Introduction
A collection of blood illnesses affecting red blood cells are called hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobin, a protein found in blood cells, transports oxygen throughout the body and absorbs carbon dioxide. A hemoglobinopathy problem can result in an abnormal level of protein production or an aberrant structure for this protein. Common types of hemoglobinopathy are Sickle cell disease (SCD), thalassemia, hemoglobin C disease, and hemoglobin E/D disease (Old, 1996; Kohne, 2011). People with thalassemia may have mild or severe anemia even as severe anemia can damage organs and lead to death (Bajwa et al., 2022; Hamamy and Al-Allawi, 2013). While this disease is commonly seen in the Mediterranean regions, southeast Asia including India is traditionally known as the “thalassemia belt”. β--thalassemia is caused by mutations in one or more alleles of the autosomal recessive Hemoglobin Subunit β- (HBB) gene ( Kohne et al ., 2011). The synthesis of the β- chain is controlled by two gene clusters of chromosomes 11. More severe symptoms result from the homozygous state in the HBB wherein there are also other associated Anemia like Aplastic Anemia (Peslak et al. 2017). The degree of globin chain imbalance in β--thalassemia is determined by the nature of the mutation of the β- gene. β- globin chains are produced by two linked β- genes present in chromosome 11. We know that two alleles of each gene and four genes encode β--globin production. The severity of β--thalassemia depends firstly on the number of genes affected, and then based on whether it’s a gene deletion or a non-deletional mutation. On the other hand, Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) affects the hemoglobin molecules in RBC ( Kato et al. 2010). The ability of hemoglobin to deliver oxygen is compromised when it is abnormal, as incase of SCD, making the RBC to curve, sickle-shaped, and become rigid. When a person inherits two hemoglobin "S" genes, they are presumed to have sickle cell anemia, the most prevalent