Submitted:
04 May 2024
Posted:
06 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the untreatable enemy of modern medicine
- A plethora of virulence factors in P. aeruginosa
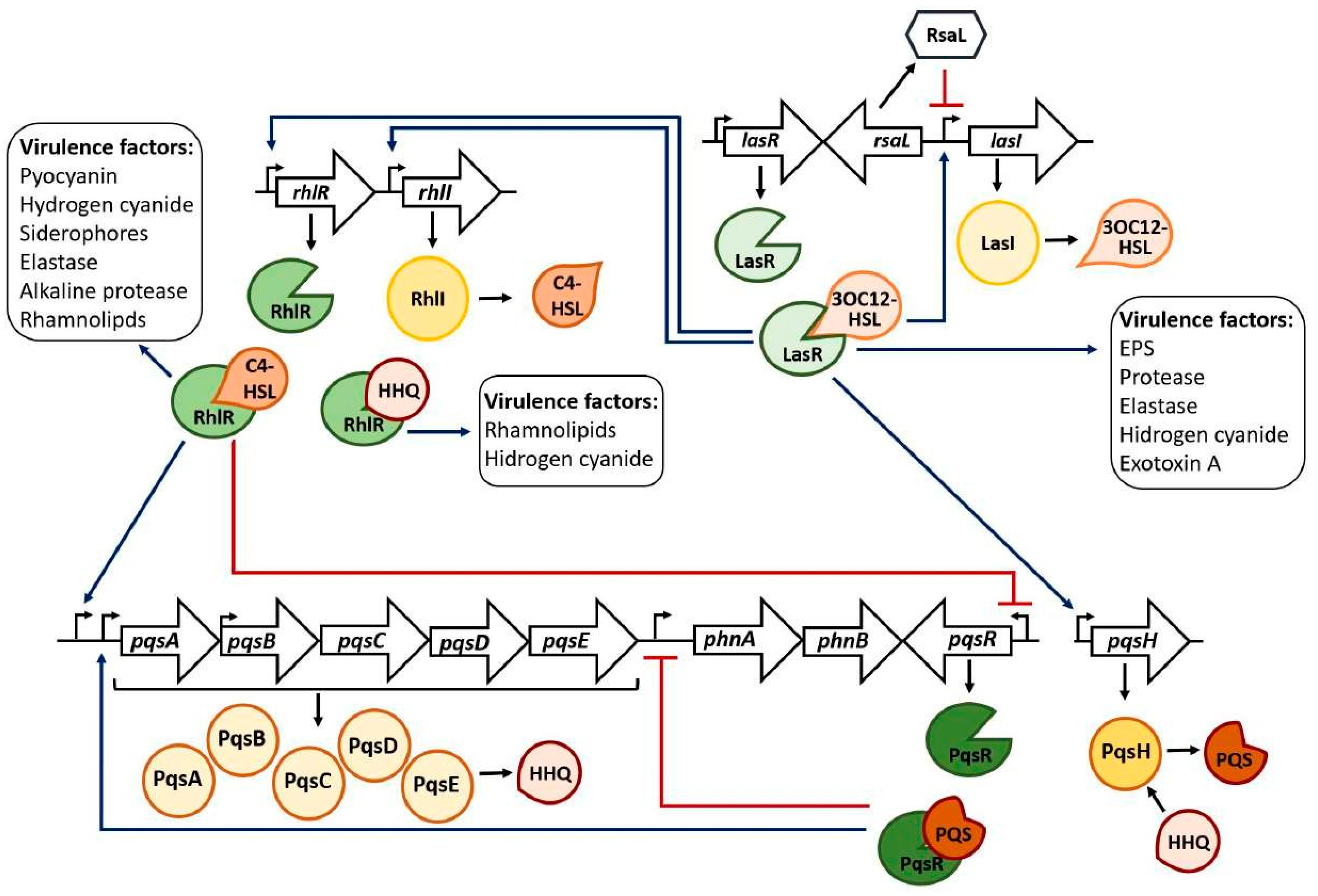
- Quorum Sensing systems and the regulation of the bacterial physiology
- Three QS systems coexist in P. aeruginosa
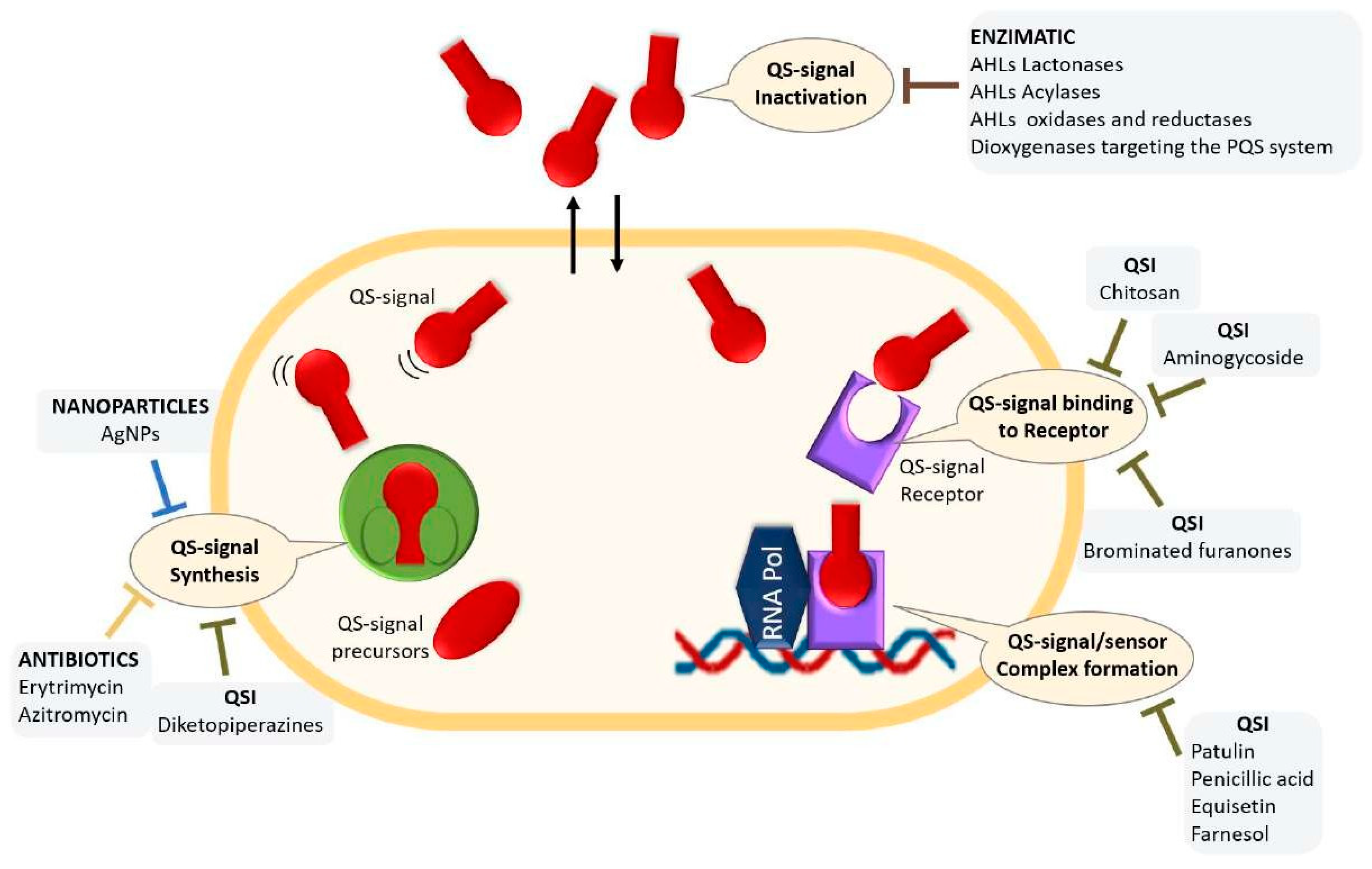
- The therapeutic potential of Quorum Quenching in the age of antibiotic resistance
- Quorum Quenching enzymes
- AHL lactonases
- AHL acylases
- AHL oxidases and oxidoreductases
- Dioxygenases targeting the PQS signals
- QS inhibitors (QSIs)
- Natural QSIs
- Synthetic QSIs
- Combination therapy for treatment of Pseudomonas infections
References
- Ahmed, S. A., Rudden, M., Smyth, T. J., Dooley, J. S., Marchant, R., & Banat, I. M. (2019). Natural quorum sensing inhibitors effectively downregulate gene expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 103, 3521-3535. [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. G., Ansari, M. A., Sajid Jamal, Q. M., Khan, H. M., Jalal, M., Ahmad, H., & Mahdi, A. A. (2017). Antiquorum sensing activity of silver nanoparticles in P. aeruginosa: an in silico study. In Silico Pharmacology, 5, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Allen, L., Dockrell, D. H., Pattery, T., Lee, D. G., Cornelis, P., Hellewell, P. G., & Whyte, M. K. (2005). Pyocyanin production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces neutrophil apoptosis and impairs neutrophil-mediated host defenses in vivo. The Journal of Immunology, 174(6), 3643-3649. [CrossRef]
