Submitted:
26 April 2024
Posted:
28 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- A visual multiclass classification approach based on a reduced number of EEG channels and deep learning architectures is proposed for BCI applications.
- Multiclass classification comparative results using EEGNet and CNN-LSTM networks are provided.
- A channel selection approach based on mutual information is implemented to accurately discriminate contributing channels.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
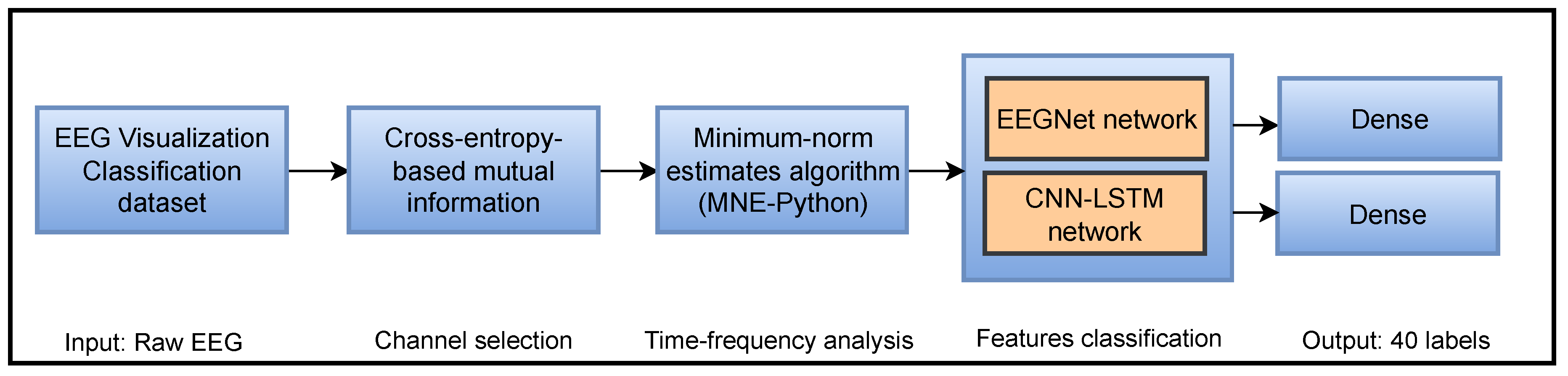
3.1. Overall Flowchart
3.2. The Perceive Lab Dataset
3.3. Mutual Information-Based Channels Selection
- The case where and are independent, therefore,
- In other cases, and channels share the totality of their respective information. Thus,
| Algorithm 1:MutIn algorithm-based-discriminant channels selection |
 |
3.4. Enhancing Signals by Minimum-Norm Estimates Algorithm
| Algorithm 2:The MNE steps implemented to enhance EEG data. |
|
1 Get EEG data from selected channels
