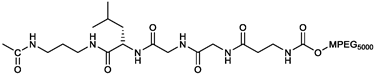
2.3. Drug Synthesis
NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian 500 MHz spectrometer in the indicated solvents at 500 MHz (
1H) and 125 MHz (
13C) or on a Varian 400 at 400 MHz (
1H) and 100 MHz (
13C); chemical shifts are in ppm (δ) in the specified solvents. Coupling constants J are given in Hertz.
1H and
13C NMR resonances were assigned using a combination of DEPT, COSY, HSQC spectra. Electrospray (ESI) mass spectra were obtained on a Bruker Daltonics Esquire 4000 spectrometer. High-Resolution Mass Spectra were obtained on a Bruker micrOTOF-Q. Flash chromatography was performed on silica gel 60 (Merck, 230−400 mesh). Yields refer to spectroscopically (
1H NMR) homogeneous materials. Commercial reagents and solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. 2c (
1) [
6], 2c-OSu (
1a) [
6], 1-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-5-aminopentane [
10], L-Phenylalanylamide ((S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropanamide) [
8], 1-[(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-aminopropane [
14], L-leucineamide ((2S)-2-Amino-4-methylpentanamide) [
15] were prepared by the indicated literature procedures. N-Boc deprotection was carried out in a 10% TFA solution in DCM, followed by solvent evaporation. Flash chromatography (FC) was run with CHCl
3 as the eluent. Yields refer to purified products.
Synthesis of VV1 (4-Hydroxy-2,6-bis(4-nitrobenzylidene)cyclohexanol). To a solution of 2c (1) (0.152 g, 0.4 mmol) in a 1:9 MeOH/THF solution (25 ml), NaBH4 (0.015 g, 0.40 mmol) was added at 0°C under stirring. After 4 hrs at rt, brine (50ml) was added and the resulting solution was extracted with diethyl ether. Evaporation of the solvent gave VV1 as a 3:2 mixture of cis/trans diastereoisomers. Yellowish solid, 93% yield. NMR spectra are given for the diastereoisomeric mixture. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.19, 8.17 (2d, ratio 3:2, 4H, o-NO2PhH), 7.57, 7.53 (2d, ratio 2:3, 4H, m- NO2PhH), 6.76, 6.74 (2s, ratio 2:3, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 5.82, 5.74 (2d, ratio 3:2, 1H, J = 4.7 Hz each, C(1)-OH), 5.05, 4.99 (2d, ratio 3:2, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz each, C(4)-OH), 4.74, 4.67 (2 bm, ratio 3:2, 1H, H-1), 3.87, 3.65 (2m, ratio 3:2, 1H, H-4), 2.95, 2.33 (2 dd, J = 13.7, 9.3 and 3.8 Hz, major diastereoisomer ring CH2), 2.73, 2.55 (dd, J = 13.3, 6.5, 3.3 Hz, minor diastereoisomer, ring CH2). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 146.08, 145.48, 145.09, 145.01, 144.59, 130.28, 130.25, 123.91, 123.85, 121.87, 120.83, 76.56, 75.49, 68.71, 68.14, 36.34, 35.18. ESI-MS, m/z: 383.1 [M+H]+. HRMS, m/z (negative ion) found: 381.1090 [M-H]-; Calcd. for C20H17N2O6: 381.1092.
Due to the hydrophobic nature of 2c and VV1, the two compounds were administered diluted in DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide).
Coupling of 2c-OSu with amines (Supplementary materials S5). General procedure for the synthesis of compounds 2 – 12. To a solution of 2c-OSu (1a) [(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl 2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate] (0.520 g, 1.0 mmol) in anhydrous DCM, the amine partner (1.2 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred at 25 °C for 18h., then it was washed with 1N aq HCl or 5% aq. citric acid, and brine. Evaporation of the solvent left a residue that was purified as indicated.
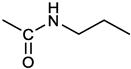
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-propylcarbamate (2). From 1a and n-propylamine, yellow solid, 75% yield after FC; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.28 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.79 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.78 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.05 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.01 (s, 1H, CHOCO), 3.19 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 2.76 (app q, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, CH2NH), 1.22 (sext, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 0.66 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, CH2CH2CH3) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.75, 155.65, 147.48, 141.99, 136.19, 135.95, 131.69, 124.07, 66.85, 42.26, 32.94, 22.88, 11.50 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z: 488.1 [M+Na]+.
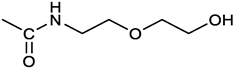
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl]carbamate (3). From 2a and 2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethanol, light yellow solid, 65% yield after FC; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ 8.29 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.91 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.60 (4H, app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 5.17 (br, 1H, CHOCO), 5.03 (br, 1H, NH), 3.71 (m, 2H, CH2OH), 3.49 (2H, NHCH2CH2O), 3.52 (t, 2H, OCH2CH2OH), 3.30 (m, 2H, CH2NH), 3.26 – 3.13 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3), δ 187.56, 155.38, 147.48, 141.54, 137.15, 134.43, 130.73, 123.77, 72.15, 69.86, 67.06, 61.60, 40.73, 33.18 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z: 534.2 [M+Na]+. HRMS, m/z, found: 535.1484; Calcd for [C25H25N3O9Na]+ 535.1483.
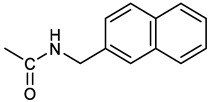
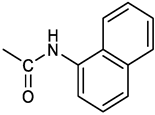
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[(naphthalen-2-yl)methyl]carbamate (4). From 1a and 2-naphtylmethylamine, yellow-orange solid, 56% yield after FC; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.26 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.82-7.80 (m, 8H, 2 x CH=C, 2 x m-NO2PhH, NHCOO, 1 ArH), 7.72 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.68 (m, 4H, ArH), 7.24 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, ArH), 5.09 (m, 1H, CHOCO), 4.19 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H, NHCH2Ar), 3.25 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.63, 155.94, 147.43, 141.94, 137.57, 136.26, 135.83, 133.12, 132.40, 131.66, 128.18, 127.85, 127.80, 126.48, 126.01, 125.89, 125.34, 124.04, 67.22, 44.18, 32.92 ppm; ESI-MS: 586.2 m/z [M+Na]+;
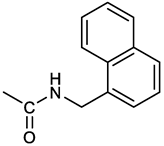
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[(naphthalen-1-yl)methyl]carbamate (5). From 1a and 1-naphtylmethylamine, orange-red solid, 82% yield after FC; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.26 (app d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.96 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.87 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.81-7.73 (m, 5H, 2 x CH=C, NHCOO, 2 ArH), 7.44 (t, 1H, ArH), 7.31 (t, 1H, ArH), 7.21 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, ArH), 5.10 (bs, 1H, CHOCO), 4.49 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H, ArCH2NH), 3.25 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.63, 155.78, 147.46, 141.96, 136.26, 135.83, 135.05, 133.60, 131.67, 131.04, 128.87, 127.82, 126.45, 126.09, 125.65, 125.28, 124.06, 123.66, 66.22, 42.08, 32.91 ppm; ESI-MS: 586.2 [M+Na]+.