- Anandan, K., & Vittal, R. R. (2019). Quorum quenching activity of AiiA lactonase KMMI17 from endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis KMCL07 on AHL-mediated pathogenic phenotype in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbial pathogenesis, 132, 230-242. [CrossRef]
- Arranz San Martín, A., Vogel, J., Wullich, S. C., Quax, W. J., & Fetzner, S. (2022). Enzyme-mediated quenching of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS): A comparison between naturally occurring and engineered PQS-cleaving dioxygenases. Biomolecules, 12(2), 170. [CrossRef]
- Aybey, A., & Demirkan, E. (2016). Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human serum paraoxonase. Journal of medical microbiology, 65(2), 105-113. [CrossRef]
- Bahari, S., Zeighami, H., Mirshahabi, H., Roudashti, S., & Haghi, F. (2017). Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by subinhibitory concentrations of curcumin with gentamicin and azithromycin. Journal of global antimicrobial resistance, 10, 21-28. [CrossRef]
- Bala, A., Kumar, R., & Harjai, K. (2011). Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by azithromycin and its effectiveness in urinary tract infections. Journal of medical microbiology, 60(3), 300-306. [CrossRef]
- Bar-Rogovsky, H., Hugenmatter, A., & Tawfik, D. S. (2013). The evolutionary origins of detoxifying enzymes: the mammalian serum paraoxonases (PONs) relate to bacterial homoserine lactonases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(33), 23914-23927.
