Submitted:
26 April 2024
Posted:
28 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Sources and Routes of Emerging Pollutants
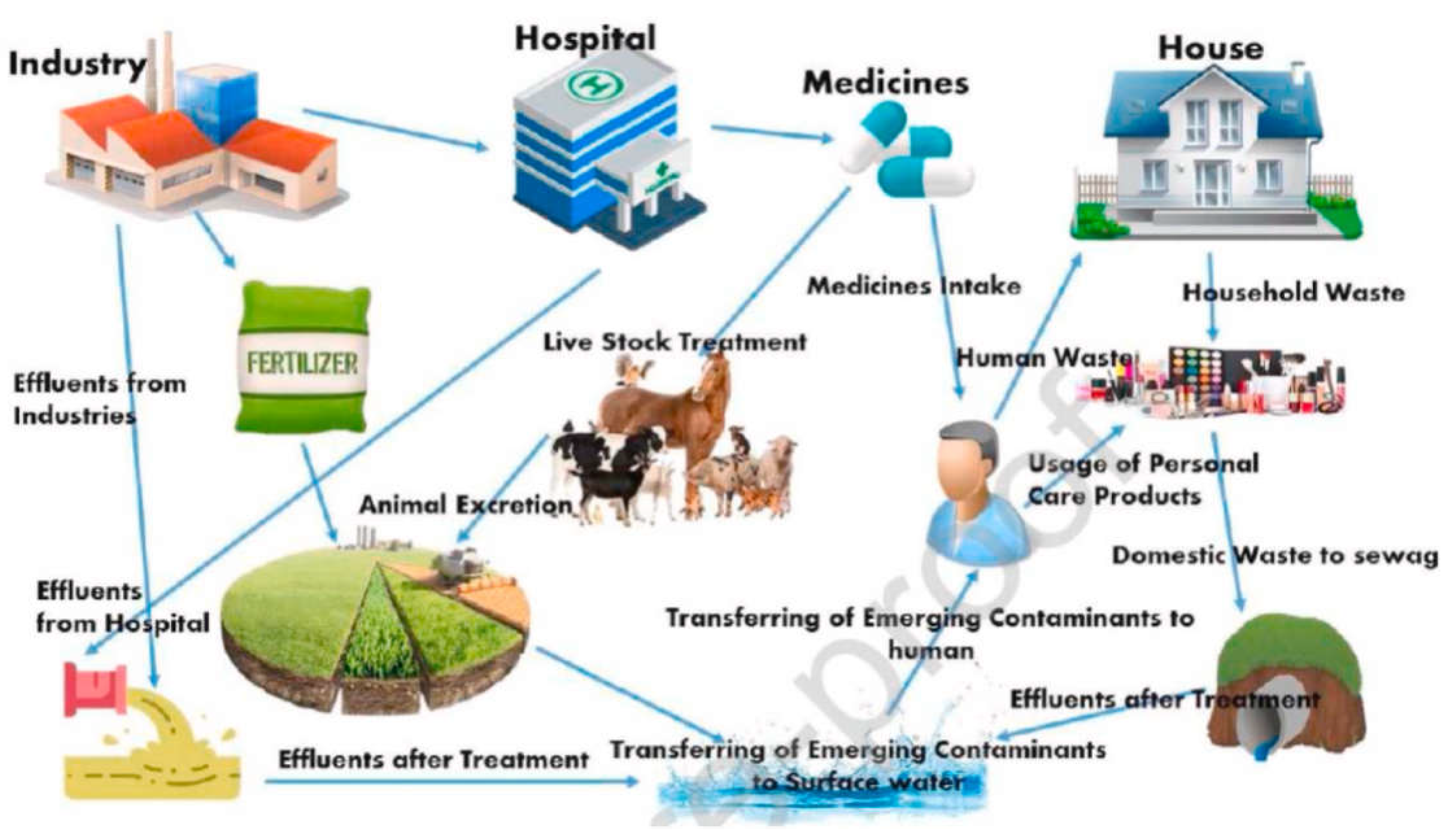
3. Known and New Emerging Contaminants
3.1. Polyfluorinated Compounds
| Type | Name | Abbreviation | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFCA | Perfluorobutanoic acid | PFBA | 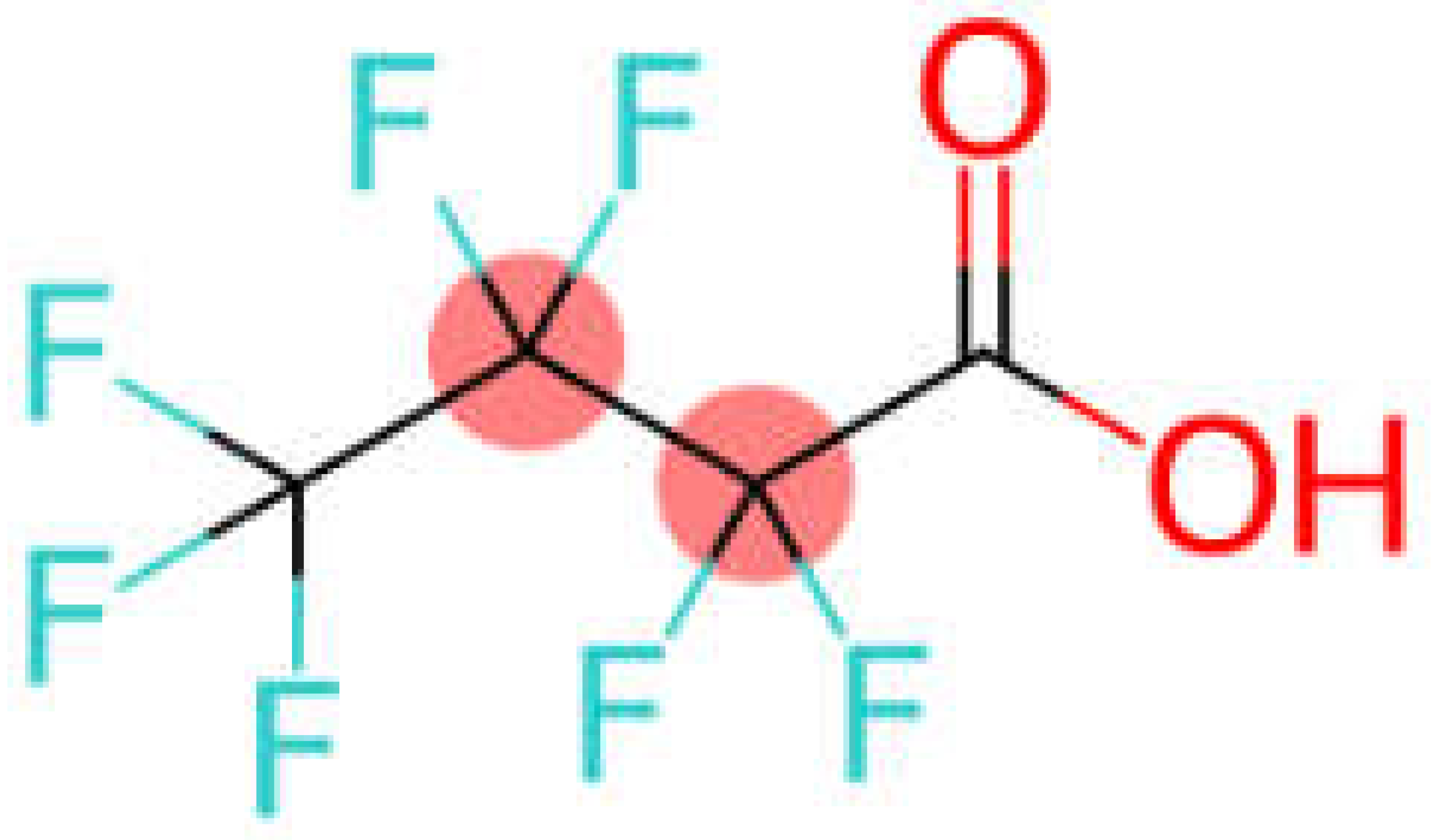 |
| Perfluoropentanoic acid | PFPeA | 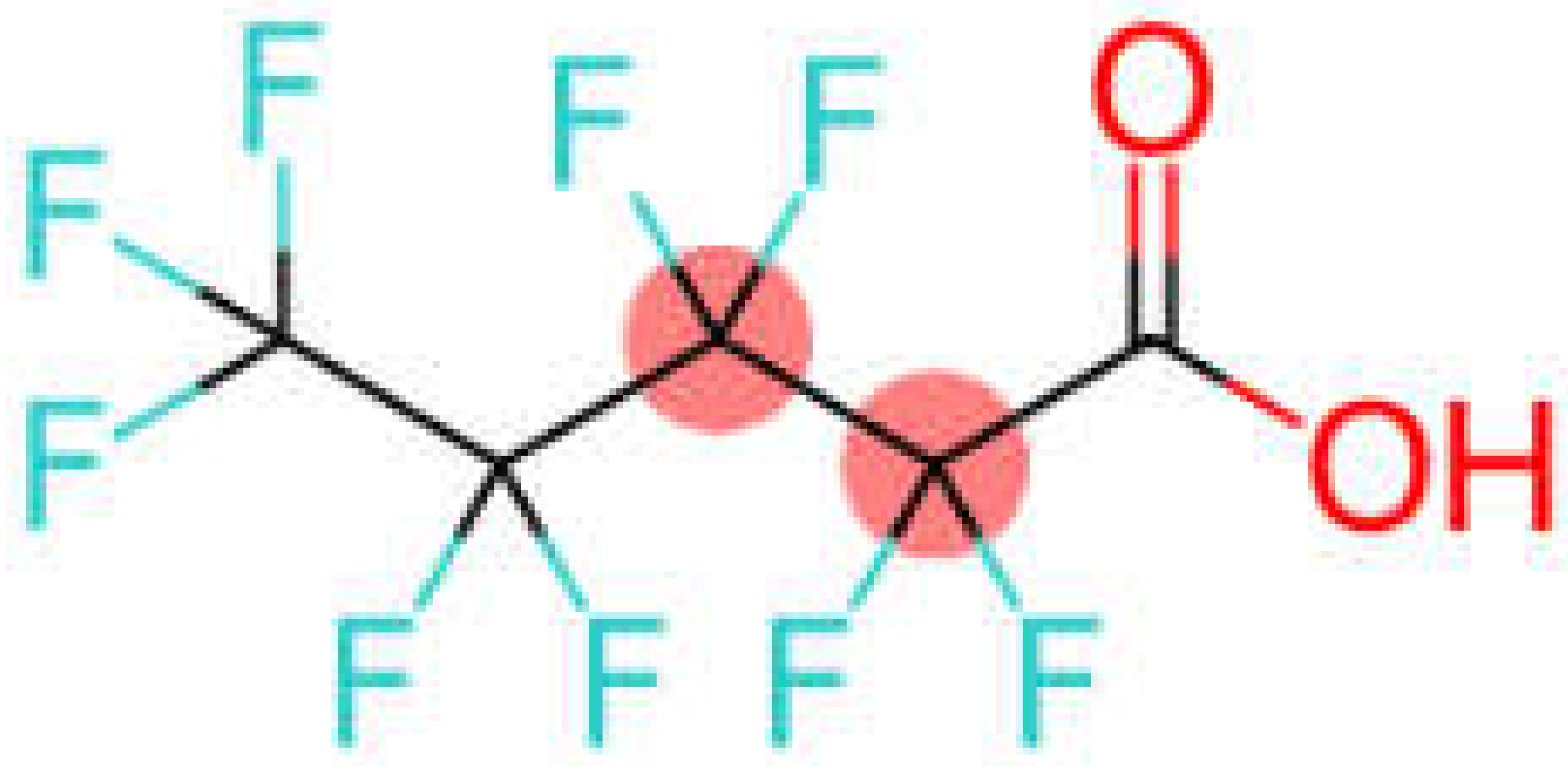 |
|
| Perfluorohexanoic acid | PFHxA | 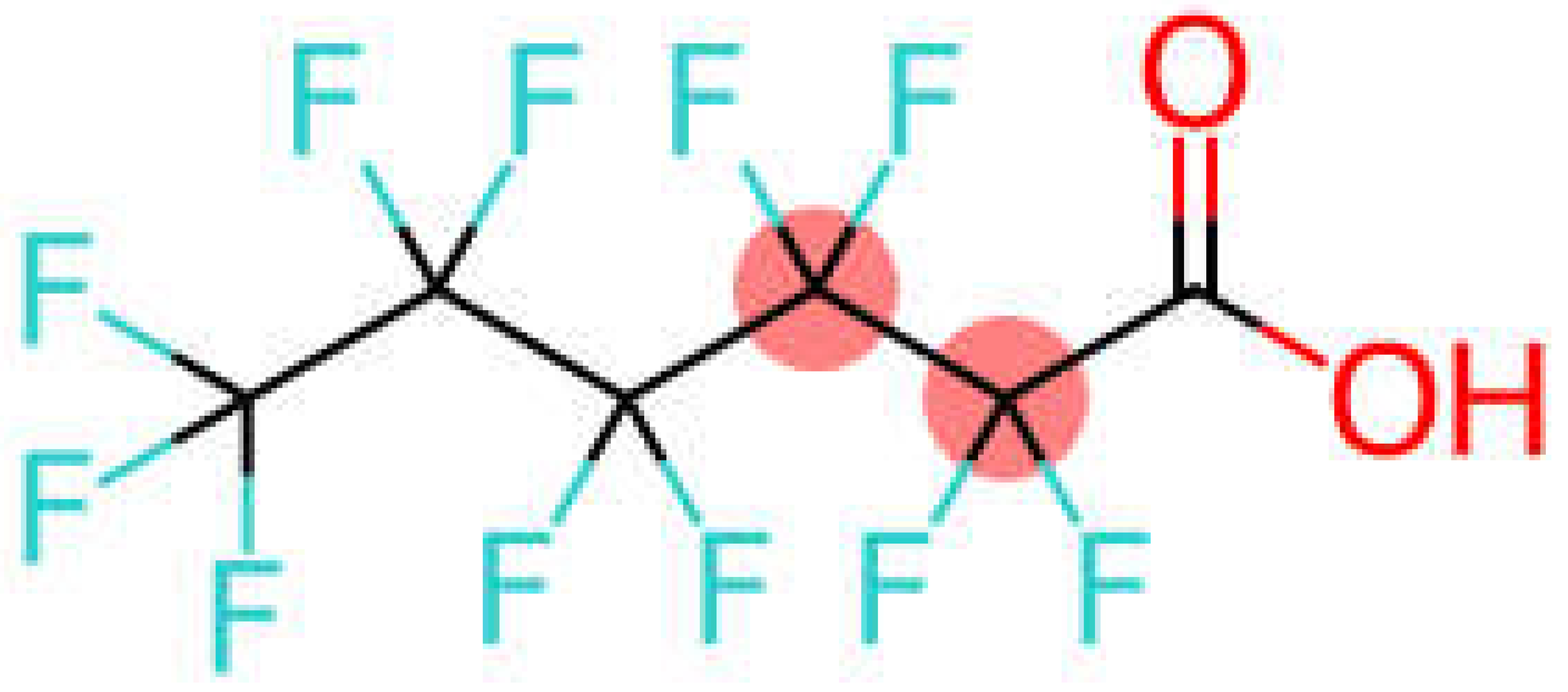 |
|
| Perfluorododecanoic acid | PFDoDA | 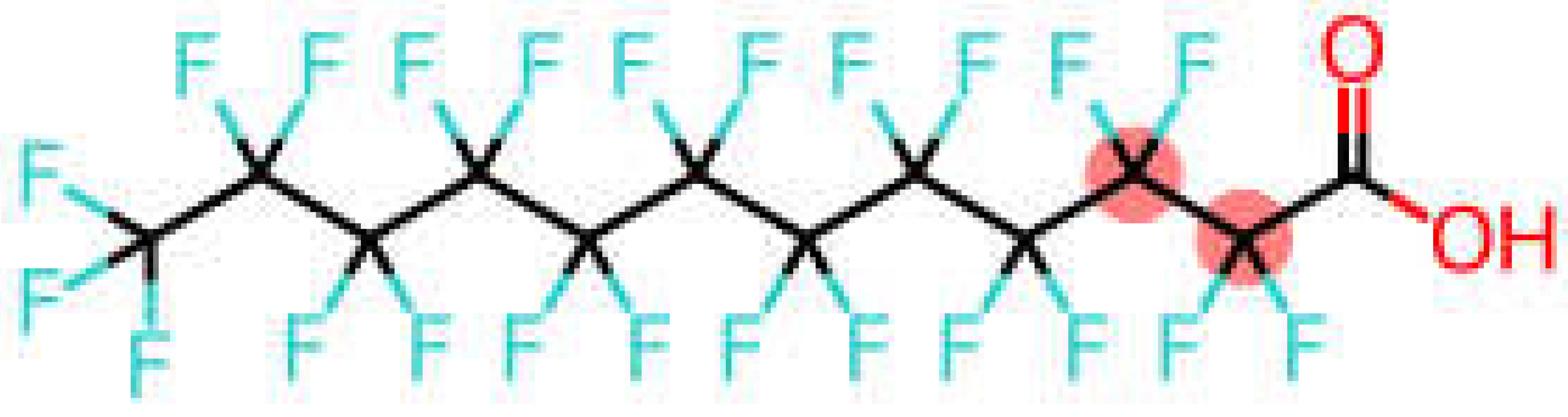 |
|
| Perfluorononanoic acid | PFNA | 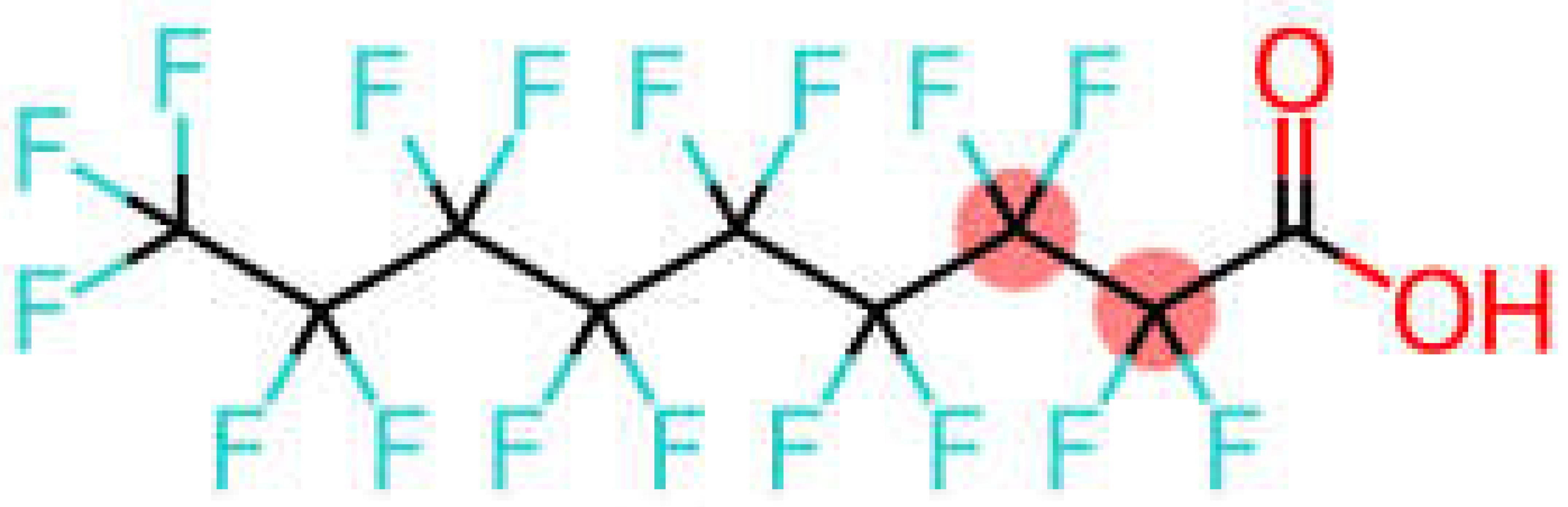 |
|
| PFSA | Perfluorobutane sulfonic acid | PFBS | 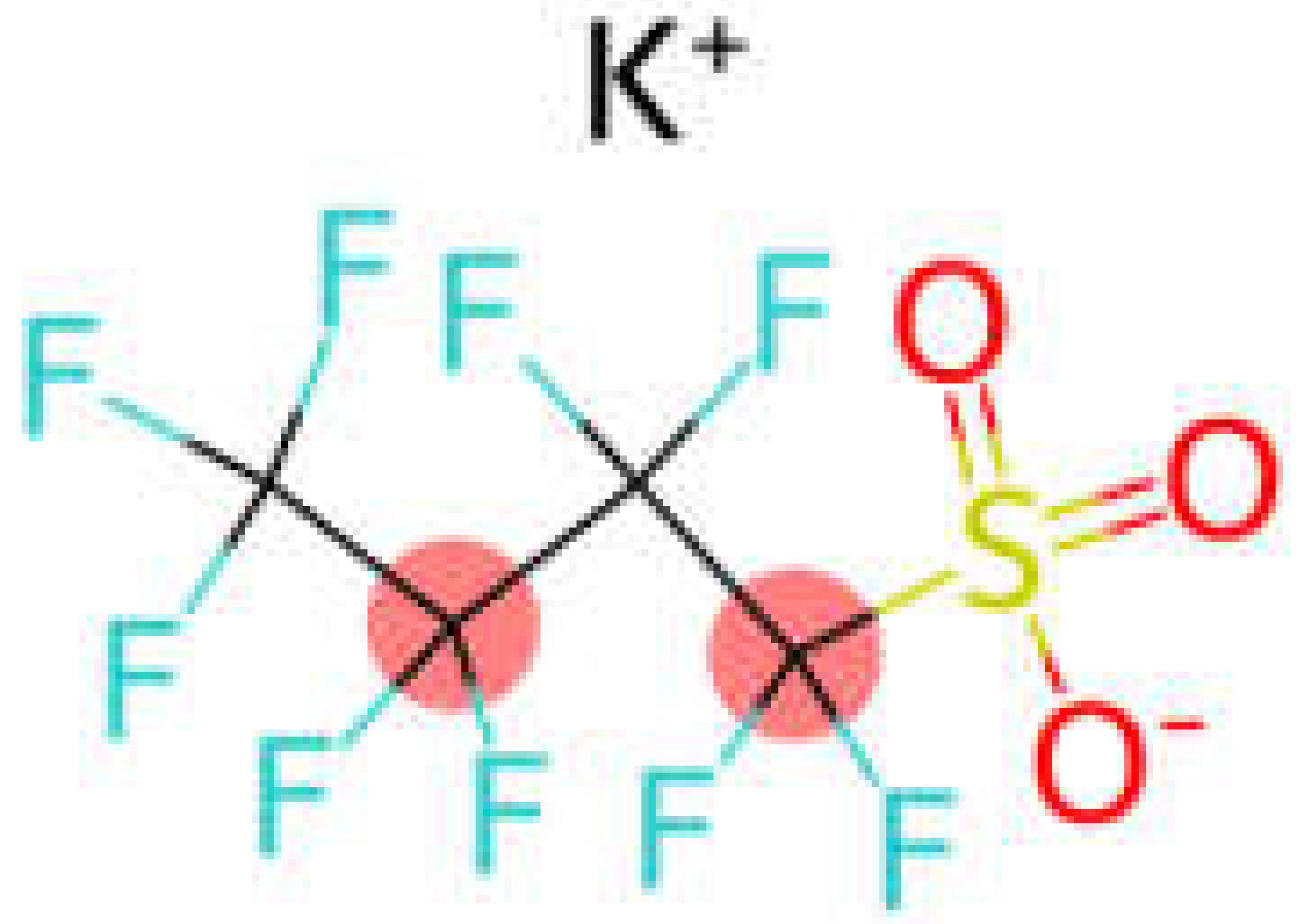 |
| Perfluorohexane sulfonic acid | PFHxS | 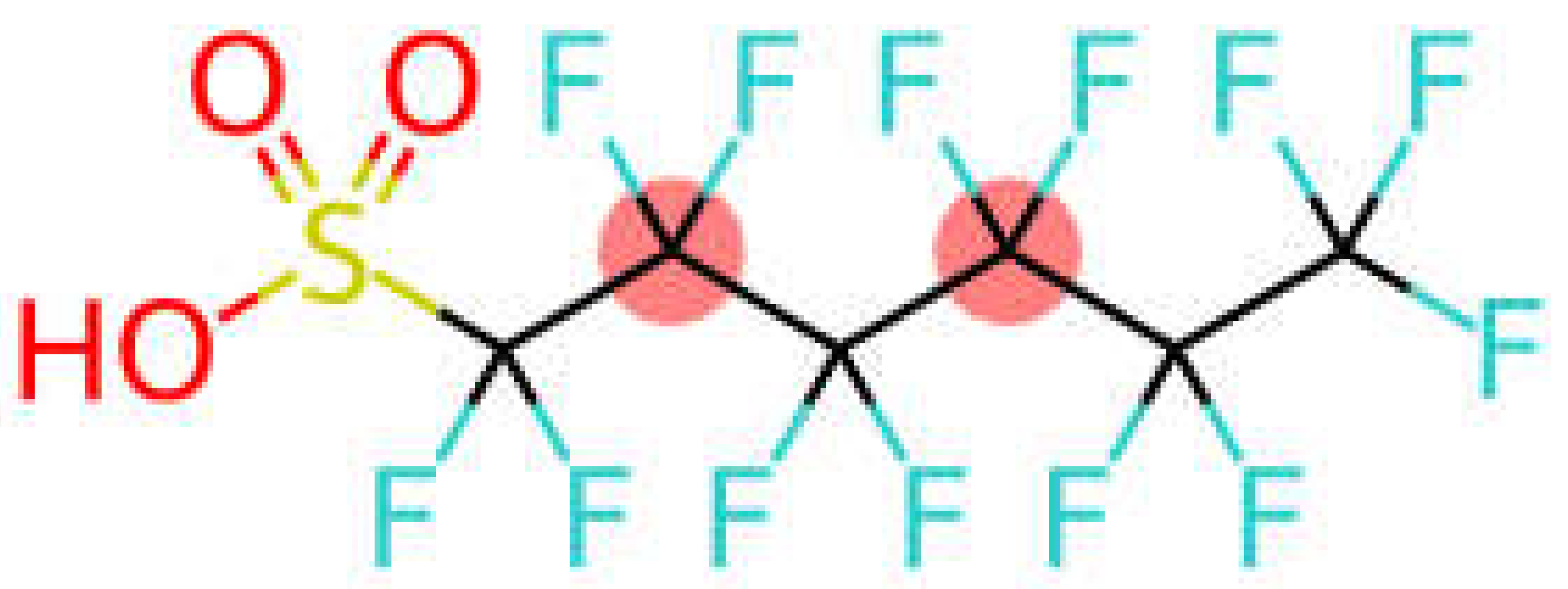 |
|
| Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid | PFOS | 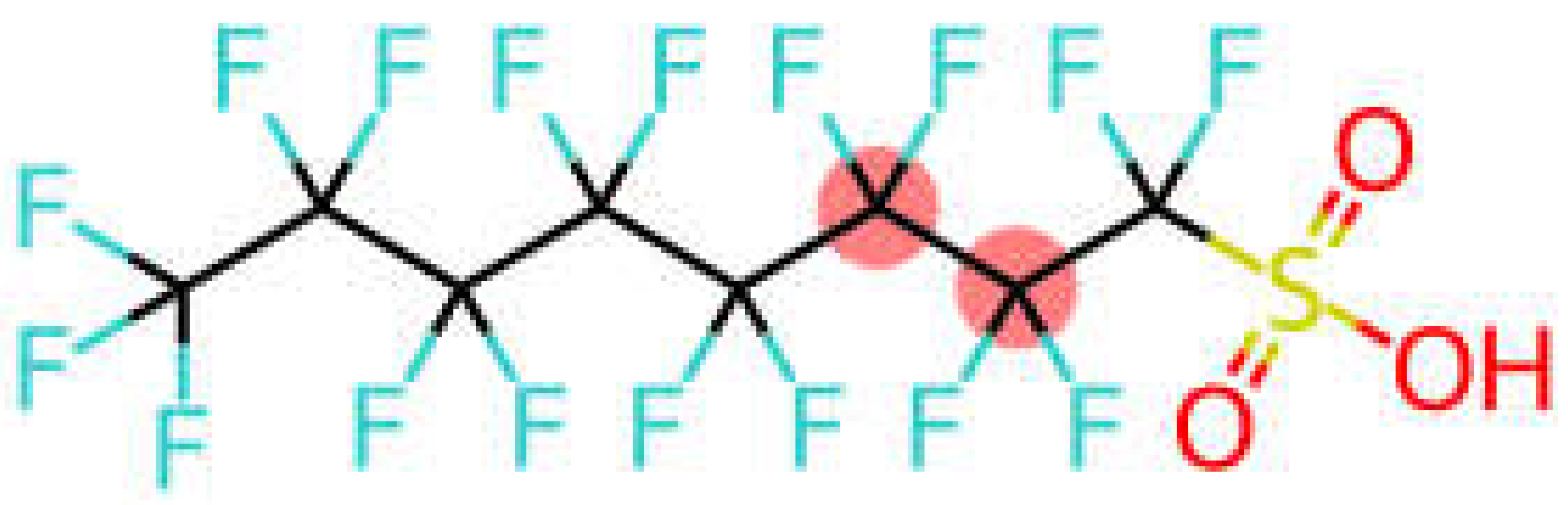 |
|
| Perfluorodecane sulfonic acid | PFDS | 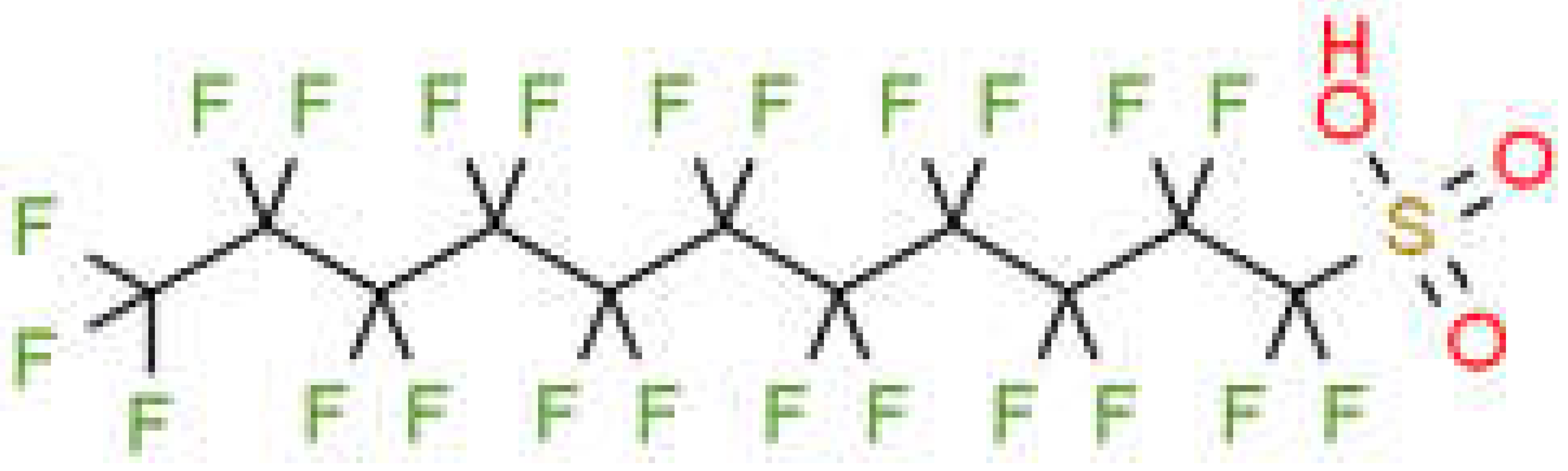 |
3.2. Antibiotic
3.3. Microplastics
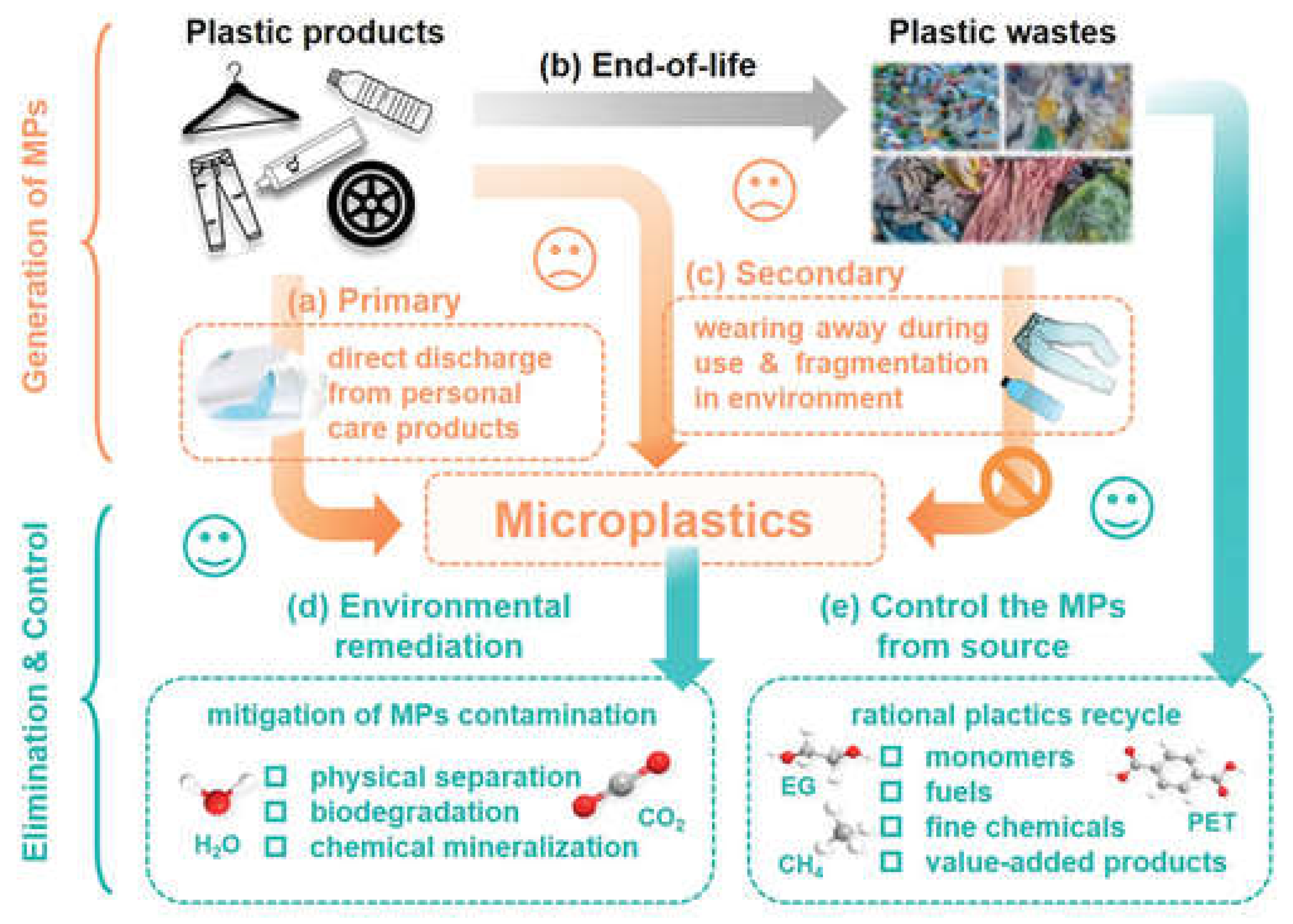
3.5. Nonylphenol
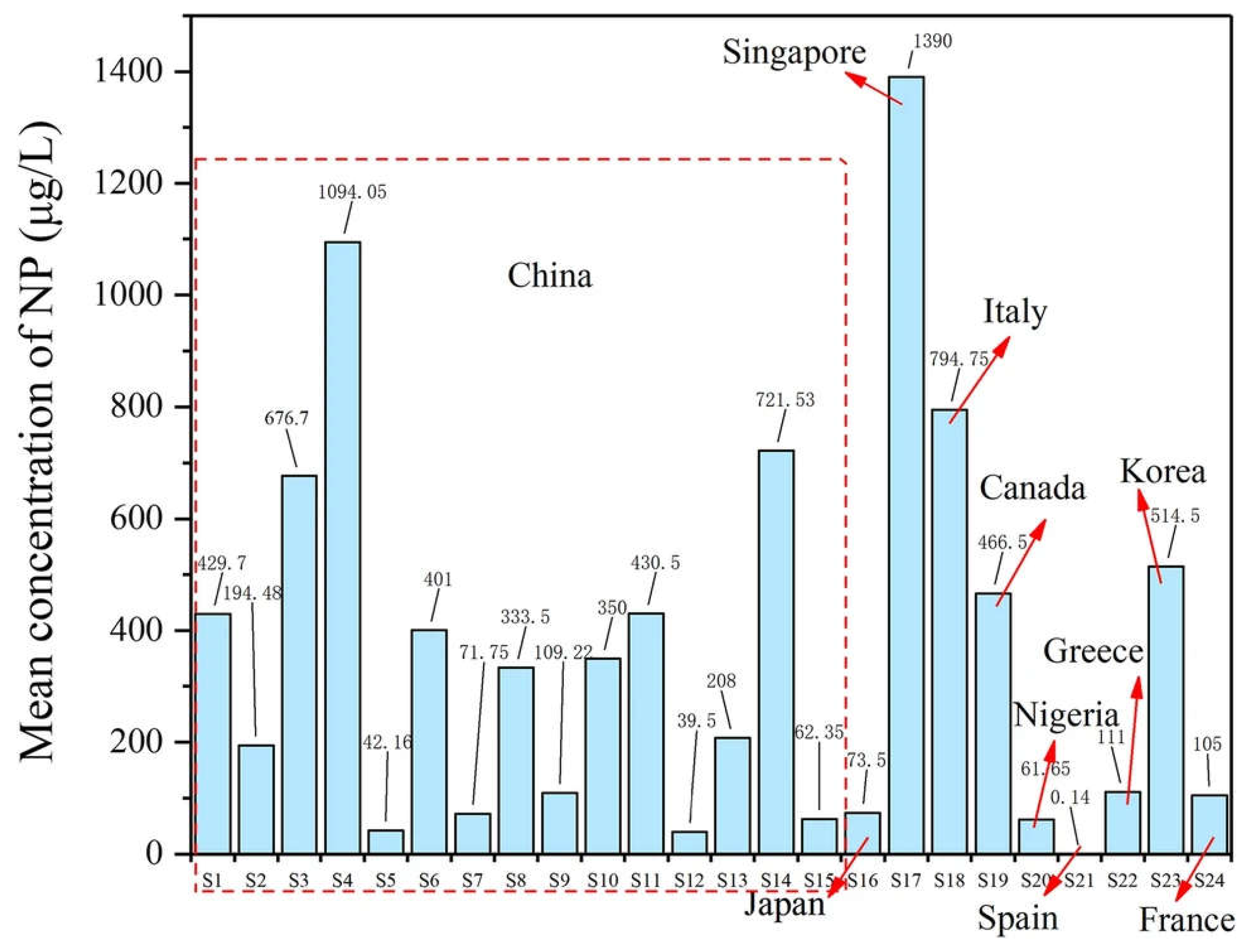
4. Effects of Chemical Structure on the Toxicity of ECs
4.1. Ecological and Environmental Risks
4.2. Hazards to Human Health
5. Interaction of New Pollutants and Reactions with Metals
6. Removal Methods
6.1. Membrane Filtration Technology
| Types of pollutants | Membrane | Influent concentration(μg/L) | Time(h) | Removal efficiency (%) | Current density(mA/cm2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline Sulfamethoxazole |
CeO2@CNT-NaClO | - | 30 30 |
98.0 99.0 |
2.0 2.0 |
[39] |
| Sulfamethoxazole Ciprofloxacin Tetracycline carbamazepine |
CeO2@CNT | - | 240 | 91.3 94.4 99.3 89.4 |
0.5 | [40] |
| Sulfamethoxazole Trimethoprim |
Electrochemical membrane aeration biofilm reactor | 50 | 2160 | 40.1 32.8 |
2.0 | [41] |
| Benzotriazole | Titanium dioxide ceramic membrane | 14200 | 30 | 98.1 | 20 | [30] |
| Tetrabromobisphenol A | F-doped Tiso electroactive film | 3.5 | 90 | 99.7 | 7.8 | [42] |
| Bisphenol A | Coal-based carbon film | 50 | 0.88 | 97 | 2 | [43] |
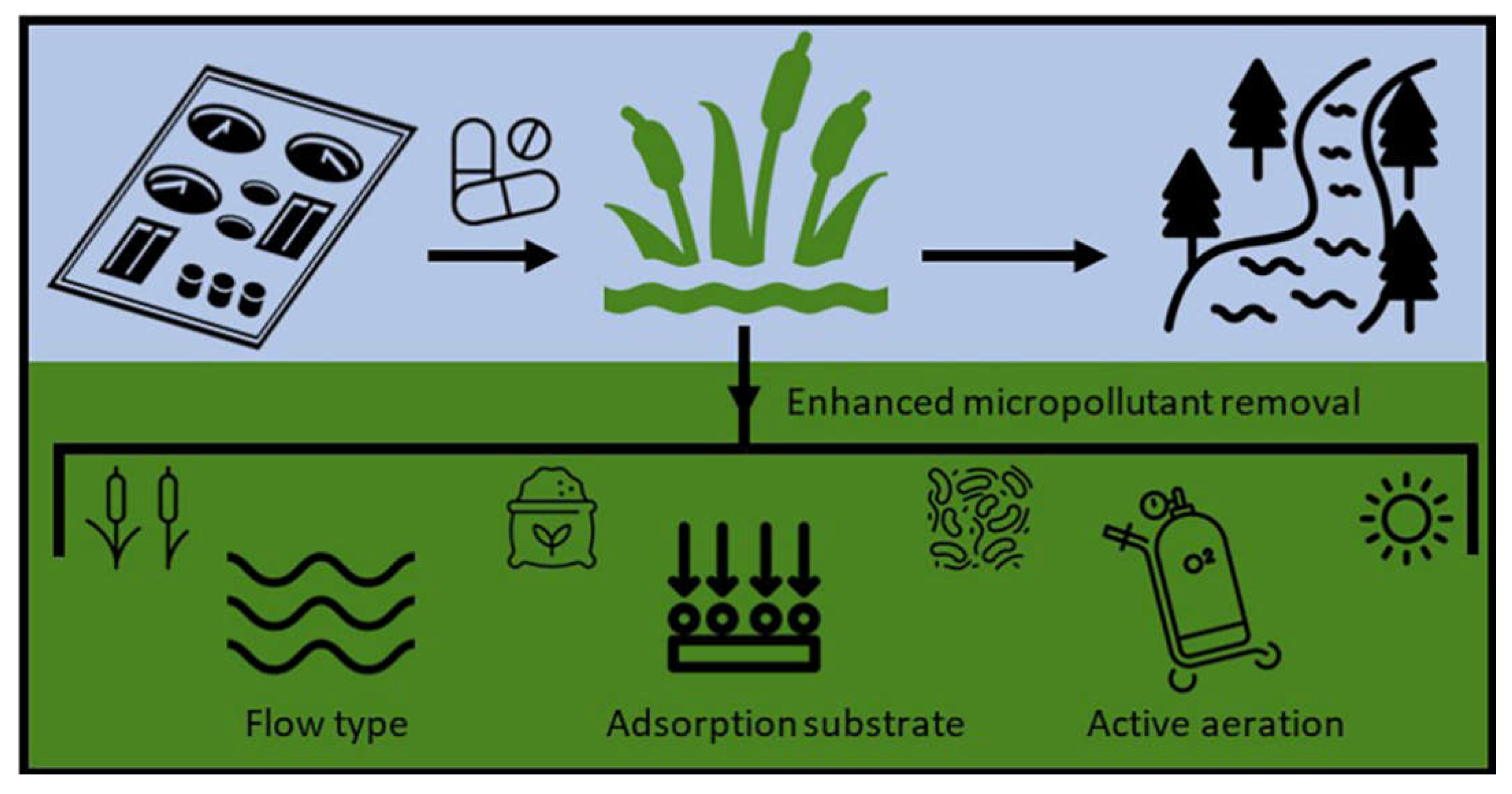
6.2. Constructed Wetland
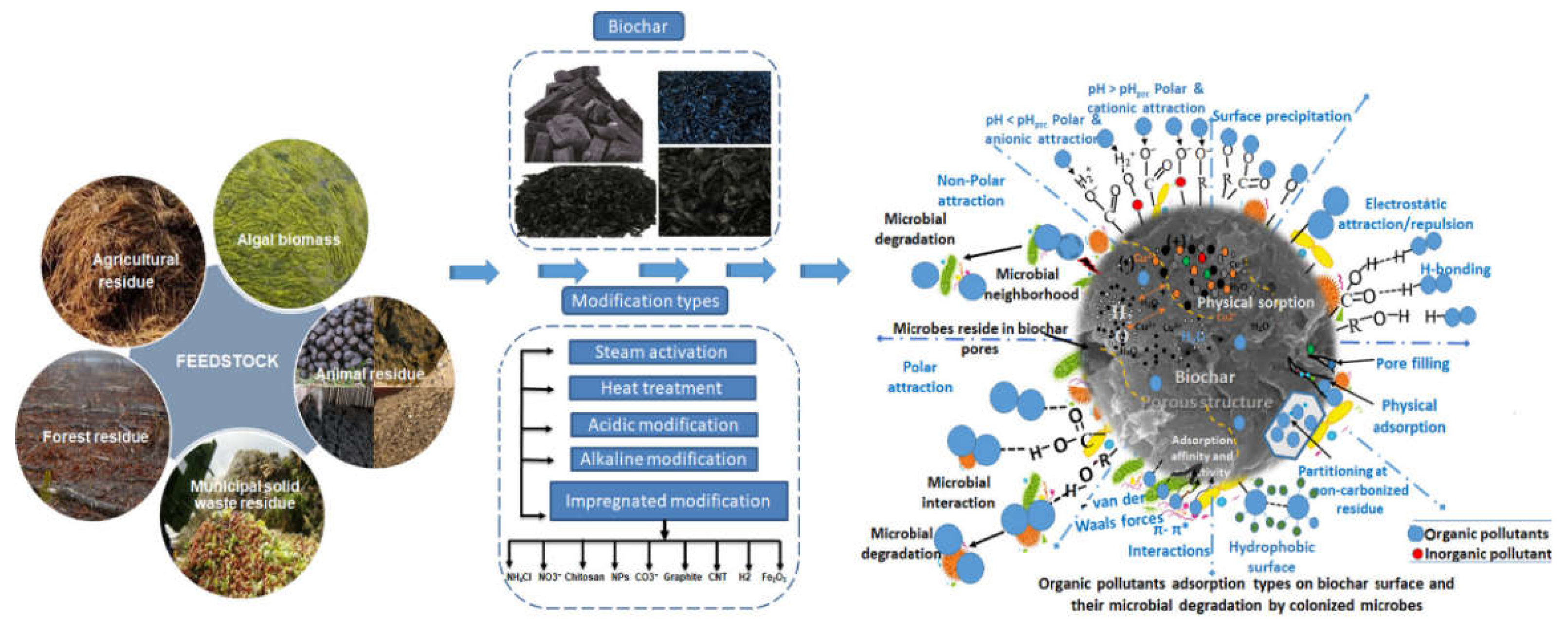
