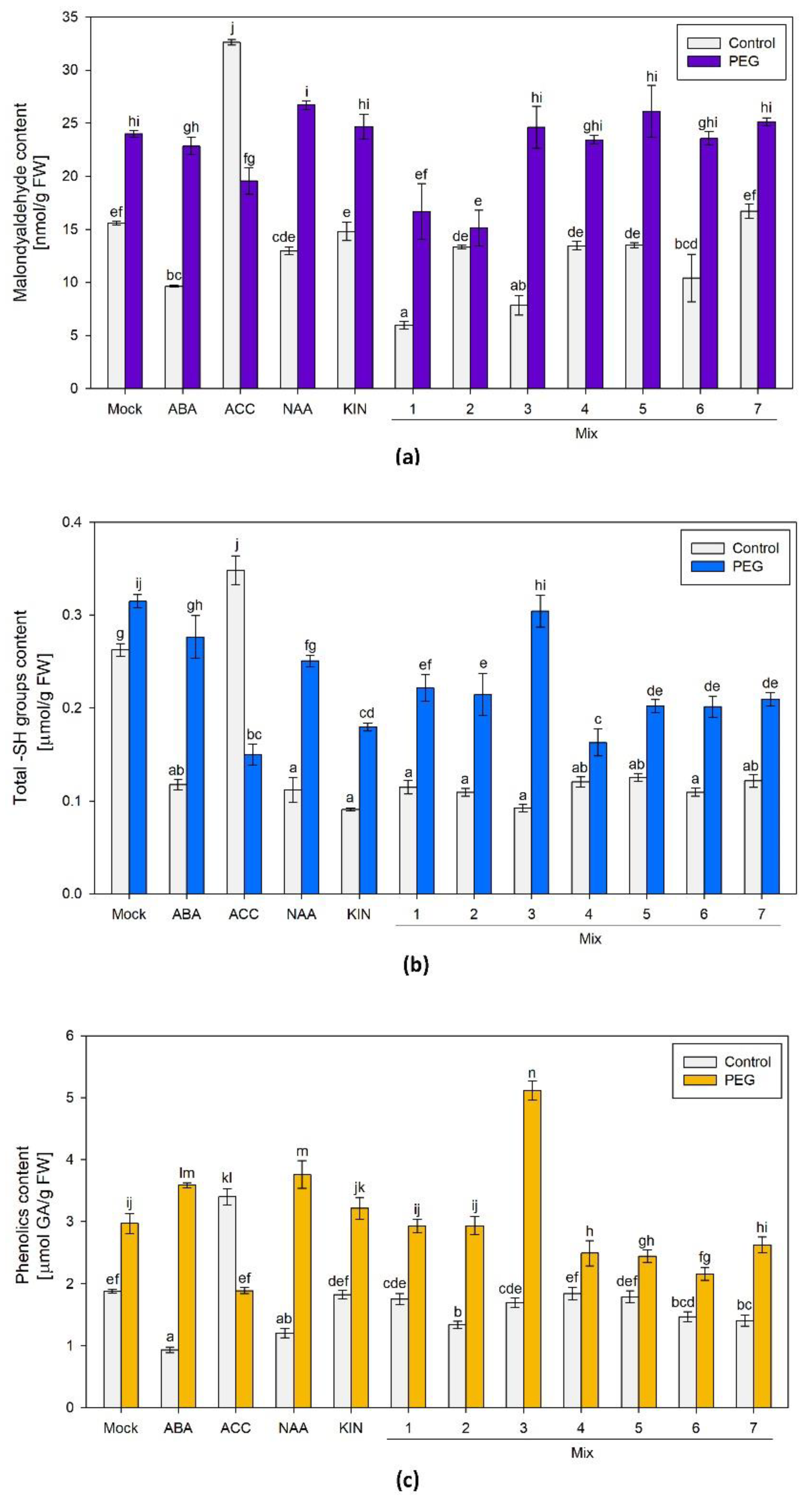
The effect of the applied hormonal treatments on malondialdehyde (MDA) and the level of the total content of sulfhydryl groups and polyphenolic compounds were screened. These are indicators of the physiological response towards the applied hormonal priming and the subsequent dehydration.
MDA is a conventional stress marker that is linked to the preserved functionality of the cellular membranes, as it is a product of lipid peroxidation by the reactive oxygen species (ROS). Usually, the lower MDA level is linked to the better plant capacity to withstand the applied stress. The broad screen of the different variants that received hormonal doses before the exposure to PEG, showed elevated MDA content comparable to the one measured in the mock-treated plants. The only pretreatment that exhibited some advantageous response when exposed to PEG, in terms of sustained lower MDA levels, was the group that received Mix 2 (the combination of the four PGRs) (
Figure 2a). An interesting observation was made in the ACC-only-treated plants. The ACC-treated individuals grown under optimal conditions had the highest level of the stress marker while in the similarly treated plants, subjected to osmotic stress, the measured MDA level was comparable to the respective "mock" group (
Figure 2a).
The total –SH group level is a molecular indicator of the intact physiological capacity of the plant to respond to various developmental and environmental cues. Low-molecular sulfhydryl groups (–SH groups), mainly associated with potent non- enzymatic antioxidants like glutathione and cysteine, are highly reactive to oxidative stress that occurs along with dehydration [
41]. The sulfhydryl groups in proteins, on the other hand, are actively involved in enzyme-based catalysis, metal coordination, protein folding, and protein-protein interactions [
41]. Overall, a comparable –SH content was measured in all the plants subjected to various hormonal treatments and grown under optimal conditions (
Figure 2b). In most of them, the measured level was lower than the one of the “mock” control. The differently PGR-treated stressed plants exhibited increased total content of sulfhydryl groups similar to or slightly below the respective control values. The only exception from these trends made the ACC-treated groups. The plants that received only a dose of the ethylene precursor and were grown under optimal conditions had the highest –SH level among all the tested treatments. In contrast, a reverse trend of diminishing sulfhydryl group content was observed in the ACC-pretreated individuals upon PEG exposure (
Figure 2b).