- Bijtenhoorn, P., Mayerhofer, H., Müller-Dieckmann, J., Utpatel, C., Schipper, C., Hornung, C., ... & Streit, W. R. (2011). A novel metagenomic short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence on Caenorhabditis elegans. PloS one, 6(10), e26278. [CrossRef]
- Birmes, F. S., Wolf, T., Kohl, T. A., Rüger, K., Bange, F., Kalinowski, J., & Fetzner, S. (2017). Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus is capable of degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signals. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 339. [CrossRef]
- Bobadilla Fazzini, R. A., Skindersoe, M. E., Bielecki, P., Puchałka, J., Givskov, M., & Martins dos Santos, V. A. (2013). Protoanemonin: a natural quorum sensing inhibitor that selectively activates iron starvation response. Environmental Microbiology, 15(1), 111-120. [CrossRef]
- Bodini, S. F., Manfredini, S., Epp, M., Valentini, S., & Santori, F. (2009). Quorum sensing inhibition activity of garlic extract and p-coumaric acid. Letters in applied microbiology, 49(5), 551-555.
- Buroni, S., Scoffone, V. C., Fumagalli, M., Makarov, V., Cagnone, M., Trespidi, G., ... & Chiarelli, L. R. (2018). Investigating the mechanism of action of diketopiperazines inhibitors of the Burkholderia cenocepacia quorum sensing synthase CepI: a site-directed mutagenesis study. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 400679. [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J., Harjai, K., & Chhibber, S. (2022). Revisiting the virulence hallmarks of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chronicle through the perspective of quorum sensing. Environmental microbiology, 24(6), 2630-2656 . [CrossRef]
- Chanda, W., Joseph, T. P., Padhiar, A. A., Guo, X., Min, L., Wang, W., ... & Zhong, M. (2017). Combined effect of linolenic acid and tobramycin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and quorum sensing. Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 14(5), 4328-4338. [CrossRef]
- Choo, J. H., Rukayadi, Y., & Hwang, J. K. (2006). Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing by vanilla extract. Letters in applied microbiology, 42(6), 637-641. [CrossRef]
- Chow, J. Y., Xue, B., Lee, K. H., Tung, A., Wu, L., Robinson, R. C., & Yew, W. S. (2010). Directed evolution of a thermostable quorum-quenching lactonase from the amidohydrolase superfamily. Journal of biological chemistry, 285(52), 40911-40920. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, P. K., Keshavan, N., Nguyen, H. Q., Peterson, J. A., González, J. E., & Haines, D. C. (2007). Bacillus megaterium CYP102A1 oxidation of acyl homoserine lactones and acyl homoserines. Biochemistry, 46(50), 14429-14437. [CrossRef]
- Cugini, C., Calfee, M. W., Farrow III, J. M., Morales, D. K., Pesci, E. C., & Hogan, D. A. (2007). Farnesol, a common sesquiterpene, inhibits PQS production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecular microbiology, 65(4), 896-906.
- Czajkowski, R., Krzyżanowska, D., Karczewska, J., Atkinson, S., Przysowa, J., Lojkowska, E., ... & Jafra, S. (2011). Inactivation of AHLs by Ochrobactrum sp. A44 depends on the activity of a novel class of AHL acylase. Environmental microbiology reports, 3(1), 59-68. [CrossRef]
- D'almeida, R. E., Molina, R. D. I., Viola, C. M., Luciardi, M. C., Peñalver, C. N., Bardón, A., & Arena, M. E. (2017). Comparison of seven structurally related coumarins on the inhibition of quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum. Bioorganic chemistry, 73, 37-42. [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W. H., & Borm, P. J. (2008). Drug delivery and nanoparticles: applications and hazards. International journal of nanomedicine, 3(2), 133-149.
- Díaz, M. A., González, S. N., Alberto, M. R., & Arena, M. E. (2020). Human probiotic bacteria attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm and virulence by quorum-sensing inhibition. Biofouling, 36(5), 597-609.
- Dong, W., Zhu, J., Guo, X., Kong, D., Zhang, Q., Zhou, Y., ... & Ruan, Z. (2018). Characterization of AiiK, an AHL lactonase, from Kurthia huakui LAM0618T and its application in quorum quenching on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Scientific reports, 8(1), 6013. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. H., Xu, J. L., Li, X. Z., & Zhang, L. H. (2000). AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(7), 3526-3531.
