Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells and HCV Infection Systems
2.2.1. HCV Cell Culture (HCVcc) System
2.2.2. HCV Replicons
2.3. Quantification of Metabolites
2.3.1. Polyamines
2.3.2. Arginine and Proline
2.4. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
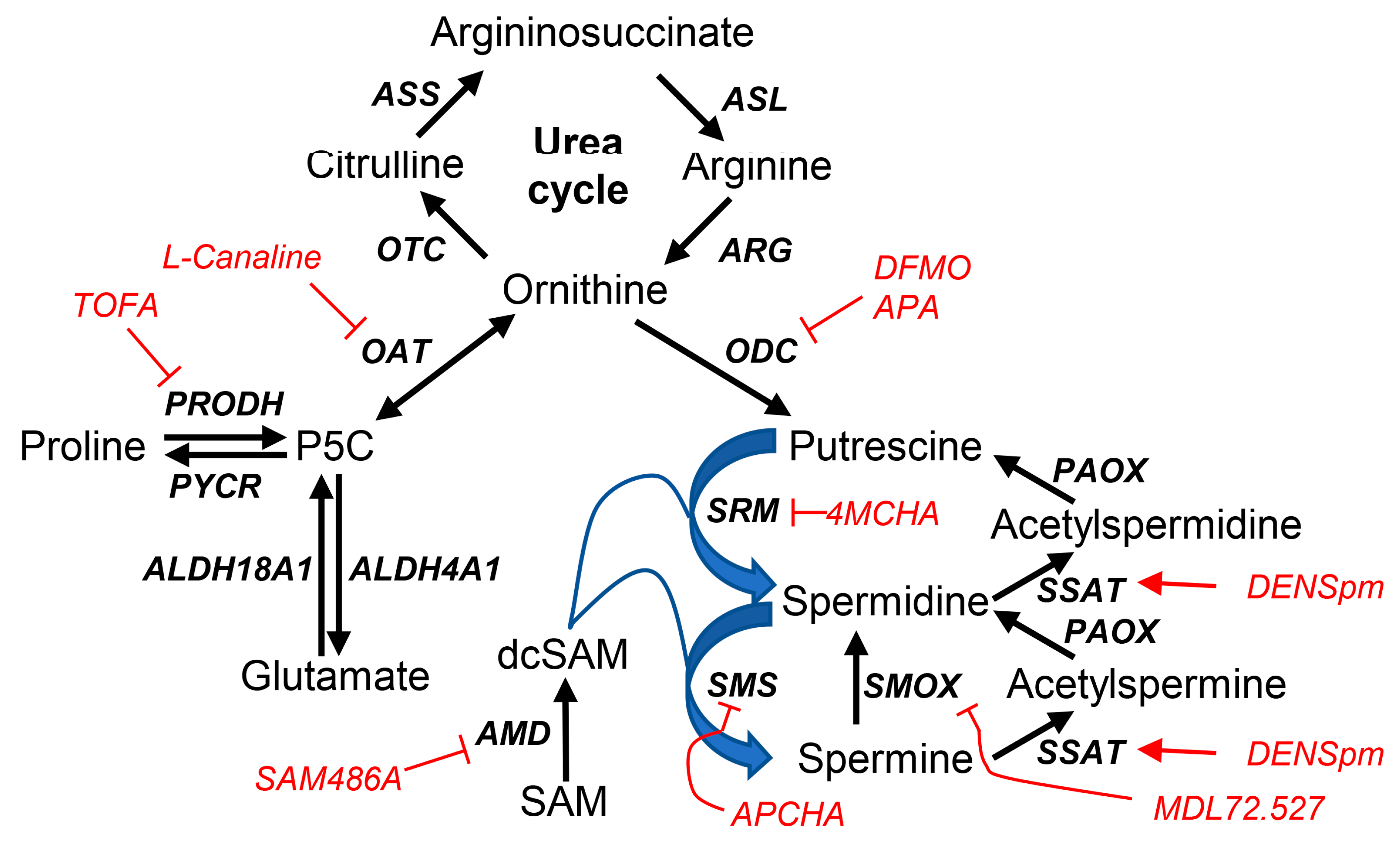
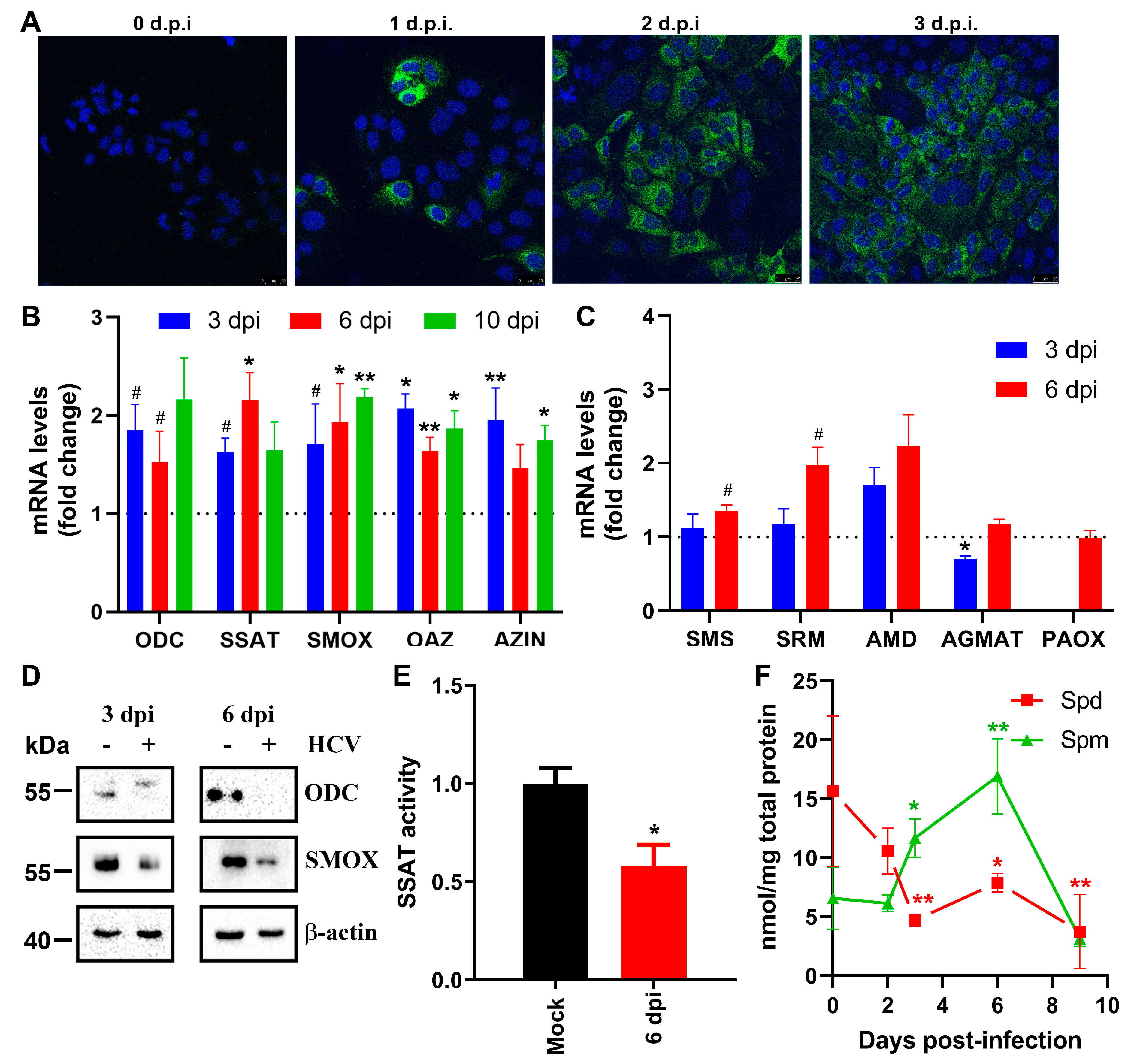
3.1. Hepatitis C Virus Perturbs Metabolism of Biogenic Polyamines
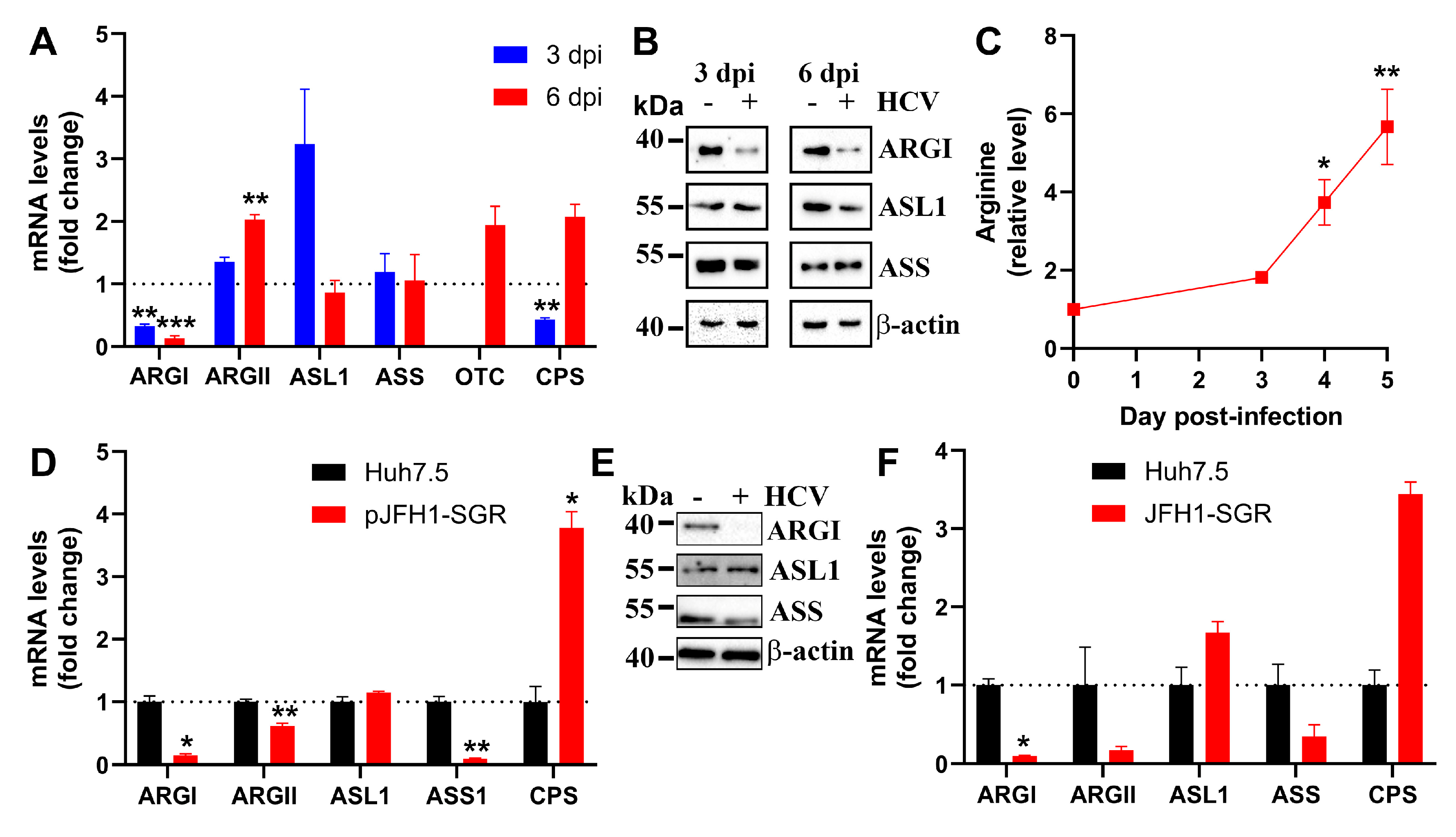
3.2. Hepatitis C Virus Down-Regulates Expression of Arginase I
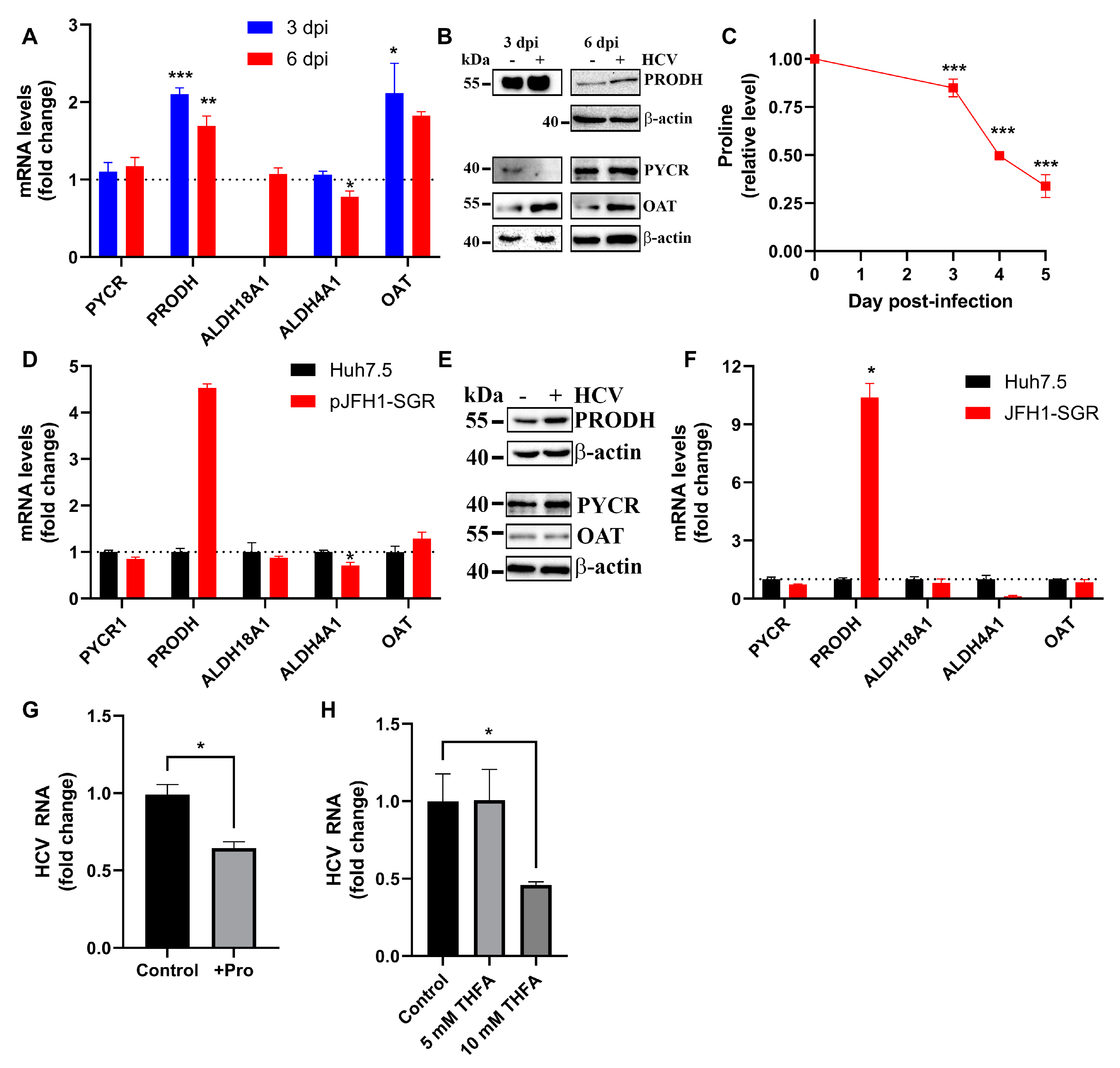