and dangerous form of SCD. Children with the syndrome may endure slow growth or delayed development, and some patients may experience chronic (long-term) pain. The brain, kidneys, liver, lungs, eyes, heart, spleen, genitals, joints, and skin are just a few of the organs that sickle cell disease may damage over time (Rees, 2010). These are caused by a qualitative defect in the genetic code that leads to structural changes in the hemoglobin molecule. Most alpha and β- globin chain variants are clinically silent and are discovered incidentally or during the screening of family members of a patient. A few variant hemoglobins are capable of causing severe disease, especially in the homozygous state (e.g.: HbS) or when inherited in conjunction with another variant or a thalassemia mutation. Common examples of variant hemoglobins in India include HbS, HbE, and HbD (Thom, 2013). In this work, we attempted to perform machine learning heuristics in discovering candidate genes associated with these diseases.
Materials and Methods
Case study 1: An inventory of 370 cases from the Genetic and Genome Sequencing Lab (2022-2023), was used to train and test the machine-learning tools, to accurately predict β-thalassemia carriers. Ethics clearance and informed consent was done apriori from Lok Nayak Hospital/Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi. The input parameters are hemoglobin count (HGB), mean cell volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH). From 370 patients’ data, we deemed that 200 of them were "index patients"; they were the point person for every request for β--thalassemia testing sent to the laboratory. 170 people were family members of the index patients who completed the family survey. Overall, there were 161 males and 209 females. One patient with hemoglobin H disease and two patients with β-thalassemia major based on genetic diagnosis were excluded from the final dataset for modeling because the study focuses on thalassemia carriers. In addition to these, the material contained certain