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-(naphthalen-1-yl)carbamate (6). From 1a and 1-naphthylamine in the ratio 1:1.5, light yellow solid, 61% yield after FC; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.46 (bs, CONH-Ar), 8.29 (app.d, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.88-7.80 (m, 7H, 2 x CH=C, 2 x m-NO2PhH, 1 ArH), 7,77 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.70 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.49-7.45 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.40 – 7.35 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.30 (d, J = 7,35 Hz, 1H, ArH), 5.17 (m, 1H, CHOCO), 3.32 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.74, 154.46, 147.49, 142.01, 136.35, 135.88, 134.06, 133.75, 131.71, 128.62, 128.40, 126.38, 126.11, 125.86, 125.79, 124.08, 123.10, 122.26, 68.04, 32.74 ppm; ESI-MS: 572.2 m/z [M+Na]+.
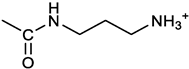
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-(3-aminopropyl)carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (7). 1a and 1-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-aminopropane [
14] gave the corresponding N-Boc protected amine (7a); yellow solid, 82% yield after FC; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.29 (apparent d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.91 (s, 2H, 2 C=CH), 7.60 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 5.24 (br, 1H), 5.13 (br, 1H, CHOCO), 4.67 (br, 1H), 3.21 – 3.05 (m, 8H, 2 x CH2 ring and 2 x CH2NHCO), 1.55 (m, 2H, CH2cH2cH2), 1.42 (s, 9H, Boc) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 187.49, 156.42, 155.45, 147.52, 141.59, 137.19, 134.51, 130.72, 123.78, 79.48, 67.11, 37.46, 36.96, 33.26, 30.47, 28.34 ppm. N-Boc deprotection of 7a gave quantitatively the ammonium salt 7 as a yellow solid product, that was washed on the filter with cold H2O; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.26 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2 PhH), 7.78 (s, 2H, 2 x C=CH), 7.77 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2 PhH), 7.52 (broad, 3H, NH3+), 7.19 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.02 (bs, 1H, CHOCO), 3.30 - 3.10 (m, 4H, 2 x CH2 ring), 2.87 (m, 2H, CH2NHCO), 2.48 (m, 2H, CH2NH3+), 1.51 (quint., J = 7.9 Hz, 2H, CH2cH2cH2) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): 187.55, 155.76, 147.45, 141.92, 135.75, 131.65, 124.04, 67.09, 37.70, 37.05, 32.97, 27.88 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z: 481.2 [M+H]+.
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-(3-aminopropyl)carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (7).1a and 1-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-aminopropane [
14] gave the corresponding N-Boc protected amine (
7a); yellow solid, 82% yield after FC;
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3), δ 8.29 (apparent d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO
2Ph
H), 7.91 (s, 2H, 2 x C
H=C), 7.60 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO
2Ph
H), 5.24 (br, 1H, NH), 5.13 (br, 1H, C
HOCO), 4.67 (br, 1H, NH), 3.21 – 3.05 (m, 8H, 2 x ring CH
2, C
H2NHBoc and C
H2NHCO), 1.55 (m, 2H, CH
2C
H2CH
2), 1.42 (s, 9H, Boc) ppm;
13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl
3), δ 187.49, 156.42, 155.45, 147.52, 141.59, 137.19, 134.51, 130.72, 123.78, 79.48, 67.11, 37.46, 36.96, 33.26, 30.47, 28.34 ppm. N-Boc deprotection of
7a gave quantitatively the ammonium salt
7 as a yellow solid product, that was washed on the filter with cold H
2O;
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d
6), δ 8.26 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO
2Ph
H), 7.78 (s, 2H, 2 x C
H=C), 7.77 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO
2 Ph
H), 7.52 (broad, 3H, N
H3+), 7.19 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, CON
H), 5.02 (bs, 1H, C
HOCO), 3.30 - 3.10 (m, 4H, 2 x CH
2 ring), 2.87 (m, 2H, C
H2NHCO), 2.48 (m, 2H, C
H2NH
3+), 1.51 (quint., J = 7.9 Hz, 2H, CH
2C
H2CH
2) ppm;
13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d
6), δ 187.55, 155.76, 147.45, 141.92, 135.75, 131.65, 124.04, 67.09, 37.70, 37.05, 32.97, 27.88 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z: 481.2 [MH]+. HRMS m/z, found: 481.1718; Calcd. for [C
24H
25N
4O
7]+ : 481.1718.
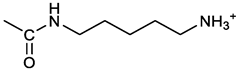
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-(5-aminopentyl) carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (8).1a and 1-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-5-aminopentane [
10] gave the corresponding N-Boc protected amine (
8a) as a yellow solid, 86% yield after FC;
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3), δ 8.27 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO
2Ph
H), 7.88 (s, 2H, 2 x C
H=C), 7.58 (app d, 4H, J = 8.7 Hz, 2 x m-NO
2Ph
H), 5.15 (bs, 1H, C
HOCO), 4.72 (br, 1H, NH), 4.53 (br, 1H, NH), 3.25 – 3.01 (m, 8H, 2 x CH
2 ring, C
H2NHCO and C
H2NHBoc), 1.43 (s, 9H, Boc), 1.33 - 1.18 (m, 6H, 3 x CH
2 chain) ppm;
13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl
3), δ 187.52, 156.08, 155.25, 147.44, 141.58, 134.54, 130.71, 123.74, 78.86, 66.86, 40.71, 40.18, 33.16, 28.36, 23.67 ppm. N-Boc deprotection of
8a gave quantitatively the ammonium salt
8 as a yellow solid product, that was washed on the filter with cold H
2O.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d
6), δ 8.28 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO
2Ph
H), 7.79 (s, 2H, 2 x C
H=C), 7.78, (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO
2Ph
H), 7.56 (broad, 3H, N
H3+), 7.05 (t, J = 5.6 Hz 1H, CON
H), 4.99 (bs, 1H, C
HOCO), 3.16 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH
2), 2.81-2.63 (m, 4H, 2 x chain CH
2), 1.42 - 1.10 (m, 6H, 3 x chain CH
2) ppm;
13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d
6), δ 187.68, 171.71, 155.64, 147.49, 141.97, 136.21, 135.90, 131.70, 124.08, 66.90, 39.10, 32.98, 26.98, 23.33 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z: 509.2 [M+]; 363.1 [M – 146; C
20H
14N
2O
5]
3-[[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyloxy carbonylamino]] propanoic acid (9). From 1a and β-alanine, yellow solid, triturated with EtOEt, 53% yield ; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 12.10 (s, 1H, COOH), 8.28 (app d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.79 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.78 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.11 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 5.02 (brs, 1H, CHOCO), 3.25-3.14 (m, 4H, 2 x CH2 ring), 3.01 (m, 2H, CH2NH), 2.21 (t, 2H, CH2COOH) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.72, 173.01, 155.53, 147.48, 141.98, 136.23, 135.88, 131.68, 124.09, 67.03, 55.36, 36.76, 34.29, 32.94 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z: 496.2 [M+H]+. HRMS, m/z, found 518.1171 [M+Na]+; calcd. for [C24H21N3O9Na]+ : 518.1170.