The accumulation of phenolics is a common reaction of plants challenged by various environmental stressors. Due to their chemical characteristics, these compounds can operate as non-enzymatic antioxidants. Therefore, this parameter was also included in the broad stress-response screen of the hormonal pretreatments and their effect upon dehydration (
Figure 3c). The highest amount of polyphenolics was detected in the PEG-treated group primed with Mix 3 (a combination of ABA, KIN, and ACC). The other stressed plants also accumulated higher polyphenol levels comparable to or slightly below the “mock”-treated dehydrated individuals. Both ACC-treated groups again show an odd response i.e. higher polyphenolics were detected in the control and lower in the PEG-affected individuals treated with the ethylene precursor (
Figure 3c). Although the changes of polyphenolics upon dehydration did not show any significant deviations as a result of the Mix 2-priming, the combination of ABA, NAA, KIN, and ACC exerted a protective effect, resulting in better growth indexes compared to the other tested hormonal combinations. The data obtained in the broad screen of differently primed experimental groups motivated the subsequent detailed analyses of the Mix 2 combination as it exhibited the best stress-mitigating effect.
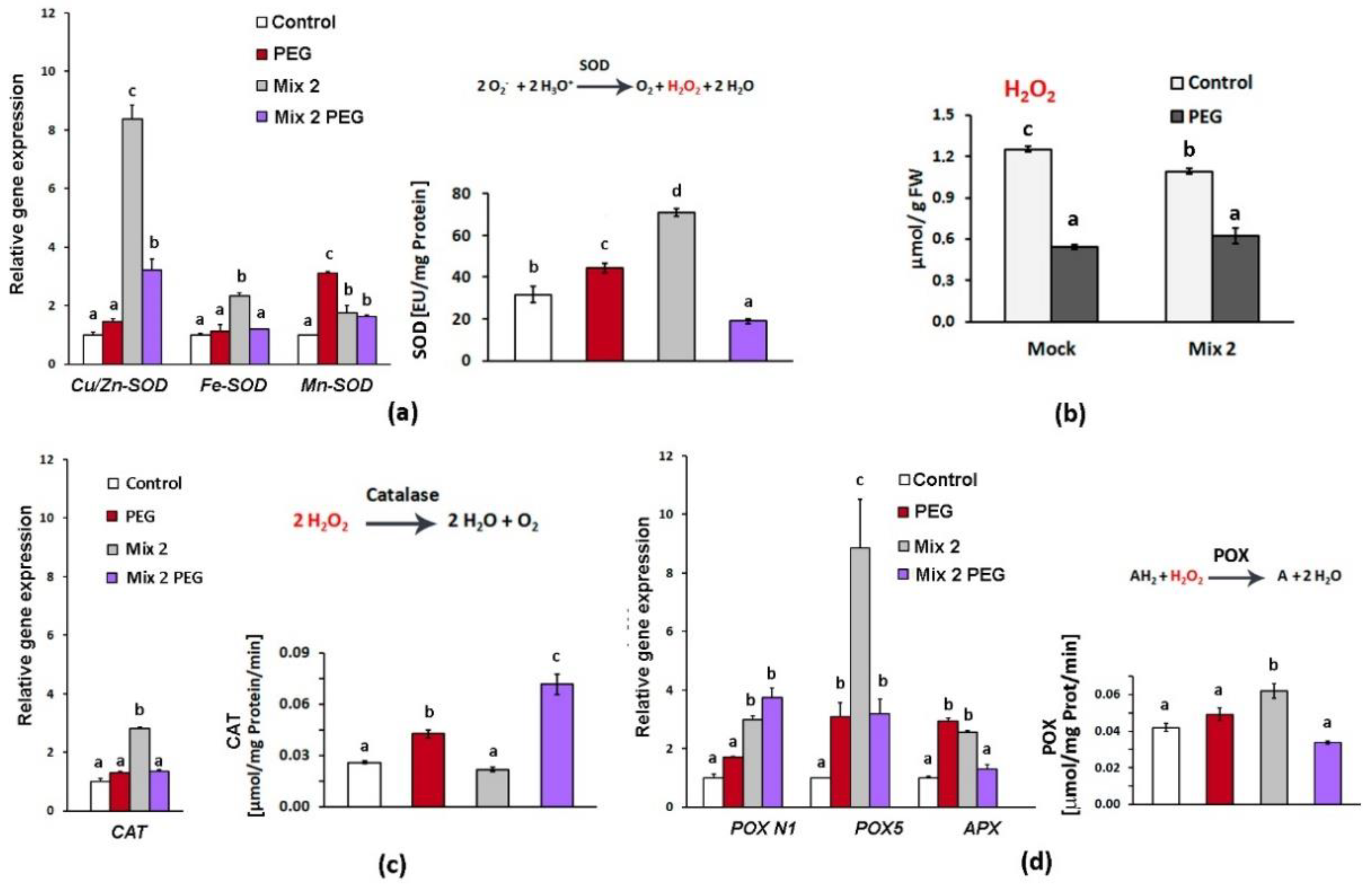
3.2. Combined Pretreatment with ABA, ACC, NAA and KIN Activates Enzymatic Antioxidant Defense
Drought is accompanied by cellular oxidative stress which triggers multiple molecular components of the antioxidative defence system. Among them are the free proline and polyphenolic compounds that usually accumulate under dehydration. The excessive amounts of hydrogen peroxide and the superoxide radical O
2˙¯ that usually accumulate under dehydration can cause oxidative damage to the cellular membrane and macromolecules. Superoxide dismutase (SOD, EC 1.15.1.11), catalase (CAT, EC1.11.1.6), and peroxidase (POX, EC 1.11.1.7) are core elements of the ROS scavenging system in plants. SOD neutralizes the extremely harmful superoxide radical O
2˙¯by converting it into molecular oxygen and H2O2 (
Figure 3a).
The registered slightly higher total SOD enzyme activity in the leaves of the mock-treated PEG-grown
L. sativa plants correlated with the relatively higher accumulation of
Mn-SOD transcripts coding for SOD isoenzyme that operates mainly in the mitochondrion and the peroxisomes [
42]. The transcript profiling of SOD-coding genes showed that Mix 2 upregulated selectively the expression of
Cu/Zn-SOD and this aligned with the higher total SOD enzymatic activity measured in the control Mix 2-treated samples (
Figure 3a). The expression of the
Cu/Zn-SOD gene in the Mix 2-primed plants remained elevated upon PEG exposure, in contrast to the plants that were not subjected to PGR pretreatment. However, the measured total SOD activity in the Mix 2/PEG individuals was lower than the one of the “Mock”/PEG-treated plants. It should be noted that the increased transcript abundance could compensate for damaged or inactivated enzymes; therefore the measured total enzyme activity could remain constant or could exhibit changes that do not always align with the transcript profiles. It should be outlined that Cu/Zn-SOD isoenzymes are the most abundant isoform in the leaves, usually found in the chloroplast, the cytosol, and the extracellular space [
42]. The observed targeted activation of this particular SOD type due to the Mix 2 priming could be an important element contributing to the overall protective effect.
