1. Introduction
Radish(Raphanus sativus L.), also known as water radish, Lu Fu, and Lai Fu, is a biennial or annual herbaceous plant belonging to the Brassicaceae family. Radish is rich in various nutrients such as vitamin C, dietary fiber, and amino acids. It is also a good source of calcium without containing oxalic acid. Medical research has found that radish has significant effects such as anticancer, antimicrobial, blood pressure-lowering, and immune-boosting properties [
1] In the past decade, the cultivation area of radish in China has been approximately 1.2 million hectares, accounting for 9% of the vegetable production area and maintaining stable development. The total production of radish has reached 26.8 million tons, making it an important economic crop in China [
2] However, in the large-scale cultivation of radish, excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, while significantly increasing yield, has also caused serious soil environmental problems such as soil compaction, salinization, reduced microbial populations, decreased soil enzyme activity, disruption of soil aggregates, and weakened water and nutrient retention capacity. These issues ultimately lead to imbalanced soil nutrients and environmental pollution [
3], which consequently have adverse effects on yield and quality, contradicting the requirements of sustainable agriculture [
4].
Previous studies have indicated that proper fertilization plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal and consistent crop production. By supplying the necessary nutrients for crop growth, we can effectively enhance both the yield and quality of vegetables. Therefore, balanced fertilization is considered an indispensable agricultural technique for maximizing agricultural productivity [
5]. Research has demonstrated that the type and quantity of fertilizer applied significantly influence the quality of radishes [
6]. Furthermore, studies have highlighted the substantial contribution of organic fertilizers in preserving and enhancing soil biological activity [
7]. In comparison to conventional fertilization methods, reducing chemical fertilizer usage while incorporating organic alternatives can improve overall porosity, decrease soil bulk density, enhance water retention capacity, and increase soil organic matter content [
8]. This approach also enhances soil microbial population and structure while modifying rhizosphere soil enzyme activity [
9], thereby promoting nutrient uptake efficiency in crops and ultimately leading to increased yields. Additionally, it has been observed that reducing chemical fertilizer usage while utilizing organic alternatives not only substantially increases crop yield but also revitalizes the soil ecosystem while mitigating environmental pollution risks associated with excessive fertilizer application [
10]. Ultimately, minimizing chemical fertilizer usage while adopting organic fertilizers represents an effective strategy for achieving high crop yields, optimizing fertilizer resource utilization efficiency, as well as safeguarding farmland environments [
11,
12].
Organic fertilizer substitution technology is a fertilization method that combines chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers, which has been widely proven to have the ability to improve soil environment, promote crop root growth, and enhance crop quality and yield [
13,
14]. Despite the slow release of nutrients in organic fertilizers, using organic fertilizers alone cannot meet the rapid growth needs of crops. Therefore, the application of organic fertilizer substitution technology can fully utilize the advantages of chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers to achieve better crop growth results [
15]. Currently, there is a substantial body of research focusing on the growth, development, quality traits [
16,
17], and nutrient requirements [
18] of radish. However, there is limited research on the effects of reducing chemical fertilizer usage and applying organic fertilizers on radish nutritional quality and soil microbial structure. Therefore, this experiment was designed to investigate the impacts of a gradient reduction in chemical fertilizer application combined with a fixed amount of organic fertilizer on various aspects of radish growth, development, yield, soil fertility, and soil microbial communities. The study aims to systematically elucidate the advantages of replacing chemical fertilizers with bio-organic fertilizers and explore appropriate combinations of reduced chemical fertilization and bio-organic fertilizer application to achieve the optimal fertilization combination that reduces chemical fertilizer usage and increases radish yield. The ultimate goal is to contribute to the healthy, green, and sustainable development of the radish cultivation industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
The field experiment was conducted from June 15, 2023, to August 15, 2023, in Guangyuan City, Sichuan Province, China. The experimental site was located at an altitude of 1800 m, with an average annual precipitation of 1600 mm. The previous crop grown at the experimental site was chili pepper. The soil type was identified as yellow soil, and it exhibited uniform fertility characteristics. Prior to the start of the experiment, the basic physicochemical properties of the topsoil (0-20 cm) were determined. The results are shown in the
Table 1 below:
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.2.1. Radish Variety
The radish variety used in the experiment was "Jierumei," (Main Characteristics of the Variety:Semi-erect leaves with semi-flower leaves, reaching maturity in approximately 55-60 days;Root length is around 26cm, with a diameter of 5.5-6cm;Straight and smooth roots with a clean, white skin;Fast growth rate, good heat tolerance, and strong disease resistance) provided by Hebei Jierumei Agricultural Technology Development Co., Ltd. This specific variety was selected for its suitability for the experimental conditions and its known characteristics.
2.2.2. Fertilizer
The chemical fertilizer used in the experiment was a ternary compound fertilizer (15-15-15), with a total nutrient content of at least 45%. This fertilizer provided balanced amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) to support the growth and development of radish plants.The boron fertilizer used in the experiment contained at least 15% boron (B) element. Specific products from JiaShiLi Chemical Fertilizer Co., Ltd., such as Bai Xing compound fertilizer and boron fertilizer, were utilized for their appropriate boron content.The organic fertilizer used in the experiment was a type of organic fertilizer containing humic acid and amino acids. It had an organic matter content of at least 40%. The organic fertilizer also had an effective microbial count of at least 0.2 billion per gram and a total content of nitrogen (N), phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), and potassium oxide (K2O) of at least 6%.
2.3. Experimental Design
The experiment was designed based on the local farming practices, with the aim of comparing different fertilizer reduction treatments. Four treatments were set up, including a control treatment based on the conventional fertilizer application by local farmers and three reduced fertilizer treatments. The details of the treatments are presented in
Table 2:
Three fertilizer reduction treatments were established, including a 12% reduction, a 20% reduction, and a 28% reduction.
Control (local fertilizer application rate: 375 kg·hm² reduction in chemical fertilizer + 4500 kg·hm² organic fertilizer),
T1 (12% reduction in chemical fertilizer + 4500 kg·hm² organic fertilizer),
T2 (20% reduction in chemical fertilizer + 4500 kg·hm² organic fertilizer),
T3 (28% reduction in chemical fertilizer + 4500 kg·hm² organic fertilizer).