2 Handle poor channels providing extremely noisy data to be usable, based on good signals delivered by other channels.
3 Discard erroneous data gaps and spans.
4 Calculate the variance of the data.
5 Remove the mean and scale to the unit variance to standardize features.
6 Create epoch of data.
7 Average epoch to obtain evoked responses.
|
3.5. The Implemented Classifiers
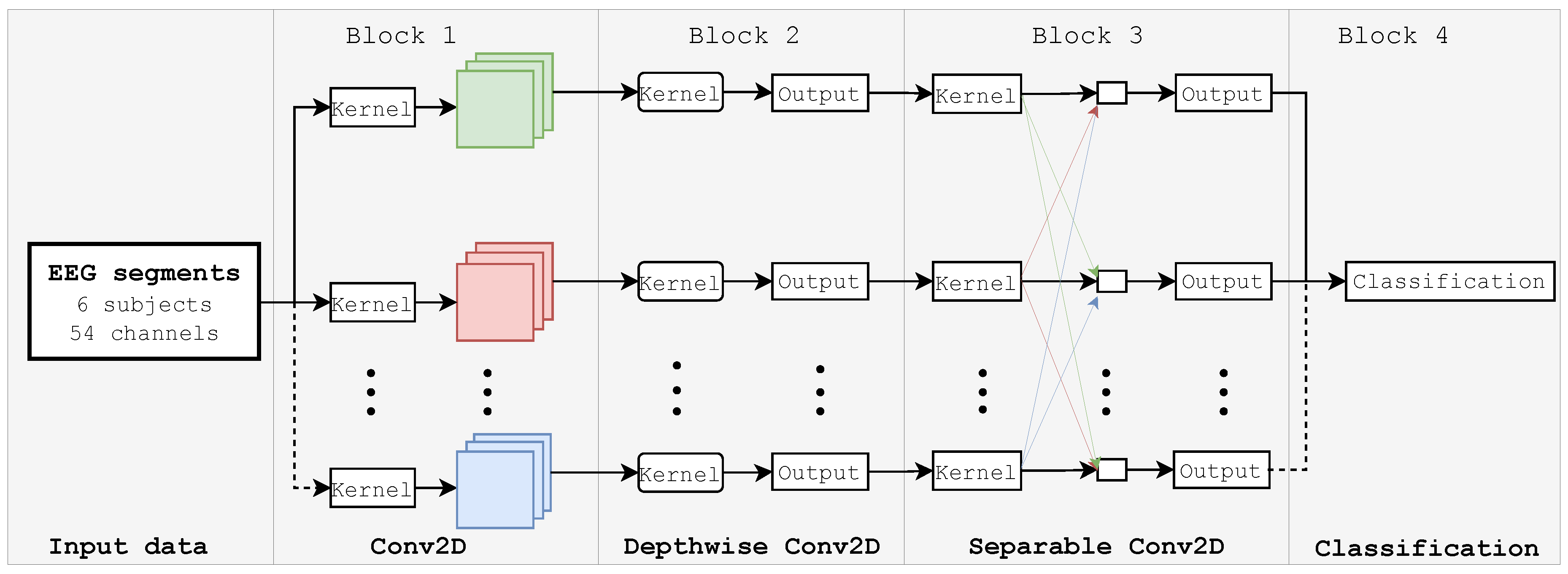
3.5.1. EEGNet Network
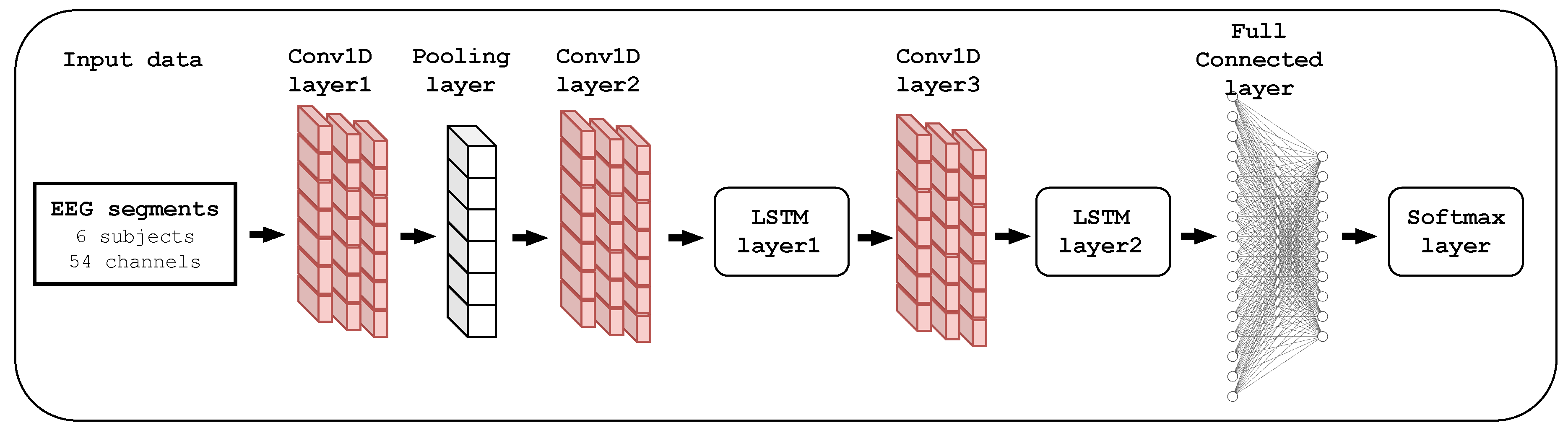
3.5.2. The Proposed CNN-LSTM Model
3.6. Experimental Settings
4. Results
4.1. Results Related to Channels Selection
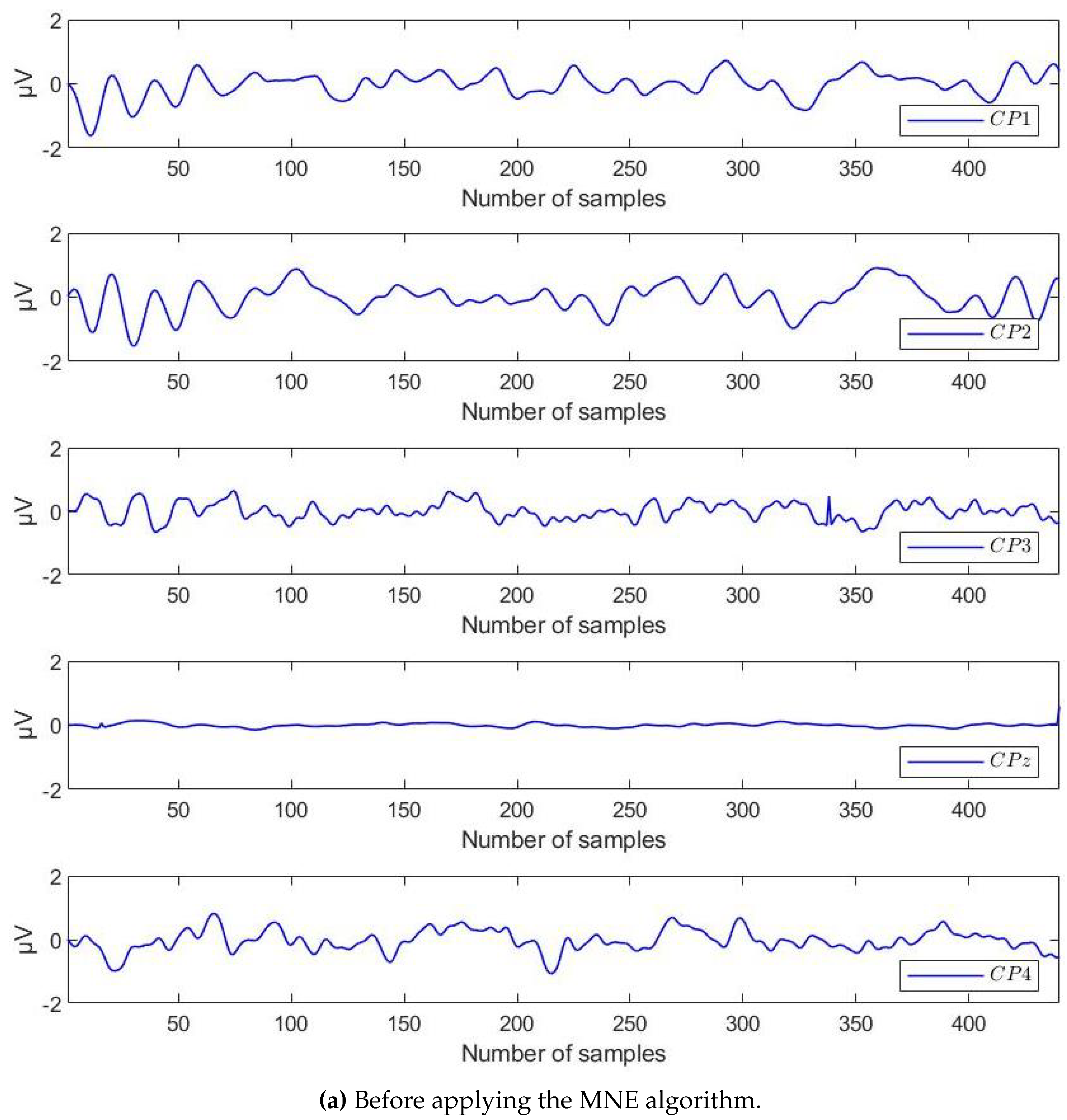
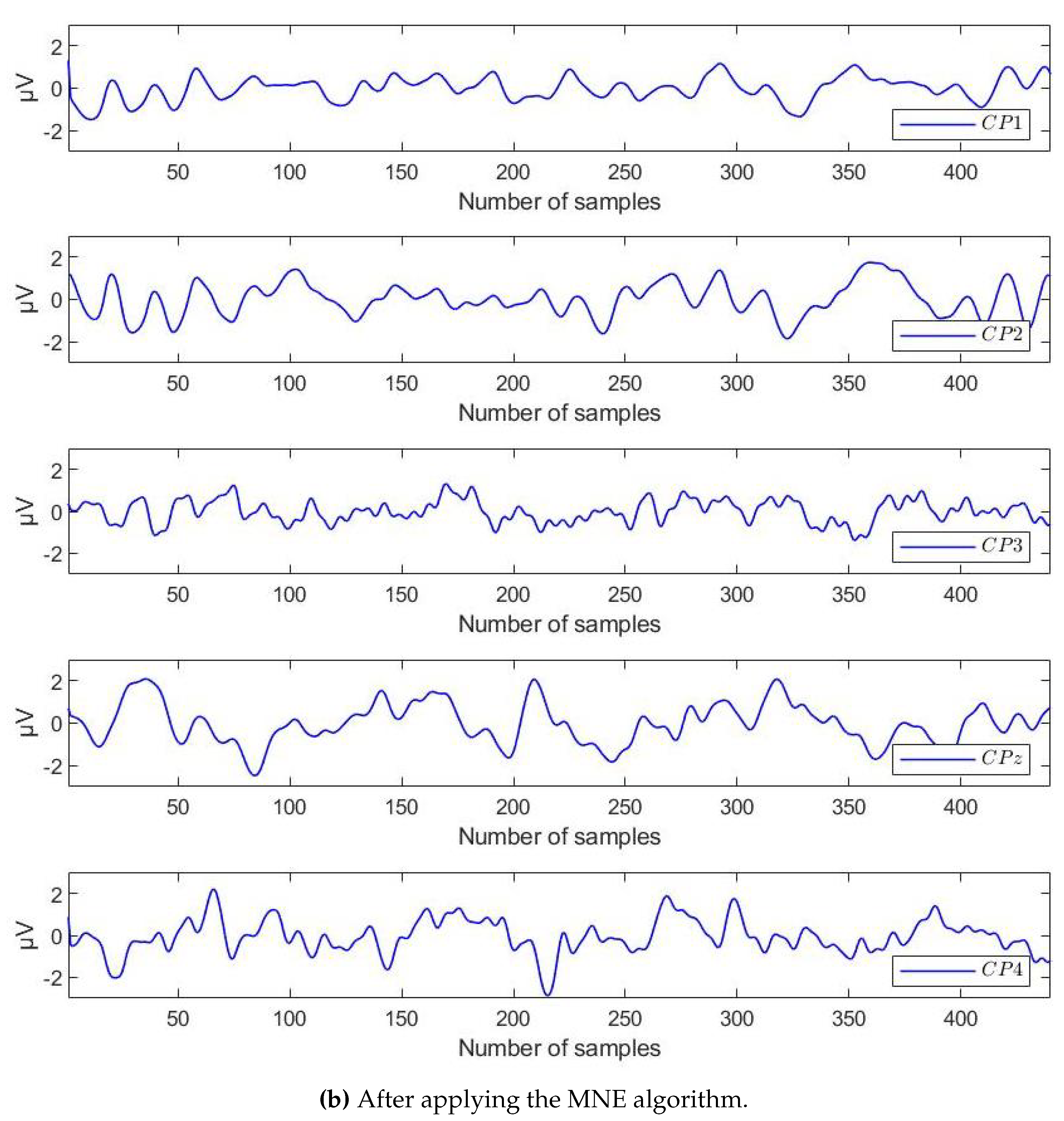
4.2. Results of Preprocessing by MNE
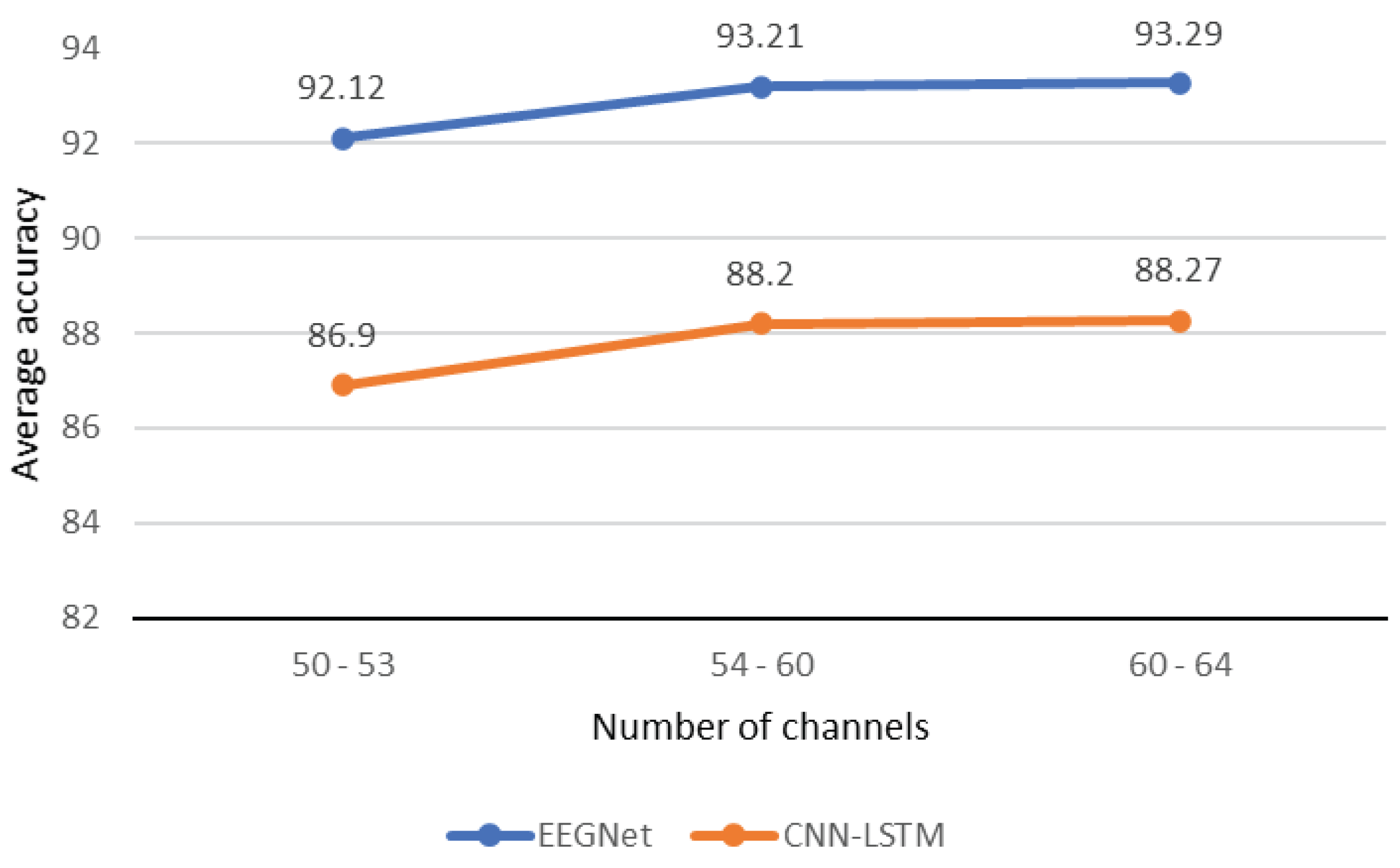
4.3. Results Related to EEG Segments Classification
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
5.1. Conclusion
5.2. Forthcoming Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCI | Brain-Computer Interface |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| CSP | Common Spatial Pattern |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long-Short-Term Memory |