6.3. Biochar Adsorption
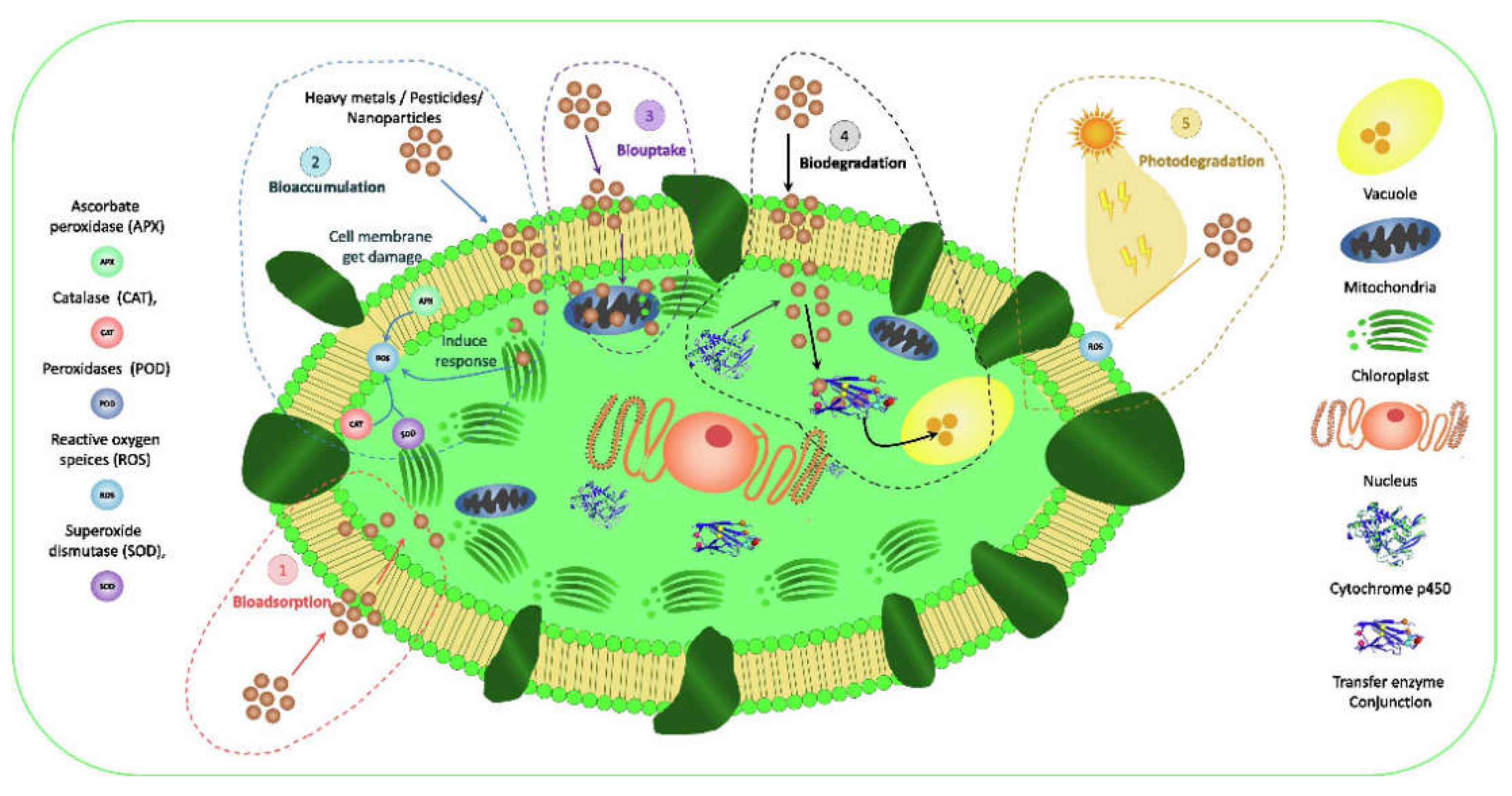
6.4. Algae Repair
7. Conclusion
- Regulation: As the understanding of neo-pollutants deepens and monitoring technologies continue to develop, the regulatory system will become more comprehensive and refined. In the future, regulation will focus more on real-time monitoring and data sharing to detect and respond to the emergence of new pollutants in a more timely manner. At the same time, we will strengthen international cooperation and information sharing to jointly address transboundary pollution.
- discover and respond to the emergence of new pollutants in a timely manner. At the same time, we will strengthen international cooperation and information sharing to jointly cope with cross -border pollution.
- Removal technologies: Future removal technologies will be more efficient, environmentally friendly and economically viable. With the development of science and technology, more advanced pollutant removal technologies, such as nanomaterials and photocatalytic technology, may emerge. At the same time, emphasis will be placed on the practical application and sustainability of the technologies to ensure their effectiveness in the real environment and long-term sustainability.
- Environmental hazards: Future research will be more in-depth and comprehensive in response to the potential environmental hazards of new pollutants. The focus of research may include studies on the ecotoxicity, bioaccumulation and potential long-term effects of pollutants in order to comprehensively assess their impacts on the ecosystem and develop corresponding countermeasures.
Acknowledgments
References
- Mafi, A.; Nejad, E. G.; Ashouri, A.; Nia, M. V. , Dinoflagellate cysts from the Upper Bajocian-Lower Oxfordian of the Dalichai Formation in Binalud Mountains (NE Iran): Their biostratigraphical and biogeographical significance. 2013.
- Carvalho, I. T.; Santos, L. , Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ Int 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M. J.; Paiga, P.; Silva, A.; Llaguno, C. P.; Carvalho, M.; Vazquez, F. M.; Delerue-Matos, C. , Antibiotics and antidepressants occurrence in surface waters and sediments collected in the north of Portugal. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seralini, G. E.; Jungers, G. , Endocrine disruptors also function as nervous disruptors and can be renamed endocrine and nervous disruptors (ENDs). Toxicol Rep 2021, 8, 1538–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, M.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Fang, F.; Li, C.; Xue, Z.; Feng, Q. , Ecotoxicity and environmental fates of newly recognized contaminants-artificial sweeteners: A review. Sci Total Environ 2019, 653, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I. J.; Kasteel, R.; Poiger, T. , Leaching of herbicides and their metabolites in lysimeters filled with soils from railway tracks. Sci Total Environ 2024, 909, 168396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathi, B. S.; Kumar, P. S.; Show, P. L. , A review on effective removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic systems: Current trends and scope for further research. J Hazard Mater 2021, 409, 124413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffen, T.; Wepener, V.; Malherbe, W.; Bervoets, L. , Distribution of perfluorinated compounds (PFASs) in the aquatic environment of the industrially polluted Vaal River, South Africa. Sci Total Environ 2018, 627, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Gu, L.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, H. , Distribution and release of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in water-sediment systems: The effect of confluence channels. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Y.; Hua, Z. L.; Gu, L. , Planktonic microbial responses to perfluorinated compound (PFC) pollution: Integrating PFC distributions with community coalescence and metabolism. Sci Total Environ 2021, 788, 147743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, D.; Pace, A. , Bioaccumulation, Biodistribution, Toxicology and Biomonitoring of Organofluorine Compounds in Aquatic Organisms. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Casey, F. X. M.; Hakk, H.; Larsen, G. L.; Khan, E. , Sorption, Fate, and Mobility of Sulfonamides in Soils. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2010; 218, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zheng, M.; Xue, H.; Pang, H. , High performance electrochemical capacitor materials focusing on nickel based materials. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers 2016, 3(2), 175–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S. M.; Ullman, J. L.; Teel, A. L.; Watts, R. J. , PH and temperature effects on the hydrolysis of three ??-lactam antibiotics: Ampicillin, cefalotin and cefoxitin. Science of The Total Environment, 2013; 466-467C, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- Bahnmuller, S.; von Gunten, U.; Canonica, S. , Sunlight-induced transformation of sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole in surface waters and wastewater effluents. Water Res 2014, 57, 183–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J. L. , Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, N.; Kumar, U. , Plastics and microplastics: A threat to environment. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2019; 14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Sherrell, P. C.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. x.; Yang, J. , How to Build a Microplastics-Free Environment: Strategies for Microplastics Degradation and Plastics Recycling. Advanced Science, 2022; 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Sherrell, P. C.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. X.; Yang, J. , How to Build a Microplastics-Free Environment: Strategies for Microplastics Degradation and Plastics Recycling. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 2022; 9, e2103764. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V. K.; Ma, X.; Lichtfouse, E.; Robert, D. , Nanoplastics are potentially more dangerous than microplastics. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2022, 21(4), 1933–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Bagheri, A. R.; Bhatt, P.; Bilal, M. , Occurrence, potential ecological risks, and degradation of endocrine disrupter, nonylphenol, from the aqueous environment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J. L. , Distribution and toxic potential of alkylphenols, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and pyrethroids in Minnesota, USA lake sediments. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Feng, C.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liao, W.; Bai, Y. , Nonylphenol occurrence, distribution, toxicity and analytical methods in freshwater. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2020, 18(6), 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V. K.; Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A. K. , Emerging contaminants in wastewater: A critical review on occurrence, existing legislations, risk assessment, and sustainable treatment alternatives. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021; 9. [Google Scholar]
