Submitted:
01 May 2024
Posted:
02 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Sphagnum Moss Extract.
2.2. Characteristics of the Obtained Nanoparticles.
2.3. The objects of the Research.
2.4. Methods of Research on Antibacterial and Antifungal Effects.
3. Results and Discussion.
3.1. Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity of SILVER nanoparticles.
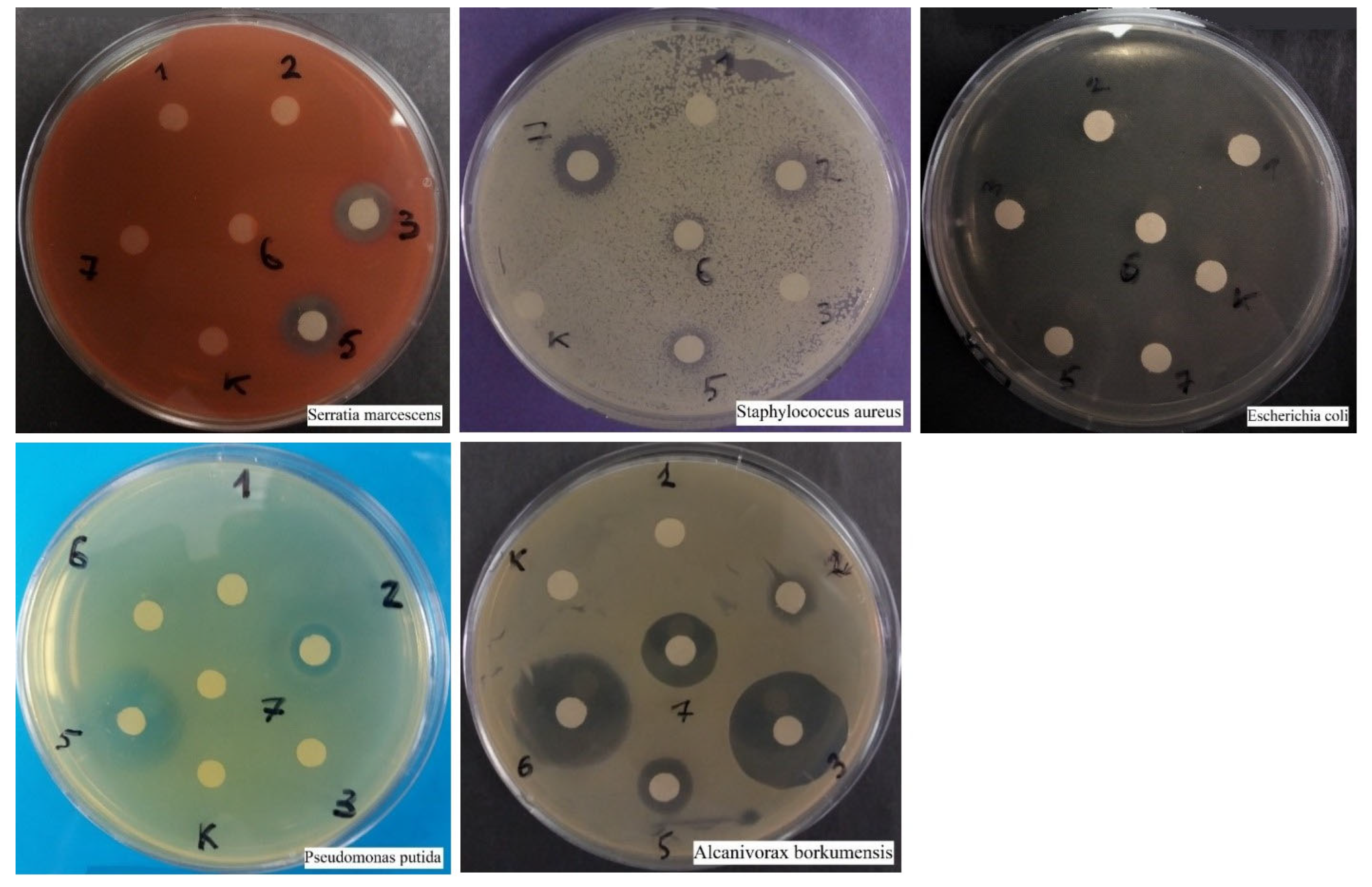
3.1.1. Disco Diffusion Analysis of Various Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Anti-biofilm bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles, shown using a replicator stamp