The experiment was conducted using open-field wide-row double-ridge planting, with a row spacing of 30 cm, plant spacing of 40 cm, and furrow depth of 35 cm. Each plot had dimensions of 7 m in length and 1 m in width, resulting in a plot area of 7 m². The experimental design employed a randomized complete bioControl design with five replications for each treatment. Standard field management practices, including drought resistance measures, pest control, and other agronomic practices, were implemented following conventional procedures.
2.4. Measurement Indices and Methods
2.4.1. Measurement of Plant Growth Parameters
The following plant growth parameters were measured at different stages of radish growth: during the seedling stage (June 28, 2023), vigorous leaf growth stage (July 5, 2023, and July 11, 2023), fleshy root enlargement stage (July 19, 2023, and July 26, 2023), and harvest stage (August 2, 2023). These measurements were conducted six times throughout the experiment. Fifteen plants with uniform and representative growth were selected from each plot.
Measurement of Maximum Leaf Length and Width:The maximum leaf length and width were measured using a precision of 0.1 cm using a measuring tape during the seedling stage, vigorous leaf growth stage, fleshy root enlargement stage, and harvest stage. These measurements were conducted six times. Fifteen plants with uniform and representative growth were selected from each plot.
Measurement of Fleshy Root Diameter and Thick skin: The fleshy root diameter and skin thiControlness were measured using a vernier caliper with a precision of 0.02 mm during the seedling stage, vigorous leaf growth stage, fleshy root enlargement stage, and harvest stage.
Measurement of Dry Matter Accumulation:For dry matter accumulation measurement, five intact plants were randomly selected from each treatment plot, resulting in a total of 25 plants. The above-ground and underground parts of the radish plants were weighed using an electronic balance with a precision of 0.001 g. After being oven-dried at 105°C for 30 minutes and then at 80°C until a constant weight was reached, the dry weight of the plants was recorded.
2.4.2. Measurement of Radish Quality Indices
Soluble protein content: The soluble protein content was determined using the Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 method 19.
Soluble sugar content: The soluble sugar content was measured using the sulfuric acid-anthrone colorimetric method 20.Cellulose content: The cellulose content was determined using the anthrone-sulfuric acid colorimetric method 20.Vitamin C content: The vitamin C content was determined using the 2,6-dichloroindophenol titration method 21. Isothiocyanate content: The isothiocyanate content was measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) 22
2.4.3. Yield Determination
Yield determination was conducted on August 15, 2023, during the radish harvest period. In each plot, a consecutive selection of 25 radish plants was harvested and weighed to measure the total yield, which was then adjusted to yield per plant and further converted to yield per hectare (hm²). The total biomass yield (weight of the whole radish plant) and economic yield (weight of the fleshy roots) were recorded.
2.4.4. Determination of Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
Soil physicochemical properties were determined using the five-point sampling method for soil samples collected from the 0-20 cm depth. Each treatment was replicated five times. The soil samples were air-dried and then ground and sieved. The fraction that passed through a 0.25 mm sieve was saved for the determination of soil available nutrients and organic matter content. Another portion was immediately sieved through a 2 mm sieve for the determination of soil microbial biomass and the three microbial groups. A third portion was sieved through a 1 mm sieve and saved for the determination of soil enzyme activity.
The organic matter content of the soil was determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation method. The total nitrogen content of the soil was determined using acid digestion and the Kjeldahl method. The soil hydrolyzable nitrogen content was determined using alkaline extraction-cultivation and volumetric methods. The total phosphorus content of the soil was determined using alkaline fusion and molybdenum antimony anti-colorimetry. The available phosphorus content of the soil was determined using ammonium fluoride-hydrochloric acid extraction and molybdenum antimony anti-colorimetry 23.
S-UE activity was determined by the colorimetric method using indophenol blue 24, with 1 mg NH3-N produced per g of soil sample per d at 37 °C as one unit of enzyme activity (U/g soil sample); S-SC activity was determined by the colorimetric method using 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 25, with 1 mg reducing sugar produced per g of soil sample per d at 37 °C as one unit of S-SC activity (U/g soil sample); S-CAT activity was determined by the UV spectrophotometric method 26, with 1 mg reducing sugar produced per g of air-dried soil sample per day; and S-CAT activity was determined by the UV spectrophotometric method. S-CAT activity was determined by UV spectrophotometry, and 1 mmol of H2O2 degradation catalyzed per g of air-dried soil sample per day was defined as a unit of enzyme activity; S-AKP activity was determined by the colorimetric method of disodium phosphate 27, and 1 umol of phenol was defined as a unit of enzyme activity per g of soil sample released per d under 37 °C incubation. One unit of enzyme activity (U/g soil sample) was defined as 1 umol of phenol per d of soil sample incubated at 37 °C.
2.4.5. Soil DNA Extraction and 16s rDNA Sequencing
The total genomic DNA of the microbial community was extracted according to the instructions of the E.Z.N.A.® soil DNA kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, U.S.), and the quality of the extracted genomic DNA was cheControled by agarose gel electrophoresis with 1% agarose, and the concentration and purity of the DNA were determined by using a NanoDrop2000 (Thermo Scientific, U.S.A.). The quality of the extracted genomic DNA was determined by agarose gel electrophoresis (1%), and the DNA concentration and purity were determined by NanoDrop2000 (Thermo Scientific). Amplification of soil bacterial sequences was performed using the extracted DNA as a template with the upstream primer 338F (5'-ACTCCTACGGGGAGGCAGCAG-3') and the downstream primer 806R (5'-GGACTACHVGGGGGGGG), which carry Barcode sequences, as templates. GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3') 28 were used to amplify the V3-V4 variable region of the 16S rRNA gene by PCR, and the amplification procedure was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95 ℃ for 3 min, 27 cycles (denaturation at 95 ℃ for 30 s, annealing at 55 ℃ for 30 s, and elongation at 72 ℃ for 30 s), and stable extension at 72 ℃ for 10 min. The PCR reaction system was as follows: 5×TransStart FastPfu buffer 4 μL, 2.5 mM dNTPs 2 μL, upstream primer (5uM) 0.8 μL, downstream primer (5uM) 0.8 μL, TransStart FastPfu DNA polymerization buffer 4 μL, 2.5 mM dNTPs 2 μL, 5uM primer 0.8 μL, 5uM primer 0.8 μL, 5uM primer 0.8 μL, 5uM primer 0.8 μL, 5uM primer 0.8 μL. TransStart FastPfu DNA polymerase 0.4 μL, template DNA 10 ng, made up to 20 μL. PCR products were recovered using a 2% agarose gel, and the recovered products were purified using the DNA Gel Recovery and Purification Kit (PCR Clean-Up Kit, Passionate, China) and analyzed by Qubit 4.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Fisher Scientific, USA) for quantification of the recovered products. The sequencing was performed by Shanghai Meiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd. on the Illumina NovaSeq platform using the NovaSeq-Next2000 PE300 strategy.