| fNIRS | Functional near-infrared spectroscopy |
| SD | Source-detector |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| EEGNet | Compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based BCI |
| PL | Perceive Lab |
| CNN-LSTM | Convolutional Neural Network-Long-Short Term Memory |
| ERP | Event-related potential |
| STFT | Short-Term Fourier Transform |
| VEP | Visual-evoked potentials |
| SSVEP | Steady-State Visually Evoked Potentials |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| EEGCapsNet | Capsule Network |
| FC-GDN | Functional connectivity-based geometric deep network |
| MutIn | Mutual Information |
| MNE | Minimum-Norm Estimates software suite |
| MI | Motor Imagery |
| MI-EEG | Motor Imagery EEG |
| EVC | EEG Visual Classification |
| EMG | Electromyogram |
| KLD | Kullback-Leibler Divergence |
| CLR | Cyclical Learning Rate |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
References
- Abdulwahab, S.S.; Khleaf, H.K.; Jassim, M.H.; Abdulwahab, S. A Systematic Review of Brain-Computer Interface Based EEG. Iraqi J. Electr. Electron. Eng 2020, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.D.; Martins, F.; Marques, F.; Sousa, J.C.; Rebelo, S. Beyond Brain Signaling. Tissue-Specific Cell Signaling 2020, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.C.; Raja, R.; Vishwakarma, S.K.; Sharma, S.; Mishra, P.K.; Kushwah, V.S. Analysis of brain signal processing and real-time EEG signal enhancement. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2022, 81, 41013–41033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, S.; Yi, H.; Duan, F.; Kang, F.; Sun, Z.; Solé-Casals, J.; Caiafa, C.F. A brain-controlled vehicle system based on steady state visual evoked potentials. Cognitive Computation 2023, 15, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacem, A.N.; Lakas, A. A cooperative EEG-based BCI control system for robot–drone interaction. 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 297–302.
