1. Introduction
Lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, primary pulmonary arterial hypertension, interstitial pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis and α-1-antitrypsin deficiency result in lung damage structural changes, with lung transplantation as a therapeutic indication when the disease reaches an advanced progression [
1]. Unfortunately, the success of lung transplantation is limited, mainly due to the scarcity of the number of organ donors and the incidence of bronchiolitis obliterans resulting from an alloimmune response caused by disparities between the donor and the recipient's antigens. The 50% survival rate after lung transplantation is confined to approximately five years [
2]. In this context, lung bioengineering is considered a potential therapeutic alternative, however research is in preliminary stages and more intense scientific efforts are needed [
3,
4].
Due to the great structural complexity of complete organs, the current approach to bioengineering is based on the use of the natural extracellular matrix (ECM) of the decellularized lung [
5,
6,
7,
8]. The use of undifferentiated cells to seed an ECM can be a more practical strategy for lung bioengineering due to the possibility of expanding these cells and their ability to differentiate into different phenotypes. This approach, however, requires stem cells to be differentiated into necessary phenotypes at specific sites within the organ structure [
6,
7]. In this sense, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) patient-derived demonstrated to be an ideal cell type due to their self-renewal and ability to differentiate into various cell types. Furthermore, dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells (DPSCs), due their feasibility to be isolated and the embryonic origin, arouses a great interest in the use in regenerative medicine [
9].
In addition to the cell type, another challenge during the lung recellularization process is the sterilization of the organ. Previous studies have shown that the methodologies applied for ECM sterilization, such as gamma irradiation, can alter the mechanical properties of the tissue, impairing the ECM-cell interaction [
10]. Therefore, a new tool and methodology for sterilization is necessary without changing the mechanical properties of the decellularized lungs. In this sense, Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) can emerge as a potential treatment alternative, whereas previous studies have shown it capacity of modulate cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, self-renewal and survival. [
11,
12].
Apart from to being a potent alternative for sterilization, the LLLT has been demonstrated to be effective in differentiating stem cells and has an anti-inflammatory role on pulmonary inflammation [
13,
14]. Therefore, the objective of this study was to verify if LLLT, can optimize lung recelularization with mesenchymal stem cells by cytokine modulation.
2. Results
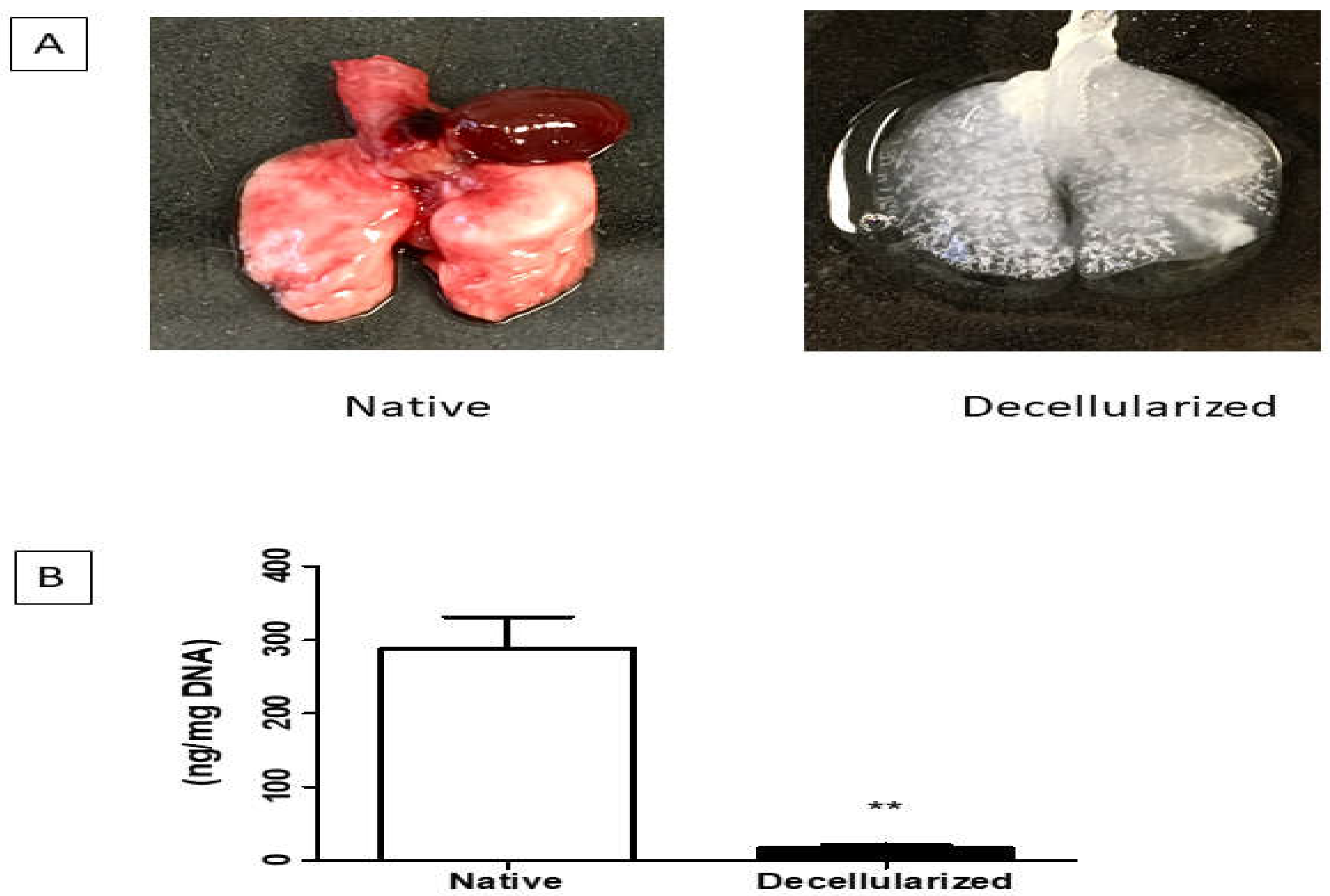
The lung decellularization was successfully performed according to the protocol described in the methods, which lasted approximately 3 to 4 hours. Through this process is possible to verify changes in the organ's color, which changed from a reddish color to a translucent color (Figure 2A). The lungs were monitored throughout the decellularization process, ensuring that the constant pressure of 20 cmH2O of the reagents was maintained, as well as the tracheal (transpulmonary) pressure of 10 cmH2O. It is worth mentioning that the decellularization was of the entire organ, which can provide the preservation of the trachea that were used in the connection to ventilatory constant positive pressure during the recellularization process.