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
The data preprocessing and graphing were performed using Microsoft Excel 2007. The statistical analysis, including one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc multiple comparisons using the Duncan method (α = 0.05), was conducted using SPSS 20.0 software. The data presented in the figures and tables are expressed as the mean ± standard error.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Organic Fertilizer on Agronomic Traits of Radish
Based on the experimental results presented in
Table 3, the monitoring of growth parameters throughout the entire growth period of radish revealed the following findings: Compared to the control, the T
2 treatment significantly influenced the maximum functional leaf width, root diameter, and root length at the harvest stage, showing an increase of 47.62%, 9.78%, and 7.23%, respectively (
p < 0.05). However, the T
2 treatment resulted in a significant reduction of 23.04% in the thick skin of radish fleshy roots compared to the control (
p < 0.05). The effects of different fertilizer treatments on the biomass yield of radish fleshy roots and leaves varied. The accumulation trend of dry matter in radish was similar among different treatments, with an increasing trend as the growth period progressed. Compared to the control, all other treatments significantly increased the dry weight of fleshy roots. The T
2 treatment showed an increase of 44.12% in dry matter accumulation compared to the control (
p < 0.05). These findings indicate that appropriate reduction in chemical fertilizer application combined with the application of organic biofertilizers can promote the growth of maximum functional leaf width, root diameter, root length, and dry weight of radish fleshy roots.
3.2. The Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Organic Fertilizer on the Nutrient Quality Content of Radish
As shown in
Table 4, the results of radish quality test indicated that all three fertilization treatments improved radish fleshy roots compared with Control, with the most significant effect of T
2 treatment. Compared with Control, T
2 treatment increased vitamin C, soluble sugar, soluble solids, soluble protein, titratable acid and lycopene content of radish fleshy roots by 10.62%, 2.15%, 50%, 26.90%, 43.90% and 44.57%, respectively; and decreased cellulose content by 10.14% (
p<0.05). This indicates that chemical fertilizer reduction with bio-organic fertilizer can improve the nutrient quality content of radish.
3.3. Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction and Organic Fertilizer Application on Radish Yield
According to
Table 5, it is evident that reducing chemical fertilizer application significantly increases the yield of radish. The order of radish yield, both per plant and total yield, is as follows: T
2 > T
1 > T
3 > Control. This indicates that reducing chemical fertilizer application and incorporating organic fertilizer is beneficial for the translocation of nutrients from the aboveground parts to the underground fleshy roots of radish. Treatment T
2 exhibited the highest increase in total radish yield, being 1.06 and 1.07 times higher than the fertilization treatments T
1 and T
3, respectively. This demonstrates that appropriate reduction in chemical fertilizer application combined with the application of organic biofertilizers can enhance radish yield.
3.4. Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Nutrient Content Content of Radish
According to
Table 6, there were no significant differences in soil hydrolyzable nitrogen content among the treatments. The T
2 treatment significantly increased the total nitrogen content in the soil compared to the Control and T
3 treatments, with increases of 7.69% and 6.67%, respectively, and no significant difference compared to theT
I treatment. The total phosphorus content in the soil was significantly higher in the T
2 treatment compared to the Control and T
1 treatments, with increases of 14.29% and 14.29%, respectively, and no significant difference compared to the T
3 treatment. The available phosphorus content was significantly higher in the T
2 treatment, showing an increase of 6.97% compared to the T
1 treatment, and no significant difference compared to the Control and T
3 treatments. These results indicate that appropriately reducing the amount of chemical fertilizer application has a significant effect on increasing soil nutrient content.
3.5. Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Organic Fertilizer on Radish Soil Enzyme Activity
According to
Table 7, different fertilizer application rates had a significant impact on soil enzyme activities. Compared to the Control treatment, the T
2 treatment significantly increased enzyme activities. The urease activity reached the highest level at 552 μg/d/g, representing a 28.97% increase compared to the control. The sucrase activity reached the highest level at 6.58 mg/d/g, showing a 55.92% increase compared to the control. The alkaline phosphatase activity reached the highest level at 1.46 μmol/d/g, indicating a 52.08% increase compared to the control. The catalase activity reached the highest level at 17.08 U/g, exhibiting a 17.47% increase compared to the control (p<0.05). These results suggest that appropriate reduction in chemical fertilizer application combined with the application of organic biofertilizers enhances the activities of urease, sucrase, alkaline phosphatase, and catalase enzymes in the soil.
