1. Introduction
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by
the Candida species. Candidiasis can present with different clinical manifestations, including bloodstream infections (candidemia), mucosal infections (e.g.,thrush and vaginal yeast infections) and invasive candidiasis affecting internal organs. Candidiasis is common in critically ill patients. Infection with
Candida is responsible for increasing morbidity and mortality, leading to prolonged treatment in the intensive care units (ICU) and longer hospital stays [
1,
2,
3].
Candida species are the most prevalent fungal infections in intensive care units, and they account for 70-90% of invasive fungal infections with a total mortality of ~40-60% [
1,
2,
3]. Candidiasis is the seventh most frequent cause of nosocomial infections, with an incidence of 7.07 per 1000 ICU admissions [
4,
5,
6].
Factors contributing to invasive fungal infections are a damaged skin barrier or mucous membrane, and the incidence is higher in immunosuppressed and neutropenic patients [
6]. Other factors favor the development of invasive candidiasis, the most important of which is the long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, age, severe hepatic failure, diabetes mellitus, septic shock, and high SOFA score [
4]. According to a retrospective cohort study by Gouel-Cheron and coworkers, long-term mechanical ventilation, the use of multi-lumen catheters, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, renal replacement therapy, long-term operations, the use of immunosuppressive drugs and antineoplastic agents were also associated with invasive candidiasis [
5,
6]. Most cases of invasive candidiasis occur from the 5th to the 12th day of treatment in intensive care units [
7]. Invasive infections are more frequent when
Candida spp is isolated from stool and urine samples, as well as in multifocal colonization (5). The gold standard for diagnosing invasive candidiasis is blood culture, but the sensitivity is variable between 21%–71% [
3].
Candida spp. can cause infections of numerous organ systems [
8]. The clinical picture is non-specific, candidemia can cause sepsis and septic shock, and the dissemination of
Candida can also occur and cause infections of the lungs, eyes, liver, spleen, CNS, heart, and heart valves, as well as other organs and tissues, causing abscesses [
2,
3]. Intra-abdominal candidiasis most often occurs due to perforations, anastomotic leak, relaparotomy, necrotizing pancreatitis, and transplantation of abdominal organs and has a higher incidence in surgical ICUs [
6].
Candida colonization refers to the presence of Candida species on mucosal surfaces or in body fluids without the presence of infection. Patients are asymptomatic but may be potential reservoirs for transmission of infection and development of candidiasis. The most common cause of fungal colonization and infection is
Candida albicans. In recent years, there has been an increase in isolates of
non-albicans Candida (NAC), causing approximately 40 to 50% of infections [
8,
9]. The NAC species include
C. glabrata, C. krusei, C. tropicalis, and
C. parapsilosis [
3,
7]. A weaker response to azole therapy is associated with NAC [
3,
7,
8].
Although they are closely related, it is especially important to distinguish between colonization and Candida infection (5). Candida colonization is present in 5-15% of patients admitted to the ICU, while during their stay in the ICU, the number of patients colonized with Candida increases to 50-80%, of which 5-30% of patients develop invasive candidiasis (5).
Patients who are admitted to surgical ICUs, in addition to surgical diseases, often have numerous other comorbid conditions that can favor candida colonization and the development of candidiasis. Such diseases certainly include hypertension, diabetes, and malignant diseases. In surgical patients, comorbidity can also affect treatment outcomes and lead to prolonged ventilation and higher mortality.
The aim of this study was to examine the frequency of any isolation of Candida spp. in the population of surgical ICU patients and to observe comorbidities which were recorded in this population compared to the control population of ICU patients. We also wanted to compare the impact of non-elective and elective admission to the ICU, as well as the initial values of laboratory findings upon the ICU admission in patients with Candida isolation, that could raise earlier suspicion of a fungal infection, and affect the treatment of the surgical diseases, the duration of mechanical ventilation, and ICU survival.
2. Results
The ICU Department at Osijek University Hospital, Croatia database includes the results of microbiological samples taken between May 22, 2016, and June 30, 2023. During that time a total of 5118 patients were admitted to the ICU, and 15,790 samples were taken for microbiological analysis. Pathogenic microorganisms were confirmed in 4971 samples, and the presence of
Candidas was confirmed in 581 isolates (11.7% of all positive samples) taken from 236 patients.
C. albicans was confirmed in 426 (73%) isolates, followed by
C. glabrata (53, 9.1%),
C. parapsilosis (45, 7.7%),
C. tropicalis (13, 2.2%), and
C. kefyr (7, 1,2%).
C. rugosa, C. famata, C. krusei, and
C. lusitaniae were registered in 4 patients (0.7%),
C. guillermondi in 2 (0.3), and
C. metapsilosis and
C. orthopsilosis in 1 patient. Their azole resistance is shown in
Table S1.