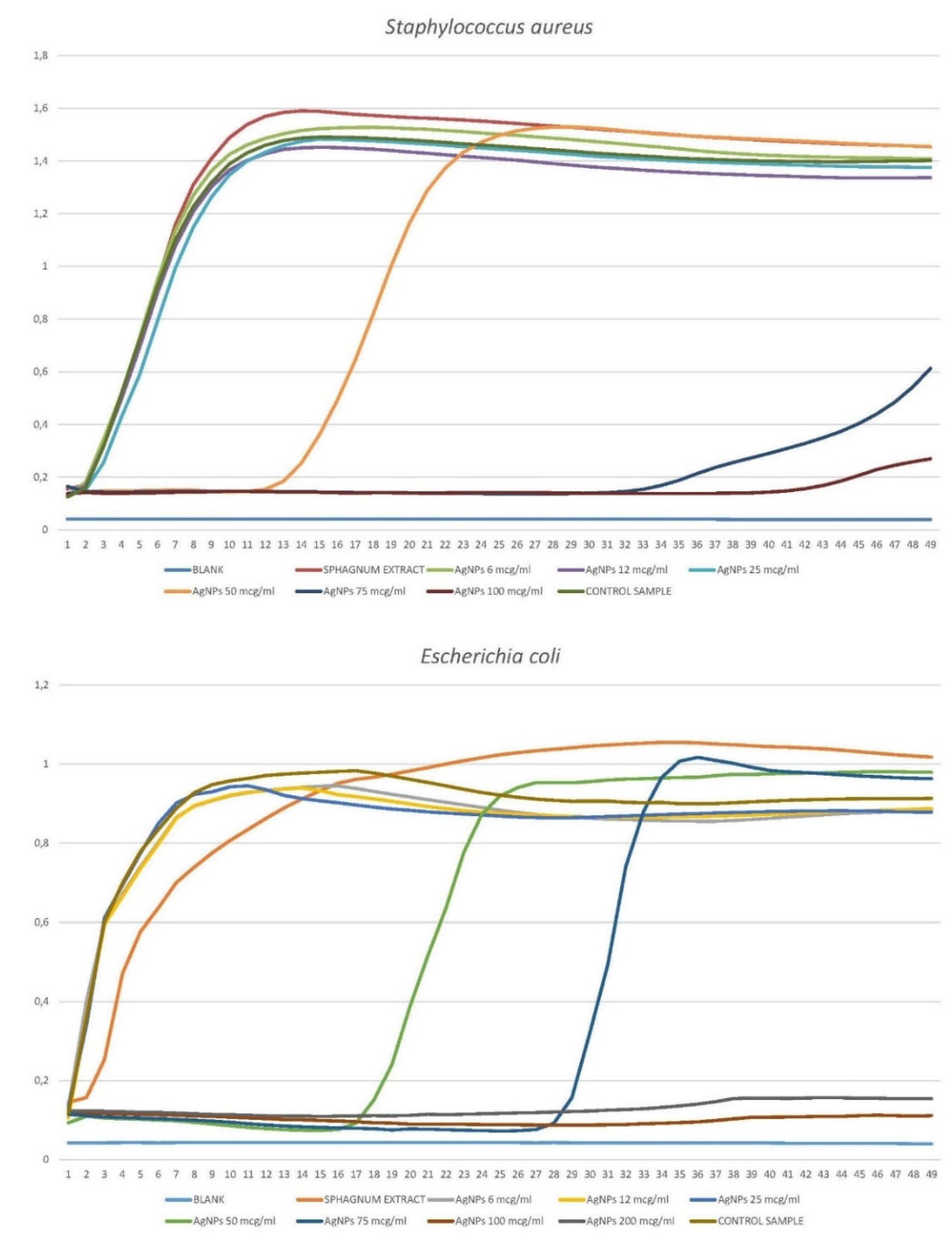
3.1.2. Growth Curves of Planktonic Crops in the Presence of Silver Nanoparticles.
3.1.2.1. Staphylococcus aureus
3.1.2.2. Escherichia coli
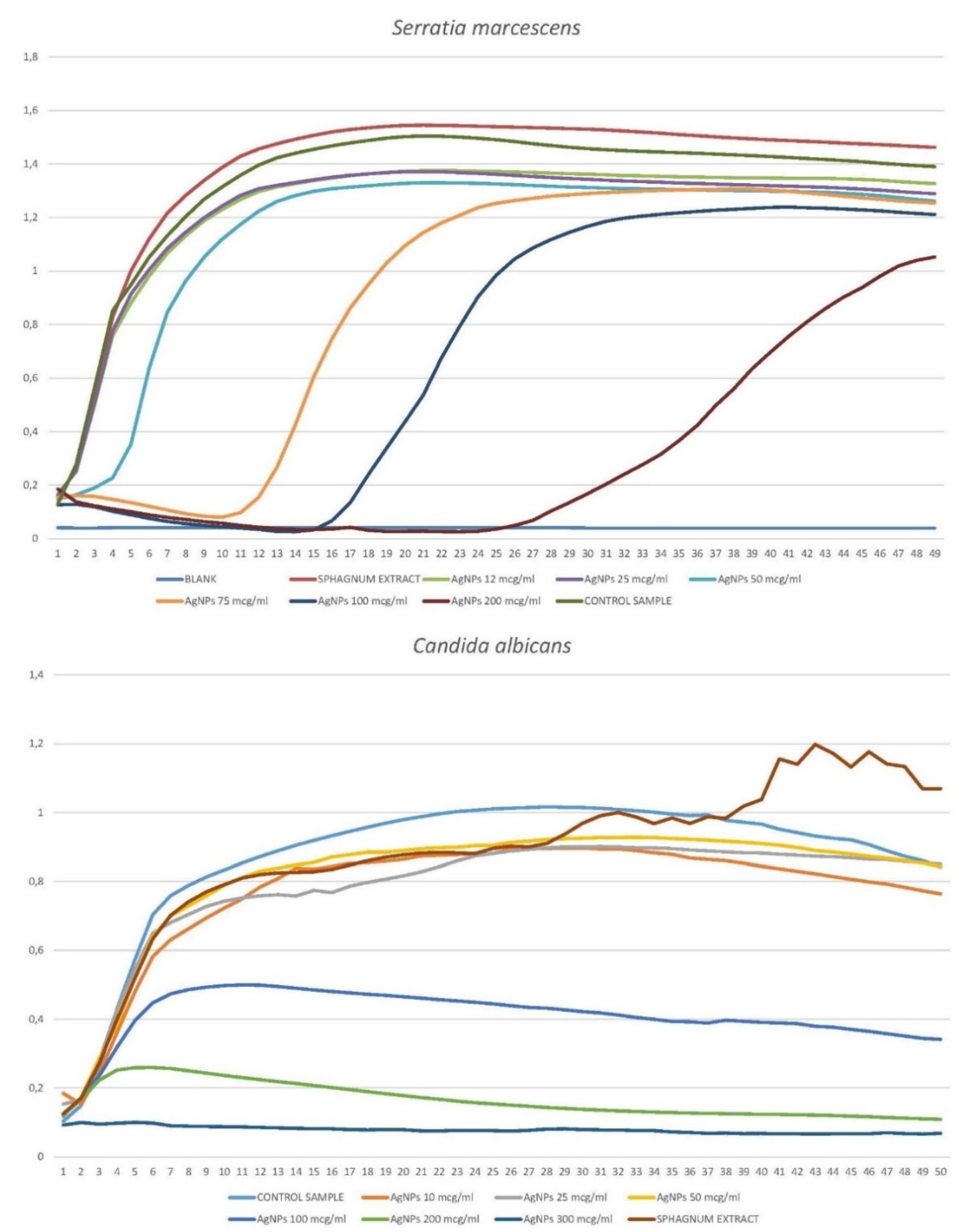
3.1.2.3. Serratia marcescens
3.1.2.4. Candida albicans
3.2. Research on the effectiveness of antibiotics and fungicides
