Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Familiarization
2.3. Experimental Session
2.4. Blood Collection and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
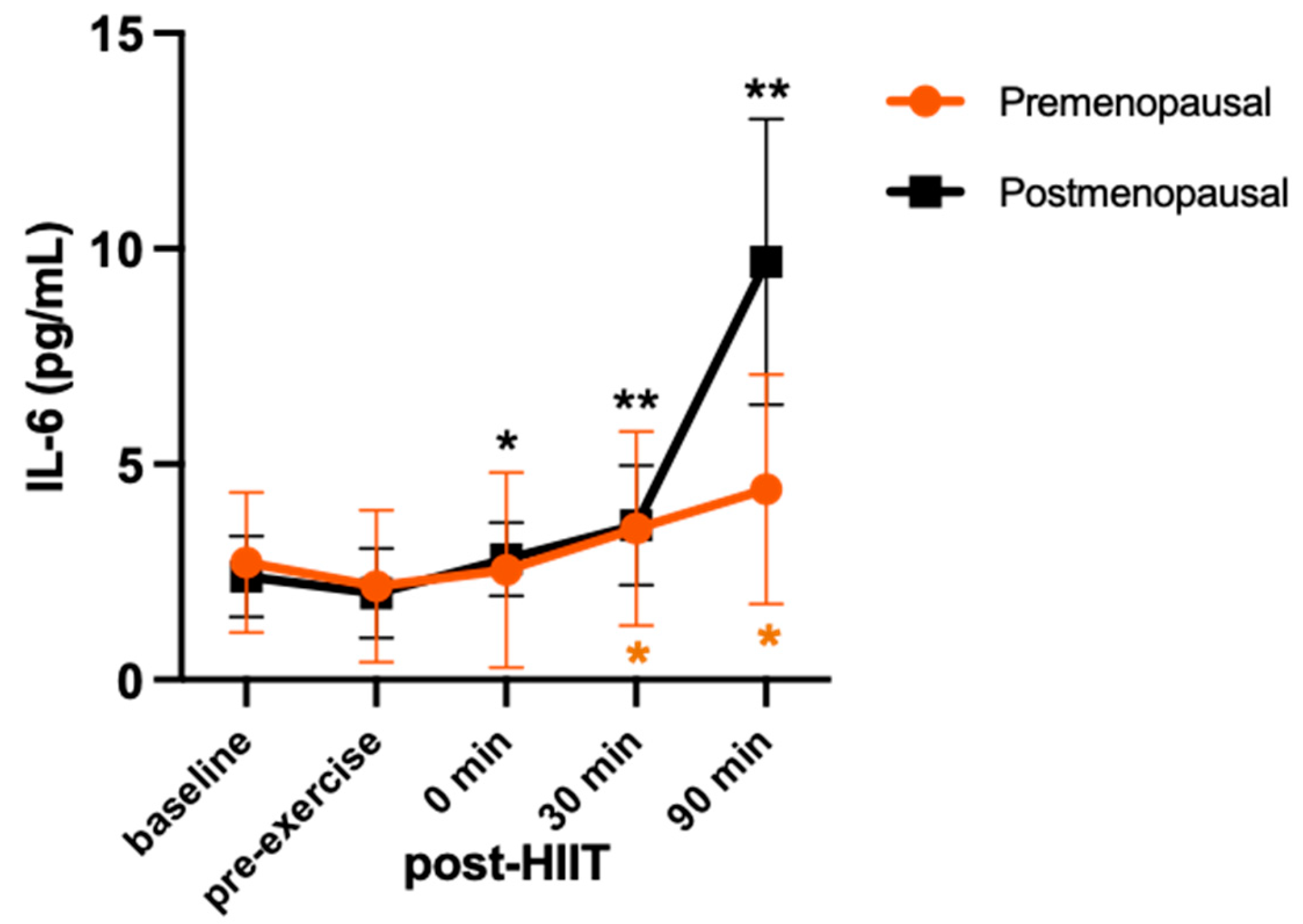
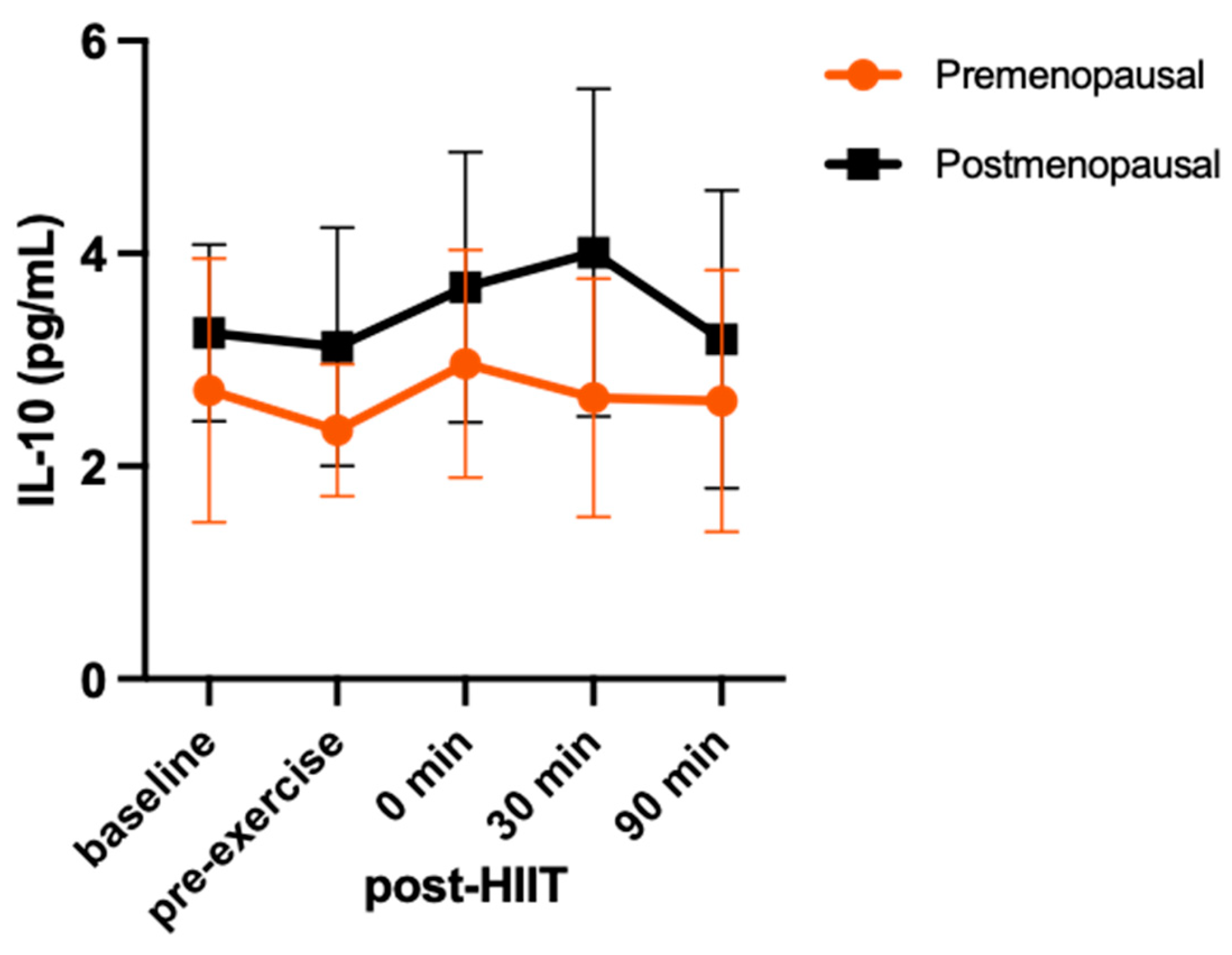
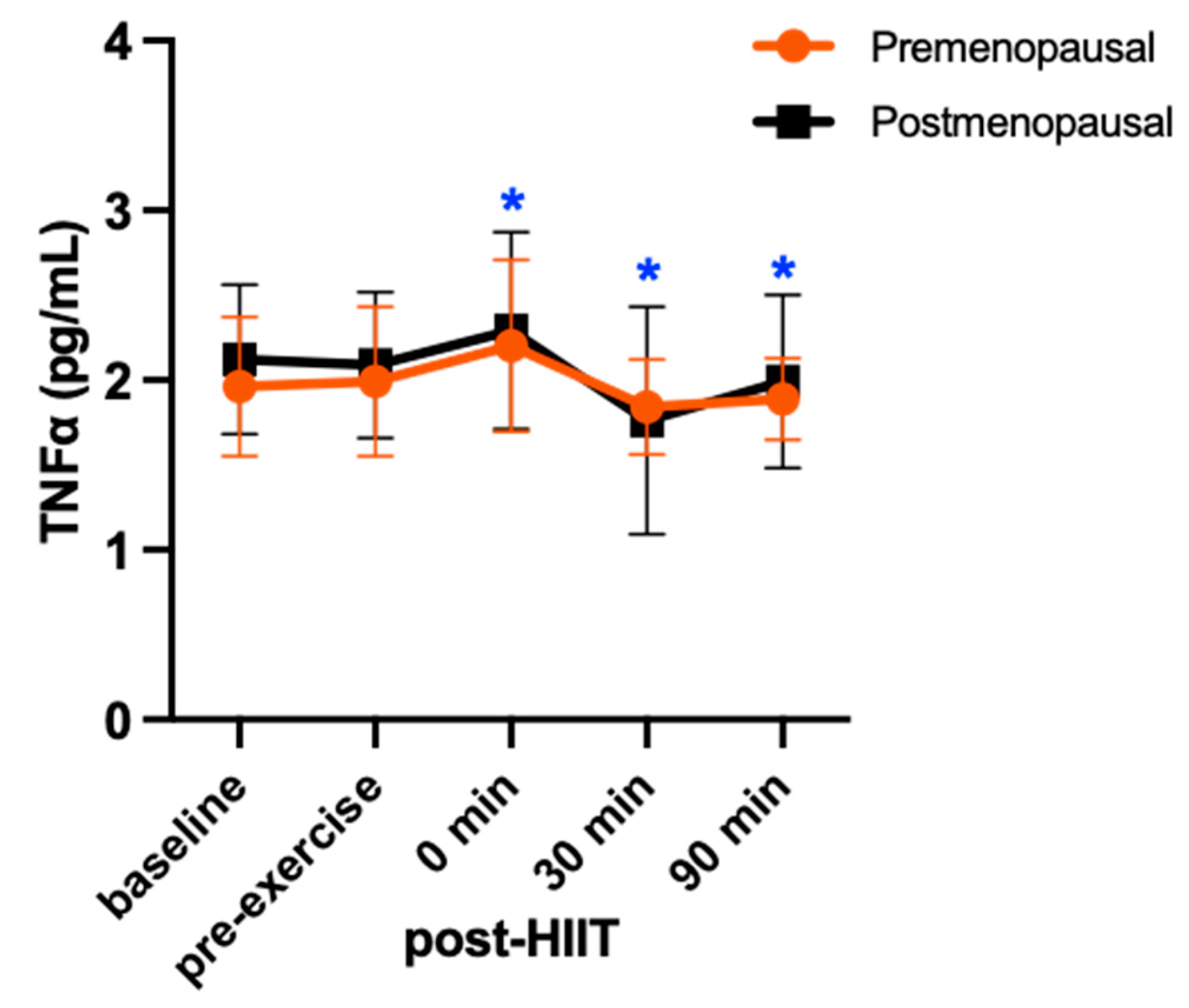
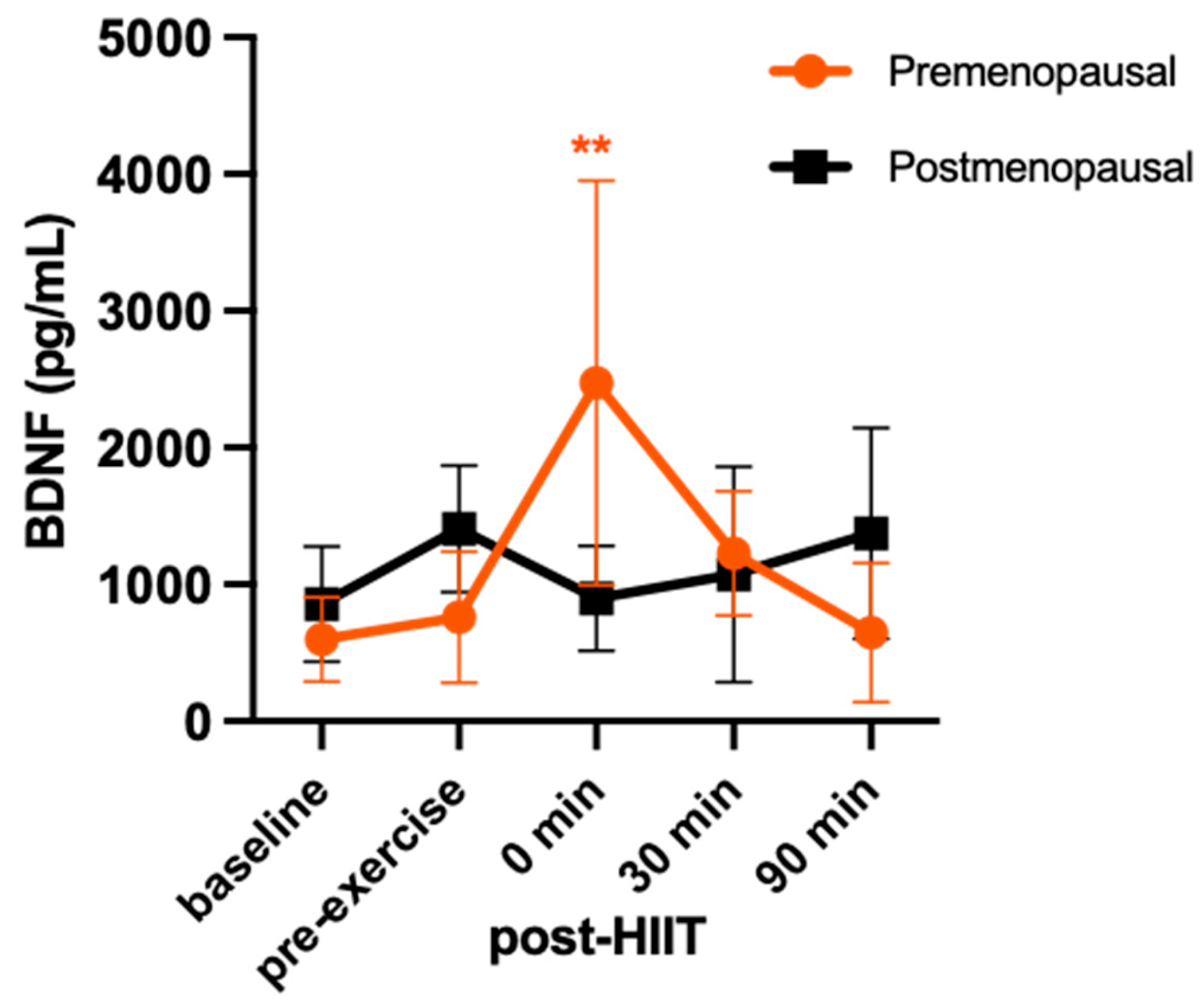
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, H. D. (2008). Menopause. The Lancet, 371(9614), 760–770. [CrossRef]
- Malutan, A. M., Dan, M., Nicolae, C., & Carmen, M. (2014). Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine changes related to menopause. Przegla̜d Menopauzalny = Menopause Review, 13(3), 162–168. [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, R., Brown, C., Puscheck, E., Friedrich, E., Slatopolsky, E., Maggio, D., McCracken, R., & Avioli, L. V. (1991). Effect of surgical menopause and estrogen replacement on cytokine release from human blood mononuclear cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88(12), 5134. [CrossRef]
- Pfeilschifter, J., Köditz, R., Pfohl, M., & Schatz, H. (2002). Changes in Proinflammatory Cytokine Activity after Menopause. Endocrine Reviews, 23(1), 90–119. [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, E., Sharma, M., Rezig, A. O., Morsy, M., Ialenti, A., Pellicori, P., Bruzzese, D., Maffia, P., & Guzik, T. J. (2023, July). Inflammatory Cytokines and Risk of Developing Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 19th World Congress of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (WCP2023), Glasgow, Scotland. [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-H., Luo, M.-Y., Liang, N.-, Gong, S.-X., Chen, W., Huang, W.-Q., Tian, Y., & Wang, A.-P. (2021). Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 745061. [CrossRef]
- Feghali, C. A., & Wright, T. M. (1997). Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Frontiers in Bioscience: A Journal and Virtual Library, 2, d12-26. [CrossRef]
- Docherty, S., Harley, R., McAuley, J. J., Crowe, L. A. N., Pedret, C., Kirwan, P. D., Siebert, S., & Millar, N. L. (2022). The effect of exercise on cytokines: Implications for musculoskeletal health: a narrative review. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation, 14(1), 5. [CrossRef]