- Faisal, A. J., Said, L. A., & Ali, M. R. (2021). Quorum quenching effect of recombinant Paraoxonase-1 enzyme against quorum sensing genes produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene Reports, 25, 101412. [CrossRef]
- Fan, X., Liang, M., Wang, L., Chen, R., Li, H., & Liu, X. (2017). Aii810, a novel cold-adapted N-acylhomoserine lactonase discovered in a metagenome, can strongly attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors and biofilm formation. Frontiers in microbiology, 8, 1950. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R., Roy, V., Wu, H. C., & Bentley, W. E. (2010). Engineered biological nanofactories trigger quorum sensing response in targeted bacteria. Nature nanotechnology, 5(3), 213-217. [CrossRef]
- Fetzner, S. (2015). Quorum quenching enzymes. Journal of biotechnology, 201, 2-14. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, L. A., & Manoil, C. (2001). Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 kills Caenorhabditis elegans by cyanide poisoning. Journal of bacteriology, 183(21), 6207-6214. [CrossRef]
- García-Lara, B., Saucedo-Mora, M. Á., Roldán-Sánchez, J. A., Pérez-Eretza, B., Ramasamy, M., Lee, J., ... & García-Contreras, R. (2015). Inhibition of quorum-sensing-dependent virulence factors and biofilm formation of clinical and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains by ZnO nanoparticles. Letters in applied microbiology, 61(3), 299-305. [CrossRef]
- García-Reyes, S., Soberón-Chávez, G., & Cocotl-Yanez, M. (2020). The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein. Journal of medical microbiology, 69(1), 25-34.
- Ghafoor, A., Hay, I. D., & Rehm, B. H. (2011). Role of exopolysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and architecture. Applied and environmental microbiology, 77(15), 5238-5246. [CrossRef]
- Girennavar, B., Cepeda, M. L., Soni, K. A., Vikram, A., Jesudhasan, P., Jayaprakasha, G. K., ... & Patil, B. S. (2008). Grapefruit juice and its furocoumarins inhibits autoinducer signaling and biofilm formation in bacteria. International journal of food microbiology, 125(2), 204-208. [CrossRef]
- Goh, E. B., Yim, G., Tsui, W., McClure, J., Surette, M. G., & Davies, J. (2002). Transcriptional modulation of bacterial gene expression by subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(26), 17025-17030. [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C., Tannières, M., Moréra, S., Dessaux, Y., & Faure, D. (2016). Quorum quenching: role in nature and applied developments. FEMS microbiology reviews, 40(1), 86-116. [CrossRef]
- Hall, S., McDermott, C., Anoopkumar-Dukie, S., McFarland, A. J., Forbes, A., Perkins, A. V., & Grant, G. D. (2016). Cellular effects of pyocyanin, a secreted virulence factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins, 8(8), 236.
- Hemmati, F., Salehi, R., Ghotaslou, R., Samadi Kafil, H., Hasani, A., Gholizadeh, P., ... & Ahangarzadeh Rezaee, M. (2020). Quorum quenching: A potential target for antipseudomonal therapy. Infection and Drug Resistance, 2989-3005. [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M., Wu, H., Andersen, J. B., Riedel, K., Rasmussen, T. B., Bagge, N., ... & Givskov, M. (2003). Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. The EMBO journal, 22(15), 3803-3815. [CrossRef]
- Heydrnejad, M. S., Samani, R. J., & Aghaeivanda, S. (2015). Toxic effects of silver nanoparticles on liver and some hematological parameters in male and female mice (Mus musculus). Biological trace element research, 165, 153-158. [CrossRef]
- Hiblot, J., Bzdrenga, J., Champion, C., Chabriere, E., & Elias, M. (2015). Crystal structure of Vmo lac, a tentative quorum quenching lactonase from the extremophilic crenarchaeon Vulcanisaeta moutnovskia. Scientific reports, 5(1), 8372. [CrossRef]
- Holden, M. T., Ram Chhabra, S., De Nys, R., Stead, P., Bainton, N. J., Hill, P. J., & Williams, P. (1999). Quorum-sensing cross talk: isolation and chemical characterization of cyclic dipeptides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative bacteria. Molecular microbiology, 33(6), 1254-1266. [CrossRef]
- Hraiech, S., Hiblot, J., Lafleur, J., Lepidi, H., Papazian, L., Rolain, J. M., & Chabriere, E. (2014). Inhaled lactonase reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing and mortality in rat pneumonia. PLoS One, 9(10), e107125. [CrossRef]
- Husain, F. M., Ahmad, I., Asif, M., & Tahseen, Q. (2013). Influence of clove oil on certain quorum-sensing-regulated functions and biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas hydrophila. Journal of biosciences, 38, 835-844. [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T. H., Bragason, S. K., Phipps, R. K., Christensen, L. D., van Gennip, M., Alhede, M., ... & Givskov, M. (2012). Food as a source for quorum sensing inhibitors: iberin from horseradish revealed as a quorum sensing inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Applied and environmental microbiology, 78(7), 2410-2421. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, V., Löns, D., Zaoui, C., Bredenbruch, F., Meissner, A., Dieterich, G., ... & Häussler, S. (2006). RhlR expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is modulated by the Pseudomonas quinolone signal via PhoB-dependent and-independent pathways. Journal of bacteriology, 188(24), 8601-8606.