3.2.1. Comparative Disco-Diffusion Analysis of Six Antibiotics
3.2.2. Comparative Disco-Diffusion Analysis of Three Fungicides
3.3. Growth Curves of Planktonic Crops, in the Presence of Silver Nanoparticles, Together with an Antibiotic or Fungicide.
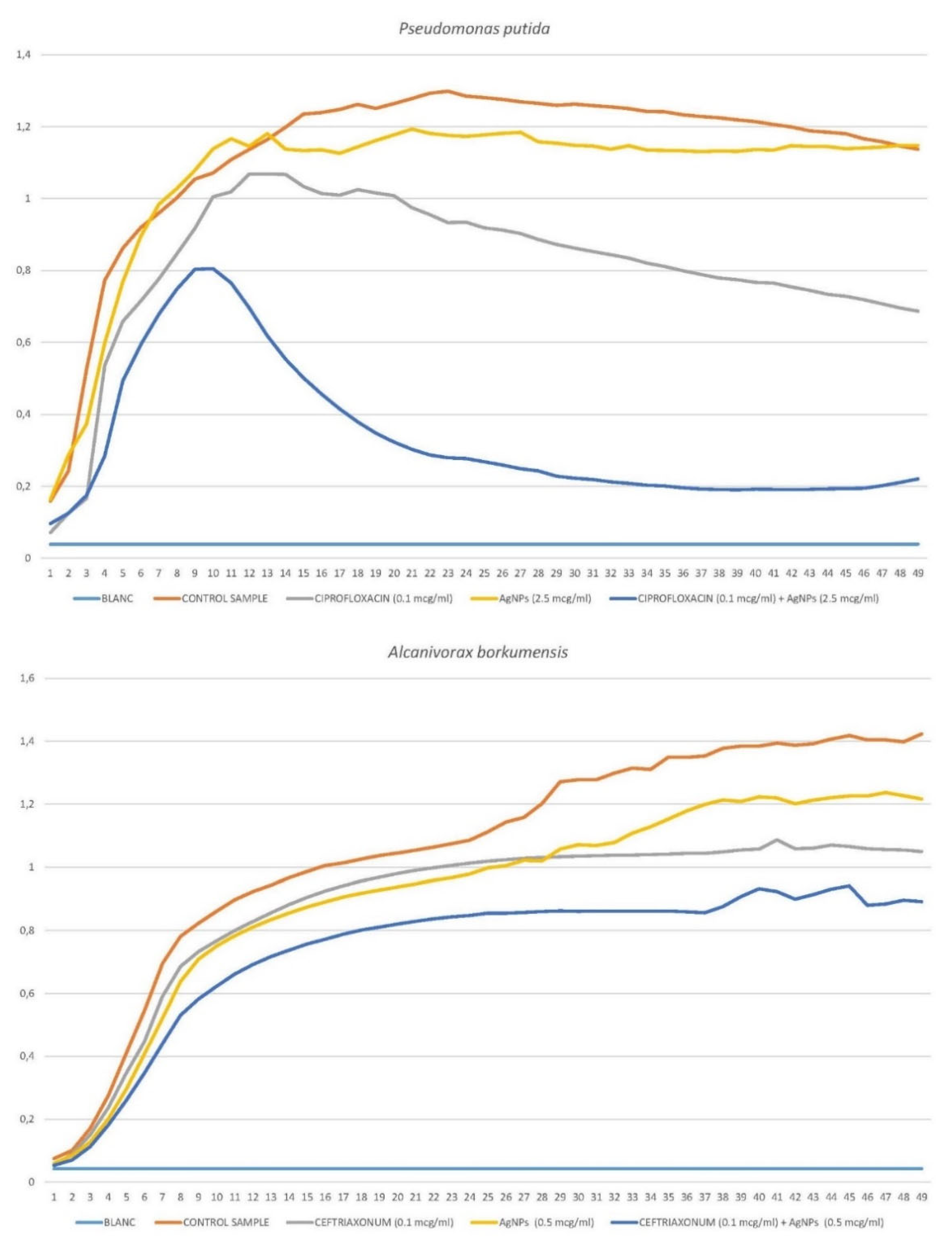
3.3.1. Pseudomonas putida
3.3.2. Alcanivorax borkumensis
3.3.3. Escherichia coli
3.3.4. Serratia marcescens