important diagnostic categories called "phenotypes." In addition to the above variables, age and gender were included in the exploratory analysis (Rustam F,). We identified two labels, viz. β-thalassemia carriers (those carrying a single gene allele mutation) and normal individuals with the input data was saved as a "comma separated value" (.csv extension).The use of machine learning makes two potential advantages of this tool: less time consumption, and less economic burden (Asmarian N et al.2022). We employed Random Forest (RF), Logistic Regression (LR), Support Vector Machine (SVM) and ANN (Artificial Neural Network) using Scikit-learn.Python programming language with Data Science libraries NumPy (version 1.24), Pandas (version 1.1.2.), Matplotlib (version 3.3.2.) and Scikit-learn (version 0.23.2) and Deep Learning library Keras (version 3.2) were imported. While the command Split was used to split training and test data for RF, LR and SVM (7:3, 8:2 and 9:1), Keras library was used to train and test neural networks in an integrated development environment (IDE) set in Jupyter Notebooks. (Sadiq, S.,),(
Case study 2: For hemoglobin variant prediction, 250 instances were collected from Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi as indicated earlier with the same duration for the prediction of Hemoglobin variants gathering the necessary details required for the prediction. We obtained MCH, MCHC, MCV besides hemoglobin count, viz. HbS (hemoglobin S) and HbE (hemoglobin E) as the input variables (Das, R., ). Gender was incorporated into the exploratory analysis in addition to the previously mentioned factors.137 females and 112 males were reported haemoglobinopathies (HbS and HbE).Two labels were found in this study: those who have hemoglobin variations and those who are normal. We used three different supervised learning algorithms like K nearest neighbors (KNN), Naive Bayes (NB), and decision trees(DTs), and the performance was measured based on the accuracy, F1 score confusion matrix with precision and accuracy metrics.(Borah, M. S., )