- Kalia, V. C., Patel, S. K., Kang, Y. C., & Lee, J. K. (2019). Quorum sensing inhibitors as antipathogens: biotechnological applications. Biotechnology advances, 37(1), 68-90.
- Kang, D., Revtovich, A. V., Chen, Q., Shah, K. N., Cannon, C. L., & Kirienko, N. V. (2019). Pyoverdine-dependent virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Frontiers in microbiology, 10, 2048. [CrossRef]
- Kariyawasam, R. M., Julien, D. A., Jelinski, D. C., Larose, S. L., Rennert-May, E., Conly, J. M., ... & Barkema, H. W. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis (November 2019–June 2021). Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control, 11(1), 45. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F., Lee, J. W., Javaid, A., Park, S. K., & Kim, Y. M. (2020). Inhibition of biofilm and virulence properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by sub-inhibitory concentrations of aminoglycosides. Microbial Pathogenesis, 146, 104249. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F., Pham, D. T. N., & Kim, Y. M. (2020). Alternative strategies for the application of aminoglycoside antibiotics against the biofilm-forming human pathogenic bacteria. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 104, 1955-1976. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. S. A., Zahin, M., Hasan, S., Husain, F. M., & Ahmad, I. (2009). Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Letters in applied microbiology, 49(3), 354-360. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. S., Lee, S. H., Byun, Y., & Park, H. D. (2015). 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Scientific reports, 5(1), 8656. [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S., Sharma, P., Harjai, K., & Capalash, N. (2011). Enzymatic quorum quenching increases antibiotic susceptibility of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Iranian Journal of Microbiology, 3(1), 1.
- Kusada, H., Tamaki, H., Kamagata, Y., Hanada, S., & Kimura, N. (2017). A novel quorum-quenching N-acylhomoserine lactone acylase from Acidovorax sp. strain MR-S7 mediates antibiotic resistance. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 83(13), e00080-17.
- LaSarre, B., & Federle, M. J. (2013). Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews, 77(1), 73-111. [CrossRef]
- Last, D., Krüger, G. H., Dörr, M., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2016). Fast, continuous, and high-throughput (bio) chemical activity assay for N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone quorum-quenching enzymes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 82(14), 4145-4154.
- Leadbetter, J. R., & Greenberg, E. P. (2000). Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. Journal of bacteriology, 182(24), 6921-6926. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. H., Kim, N. H., Jang, K. M., Jin, H., Shin, K., Jeong, B. C., ... & Lee, S. H. (2023). Prioritization of Critical Factors for Surveillance of the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15209. [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y. H., Ng, A. M., Xu, X., Shen, Z., Gethings, L. A., Wong, M. T., ... & Leung, F. C. (2014). Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of MgO: non-ROS mediated toxicity of MgO nanoparticles towards Escherichia coli. Small, 10(6), 1171-1183. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Huang, J., Li, L., & Liu, L. (2017). Synergistic activity of berberine with azithromycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis of lung in vitro and in vivo. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(4), 1657-1669. [CrossRef]
- Liao, C., Huang, X., Wang, Q., Yao, D., & Lu, W. (2022). Virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and antivirulence strategies to combat its drug resistance. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 12, 926758. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. H., Xu, J. L., Hu, J., Wang, L. H., Ong, S. L., Leadbetter, J. R., & Zhang, L. H. (2003). Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Ralstonia strain XJ12B represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Molecular microbiology, 47(3), 849-860.
- López-Jácome, L. E., Garza-Ramos, G., Hernández-Durán, M., Franco-Cendejas, R., Loarca, D., Romero-Martínez, D., ... & García-Contreras, R. (2019). AiiM lactonase strongly reduces quorum sensing controlled virulence factors in clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burned patients. Frontiers in microbiology, 10, 2657. [CrossRef]
- Malešević, M., Stanisavljević, N., Novović, K., Polović, N., Vasiljević, Z., Kojić, M., & Jovčić, B. (2020). Burkholderia cepacia YtnP and Y2-aiiA lactonases inhibit virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via quorum quenching activity. Microbial Pathogenesis, 149, 104561. [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, D., Grossmann, G., Séquin, U., Brandl, H., & Bachofen, R. (2004). Effects of natural and chemically synthesized furanones on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum. BMC microbiology, 4, 1-10.