Figure 1.
A. Lungs before and after the decellularization process (one lobe). B. Analysis of DNA quantification in decellularized lungs (n = 1). Data represent mean ± standard error (SEM). Asterisk indicates significance of difference between the groups (** p < 0.001). Lung scaffolds obtained by decellularization showed genomic DNA content in the 17.75 ± 2.05 ng/mg (below the 50 ng/mg suggested by Crapo et al. [
24]) (Figure 1B).
Figure 1.
A. Lungs before and after the decellularization process (one lobe). B. Analysis of DNA quantification in decellularized lungs (n = 1). Data represent mean ± standard error (SEM). Asterisk indicates significance of difference between the groups (** p < 0.001). Lung scaffolds obtained by decellularization showed genomic DNA content in the 17.75 ± 2.05 ng/mg (below the 50 ng/mg suggested by Crapo et al. [
24]) (Figure 1B).
Lung scaffolds obtained by decellularization showed genomic DNA content in the 17.75 ± 2.05 ng/mg (below the 50 ng/mg suggested by Crapo et al. [
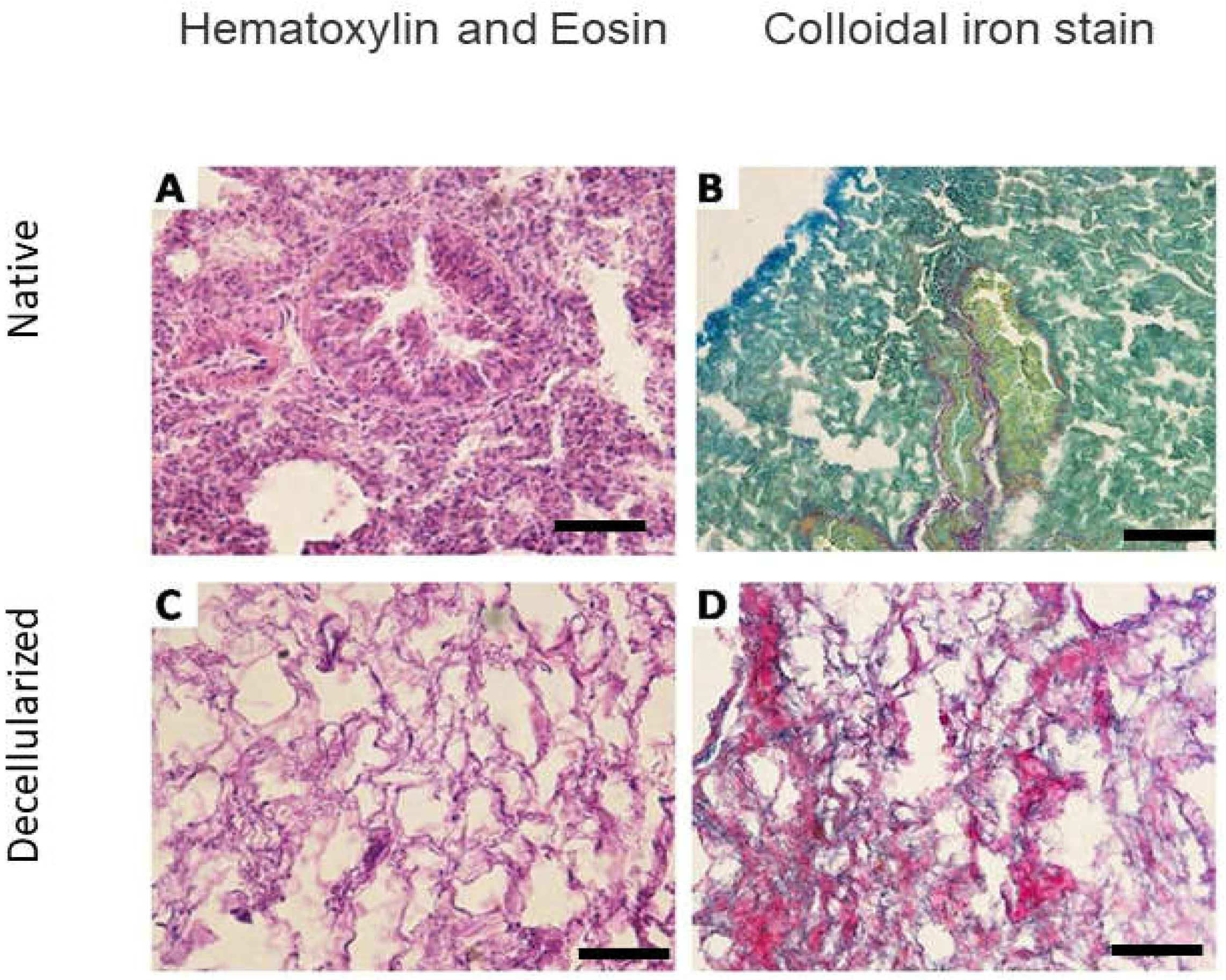
24]) (Figure 2B) and lacked cellular nuclei assessed by H&E (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Microscopic analysis of the lungs of mice before and after decellularization (one lobe). Representative native and decellularized lung tissue, as visualized by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and colloidal ironstain. Sections indicate removal of debris and blood, and lack of visible nuclear material. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Figure 2.
Microscopic analysis of the lungs of mice before and after decellularization (one lobe). Representative native and decellularized lung tissue, as visualized by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and colloidal ironstain. Sections indicate removal of debris and blood, and lack of visible nuclear material. Scale bar = 100 µm.