- Choi, J.; Kim, K.T.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, L.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H. Developing a motor imagery-based real-time asynchronous hybrid BCI controller for a lower-limb exoskeleton. Sensors 2020, 20, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwafi, K.; Ghaffari, F.; Djemal, R.; Romain, O. A hardware/software prototype of EEG-based BCI system for home device control. Journal of Signal Processing Systems 2017, 89, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qian, L.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guan, C.; Sun, Y. Design a novel BCI for neurorehabilitation using concurrent LFP and EEG features: A case study. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2021, 69, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandikolla, V.; Medina Portilla, D.A.; others. Teleoperation robot control of a hybrid eeg-based bci arm manipulator using ros. Journal of Robotics 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Trivailo, P.M.; Simic, M. EEG-based BCI control schemes for lower-limb assistive-robots. Frontiers in human neuroscience 2018, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Nakagawa, M. BCI-based control of electric wheelchair using fractal characteristics of EEG. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2018, 13, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onose, G.; Grozea, C.; Anghelescu, A.; Daia, C.; Sinescu, C.J.; Ciurea, A.V.; Spircu, T.; Mirea, A.; Andone, I.; Spânu, A.; others. On the feasibility of using motor imagery EEG-based brain–computer interface in chronic tetraplegics for assistive robotic arm control: a clinical test and long-term post-trial follow-up. Spinal cord 2012, 50, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, P. A hybrid BCI based on SSVEP and EOG for robotic arm control. Frontiers in neurorobotics 2020, 14, 583641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Moral, P.; Nowaczyk, S.; Pashami, S. Why is multiclass classification hard? IEEE Access 2022, 10, 80448–80462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurgansky, A. Functional organization of the human brain in the resting state. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2019, 49, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Tripathy, D.; Raheja, J.L. Real-time BCI system design to control arduino based speed controllable robot using EEG; Springer, 2019.
- Mahmood, A.; Zainab, R.; Ahmad, R.B.; Saeed, M.; Kamboh, A.M. Classification of multi-class motor imagery EEG using four band common spatial pattern. 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1034–1037.
- Fadel, W.; Kollod, C.; Wahdow, M.; Ibrahim, Y.; Ulbert, I. Multi-class classification of motor imagery EEG signals using image-based deep recurrent convolutional neural network. 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–4.
- Kwon, J.; Shin, J.; Im, C.H. Toward a compact hybrid brain-computer interface (BCI): Performance evaluation of multi-class hybrid EEG-fNIRS BCIs with limited number of channels. PloS one 2020, 15, e0230491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spampinato, C.; Palazzo, S.; Kavasidis, I.; Giordano, D.; Souly, N.; Shah, M. Deep learning human mind for automated visual classification. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 6809–6817.
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Goj, R.; Jas, M.; Brooks, T.; Parkkonen, L. ; others. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. frontiers in Neuroscience, 267, 2013.
- Esch, L.; Dinh, C.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.; Jas, M.; Khan, S.; Gramfort, A.; Hämäläinen, M.S. MNE: software for acquiring, processing, and visualizing MEG/EEG data. Magnetoencephalography: From Signals to Dynamic Cortical Networks 2019, 355–371. [Google Scholar]
- Waytowich, N.; Lawhern, V.J.; Garcia, J.O.; Cummings, J.; Faller, J.; Sajda, P.; Vettel, J.M. Compact convolutional neural networks for classification of asynchronous steady-state visual evoked potentials. Journal of neural engineering 2018, 15, 066031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, T.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, T. Automated detection of abnormalities from an EEG recording of epilepsy patients with a compact convolutional neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 70, 103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Sulaiman, N.; PP Abdul Majeed, A.; Musa, R.M.; Ab Nasir, A.F.; Bari, B.S.; Khatun, S. Current status, challenges, and possible solutions of EEG-based brain-computer interface: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in neurorobotics 2020, 14, 515104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, S.; Craik, A.; Sujatha Ravindran, A.; He, Y.; Cruz-Garza, J.G.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Deep learning methods for EEG neural classification. In Handbook of Neuroengineering; Springer, 2022; pp. 1–39.
- Yedukondalu, J.; Sharma, L.D. Cognitive load detection using circulant singular spectrum analysis and Binary Harris Hawks Optimization based feature selection. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 79, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaga, E.G.M.; Thanka, M.R.; Anitha, J. ; others. A Pilot Investigation on the Performance of Auditory Stimuli based on EEG Signals Classification for BCI Applications. 2022 Third International Conference on Intelligent Computing Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT). IEEE, 2022, pp. 632–637.
- Kalafatovich, J.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.W. Learning Spatiotemporal Graph Representations for Visual Perception Using EEG Signals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2022, 31, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, W. An attention-based bi-LSTM method for visual object classification via EEG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 63, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, W.; You, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, T. Ensemble deep learning for automated visual classification using EEG signals. Pattern Recognition 2020, 102, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Anwar, S.; Bhattacharjee, V. Automated visual stimuli evoked multi-channel EEG signal classification using EEGCapsNet. Pattern Recognition Letters 2022, 153, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, N.; Rezaii, T.Y.; Beheshti, S.; Meshgini, S. Developing an efficient functional connectivity-based geometric deep network for automatic EEG-based visual decoding. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 80, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeck, M.; Koessler, L.; Bast, T.; Leijten, F.; Michel, C.; Baumgartner, C.; He, B.; Beniczky, S. The standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN. Clinical neurophysiology 2017, 128, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.S.; Sudirman, R. Decomposition level comparison of stationary wavelet transform filter for visual task electroencephalogram. Jurnal Teknologi 2015, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, M.Z.; Aslam, N.; Shum, H.P. Filtering techniques for channel selection in motor imagery EEG applications: a survey. Artificial intelligence review 2020, 53, 1207–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Suresh, S. An effect-size based channel selection algorithm for mental task classification in brain computer interface. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. IEEE, 2015, pp. 3140–3145.