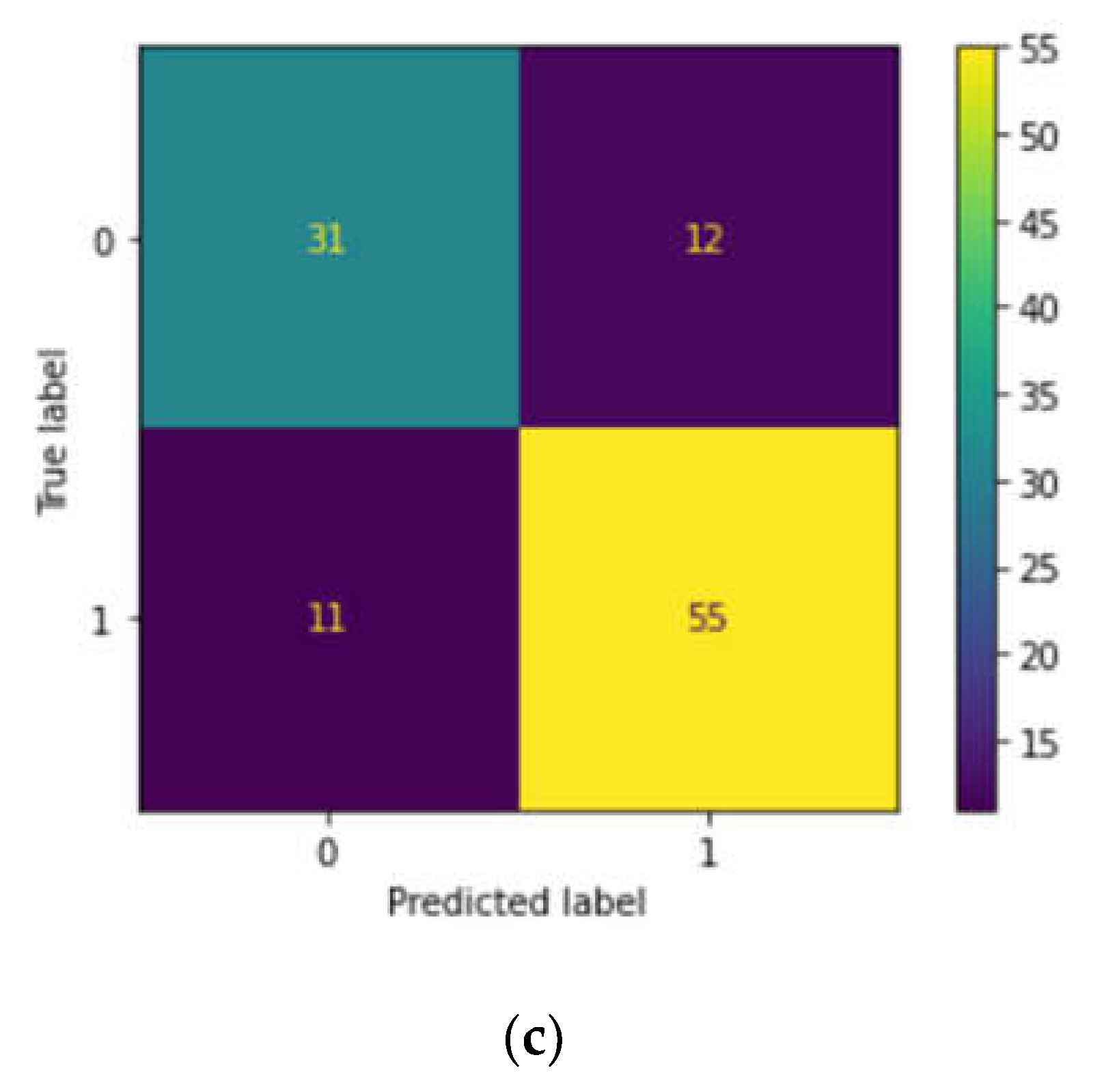
Case study 3: We also downloaded 597 instances from the ClinVar database which we deem as a validation cohort to predict clinical significance, obtaining the necessary details for prediction using RF, SVM and LR. The input variables chosen were Protein change (numbered as 1 if there is any protein change and if there is no change, numbered as 0), Review status (numbered as 1 if the review status is provided and if not provided, numbered as 0), and Condition (Beta-thalassemia (1), Other hemoglobinopathies(2) and no disease reported (0).The output data chosen is clinical significance(Pathogenic (1) or benign (0)) and after training each model, we assessed their performance using metrics using the confusion matrix, precision and accuracy. By comparing the performance on both the training and test sets, we evaluated and compared the accuracy of the three models taking the following attributes from ClinVar data, viz. clinical significance, protein change, condition and review status.
Results and Discussion
Random Forest Proved to Be the Most Accurate Classifier to Predict β—Thalassemia Carriers
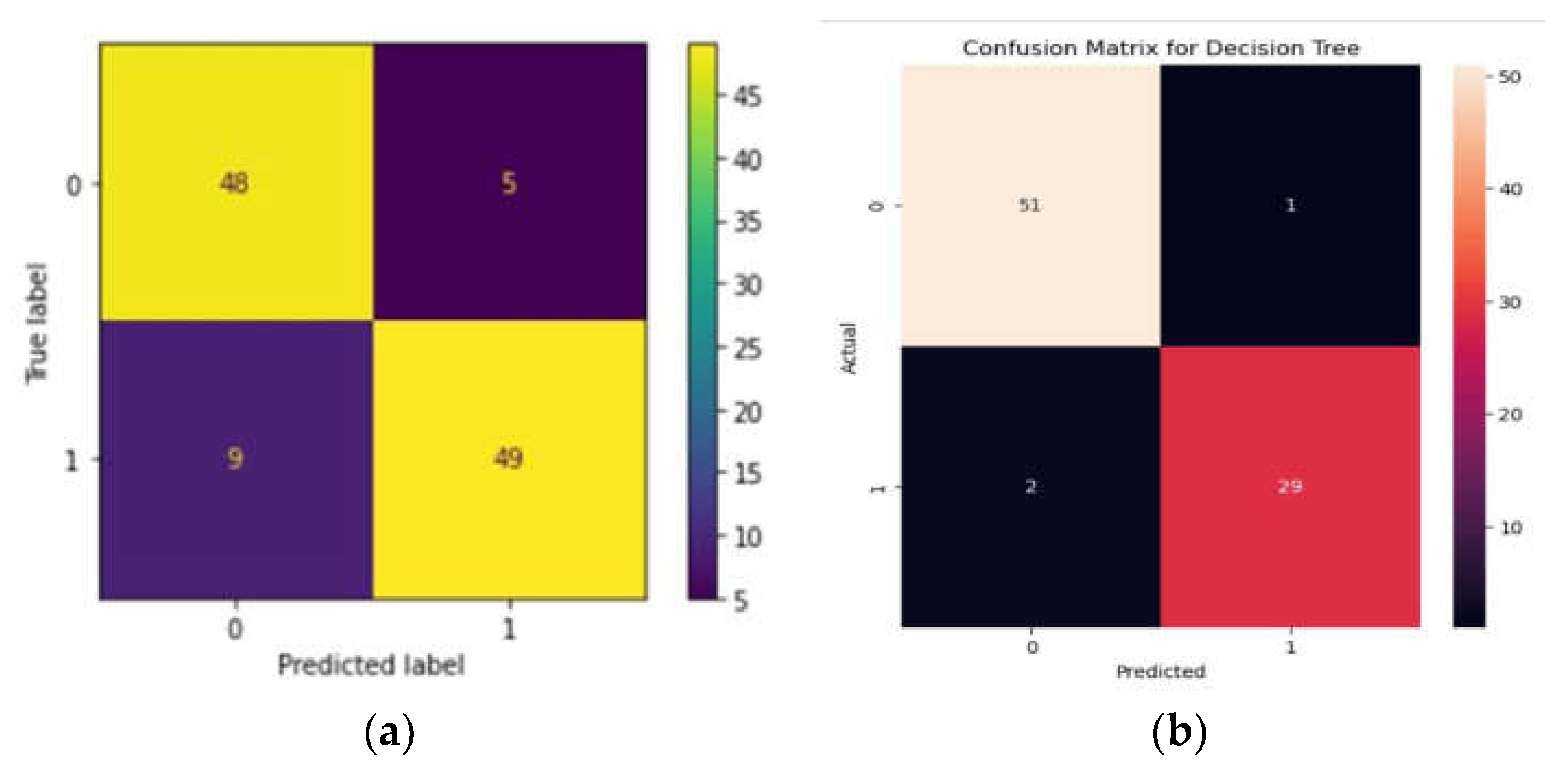
The RF algorithm yielded an accuracy of 87.39%, with an F1 score of 87%. The precision shown by the algorithm is 84% with a sensitivity of 90%. Precision, accuracy, and sensitivity was calculated using a confusion matrix (
Figure 1a). Beta-thalassemia carriers are denoted as 1 and normal denoted as 0.
Variant Prediction Using DT Yielded Good Accuracy
When the data was subjected to machine learning heuristics, we observed that among all the algorithms, the DT performed well with an accuracy of 96% while the NB algorithm showed 93% and KNN showed 80% respectively. We predicted accuracy and from the confusion matrix, 0 represents the presence of variants and 1 represents the absence of variants. We plotted TP, TN, FP and FNs with TPs showing 51% and TN - 29% while FP and FN showing 2% and 1% respectively(
Figure 1b).