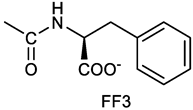
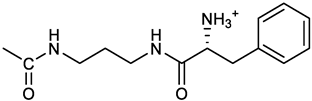
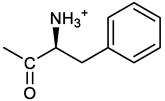
(2S)-2-[[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyloxy carbonyl amino]]-3-phenylpropanoic acid (10). From 1a and L-phenylalanine, yellow solid, triturated with EtOEt, 75% yield; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3), δ 8.29-8.23 (2 app d, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.90, 7.85 (2s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.56-7.52 (m, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.27-7.20 (m, 5H, PhH), 5.13 (br, 1H, CHOCO), 5.06 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 4.55 (m, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.30-3.00 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 3.04-2.89 (m, 2H, PhCH2) ppm ; 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3), δ 187.38, 175.32, 154.75, 147.55, 141.49, 137.39, 135.38, 134.20, 130.72, 129.14, 128.67, 127.27, 123.80, 67.70, 54.41, 37.43, 35.15 ppm. ESI-MS: 594.1 [M+Na]+.
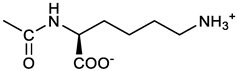
(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyloxy carbonylamino]]hexanoic acid (11). From 1a and L-lysine, yellow solid, triturated with EtOEt, 75% yield; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 12.46 (br, 1H, COOH), 8.29 (4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.82 – 7.50 (m, 10H, 2 x CH=C, 2 x m-NO2PhH, NH3+ and NHCO), 5.05 (br, 1H, CHOCO), 4.18 – 3.61 (m, 1H, Lys α-CH), 3.44 – 2.95 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 2.69 (br, 2H, Lys ε-CH2), 1.72 – 1.23 (m, 6H, Lys β-CH2, δ-CH2, γ-CH2); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.17, 173.65, 155.34, 147.02, 141.60, 135.84, 135.38, 131.15, 123.64, 66.88, 53.53, 38.48, 32.35, 29.88, 26.43, 22.45. ESI-MS: m/z 554.2 [M+H]+.
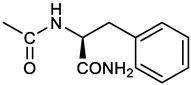
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[(1S)-1-carbamoyl-2-phenylethyl)carbamate (12). From 1a and L-phenylalaninamide, yellow solid, 63% yield after FC; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3), δ 8.29, 8.27 (2 app d, J = 8.4 Hz each, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.86 (s, 2H, CH=C), 7.58, (app d, 4H, J = 8.4 Hz each, m-NO2PhH), 7.21-7.08 (m, 5H, PhH), 5.36 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, NHCOO), 5.30, 5.26 (2 br s, 1H each, CONH2), 5.14 (brs, 1H, CHOCO), 4.28 (app q, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.25-3.10 (ddd, part AB of an ABX, J = 2.4, 6.0, 16.4 Hz, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 3.02 (dd, J = 6.0, 13.7 Hz, part A of an ABX, PhCHH), 2.89 (dd, part B of an ABX, J = 7.5 and 13.7 Hz, PhCHH) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3), δ 187.29, 137.05, 154.78, 147.49, 141.50, 137.36, 136.10, 134.23, 130.72, 129.16, 128.67, 127.13, 123.76, 67.69, 55.68, 38.71, 33.01 ppm; ESI-MS: 593.2 [M+Na]+.
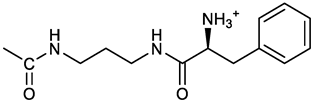
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[3-[(2S)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanamido]propyl]carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (13). HOBT (0.162 g, 1.2 mmol), EDC (0.230 g, 1.2 mmol) and TEA (0.16 ml, 1.2 mmol) were added in order to a solution of N-Boc-(L)Phe (2.0 mmol) in the minimum amount of DCM. After 30 min stirring at 25 °C, compound 7 was added (1.0 mmol) and the apparent pH was adjusted to 9 with Et3N. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight, and washed with 5% aq. citric acid, sat. aq. NaHCO3 and brine, and the solvent was evaporated giving a crude solid that was purified on column (eluent: CHCl3) giving compound 13a as a yellow solid, 61% yield after FC; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3), δ 8.28 (2d, J = 8.6, 4H, o-NO2PhH), 7.90 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.60 (2d, J = 8.6 4H, m-NO2PhH), 7.25 (m, 5H, PhH), 6.03 (bt, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 5.29 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H, NHCOO), 5.11 (quint, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, CHOCO), 4.95 (brs, 1H, NHBoc), 4.24 (m, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.17 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 3.12 (m, 2H, CH2NHCO), 3.02 (m, 2H, PhCH2), 2.94 (m, 2H, CH2NHCOO), 1.42 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH2), 1.40 (s, 9H, Boc) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3), δ 187.46, 172.00, 155.49, 147.50, 141.58, 137.16, 136.53, 134.51, 130.74, 129.20, 128.64, 126.97, 123.77, 80.29, 67.11, 56.05, 38.45, 37.10, 35.78, 33.27, 29.68, 28.22 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z: 750.3 [M + Na]+; 650.1 [M + Na+ – CO2 - C4H8]. N-Boc deprotection was carried out quantitatively as described above for 7 giving compound 13. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.27 (app. d, J = 8.8 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 8.18 (m, 1H, NHCO), 8.11 (brs, 3H, NH3+), 7.79 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.78 (app. d, J = 8.8 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.26-7.13 (m, 5H, PhH), 7.04 (m, 1H, NHCOO), 5.01 (s, 1H, CHOCO), 3.83 (s, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.27-3.13 (m 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 2.99-2.84 (m, 4H, PhCH2 and CH2NHCO), 2.73 (m, 2H, CH2NHCOO), 1.29 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH2) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.61, 168.06, 155.62, 147.45, 141.96, 136.23, 135.83, 135.36, 131.68, 129.80, 128.84, 127.46, 124.05, 66.97, 54.01, 38.26, 37.49, 36.77, 33.00, 29.25 ppm. ESI-MS: m/z 628.1 [M + H]+.
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[3-[(2R)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanamido]propyl]carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (14). From 7 and N-Boc-(D)Phe, as described above for 13. Yield: 65%.