3.3.5. Staphylococcus aureus
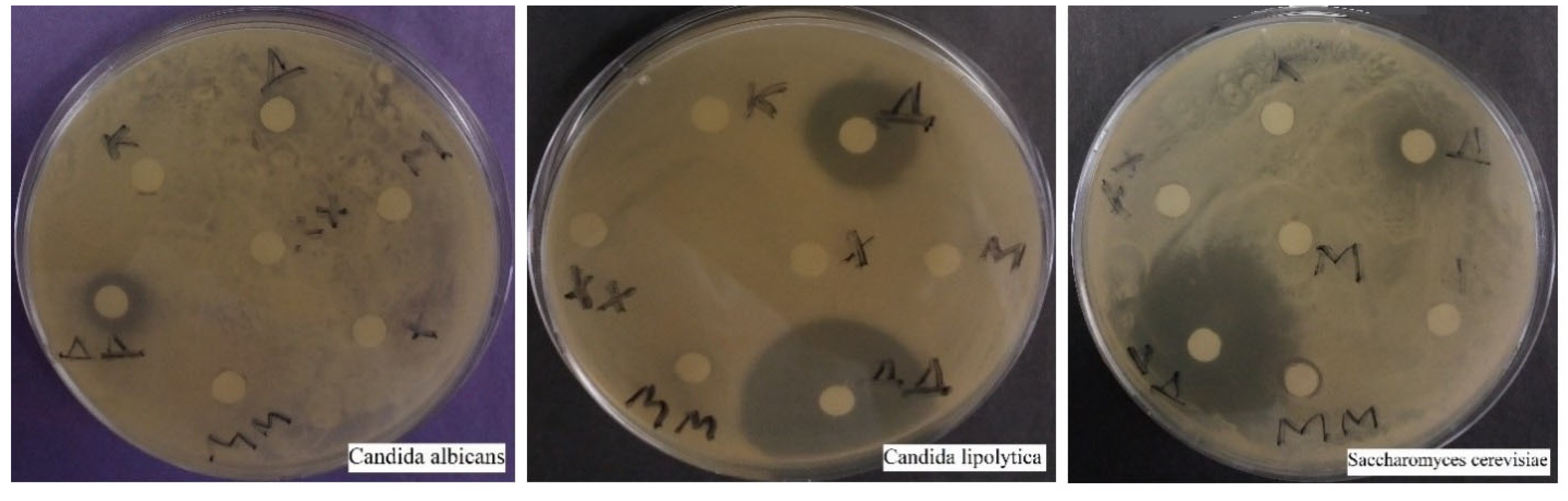
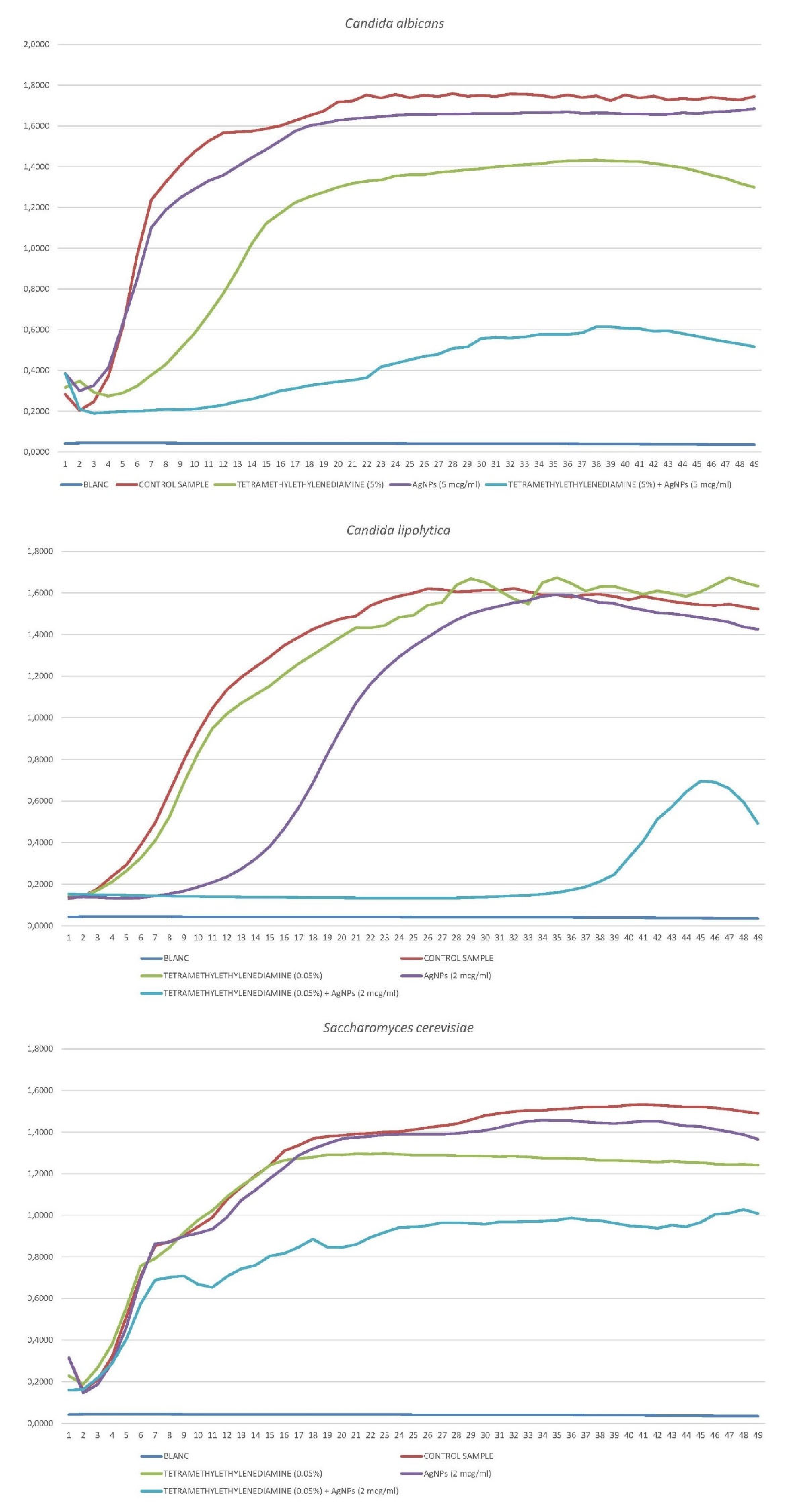
3.3.6. Candida albicans
3.3.7. Candida lipolytica
3.3.8. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
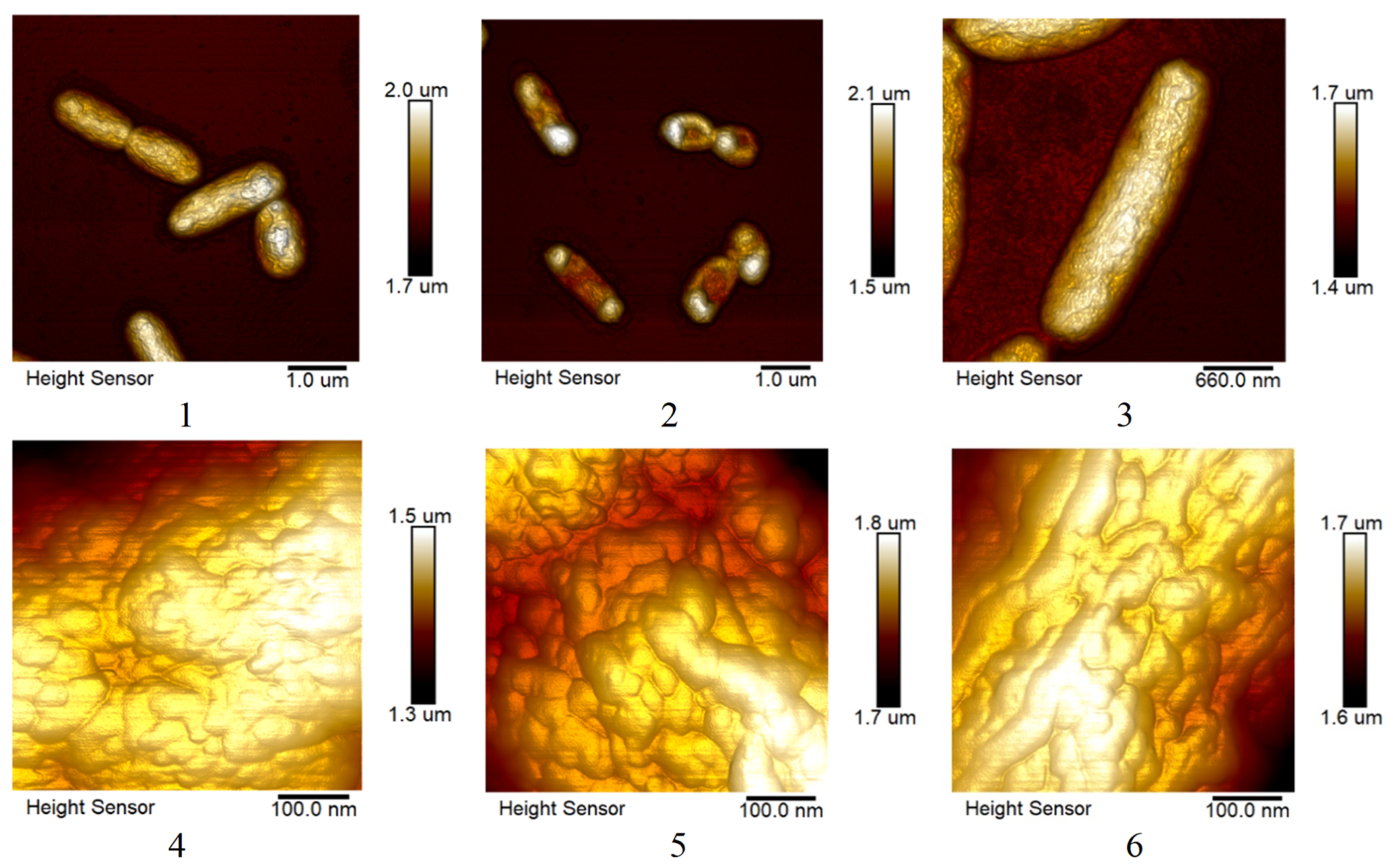
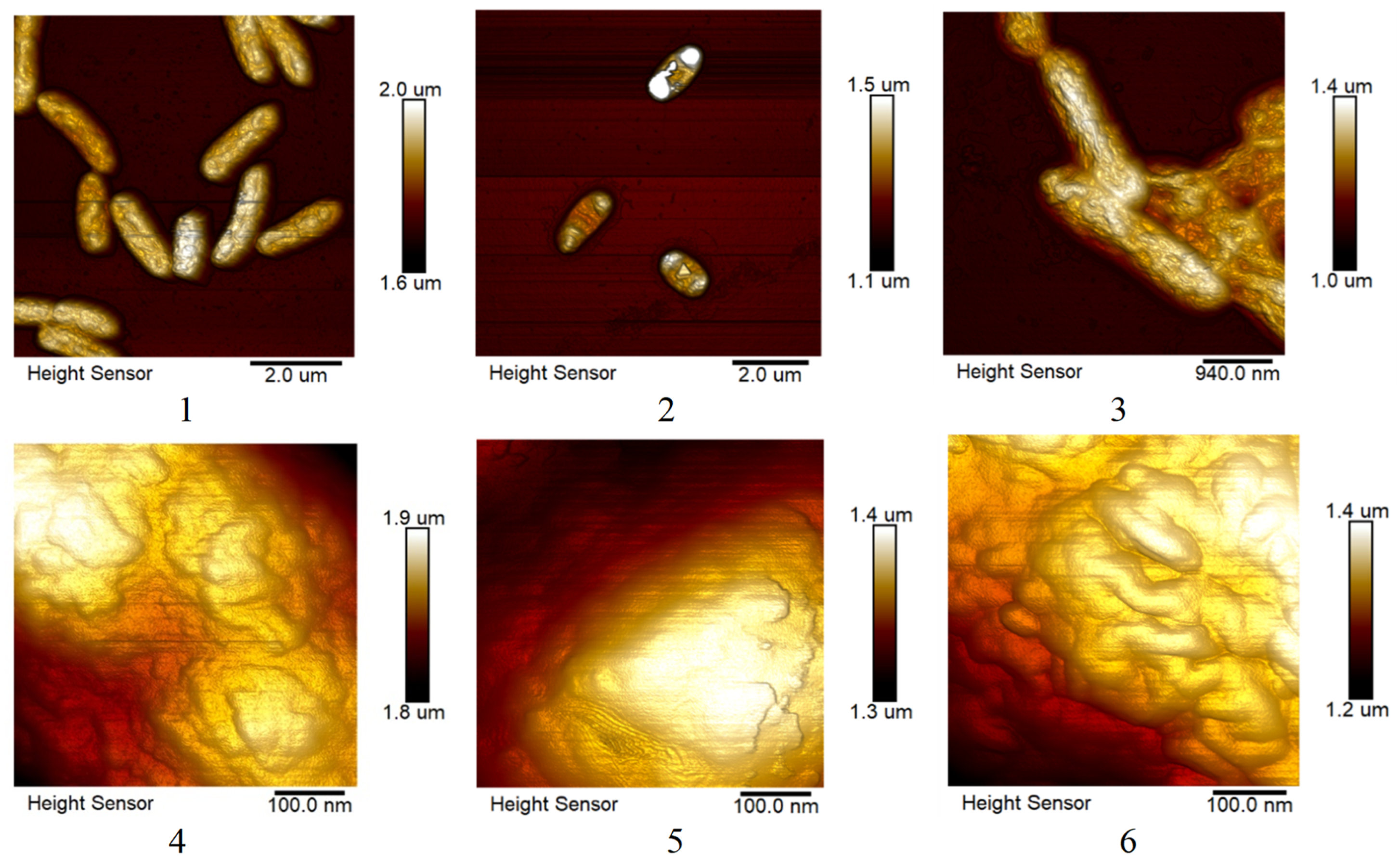
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy Study Results.