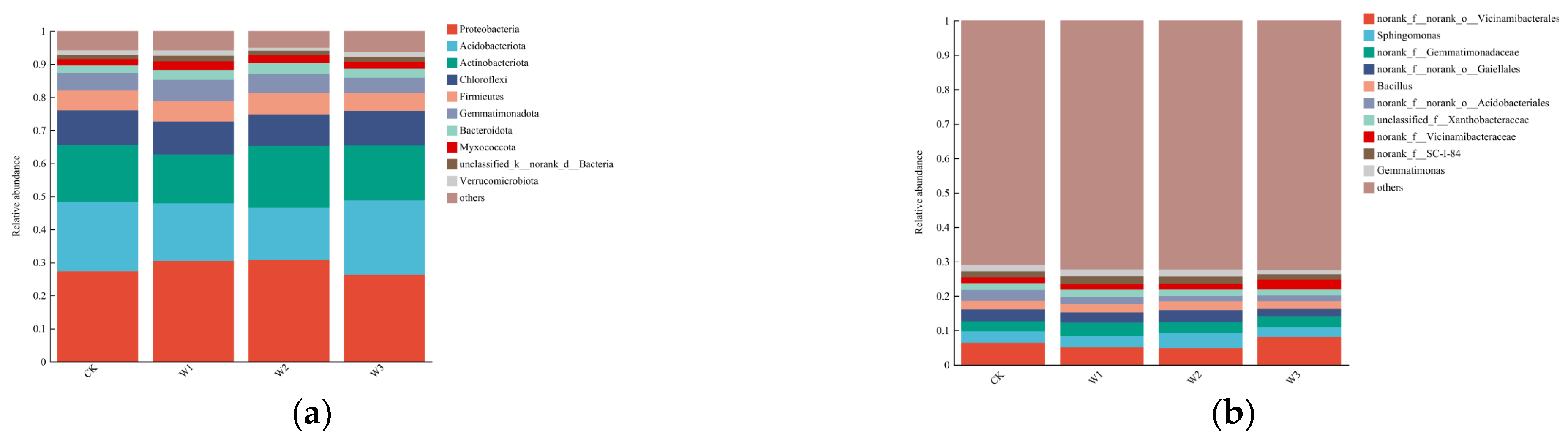
3.6. Effect of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Organic Fertilizer on the Structural Components of Radish Soil Bacterial Community
At a 97% similarity level, the analysis of OTU sequences detected 41 bacterial phyla. As shown in
Figure 1a, the dominant bacterial phyla in the soil were Proteobacteria (26.25%-30.70%), Acidobacteria (15.74%-22.49%), Actinobacteria (14.73%-18.84%), Chloroflexi (9.53%-10.47%), Firmicutes (5.37%-6.44%), and Gemmatimonadetes (4.71%-6.41%). Compared to the Control treatment, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria increased by 12.25% and 10.43% in the T
2 treatment, while the relative abundance of Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi decreased by 25.30% and 8.98%, respectively.
In the sequence analysis, a total of 1007 bacterial genera were detected. As shown in
Figure 1b, the top 10 bacterial genera accounted for approximately 29.01% of the total genera. Excluding undefined bacterial genera, the dominant bacterial genera in the soil were Vicinamibacterales (4.77%-8.10%), Sphingomonas (2.80%-4.45%), Gemmatimonadaceae (2.99%-3.88%), Gaiellales (2.29%-3.6%), Bacillus (2.25%-2.61%), and Acidobacteriales (1.50%-3.22%). Compared to the Control treatment, the relative abundance of Sphingomonas in the T
2 treatment increased by 34.44%.
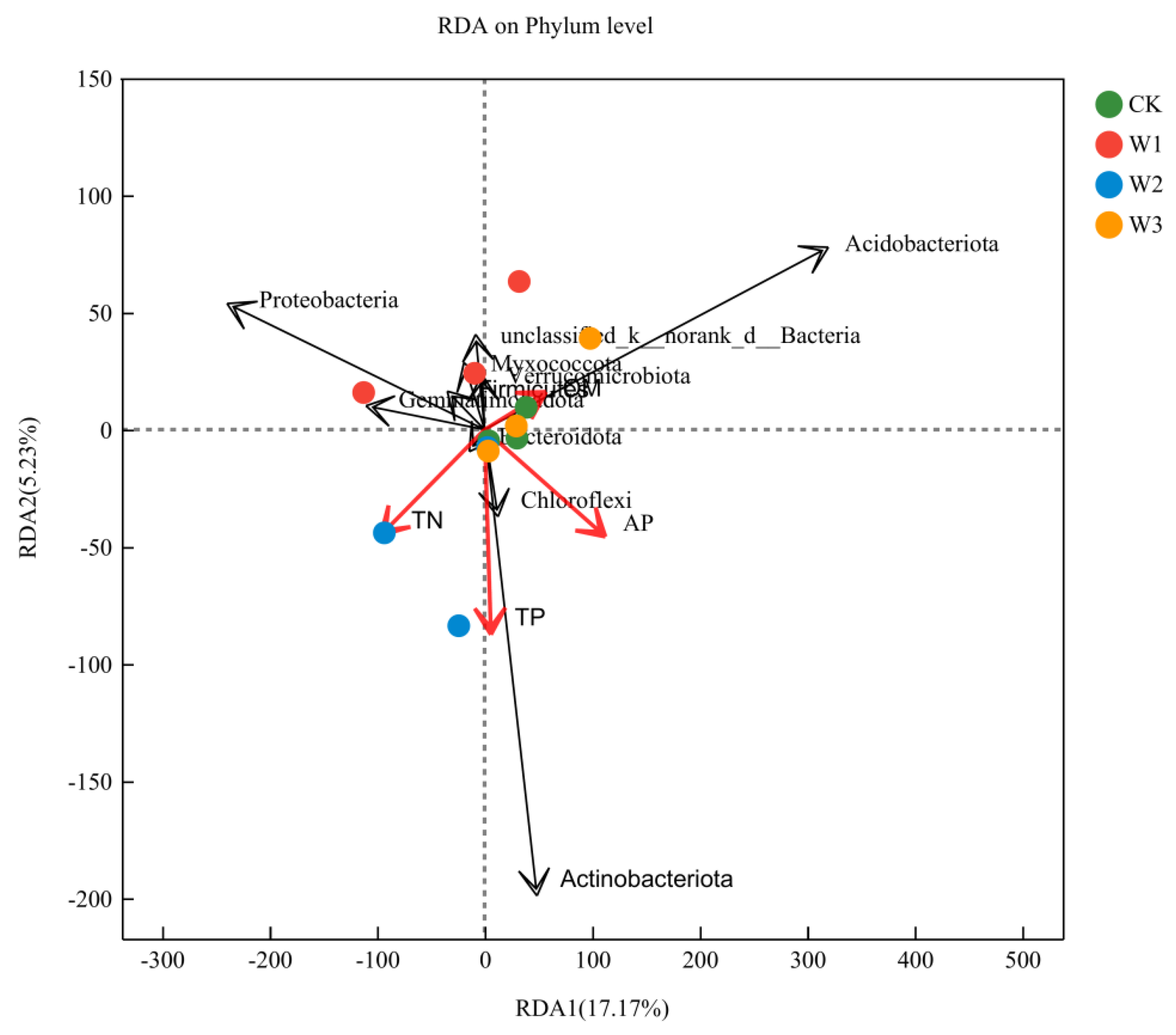
3.7. RDA Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Environmental Factors
Correlation between Community Composition of Bacterial Phyla at the Soil Level and Environmental Factors through Redundancy Analysis (RDA) (
Figure 2), indicating significant influence of environmental factors on bacterial communities. The first and second axes explain 17.17% and 5.23% of the bacterial community variation, respectively. Using Canoco5 software's constrained ordination, four environmental factors contribute the most to the composition of bacterial communities: organic matter (OM, 4.05%), total nitrogen (TN, 14.46%), total phosphorus (TP, 33.27%), and available phosphorus (AP, 42.66%). The dominant phyla Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi show a positive correlation with TN, TP, and AP, while exhibiting a negative correlation with OM. The phylum Proteobacteria shows a positive correlation with TN, but a negative correlation with OM, TP, and AP. These results suggest that organic matter (p=0.845), total nitrogen (p=0.551), total phosphorus (p=0.144), and available phosphorus (p=0.096) are the major driving factors shaping the composition of soil bacterial communities.