- McClure, C. D., & Schiller, N. L. (1996). Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids in vitro and in vivo. Current microbiology, 33, 109-117. [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, J. S., Groenaga Infante, H., Stokes, E., & Shaw, A. M. (2012). Silver nanoparticle enhanced silver ion stress response in Escherichia coli K12. Nanotoxicology, 6(8), 857-866. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J. M., Neely, A., Stintzi, A., Georges, C., & Holder, I. A. (1996). Pyoverdin is essential for virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infection and immunity, 64(2), 518-523. [CrossRef]
- Müller, C., Birmes, F. S., Rückert, C., Kalinowski, J., & Fetzner, S. (2015). Rhodococcus erythropolis BG43 genes mediating Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal degradation and virulence factor attenuation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(22), 7720-7729. [CrossRef]
- Muslim, S. N., Kadmy, I. M. A., Ali, A. N. M., Salman, B. K., Ahmad, M., Khazaal, S. S., ... & Muslim, S. N. (2018). Chitosan extracted from Aspergillus flavus shows synergistic effect, eases quorum sensing mediated virulence factors and biofilm against nosocomial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International journal of biological macromolecules, 107, 52-58.
- Nafee, N., Husari, A., Maurer, C. K., Lu, C., de Rossi, C., Steinbach, A., ... & Schneider, M. (2014). Antibiotic-free nanotherapeutics: ultra-small, mucus-penetrating solid lipid nanoparticles enhance the pulmonary delivery and anti-virulence efficacy of novel quorum sensing inhibitors. Journal of Controlled Release, 192, 131-140. [CrossRef]
- Nazari, Z. E., Banoee, M., Sepahi, A. A., Rafii, F., & Shahverdi, A. R. (2012). The combination effects of trivalent gold ions and gold nanoparticles with different antibiotics against resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gold Bulletin, 45, 53-59. [CrossRef]
- Ng, F. S., Wright, D. M., & Seah, S. Y. (2011). Characterization of a phosphotriesterase-like lactonase from Sulfolobus solfataricus and its immobilization for disruption of quorum sensing. Applied and environmental microbiology, 77(4), 1181-1186. [CrossRef]
- Nithya, C., Devi, M. G., & Karutha Pandian, S. (2011). A novel compound from the marine bacterium Bacillus pumilus S6-15 inhibits biofilm formation in gram-positive and gram-negative species. Biofouling, 27(5), 519-528.
- Oliver, A., Cantón, R., Campo, P., Baquero, F., & Blázquez, J. (2000). High frequency of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis lung infection. Science, 288(5469), 1251-1253. [CrossRef]
- Ozer, E. A., Pezzulo, A., Shih, D. M., Chun, C., Furlong, C., Lusis, A. J., ... & Zabner, J. (2005). Human and murine paraoxonase 1 are host modulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing. FEMS microbiology letters, 253(1), 29-37. [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K., & Bassler, B. L. (2016). Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14(9), 576-588.
- Pujalté, I., Passagne, I., Brouillaud, B., Tréguer, M., Durand, E., Ohayon-Courtès, C., & L'Azou, B. (2011). Cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by different metallic nanoparticles on human kidney cells. Particle and fibre toxicology, 8, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Pustelny, C., Albers, A., Büldt-Karentzopoulos, K., Parschat, K., Chhabra, S. R., Cámara, M., ... & Fetzner, S. (2009). Dioxygenase-mediated quenching of quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemistry & biology, 16(12), 1259-1267. [CrossRef]
- Qais, F. A., Khan, M. S., & Ahmad, I. (2018). Nanoparticles as quorum sensing inhibitor: Prospects and limitations. Biotechnological applications of quorum sensing inhibitors, 227-244.
- Qin, S., Xiao, W., Zhou, C., Pu, Q., Deng, X., Lan, L., ... & Wu, M. (2022). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 7(1), 199. [CrossRef]
- Raafat, M. M., Ali-Tammam, M., & Ali, A. E. (2019). Quorum quenching activity of Bacillus cereus isolate 30b confers antipathogenic effects in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infection and Drug Resistance, 1583-1596. [CrossRef]
- Rajkumari, J., Borkotoky, S., Murali, A., Suchiang, K., Mohanty, S. K., & Busi, S. (2018). Cinnamic acid attenuates quorum sensing associated virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Biotechnology letters, 40, 1087-1100. [CrossRef]
- Ramadi, K. B., Mohamed, Y. A., Al-Sbiei, A., Almarzooqi, S., Bashir, G., Al Dhanhani, A., ... & Al-Ramadi, B. K. (2016). Acute systemic exposure to silver-based nanoparticles induces hepatotoxicity and NLRP3-dependent inflammation. Nanotoxicology, 10(8), 1061-1074. [CrossRef]
- Rasch, M., Buch, C., Austin, B., Slierendrecht, W. J., Ekmann, K. S., Larsen, J. L., ... & Gram, L. (2004). An inhibitor of bacterial quorum sensing reduces mortalities caused by vibriosis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 27(3), 350-359 . [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T. B., Skindersoe, M. E., Bjarnsholt, T., Phipps, R. K., Christensen, K. B., Jensen, P. O., ... & Givskov, M. (2005). Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology, 151(5), 1325-1340. [CrossRef]
- Rather, M. A., Saha, D., Bhuyan, S., Jha, A. N., & Mandal, M. (2022). Quorum quenching: a drug discovery approach against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiological Research, 264, 127173. [CrossRef]
- Reimmann, C., Ginet, N., Michel, L., Keel, C., Michaux, P., Krishnapillai, V., ... & Haas, D. (2002). Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology, 148(4), 923-932 . [CrossRef]
- Reina, J. C., Romero, M., Salto, R., Cámara, M., & Llamas, I. (2021). AhaP, A quorum quenching acylase from Psychrobacter sp. M9-54-1 that attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio coralliilyticus virulence. Marine drugs, 19(1), 16.