- Krkstrm, M.; Saeid, S.; Tolvanen, P.; Salmi, T.; Kronberg, L. , Catalytic ozonation of the antibiotic sulfadiazine: Reaction kinetics and transformation mechanisms. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X. , Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the Laizhou Bay, China: impacts of river discharge. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2012, 80, 208–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Nie, X.; Guan, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liao, W. , Growth response and toxic effects of three antibiotics on Selenastrum capricornutum evaluated by photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll biosynthesis. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2011, 23(9), 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, C. E.; Ramirez-Morales, D.; Masis-Mora, M.; Montiel-Mora, J. R.; Soto-Garita, C.; Araya-Valverde, E.; Cambronero-Heinrichs, J. C.; Sanchez-Melsio, A.; Briceno-Guevara, S.; Mendez-Rivera, M.; Balcazar, J. L. , Occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater in Costa Rica. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhler, J. S.; Kolmar, T.; Synnatschke, K.; Hergert, M.; Wilson, L. A.; Ramu, S.; Elliott, A. G.; Blaskovich, M. A. T.; Sidjabat, H. E.; Paterson, D. L.; Schenk, G.; Cooper, M. A.; Ziora, Z. M. , Enhancement of antibiotic-activity through complexation with metal ions - Combined ITC, NMR, enzymatic and biological studies. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 2017, 167, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; He, X.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L. , Structure, mechanism, and toxicity in antibiotics metal complexation: Recent advances and perspectives. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1-s2.0-S0010854516300017-main.pdf.
- 32. Wendell; Guerra; Priscila; P.; Silva-Caldeira; Hernán; Terenzi; Elene; C.; Pereira-Maia, Impact of metal coordination on the antibiotic and non-antibiotic activities of tetracycline-based drugs. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2016.