Hydrogen peroxide produced after the dismutation of the superoxide radical by SOD activity is a relatively stable ROS species that can also act as a stress signal transducer [
43]. The levels of H
2O
2 measured in the second true leaves of the PEG-grown plants, both Mock- and Mix 2-treated ones, were lower than the controls, reflecting the effectively controlled local content (
Figure 3b). This could be explained by the efficient catalase (CAT) and peroxidases (POX) activities that handled the excessive hydrogen peroxide produced therein. CAT, neutralizes H
2O
2 in peroxisomes releasing H
2O and O
2 [
44]. The pretreatment with Mix 2 had a slight but significant effect on the
CAT gene expression in the leaves of the control group. Nevertheless, a significant increase in enzyme activity was registered in the Mix 2-primed group subjected to PEG-provoked dehydration (
Figure 3c).
Peroxidase enzymes operate in the vacuoles, the cell walls and the cytosol [
44]. They use aromatic compounds (marked with “A” in
Figure 3d) such as guaiacol as electron donors, to convert H
2O
2 into two water molecules. Total peroxidase activity measured in the PEG-treated plants that did not receive the hormonal mix was slightly higher than the control but on the level of gene expression we registered moderate (approximately 3-fold) upregulation of
POX 5 and
.APX transcripts (
Figure 3d). Mix 2-priming exerted stimulation of
POX gene expression, with particularly significant upregulation of
POX 5 transcripts (up to ten-fold in the primed plants grown under normal conditions). The effect was confirmed at the level of total enzyme activity measured in the Mix 2-primed control group whereas POX activity in the PEG-stressed individuals that received the hormonal combination was lower than the respective ”Mock”-treated group (
Figure 3d).
The consistently observed increased SOD and peroxidase activity in the control group of the Mix 2 pre-treated plants could be a result of the ABA component in the hormonal mix. The potential of exogenous ABA as a priming agent that could lower oxidative damage under stress by activating antioxidant enzymes has been previously demonstrated [
45,
46]. The prior-to-dehydration elevated levels of these enzymes might be advantageous during water limitation, as it would lessen the ROS burden on the plant cells.
3.3. Combined Pretreatment with ABA, ACC, NAA and KIN Positively Affects the Accumulation of Free Proline upon Dehydration
It is well known that at water limitation, plants alter sink/source allocation [
47], slow down respiration and photosynthesis, and start to accumulate high levels of dehydrins, chaperons and osmotically active substances like sugars, polyols, and free amino acids like proline [
48]. Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (EC:2.7.2.11, P5CS) catalyzes the conversion of L-glutamate to pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) which is the limiting step for the biosynthesis of two essential proteinogenic amino acids L-proline (L-Pro) and L-arginine [
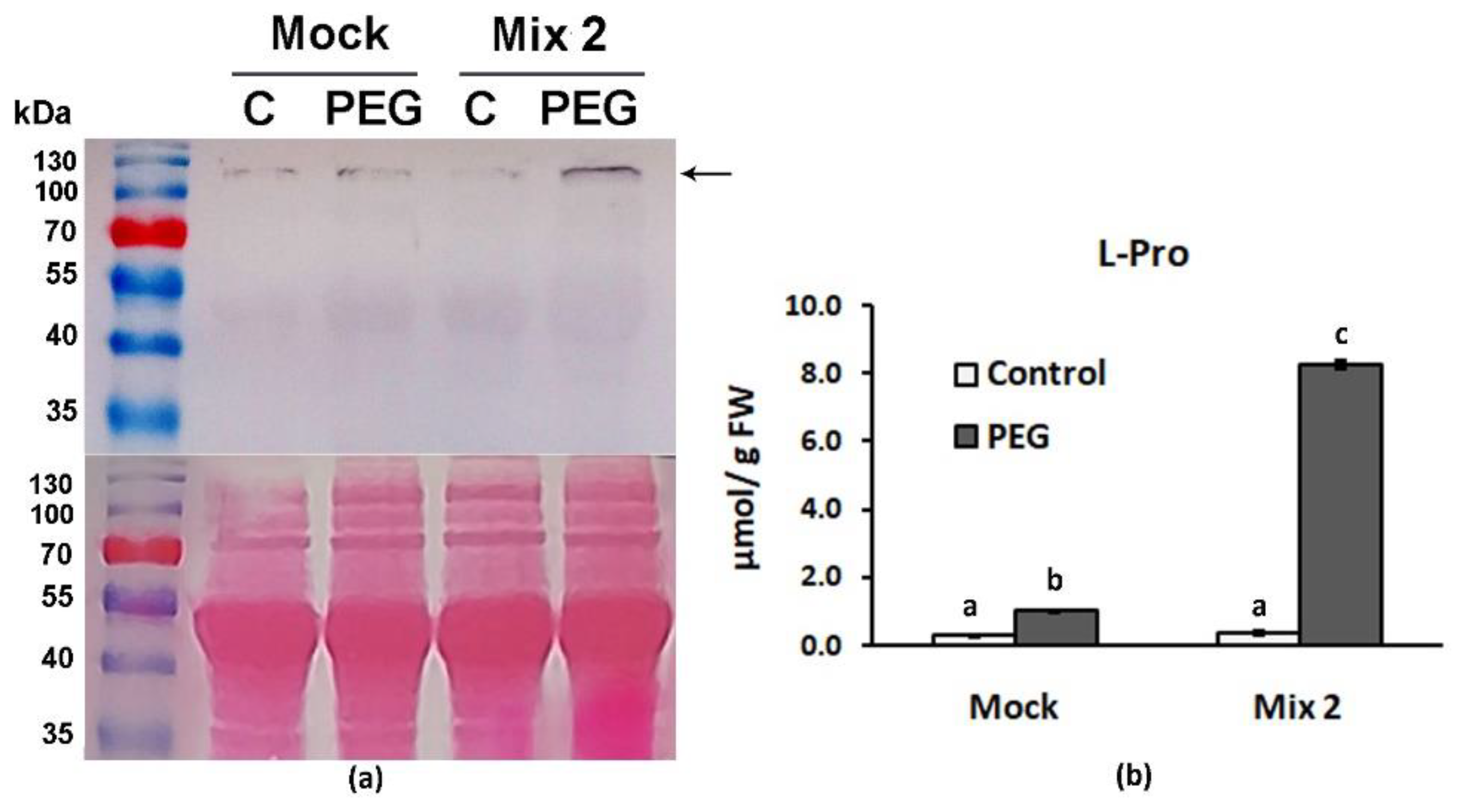
49]. Free L-Pro particularly is considered a stress-defense molecule capable of adjusting cellular osmotic potential. The immunoblot analyses of the samples derived from Mix-2 pretreated individuals that have experienced dehydration showed increased levels of P5CS compared to the respective “Mock“-PEG experimental group (
Figure 4a). The positive effect of Mix 2 on proline biosynthesis was further confirmed by the measured elevated free L-Pro content in the same treatment group (
Figure 4b).