3.3. Hepatitis C Virus Up-Regulates Expression of Proline Dehydrogenase and Decreases Intracellular Level of Proline
3.4. HCV Does Not Affect Expression of the Genes that Channel Glutamate into Proline/Ornithine
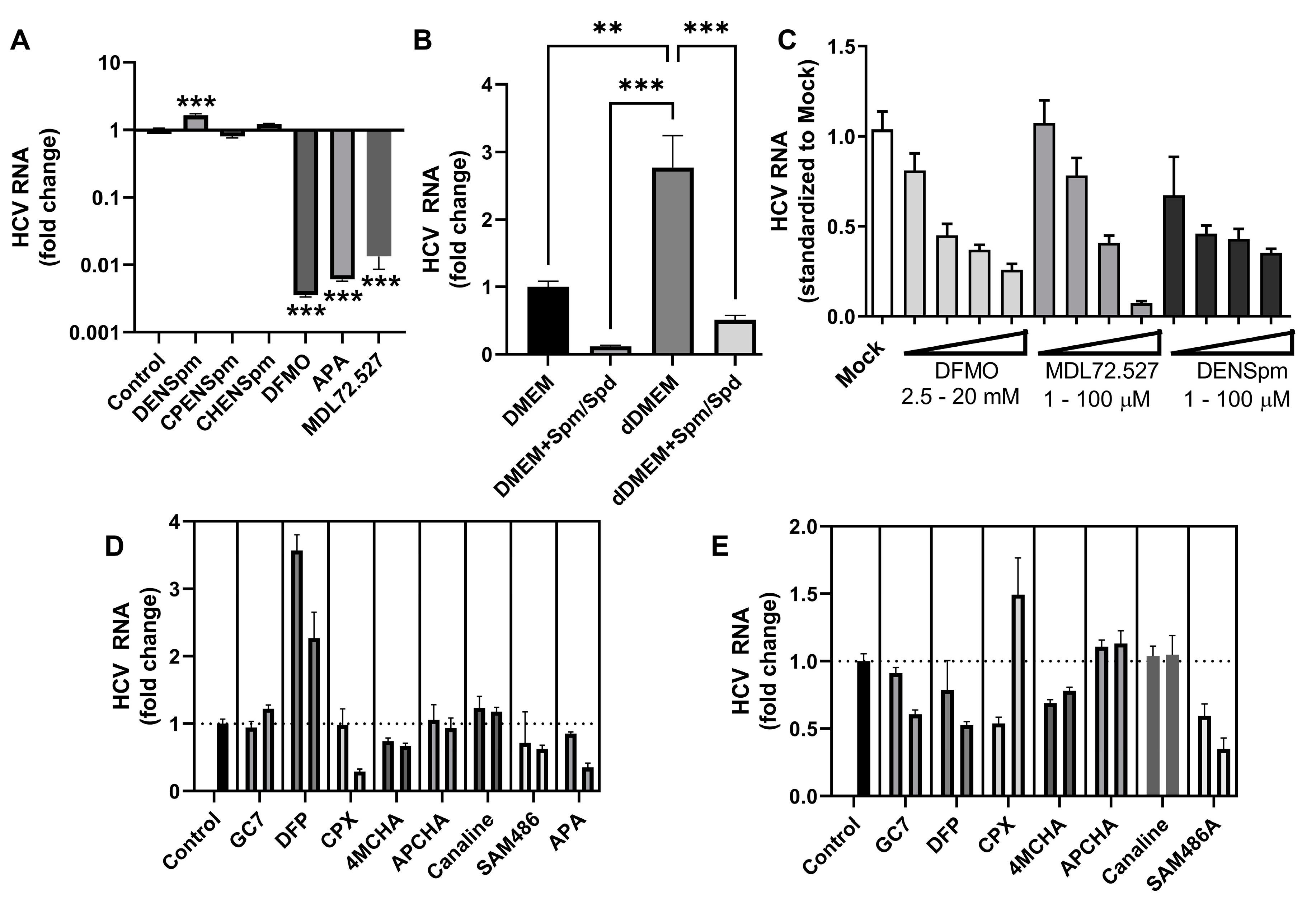
3.5. Inhibition of Polyamine Biosynthesis or Catabolism Suppresses HCV Replication
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moon, A.M.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020, 18, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepatitis, C.; Fact sheet. Updated 24.06.2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 03.02.2023).