4. Discussion
Numerous studies have demonstrated that the appropriate combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers is beneficial for crop growth, as it increases cabbage yield and soil nutrient content, maintains soil productivity, and reduces the use of chemical fertilizers 29. Previous research has shown that appropriate application of organic fertilizers promotes tomato growth, enhances fruit yield and quality 30. The results of this study indicate that a 20% reduction in chemical fertilizers combined with organic fertilizer significantly increases the content of vitamin C, soluble sugars, soluble solids, soluble proteins, titratable acidity, and glucosinolates in radish fleshy roots. This finding is consistent with the research results of Zhang Yu 31 and Tang Guirong 32 on the effects of organic-inorganic fertilizer ratios on vegetable quality. Qiu Wen et al. 33 found that under conventional fertilization conditions, reducing chemical fertilizer application by 50% and applying bio-organic fertilizer significantly improves the fresh cob and fresh grain yield, as well as dry matter accumulation, of sweet corn. Zhou Jianxiong et al. 34 also reported that compared to conventional fertilization, optimizing fertilization and replacing 30% of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers increased radish yield. In this experiment, the radish plants treated with various reductions in chemical fertilizers combined with bio-organic fertilizers exhibited greater functional leaf width and fleshy root dry weight than the control group (Control) using conventional fertilization. Crop biomass is closely related to nutrient accumulation, which serves as the foundation for biomass accumulation and yield formation 35. Under the same application rate of bio-organic fertilizers, the radish plants treated with a 20% reduction in chemical fertilizers showed the maximum functional leaf width, root length, root diameter, and fleshy root dry weight during the harvest period. Additionally, the T2 treatment (20% reduction in chemical fertilizers + 4500 kg · hm-2 of bio-organic fertilizers) achieved the highest individual and total radish yield, with increases of 19.05% and 12.92% respectively, compared to the Control group. This may be due to the significant increase in the content of beneficial microorganisms such as actinomycetes, deformable bacteria, Burkholderia, and Bacillus in the soil when chemical fertilizers are combined with bio-organic fertilizers, which improves the efficiency of nutrient acquisition by plants 36. Furthermore, it improves the biological properties of the soil and enhances nutrient release to meet the nutritional requirements for crop growth 37, thereby promoting radish growth, improving nutritional quality, and increasing yield.
The application of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer has a comprehensive effect on improving crop yield, which is related to soil nutrient content, soil enzyme activity, and the improvement of soil microbial community 38,39. They collectively promote the formation of crop yield. Therefore, reducing the use of chemical fertilizer and properly applying organic fertilizer can effectively regulate the structure of soil microbial communities, enhance various enzyme activities, improve soil fertility, achieve the highest yield, and realize efficient nutrient utilization. Research has shown a significant correlation between soil nutrient content and the activity of soil enzymes such as peroxidase, urease, alkaline phosphatase, and sucrase, indicating an inseparable relationship between soil enzyme activity and soil nutrient content 40. This is consistent with the results of this experimental study. During the radish harvest period, in the T2 treatment with a 20% reduction in chemical fertilizer application, soil total nitrogen content, total phosphorus content, and available phosphorus content were higher than the Control treatment, with soil total phosphorus content and available phosphorus content significantly higher than the T1 treatment. Proper reduction of chemical fertilizer combined with the application of bioorganic fertilizer can increase the content of available nutrients in the soil. The reason may be that bioorganic fertilizer contains a large amount of organic matter and various active bacteria, and microorganisms continuously promote the release of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the slow-release state of the soil during their life activities, thereby improving the soil microecological environment and increasing the content of available nutrients in the soil 41. This is also consistent with the research results of Zhou Xiaotian et al. 42. Soil enzyme activity can be widely used to evaluate soil fertility and the effectiveness of various agricultural measures and fertilization practices. Fertilization treatments primarily alter the composition, biomass, and metabolic processes of soil microbial communities, thereby changing soil enzyme activity 39. Studies have shown that the combined application of bioorganic fertilizer can significantly enhance the activity of soil sucrase, alkaline phosphatase, peroxidase, and urease 4344. In this study, compared to the Control treatment, the 20% reduction in chemical fertilizer combined with the application of organic fertilizer significantly increased the activity of soil urease, peroxidase, sucrase, and alkaline phosphatase, which is consistent with the research results of Wang Xinglong et al. 39 and Qu Chengchuang et al. 45. On the one hand, organic fertilizer can increase soil organic matter content, providing the necessary carbon source for soil microorganisms and synergistically improving the stability and biological properties of soil aggregates 46, thereby providing a favorable environment for microorganisms and increasing the substrates required by soil enzymes 47. On the other hand, bioorganic fertilizer increases soil microbial biomass and enhances microbial activity, and the combined application of reduced chemical fertilizer and two types of organic fertilizer has a better effect.
