Submitted:
05 May 2024
Posted:
06 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
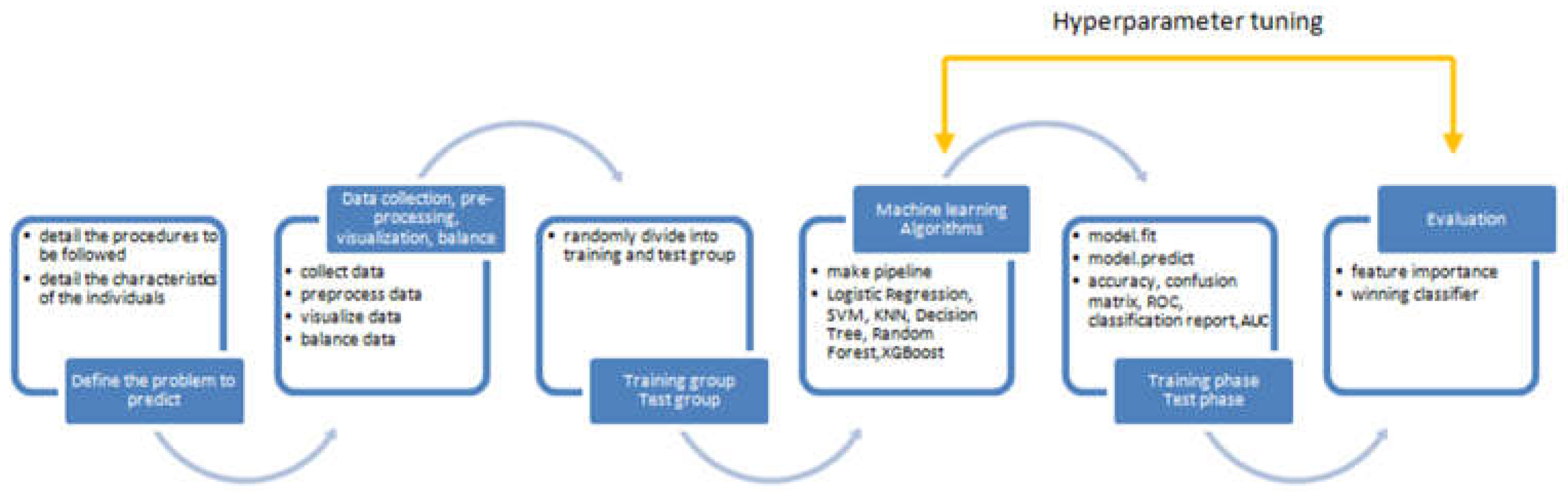
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Overview of Research Design and Participant Details
2.2. Strategy for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Implementation
2.3. Labeling of Medical Data
2.4. Data Manipulation Techniques
3. Results
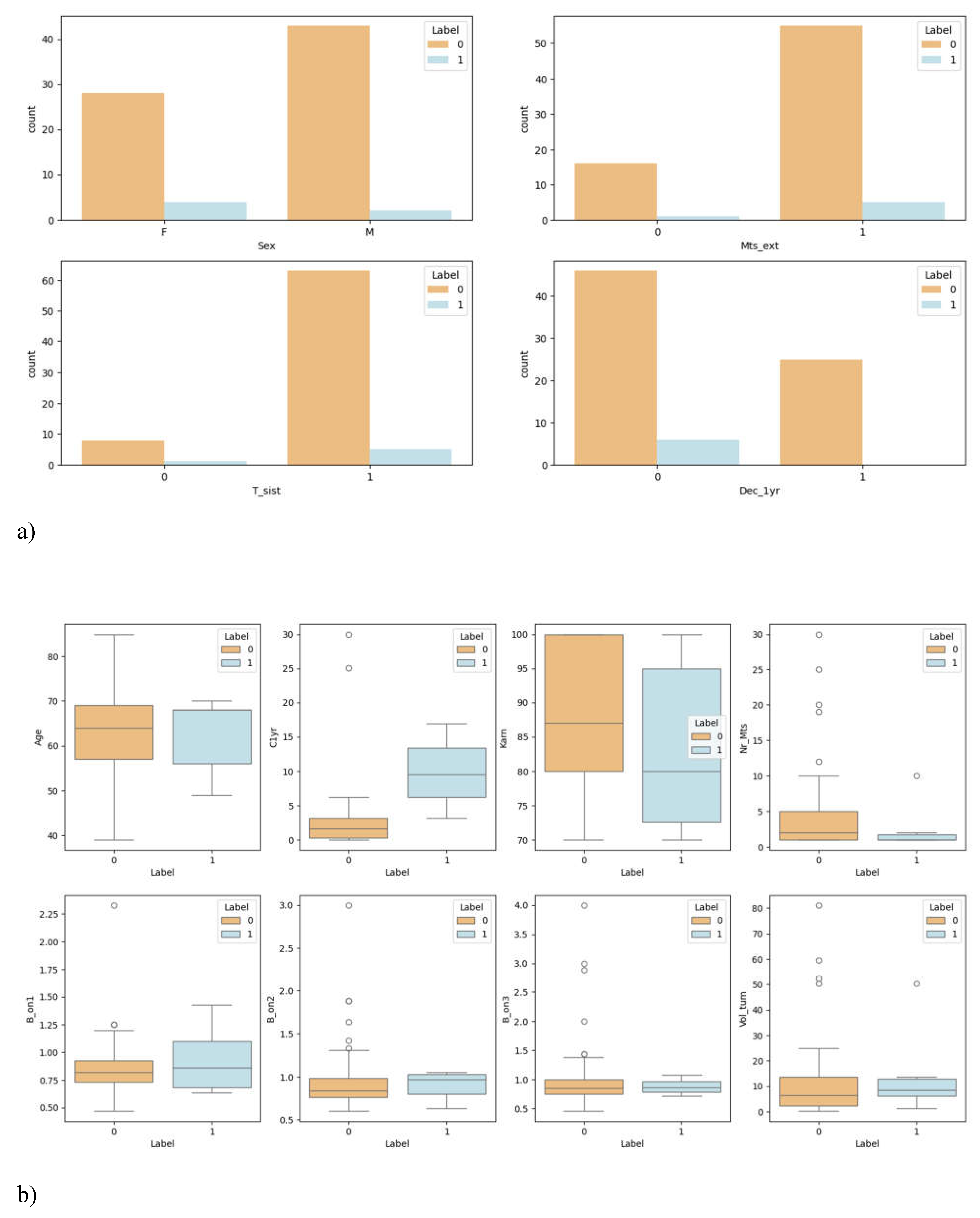
3.1. Overview of Data
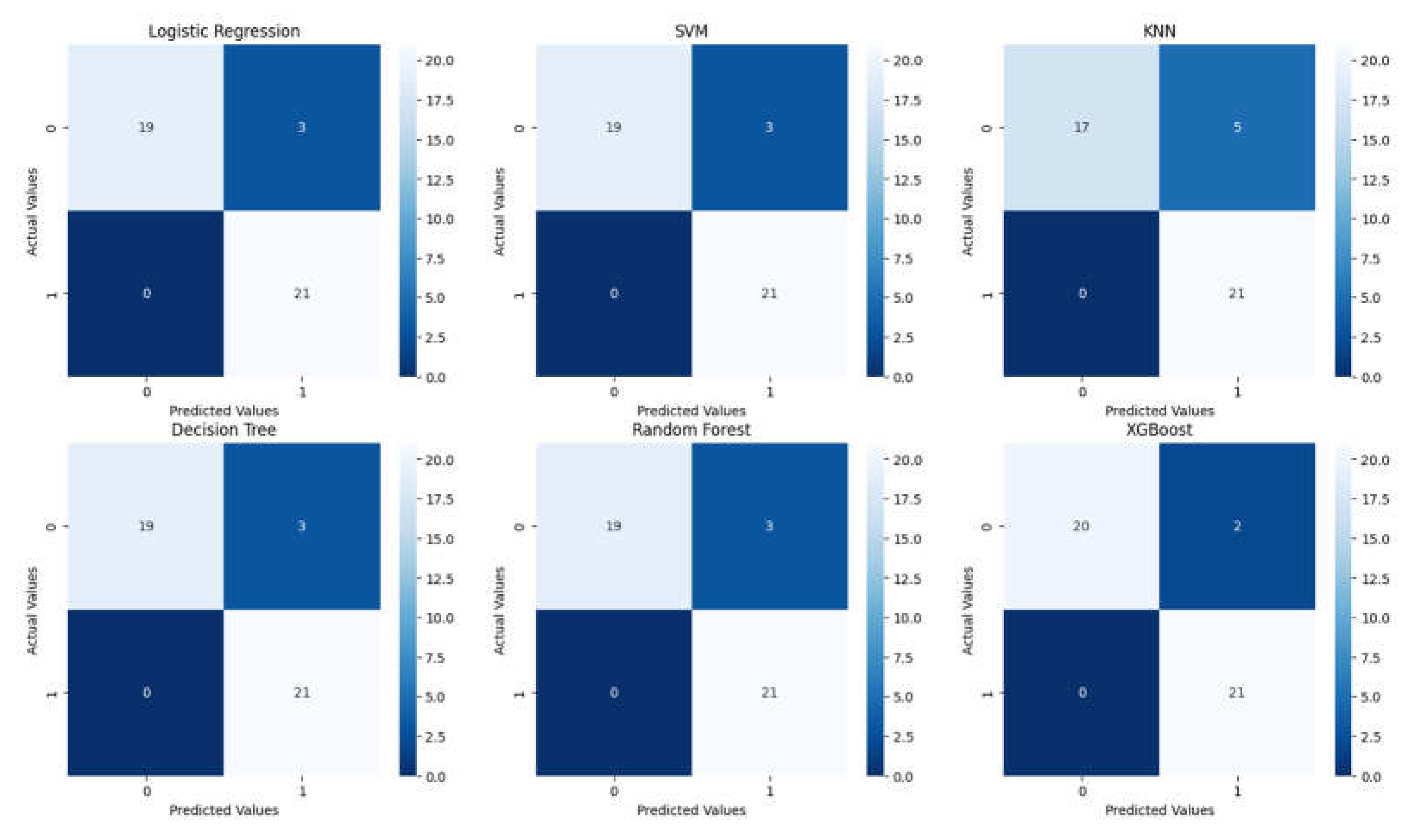
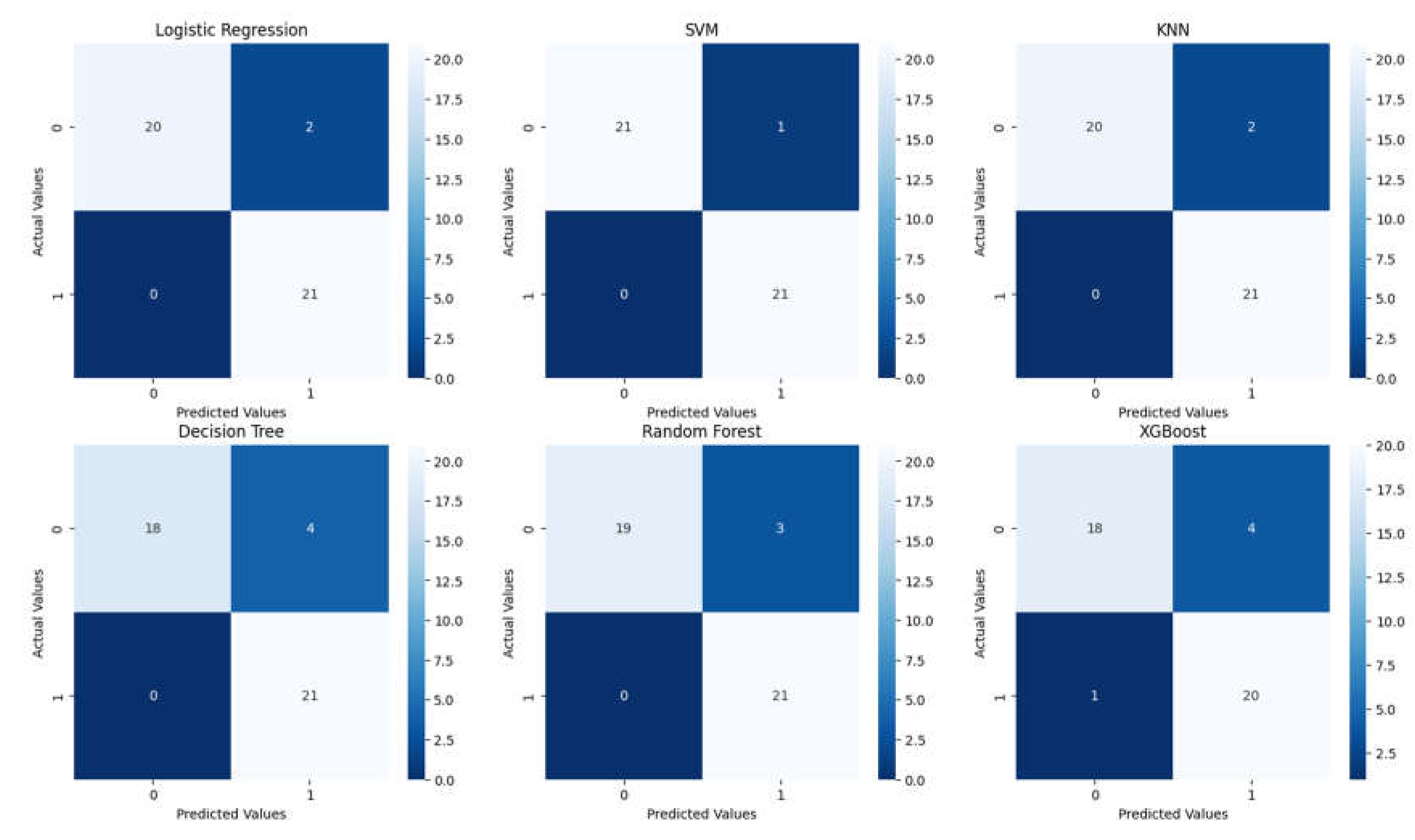
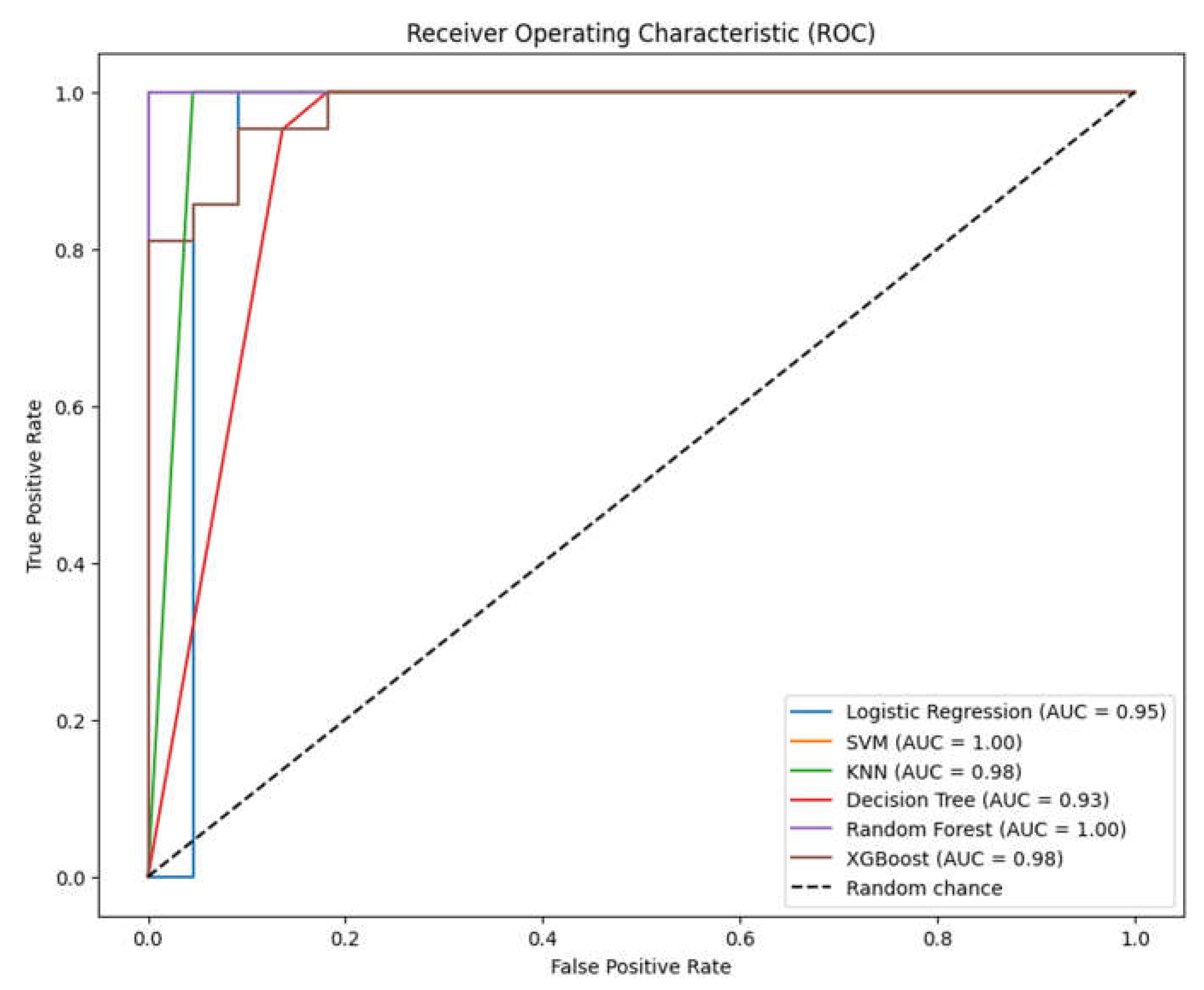
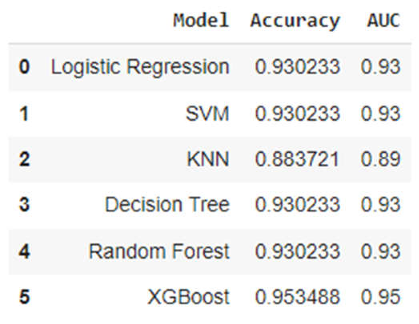
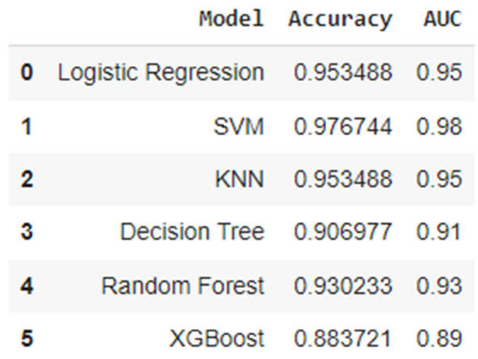
3.2. Analysis of ML Models
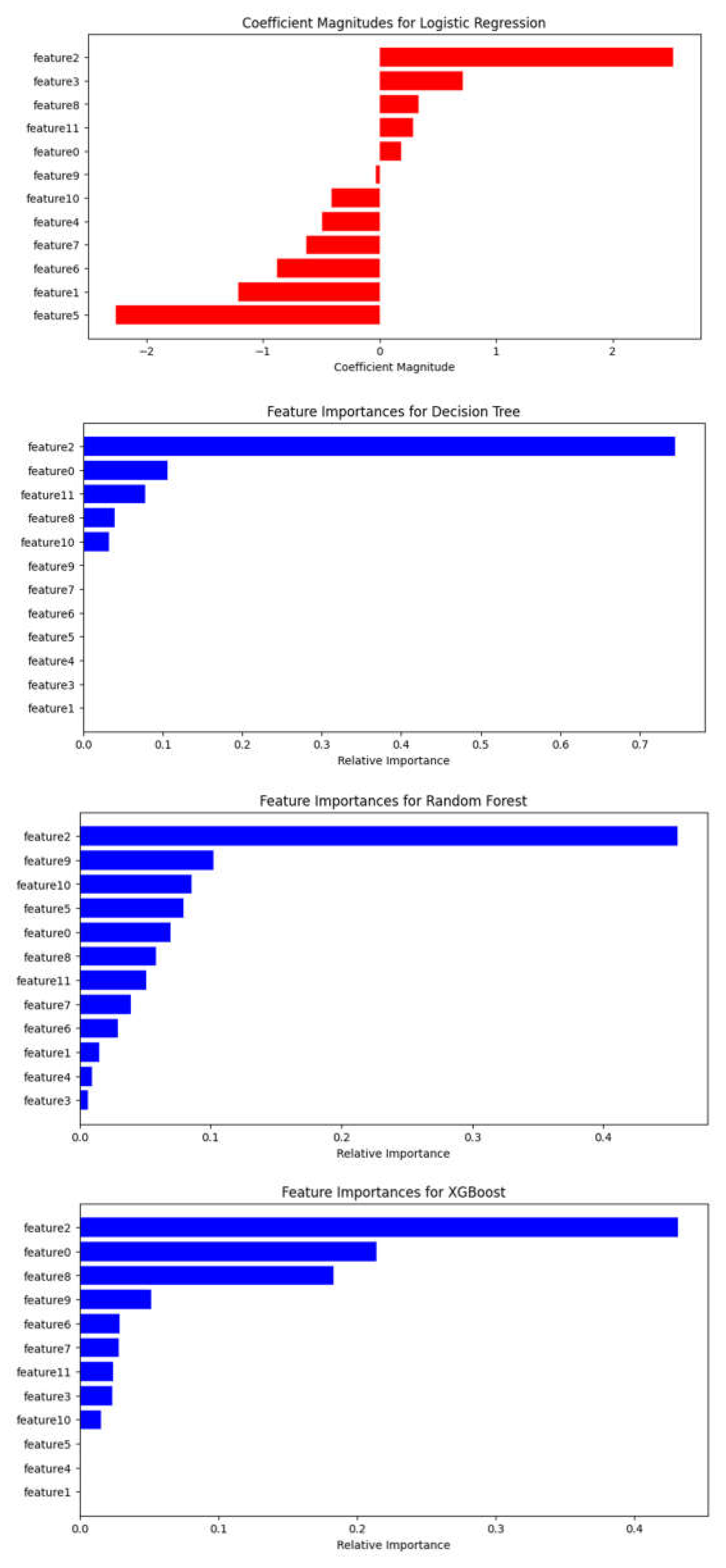
3.3. Assessment of Feature Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author contributions
References
- Berghoff, A.S.; Schur, S.; Füreder, L.M.; Gatterbauer, B.; Dieckmann, K.; Widhalm, G.; Hainfellner, J.; Zielinski, C.C.; Birner, P.; Bartsch, R.; et al. Descriptive statistical analysis of a real life cohort of 2419 patients with brain metastases of solid cancers. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markesbery, W.R.; Brooks, W.H.; Gupta, G.D.; Young, A.B. Treatment for Patients With Cerebral Metastases. Arch. Neurol. 1978, 35, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondziolka, D.; Patel, A.; Lunsford, L.; Kassam, A.; Flickinger, J.C. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 45, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Walsh, J.W.; Dempsey, R.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Young, B. A Randomized Trial of Surgery in the Treatment of Single Metastases to the Brain. New Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.G.; Choi, J.Y.; Chang, J.W.; Chung, S.S. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2001, 76, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villà, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Versus Observation After Radiosurgery or Surgical Resection of One to Three Cerebral Metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952-26001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lim, Y.K.; Min, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Gwak, H.S.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S.H. Single-Dose Versus Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 81, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, T.K.; Seol, H.J.; Im, Y.-S.; Kong, D.-S.; Nam, D.-H.; Park, K.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.-I. Fractionated Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Benign Perioptic Tumors: Outcomes of 38 Patients in a Single Institute. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2014, 2, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst-Stecken, A.; Ganslandt, O.; Lambrecht, U.; Sauer, R.; Grabenbauer, G. Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: Results and toxicity. Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 81, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim JW, Park HR, Lee JM, et al. Fractionated stereotactic gamma knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a retrospective, single center study. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0163304.
- Ewend, M.G.; Elbabaa, S.; Carey, L.A. Current Treatment Paradigms for the Management of Patients with Brain Metastases. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, S4–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.R.; Lee, M.H.; Kong, D.-S.; Seol, H.J.; Nam, D.-H.; Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K.; Kim, S.T.; et al. Outcome of gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors derived from non-small cell lung cancer. J. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 125, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1243–60.