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Ieee, 2009, pp. 248–255.
- Palazzo, S.; Spampinato, C.; Kavasidis, I.; Giordano, D.; Schmidt, J.; Shah, M. Decoding brain representations by multimodal learning of neural activity and visual features. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2020, 43, 3833–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Hu, S.Y.; Song, H. Channel selection method for EEG emotion recognition using normalized mutual information. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143303–143311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, P.; Vanthornhout, J.; Vandermosten, M.; Francart, T. Beyond linear neural envelope tracking: a mutual information approach. Journal of Neural Engineering 2023, 20, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.a.; Wang, Y.f.; Sun, Y.j. Minimum norm estimates based dipole source estimation. BIBE 2018; International Conference on Biological Information and Biomedical Engineering. VDE, 2018, pp. 1–5.
- Jatoi, M.A.; Kamel, N. Brain source localization using reduced EEG sensors. Signal, Image and video processing 2018, 12, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoi, M.A.; Kamel, N.; Teevino, S.H. Trend analysis for brain source localization techniques using EEG signals. 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–5.
- Kyriaki, K.; Koukopoulos, D.; Fidas, C.A. A Comprehensive Survey of EEG Preprocessing Methods for Cognitive Load Assessment. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, O. Keep it simple: a case for using classical minimum norm estimation in the analysis of EEG and MEG data. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Ao, B.; Wu, X.; Wen, Q.; Ul Haq, E.; Yin, J. Parkinson’s disease detection and classification using EEG based on deep CNN-LSTM model. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efe, E.; Ozsen, S. CoSleepNet: Automated sleep staging using a hybrid CNN-LSTM network on imbalanced EEG-EOG datasets. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 80, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. others 2015; Keras. GitHub. Retrieved fromhttps. github. com/fchollet/keras.
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M. ; others. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems, 2015.
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Automated recognition of epilepsy from EEG signals using a combining space–time algorithm of CNN-LSTM. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Ghassemi, N.; Namadchian, Z.; Zare, A.; Gorriz, J.M. Automatic diagnosis of schizophrenia in EEG signals using functional connectivity features and CNN-LSTM model. International work-conference on the interplay between natural and artificial computation. Springer, 2022, pp. 63–73.
- Yam, J.Y.; Chow, T.W. A weight initialization method for improving training speed in feedforward neural network. Neurocomputing 2000, 30, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.N. Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks. 2017 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, 2017, pp. 464–472.
- Wang, X.; Hersche, M.; Magno, M.; Benini, L. Mi-bminet: An efficient convolutional neural network for motor imagery brain–machine interfaces with eeg channel selection. IEEE Sensors Journal 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwafi, K.; Romain, O.; Gannouni, S.; Ghaffari, F.; Djemal, R.; Ouni, B. An embedded implementation based on adaptive filter bank for brain–computer interface systems. Journal of neuroscience methods 2018, 305, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Kumar, J.; Sheoran, P. Integration of cloud computing in BCI: A review. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2024, 87, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwata-Velu, T.; Avina-Cervantes, J.G.; Ruiz-Pinales, J.; Garcia-Calva, T.A.; González-Barbosa, E.A.; Hurtado- Ramos, J.B.; González-Barbosa, J.J. Improving motor imagery eeg classification based on channel selection using a deep learning architecture. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Works | Models | Dataset | Channels | Acc. [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zheng and Chen [30] | Bi-LSTM-AttGW | PL | 128 | 99.50 |
| Zheng et al. [31] | LSTMS_B | PL | 128 | 97.13 |
| Spampinato et al. [20] | RNN/CNN | PL | 128 | 82.9 |
| Kumari et al. [32] | STFT + EEGCapsNet | PL | 128 | 81.59 |
| Khaleghi et al. [33] | FC-GDN | PL | 128 | 98.4 |
| Order | Subject | Segments order | Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | from 1 to 1995 | 1995 |
| 2 | 1 | from 1996 to 3980 | 1985 |
| 3 | 6 | from 3981 to 5976 | 1996 |
| 4 | 3 | from 5977 to 7972 | 1996 |
| 5 | 2 | from 7973 to 9968 | 1996 |
| 6 | 5 | from 9969 to 11964 | 1996 |
| Total | All subjects | from 1 to 11964 | 11964 |
| Parameter | Number |
|---|---|
| Total number of images | 2000 |
| Number of images per class | 50 |
| Number of classes | 40 |