- Allen, J., Sun, Y., & Woods, J. (2015). Exercise and the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 135. [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M., Bishop, N. C., Stensel, D. J., Lindley, M. R., Mastana, S. S., & Nimmo, M. A. (2011). The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nature Reviews Immunology, 11(9), 607–615. [CrossRef]
- Azizbeigi, K., Azarbayjani, M. A., Atashak, S., & Stannard, S. (2015). Effect of Moderate and High Resistance Training Intensity on Indices of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress. Research in Sports Medicine (Print), 23, 73–87. [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, É., Marinho, D. A., Neiva, H. P., & Lourenço, O. (2020). Inflammatory Effects of High and Moderate Intensity Exercise—A Systematic Review. Frontiers in Physiology, 10, 1550. [CrossRef]
- Zwetsloot, K. A., John, C. S., Lawrence, M. M., Battista, R. A., & Shanely, R. A. (2014). High-intensity interval training induces a modest systemic inflammatory response in active, young men. Journal of Inflammation Research, 7, 9–17. [CrossRef]
- Kapilevich, L. V., Zakharova, A. N., Kabachkova, A. V., Kironenko, T. A., & Orlov, S. N. (2017). Dynamic and Static Exercises Differentially Affect Plasma Cytokine Content in Elite Endurance- and Strength-Trained Athletes and Untrained Volunteers. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, 35. [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W. J., & Ratamess, N. A. (2005). Hormonal Responses and Adaptations to Resistance Exercise and Training. Sports Medicine, 35(4), 339–361. [CrossRef]
- Fragala, M. S., Kraemer, W. J., Denegar, C. R., Maresh, C. M., Mastro, A. M., & Volek, J. S. (2011). Neuroendocrine-Immune Interactions and Responses to Exercise. Sports Medicine, 41(8), 621–639. [CrossRef]
- Bogdanis, G. C. (2012). Effects of Physical Activity and Inactivity on Muscle Fatigue. Frontiers in Physiology, 3, 142. [CrossRef]
- Kany, S., Vollrath, J. T., & Relja, B. (2019). Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6008. [CrossRef]