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.; Kano, H.; Caparosa, E.; Park, S.-H.; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.; Lunsford, L.D. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for the management of cerebral metastases from non–small cell lung cancer. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.; Komaki, R. Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 2100–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linskey, M.E.; Andrews, D.W.; Asher, A.L.; Burri, S.H.; Kondziolka, D.; Robinson, P.D.; Ammirati, M.; Cobbs, C.S.; Gaspar, L.E.; Loeffler, J.S.; et al. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 96, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abacioglu, U.; Caglar, H.; Atasoy, B.M.; Abdulloev, T.; Akgun, Z.; Kilic, T. Gamma knife radiosurgery in non small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: treatment results and prognostic factors. . 2010, 15, 274–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Moon, K.-S.; Kim, I.-Y.; Jung, S.; Kim, S.-K.; Oh, I.-J.; Hong, J.-H.; Jung, T.-Y. The Tumor Control According to Radiation Dose of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Small and Medium-Sized Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2021, 64, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J.P.; Sun, M.-H.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.; Lunsford, L.D. Radiosurgery for non—small cell lung carcinoma metastatic to the brain: long-term outcomes and prognostic factors influencing patient survival time and local tumor control. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.-P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.P.; Rodrigus, P.; Terhaard, C.; Rao, A.; Suh, J.; Roa, W.; Souhami, L.; Bezjak, A.; Leibenhaut, M.; Komaki, R.; et al. Survival and Neurologic Outcomes in a Randomized Trial of Motexafin Gadolinium and Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy in Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakibuzzaman, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Mahmud, S.; Afroze, T.; Fathma, S.; Zakia, U.B.; Afroz, S.; Zafar, F.; Hossain, M.; Barua, A.; Akter, S.; et al. Pathology of breast cancer metastasis and a view of metastasis to the brain. Int. J. Neurosci. 2023, 133, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarria, P.; Minniti, G.; Clerici, E.; Comito, T.; Cozzi, S.; Pinzi, V.; Fariselli, L.; Ciammella, P.; Scoccianti, S.; Borzillo, V.; et al. Brain metastases from primary colorectal cancer: is radiosurgery an effective treatment approach? Results of a multicenter study of the radiation and clinical oncology Italian association (AIRO). Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DE LA Pinta, C. Radiotherapy in Prostate Brain Metastases: A Review of the Literature. Anticancer. Res. 2023, 43, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambhvani, H.P.; Greenberg, D.R.; Srinivas, S.; Gephart, M.H. Prostate Cancer Brain Metastases: A Single -Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2020, 138, E445–E449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathiou, G.; Camy, F.; Chauleur, C.; Dridi, M.; Col, P.D.; Peoc’h, M. Brain Metastases from Gynecologic Malignancies. Medicina 2022, 58, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrard, J.; Tison, T.; Grisay, G.; Seront, E. Global management of brain metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2022, 171, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, A.; Kosecoff, J.; Chassin, M.; Brook, R.H. Consensus methods: characteristics and guidelines for use. Am. J. Public Heal. 1984, 74, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putora, P.M.; Panje, C.M.; Papachristofilou, A.; Pra, A.D.; Hundsberger, T.; Plasswilm, L. Objective consensus from decision trees. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorelec, V.; Kokol, P.; Stiglic, B.; Rozman, I. Decision Trees: An Overview and Their Use in Medicine. J. Med Syst. 2002, 26, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg SL. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning by J. Ross Quinlan. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. 1993;16:235–240.