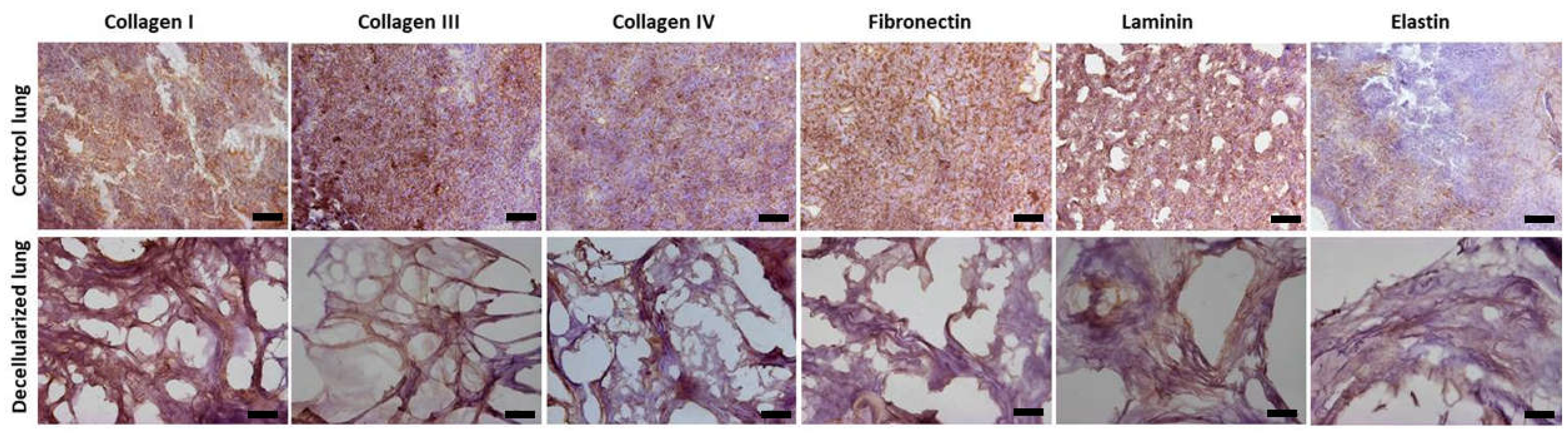
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemistry analysis (one lobe). Presence of collagen I, collagen III, collagen IV, fibronectin, laminin and elastin. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemistry analysis (one lobe). Presence of collagen I, collagen III, collagen IV, fibronectin, laminin and elastin. Scale bar = 100 µm.
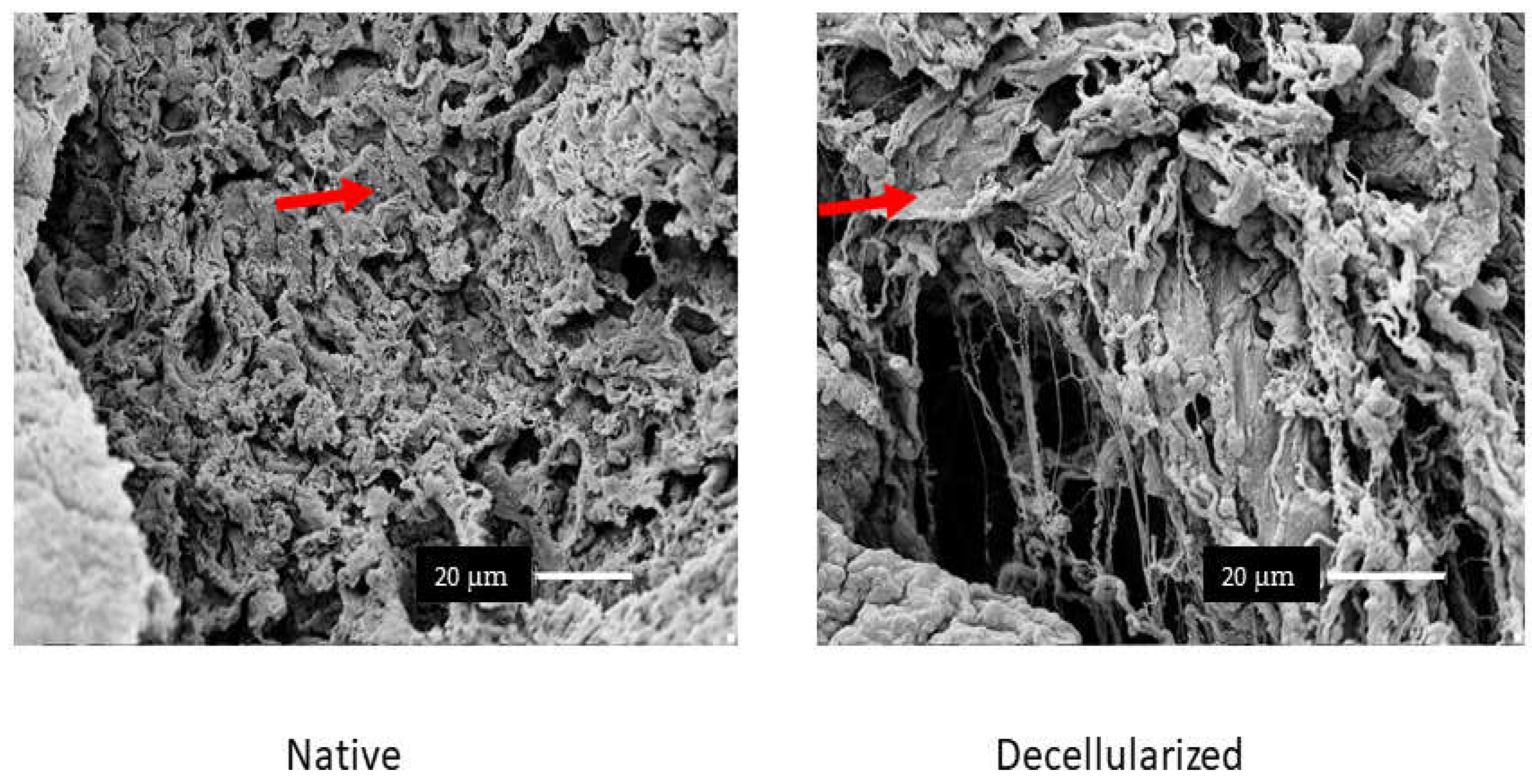
The components of the ECM such as glycosaminoglycans (Figure 3), elastin, fibronectin, and collagen I, III, and IV remained similar in both groups (Figure 4). Furthermore, observation by SEM showed that the microscopic lung structures were also well maintained (Figure 5).