- Pluchino, N., Russo, M., Santoro, A. N., Litta, P., Cela, V., & Genazzani, A. R. (2013). Steroid hormones and BDNF. Neuroscience, 239, 271–279. [CrossRef]
- Gyorkos, A., Baker, M. H., Miutz, L. N., Lown, D. A., Jones, M. A., & Houghton-Rahrig, L. D. (2019). Carbohydrate-restricted Diet and Exercise Increase Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor and Cognitive Function: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Cureus, 11(9), e5604. [CrossRef]
- Marston, K. J., Newton, M. J., Brown, B. M., Rainey-Smith, S. R., Bird, S., Martins, R. N., & Peiffer, J. J. (2017). Intense resistance exercise increases peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 20(10), 899–903. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P., Brassard, P., Adser, H., Pedersen, M. V., Leick, L., Hart, E., Secher, N. H., Pedersen, B. K., & Pilegaard, H. (2009). Evidence for a release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from the brain during exercise. Experimental Physiology, 94(10), 1062–1069. [CrossRef]
- Reycraft, J. T., Islam, H., Townsend, L. K., Hayward, G. C., Hazell, T. J., & Macpherson, R. E. K. (2020). Exercise Intensity and Recovery on Circulating Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 52(5), 1210–1217. [CrossRef]
- Barha, C. K., Falck, R. S., Davis, J. C., Nagamatsu, L. S., & Liu-Ambrose, T. (2017). Sex differences in aerobic exercise efficacy to improve cognition: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in older rodents. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 46, 86–105. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayes, J., Turco, C. V., Skelly, L. E., Nicolini, C., Fahnestock, M., Gibala, M. J., & Nelson, A. J. (2019). The Effects of Biological Sex and Ovarian Hormones on Exercise-Induced Neuroplasticity. Neuroscience, 410, 29–40. [CrossRef]
- Begliuomini, S., Casarosa, E., Pluchino, N., Lenzi, E., Centofanti, M., Freschi, L., Pieri, M., Genazzani, A. D., Luisi, S., & Genazzani, A. R. (2007). Influence of endogenous and exogenous sex hormones on plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 22(4), 995–1002. [CrossRef]