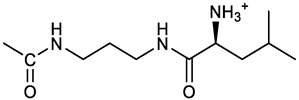
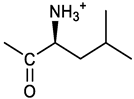
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl N-[3-[(2S)-2-amino-4-methylpentanamido]propyl]carbamate (trifluoroacetate salt) (15). N-Boc protected 15a was obtained from 7 and N-Boc-(L)Leu, as described above for 13. Yellow solid, 70% yield after FC; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.28 (app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.90 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.60 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, m-NO2PhH), 6.38 (bt, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 5.46 (t, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H, NHCOO), 5.11 (quint, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, CHOCO), 4.79 (brs, 1H, NHBoc), 4.01 (m, 1H, CHNHBoc), 3.23 (m, 2H, CH2NHCOO), 3.18 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 3.09 (m,, 2H, CH2NHCO), 1.63 (overlapped, 1H, CH(CH3)2, 1.54 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH2), 1.43 (overlapped m, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H, Boc), 0.93 (2d overlapped, J = 6.0 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.46, 173.53, 155.50, 147.53, 141.60, 137.19, 134.52, 130.73, 123.78, 80.13, 67.12, 53.35, 40.98, 37.01, 35.68, 33.32, 29.95, 28.25, 24.79, 22.89, 21.93 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z: 716.3 [M + Na]+. N-Boc deprotection of 15a gave the amine 15 as trifluoroacetate salt; 1H NMR (500 MHz), δ 8.32 (t, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H, NHCO), 8.28 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 8.03 (brs, 3H, NH3+), 7.80 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.79 (app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.09 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, NHCOO), 5.02 (brm, 1H, CHOCO), 3.61 (br, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.27 - 3.15 (m, 4H, 2 x ring CH2), 3.02, 2.96 (2m, 2H, CH2NHCO), 2.84 (m, 2H, CH2NHCOO), 1.57-1.39 (m, 5H, CH(CH3)2 + CH2CH(CH3)2 + CH2CH2CH2), 0.83 (2d, J = 8.0 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2 ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.67, 169.13, 155.65, 147.49, 141.98, 136.23, 135.88, 131.68, 124.08, 67.01, 51.43, 40.00, 38.34, 36.88, 32.97, 29.42, 24.07, 22.85, 22.40 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z: 594.2 [M + H]+;
Coupling of 2c with carboxylic acids (Supplementary materials S5). General Procedure for the synthesis of compounds 16 and 17.
To a solution of N-Boc-aminoacid (1.2 mmol) in the minimum amount of DCM, HOBT (0.32 g, 1.2 mmol), EDC (0.46 g, 1.2 mmol) and TEA (0.36 ml, 1.2 mmol), were added in the order and the mixture was stirred for 30 min. 2c (1) (0.76 g, 1.0 mmol) was added in small portions and the mixture was stirred at 25 °C overnight. The organic phase was washed with 5% aq citric acid, sat. aq NaHCO3 and brine, and dried over Na2SO4. Evaporation of the solvent gave a residue that was purified as indicated.
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl (2S)-4-methylpentanoate (16). From 1 and N-Boc-(L)Leu, protected 16a was obtained after FC, yellow solid, 74 % yield; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3), δ 8.29 (app d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.94 (s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.59, 7.57 (2 app. d, J = 8.5 Hz each, 4H, 2 x m- NO2PhH), 5.28 (m, 1H, H-4), 4.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, NHBoc), 4.14 (m, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.27-3.08 (m, 4H, CH2 ring)), 1.55-1.50 (m, 2H, (CH3)2CHCH2)), 1.37 (s, 9H, Boc), 1.36 (overlapped, 1H, (CH3)2CH)), 0.85 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 6H, (CH3)2CH) ppm; 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 186.96, 172.79, 155.28, 147.62, 141.40, 137.67, 133.83, 130.71, 123.83, 80.03, 67.68, 52.09, 41.34, 32.73, 28.19, 24.81, 22.69, 21.84 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z 594.1 [M + H]+. N-Boc deprotection as described for 7 gave the amine 16 as a yellow solid that was purified by precipitation with hexane from an ethyl acetate solution; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 8.30-8.27 (broad, 3H, NH3+), 8.29, 8.28 (2 app d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, o- NO2PhH), 7.86, 7.84 (2brs, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.81, 7.77 (2 app d, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H, 2 x m- NO2PhH), 5.38 (brm, 1H, CHOCO), 3.79 (brt, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, CHNH3+), [3.39 (dt, J = 3.1 and 17.4, 1H), 3.33 (dt, J = 2.9 and 17.7, 1H), 3.20 (dt, J = 3.7 and 17.7, 1H), 3.19 (dd, J = 4.2 and 17.4 Hz, 1H), 2 x ring CH2), 1.44 - 1.29 (m, 3H, CHCH2 ), 0.70, 0.69 (2d, J = 6.1 Hz, 6H, (CH3)2CH)) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ 187.05, 169.79, 147.54, 141.83, 135.01, 131.77, 124.05, 69.52, 50.77, 32.49, 32.07, 24.32, 22.71, 21.96 ppm; ESI-MS, m/z 494.2 [M + H]+. HRMS, m/z, found: 494.1923; calcd for [C26H28N3O7]+: 494.1922.
[(3E, 5E)-3,5-bis[(4-nitrophenyl)methylidene]-4-oxocyclohexyl (2S)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoate (17). From 1 and N-Boc-(L)Phe, protected 17a was obtained after FC as a yellow solid, 68% yield; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ: 8.31, 8.29 (2 app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o-NO2PhH), 7.91 (2s, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.57 (2 app. d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.11 (m, 3H, PhH), 7.01 (m, 2H, PhH), 5.19 (brm, 1H, CHOCO), 4.84 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H, NHBoc), 4.45 (q, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, CH(NH)CO), 3.19-2.90 (m, 6H, CH2Ph and 2 x ring CH2), 1.37 (s, 9H, Boc) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3), δ 186.91, 171.36, 154.99, 147.50, 141.56, 137.49, 135.37, 133.73, 130.73, 129.06, 128.37, 127.12, 123.82, 80.27, 67.89, 54.37, 38.07, 32.62, 27.99 ppm. ESI-MS, m/z 628.3 [M + H]+; N-Boc deprotection gave 17 as a yellow solid that was purified by precipitation with hexane from an ethyl acetate solution; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 8.34-8.27 (overlapped, 3H, NH3+), 8.33, 8.29 (2 app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x o- NO2PhH), 7.79 (brs, 2H, 2 x CH=C), 7.78, 7.76 (2 app d, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H, 2 x m-NO2PhH), 7.09 - 6.99 (2m, 5H, PhH), 5.21 (brm, 1H, CHOCO), 4.18 (brs, 1H, CHNH3+), 3.31 (dt, J = 3.5 and 17.0, 1H), 3.20 (dt, J = 4.0 and 16.3, 1H), 3.12 (dd, J = 6.1 and 16.6 Hz, 1H), 2.94 (dd, J = 6.2 and 14.4 Hz, 1H), 2.89 (dd, J = 5.8 and 16.6 Hz, 1H), 2.82 (dd, J = 8.2 and 14.5Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 186.91, 168.97, 147.60, 141.83, 136.58, 134.81, 131.81, 129.48, 128.86, 127.57, 124.08, 69.55, 53.33, 36.53, 32.3; ESI-MS, m/z 529.2 [M + H]+.