The increased proline biosynthesis in the PEG-stressed plants resulting from the combined hormonal pretreatment may significantly contribute to a better physiological status. The multifaceted function of proline in plant growth and development has been acknowledged by multiple studies that gave evidence for its active involvement in sustaining cellular redox balance and osmoregulation [
50]. Previously published research suggests that ABA and ethylene signals regulate P5CS gene expression [
51,
52]. The obtained results aligned well with these findings as the observed stimulated activity of the enzyme in the primed plants corresponds to the presence of the ethylene precursor and ABA in the mix.
3.4. Combined Pretreatment with ABA, ACC, NAA and KIN Stimulates the Accumulation of Certain Dehydrin Types
Dehydrins (DHN) belong to a broad class of stress-inducible proteins that are an essential part of the drought stress response. Due to their unique molecular characteristics, they are capable of stabilizing biomolecules and membranes, acting as chaperones but also they have been recently found to regulate stress-responsive genes (reviewed in [
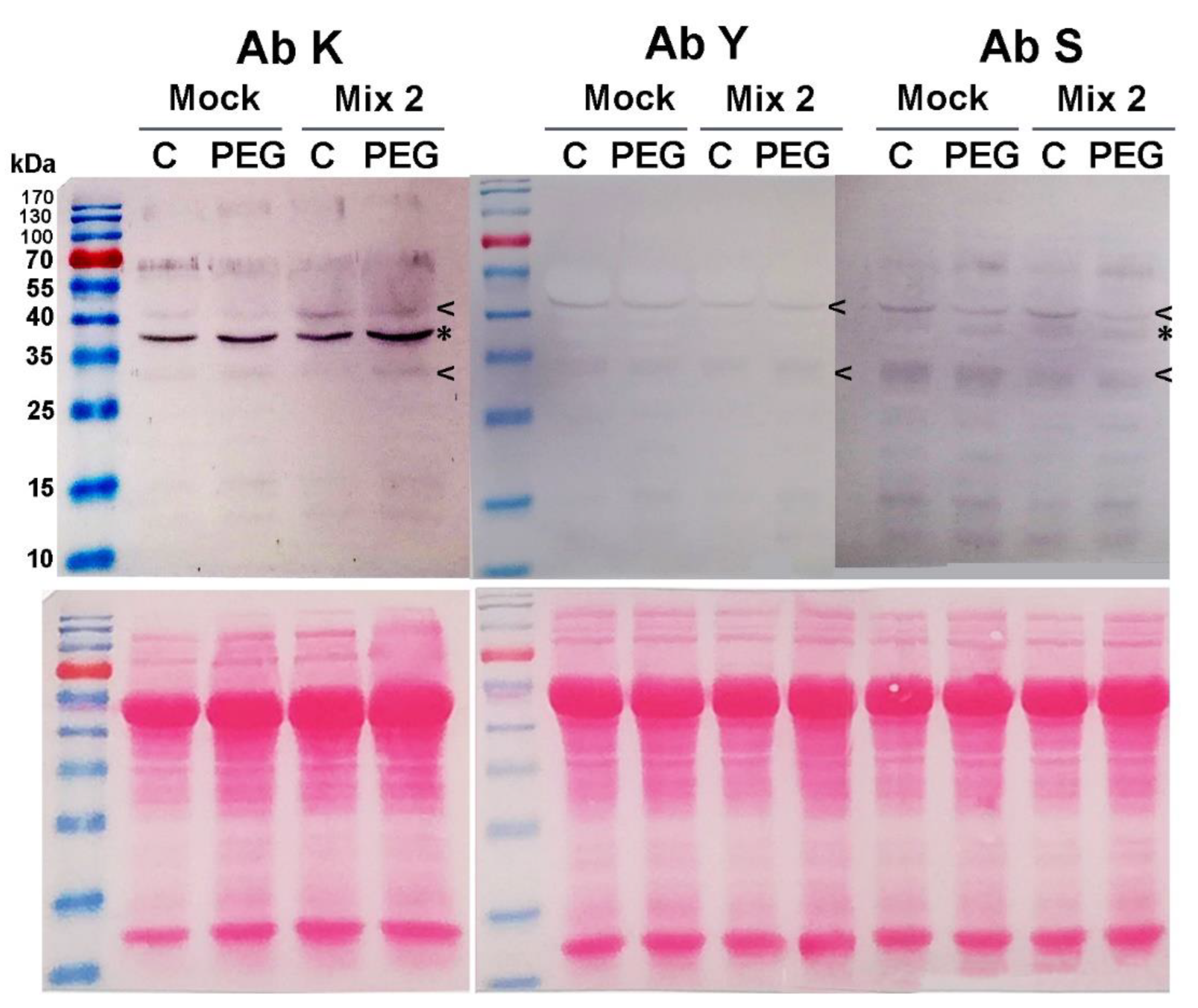
53]). DHNs are characterized by the presence of one or more copies of a highly conserved amphipathic α-helix-forming domain of a 15-residue consensus sequence called the K-segment (EKKGIMDKIKEKLPG). It is usually situated near the C-end of the DHN molecule. Many dehydrins contain also a serine-rich S segment, which is prone to phosphorylation. Another dehydrin subfamily is characterized by the presence of the so-called Y-segments that are usually found close to the N terminus of the amino acid chain. The performed immunoblot analyses using antibodies against the three conservative DHN domains (K, Y, and S) allow us to identify the molecular type of the detected dehydrin signals. However, it should be noted that the absence of a signal upon immunoblotting with a given antibody must be interpreted conditionally. The lack of immunosignal could be due to transient spatial inaccessibility of the epitope resulting from dimerization, post-translational modifications, etc. In the performed immunodetection we registered a specific induction of certain dehydrin signals resulting from the priming with Mix 2 (
Figure 5).