- Fowles, J. R., O’Brien, M. W., Wojcik, W. R., d’Entremont, L., & Shields, C. A. (2017). A pilot study: Validity and reliability of the CSEP-PATH PASB-Q and a new leisure time physical activity questionnaire to assess physical activity and sedentary behaviours. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism = Physiologie Appliquee, Nutrition Et Metabolisme, 42(6), 677–680. [CrossRef]
- Elliott-Sale, K. J., Minahan, C. L., de Jonge, X. A. K. J., Ackerman, K. E., Sipilä, S., Constantini, N. W., Lebrun, C. M., & Hackney, A. C. (2021). Methodological Considerations for Studies in Sport and Exercise Science with Women as Participants: A Working Guide for Standards of Practice for Research on Women. Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 51(5), 843–861. [CrossRef]
- Hagobian, T. A., & Braun, B. (2010). Physical activity and hormonal regulation of appetite: Sex differences and weight control. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, 38(1), 25–30. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S. F., Islam, H., & Hazell, T. J. (2020). The emerging role of lactate as a mediator of exercise-induced appetite suppression. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 319(4), E814–E819. [CrossRef]
- D.), S. G. (Ph, Dwyer, G. B., & Medicine, A. C. of S. (2007). ACSM’s Metabolic Calculations Handbook. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Routledge. [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G. (2013). Cohen’s d needs to be readily interpretable: Comment on Shieh (2013). Behavior Research Methods, 45. [CrossRef]
- Sinatora, R., Chagas, E., Mattera, F., Mellem, L., de Oliveira dos Santos, A., Pereira, L., Aranão, A., Landgraf Guiguer, E., Cressoni Araujo, A., Haber, J., Campos, L., & Barbalho, S. (2022). Relationship of Inflammatory Markers and Metabolic Syndrome in Postmenopausal Women. Metabolites, 12, 73. [CrossRef]
- Kouvelioti, R., Kurgan, N., Falk, B., Ward, W. E., Josse, A. R., & Klentrou, P. (2019). Cytokine and Sclerostin Response to High-Intensity Interval Running versus Cycling. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 51(12), 2458–2464. [CrossRef]