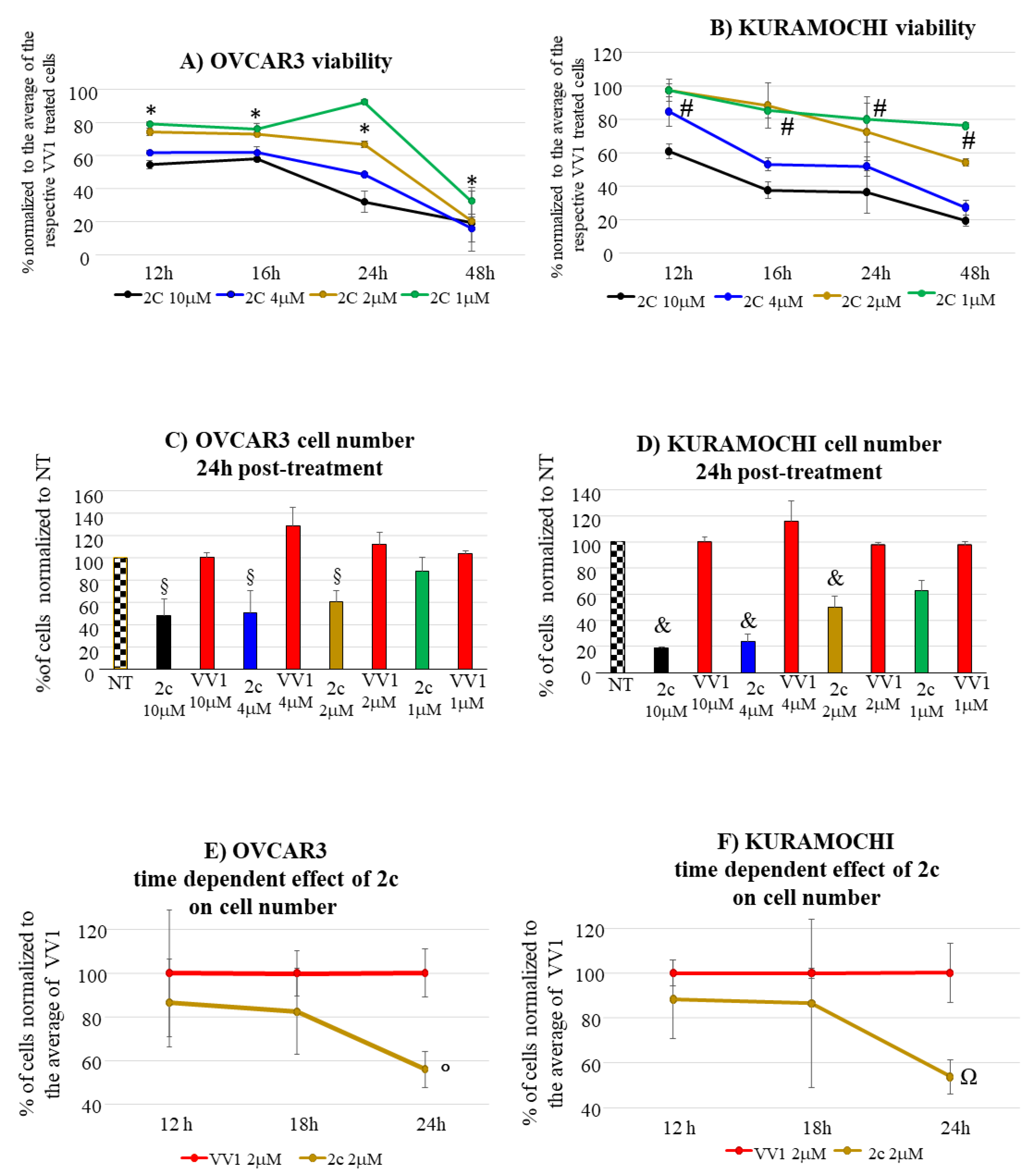
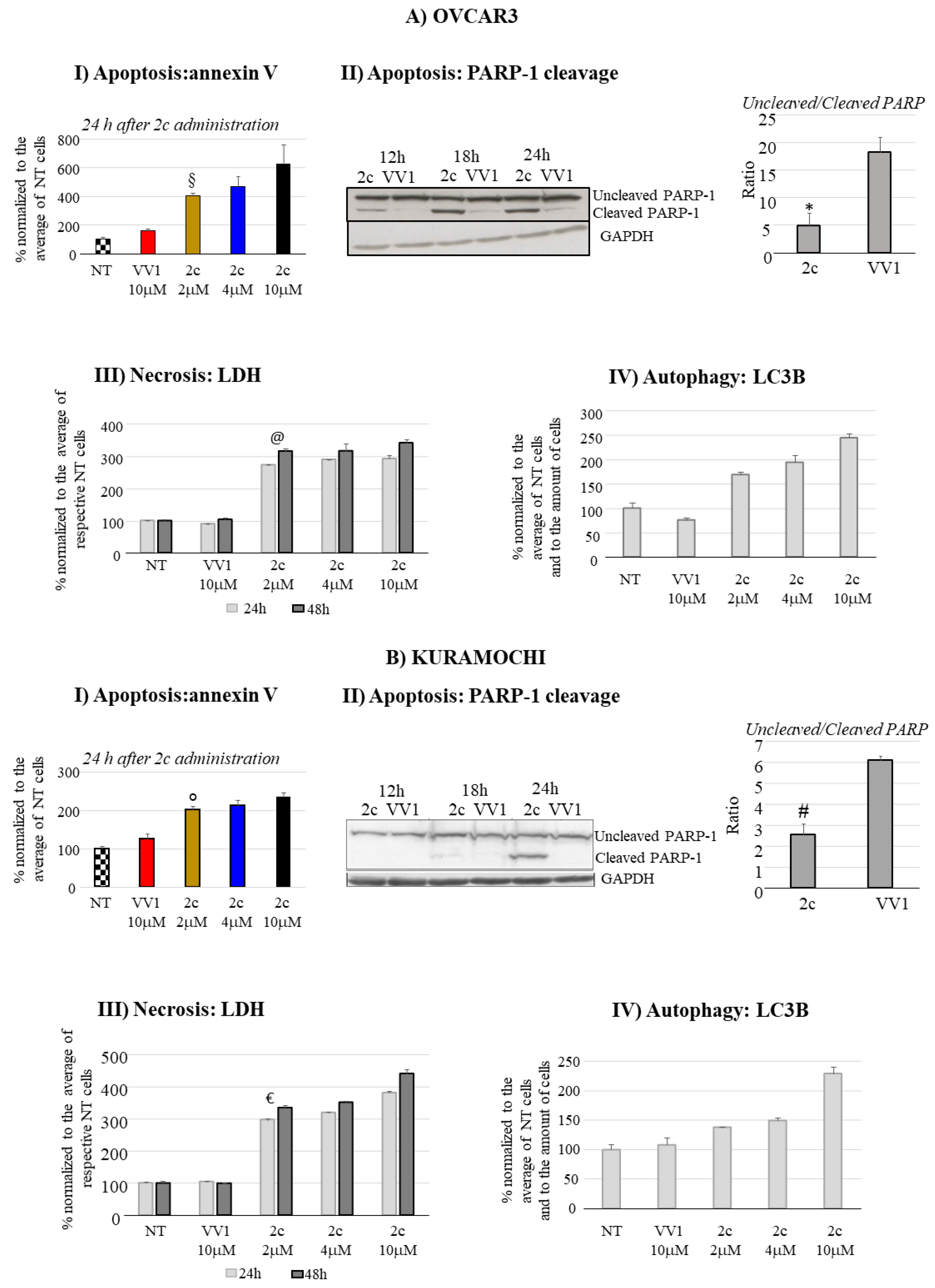