Cell growth was observed daily through an inverted microscope to observe its morphological characteristics, until reaching 80% confluence for the subculture and the culture medium was monitored and changed every 24 hours for cell proliferation (Figure 6).
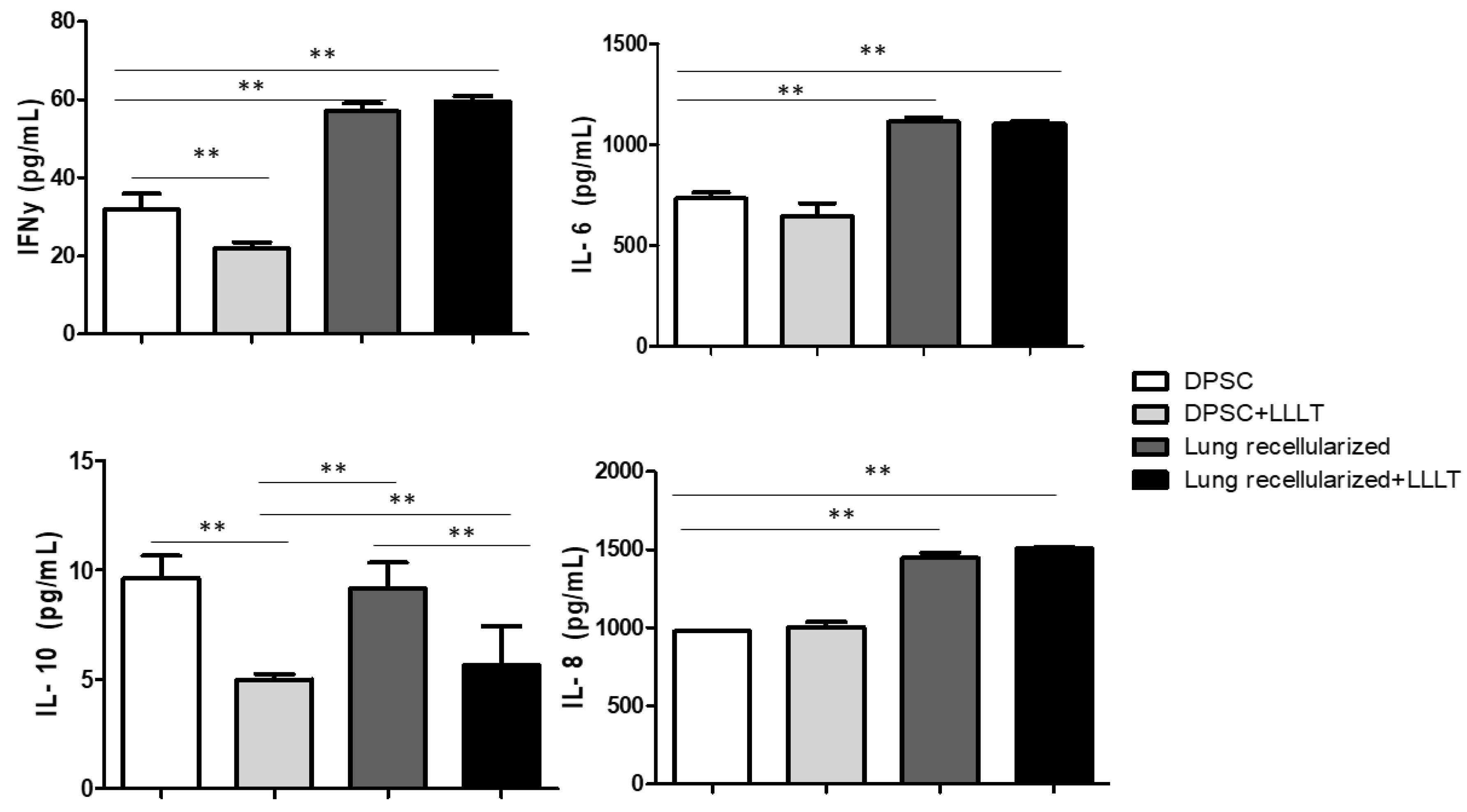
The results regarding the quantification of the levels of IL-6, IL-8, IFN-γ and IL-10 are shown in the Figure 7. Cytokines were previously evaluated in isolated cells and treated with laser. We noticed that the levels of IL-6 and IL-8 were stable during the 24 hours of culture. IFN-γ levels showed significant difference in the DPSc and DPSc + LLLT group in the 24-hour evaluation. The levels of IL-10 decreased after LLLT.
Figure 4.
Analysis by scanning electron microscopy (n = 1). In native lung is possible to visualize cells and in decellularized lung is possible to visualize a great removal of cells and preserved lung parenchyma. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 4.
Analysis by scanning electron microscopy (n = 1). In native lung is possible to visualize cells and in decellularized lung is possible to visualize a great removal of cells and preserved lung parenchyma. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 5.
Effect of low-level laser on lung recelularization on levels of IL-6, IL-8, IFN-y, and IL-10 after 24 h in cell culture supernatant of tooth pulp stem cell. Data represent mean ± standard error (SEM). Asterisk indicates significance of difference between the groups (** p < 0.001).
Figure 5.
Effect of low-level laser on lung recelularization on levels of IL-6, IL-8, IFN-y, and IL-10 after 24 h in cell culture supernatant of tooth pulp stem cell. Data represent mean ± standard error (SEM). Asterisk indicates significance of difference between the groups (** p < 0.001).