- Karim, R., Stanczyk, F. Z., Hodis, H. N., Cushman, M., Lobo, R. A., Hwang, J., & Mack, W. J. (2010). Associations between markers of inflammation and physiological and pharmacological levels of circulating sex hormones in postmenopausal women. Menopause (New York, N.Y.), 17(4), 785–790.
- Arent, S. M., Senso, M., Golem, D. L., & McKeever, K. H. (2010). The effects of theaflavin-enriched black tea extract on muscle soreness, oxidative stress, inflammation, and endocrine responses to acute anaerobic interval training: A randomized, double-blind, crossover study. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 7(1), 11. [CrossRef]
- Mezil, Y. A., Allison, D., Kish, K., Ditor, D., Ward, W. E., Tsiani, E., & Klentrou, P. (2015). Response of Bone Turnover Markers and Cytokines to High-Intensity Low-Impact Exercise. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 47(7), 1495–1502. [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M. A., & Pedersen, B. K. (2002). Muscle-derived interleukin-6: Mechanisms for activation and possible biological roles. FASEB Journal: Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 16(11), 1335–1347. [CrossRef]
- Hojman, P., Brolin, C., Nørgaard-Christensen, N., Dethlefsen, C., Lauenborg, B., Olsen, C. K., Åbom, M. M., Krag, T., Gehl, J., & Pedersen, B. K. (2019). IL-6 release from muscles during exercise is stimulated by lactate-dependent protease activity. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 316(5), E940–E947. [CrossRef]
- Zaldivar, F., Wang-Rodriguez, J., Nemet, D., Schwindt, C., Galassetti, P., Mills, P. J., Wilson, L. D., & Cooper, D. M. (2006). Constitutive pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine and growth factor response to exercise in leukocytes. Journal of Applied Physiology (Bethesda, Md.: 1985), 100(4), 1124–1133. [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, C. A. Z., Sierra, A. P. R., Martínez Galán, B. S., Maciel, J. F. de S., Manoel, R., Barbeiro, H. V., de Souza, H. P., & Cury-Boaventura, M. F. (2021). Time Course and Role of Exercise-Induced Cytokines in Muscle Damage and Repair After a Marathon Race. Frontiers in Physiology, 12, 752144. [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A. M. W., & Pedersen, B. K. (2005). The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology (Bethesda, Md.: 1985), 98(4), 1154–1162. [CrossRef]