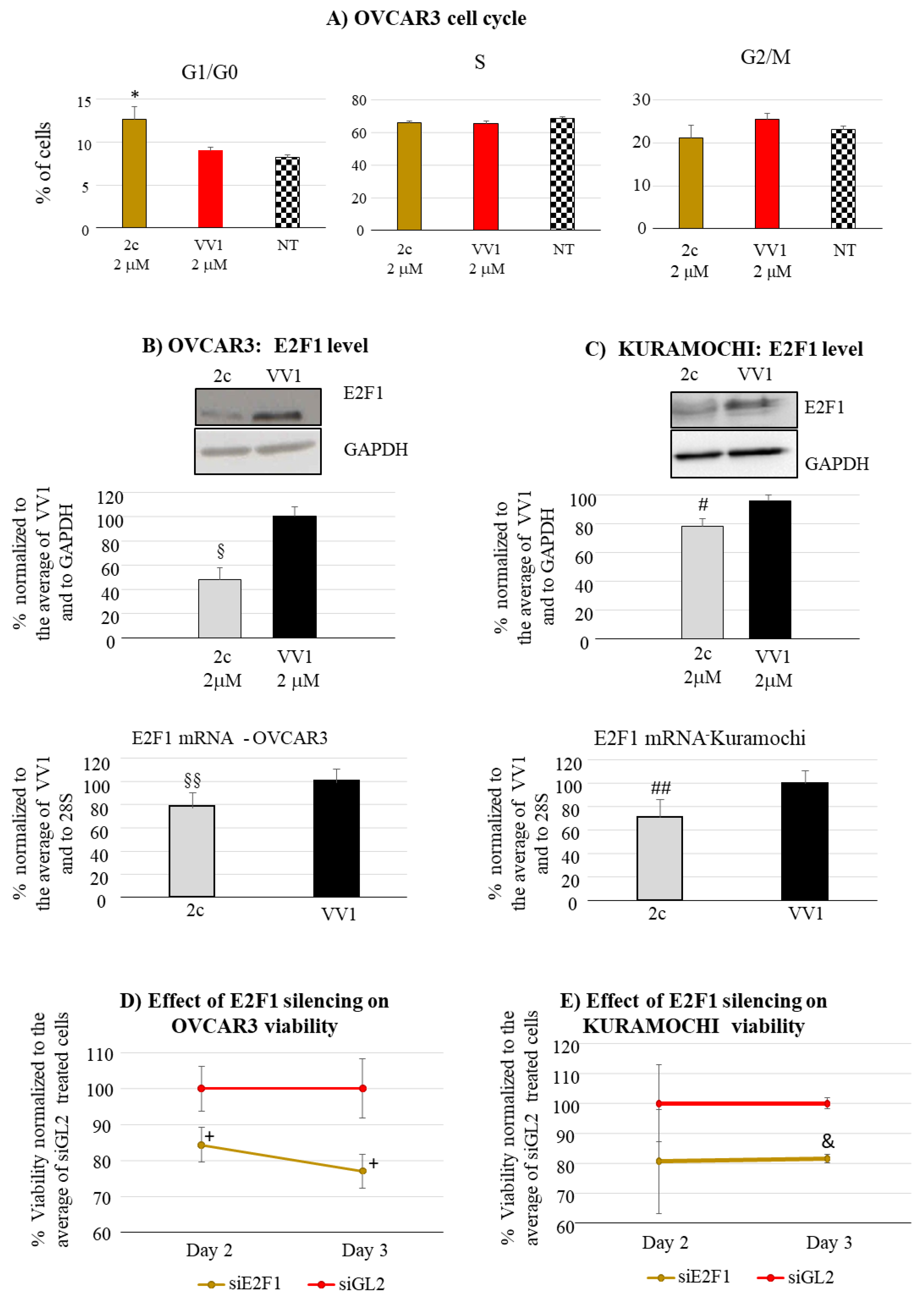
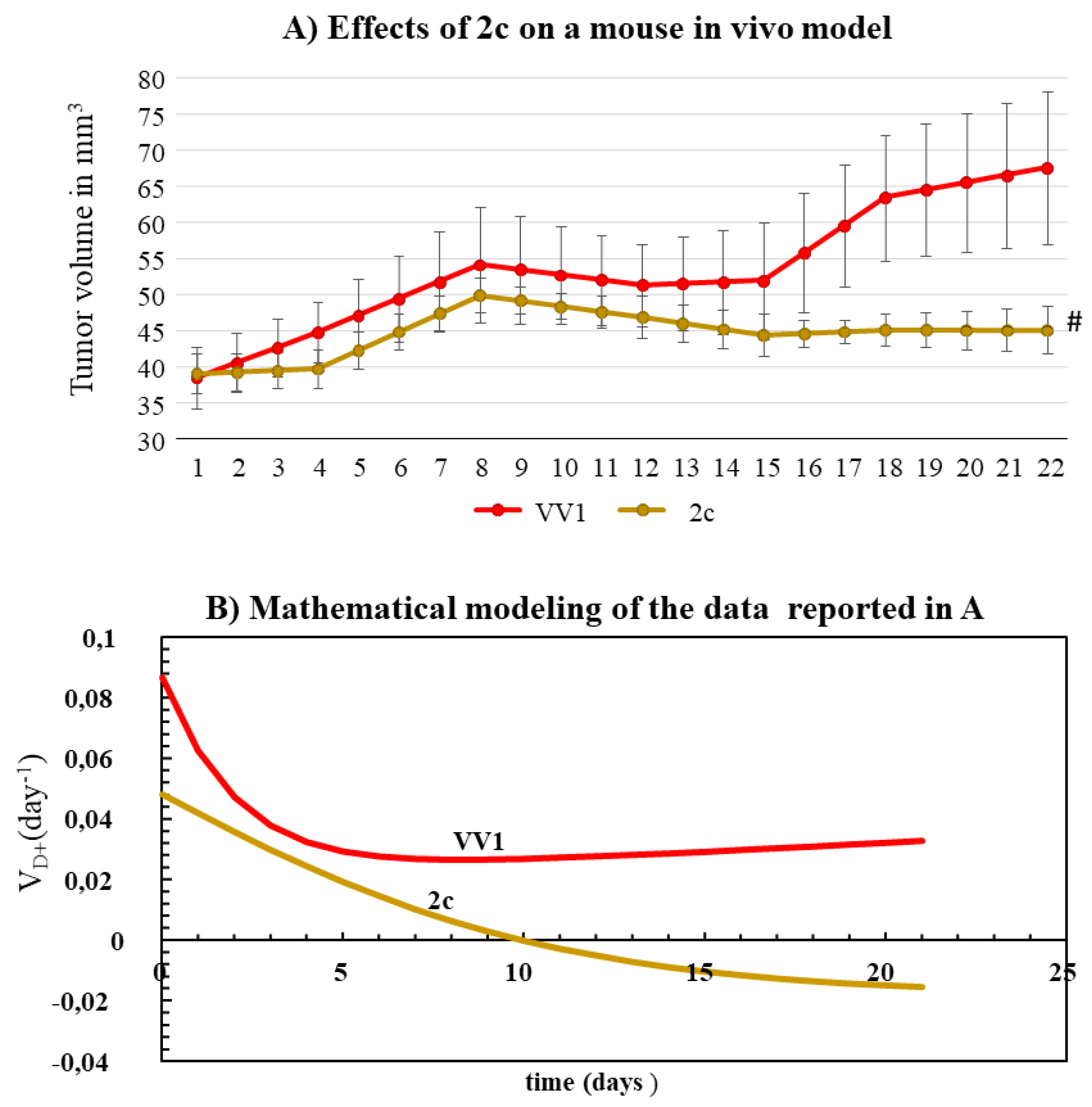