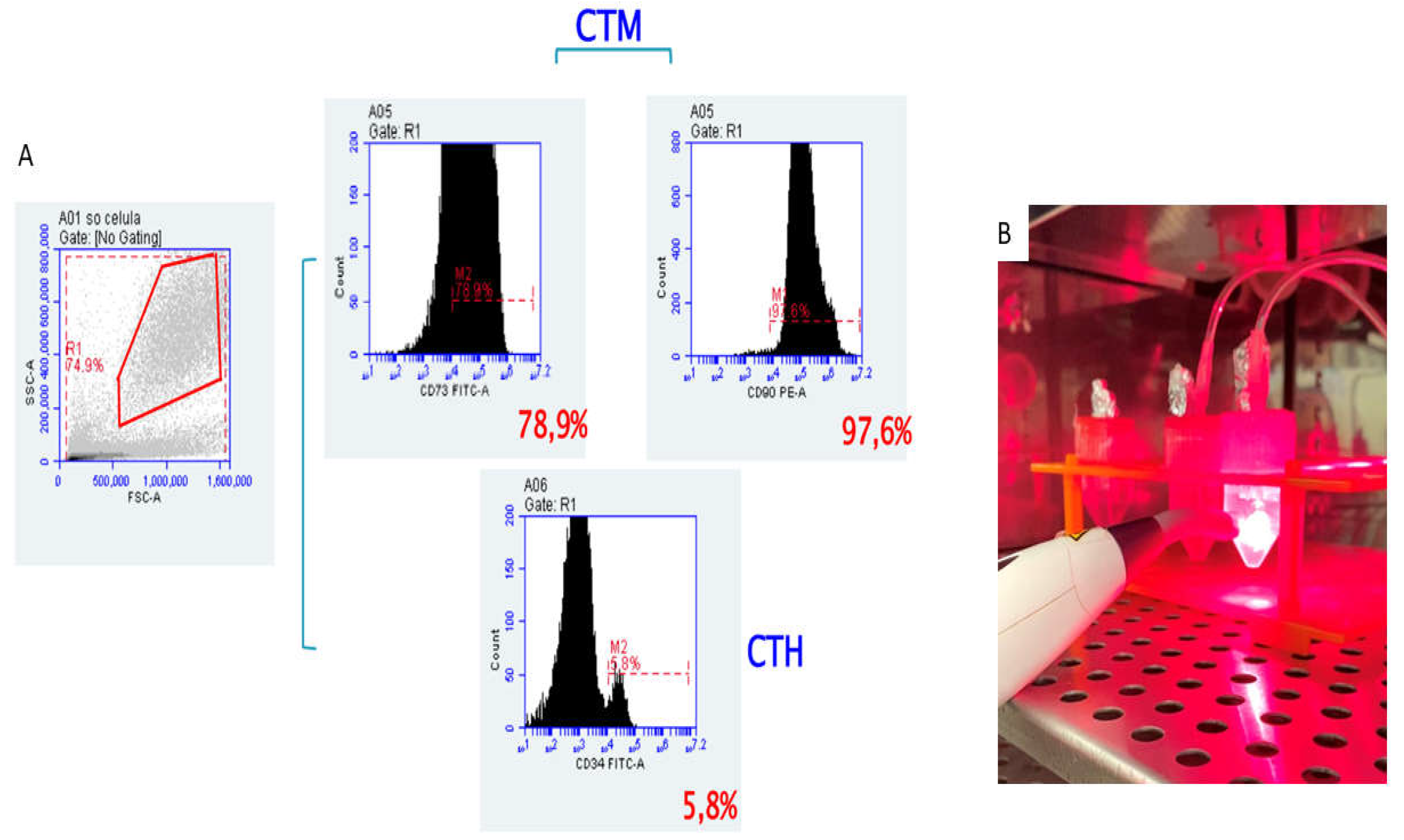
Figure 6.
A. Characterization of Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) The passage 4 of the culture was used and the phenotype of the cells showed that they were positive for the mesenchymal markers, CD90 and CD73 (upper histograms), but did not express the hematopoietic markers, such as CD34 (lower histogram) B. Sterilization and cell proliferation. Sterilization by means of irradiation in length of red light and cell proliferation by means of irradiation in wavelength of infrared light.
Figure 6.
A. Characterization of Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) The passage 4 of the culture was used and the phenotype of the cells showed that they were positive for the mesenchymal markers, CD90 and CD73 (upper histograms), but did not express the hematopoietic markers, such as CD34 (lower histogram) B. Sterilization and cell proliferation. Sterilization by means of irradiation in length of red light and cell proliferation by means of irradiation in wavelength of infrared light.
3. Discussion
Authors should discuss the results and how they can be interpreted from the perspective of previous studies and of the working hypotheses. The findings and their implications should be discussed in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted.
It´s a remarkable study where for the first time LLLT was associated with lung recellularization process. Here we showed tree important finds: i) LLLT can be used as a tool for acellular ECM sterilization, ii) LLLT increase cell proliferation, iii) LLLT and ECM play a role in cytokine modulation. We believe that this work will be relevant for future studies in the field of lung bioengineering.
The production of biomaterials has shown to be a promising technique, through the different approaches in the processes of decellularization, which is possible to obtain a biological scaffold with the ability to maintain physiological and adequate functions to consequently perform a transplant [
8]. Considering that, here we were able to obtain a biological scaffold through the decellularization protocol carried out through the pulmonary artery, due to the agility in the process in which it can be completed with an average of 3 to 4 hours. In addition, this protocol allows the control of the perfusion pressure in the pulmonary artery (physiological pressure of 20 cmH
2O), which may prevent barotrauma [
16].
The lungs were effectively decellularized (Figure 2), resulting in biological scaffolds with cell content removed and an extracellular matrix preserved and translucent by the perfusion of the chemical agent SDS ionic detergent. We choose SDS, because this ionic detergent can remove cells without inducing significant changes in the micromechanical properties of acellular lungs [
21]. In addition to cell nuclei removed, visualized by H&E and demonstrated by DNA quantification, the preservation of the ECM is relevant for organ bioengineering. Our protocol was efficient in maintain the ECM proteins demonstrated by collagen I, III and IV; fibronectin, laminin and elastin (Figure 4). Moreover, glycosaminoglycans and intact alveolar and vascular structures of the lungs were showed (Figures 3 and 5). These results meet all the criteria for a successful Lung decellularization [
22].
Recent works has shown potential benefits with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that can be isolated from a patient, from sources such as tooth pulp and expanded in culture to physiologically relevant numbers. In addition to their fibroblastic morphology and self-renewal, their full ability to differentiate into various cell types, the MSCs demonstrated be efficient in adhering to lung structures regardless of decellularization method, sterilization method, storage time or disease state. In this sense, MSCs have a wide range of applications in recelularization becoming a physiologically relevant cell source in this process [
11,
23,
24].