Candida isolation was most often confirmed in urine cultures followed by tracheal aspirates (27 and 18/1000 admissions). The overall incidence of
Candida isolation was 46 cases per 1000 admissions. Invasive candidiasis was registered in 54 patients (1.06% of all ICU admissions). The characteristics of these isolates are shown in
Table 1.
As shown in
Table 1, the largest number of
Candida was isolated from urine cultures (58.5%), followed by tracheal aspirates (39.8%) and blood cultures (13.1%).
Candida was isolated from one sample only in 58.3%, and from ≥2 samples in 41.7% of patients.
C. albicans were isolated in the largest number of patients (68.2%), while NAC were isolated in 31.8% of patients. A significant increase in the frequency of NAC was observed within a period after the COVID-19 pandemic (chi-square test P= 0.009). In 13.6% of the patients, two or more Candidas were isolated, and in 30.5% of the patients, in addition to
Candida, various pathogenic bacteria were also isolated (
Table 1.). The presence of pathogenic bacteria in microbiological samples was associated with the isolation of
Candida from ≥2 samples (Spearman ρ=0.177, P=0.007). Candidemia was observed in 31 patients, and it was caused by NAC in 17 (55%) patients.
Men were the majority both in the population with
Candida isolation and in the control ICU population (
Table 2).
Although non-elective patients predominate among all ICU patients, the proportion of non-elective patients is significantly higher in the population with Candida isolation (P <0.001). In patients with Candida isolation, mortality is significantly higher and was 42%, while in the control group, it was 19% (P<0.001). There were no differences in ICU mortality between patients colonized with C. albicans and NAC (P=0.908).
The most common comorbidities were vascular diseases, and the most common diagnosis was arterial hypertension. Among the patients in the
Candida group, there were significantly more heart diseases, respiratory diseases, renal, coagulopathies, hepatobiliary, sepsis, soft tissue infections, and metabolic diseases, whereas neoplasms were less frequent than in the control population of surgical ICU patients (
Table S2).
The frequency of candiduria was higher in women and was associated only with a higher SAPS II score at admission within that group (Spearman’s correlation ρ=0.13, P=0.046).
The presence of
Candida isolation between May 22, 2016, and June 30, 2023, was registered more often after abdominal surgical procedures, with the highest frequency after reoperation, as shown in
Table S3. Also,
Candida isolation occurs more often in hospitalized patients with nosocomial bacterial infections. In patients with nosocomial infections, the frequency of
Candida isolation from multiple samples is also higher (Spearman’s rank correlation, ρ=0.177, P=0.007), as well as
Candida isolation from the abdominal cavity (ρ=172, P=0.008). NAC was in a significant correlation with diabetes (ρ=0.192, P=0.003) and abdominal procedures (ρ=0.2, P=0.002).
The patients with
Candida isolation had a significantly longer ICU stay, higher median values of CRP and PCT at admission to the ICU, the value of the SAPS II score within 24 hours of ICU admission and the SAPS II score before discharge than control patients (