Discussion
Hemoglobinopathies and thalassemias are genetic diseases and are common worldwide. In this work, we exploited the accuracy of machine learning tools to improve the screening for β--thalassemia carriers that can then be adapted to deal with similar issues both internally and externally. The lack of a current screening process has been one of the main problems with the increase in β--thalassemia carriers. If a predictive tool based on machine learning can help in this process, it also takes less time to conduct screening, because machine learning tools are used in the form of computer software, and inputs can be processed much faster than manual testing, saving valuable time and costs of traditional surveys. However, using such a tool in a practical clinical context is not easy. Although machine learning models have proven accurate in many clinical problems, including tabular data processing, few have been translated into real-world applications. Machine learning models have inherent issues since they are only intelligent in a limited range and cannot extend their intelligence to things they have not seen. With the data dynamic and inviting bias, if the inputs are not of the expected quality, models can produce incorrect results. This also implies that when the model is verified in a real-world setting in the future, it will be given the opportunity to be exposed to fresh data and further trained, which will increase its accuracy and dependability. Therefore, experimenting with these technologies to find innovative solutions where traditional methods are insufficient can provide unique solutions. We aimed to find such a solution to a disease with a significant global burden, and the tool was used to predict the β--thalassemia carriers and haemoglobinopathies. We further discovered mutations in SCD pertaining to the North Indian registry. Upon employing machine learning heuristics, the DT models have shown great performance and have the potential to be used as a tool for hemoglobinopathy identification in medical laboratory work methods. These findings suggest that our machine learning algorithms are provided with sufficient, which could predict a variety of hemoglobin variants. Our models, however, need to be evaluated using a large number of datasets employing a wider range of patient data associated with hemoglobinopathies. We identified significant ClinVar pathogenic variants and protein changes, if any utilizing machine learning heuristics, viz. LR models. Our analyses demonstrated modest performance and could serve as a valuable tool for identifying hemoglobinopathies in medical laboratory procedures. These results indicate that our machine learning algorithms possess the capability to predict highly heterogeneous and clinically relevant data given adequate test data. Nonetheless, it is crucial to assess our models using a diverse array of datasets and a broader range of patient data related to hemoglobinopathies for comprehensive evaluation. While this could be a limitation, we argue that clinically relevant data have a difficulty in manifesting the predictions using ML models. While it is very important to comprehend and identify the pathophysiology for the treatment and disease prediction, the application of prenatal diagnosis, and awareness programs is the only way to prevent the occurrence of this type of rare and genetic disease.
Conclusions
As the number of hemoglobinopathies (especially β-thalassemia and SCD) patients increases, the need to analyze Hemoglobin variants and β-thalassemia carriers at an early stage increases. Current methods for detecting these are expensive and time-consuming and therefore our screening of mutations in a cohort of β--thalassemia and SCD was used to propose an ensemble classifier for β-thalassemia carrier screening and to analyze hemoglobin variants. The dataset used in this work was compiled from whole blood analysis tests. We further utilized ClinVar data to predict the clinical significance of genetic variations in hemoglobinopathies and attempted to unravel the implications of specific genetic alterations related to hemoglobin disorders. By analyzing a diverse range of genetic variants associated with these conditions, our research contributes to a better understanding of the molecular aspects of hemoglobinopathies.
References
- Antonio Cao, Renzo Galanello , β--thalassemia, Genetics in Medicine Volume 12, Issue 2010,Pages 61-76,ISSN 1098-3600. [CrossRef]
- Arica V, Arica S, Özer C, Çevik M. Serum Lipid Values in Children with β--thalassemia Major. Pediat Therapeut. 2012; 2:130. [CrossRef]
- Asmarian N, Kamalipour A, Hosseini-Bensenjan M, Karimi M, Haghpanah S. Prediction of Heart and Liver Iron Overload in β-Thalassemia Major Patients Using Machine Learning Methods. Hemoglobin. 2022 Nov;46(6):303-307. [CrossRef]
- Aszhari FR, Rustam Z, Subroto F, Semendawai AS. Classification of thalassemia data using random forest algorithm. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020 Mar;1490:012050. [CrossRef]
- Aydinok Y, Kattamis A, Viprakasit V. Current approach to iron chelation in children. Br J Haematol 2014;745–755. [CrossRef]
- Bajwa H, Basit H. Thalassemia. 2022 Aug 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
- Barnhart-Magen G, Gotlib V, Marilus R, Einav Y. Differential Diagnostics of Thalassemia Minor by Artificial Neural Networks Model. J Clin Lab Anal. 2013 Nov 11;27(6):481–6. [CrossRef]
- Borah, M. S., Bhuyan, B. P., Pathak, M. S., & Bhattacharya, P. (2018). Machine learning in predicting hemoglobin variants. Int J Mach Learn Comput, 8(2), 140-143. [CrossRef]
- Brancaleoni V, Di Pierro E, Motta I, Cappellini MD. Laboratory diagnosis of thalassemia. International Journal of laboratory hematology. 2016 May;38:32-40. [CrossRef]
- Brittenham GM, Griffith PM, Nienhuis AW, et al. Efficacy of deferoxamine in preventing complications of iron overload in patients with thalassemia major. N Engl J Med 1994;331:567-573. [CrossRef]
- Cao A, Galanello R. β--thalassemia. Genet Med. 2010 Feb;12(2):61-76. [CrossRef]
- Chapin J, Giardina PJ. Thalassemia syndromes. InHematology 2018 Jan 1 (pp. 546570). Elsevier.