- Islam, H., Neudorf, H., Mui, A. L., & Little, J. P. (2021). Interpreting “anti-inflammatory” cytokine responses to exercise: Focus on interleukin-10. The Journal of Physiology, 599(23), 5163–5177. [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, C., & Thompson, P. D. (2005). The effects of physical activity on serum C-reactive protein and inflammatory markers: A systematic review. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 45(10), 1563–1569. [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J. R., Hoffman, J. R., Fragala, M. S., Jajtner, A. R., Gonzalez, A. M., Wells, A. J., Mangine, G. T., Fukuda, D. H., & Stout, J. R. (2015). TNF-α and TNFR1 responses to recovery therapies following acute resistance exercise. Frontiers in Physiology, 6, 48. [CrossRef]
- Bathina, S., & Das, U. N. (2015). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Archives of Medical Science : AMS, 11(6), 1164–1178. [CrossRef]
- Knaepen, K., Goekint, M., Heyman, E. M., & Meeusen, R. (2010). Neuroplasticity - exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 40(9), 765–801. [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, S. F., Henry, J., Al-Haddad, R., El Hayek, L., Abou Haidar, E., Stringer, T., Ulja, D., Karuppagounder, S. S., Holson, E. B., Ratan, R. R., Ninan, I., & Chao, M. V. (2016). Exercise promotes the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through the action of the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate. eLife, 5, e15092. [CrossRef]
- Vaynman, S., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2004). Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 20(10), 2580–2590. [CrossRef]
- Matthews, V. B., Aström, M.-B., Chan, M. H. S., Bruce, C. R., Krabbe, K. S., Prelovsek, O., Akerström, T., Yfanti, C., Broholm, C., Mortensen, O. H., Penkowa, M., Hojman, P., Zankari, A., Watt, M. J., Bruunsgaard, H., Pedersen, B. K., & Febbraio, M. A. (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is produced by skeletal muscle cells in response to contraction and enhances fat oxidation via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetologia, 52(7), 1409–1418. [CrossRef]