- Roudashti, S., Zeighami, H., Mirshahabi, H., Bahari, S., Soltani, A., & Haghi, F. (2017). Synergistic activity of sub-inhibitory concentrations of curcumin with ceftazidime and ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing related genes and virulence traits. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 33, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, T., & Bais, H. P. (2008). Curcumin, a known phenolic from Curcuma longa, attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in whole plant and animal pathogenicity models. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 56(6), 1955-1962. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D. H., Lee, S. W., Mikolaityte, V., Kim, Y. W., Jeong, H., Lee, S. J., ... & Lee, J. K. (2020). Identification of a second type of AHL-lactonase from Rhodococcus sp. BH4, belonging to the α/β hydrolase superfamily. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30(6), 937.
- Salim, S. A., Mohan, M. S., Forgia, N., & Busi, S. (2024). Medical Importance of ESKAPE Pathogens. In ESKAPE Pathogens: Detection, Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies (pp. 1-32). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Samanta, S., Singh, B. R., & Adholeya, A. (2017). Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using an ectomycorrhizal strain EM-1083 of Laccaria fraterna and its nanoanti-quorum sensing potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian journal of microbiology, 57, 448-460. [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, R., & Elias, M. (2020). Quorum quenching enzymes and their effects on virulence, biofilm, and microbiomes: a review of recent advances. Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 18(12), 1221-1233. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R., Shedbalkar, U. U., Wadhwani, S. A., & Chopade, B. A. (2015). Bacteriagenic silver nanoparticles: synthesis, mechanism, and applications. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 99, 4579-4593. [CrossRef]
- Skindersoe, M. E., Alhede, M., Phipps, R., Yang, L., Jensen, P. O., Rasmussen, T. B., ... & Givskov, M. (2008). Effects of antibiotics on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 52(10), 3648-3663. [CrossRef]
- Slavin, Y. N., Asnis, J., Hńfeli, U. O., & Bach, H. (2017). Metal nanoparticles: understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. Journal of nanobiotechnology, 15, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Sofer, D., Gilboa-Garber, N., Belz, A., & Garber, N. C. (1999). ‘Subinhibitory’erythromycin represses production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectins, autoinducer and virulence factors. Chemotherapy, 45(5), 335-341.
- Song, Z., Kong, K. F., Wu, H., Maricic, N., Ramalingam, B., Priestap, H., ... & Mathee, K. (2010). Panax ginseng has anti-infective activity against opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa by inhibiting quorum sensing, a bacterial communication process critical for establishing infection. Phytomedicine, 17(13), 1040-1046. [CrossRef]
- Tang, K. W. K., Millar, B. C., & Moore, J. E. (2023). Antimicrobial resistance (AMR). British Journal of Biomedical Science, 80, 11387.
- Tang, K., Su, Y., Brackman, G., Cui, F., Zhang, Y., Shi, X., ... & Zhang, X. H. (2015). MomL, a novel marine-derived N-acyl homoserine lactonase from Muricauda olearia. Applied and environmental microbiology, 81(2), 774-782. [CrossRef]
- Tateda, K., Comte, R., Pechere, J. C., Köhler, T., Yamaguchi, K., & Van Delden, C. (2001). Azithromycin inhibits quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 45(6), 1930-1933. [CrossRef]
- Thi, M. T. T., Wibowo, D., & Rehm, B. H. (2020). Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(22), 8671.
- Thill, A., Zeyons, O., Spalla, O., Chauvat, F., Rose, J., Auffan, M., & Flank, A. M. (2006). Cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles for Escherichia coli. Physico-chemical insight of the cytotoxicity mechanism. Environmental science & technology, 40(19), 6151-6156.
- Tielen, P., Narten, M., Rosin, N., Biegler, I., Haddad, I., Hogardt, M., ... & Jahn, D. (2011). Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from urinary tract infections. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 301(4), 282-292. [CrossRef]
- Tigabu, A., & Getaneh, A. L. E. M. (2021). Staphylococcus aureus, ESKAPE Bacteria Challenging Current Health Care and Community Settings: a Literature Review. Clinical Laboratory, (7). [CrossRef]
- Tinh, N. T. N., Linh, N. D., Wood, T. K., Dierckens, K., Sorgeloos, P., & Bossier, P. (2007). Interference with the quorum sensing systems in a Vibrio harveyi strain alters the growth rate of gnotobiotically cultured rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Journal of applied microbiology, 103(1), 194-203. [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J. S., Maynard, A. D., Howard, P. C., James, J. T., Lam, C. W., Warheit, D. B., & Santamaria, A. B. (2006). Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part IV: risk assessment of nanoparticles. Toxicological sciences, 89(1), 42-50. [CrossRef]
- Uroz, S., Chhabra, S. R., Camara, M., Williams, P., Oger, P., & Dessaux, Y. (2005). N-Acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing molecules are modified and degraded by Rhodococcus erythropolis W2 by both amidolytic and novel oxidoreductase activities. Microbiology, 151(10), 3313-3322. [CrossRef]
- Vadekeetil, A., Chhibber, S., & Harjai, K. (2019). Efficacy of intravesical targeting of novel quorum sensing inhibitor nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm-associated murine pyelonephritis. Journal of drug targeting, 27(9), 995-1003.