- Chong SC, Metassan S, Yusof N, Idros R, Johari N, Zulkipli IN, Ghani H, Lim MA, Taib S, Lu ZH, Abdul-Hamid MRW. Thalassemia in Asia 2021 Thalassemia in Brunei Darussalam. Hemoglobin. 2022 Jan;46(1):15-19. [CrossRef]
- Choudhry VP. Thalassemia Minor and Major: Current Management. Indian J Pediatr. 2017 Aug;84(8):607-611. Epub 2017 Apr 24. [CrossRef]
- Colah RB, Seth T. Thalassemia in India. Hemoglobin. 2022 Jan;46(1):20-26.. [CrossRef]
- Cousens NE, Gaff CL, Metcalfe SA, Delatycki MB. Carrier screening for β-thalassaemia: a review of international practice. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 Oct;18(10):1077– 83. [CrossRef]
- Das, R., Datta, S., Kaviraj, A., Sanyal, S. N., Nielsen, P., Nielsen, I., ... & Saha, S. (2020). A decision support scheme for beta thalassemia and HbE carrier screening. Journal of advanced research, 24, 183-190. [CrossRef]
- Esteva A, Robicquet A, Ramsundar B, Kuleshov V, DePristo M, Chou K, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nature Medicine 2019 Jan;25(1):24–9. [CrossRef]
- Elshami EH, Alhalees AM. Automated diagnosis of thalassemia based on data mining classifiers. InThe International Conference on Informatics and Applications (ICAI 2012) 2012 (pp. 440-445).
- El Hasbani G, Musallam KM, Uthman I, Cappellini MD, Taher AT. Thalassemia and autoimmune diseases: Absence of evidence or evidence of absence? Blood Rev. 2022 Mar;52:100874. Epub 2021 Aug 14. [CrossRef]
- Feng P, Li Y, Liao Z, Yao Z, Lin W, Xie S, Hu B, Huang C, Liu W, Xu H, Liu M, Gan W. An online alpha-thalassemia carrier discrimination model based on random forest and red blood cell parameters for low HbA2 cases. Clin Chim Acta. 2022 Jan 15;525:1-5. Epub 2021 Dec 6. [CrossRef]
- Galanello R, Origa R. β--thalassemia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010 May 21;5:11. [CrossRef]
- Grady RW. The development of new drugs for use in iron chelation therapy. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 1976;12:161–175.
- Hagag AA, Elfrargy MS, Elfatah MA, et al. Comparative Study of Deferiprone and Silymarin versus Deferiprone and Placebo as Iron Chelators in Children with β--thalassemia with Iron Overload. J Leuk (Los Angel). 2014; 2:130.
- Kacian DL, Gambino R, Dow LW, et al. Decreased globin messenger RNA in thalassemia detected by molecular hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1973;70:1886–1890.
- Kohne E. Hemoglobinopathies: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011 Aug;108(31-32):532-40. Epub 2011 Aug 8. [CrossRef]
- Kumar R, Sagar C, Sharma D, Kishor P. β-globin genes: mutation hot-spots in the global thalassemia belt. Hemoglobin. 2015;39(1):1-8. Epub 2014 Dec 19. [CrossRef]
- Langlois S, Ford JC, Chitayat D; CCMG PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS COMMITTEE; SOGC GENETICS COMMITTEE. Carrier screening for thalassemia and hemoglobinopathies in Canada. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2008 Oct;30(10):950-959. English, French. PMID: 19038079. [CrossRef]
- Loukopoulos D. Haemoglobinopathies in Greece: prevention programme over the past 35 years. Indian Journal of Medicine Research. 2011 Oct;134(4):572–6.