3.4.1. Effect of Ciprofloxacin and Silver Nanoparticles on S. marcescens Biofilms.
3.4.2. Changes in the Morphology of E. coli and S. marcescens cells when Exposed to AgNPs.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Oliveira Santos, J. V., da Costa Júnior, S. D., de Fátima Ramos dos Santos Medeiros, S. M., Cavalcanti, I. D. L., de Souza, J. B., Coriolano, D. L., ... & Cavalcanti, I. M. F. [2022]. Panorama of bacterial infections caused by epidemic resistant strains. Current Microbiology, 79[6], 175.
- Bai, H.-J.; Geng, Q.-F.; Jin, F.; Yang, Y.-L. Epidemiologic analysis of antimicrobial resistance in hospital departments in China from 2022 to 2023. J. Heal. Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastmeier, P.; Kola, A.; Schwab, F.; Behnke, M.; Geffers, C. Etiology of nosocomial infections in intensive care patients in German hospitals: An analysis of trends between 2008 and 2022. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2024, 314, 151594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Martínez, N.F.; Rivera-Izquierdo, M.; Ortiz-González-Serna, R.; Martínez-Ruiz, V.; Lardelli-Claret, P.; Aginagalde-Llorente, A.H.; Valero-Ubierna, M.d.C.; Vergara-Díaz, M.A.; Lorusso, N. Healthcare-associated infections by multidrug-resistant bacteria in Andalusia, Spain, 2014 to 2021. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nițescu, B.; Pițigoi, D.; Tălăpan, D.; Nițescu, M.; Aramă, S.; Pavel, B.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Rafila, A.; Aramă, V. Etiology and Multi-Drug Resistant Profile of Bacterial Infections in Severe Burn Patients, Romania 2018–2022. Medicina 2023, 59, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerini, P.; Meduri, F.R.; Tomassetti, F.; Polidori, I.; Brugneti, M.; Nicolai, E.; Bernardini, S.; Pieri, M.; Broccolo, F. Trends in Antibiotic Resistance of Nosocomial and Community-Acquired Infections in Italy. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Garfias, F.; Ríos-Cifuentes, L.; Sánchez, N.S.; Calahorra, M.; Peña, A. Study of the mechanism of ε-poly-l-lysine as an antifungal on Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franconi, I.; Rizzato, C.; Poma, N.; Tavanti, A.; Lupetti, A. Candida parapsilosis sensu stricto Antifungal Resistance Mechanisms and Associated Epidemiology. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Kadosh, D. Perspective on the origin, resistance, and spread of the emerging human fungal pathogen Candida auris. PLOS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Torrado, R.; Querol, A. Opportunistic Strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A Potential Risk Sold in Food Products. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1522–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardımcı, B. K., Şarkaya, K., & Güler, A. [2024]. Evaluation of the antiproliferative and oxidative effects of polymeric cryogels on the model eukaryotic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Palani, G.; Trilaksana, H.; Sujatha, R.M.; Kannan, K.; Rajendran, S.; Korniejenko, K.; Nykiel, M.; Uthayakumar, M. Silver Nanoparticles for Waste Water Management. Molecules 2023, 28, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, A.; Hussain, S.; Mushtaq, W.; Zubair, M.; Siddique, K.; Attia, K.; Khan, N.; Fiaz, S.; Azeem, F.; Chen, Y. Application of silver nanoparticles synthesized through varying biogenic and chemical methods for wastewater treatment and health aspects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.A.; Virk, P.; Hendi, A.A.; Ortashi, K.M.; AlMasoud, N.; Alomar, T.S. Role of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles with Trigonella foenum-graecum Seeds in Wastewater Treatment. Processes 2023, 11, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Zahoor, M.; Khan, R.S.; Ikram, M.; Islam, N.U. The impact of silver nanoparticles on the growth of plants: The agriculture applications. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, P.; Paret, M.L.; Mondal, R.; Mandal, A.K. Advancement of noble metallic nanoparticles in agriculture: A promising future. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Mohammad, K.N.; Ahmed, B.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Lee, J. Biological Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Prospects in Plant Disease Management. Molecules 2022, 27, 4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Lyu, G.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Ni, Y. Preparation of ultrafine and highly loaded silver nanoparticle composites and their highly efficient applications as reductive catalysts and antibacterial agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Sayed, M.A.A.; Zikry, M.M.; Khalifa, M.E.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Optimization strategy for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) as catalyst for the reduction of 2,4-dinitrophenol via supported mechanism. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Das, N.C. Green synthesis of a reduced graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles-based catalyst for degradation of a wide range of organic pollutants. Nano-Structures Nano-Objects 2023, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhler, J.S.; Sim, W.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Ziora, Z.M. Silver bullets: A new lustre on an old antimicrobial agent. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princy, S.S.J.; Hentry, C.; Alodaini, H.A.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Bindhu, M. Hibiscus cannabinus seeds assisted spherical silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Chem. Phys. Impact 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balčiūnaitienė, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Puzerytė, V.; Viškelis, J.; Janulis, V.; Viškelis, P.; Griškonis, E.; Jankauskaitė, V. Eucalyptus globulus and Salvia officinalis Extracts Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Application as an Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agent. Plants 2022, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Yang, R.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, W. Functional bacterial cellulose nanofibrils with silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandraker, S.K.; Kumar, R. Biogenic biocompatible silver nanoparticles: a promising antibacterial agent. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2022, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeer Mohammed, A.B.; Abd Elhamid, M.M.; Khalil, M.K.M.; Ali, A.S.; Abbas, R.N. The potential activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as an antibacterial agent against multidrug-resistant isolates from intensive care unit and anticancer agent. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, S.; Ali, S.; Mumtaz, S.; Mughal, T.A.; Tahir, H.M.; Shakir, H.A. Chitosan conjugated silver nanoparticles: the versatile antibacterial agents. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 4719–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, B.H.; Inamdar, S.N.; Nalawade, S.A.; Chaudhari, S.B. A systematic review on antifungal and insecticidal applications of biosynthesized metal nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 2023, 73, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.G.; Roque, G.S.C.; Conrado, R.; De Souza, A.O. Antifungal Activity of Mycogenic Silver Nanoparticles on Clinical Yeasts and Phytopathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweedan, E.G.; Majeed, S.M.A. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Phenolic Extract of Agaricus bisporus Against Pathogenic Bacteria and Yeasts. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, R. M., Elshaer, M., El-Raouf, A., & Mona, A. [2023]. Silver nanoparticles display inhibitory effect against drug-resistant pathogenic Candida isolates from different clinical specimens. Egyptian Journal of Botany, 63[1], 305-314.).
- Al-Askar, A. A., Aseel, D. G., El-Gendi, H., Sobhy, S., Samy, M. A., Hamdy, E., ... & Abdelkhalek, A. [2023]. Antiviral Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Peel Extract against Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Plants, 12[11], 2103.).