In this study, the dominant bacterial phyla in the four different fertilization treatments were similar and included Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Firmicutes, which is consistent with the dominant bacterial groups found in previous studies 48,49. However, there were certain differences in the relative abundance of dominant groups among the treatments. The T2 treatment, which involved a reduction in chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer application, enriched soil nutrient resources, promoted the growth of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria, and inhibited the growth of oligotrophic bacteria such as Chloroflexi and Acidobacteria 50,51. Studies have shown that the increased abundance of Actinobacteria under the T2 treatment may play an important role in improving agricultural soil quality, as it has been found to degrade organic matter in fertilizers in field practices 52. Chemoheterotrophy and aerobic chemoorganotrophy are considered widespread ecosystem functions performed by most microorganisms 40, such as Acidobacteria and Proteobacteria 53. In the Control treatment, the relative abundance of Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi was higher than in the other treatments, as Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi tend to enrich in low-fertility soils 54. Chemoheterotrophy and aerobic chemoorganotrophy are important ecological functions related to carbon cycling 55. Compared to the Control treatment, the T2 treatment significantly increased the abundance of chemoheterotrophic functional populations, indicating a significant increase in bacterial population abundance in the T2 treatment. This is beneficial for the release of more inorganic nutrients that are available for crop utilization, which may be one of the reasons for the increase in crop yield under the T2 treatment.The main bacterial groups in soil microbial communities are Acidobacteria and Proteobacteria 56, and they play crucial roles in soil nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition processes 57. In this study, we observed that Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Actinobacteria were the most abundant phyla. Compared to the T2 treatment, the Control treatment significantly reduced the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria in the soil, indicating that excessive fertilizer application may lead to soil fertility decline. Bacteria belonging to the phylum Acidobacteria may have numerical dominance and metabolic activity in soil samples, suggesting their important role in the biogeochemical cycling of rhizosphere soil 58. According to the research by Li Hongbo, soil organic matter, total phosphorus, available phosphorus, and total nitrogen content are the main environmental factors influencing the structure of rhizosphere soil bacterial communities during the rice maturation stage 59. Additionally, fertilization can significantly alter soil pH and nutrient cycling 60,61. Furthermore, Zhang Yan's study indicated that pH value, soil moisture content, and water-soluble organic carbon are the major factors influencing the structure of soil bacterial communities, with soil moisture content being considered the most critical environmental factor 62,63. Therefore, based on the results of this study, the content of ammonia nitrogen (AN), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and pH value in the soil are the main factors determining the characteristics of soil bacterial communities, while other factors such as soil organic matter and available phosphorus (AP) have relatively minor effects. Chai Zhiwei's research showed a positive correlation between ammonia nitrogen content in the soil and the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, while ammonia nitrogen content was negatively correlated with the relative abundance of Acidobacteria 64. In this study, we found that the relative abundance of Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi, two dominant phyla, was positively correlated with total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and available phosphorus (AP) in the soil, while negatively correlated with organic matter (OM) abundance. This suggests that the relative abundance of these phyla is influenced by nutrient content, with nitrogen and phosphorus elements positively regulating their relative abundance, while organic matter may have a negative impact. These results are partially consistent with previous studies 65. In summary, the physicochemical properties of soil, especially the variations in soil organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and available phosphorus (AP), have a decisive influence on the spatial patterns of soil microorganisms.
5. Conclusions
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, providing long-term nutrient supply for crops, while chemical fertilizers have Control fertilizer effects and are easily absorbed and utilized by crops. The combination of chemical and organic fertilizers can regulate the release rate and intensity of soil and fertilizer nutrients, allowing crops to obtain a stable and balanced nutrient supply at different growth stages, thereby promoting their growth and development 66. Based on the above considerations, the T2 treatment (20% reduction in chemical fertilizer + 4500 kg·hm2 of bio-organic fertilizer) is determined to be the optimal ratio for reducing chemical fertilizer and applying bio-organic fertilizer in local radish cultivation. This approach can reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, increase yield, promote radish growth, improve nutrient quality, enhance soil enzyme activity, increase soil microbial population, and increase the content of readily available nutrients in the soil.In summary, the combination of reducing chemical fertilizer and applying bioorganic fertilizer is an effective approach. It can reduce fertilizer usage, increase yield, promote radish growth and nutrient quality, improve soil enzyme activity and soil microbial population, and increase the content of readily available nutrients in the soil.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Duo Jin; Software, Duo Jin; Validation, ZeWei Lu; Formal analysis, Duo Jin; Investigation, ZeWei Lu and Xiangcan Song; Resources, Duo Jin, Yan Yan and Shuangchen Chen; Data curation, ZeWei Lu; Writing – review & editing, Duo Jin and Golam Jalal Ahammed; Funding acquisition, Shuangchen Chen.
Funding
This research was funded by the national Key Research and Development Project (2023YFD1401200); National Natural Science Foundation of China (32372793, 32372680) and Henan University Science and Technology Innovation Team (23IRTSTHN024).
References
- Li, L., Zhang, X., Zhou, Z., Lu, C., Pan, X., & Deng, X. (2020). Comparison of extraction methods for insoluble dietary fiber from radish and their effects on biscuit digestion. Agricultural Products Processing, 14, 38-41.
- Shan, N., Chuan, L., Liu, J., Zheng, H., & Zhao, T. Application effects of nutrient expert system recommended fertilization on radish. Journal of Applied Ecology 2020, 31.
- Du, G. (2012). Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil microbial communities in the Huang-Huai-Hai region (Doctoral dissertation, Beijing: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
- Li, D., & Wu, Z. (2008). Ecological environmental effects of chemical fertilizers. Journal of Applied Ecology. (In Chinese)Sun Z, Li X. Technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer use and its influencing factors in China’s rice production[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(3): 1155.
- Sun, Z., & Li, X. Technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer use and its influencing factors in China’s rice production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1155. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Sun, Z., Xue, C., & Ma, W. Comparative study on yield and nutrient utilization efficiency of radish under different nutrient management measures. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University 2017, 40, 25–30.
- Fei, L., Pan, Y., Ma, H., Guo, R., Wang, M., Ling, N., ... & Guo, S. (2024). Optimal organic-inorganic fertilization increases rice yield through source-sink balance during grain filling. Field Crops Research, 308, 109285.
- Xu, X., Bi, R., Song, M., Dong, Y., Jiao, Y., Wang, B., & Xiong, Z. (2024). Organic substitutions enhanced soil carbon stabilization and reduced carbon footprint in a vegetable farm. Soil and Tillage Research, 236, 105955.