- Mehta S, Medicherla KM, Gulati S, et al. Whole exome sequencing of adult Indians with apparently acquired Aplastic Anemia: initial experience at tertiary care hospital. Research Square; 2023. [CrossRef]
- Monalisha Saikia Borah and Prasanta Kumar Bhattacharya and Mauchumi Saikia Pathak. Study of IVS 1-5 (G→C) Mutation in the β- Thalassaemia Patients of a Tertiary Care Hospital of North East India. 2015.
- Mondal SK, Mandal S. Prevalence of thalassemia and hemoglobinopathy in eastern India: A 10-year high-performance liquid chromatography study of 119,336 cases. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2016 Jan-Jun;10(1):105-10. PMID: 27011683; PMCID: PMC4782486. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad LJ, Al-Shourbaji I, Haruna AA, Mohammed IA, Ahmad A, Jibrin MB. Machine Learning Predictive Models for Coronary Artery Disease. SN Comput Sci. 2021;2(5):350. Epub 2021 Jun 22. [CrossRef]
- Muncie HL Jr, Campbell J. Alpha and β--thalassemia. Am Fam Physician. 2009 Aug 15;80(4):339-44. PMID: 19678601.
- Ohba Y, Hattori Y, Harano T, Harano K, Fukumaki Y, Ideguchi H. β--thalassemia mutations in Japanese and Koreans. Hemoglobin. 1997 Mar;21(2):191-200. Erratum in: Hemoglobin 1997 Jul;21(4):389. [CrossRef]
- Origa R. β-Thalassemia. Genet Med. 2017 Jun;19(6):609-619. Epub 2016 Nov 3. [CrossRef]
- Rustam F, Ashraf I, Jabbar S, Tutusaus K, Mazas C, Barrera AEP, de la Torre Diez I. Prediction of [Formula: see text]-Thalassemia carriers using complete blood count features. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 21;12(1):19999. [CrossRef]
- Sambrook J, Russell DW. Purification of nucleic acids by extraction with phenol:chloroform. CSH Protoc. 2006 Jun 1;2006(1):pdb.prot4455. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot4455.Sabath DE. Molecular Diagnosis of Thalassemias and Hemoglobinopathies: An ACLPS Critical Review. Am J Clin Pathol. 2017 Jul 1;148(1):6-15. PMID: 28605432. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqx047.
- Saboor M, Qudsia F, Qamar K, et al. Levels of Calcium, Corrected Calcium, Alkaline Phosphatase and Inorganic Phosphorus in Patients’ Serum with β-Thalassemia Major on Subcutaneous Deferoxamine. J Hematol Thromb Dis. 2014; 2:130.
- Sadiq, S., Khalid, M. U., Ullah, S., Aslam, W., Mehmood, A., Choi, G. S., & On, B. W. (2021). Classification of β-thalassemia carriers from red blood cell indices using ensemble classifier. IEEE access, 9, 45528-45538.
- Shine I, Lal S. A strategy to detect β--thalassaemia minor. Lancet Lond Engl. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):692–4.
- Tarca AL, Carey VJ, Chen XW, Romero R, Drăghici S. Machine learning and its applications to biology. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jun;3(6):e116. PMID: 17604446; PMCID: PMC1904382. [CrossRef]
- Thacker N. Prevention of thalassemia in India. Indian Pediatr. 2007 Sep;44(9):647-8. PMID: 17921552.
- Topol E. Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again. Basic Books; 2019. 373 p.
- Viprakasit V, Ekwattanakit S. Clinical Classification, Screening and Diagnosis for Thalassemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018 Apr;32(2):193-211. PMID: 29458726. [CrossRef]
- Webb S. Deep learning for biology. Nature. 2018 Feb 22;554(7693):555-557. Erratum in: Nature. 2018 Mar 22;555(7697):547. PMID: 29469107. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).