Apart from cell source, LLLT have been showing excellent results to be considered an alternative tool approach to recellularization process. LLLT is capable of modulating cell growth, viability and differentiation, as well as inducing increased cell proliferation, self-renewal, survival and angiogenesis [
14,
15]. However, an important issue that we need to consider before to recellularization is the scaffold sterilization to eliminate any risk of transmission of viruses and bacteria from the tissue/organ´s donor to the transplanted receptor. Different sterilization methods have been applied but they usually are aggressive sterilization deteriorating structural components and alter the tissue mechanical performance [
10,
25,
26]. Our work proposes a new sterilization methodology where the LLLT could not only assist in cell proliferation through irradiation at infrared light wavelength (660 nm) but could also assist in sterilization by means of irradiation at red light wavelength (808 nm). Future evaluation on lung mechanical after sterilization by LLLT should be considered.
LLLT has been described as a tool with a potential to decrease the severity of the disease through the positive regulation of IL-10 release. Previous studies associated LLLT and mesenchymal stem cells in an experimental model of COPD, showed increased expression and levels of IL-10 in the lung [
27,
28]. Furthermore, LLLT showed to modulate the immunologic response of bleomycin-stimulated lung fibroblasts leading to increase the anti-inflammatory IL-10 secretion. However, here in this work we expected a greater immunological response from the acellular ECM, considering the biological signs it maintains. In fact, greater immunological modulation was observed in the recellularized groups (Recellularized and Recellularized + LLLT) regarding to pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-8). In the other hand, LLLT decreased IL-10 release different from studies relating to disease, probably because here the cells do not need be activated by inflammatory process.
We consider this work an open new window for the field of tissue engineered associated with LLLT. We produced a viable and sterilized ideal scaffold for recellularization process. Complementary studies should be carried out to elucidate new hypotheses that emerged in this study.
4. Materials and Methods
The experimental procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Research of the University of São Paulo and carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publications no. 8023, revised 1978).
4.1. Lung Decellularization
The lungs were obtained from 15 male mice C57 / BL6, weighing 17 to 20 g. Initially, the mice were anesthetized with xylazine and ketamine (1 mg / kg, intraperitoneal), according to the standard protocol adopted by the laboratory and subsequently sacrificed by exsanguination through the abdominal aorta [
15]. Immediately after euthanasia, the diaphragm was punctured, and the rib cage was cut to reveal the lungs. The pulmonary artery was cannulated, and the mice's lungs were perfused through the right ventricle with a phosphate buffer solution (PBS) containing 50 U / ml heparin and 1 μg / ml sodium nitroprusside (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) to prevent the formation of blood clots. Finally, the heart, lungs, and trachea were dissected and removed in bloc, and stored in a −80 °C freezer until the decellularization process was performed.
The lung decellularization protocol included the steps of collection, cleaning, freezing and thawing, washing with 1% SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) and PBS, as previously described [
16,
17]. After cannulation of the trachea and pulmonary artery, thirteen lungs were placed into the experimental system. The trachea was cannulated and connected to a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device that was set to provide a tracheal (i.e., transpulmonary) pressure of 10 cmH
2O to inflate the lung at a physiological volume to prevent atelectasis. The following decellularizing steps were followed through the pulmonary artery: 1) PBS 1× for 30 min, 2) deionized water for 15 min, 3) 1% SDS for 150 min, and 4) PBS for 30 min, at a pressure of 20 cmH
2O.
4.2. Histological and Immunohistochemistry Analysis of Samples
After decellularization one lobe lung scaffold (as well a native lung for comparison) was divided into their lobes and fixed in paraformaldehyde at 4% for 48 h and then dehydrated, diaphanized and embedded in paraffin. Subsequently, 5 um sections were made with the aid of a microtome (RM2265, Leica—Nussloch, GE) and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and colloidal iron stains were used to locate possible remaining cell nuclei in the ECM. The counting of the central nuclei was performed using the ImageJ program (version 1.39u), using the “cell counter” plugin.
For immunohistochemistry the sections were rehydrated and microwaved (1 min at 160 W) in citrate buffer (1.83 mM of monohydrate citric acid and 8.9 mM of sodium citrate tribasic dehydrate; pH 6.0) for antigen retrieval. The endogenous peroxidase block was performed with 3% hydrogen peroxide in distillated water for 30 min in the dark. Nonspecific protein interaction was blocked with 2% of bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS for 30 min. Then, the slides were incubated with antibodies primary: anti-collagen I (# 600-401-103S, 1:100, Rockland - Limerick, USA), anti-collagen III (# sc-8779, 1:100, Santa Cruz Biotechnology - Dallas, USA), anti-collagen IV (# 1-CO083-0, 1:100, Quartett - Berlin, GE), anti-laminin alfa-2 subunit (# bs-8561R, 1:100, Bioss Antibodies - Woburn, USA) and anti-fibronectin (# NBP1-91258, 1:200, Novus Biologicals - Littleton, USA), overnight in a humid chamber at 4 °C. For negative controls, irrelevant anti-mouse IgG (# M5284, Sigma) or anti-rabbit IgG (# ab27478, Abcam - Cambridge, UK) were used under the same conditions to replace the primary antibody. The reaction was detected by a Dako Advance HRP kit that included the secondary antibody (# K6068, Dako - Carpinteria, USA) and the color developed with DAB (# K3468, Dako). The slides were slightly counterstained with hematoxylin. Between each step after antibody incubation, the slides were washed in PBS containing 0.2% BSA. Finally, the slides were assembled and visualized under a Nikon Eclipse 80I microscope.
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Samples from control and decellularized lungs (one lobe each) were prepared for analysis in a scanning electron microscope, following a standard protocol in the preparation of tissue samples. The samples were fixed with 2% glutaraldehyde and 2.5% paraformaldehyde in 0.1-M cacodylate buffer (EMD Biosciences) for 2 h at room temperature, then washed with distilled water in a computerized ultrasonic washer (UltraSonicCleaner) and dehydrated in different concentrations of 70% alcohol for 24 h, then 80% alcohol, 90%, 100% for 10 min each, followed by dry dehydration at a critical point (Balzers CPD 020). Subsequently, the material was placed on a metallic support for gold plating (“sputtering” Emitech K550). To observe the results, we used the scanning electron microscope Hitachi Analytical Table Top Microscope TM3000 (Hitachi) with 15-kVa acceleration.