Mix 2-induced DHNs with approximate weights of 34 kDa and 40 kDa were revealed when the membranes were probed with the three primary antibodies (marked with “<” symbol in
Figure 5). This classifies them as YSK-type dehydrins. On the K- and the S-probed membranes, an immunosignal of about 36 kDa had higher intensity in the Mix 2-pretreated samples (marked with “*” in
Figure 5). The accumulation of specific dehydrin types as a result of the hormonal priming may also contribute to the better physiological status of the plants grown in the presence of 12% PEG..
3.5. Testing of the Stress-Mitigating Potential of Mix 2 in Soil-Grown L. sativa Plants Subjected to Moderate Drought
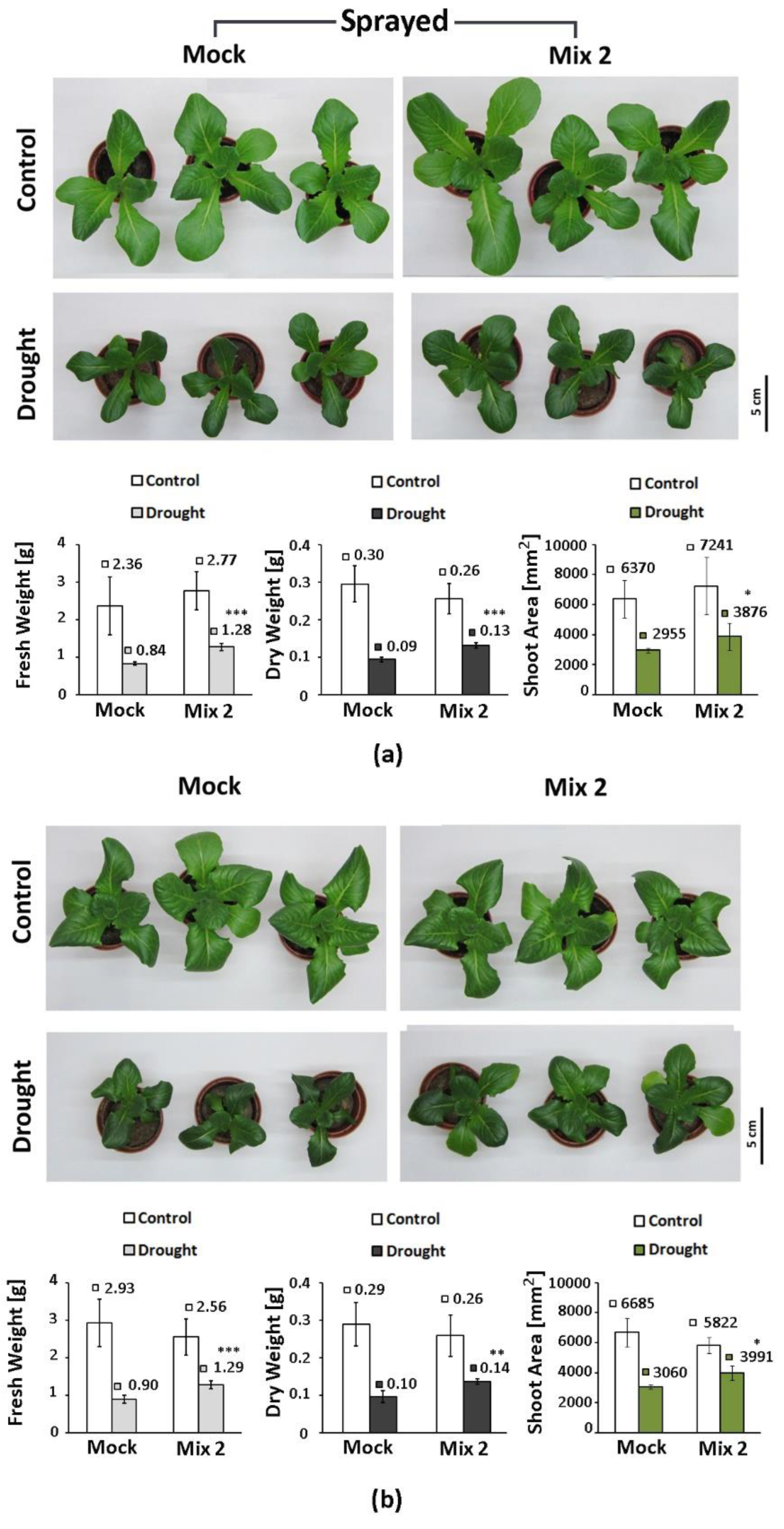
Testing the “transferability” of the positive effect of a hormonal preparation observed in a particular experimental setting is mandatory to confirm its consistent action. This is largely due to the extremely versatile and dynamic nature of the PGR’s inputs which strongly depend on the developmental stage, the plant species, and the particular environmental factors in which the trials are conducted. Therefore, the effect of the PGR mix was evaluated also on soil-grown lettuce plants subjected to moderate drought. The solution was administered either by spraying, using the same amount of preparation as in the PEG experiment (
Figure 6a), or it was applied through the roots in a 1 ml dose per plant (
Figure 6b).
Overall, we observed a similar beneficial effect of the combined hormonal pretreatment which was not influenced by the application method. The primed plants had 15-20% higher fresh and dry weight compared to the “Mock”-treated drought-stressed individuals and relatively larger leaf area. The variations in these growth indexes of the differently treated control plants were not statistically significant.
The validated drought-mitigation properties of the mix in soil-grown plants suggest its consistent action in alleviating the negative impact of dehydration in this vegetable crop. Additional extended testing of the hormonal combination in field conditions is necessary to confirm its efficiency as a drought-protective agent in other leafy greens.
3.6. Comprehensive Analysis of the Observed Drought–Mitigating Property of the Applied PGR Combination
To elaborate on the protective effect of the hormonal combination in Mix 2, one should consider several well-established properties of its comprising components as elements of the hormonal blueprint that govern the drought response. Ethylene and ABA, control the synthesis of many stress-inducible proteins, including dehydrins and antioxidant enzymes [
54,
55,
56,
57]. ABA is also considered the master regulator of stomata closure and opening [
58] hence it is a core factor for water loss regulation, justifying its compulsory presence in the blend. As the best ethylene proxy, we used ACC which in theory should provide an equimolar concentration of ethylene gas [
59].