| Display mode | sequential |
| Display time per image | 0.5 s |
| Sampling frequency | 1000 Hz |
| Pause time between classes | 10 s |
| Number of sessions | 4 |
| Session running time | 350 s |
| Total running time | 1400 s |
| Layer (type) | Output Shape | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | (None, 54, 440, 1) | 0 |
| Conv2D | (None, 54, 440, 8) | 320 |
| Batch_normalization_1 | (None, 54, 440, 8) | 32 |
| Depthwise_conv2D | (None, 1, 440, 80) | 4320 |
| Batch_normalization_2 | (None, 1, 440, 80) | 320 |
| Activation_1 | (None, 1, 440, 80) | 0 |
| Average_pooling2D_1 | (None, 1, 110, 80) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 1, 110, 80) | 0 |
| Separable_conv2D | (None, 1, 110, 80) | 7680 |
| Batch_normalization_3 | (None, 1, 110, 80) | 320 |
| Activation_2 | (None, 1, 110, 80) | 0 |
| Average_pooling2D_2 | (None, 1, 13, 80) | 0 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 1, 13, 80) | 0 |
| Flatten | (None, 1040) | 0 |
| Dense | (None, 40) | 41640 |
| Softmax | (None, 40) | 0 |
| Layer (type) | Output Shape | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Conv1D_layer1 | (None, 440, 128) | 20864 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 440, 128) | 0 |
| Activation_1 | (None, 440, 128) | 0 |
| Max_Pooling | (None, 220, 128) | 0 |
| Conv1D_layer2 | (None, 220, 64) | 24640 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 220, 64) | 0 |
| Activation_2 | (None, 220, 64) | 0 |
| LSTM_layer1 | (None, 220, 64) | 33024 |
| Conv1D_layer3 | (None, 220, 64) | 12352 |
| Dropout_3 | (None, 220, 64) | 0 |
| Activation_3 | (None, 220, 64) | 0 |
| LSTM_layer2 | (None, 32) | 12416 |
| Dropout_4 | (None, 32) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | (None, 54) | 1782 |
| Activation_4 | (None, 54) | 0 |
| Dense_2 | (None, 40) | 2200 |
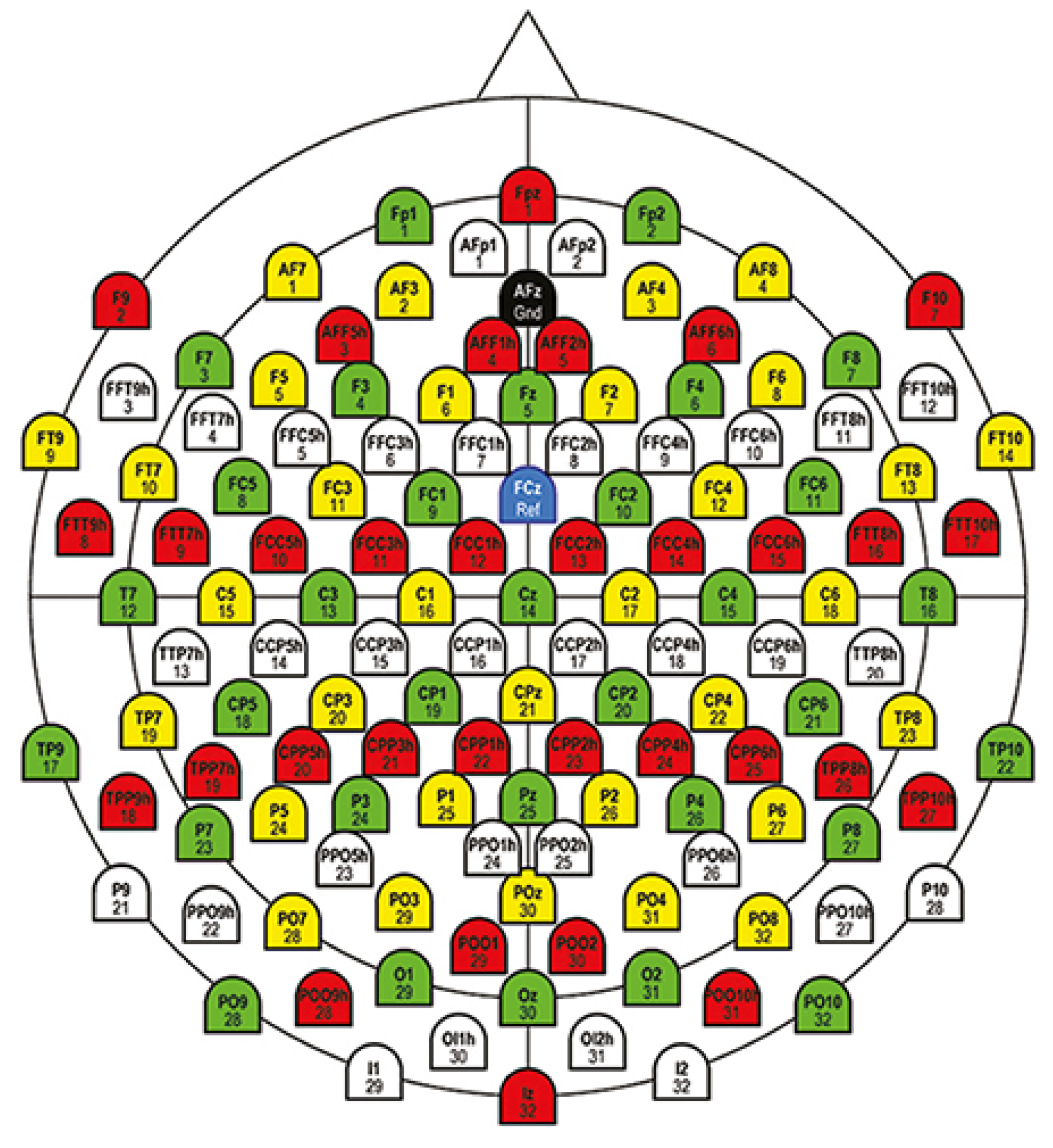
| Brain Area | Nr.Ch. | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal-Central-Central | 3 | FCC1h,FCC2h,FCC4h |
| Frontal-Central | 2 | FC1,FC2, |
| Central | 7 | C1,C2,C3,Cz,C4,C5,C6 |
| Central-Parietal | 5 | CP1,CP2,CP3,CPz,CP4 |
| Central-Central-Parietal | 4 | CCP1h,CCP2h,CCP3h,CCP4h |
| Occipital | 7 | O1,Oz,O2,I1,O11h,O12h,I2 |
| Parietal | 8 | Pz,P1,P2,P3,P4,P5,P6,P8 |
| Parietal-Occipital | 7 | PO7,PO3,POz,PO4,PO8,PO9,PO10 |
| Parietal-Parietal-Occipital | 6 | PPO9h,PPO5h,PPO1h,PPO2h,PPO6h, PPO10h |
| Parietal-Occipital-Occipital | 5 | POO1,POO2,POO9h,POO10h,Iz |
| TOTAL | 54 |
| k-fold | Number of segments | Classification accuracy [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Testing | EEGNet | CNN-LSTM | ||
| 1 | 10768 | 1197 | 92.8 | 88.7 | |
| 2 | 10768 | 1197 | 93.1 | 88.9 | |
| 3 | 10768 | 1197 | 92.2 | 89.1 | |
| 4 | 10768 | 1197 | 93.6 | 87.3 | |
| 5 | 10768 | 1197 | 94.3 | 88.8 | |
| 6 | 10769 | 1196 | 93.7 | 88.2 | |
| 7 | 10769 | 1196 | 92.8 | 87.9 | |
| 8 | 10769 | 1196 | 94.1 | 88.1 | |
| 9 | 10769 | 1196 | 92.9 | 87.5 | |
| 10 | 10769 | 1196 | 93.3 | 88.4 | |
| Average | 93.2 | 88.2 | |||
| N° | EEG time interval [ms] | Average accuracy [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEGNet | CNN-LSTM | ||
| 1 | [20 - 240] | 87.2 | 81.3 |
| 2 | [20 - 350] | 90.8 | 85.9 |
| 3 | [20 - 440] | 91.4 | 87.8 |
| 4 | [40 - 200] | 91.1 | 84.9 |
| 5 | [40 - 360] | 90.5 | 85.6 |
| 6 | [130 - 350] | 92.6 | 87.9 |
| 7 | [130 - 440] | 92.9 | 88.3 |
| 8 | [240 - 440] | 94.4 | 89.1 |
| 9 | [360 - 440] | 94.8 | 89.8 |
| N° | Class | Average accuracies per class label ([%]) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [130-350] | [130-440] | [240-440] | [360-440] | |||
| 1 | cats | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 2 | sorrels | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 3 | elephants | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 4 | fish | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 5 | dogs | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 6 | airliners | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 7 | brooms | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 8 | pandas | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 9 | canoes | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 10 | phones | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 11 | mugs | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 12 | convertibles | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 13 | computers | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 14 | fungi | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 15 | locomotives | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 16 | espresso | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 17 | chairs | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 18 | butterflies | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 19 | golf | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 20 | piano | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 21 | iron | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 