- Tong, F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Fan, G.; Gao, Y.; Gu, X.; Gu, C. , Heavy metal-mediated adsorption of antibiotic tetracycline and ciprofloxacin on two microplastics: Insights into the role of complexation. Environ Res 2023, 216 Pt 3, 114716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, F.; Qian, J.; Liu, S. , Adsorption of levofloxacin by ultraviolet aging microplastics. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. , Adsorption behavior of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) on aged microplastics in antibiotics-heavy metals coexisting system. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, Z. C.; Shuai, X. Y.; Lin, Z. J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J. Y.; Lin, Y. H.; Zeng, G. S.; Ge, Z. Y.; Chen, H. , Microplastics exacerbate co-occurrence and horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. J Hazard Mater 2023, 451, 131130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T. H.; Ng, C.; Tran, N. H.; Chen, H.; Gin, K. Y. , Removal of antibiotic residues, antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater by membrane bioreactor systems. Water Res 2018, 145, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, J.; Quan, X. , Enhanced permeability, contaminants removal and antifouling ability of CNTs-based hollow fiber membranes under electrochemical assistance. Journal of Membrane Science 2019, 582, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Hou, X.; Ma, D.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y. , Simultaneous removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes using a CeO(2)@CNT electrochemical membrane-NaClO system. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chu, Y.; Ni, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y. , CeO(2) modified carbon nanotube electrified membrane for the removal of antibiotics. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. , Efficacy of a novel electrochemical membrane-aerated biofilm reactor for removal of antibiotics from micro-polluted surface water and suppression of antibiotic resistance genes. Bioresour Technol 2021, 338, 125527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.; You, S. , Electrochemical removal of tetrabromobisphenol A by fluorine-doped titanium suboxide electrochemically reactive membrane. J Hazard Mater 2021, 419, 126434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Yu, F.; Li, L.; Song, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Wang, T. , Electrochemical microfiltration treatment of bisphenol A wastewater using coal-based carbon membrane. Separation and Purification Technology 2019, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinen, H.; Havran, I.; Hubau, L.; Vanseveren, L.; Gebhardt, W.; Linnemann, V.; Van Oirschot, D.; Du Laing, G.; Rousseau, D. P. L. , Removal of pharmaceuticals by a pilot aerated sub-surface flow constructed wetland treating municipal and hospital wastewater. Ecological Engineering 2017, 100, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N. A.; Schmitt, H.; van der Zaan, B. M.; Gerritsen, H. W.; Rijnaarts, H. H. M.; Langenhoff, A. A. M. , Performance of full scale constructed wetlands in removing antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. , Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286 Pt 1, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T. V.; Rempe, F.; Hoek, M.; Schuman, E.; Langenhoff, A. , Key constructed wetland design features for maximized micropollutant removal from treated municipal wastewater: A literature study based on 16 indicator micropollutants. Water Res 2023, 244, 120534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Yao, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Tian, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y. , Novel insights into the adsorption of organic contaminants by biochar: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 287 (Pt 2) Pt 2, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, C.; Gunatilake, S. R.; Mlsna, T. E.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M. , Biochar based removal of antibiotic sulfonamides and tetracyclines in aquatic environments: A critical review. Bioresour Technol 2017, 246, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Moreno, L.; Bazhari, S.; Gasco, G.; Mendez, A.; El Azzouzi, M.; Romero, E. , New insights into the efficient removal of emerging contaminants by biochars and hydrochars derived from olive oil wastes. Sci Total Environ 2021, 752, 