- Mazo, C. E., Miranda, E. R., Shadiow, J., Vesia, M., & Haus, J. M. (2022). High Intensity Acute Aerobic Exercise Elicits Alterations in Circulating and Skeletal Muscle Tissue Expression of Neuroprotective Exerkines. Brain Plasticity (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 8(1), 5–18. [CrossRef]
- Wiet, R. (2018). The effects of acute aerobic exercise on BDNF levels and cognition in postmenopausal women [ClevelandStateUniversity]. https://etd.ohiolink.edu/acprod/odb_etd/etd/r/1501/10?clear=10&p10_accession_num=csu1527873335485353.
- Berchtold, N. C., Kesslak, J. P., Pike, C. J., Adlard, P. A., & Cotman, C. W. (2001). Estrogen and exercise interact to regulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein expression in the hippocampus. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 14(12), 1992–2002. [CrossRef]
- Islam, H., Townsend, L. K., & Hazell, T. J. (2017). Modified sprint interval training protocols. Part I. Physiological responses. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 42(4), 339–346. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S. F., Ferguson, E. J., Jarosz, C., Kenno, K. A., & Hazell, T. J. (2023). Similar Postexercise Hypotension After MICT, HIIT, and SIT Exercises in Middle-Age Adults. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 55(1), 101–109. [CrossRef]
- Vanderheyden, L. W., McKie, G. L., Howe, G. J., & Hazell, T. J. (2020). Greater lactate accumulation following an acute bout of high-intensity exercise in males suppresses acylated ghrelin and appetite postexercise. Journal of Applied Physiology (Bethesda, Md.: 1985), 128(5), 1321–1328. [CrossRef]
| Baseline (fasted) | pre-exercise (postprandial) |
0 min post-HIIT |
30 min post-HIIT |
30 min Post-HIIT |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Lactate (mmol/L) | |||||
| Premenopausal | 0.72 ± 0.52* | 1.19 ± 0.70# | 1.80 ± 1.02#* | 1.14 ± 0.60# | 0.77 ± 0.36* |
| Postmenopausal | 0.50 ± 0.18* | 0.80 ± 0.29# | 2.28 ± 0.94#* | 1.17 ± 0.35#* | 0.86 ± 0.17# |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