- Alabi, R.O.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Pirinen, M.; Elmusrati, M.; Leivo, I.; Almangush, A. Comparison of nomogram with machine learning techniques for prediction of overall survival in patients with tongue cancer. Int. J. Med Informatics 2020, 145, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schag, C.C.; Heinrich, R.L.; A Ganz, P. Karnofsky performance status revisited: reliability, validity, and guidelines. J. Clin. Oncol. 1984, 2, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J. The Linear-Quadratic Model Is an Appropriate Methodology for Determining Isoeffective Doses at Large Doses Per Fraction. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 18, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.F. The linear-quadratic formula and progress in fractionated radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 1989, 62, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Serizawa, T.; Nagano, O.; Matsuda, S.; Ono, J.; Sato, M.; Iwadate, Y.; Saeki, N. Three-Staged Stereotactic Radiotherapy Without Whole Brain Irradiation for Large Metastatic Brain Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 74, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; Bautista, M.A.; Gonzàlez, J.; Escalera, S. Beyond one-hot encoding: Lower dimensional target embedding. Image Vis. Comput. 2018, 75, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. Learning from Imbalanced Data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2009, 634 21(9), pp. 1263–1284.
- by Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer, W. P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. 636 Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 2002, 16, pp. 321–357. 637.
- Batista, G. E.; Prati, R. C.; Monard, M. C. Class Imbalance Problem in Data Mining: Review. ACM SIGKDD Explorations News- 638 letter 2004, 6(1), pp. 1–10.
- Elkan, C. Cost-Sensitive Learning and the Class Imbalance Problem. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on 640 Machine Learning (ICML); 2000; pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Sun, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, C. A systematic study of the class imbalance problem in convolutional 642 neural networks. Neural Networks 2019, 110, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Raschka, S.; Patterson, J.; Nolet, C. Machine Learning in Python: Main Developments and Technology Trends in Data Science, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence. Information 2020, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Noi, P.; Kappas, M. Comparison of Random Forest, k-Nearest Neighbor, and Support Vector Machine Classifiers for Land Cover Classification Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberioon, M.; Císař, P.; Labbé, L.; Souček, P.; Pelissier, P.; Kerneis, T. Comparative Performance Analysis of Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, Logistic Regression and k-Nearest Neighbours in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Classification Using Image-Based Features. Sensors 2018, 18, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T., & Guestrin, C., XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 2016; 785-94.
- Altmann, A.; Toloşi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. Permutation importance: a corrected feature importance measure. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneed, P.K.; Mendez, J.; Vemer-van den Hoek, J.G.M.; Seymour, Z.A.; Ma, L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Fogh, S.E.; Nakamura, J.L.; McDermott, M.W.; Sperduto, P.W.; Philips, T.G. Adapting the Predictive Power of the Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Can Machine Learning Improve Outcomes? International Journal of Radiation Oncology 2016, 96, 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.J.; Yao, X.; Dixit, S.; Warner, E.T.; Chappell, R.J. Deep Learning Predictive Models for Patient Survival Prediction in Brain Metastasis after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Vallières, M.; Bai, H.X.; Su, C.; Tang, H.; Oldridge, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, B.; Liao, W.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, P. MRI Features Predict Survival and Molecular Markers in Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer: A Machine Learning Approach. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2019, 37, 999–1006. [Google Scholar]
- El Naqa, I.; Pater, P.; Seuntjens, J. Machine Learning Algorithms in Radiation Therapy Planning and Delivery. Medical Physics 2017, 44, e391–e412. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Wright, J.; Chetty, I.J. Machine Learning for Improved Decision-Making in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Planning. Radiation Oncology 2020, 15, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Stojadinovic, S.; Hrycushko, B.; Wardak, Z.; Lau, S.; Lu, W.; Yan, Y.; Timmerman, R.; Nedzi, L.; Jiang, S. Machine Learning-Based Treatment Margin Optimization for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2021, 66, 045006. [Google Scholar]