4.4. Quantification of DNA in Decellularized Lungs
One lobe lung scaffold (as well as one native lungs for comparison) were divided into their lobes and fixed by bronchial infusion of a 3:1 ratio mixture of Optimal Cutting Temperature compound (OCT, Sakura) and PBS. Subsequently, cryosections (12 mm) of frozen lung samples were obtained using a cryostat (Thermo Scientific, HM 560 CryoStar). DAPI staining was used to verify the absence of nuclei or DNA after the decellularization process. For DAPI staining, a stock solution of DAPI (5 mg / mL; 14.3 mm for dihydrochloride or 10.9 mm for dilate) was made by dissolving 10 mg of DAPI in 2 mL of deionized water, followed by sonication for 2 h.
In addition, the amount of DNA remaining in the decellularized samples was extracted as previously described [
16]. One randomly selected decellularized lung and in one native lung were separated by electrophoresis on 3% LMP agarose gel with 60V ethidium bromide for 1h and observed with ultraviolet transillumination.
4.5. Isolation and Culture of Dental Pulp Stem Cells (DPSCs)
The stem cells derived from the dental pulp were inherited from healthy patients, provided by Prof. Dra. Auriléia Aparecida de Brito. After tooth extraction, it was kept in a container with PBS 1x a storage solution consisting of 3 mL αMEM (MinimumEssentialMediumEagle - α modification, Sigma®, M4526) with 2% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (Gibco®, A5955), 10% fetal bovine serum (Fetal BovineSerum, Gibco®, 10437028) and 2 mM L-Glutamine (Gluta MAXTM, Gibco®, 35050061) [
14,
18,
19]. Right after extraction of the dental pulp, the MSCs were separated and purified by gradient centrifugation and transferred to a culture plate with medium consisting of αMEM (Sigma®, M4526) supplemented with 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (Gibco®, A5955), 10% fetal bovine serum (FetalClone® III, Hyclone®, SH 30109.03), 100 μM ascorbic acid and 2 mM L-glutamine (GlutaMAXTM, Gibco®, 35050061) and kept in an oven at 37 °C, under 5% CO
2 and 95% of atmospheric air [
19]. Cell growth was observed daily under an inverted microscope to observe its morphological characteristics, until it reached 80% confluence for the subculture and the culture medium was monitored and changed every 24 hours for cell proliferation.
4.6. Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells (DPSCs)
In the fourth passage, the cells were removed for analysis of the degree of purity. The results guaranteed the phenotypic characterization by flow cytometry of these stem cells, which revealed the expression of CD105 (SH2) and CD73 (SH3/4) being negative for markers of lineage Hematopoietic CD34 (Figure 6A).
4.7. Cultivation of DPSCs in Decellularized Lungs
Lung recellularization was performed in twelve decellularized lungs, for a period of 24 hours divided in 2 groups. Group Recellularized Lung (n = 6): the lungs were seeding with 1 × 106 pulp dent stem cells; and Group Recellularized Lung + LLLT (n = 6): the lungs were seeding with 1 × 106 pulp dent stem cells and irradiated wit Low-Level Laser Therapy.
Initially, the DPSCs (1 × 10
6) were suspended in 1 ml of RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 15% SFB, 2 mM glutamine and 1% of penicillin -streptomycin [
18], filtered through a 40um cell filter to remove groups of cells and injected into the left and right bronchi of the decellularized lungs using a 20-gauge catheter. The lungs were placed with medium in a 25mL falcon tube of ideal size to simulate a rib cage and sterilized with Low-Level Laser Therapy by irradiation at 808 nm in red light wavelength, being applied the dose of 3 joules (30 seconds each) (Figure 6B). To induce cell proliferation the Group Recellularized Lung + LLLT, was irradiated in the wavelength of infrared light at 660 nm, being applied in the same dose of 3 joules (30 seconds each). The lungs from both groups were left in an incubator to allow the cultivation of cells at 37 °C under 5% CO
2 and 95% of atmospheric air in pulmonary differentiation medium, totally sealed and sterile, remaining for a culture period of 24 hours [
8], maintaining a ventilatory method with constant positive pressure 20 cmH
2O, 90% O
2 [
20]. During the recellularization process, 2 ml of medium were removed, and new medium added in the same amount every 12 and 24 h for ELISA evaluation.
To compared with recellularized groups, we did a DPSCs flask culture with LLLT irradiation and without irradiation in the same conditions. Here, the main was demonstrated the difference between two-dimensional (2D) culture and three-dimensional (3D) culture.
4.8. Evaluation of Cytokine Levels by ELISA
The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IFN-γ and IL-10 were assessed using the Biolegends and R&D Systems kit. ELISA is short for Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), an enzyme-linked immunoassay that allows the detection of specifics antibodies.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis was performed using the GraphyPad Prisma software. All values were expressed as mean and standard error of the mean (SEM). The comparison values of the control and decellularized groups were obtained by means of the paired test group. ANOVA was used in the evaluations comparing DPSc, DPSc + LLLT, Lung recellularized and Lung recellularized+LLLT groups during the recellularization process and Tukey's was posthoc test used. Statistical significance was considered when p < 0.05.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, these results demonstrated that low-level laser modulated cytokine levels and could prevent contamination during the lung recellularization process with mesenchymal stem cells. Moreover, the ECM can play an important role in cytokine levels as well which should be considered in further studies.