- Luceri, A.; Francese, R.; Lembo, D.; Ferraris, M.; Balagna, C. Silver Nanoparticles: Review of Antiviral Properties, Mechanism of Action and Applications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algazlan, A.S.; Almuraikhi, N.; Muthurangan, M.; Balto, H.; Alsalleeh, F. Silver Nanoparticles Alone or in Combination with Calcium Hydroxide Modulate the Viability, Attachment, Migration, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes-Gouvea, C.C.; Danelon, M.; Vieira, A.P.M.; Amaral, J.G.D.; Neto, F.N.d.S.; Gorup, L.F.; Camargo, E.R.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Barbosa, D.B. Silver nanoparticles associated with a polyphosphate and fluoride enhance the prevention of enamel demineralization and impact on dual-biofilm adhesion. J. Dent. 2022, 125, 104245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallineni, S.K.; Sakhamuri, S.; Kotha, S.L.; AlAsmari, A.R.G.M.; AlJefri, G.H.; Almotawah, F.N.; Mallineni, S.; Sajja, R. Silver Nanoparticles in Dental Applications: A Descriptive Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarviya, N.; Mahanta, U.; Dart, A.; Giri, J.; Deshpande, A.S.; Khandelwal, M.; Bhave, M.; Kingshott, P. Biocompatible and antimicrobial multilayer fibrous polymeric wound dressing with optimally embedded silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.S.; Aytac, A. Fabrication and characterization as antibacterial effective wound dressing of hollow polylactic acid/polyurethane/silver nanoparticle nanofiber. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, M.; Mazurek, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Konop, M. Beneficial Effect of Wound Dressings Containing Silver and Silver Nanoparticles in Wound Healing—From Experimental Studies to Clinical Practice. Life 2022, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rugaie, O.; Abdellatif, A.A.H.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Sabet, M.A.; Abdelfattah, A.; Alsharidah, M.; Aldubaib, M.; Barakat, H.; Abudoleh, S.M.; Al-Regaiey, K.A.; et al. Retardation of Bacterial Biofilm Formation by Coating Urinary Catheters with Metal Nanoparticle-Stabilized Polymers. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Rodríguez, O.; Trejo-Valdez, M.D.; Torres-SanMiguel, C.R.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Bañuelos-Hernández, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Manríquez-Ramírez, M.E.; Hernández-Benítez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Tovar, A.V. Evaluation of the performance of TiO2 thin films doped with silver nanoparticles as a protective coating for metal prostheses. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2023, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, L.C.F.; Almeida, N.L.M.; Pontes, F.M.L.; Rinaldo, D.; Carneiro, C.A.; Neppelenbroek, K.H.; Lara, V.S.; Porto, V.C. Silver nanoparticles in denture adhesive: An antimicrobial approach against Candida albicans. J. Dent. 2023, 131, 104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hublikar, L.V.; Ganachari, S.V.; Patil, V.B.; Nandi, S.; Honnad, A. Anticancer potential of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Lantana camara leaf extract. Prog. Biomater. 2023, 12, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, T. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles loaded with carboplatin as a potential antimicrobial and cancer therapy. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáč, P.; Michalková, R.; Čižmáriková, M.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Balážová, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Takáčová, G. The Role of Silver Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer: Are There Any Perspectives for the Future? Life 2023, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N. P. U., Dang, N. T., Doan, L., & Nguyen, T. T. H. [2023]. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: from conventional to ‘modern’methods—a review. Processes, 11[9], 2617..).
- Ajaykumar, A.P.; Mathew, A.; Chandni, A.P.; Varma, S.R.; Jayaraj, K.N.; Sabira, O.; Rasheed, V.A.; Binitha, V.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Basheer, V.S.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Leaf Extract of the Medicinal Plant, Uvaria narum and Its Antibacterial, Antiangiogenic, Anticancer and Catalytic Properties. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, M. F., Keskin, C., Baran, A., Hatipoğlu, A., Yildiztekin, M., Küçükaydin, S., ... & Eftekhari, A. [2023]. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Allium cepa L. Peel extract, their antioxidant, antipathogenic, and anticholinesterase activity. Molecules, 28[5], 2310.).
- Singh, C.; Anand, S.K.; Upadhyay, R.; Pandey, N.; Kumar, P.; Singh, D.; Tiwari, P.; Saini, R.; Tiwari, K.N.; Mishra, S.K.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by root extract of Premna integrifolia L. and evaluation of its cytotoxic and antibacterial activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Ullah, R.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, A.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, M.; Al-Joufi, F.A.; Zahoor, M.; Sher, H. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Euphorbia wallichii Leaf Extract: Its Antibacterial Action against Citrus Canker Causal Agent and Antioxidant Potential. Molecules 2022, 27, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labulo, A.H.; David, O.A.; Terna, A.D. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Morinda lucida leaf extract and evaluation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 7313–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylyak, L. I., Kytsya, A. R., Lyutyy, P. Y., Korets’ ka, N. I., Pilyuk, Y. V., & Kuntyi, O. I. [2023]. Silver nanoparticles produced via a green synthesis using the rhamnolipid as a reducing agent and stabilizer. Applied Nanoscience, 13[7], 5251-5263.).
- Motti, R., Palma, A. D., & de Falco, B. [2023]. Bryophytes used in folk medicine: An ethnobotanical overview. Horticulturae, 9[2], 137.).
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Dey, A. The ethno-medicinal and pharmaceutical attributes of Bryophytes: A review. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, T.J. Concerning the wound-healing properties of Sphagnum holocellulose: the Maillard reaction in pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 88, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeeva, L.R.; Dague, A.L.; Hall, M.H.; Tikhonova, A.E.; Sharipova, M.R.; Valentovic, M.A.; Bogomolnaya, L.M.; Shakirov, E.V. Antimicrobial Activities of Secondary Metabolites from Model Mosses. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benek, A.; Canli, K.; Altuner, E.M. Traditional Medicinal Uses of Mosses. Anatol. Bryol. 2022, 8, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, A. Alternative mechanisms of action of metallic nanoparticles to mitigate the global spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Cell Surf. 2023, 10, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Thakur, V.; Kumar, V.; Raj, M.; Gupta, S.; Devi, N.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Macho, M.; Banerjee, A.; Ewe, D.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles and Its Mechanistic Insight for Chronic Wound Healing: Review on Recent Progress. Molecules 2022, 27, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, B.; Piechowiak, T.; Szychowski, K.A. Dual mechanism of silver nanoparticle-mediated upregulation of adipogenesis in mouse fibroblasts (3T3-L1) in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 479, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, H. P., Patil, C. D., Sauter, I. P., Rott, M. B., & Patil, S. V. [2013]. Amoebicidal activity of phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles and their in vitro cytotoxicity to human cells. FEMS microbiology letters, 345[2], 127-131.).
- Nagesh, M.R.; Vijayakumar, N.; Anandan, R.; Renuka, M.; Amalan, V.; Kavitha, R.; Arulmani, S.R.B.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Nasr, F.A.; et al. Cytotoxic and genotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by ethanolic extract of Salacia chinensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachicho, N., Hoffmann, P., Ahlert, K., & Heipieper, H. J. [2014]. Effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on growth and adaptive response mechanisms of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. FEMS microbiology letters, 355[1], 71-77.).
- More, P.R.; Pandit, S.; De Filippis, A.; Franci, G.; Mijakovic, I.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles: Bactericidal and Mechanistic Approach against Drug Resistant Pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Action and Probable Bio-Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Paliya, B.S.; Singh, B.N. Superior inhibition of virulence and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by phyto-synthesized silver nanoparticles through anti-quorum sensing activity. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 170, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabadi, H., Hosseini, O., Jounaki, K., Sadeghian-Abadi, S., Ashouri, F., Alrikabi, A. M. A., ... & Mostafavi, E. [2023]. Bioinspired green-synthesized silver nanoparticles: in vitro physicochemical, antibacterial, biofilm inhibitory, genotoxicity, antidiabetic, antioxidant, and anticoagulant performance. Materials Advances, 4[14], 3037-3054.).