- Mayinger, M.; Kraft, J.; Lasser, T.; Rackerseder, J.; Schichor, C.; Thon, N. The Future of Personalized Medicine in Oncology: A Digital Revolution for the Development of Precision Therapies. Cancer Research 2020, 80, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, A.T.; Bhatt, A.A.; Fink, K.R.; Lo, S.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Chao, S.T. Integrating Machine Learning and Genomics in Precision Oncology: Current Status and Future Directions. Nature Medicine 2021, 27, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, R.; Kawashima, M.; Segawa, M.; Tsunoda, S.; Inoue, T.; Akabane, A. Fractionated versus staged gamma knife radiosurgery for mid-to-large brain metastases: a propensity score-matched analysis. J. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 164, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 77 |
| Age(yr) Median (range) |
64(39-85) |
| Sex Male(%) Female(%) |
45(58.44%) 32(41.56%) |
| C1yr – control over one year (cm3) Median(range) |
17 missing data* 0.9(0-30) |
| Patience with extra cranial MTS |
6 missing data* 54 |
| Receiving pre-treatment, systemic treatment | 68 |
| Deceased before 1 year | 1 missing data* 25 |
| KPS score 100 90 80 70 |
9 missing data (11.69%)* 26(33.77%) 8(10.39%) 22(28.57%) 12(15.58%) |
| The number of lesions Median(range) 1-3 4-6 7-10 >10 |
2(1-30) 52 12 8 5 |
| Beam on time on V1 (min/cm3) Median(range) |
0.82(0.47-2.33) |
| Beam on time on V2 (min/cm3) Median(range) |
1 missing data* 0.83(0.60-3.00) |
| Beam on time on V3 (min/cm3) Median(range) |
2 missing data* 0.83(0.46-4.00) |
| Total tumor volume (# of patients with) : < 5 cm3 <= 10 cm3 > 10 cm3 |
34 13 30 |
| Tumor dynamics (# of patients with) : - Progression - Regression |
6 71 |
| Feature | Feature number |
Description | Categorical/numeric data for machine learning algorithm |
Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0 | Age at time of treated GKRS | No categorical | Discrete |
| Sex | 1 | Biological sex | 0 = Female; 1 = Male Label encoding |
Numeric |
| C1yr – control over one year | 2 | Volume of lesion measured at the 1 year control | No categorical | Numeric |
| Patience with extra cranial MTS | 3 | Patients having detected with extracranial metastases | 0 = No; 1 = Yes Label encoding |
Numeric |
| Receiving pre-treatment | 4 | Before GKRS, treated by surgery or radiotherapy, or performed chemotherapy | 0 = No pretreatment; 1 = Pretreatment Label encoding |
Numeric |
| Deceased before 1 year | 5 | Patients who passed away before 1 year after receiving GKRS | 0 = Alive; 1 = Deceased Label encoding |
Numeric |
| KPS score | 6 | KPS score runs from 0 to 100. Three physicians allow to evaluate the patient ability to receive GKS for BM. |
No categorical | Numeric |
| The number of lesions | 7 | This divided the 4 groups from the number of lesions. | No categorical | Discrete |
| Beam on time on V1 | 8 | The beam on time on V1 treated over the number of isocenters in V1 | No categorical | Numeric |
| Beam on time on V2 | 9 | The beam on time on V2 treated over the number of isocenters in V2 | No categorical | Numeric |
| Beam on time on V3 | 10 | The beam on time on V3 treated over the number of isocenters in V3 | No categorical | Numeric |
| Total tumor volume | 11 | This divided the 3 groups from the number of volumes. | No categorical | Numeric |
| Tumor dynamics | Label | Tumor progression or regression within 3 months following GKRS treatment. | 0 = Regression; 1 = Progression |
Discrete |
| Classification Report for Logistic Regression | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.93 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| Classification Report for SVM | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.93 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| Classification Report for KNN | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.77 | 0.87 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.88 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 43 |
| Classification Report for Decision Tree | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.93 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| Classification Report for Random Forest | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.93 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 43 |
| Classification Report for XGBoost | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.95 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| Classification Report for Logistic Regression | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.95 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| Classification Report for SVM | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.98 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 43 |
| Classification Report for KNN | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.95 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| Classification Report for Decision Tree | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.91 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 43 |
| Classification Report for Random Forest | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.95 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 43 |
| Classification Report for XGBoost | ||||
| precision | recall | F1-score | Support | |
| 0 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 22 |
| 1 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 21 |
| accuracy | 0.88 | 43 | ||
| macro avg | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 43 |
| weighted avg | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