22 | daisy | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 23 | jacks | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 24 | mailbags | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 25 | capuchin | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 26 | missiles | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 27 | mittens | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 28 | bikes | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 29 | tents | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 30 | pajama | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 31 | parachutes | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 32 | pools | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 33 | radios | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 34 | cameras | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 35 | guitar | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 36 | guns | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 37 | shoes | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 38 | bananas | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 39 | pizzas | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| 40 | watches | 91 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 91.5 |
| N° | Class | Average accuracies per class label ([%]) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [130-350] | [130-440] | [240-440] | [360-440] | |||
| 1 | cats | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 2 | sorrels | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 3 | elephants | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 4 | fish | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 5 | dogs | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 6 | airliners | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 7 | brooms | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 8 | pandas | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 9 | canoes | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 10 | phones | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 11 | mugs | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 12 | convertibles | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 13 | computers | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 14 | fungi | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 15 | locomotives | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 16 | espresso | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 17 | chairs | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 18 | butterflies | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 19 | golf | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 20 | piano | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 21 | iron | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 22 | daisy | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 23 | jacks | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 24 | mailbags | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 25 | capuchin | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 26 | missiles | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 27 | mittens | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 28 | bikes | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 29 | tents | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 30 | pajama | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 31 | parachutes | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 32 | pools | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 33 | radios | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 34 | cameras | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 35 | guitar | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 36 | guns | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 37 | shoes | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 38 | bananas | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 39 | pizzas | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| 40 | watches | 86 | 87 | 86 | 88 | 86.7 |
| N° | Interval [ms] | EEGNet’s accuracy [%] | CNN-LSTM’s accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with MNE | without MNE | with MNE | without MNE | |||
| 1 | [130 - 350] | 92.6 | 80.3 | 87.9 | 73.8 | |
| 2 | [130 - 440] | 92.9 | 79.2 | 88.3 | 74.1 | |
| 3 | [240 - 440] | 94.4 | 81.8 | 89.1 | 75.4 | |
| 4 | [360 - 440] | 94.8 | 82.1 | 89.8 | 76.2 | |
| Average benefit | 12.8 | 13.9 | ||||
| Works | Models | Dataset | Channels | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zheng and Chen [30] | Bi-LSTM-AttGW | PL | 128 | 99.50% |
| Zheng et al. [31] | LSTMS_B | PL | 128 | 97.13% |
| [20] | RNN/CNN | PL | 128 | 82.9% |
| Kumari et al. [32] | STFT + EEGCapsNet | PL | 128 | 81.59% |
| Khaleghi et al. [33] | FC-GDN | PL | 128 | 98.4% |
| Proposed method | EEGNet/CNN-LSTM | PL | 54 | 94.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