The other two components in the preparation, the auxin and the cytokinin analogue target the appropriate hormonal background for establishing a strong root system that is an essential prerequisite for optimal water and nutrient assimilation, especially under drought. Plant survival under limiting water and nutrient availability requires a well-developed root system, an anatomical feature that largely depends on the proper auxin-to-cytokinin ratio [
47]. By including the cytokinin analogue along with auxin in the desired ratio in the hormonal mix, we target growth stimulation of the root system. In our approach, we also take into account the fact that the intrinsic hormonal interactions can be synergistic or antagonistic depending on the physiological and developmental context [
60,
61]. Auxins and cytokinins are known to form such a complex partnership [
47]. They control synergistically the shoot stem-cell niche while acting as antagonists in maintaining the root meristem. This qualifies them as important regulatory components establishing the shoot-to-root ratio under given environmental requirements.
A previous study has demonstrated that exogenously applied auxin is capable of upregulating multiple transcription factor genes responding to drought [
11]. In the same study, conducted on white clover grown on PEG, the authors showed that exogenous auxin induced the endogenous levels of ABA and jasmonate. The capacity of exogenous PGRs to activate hormonal crosstalk networks is a central feature that integrates adequate and physiologically relevant responses to the imposed stressor. Consequently, we assume that Mix 2 alleviates dehydration through a multiplied exogenous effect on various signaling pathways that activate different protective mechanisms.
4. Conclusions
The priming with a mix combining ABA and ACC in concentrations mimicking hormetic stress exposure, and coupled with physiologically relevant levels of growth-promoting substances (auxin and cytokinin analogues), could alleviate the negative impact of moderate dehydration stress in lettuce.
The study outlines the advantages of combined PGR treatment for stress management that are probably due to the activation of multiple signalling relays.
The demonstrated drought-protective potential of bioequivalent doses of PGRs suggests the relevance of testing such a "bioequivalence" strategy in other experimental models using different crops and environmental stress factors.
The acquired knowledge could be implemented in environment-friendly stress-mitigating methods based on low phytohormonal doses that correspond to the naturally occurring levels capable of exerting efficient protective reactions under stress.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.I.V., D.T. and I.S.; methodology, I.I.V., D.T., I.S and M.U.; formal analysis, I.I.V., D.T. and I.S.; investigation, I.I.V., I.S. and D.T.; resources, L.S., G.S, and D.T.; data curation, I.S. and D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, I.I.V.; writing—review and editing, I.S., D.T., L.S., M.U. and G.S.; visualization, I.I.V. and I.S.; funding acquisition, I.I.V. and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a joint research project “Physiological and molecular mechanisms of phytohormones-mediated drought stress tolerance – HormOnDrought” under the agreement for Scientific Cooperation between the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) and the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Prof. Urs Feller (Professor emeritus at Universität Bern, Switzerland) who provided the specific primary antibodies against P5CS and against the three conservative amino acid sequences (K-, Y-, and S-segments) in dehydrin proteins used in the present study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- European Commission. The European Green Deal. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- European Commission. Farm to Fork Strategy Action Plan. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- de Vasconcelos, A.C.F.; Chaves, L.H.G. Biostimulants and their role in improving plant growth under abiotic stresses. Biostimulants in Plant Science. Intech Open 2020, 88829, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, P.; Nelson, L; Kloepper, J. W. Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant and soil 2014, 383, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.S. Seaweed extract stimuli in plant science and agriculture. J Appl Phycol 2011, 23, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhin, O.I.; Lubyanov, A.A.; Yakhin, I.A.; Brown, P.H. Biostimulants in plant science: a global perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Conejo, M.I.; Prieto-Fernández, Á.; Kidd, P.S. Exogenous treatments with phytohormones can improve growth and nickel yield of hyperaccumulating plants. Sci Total Environ 2014, 494–495, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Asami, T. Chemical regulators of plant hormones and their applications in basic research and agriculture. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2018, 82, 1265–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, F.; Mullet, J.E. Increased abscisic acid biosynthesis during plant dehydration requires transcription. Plant Physiol 1986, 80, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.A.; Santos, I.S.; Torres, M.E.L.; Cardon, C.H.; Caldeira, C.F.; Lima, R.R.; Chalfun-Junior, A. Drought and re-watering modify ethylene production and sensitivity, and are associated with coffee anthesis. Environ Exp Bot 2021, 181, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hassan, M.J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y. Indole-3-acetic acid improves drought tolerance of white clover via activating auxin, abscisic acid and jasmonic acid related genes and inhibiting senescence genes. BMC Plant Biol 2020, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.Y.; Azhar, N.; Hussain, M. Indole acetic acid (IAA) induced changes in growth, relative water contents and gas exchange attributes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) grown under water stress conditions. Plant Growth Regul 2006, 50, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Ivanchenko, M.G.; Muday, G.K. Ethylene regulates lateral root formation and auxin transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2008, 55, 175–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchenko, M.G.; Muday, G.K.; Dubrovsky, J.G. Ethylene–auxin interactions regulate lateral root initiation and emergence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 2008, 55, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramireddy, E.; Hosseini, S.A.; Eggert, K.; Gillandt, S.; Gnad, H.; von Wirén, N.; Schmülling, T. Root engineering in barley: Increasing cytokinin degradation produces a larger root system, mineral enrichment in the shoot and improved drought tolerance. Plant Physiol 2018, 177, 1078–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants 2021, 28, 10–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.F.; Huda, S.; Yong, M.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ahmed, T. Alleviation of drought and salt stress in vegetables: crop responses and mitigation strategies. Plant Growth Regul 2023, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, A.; Dzinyela, R.; Aghaei-Dargiri, S.; Alhassan, A.R.; Yang, L.; Xu, C. Advanced Study of Drought-Responsive Protein Pathways in Plants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, F.A.; Golovina, E.A.; Buintink, J. Mechanisms of plant desiccation tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 2001, 6, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, T.J. Dehydrins: A Commonalty in the response of plants to dehydration and low temperature. Physiol Plant 1997, 100, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Morales, S.; Solís-Gaona, S.; Valdés-Caballero, M.V.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Loredo-Treviño, A.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. Transcriptomics of biostimulation of plants under abiotic stress. Front. Genet 2021, 12, 583888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, I.I.; Simova-Stoilova, L.; Kostadinova, A.; Yuperlieva-Mateeva, B.; Karakicheva, T.; Vassileva, V. Heat-stress-mitigating effects of a protein-hydrolysate-based biostimulant are linked to changes in protease, DHN, and HSP gene expression in maize. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vylder, J.; Vandenbussche, F.; Hu, Y.; Philips, W.; Van Der Straeten, D. Rosette tracker: an open source image analysis tool for automatic quantification of genotype effects. Plant Physiol 2012, 160, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, D.C.; Zayed, A.M.; Ascenzi, R.; McCaskill, A.J.; Hoffman, N.E.; Davis, K.R.; Görlach, J. Growth stage-based phenotypic analysis of Arabidopsis: a model for high throughput functional genomics in plants. Plant Cell 2001 13, 1499–1510. [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.; Norman, H.; Krizek, D.; Mirecki, R. Influence of UV-B radiation on polyamines, lipid peroxidation and membrane lipids in cucumber. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexieva, V.; Sergiev, I.; Mapelli, S.; Karanov, E. The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.; Waldren, R.; Teare, I. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, T.; Goldstein, L. Methods in Polyphenol Chemistry; Pridham, J.B., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1964; pp. 131–146.