- Vattem, D. A., Mihalik, K., Crixell, S. H., & McLean, R. J. (2007). Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia, 78(4), 302-310. [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Bucheli, R., Hormigo, D., Fernández-Lucas, J., Torres-Ayuso, P., Alfaro-Ureña, Y., Saborido, A. I., ... & de la Mata, I. (2020). Penicillin acylase from Streptomyces lavendulae and aculeacin A acylase from Actinoplanes utahensis: Two versatile enzymes as useful tools for quorum quenching processes. Catalysts, 10(7), 730. [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V. (2006). Regulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas. FEMS microbiology reviews, 30(2), 274-291. [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A., Jayaprakasha, G. K., Jesudhasan, P. R., Pillai, S. D., & Patil, B. S. (2010). Suppression of bacterial cell–cell signalling, biofilm formation and type III secretion system by citrus flavonoids. Journal of applied microbiology, 109(2), 515-527. [CrossRef]
- Vilar Junior, J. C., Ribeaux, D. R., Alves da Silva, C. A., Campos-Takaki, D., & Maria, G. (2016). Physicochemical and antibacterial properties of chitosan extracted from waste shrimp shells. International Journal of Microbiology, 2016.
- Wang, W. Z., Morohoshi, T., Someya, N., & Ikeda, T. (2012). AidC, a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the potato root-associated cytophaga-flavobacteria-bacteroides (CFB) group bacterium Chryseobacterium sp. strain StRB126. Applied and environmental microbiology, 78(22), 7985-7992. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Gong, L., Liang, S., Han, X., Zhu, C., & Li, Y. (2005). Algicidal activity of rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Harmful algae, 4(2), 433-443. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Z., Morohoshi, T., Ikenoya, M., Someya, N., & Ikeda, T. (2010). AiiM, a novel class of N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the leaf-associated bacterium Microbacterium testaceum. Applied and environmental microbiology, 76(8), 2524-2530. [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G. M. (2005). Nanoscience, nanotechnology, and chemistry. Small, 1(2), 172-179. [CrossRef]
- Williams, P., Winzer, K., Chan, W. C., & Camara, M. (2007). Look who's talking: communication and quorum sensing in the bacterial world. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 362(1483), 1119-1134. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H., Song, Z., Hentzer, M., Andersen, J. B., Molin, S., Givskov, M., & Høiby, N. (2004). Synthetic furanones inhibit quorum-sensing and enhance bacterial clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 53(6), 1054-1061. [CrossRef]
- Wullich, S. C., Arranz San Martín, A., & Fetzner, S. (2020). An α/β-hydrolase fold subfamily comprising Pseudomonas quinolone signal-cleaving dioxygenases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 86(9), e00279-20. [CrossRef]
- Yates, E. A., Philipp, B., Buckley, C., Atkinson, S., Chhabra, S. R., Sockett, R. E., ... & Williams, P. (2002). N-acylhomoserine lactones undergo lactonolysis in a pH-, temperature-, and acyl chain length-dependent manner during growth of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infection and immunity, 70(10), 5635-5646. [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S., Misba, L., & Khan, A. U. (2017). Nano-therapeutics: a revolution in infection control in post antibiotic era. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 13(7), 2281-2301. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Wang, M., Zhu, X., Yu, W., & Gong, Q. (2018). Equisetin as potential quorum sensing inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnology letters, 40, 865-870. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Brackman, G., & Coenye, T. (2017). Pitfalls associated with evaluating enzymatic quorum quenching activity: the case of MomL and its effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii biofilms. PeerJ, 5, e3251.
- Zhou, L., Zhang, Y., Ge, Y., Zhu, X., & Pan, J. (2020). Regulatory mechanisms and promising applications of quorum sensing-inhibiting agents in control of bacterial biofilm formation. Frontiers in microbiology, 11, 589640. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X., Chen, W. J., Bhatt, K., Zhou, Z., Huang, Y., Zhang, L. H., ... & Wang, J. (2023). Innovative microbial disease biocontrol strategies mediated by quorum quenching and their multifaceted applications: A review. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 1063393. [CrossRef]
- Zimper, U., Aaltonen, J., McGoverin, C. M., Gordon, K. C., Krauel-Goellner, K., & Rades, T. (2010). Quantification of process induced disorder in milled samples using different analytical techniques. Pharmaceutics, 2(1), 30-49. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