- AboElmaaty, S.A.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Sheraba, N.S.; Hassan, M.G.; Badawy, M.S.E.M.; Ghareeb, A.; Hamed, A.A.; Gabr, E.Z. Biofilm Inhibitory Activity of Actinomycete-Synthesized AgNPs with Low Cytotoxic Effect: Experimental and In Silico Study. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Glińska, S.; Gapińska, M.; Ruman, T.; Nowak, A.; Aydin, E.; Gutarowska, B. Silver nanoparticles: a mechanism of action on moulds. Metallomics 2016, 8, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, P.H.F.D.; Garcia, M.T.; Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Lage, A.C.P.; da Silva, N.S.; Junqueira, J.C. Metal Nanoparticles to Combat Candida albicans Infections: An Update. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szerencsés, B.; Igaz, N.; Tóbiás, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Prucsi, Z.; Rónavári, A.; Bélteky, P.; Madarász, D.; Papp, C.; Makra, I.; Vágvölgyi, C.; et al. Size-dependent activity of silver nanoparticles on the morphological switch and biofilm formation of opportunistic pathogenic yeasts. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; De Conti, R.; Alves, O.L.; Costa, F.T.M.; Brocchi, M. Potential use of silver nanoparticles on pathogenic bacteria, their toxicity and possible mechanisms of action. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoladori, L.F.d.A.; Andriani, G.M.; de Castro, I.M.; Suzukawa, H.T.; Gimenes, A.C.R.; Bartolomeu-Gonçalves, G.; Ishida, K.; Nakazato, G.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Machado, R.R.B.; et al. Synergistic Antifungal Interaction between Pseudomonas aeruginosa LV Strain Metabolites and Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles against Candida auris. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Chávez, J.A.; García-Bouchot, G.; García-Gutiérrez, N.; Castañeda, H.A.V.; Nava-Mendoza, R.