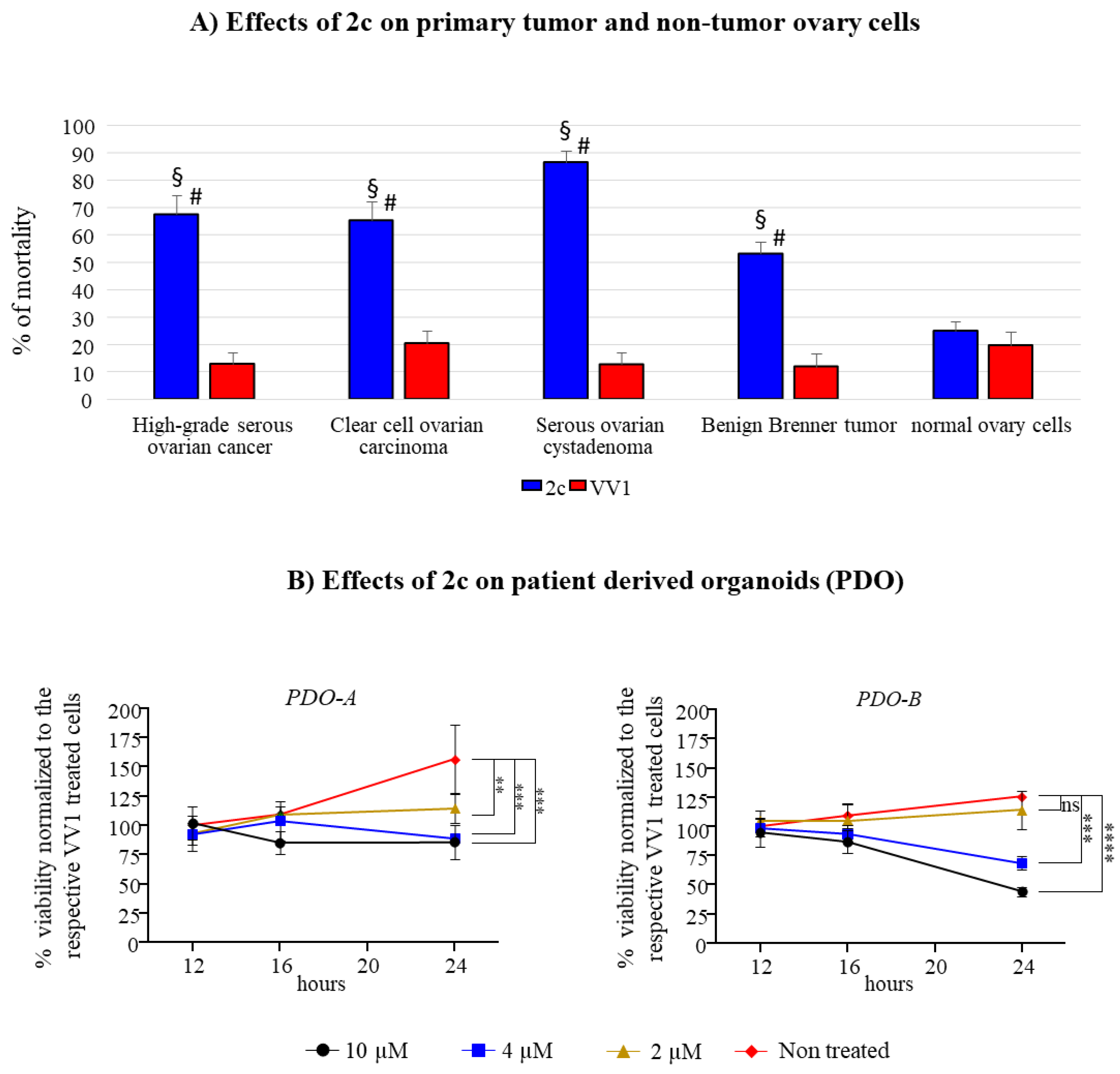