141838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xi, F.; Tan, W.; Meng, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. , Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 2021, 3(3), 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. K.; Singhania, R. R.; Pal, A.; Chen, C. W.; Pandey, A.; Dong, C. D. , Advances on tailored biochar for bioremediation of antibiotics, pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants from aqueous and solid phases. Sci Total Environ 2022, 817, 153054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, M.; Dai, L. , Interaction between chlortetracycline and calcium-rich biochar: Enhanced removal by adsorption coupled with flocculation. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C. M.; Huang, C. P.; Chen, C. W.; Wu, C. H.; Lin, Y. L.; Dong, C. D. , Activation of percarbonate by water treatment sludge-derived biochar for the remediation of PAH-contaminated sediments. Environ Pollut 2020, 265 (Pt B), 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, R.; Kavitha, S.; Yukesh Kannah, R.; Parthiba Karthikeyan, O.; Kumar, G.; Kumar Tyagi, V.; Rajesh Banu, J. , Algal-based system for removal of emerging pollutants from wastewater: A review. Bioresour Technol 2022, 344 (Pt B), 126245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Gutierrez, R.; Ferrer, I.; Garcia, J.; Bayona, J. M. , Capability of microalgae-based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants: a pilot-scale study. J Hazard Mater 2015, 288, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Acharya, K. , Algae-mediated removal of selected pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from Lake Mead water. Sci Total Environ, 2017; 581-582, 734–740. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, J. , Enhanced removal of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals from coastal waters by intertidal macroalgae. J Hazard Mater 2021, 411, 125105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasari, A.; Syafiuddin, A.; Zaidi, N. S.; Hong Kueh, A. B.; Hadibarata, T.; Prastyo, D. D.; Ravikumar, R.; Sathishkumar, P. , Bioremediation of micropollutants using living and non-living algae - Current perspectives and challenges. Environ Pollut 2022, 292 (Pt B), 118474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