- Wu, X., Zhang, T., Zhao, J., Wang, L., Yang, D., Li, G., & Xiu, W. (2021). Variation of soil bacterial and fungal communities from fluvo-aquic soil under chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic materials in North China Plain. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2021, 21, 349–363. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P., Li, J., & Wang, D. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on physiological characteristics, soil nutrients, and microorganisms of spring wheat. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2018, 46, 66–72.
- Niu, X., Ju, X. Organic fertilizer resources and utilization in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017,23(6), 1462-1479.
- Liu, X., Wang, S., Li, L.; et al. Changes in main agronomic traits during the fleshy root swelling process of radish[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2010(4), 31-33.
- Ma, Y., Shen, S., Wan, C., Wang, S., Yang, F., Zhang, K., & Gao, W. (2023). Organic fertilizer substitution over six years improves the productivity of garlic, bacterial diversity, and microbial communities network complexity. Applied Soil Ecology 2023, 182, 104718. [CrossRef]
- Kakar, K., Xuan, T. D., Noori, Z., Aryan, S., & Gulab, G. Effects of organic and inorganic fertilizer application on growth, yield, and grain quality of rice. Agriculture 2020, 10, 544. [CrossRef]
- Hayatu, N., Yiren, L., Shuxiang, Z., Jing, H., Tianfu, H., Jiangxue, D& Huimin, Z. (2022). Phosphorus use efficiency, uptake and apparent balance response to substituting long-term chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer in a double-rice cropping system.
- Wang, T., Wang, J., Jia, Y., Wang, Y., Bao, W., & Zhang, G. Study on quality and volatile substances of different radish varieties. Journal of Food Safety & Quality 2023, 14.
- Gamba, M., Asllanaj, E., Raguindin, P. F., Glisic, M., Franco, O. H., Minder, B., ... & Muka, T. (2021). Nutritional and phytochemical characterization of radish (Raphanus sativus): A systematic review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 113, 205-218.Yang, L.,.
- hao, G., Zhang, L., Zuo, Q., Wang, X., Dou, T., & Bian, X. (2010). Effects of potassium nutrition on nutrient uptake and yield of radish in alpine cold region. Northern Horticulture, (14), 5-8.
- Zhao, Y., Dai, Y., Cui, X., Zhang, W., & Ma, N. Determination of soluble protein content in Radix AuControllandiae by Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 staining method. Journal of Yunnan Minzu University: Natural Sciences Edition 2006, 15, 235–237.
- Leng, F., Sun, S., Jing, Y., Wang, F., Wei, Q., Wang, X., & Zhu, X. A rapid and sensitive method for determination of trace amounts of glucose by anthrone-sulfuric acid method. Bulg. Chem. Commun 2016, 48, 109–113.
- Xiao, Y., Lei, E., Guan, X., & Guan, X. Comparison of two methods for determining reduced vitamin C in vegetables. Hubei Agricultural Sciences 2011, 50, 1035–1037.
- Hua, B., Qiu, Y., Duan, Y., Cui, N., Zhang, X., Shen, D., & Li, X. Analysis and evaluation of glucosinolate content in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) germplasm resources. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources 2013, 14, 1038–1044.
- Lu, R. (2000). Soil agricultural chemical analysis methods. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
- Guo, H., Yao, J., Cai, M., Qian, Y., Guo, Y., Richnow, H. H., ... & Ceccanti, B. Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1273–1280.
- Gao, M., Song, W., Zhou, Q., Ma, X., & Chen, X. Interactive effect of oxytetracycline and lead on soil enzymatic activity and microbial biomass. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2013, 36, 667–674. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L., Zeng, Q., Li, H., & Yan, J. Determination of soil catalase activity by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Soil Bulletin 2011, 42, 207–210.
- Cao, H., Sun, H., Yang, H., Sun, B., & Zhao, Q. Research progress on soil enzyme activity and its indication of soil quality. Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology 2003, 9, 105–109.
- Liu, C., Zhao, D., Ma, W., Guo, Y., Wang, A., Wang, Q., & Lee, D. J. (2016). Denitrification and sulfide removal from saline wastewater by salt-tolerant bacteria. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100, 1421-1426.
- Xu, L. Effects of organic-inorganic combined application on yield, quality, and soil fertility of Chinese cabbage under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2021, 49, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y., Cui, J., Xie, H., Pei, H., & Gao, J. Effects of different organic fertilizers on the growth, development, and yield of sand-cultured tomatoes. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences 2017, 45, 69–71.
- Zhang, Y., Fan, X., Xu, G., Yang, Y., Li, Y., & Sun, Y. Effects of different nitrogen and organic fertilizer combinations on garlic yield and quality. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2019, 47, 114–117.
- Tang, G., Zhou, X., Tian, C., Peng, H., Zhang, Y., & Rong, X. Effects of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer combinations on vegetable yield, quality, and economic benefits. Chinese Journal of Ecology 2017, 36, 1292–1299.
- Qiu, W., Yao, X., Lu, H., Guo, J., & Lu, D. (2023). Effects of different fertilization treatments on yield, quality, and nitrogen uptake efficiency of spring-sown sweet corn. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Sciences Edition), (06), 26-35. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J., Tian, W., Zhao, S., Xu, D., Han, W., & Chen, X. Effects of optimized fertilization on yield, quality, and nutrient utilization efficiency of radish-cabbage rotation system in Emei Mountain region. Hubei Agricultural Sciences 2023, 62, 21.
- Wang, X., Zhang, P., Zhang, J., Ji, X., Zhang, X., & Liang, J. (2021). Regulation of fertilization patterns on root system morphology construction and yield formation of soybean in loess plateau area. Soybean Science.
- Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Zhu, G., Zhang, C., Zhang, Y., Yao, Q., & Sun, Z. (2021). Effects of localized application of chemical fertilizer combined with cow manure on vegetable yield and soil fertility. Chinese Journal of Soil and Fertilizer, (1), 161-168.
- Wang, N., Nan, H., & Feng, K. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer application combined with organic fertilizer on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and cotton yield in cotton field. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2020, 31, 173.
- Liu, J., Zhang, W., Li, Y., Sun, Y., & Bian, X. Effects of long-term continuous cotton cropping on soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activity in Xinjiang oasis. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 2009, 42, 725–733.