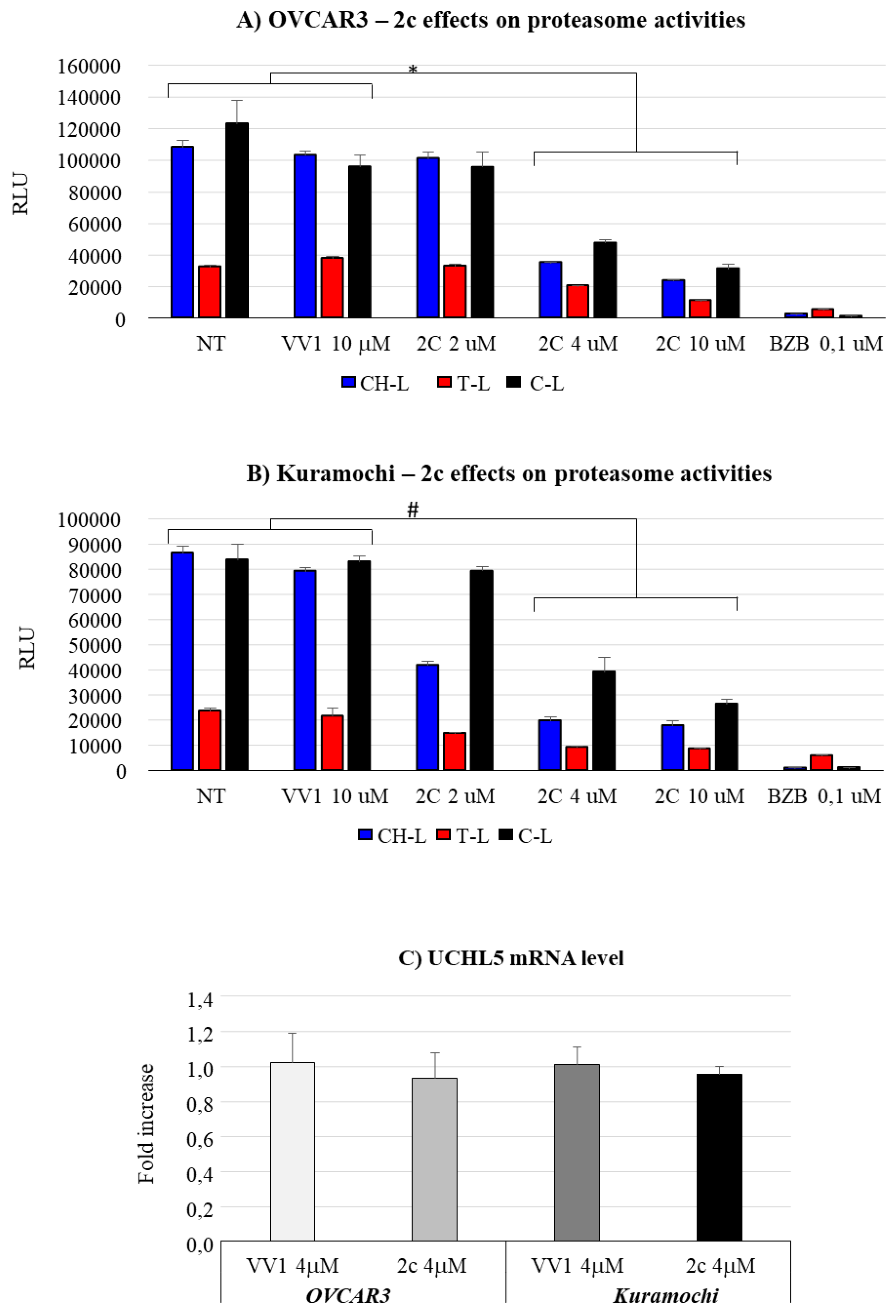
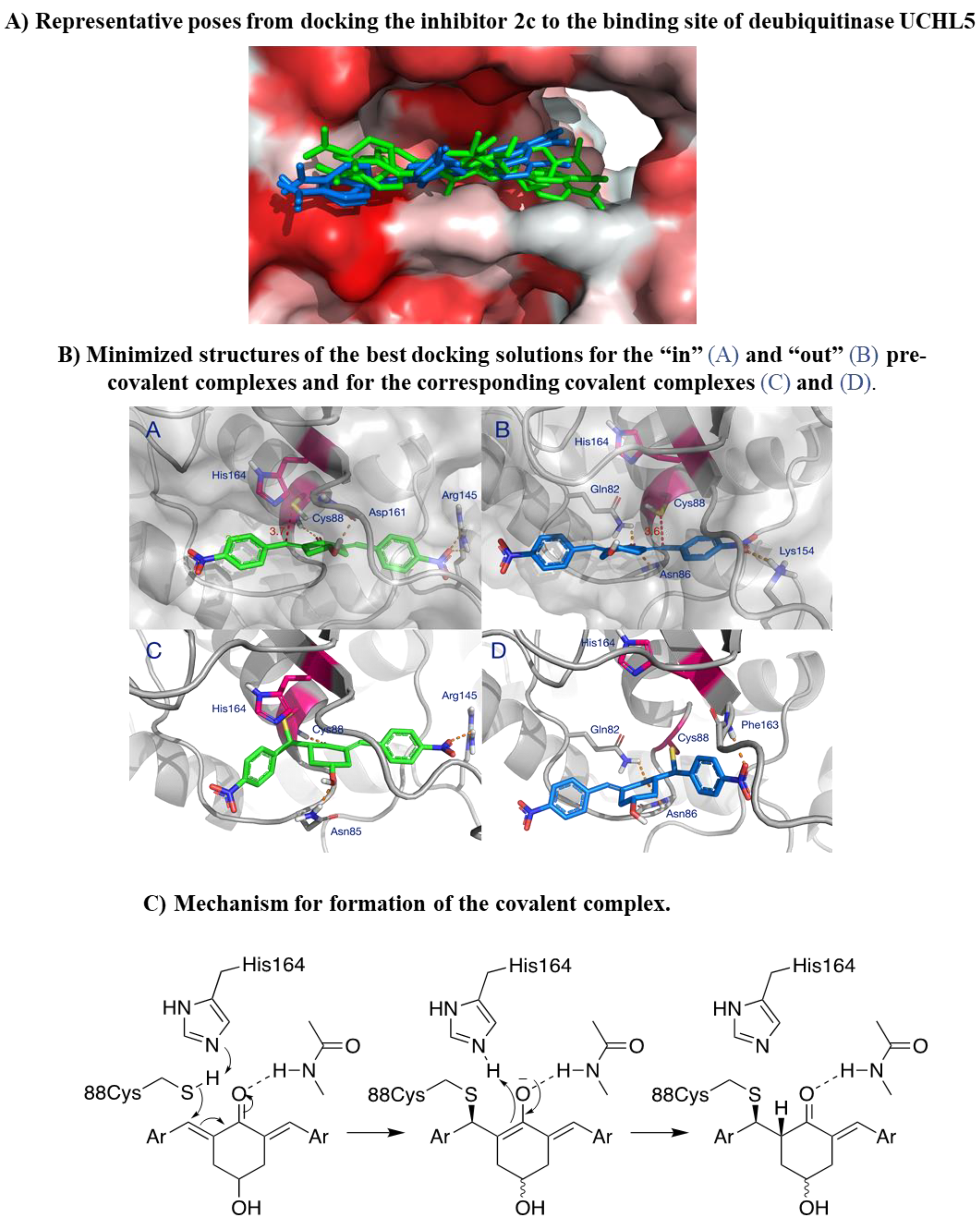
 2c
2c