6. Patents
This section is not mandatory but may be added if there are patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Author Contributions
R.K.P., L.L.G., A.A.B., A.P.L.O., L.V.F.O. and G.I. designed the study; L.L.G., J.P.R.A., A.D.C., D.A.C.P.G.M. and A.A.B. participated in data collection; L.L.G., A.A.B., I.O.S., D.A.A.P.O., C.H.M.S., R.F.O. and G.I. participated in the statistical analysis of the data; R.K.P., G.I., A.A.B., L.L.G. and L.V.F.O. conceived, designed and wrote the paper; C.H.M.S., R.P.V., I.O.S., D.B.S., D.A.C.P.G.M., G.I. and R.K.P. participated in the critical review of the data; R.K.P., G.I. and L.V.F.O. revised the final version of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. LVFO received grants from Research Productivity, modality PQII; process no. 310241/2022-7 of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico (local acronym CNPq), Brazil. RPV receive grants Research Productivity, modality PQII; process no. 313299/2018-8 of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico (local acronym CNPq), Brazil. JPRA receives a grant from the Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Goias (FAPEG), (GO), Brazil. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (CEUA) of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and Zootechnics of the University of São Paulo (USP), São Paulo (SP), Brazil by protocol number 9335060218 and carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publications no. 8023, revised 1978).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. It was not necessary because it was animal experimentation.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated in this study will be available to the scientific community upon request.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) - (132522/2018-7). The authors are thankful to the Advanced Center of Image Diagnosis (CADI-FMVZ-USP) facility and staff for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Shin’oka, T.; Imai, Y.; Ikada, Y. Trasplantation of a tissue- engineered pulmonary artery. The New England journal of medicine 2001, 344, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusen, R.D.; Shearon, T.H.; Qian, Y.; et al. Lung transplantation in the United States, 1999–2008. Am J Transplantation 2010, 10, 1047–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.E.; Cortiella, J. Engineering of a Complex Organ: Progress Toward Development of a Tissue-Engineered Lung. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008, 5, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, Y.S.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Stenmark, K.R. Bioengineering the Lung: Molecules, Materials, Matrix, Morphology, and Mechanics. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015, 309, L625–L638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.H.; Calle, E.A.; Zhao, L.; et al. Tissue-engineered lungs for in vivo implantation. Science 2010, 329, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.P.; England, K.A.; Matson, A.M.; et al. Development of a Decellularized Lung Bioreactor System for Bioengineering the Lung: The Matrix Reloaded. Tissue engineering Part A 2010, 16, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, H.C.; Clippinger, B.; Conrad, C.; et al. Regeneration and Orthotopic Transplantation of a Bioartificial Lung. Nature medicine 2010, 16, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, S.E.; Charest, J.M.; Ren, X.; et al. Bioengineerring lungs for transplantation. Thorac Surg Clin 2016, 26, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, P.; Altanerova, U.; Jakubechova, J.; Repiska, V.; Altaner, C. Dental Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Their Exosomes. Stem Cells Int 2018, 2018, 8973613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, J.J.; Nonaka, P.N.; Campillo, N.; et al. Mechanical properties of acellular mouse lungs after sterilization by gamma irradiation. Journal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials 2014, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.R.; Cho, S.; Discher, D.E. Stem Cell Differentiation Is Regulated by Extracellular Matrix Mechanics. Physiology (Bethesda) 2018, 33, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrabi, B.; Tavirani, M.R.; Khoramgah, M.S.; et al. The Effect of Photobiomodulation Therapy on the Differentiation, Proliferation, and Migration of the Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Review. J Lasers Med Sci 2019, 10 (Suppl. 1), S96–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimbire, F.; Oliveira, A.P.; Albertini, R.; et al. Low level laser therapy (LLLT) decreases pulmonary microvascular leakage, neutrophil influx and IL-1beta levels in airway and lung from rat subjected to LPS-induced inflammation. Inflammation 2008, 31, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak-mnich, K.; Ziemba, B.; Szwed, A.; et al. Effect of Photobiomodulation Therapy on the Increase of Viability and Proliferation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Lasers Surg Med 2019, 51, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, A.; Rojas, M.; Tsapikouni, T.; et al. Obstructive apnea induce early active action of mesenchymal stem cells and enhancement of endothelial wound healing. Respir Res 2010, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Palma, R.K.; Campillo, M.; Uriarte, J.J.; et al. Pressure- And Flow-Controlled Media Perfusion Differently Modify Vascular Mechanics in Lung Decellularization. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2015, 49, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da palma, R.K.; Nonaka, P.N.; Campillo, N.; Uriarte, J.J.; Urbano, J.J.; Navajas, D.; Farré, R.; Oliveira, L.V.F. Behavior of vascular resistance undergoing various pressure insufflation and perfusion on decellularized lungs. J Biomech 2016, 49, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronthos, S.; Mankani, M.; Brahim, J.; et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 13625–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnoli, C.; Roberts, I.A.G.; Kumar, S.; et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood 2001, 98, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franziska, E.; Uhl, A.B.; Zhang, F.; Pouliot, R.A.; et al. Functional role of glycosaminoglycans in decellularized lung extracellular matrix. Acta Biomaterialia 2020, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, E.; Garreta, E.; Luque, T.; et al. Effects of the decellularization method on the local stiffness of acellular lungs. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 2014, 20, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapo, P.M.; Gilbert, T.W.; Stephen, F.B. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomateriais 2011, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonenfant, N.R.; Sokocevic, D.; Wagner, D.E.; et al. The effects of storage and sterilization on decellularized and recellularized whole lung. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3231–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarritt, M.E.; Bonvillain, R.W.; Burkett, B.J.; et al. Hypertensive rat lungs retain hallmarks of vascular disease upon decellularization but support the growth of mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A 2014, 20, 1426–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouk, S.S.; Lim, T.M.; Teoh, S.H.; et al. Alterations of human acellular tissue matrix by gamma irradiation: histology, biomechanical property, stability, in vitro cell repopulation, and remodeling. Biomater J Biomed Mater Res B Appl 2008, 84, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcgilvray, K.C.; Santoni, B.G.; Turner, A.S.; et al. Effects of (60)Co gamma radiation dose on initial structural biomechanical properties of ovine bone–patellar tendon–bone allografts. Cell Tissue Bank 2011, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, J.P.; De Brito, A.A.; Pelatti, M.; et al. Human tubal derived mesenchymal stromal cells associated with low level laser therapy significantly reduces cigarette smoke-induced COPD in C57 BL/ 6 mice. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0136942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, G.C.; Vitoretti, L.B.; Alves, C.E.; et al. Low-Level Laser Therapy Reduces Lung Inflammation in an Experimental Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Involving P2X7 Receptor. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).