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, M. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, I.; Costa, M. Effect of low salt concentration on nitrate reductase and peroxidase of sugar beet leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 1983, 34, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase. Improved assay and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analyt. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, I.; Akiscan, Y.; Simova-Stoilova, L.; Kostadinova, A.; Nenkova, R.; Anders, I.; Feller, U.; Demirevska, K. Аntioxidant response to drought in red and white clover. Acta Physiol. Plant 2012, 34, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, I.; Anders, I.; Feller, U. Identification and expression of different dehydrin subclasses involved in the drought response of Trifolium repens. J Plant Physiol 2014, 171, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, W.; Feller, U. Effects of light and external solutes on the catabolism of nuclear-encoded stromal proteins in intact chloroplasts isolated from pea leaves. Plant Physiol 1992, 100, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCq method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Dai, M. Improving crop drought resistance with plant growth regulators and rhizobacteria: Mechanisms, applications, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenya, E.; Dutta, E.; Herron, B.; Walden, L.H.; Roberts, D.M.; Binder, B.M. Ethylene-mediated metabolic priming increases photosynthesis and metabolism to enhance plant growth and stress tolerance. 2023, 2, pgad216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, P.; Papenbrock, J. Possible roles of plant sulfurtransferases in detoxification of cyanide, reactive oxygen species, selected heavy metals and arsenate. Molecules 2015, 20, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alscher, R.G.; Erturk, N.; Heath, L.S. Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, N.A.; Gill, S.S.; Corpas, F.J.; Ortega-Villasante, C.; Hernandez, L.E.; Tuteja, N.; Sofo, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Fujita, M. Editorial: Recent insights into the double role of hydrogen peroxide in plants. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 843274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozfidan, C.; Turkan, I.; Sekmen, A.H.; Seckin, B. Abscisic acid-regulated responses of aba2-1 under osmotic stress: the abscisic acid-inducible antioxidant defence system and reactive oxygen species production. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2012, 14, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y. Effects of spraying abscisic acid on growth and antioxidant enzyme of lettuce seedlings under salt stress. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 199, 032015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurepa, J.; Smalle, J.A. Auxin/cytokinin antagonistic control of the shoot/root growth ratio and its relevance for adaptation to drought and nutrient deficiency stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M.; Oliveira, M.M. Mechanisms underlying plant resilience to water deficits: prospects for water-saving agriculture. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2365e2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.A.; Delauney, A.J.; Verma, D.P. A bifunctional enzyme (delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase) catalyzes the first two steps in proline biosynthesis in plants. PNAS 1992, 89, 9354–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Savouré, A.; László Szabados, L. Proline metabolism as regulatory hub. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Cudjoe, D.K.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Siddique, S.; Fiorani, F.; Léon, J.; Naz, A.A. Abscisic acid-responsive element binding transcription factors contribute to proline synthesis and stress adaptation in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol. 2021, 261, 153414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, I.I.; Simova-Stoilova, L.; Kirova, E.; Mishev, K.; Depaepe, T.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Vassileva, V. Ethylene signaling in salt-stressed Arabidopsis thaliana ein2-1 and ctr1-1 mutants - A dissection of molecular mechanisms involved in acclimation. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021, 167, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Chakrabarty, D. Dehydrin in the past four decades: From chaperones to transcription co-regulators in regulating abiotic stress response. Curr Res Biotech 2021, 3, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Tayal, D.; Chinnusamy, V.; Bansal, K.C. Abiotic stress and ABA-inducible Group 4 LEA from Brassica napus plays a key role in salt and drought tolerance. J Biotech. 2009, 139, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, H.; Tao, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Li, M. Exogenous ABA enhances the antioxidant defense system of maize by regulating the AsA-GSH cycle under drought stress. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehar, Z.; Gautam, H.; Masood, A.; Khan, N.A. Ethylene- and proline-dependent regulation of antioxidant enzymes to mitigate heat stress and boost photosynthetic efficacy in wheat plants. J Plant Growth Regul 2023, 42, 2683–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Fan, J.; Chen, K.; Amombo, E.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. . Effects of ethylene on photosystem II and antioxidant enzyme activity in Bermuda grass under low temperature. Photosynth Res 2016, 128, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckie, C.P.; McAinsh, M.R.; Allen, G.J.; Sanders, D.; Hetherington, A.M. Abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure mediated by cyclic ADP-ribose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15837–15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarembinski, T.I.; Theologis, A. Ethylene biosynthesis and action: a case of conservation. In: Signals and Signal Transduction Pathways in Plants; Palme, K., Eds.; Springer, Dordrecht The Netherlands, 1994. Pp. 343-361.
- Lakehal, A.; Bellini, C. Control of adventitious root formation: insights into synergistic and antagonistic hormonal interactions. Physiol Plantarum, 2019, 165, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.H.; Hirakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ito, T. The roles of plant hormones and their interactions with regulatory genes in determining meristem activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Representative phenotype (a), shoot area (b), fresh (c), and dry weight (d) of the aboveground part of Lactuca sativa plants subjected to different hormonal pre-treatments and subsequent 10 days dehydration stress provoked by 12% PEG. The graphs show the absolute values of the parameters and the error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=20). The asterisk marks statistically significant differences with the PEG-affected “mock”-treated group (one-way ANOVA Student’s t-test).