- Westbrook, R.H.; Dusheiko, G. Natural history of hepatitis C. Journal of hepatology 2014, 61, S58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingala, S.; Ghany, M.G. Natural History of Hepatitis C. Gastroenterology clinics of North America 2015, 44, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade-Nwulia, O.; Suarez-Cuervo, C.; Nelson, D.R.; Fried, M.W.; Segal, J.B.; Sulkowski, M.S. Oral Direct-Acting Agent Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Systematic Review. Ann Intern Med 2017, 166, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.P.; Maasoumy, B. Breakthroughs in hepatitis C research: from discovery to cure. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology 2022, 19, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, G.S.; Andrieux-Meyer, I.; Applegate, T.L.; Atun, R.; Burry, J.R.; Cheinquer, H.; Dusheiko, G.; Feld, J.J.; Gore, C.; Griswold, M.G.; et al. Accelerating the elimination of viral hepatitis: a Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. The lancet. Gastroenterology & hepatology 2019, 4, 135–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, F. Residual risk of liver disease after hepatitis C virus eradication. Journal of hepatology 2021, 74, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Murata, M.; Yoshida, K.; Sekimoto, G.; Uemura, Y.; Sakaida, N.; Kaibori, M.; Kamiyama, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Fujisawa, J.; et al. Chronic inflammation associated with hepatitis C virus infection perturbs hepatic transforming growth factor beta signaling, promoting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2007, 46, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, I.; Caballero-Diaz, D. Transforming Growth Factor-beta-Induced Cell Plasticity in Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Front Oncol 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzi, A.; Roca Suarez, A.A.; Baumert, T.F.; Lupberger, J. Oncogenic Signaling Induced by HCV Infection. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Tyurina, D.A.; Ivanova, O.N.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Bartosch, B.; Isaguliants, M.G. Oxidative stress, a trigger of hepatitis C and B virus-induced liver carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3895–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Santa, T.; Shintani, Y.; Fujie, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Ishibashi, K.; Horie, T.; et al. Oxidative stress in the absence of inflammation in a mouse model for hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 4365–4370. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, P.; Bartosch, B. Metabolic reprogramming: a hallmark of viral oncogenesis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupberger, J.; Croonenborghs, T.; Roca Suarez, A.A.; Van Renne, N.; Juhling, F.; Oudot, M.A.; Virzi, A.; Bandiera, S.; Jamey, C.; Meszaros, G.; et al. Combined Analysis of Metabolomes, Proteomes, and Transcriptomes of Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Cells and Liver to Identify Pathways Associated With Disease Development. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiere, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Enache, L.S.; Lotteau, V.; Andre, P.; Diaz, O. Activity of Hexokinase Is Increased by Its Interaction with Hepatitis C Virus Protein NS5A. J Virol 2014, 88, 3246–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, D.L.; Syder, A.J.; Jacobs, J.M.; Sorensen, C.M.; Walters, K.A.; Proll, S.C.; McDermott, J.E.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, R.; et al. Temporal proteome and lipidome profiles reveal hepatitis C virus-associated reprogramming of hepatocellular metabolism and bioenergetics. PLoS pathogens 2010, 6, e1000719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, P.L.; Duponchel, S.; Eischeid, H.; Molle, J.; Michelet, M.; Diserens, G.; Vermathen, M.; Vermathen, P.; Dufour, J.F.; Dienes, H.P.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection triggers a tumor-like glutamine metabolism. Hepatology 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, B.; Kensicki, E.; Mohney, R.; Hall, W.W. Metabolomic profile of hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewaid, H.; Aoyagi, H.; Arita, M.; Watashi, K.; Suzuki, R.; Sakai, S.; Kumagai, K.; Yamaji, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Kato, F.; et al. Sphingomyelin Is Essential for the Structure and Function of the Double-Membrane Vesicles in Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication Factories. J Virol 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, A.E. Mammalian polyamine metabolism and function. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.A.; Bartosch, B.; Zakirova, N.F.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V. Polyamine Metabolism and Oxidative Protein Folding in the ER as ROS-Producing Systems Neglected in Virology. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, I.S.; Delling, M.; Clapham, D.E. An introduction to TRP channels. Annual review of physiology 2006, 68, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casero, R.A., Jr.; Murray Stewart, T.; Pegg, A.E. Polyamine metabolism and cancer: treatments, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2018, 18, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Asim, M.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Barry, D.P.; Hoge, S.; de Sablet, T.; Delgado, A.G.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Yan, F.; et al. Spermine oxidase mediates the gastric cancer risk associated with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.C.; Destefano Shields, C.E.; Wu, S.; Huso, D.L.; Wu, X.; Murray-Stewart, T.R.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Woster, P.M.; Sears, C.L.; et al. Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2011, 108, 15354–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evageliou, N.F.; Haber, M.; Vu, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Murray, J.; Gamble, L.D.; Cheng, N.C.; Liu, K.; Reese, M.; Corrigan, K.A.; et al. Polyamine Antagonist Therapies Inhibit Neuroblastoma Initiation and Progression. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 4391–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier Sholler, G.L.; Gerner, E.W.; Bergendahl, G.; MacArthur, R.B.; VanderWerff, A.; Ashikaga, T.; Bond, J.P.; Ferguson, W.; Roberts, W.; Wada, R.K.; et al. A Phase I Trial of DFMO Targeting Polyamine Addiction in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0127246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.A.; A. , K.T.; Ivanova, O.N.; Hyvonen, M.T.; Khomutov, A.R.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Bartosch, B.; Ivanov, A.V. Hepatitis C virus alters metabolism of biogenic polyamines by affecting expression of key enzymes of their metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Pulido, Y.E.; Mounce, B.C. Good cop, bad cop: Polyamines play both sides in host immunity and viral replication. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2023, 146, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomutov, A.R.; Vepsalainen, J.J.; Shvetsov, A.S.; Hyvonen, T.; Keinanen, T.A.; Pustobaev, V.N.; Eloranta, T.O.; Khomutov, R.M. Synthesis of hydroxylamine analogues of polyamines. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 13751–13766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golikov, M.V.; Karpenko, I.L.; Lipatova, A.V.; Ivanova, O.N.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Larichev, V.F.; Zakirova, N.F.; Leonova, O.G.; Popenko, V.I.; Bartosch, B.; et al. Cultivation of Cells in a Physiological Plasmax Medium Increases Mitochondrial Respiratory Capacity and Reduces Replication Levels of RNA Viruses. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Voorde, J.; Ackermann, T.; Pfetzer, N.; Sumpton, D.; Mackay, G.; Kalna, G.; Nixon, C.; Blyth, K.; Gottlieb, E.; Tardito, S. Improving the metabolic fidelity of cancer models with a physiological cell culture medium. Sci Adv 2019, 5, eaau7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Date, T.; Murayama, A.; Morikawa, K.; Akazawa, D.; Wakita, T. Cell culture and infection system for hepatitis C virus. Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukhanova, M.K.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Smirnova, O.A.; Khomich, O.A.; Zakirova, N.F.; Ivanova, O.N.; Ziganshin, R.; Bartosch, B.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V. Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Is Regulated by Cysteine S-Glutathionylation. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019, 2019, 3196140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyvonen, M.T.; Keinanen, T.A.; Nuraeva, G.K.; Yanvarev, D.V.; Khomutov, M.; Khurs, E.N.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Vepsalainen, J.; Zhgun, A.A.; Khomutov, A.R. Hydroxylamine Analogue of Agmatine: Magic Bullet for Arginine Decarboxylase. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindlisbacher, B.; Schmid, C.; Geiser, T.; Bovet, C.; Funke-Chambour, M. Serum metabolic profiling identified a distinct metabolic signature in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - a potential biomarker role for LysoPC. Respir Res 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.R. Calf liver nuclear N-acetyltransferases. Purification and properties of two enzymes with both spermidine acetyltransferase and histone acetyltransferase activities. J Biol Chem 1978, 253, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, J.; Williams-Ashman, H.G. On the purification of L-ornithine decarboxylase from rat prostate and effects of thiol compounds on the enzyme. J Biol Chem 1971, 246, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Smirnova, O.A.; Ivanova, O.N.; Masalova, O.V.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Isaguliants, M.G. Hepatitis C virus proteins activate NRF2/ARE pathway by distinct ROS-dependent and independent mechanisms in HUH7 cells. PLoS One 2011, 6, e24957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunitskaya, V.L.; Eliseeva, O.V.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Tyurina, D.A.; Zakirova, N.F.; Khomich, O.A.; Kalis, M.; Latyshev, O.E.; Starodubova, E.S.; Ivanova, O.N.; et al. Prokaryotic Expression, Purification and Immunogenicity in Rabbits of the Small Antigen of Hepatitis Delta Virus. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golikov, M.V.; Bartosch, B.; Smirnova, O.A.; Ivanova, O.N.; Ivanov, A.V. Plasma-Like Culture Medium for the Study of Viruses. mBio 2023, 14, e0203522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalecka, M.; Kazberuk, A.; Palka, J.; Surazynski, A. P5C as an Interface of Proline Interconvertible Amino Acids and Its Role in Regulation of Cell Survival and Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, K.R.; Marek, S.; Linehan, J.A.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Payne, C.M.; Gerner, E.W. Detoxification of the polyamine analogue N1-ethyl-N11-[(cycloheptyl)methy]-4,8-diazaundecane (CHENSpm) by polyamine oxidase. Clin Cancer Res 2002, 8, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lou, F.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Niu, L.; Wang, Z.; Deng, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Bai, J.; Yin, Q.; et al. Excessive Polyamine Generation in Keratinocytes Promotes Self-RNA Sensing by Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis. Immunity 2020, 53, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Wang, C.; Fessler, J.; DeTomaso, D.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Kaminski, J.; Zaghouani, S.; Christian, E.; Thakore, P.; Schellhaass, B.; et al. Metabolic modeling of single Th17 cells reveals regulators of autoimmunity. Cell 2021, 184, 4168–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, U.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Park, A.; Jung, K.L.; Lee, S.A.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.R.; Lai, C.J.; Eoh, H.; Jung, J.U. Herpesvirus-induced spermidine synthesis and eIF5A hypusination for viral episomal maintenance. Cell Rep 2022, 40, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Gan, Y.J.; Davis, T.O.; Scott, R.S. Downregulation of the polyamine regulator spermidine/spermine N(1)-acetyltransferase by Epstein-Barr virus in a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. Virus Res 2013, 177, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, B.; Bragado, L.; Mammi, P.; Torti, M.F.; Gaioli, N.; Gebhard, L.G.; Garcia Sola, M.E.; Vaz-Drago, R.; Iglesias, N.G.; Garcia, C.C.; et al. Dengue virus targets RBM10 deregulating host cell splicing and innate immune response. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 6824–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiches, G.N.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Biswas, A.; Li, T.W.; Kong, W.; Jean, M.; Santoso, N.G.; Zhu, J. Polyamine biosynthesis and eIF5A hypusination are modulated by the DNA tumor virus KSHV and promote KSHV viral infection. PLoS pathogens 2022, 18, e1010503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassen, N.C.; Papies, J.; Bajaj, T.; Emanuel, J.; Dethloff, F.; Chua, R.L.; Trimpert, J.; Heinemann, N.; Niemeyer, C.; Weege, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, Z.; Fang, L.; Ke, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, P.; Xiao, S. Polyamine regulation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection depends on spermidine-spermine acetyltransferase 1. Vet Microbiol 2020, 250, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ai, Q.; Tong, T.; Liao, M.; Fan, H. PEDV infection affects the expression of polyamine-related genes inhibiting viral proliferation. Virus Res 2022, 312, 198708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrodomenico, V.; LoMascolo, N.J.; Firpo, M.R.; Villanueva Guzman, M.D.M.; Zaporowski, A.; Mounce, B.C. Persistent Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in Pancreatic Ductal Cells In Vitro Downregulates Cellular Polyamine Metabolism. mSphere 2023, 8, e0003623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrodomenico, V.; Esin, J.J.; Qazi, S.; Khomutov, M.A.; Ivanov, A.V.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Mounce, B.C. Virion-Associated Polyamines Transmit with Bunyaviruses to Maintain Infectivity and Promote Entry. ACS infectious diseases 2020, 6, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrodomenico, V.; LoMascolo, N.J.; Cruz-Pulido, Y.E.; Cunha, C.R.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamine-Linked Cholesterol Incorporation in Rift Valley Fever Virus Particles Promotes Infectivity. ACS infectious diseases 2022, 8, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, M.R.; Mastrodomenico, V.; Hawkins, G.M.; Prot, M.; Levillayer, L.; Gallagher, T.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Mounce, B.C. Targeting Polyamines Inhibits Coronavirus Infection by Reducing Cellular Attachment and Entry. ACS infectious diseases 2021, 7, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicmal, T.M.; Tate, P.M.; Dial, C.N.; Esin, J.J.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamine Depletion Abrogates Enterovirus Cellular Attachment. J Virol 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrodomenico, V.; Esin, J.J.; Graham, M.L.; Tate, P.M.; Hawkins, G.M.; Sandler, Z.J.; Rademacher, D.J.; Kicmal, T.M.; Dial, C.N.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamine Depletion Inhibits Bunyavirus Infection via Generation of Noninfectious Interfering Virions. J Virol 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.E.; Filone, C.M.; Rozelle, D.; Mire, C.E.; Agans, K.N.; Hensley, L.; Connor, J.H. Polyamines and Hypusination Are Required for Ebolavirus Gene Expression and Replication. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounce, B.C.; Cesaro, T.; Moratorio, G.; Hooikaas, P.J.; Yakovleva, A.; Werneke, S.W.; Smith, E.C.; Poirier, E.Z.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Prot, M.; et al. Inhibition of Polyamine Biosynthesis Is a Broad-Spectrum Strategy against RNA Viruses. J Virol 2016, 90, 9683–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Luna, L.; Posadas-Modragon, A.; Avila-Trejo, A.M.; Alcantara-Farfan, V.; Rodriguez-Paez, L.I.; Santiago-Cruz, J.A.; Pastor-Alonso, M.O.; Aguilar-Faisal, J.L. Inhibition of chikungunya virus replication by N-omega-Chloroacetyl-L-Ornithine in C6/36, Vero cells and human fibroblast BJ. Antivir Ther 2023, 28, 13596535231155263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Wang, Z.; Pi, S.; Long, Q.; Chen, K.; Cui, J.; Huang, A.; Hu, Y. Difluoromethylornithine, a Decarboxylase 1 Inhibitor, Suppresses Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Reducing HBc Protein Levels. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korovina, A.N.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Khomutov, M.A.; Simonian, A.R.; Khomutov, A.R.; Ivanov, A.I.; Kochetkov, S.N. Biogenic Polyamines Spermine and Spermidine Activate RNA Polymerase and Inhibit RNA Helicase of Hepatitis C Virus. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2012, 77, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsebosch, B.M.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamine Analog Diethylnorspermidine Restricts Coxsackievirus B3 and Is Overcome by 2A Protease Mutation In Vitro. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.A.; Isaguliants, M.G.; Hyvonen, M.T.; Keinanen, T.A.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Vepsalainen, J.; Alhonen, L.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V. Chemically induced oxidative stress increases polyamine levels by activating the transcription of ornithine decarboxylase and spermidine/spermine-N1-acetyltransferase in human hepatoma HUH7 cells. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, M.R.; LoMascolo, N.J.; Petit, M.J.; Shah, P.S.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamines and eIF5A hypusination facilitate SREBP2 synthesis and cholesterol production leading to enhanced enterovirus attachment and infection. PLoS pathogens 2023, 19, e1011317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, R.; Llamas-Gonzalez, Y.Y.; Vidal, S.; El Motiam, A.; Bouzaher, Y.H.; Fonseca, D.; Farras, R.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Gonzalez-Santamaria, J.; Rivas, C. eIF5A is activated by virus infection or dsRNA and facilitates virus replication through modulation of interferon production. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 960138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.E.; Cressey, T.N.; Muhlberger, E.; Connor, J.H. Differential Mechanisms for the Involvement of Polyamines and Hypusinated eIF5A in Ebola Virus Gene Expression. J Virol 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.; Hanauske-Abel, H.M.; Palumbo, P.; Saxena, D.; D'Alliessi Gandolfi, D.; Park, M.H.; Pe'ery, T.; Mathews, M.B. Inhibition of HIV-1 gene expression by Ciclopirox and Deferiprone, drugs that prevent hypusination of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polvinen, K.; Sinervirta, R.; Alhonen, L.; Janne, J. Overproduction of ornithine decarboxylase confers an apparent growth advantage to mouse tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1988, 155, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, M.; Riviere, B.; Vegna, S.; Aoun, M.; Gard, C.; Ramos, J.; Assenat, E.; Hibner, U. Hepatitis C viral proteins perturb metabolic liver zonation. Journal of hepatology 2015, 62, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Comparcola, D.; De Stefanis, C.; Nobili, V. Arginase 1: a potential marker of a common pattern of liver steatosis in HCV and NAFLD children. Journal of hepatology 2015, 62, 1207–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Sun, B.; Feitelson, M.A.; Wu, T.; Tur-Kaspa, R.; Fan, Q. Hepatitis C virus targets over-expression of arginase I in hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 2009, 124, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerresheim, G.K.; Bathke, J.; Michel, A.M.; Andreev, D.E.; Shalamova, L.A.; Rossbach, O.; Hu, P.; Glebe, D.; Fricke, M.; Marz, M.; et al. Cellular Gene Expression during Hepatitis C Virus Replication as Revealed by Ribosome Profiling. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakehashi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Ishii, N.; Okuno, T.; Kuwae, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Gi, M.; Stefanov, V.; Wanibuchi, H. Accumulation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, L-arginine and Glucose Metabolites by Liver Tumor Cells Are the Important Characteristic Features of Metabolic Syndrome and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadka, S.; Arthur, K.; Barekatain, Y.; Behr, E.; Washington, M.; Ackroyd, J.; Crowley, K.; Suriyamongkol, P.; Lin, Y.H.; Pham, C.D.; et al. Impaired anaplerosis is a major contributor to glycolysis inhibitor toxicity in glioma. Cancer & metabolism 2021, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, D.C.; Dechaume, A.L.; Murray, P.M.; Katt, W.P.; Baguley, B.C.; Leung, E.Y. Pyruvate anaplerosis is a mechanism of resistance to pharmacological glutaminase inhibition in triple-receptor negative breast cancer. Bmc Cancer 2020, 20, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankouri, J.; Tedbury, P.R.; Gretton, S.; Hughes, M.E.; Griffin, S.D.; Dallas, M.L.; Green, K.A.; Hardie, D.G.; Peers, C.; Harris, M. Enhanced hepatitis C virus genome replication and lipid accumulation mediated by inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107, 11549–11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, J.R.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Kanarek, N.; Freinkman, E.; Gao, X.; Louissaint, A., Jr.; Lewis, C.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Physiologic Medium Rewires Cellular Metabolism and Reveals Uric Acid as an Endogenous Inhibitor of UMP Synthase. Cell 2017, 169, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.J.; Fendt, S.M.; Becker, D.F. The Proline Cycle As a Potential Cancer Therapy Target. Biochemistry-Us 2018, 57, 3433–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, M.R.; Lerat, H.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Hepatitis C virus-induced activation of beta-catenin promotes c-Myc expression and a cascade of pro-carcinogenetic events. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Kohara, M.; Izumi, K.; Kasama, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shuda, M.; Mukaidani, C.; Takano, T.; Tokunaga, Y.; et al. Hepatitis C virus impairs p53 via persistent overexpression of 3beta-hydroxysterol Delta24-reductase. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 36442–36452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Dennis, C.; Naqvi, I.; Dailey, L.; Lorzadeh, A.; Ye, G.; Zaytouni, T.; Adler, A.; Hitchcock, D.S.; Lin, L.; et al. Ornithine aminotransferase supports polyamine synthesis in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 616, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, O.N.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Khomich, O.A.; Khomutov, A.R.; Keinanen, T.A.; Alhonen, L.; Bartosch, B.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; et al. Activation of Polyamine Catabolism by N(1),N(11)-Diethylnorspermine in Hepatic HepaRG Cells Induces Dedifferentiation and Mesenchymal-Like Phenotype. Cells 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, S.K.; Burwell, T.J.; Chambers, R.M.; Rudolph-Owen, L.; Spaltmann, F.; Cook, W.J.; Morris, S.M., Jr. Cloning of human agmatinase. An alternate path for polyamine synthesis induced in liver by hepatitis B virus. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology 2002, 282, G375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Iyo, A.; Piletz, J.E.; Regunathan, S. Expression of human arginine decarboxylase, the biosynthetic enzyme for agmatine. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004, 1670, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell line | Compound | Polyamine (nmol/mg DNA) |
Enzyme activity (nmol/h/mg total protein) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spermidine | Spermine | ODC | SSAT | ||
| Naïve Huh7.5 | Control | 55,3 ± 10,8 | 49,6 ± 8,3 | 9,3 ± 1,2 | 33,1 ± 2,6 |
| DENSpm | 41,8 ± 9,5 | 17,9 ± 3,9 | 54,7 ± 3,2 | 217,5 ± 18,6 | |
| DFMO | 47,0 ± 10,1 | 37,2 ± 5,4 | 5,5 ± 0,6 | 2,7 ± 1,5 | |
| MDL72.527 | 63,5 ± 13,8 | 51,2 ± 13,7 | 4,4 ± 0,7 | 2,3 ± 0,2 | |
| HCV replicon- harboring Huh7.5 cells |
Control | 38,7 ± 6,1 | 27,9 ± 10,6 | 4,3 ± 1,1 | 8,6 ± 0,8 |
| DENSpm | 33,3 ± 8,3 | 14,1 ± 7,4 | 38,7 ± 2,1 | 190,3 ± 10,7 | |
| DFMO | 177,3 ± 42,2 | 140,1 ± 52,1 | 7,1 ± 1,5 | 1,2 ± 0,1 | |
| MDL72.527 | 227,6 ± 39,4 | 177,6 ± 27,8 | 17,4 ± 3,3 | 1,2 ± 0,2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