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Elizalde-Peña, E.A.; Esquivel-Naranjo, E.U.; Landeros-Jaime, F.; Rojas-Avelizapa, N.G.; et al. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Stressors Generate Synergistic Growth Inhibition in Candida Species through Cell Wall Damage, Osmotic Stress, and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 24, 1682–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, G.; Kubo, A.-L.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A.; Bondar, D.; Karpichev, Y.; Bondarenko, O. Synergistic antibacterial effect of copper and silver nanoparticles and their mechanism of action. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnova, S.A.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Badrutdinov, A.R.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Silver nanoparticle-coated “cyborg” microorganisms: rapid assembly of polymer-stabilised nanoparticles on microbial cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13530–13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

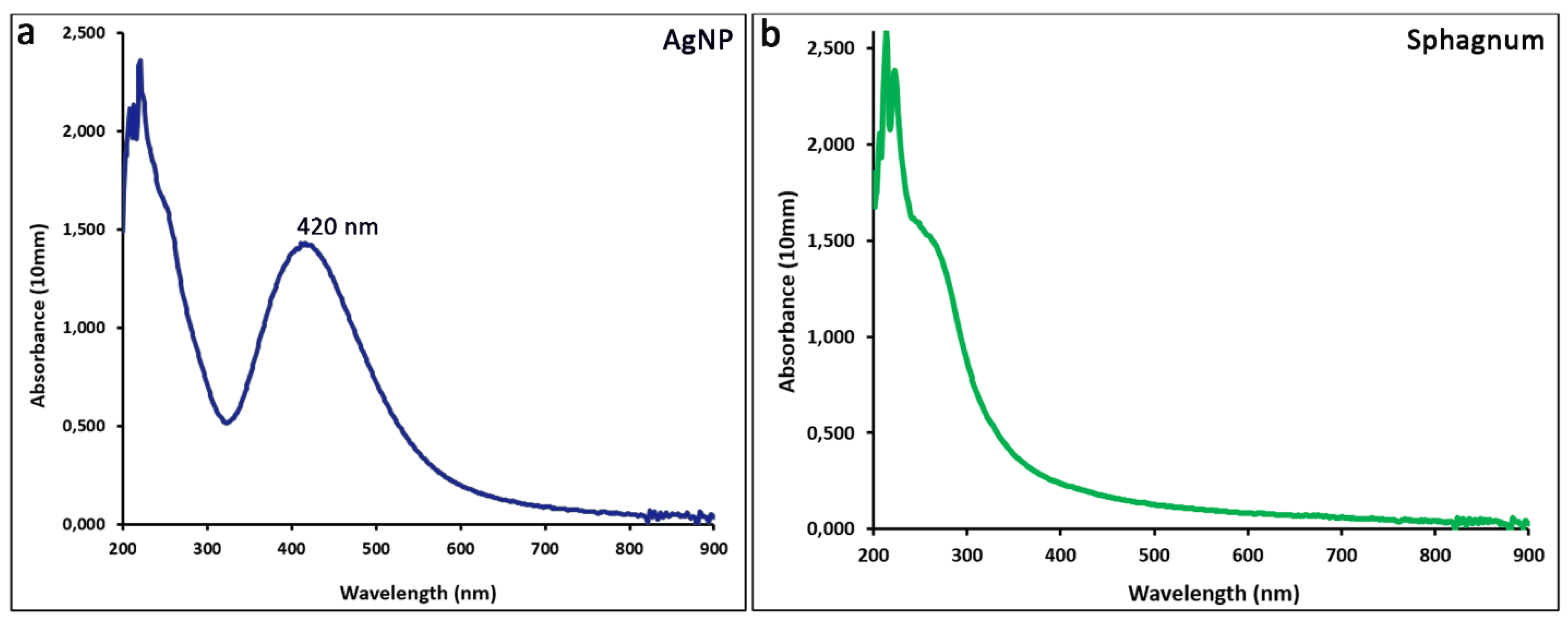
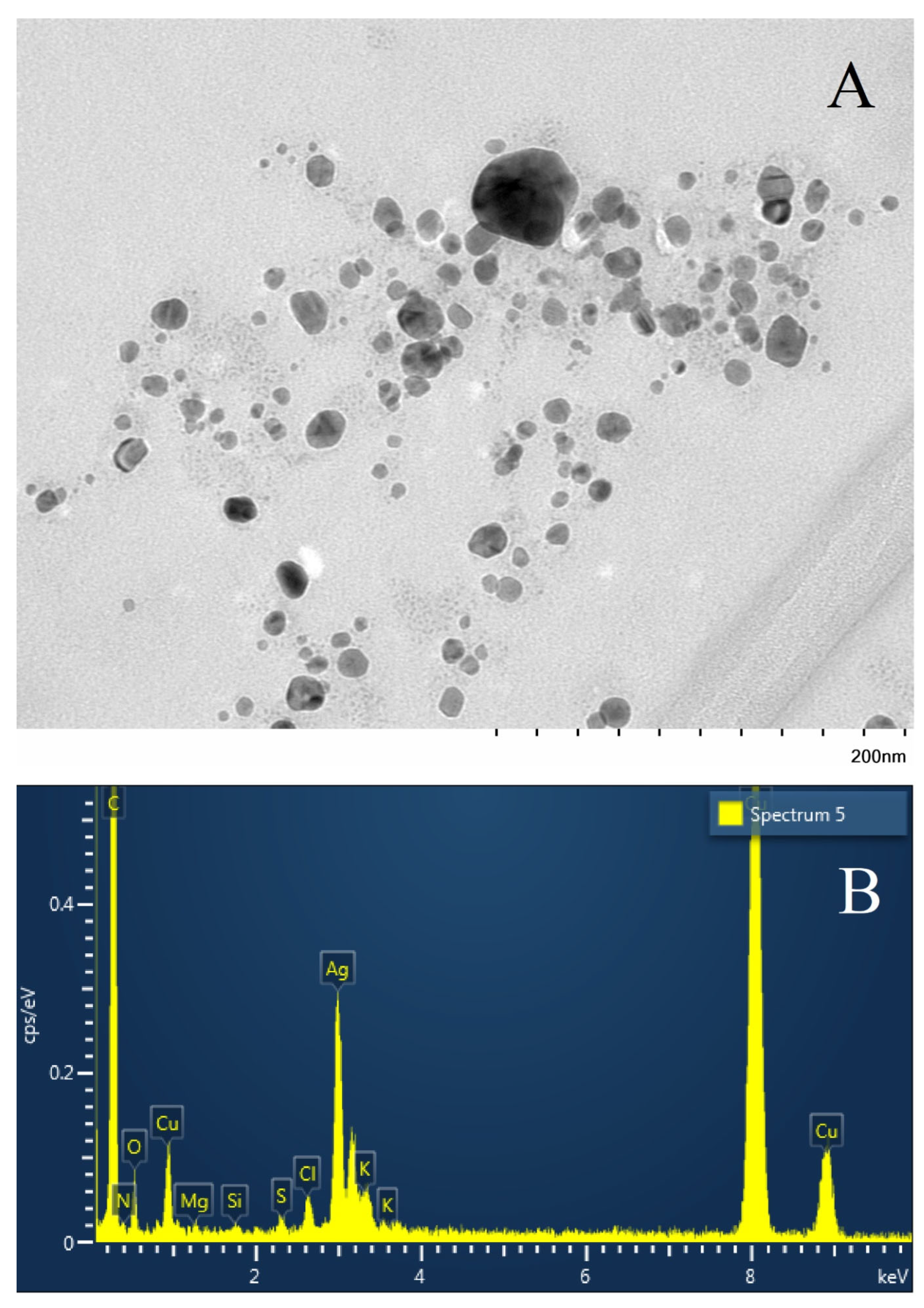
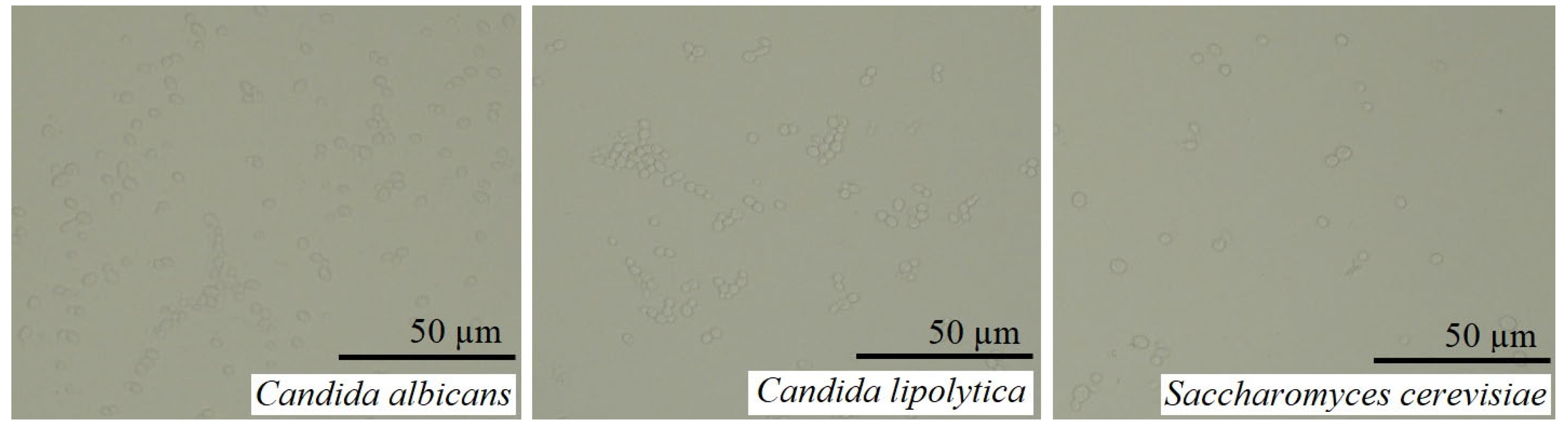
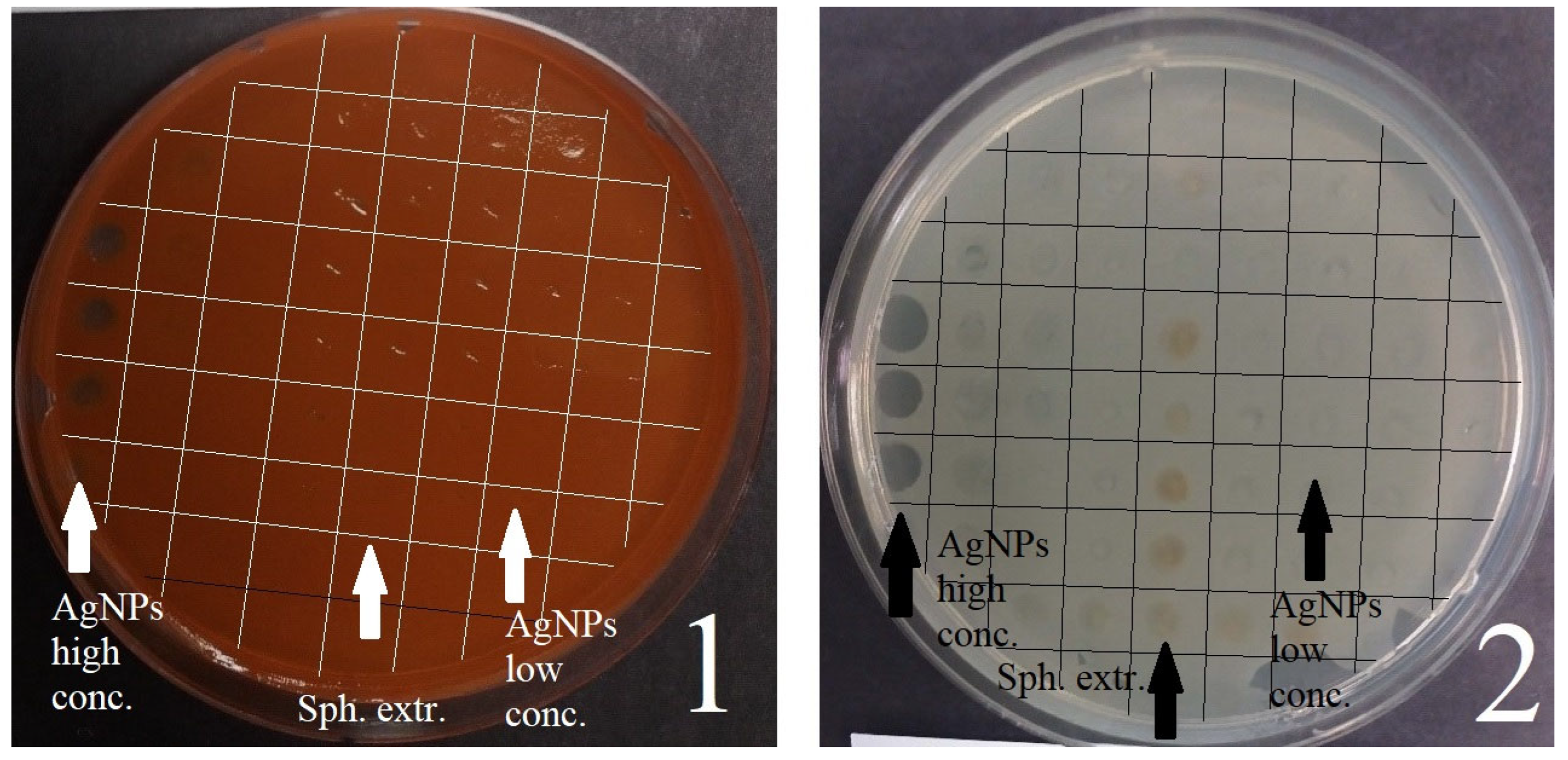


| Active substance | E. coli | S. marcescens | S. aureus | C. albicans |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Сontrol sample (water) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AgNPs (25 μg/ml) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AgNPs (50 μg/ml) | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AgNPs (75 μg/ml) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| AgNPs (100 μg/ml) | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| AgNPs (200 μg/ml) | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| AgNPs (500 μg/ml) | 3 | 3 | 3.5 | 5 |
| AgNPs (1000 μg/ml) | 3 | 3 | 3.5 | 6 |
| Sphagnum extract | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