Figure 1.
Representative phenotype (a), shoot area (b), fresh (c), and dry weight (d) of the aboveground part of Lactuca sativa plants subjected to different hormonal pre-treatments and subsequent 10 days dehydration stress provoked by 12% PEG. The graphs show the absolute values of the parameters and the error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=20). The asterisk marks statistically significant differences with the PEG-affected “mock”-treated group (one-way ANOVA Student’s t-test).
Figure 2.
(a) Malondialdehyde (MDA); (b) free sulfhydryl groups (SH-groups); (c) total phenolic compounds in differently pretreated Lactuca sativa plants grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG- for 10 days. The graphs show the absolute values of the parameters and the error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=6). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 2.
(a) Malondialdehyde (MDA); (b) free sulfhydryl groups (SH-groups); (c) total phenolic compounds in differently pretreated Lactuca sativa plants grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG- for 10 days. The graphs show the absolute values of the parameters and the error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=6). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 3.
Mix 2 priming effect on antioxidant enzymes in the second true leaf of Lactuca sativa plants grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. (a) Cu/Zn-SOD, Fe-SOD, and Mn-SOD transcript accumulation and total SOD activity; (b) Hydrogen peroxide level in the second true leaves of the differently treated plants; (c) CAT transcript accumulation and total CAT activity; (d) POX N1, POX5, and APX transcript accumulation and total guaiacol POX activity. The error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=3). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 3.
Mix 2 priming effect on antioxidant enzymes in the second true leaf of Lactuca sativa plants grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. (a) Cu/Zn-SOD, Fe-SOD, and Mn-SOD transcript accumulation and total SOD activity; (b) Hydrogen peroxide level in the second true leaves of the differently treated plants; (c) CAT transcript accumulation and total CAT activity; (d) POX N1, POX5, and APX transcript accumulation and total guaiacol POX activity. The error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=3). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 4.
Mix 2 priming effect on L-Proline biosynthesis in Lactuca sativa grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. (a) Immunodetection of P5CS signal (marked with arrow) in leaves of control and PEG-stressed plants that have received “Mock” or “Mix 2” pretreatments. Ponceao-S staining of the membrane is shown below the immunoblot; (b) Leaf L-Pro content measured in samples derived from the same individuals analyzed in the immunoblot. The error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=6). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 4.
Mix 2 priming effect on L-Proline biosynthesis in Lactuca sativa grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. (a) Immunodetection of P5CS signal (marked with arrow) in leaves of control and PEG-stressed plants that have received “Mock” or “Mix 2” pretreatments. Ponceao-S staining of the membrane is shown below the immunoblot; (b) Leaf L-Pro content measured in samples derived from the same individuals analyzed in the immunoblot. The error bars indicate standard error (SE, n=6). The lowercase letters designate statistically different results (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range test at p<0.05).
Figure 5.
Mix 2 priming effect on dehydrin profiles in Lactuca sativa grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. Immunodetection with K-, Y- and S primary antibodies is presented. Mix 2-induced “KYS” signals are marked with “<”, and the “KS” – with “*”. Ponceao-S staining of the same membranes is shown below the immunoblots to visualize the equal protein loading.
Figure 5.
Mix 2 priming effect on dehydrin profiles in Lactuca sativa grown on nutrient media -/+ 12% PEG for 10 days. Immunodetection with K-, Y- and S primary antibodies is presented. Mix 2-induced “KYS” signals are marked with “<”, and the “KS” – with “*”. Ponceao-S staining of the same membranes is shown below the immunoblots to visualize the equal protein loading.
Figure 6.
Representative phenotype, fresh weight, dry weight and shoot area of Lactuca sativa plants pretreated with Mix 2 by spraying (a) or through the roots (b) and subjected to moderate soil drought. The error bars indicate the standard deviation (SD, n=10). The asterisks mark statistically significant differences compared to the respective “Mock” (* p<0.05; ** p<0.01, *** p<0. 001; one-way ANOVA) and the numbers next to the bars indicate the mean value of the parameter measured in each treatment group.
Figure 6.
Representative phenotype, fresh weight, dry weight and shoot area of Lactuca sativa plants pretreated with Mix 2 by spraying (a) or through the roots (b) and subjected to moderate soil drought. The error bars indicate the standard deviation (SD, n=10). The asterisks mark statistically significant differences compared to the respective “Mock” (* p<0.05; ** p<0.01, *** p<0. 001; one-way ANOVA) and the numbers next to the bars indicate the mean value of the parameter measured in each treatment group.
Table 1.
Oligonucleotides for RT-qPCR analyses of transcripts coding for antioxidant enzymes in Lactuca sativa.
Table 1.
Oligonucleotides for RT-qPCR analyses of transcripts coding for antioxidant enzymes in Lactuca sativa.
| Gene Name |
Locus |
Forward primer (5’-3’) |
Reverse primer (5’-3’) |
| Ls Mn-SOD |
LOC111900556 |
CACCCCAGTATTTGGATGGCT |
CTCCCTCCCCCTATGTGCTA |
| Ls Fe-SOD |
LOC111884404 |
GGGAATCCATGCAACCAGGA |
AAAACAAGCCAAACCCAGCC |
| Ls Cu/Zn-SOD |
LOC111882980 |
CACTCTTACAGACGCTTTGCG |
ATGGTGCCACTAACACCCTC |
| Ls Catalase |
LOC111878432 |
GCCATGCTGAACAGTACCCT |
TCTCTCTCCTGGCTGCTTGA |
| Ls APX2 |
LOC111882573 |
GACATCGGCGATCTTCTGGT |
TCTCGAAGCTTCCTCTTCGC |
| Ls POX N1 |
LOC111896420 |
CTATGGTTGATATTGGCGTCGT |
ACAAAGTCGGCCATTGGAGAT |
| Ls POX5 |
LOC111879417 |
GGTCGCTAAAGCCTACTCCC |
ACTTGGGTTGTTTGCTGGTG |
| Ls18S RNA |
AH001680 |
CGGGTGACGGAGAATTAGGG |
TACCTCCCCGTGTCAGGATT |
| Ls Actin-7 |
LOC111882438 |
CTGGTGATGGTGTCTCCCAC |
GGCGAGCTTCTCCTTCATGT |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).