- Wang, X., Zhu, M., Yang, F., Dou, P., Zhang, J., Ma, X., ... & Kong, F. Effects of organic fertilizer combined with reduced nitrogen on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in hilly area of Sichuan Province. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 2017, 31, 271–276.
- Hu, W., Jiao, Z., Wu, F., Liu, Y., Dong, M., Ma, X., ... & Feng, H. (2014). Long-term effects of fertilizer on soil enzymatic activity of wheat field soil in Loess Plateau, China. Ecotoxicology, 23, 2069-2080.
- Sun, S. (2019). Study on the Effects of Microbial Fertilizers and Controlled-Release Chemical Fertilizers on Potato Growth, Yield, and Quality (Doctoral dissertation, Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University).
- Zhou, X., Liu, P., Chang, J., Guo, L., Zhang, Q., & Ma, Y. (2022). Effects of Pig Manure Substitution for Chemical Fertilizers on Tea Yield, Quality, and Soil Fertility. Soil Bulletin, (02), 413-420. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L., Cao, M., Sang, C., Chen, R., Xu, S., Li, L., & Liu, T. Effects of Biological Organic Fertilizer Substituting Chemical Fertilizer on Soil Fertility and Enzyme Activity in Maize. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University 2022, 40, 67–72.
- Zhou, G., Wang, X., Ma, Y., & Wang, X. Effects of Different Biogas Slurry Organic Fertilizer Treatments on Yield, Disease Resistance, and Quality of Autumn Cucumber. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University 2017, 40, 39–44.
- Qu, C., Chen, X., Han, Z., Zhang, X., Huang, C., & Liu, Y. (2017). Effects of Applying Biological Organic Fertilizer on Soil Fertility Characteristics and Enzyme Activity at Different Growth Stages of Cucumber. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, (6), 279-284.
- Li, R., Tao, R., Wang, D., & Chu, G. Effects of Reduced Nitrogen Combined with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Biological Properties and Aggregate Characteristics in Drip-Irrigated Cotton Field. Journal of Applied Ecology 2017, 28.
- Shang, L., Wan, L., Zhou, X., Li, S., & Li, X. Effects of organic fertilizer on soil nutrient status, enzyme activity, and bacterial community diversity in Leymus chinensis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240559.
- Sun, R., Guo, X., Wang, D., & Chu, H. The impact of long-term application of chemical fertilizers and straw returning on soil bacterial community. Microbiology China 2015, 42, 2049–2057.
- Mayerhofer, H., & Mueller-DieControlmann, J. Cloning, expression, purification and preliminary X-ray analysis of the dimerization domain of ethylene response sensor 1 (ERS1) from Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Crystallographica Section F: Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications 2013, 69, 1029–1032.
- Fierer, N., Bradford, M. A., & JaControlson, R. B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364.
- Kirchman, D. L. The ecology of Cytophaga–Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS microbiology ecology 2002, 39, 91–100.
- Singh, U., Choudhary, A. K., & Sharma, S. A 3-year field study reveals that agri-management practices drive the dynamics of dominant bacterial taxa in the rhizosphere of Cajanus cajan. Symbiosis 2022, 86, 215–227.
- Yan, D., Zhang, T., Su, J., Zhao, L. L., Wang, H., Fang, X. M., ... & Yu, L. Y. Structural variation in the bacterial community associated with airborne particulate matter in Beijing, China, during hazy and nonhazy days. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2018, 84, e00004-18.
- Ai, C., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., Guo, D., Zhou, W., & Huang, S. (2018). Distinct responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to changes in fertilization regime and crop rotation. Geoderma, 319, 156-166.
- Liang, Z., Yu, Y., Ye, Z., Li, G., Wang, W., & An, T. (2020). Pollution profiles of antibiotic resistance genes associated with airborne opportunistic pathogens from typical area, Pearl River Estuary and their exposure risk to human. Environment International 2020, 143, 105934.
- Hartmann, M., Frey, B., Mayer, J., Mäder, P., & Widmer, F. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. The ISME journal 2015, 9, 1177–1194.
- Bi, Q., (2020). Microbiological Mechanisms of Soil Phosphorus Availability and Carbon-Nitrogen-Phosphorus Coupling Transformation Affected by Fertilization Modes and Years of Cultivation (Doctoral dissertation, Hangzhou: Zhejiang University).
- ee, S. H., Ka, J. O., & Cho, J. C. Members of the phylum Acidobacteria are dominant and metabolically active in rhizosphere soil. FEMS microbiology letters 2008, 285, 263–269.
- Li, H. (2018). Effects of Fertilization Levels on Growth of Super Hybrid Rice and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics (Master's thesis, Hunan University).
- Yuan, H., Wu, H., Ge, T., Li, K., Wu, J., & Wang, J. Effects of Long-Term Fertilization on Bacterial and Archaeal Diversity and Community Structure in Rice Field Soil. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2015, 26, 1807–1813.
- Yu, B. (2017). Effects of Long-Term Different Fertilization Treatments on the Degradation of 13C-Labeled Maize Straw and Associated Microorganisms in Red Soil (Doctoral dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
- Rousk, J., Bååth, E., Brookes, P. C., Lauber, C. L., Lozupone, C., Caporaso, J. G., ... & Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. The ISME journal 2010, 4, 1340–1351.
- Zhang, Y. (2020). Effects of Fertilization Gradient on Soil Environment and Maize Growth under Furrow Mulching Cultivation (Doctoral dissertation, Northwest A&F University).
- Chai, Z. (2021). Analysis of Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Different Origins of Ginger and the Effects of Fertilization (Master's thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
- Lu, Y., Liao, Y., Nie, J., Zhou, X., Xie, J., & Yang, Z. Evolution Characteristics of Phosphorus in Long-Term Fertilized Red Paddy Soils and Its Response to Phosphorus Surplus or Deficiency. Acta Pedologica Sinica 2017, 54, 1471–1485.
- Zhao, J., Li, Y., Ran, W., Zhang, R., Shen, B., & Shen, Q. Effects of Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizers with Organic Fertilizers on Yield and Soil Microbial Flora in a Rice-Wheat Rotation System. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University 2016, 39.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).