Table 3.).
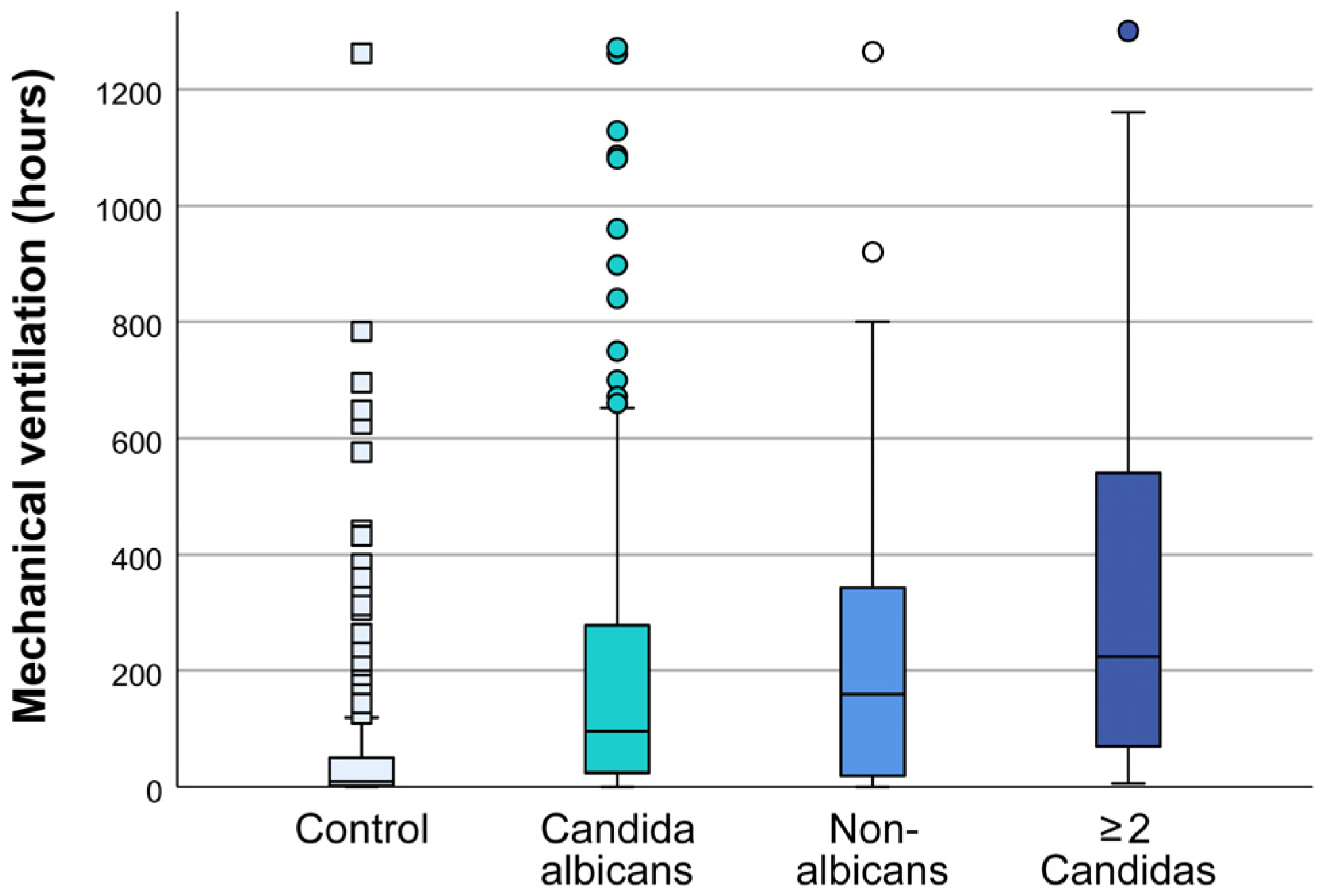
The duration of mechanical ventilation in patients with multiple samples positive for
Candida is longer compared to patients in whom
Candida was isolated from one sample only with a median of 71(22-214) h vs. 244 (76-246) hours (one-way ANOVA, P<0.001) (
Figure S1). The duration of mechanical ventilation depends on the type of isolated type of
Candida. The average duration of mechanical ventilation in patients with isolated
C. albicans was 103 hours, 160 hours in patients with NAC, and 224 hours for isolated 2 or more
Candidas (one-way ANOVA, all P≤.05 vs control) (
Figure 1).
The association of individual risk factors with mortality was examined for the whole population in a bivariate analysis. The highest OR (Odds ratio) for mortality was confirmed for non-elective admission, isolation of Candida vs. control group, heart, and renal diseases (
Table 4).
Factors that were significant in bivariate analysis were tested in multivariate analysis, adjusted for age, SAPS II score, days of ICU, and type of admission classified as elective or non-elective. The model is statistically significant as a whole, (χ
2=389.5, P < 0.001), and it explains between 55% (according to Cox & Snell) to 78% (according to Negelkerke) of the variance of the negative outcome (death), and exactly classifies 92% of cases. Only one predictor in the multivariate analysis was significant and that is the presence of sepsis (OR = 2.27) (
Table S4). The same results were obtained in the logistic regression performed within the group with Candida isolation, where sepsis was also the most important predictor of mortality (
Table S5).
3. Discussion
This study confirmed the association of Candida with heart, renal and metabolic comorbidities, with more non-elective admissions and increased mortality in the group of surgical patients with candidiasis.
High mortality in patients with candidiasis has been observed in other studies and meta-analyses. In a large meta-analysis including 10,692 patients with candidaemia, Zhang et al. recorded a mortality of 49.3% (95% CI 45.0% to 53.5%) and significantly prolonged ICU stay [
3]. High mortality in patients with candidiasis was also found in other studies. According to the results of the EUCANDICU project, mortality in invasive candidiasis was 42% [
4]. Aguilar et al. confirmed a mortality of 33% in 1149 surgical patients with invasive candidiasis, while the mortality in the total population of surgical patients in the ICU was 13%. All cases of invasive candidiasis were confirmed in patients with peritonitis and severe sepsis or septic shock [
9]. The total frequency of invasive candidiasis was 19.1 per 1000 stays, similar to our study where we recorded 18.3 per 1000 ICU admissions, respectively. The authors confirmed the presence of central venous catheters, urinary catheters, antibiotic therapy, mechanical ventilation, prolonged stay in the ICU and total parenteral nutrition as risk factors [
3,
9,
10]. Apart from total parenteral nutrition, these risk factors are present in most patients in the ICU.
Most of these studies did not analyze the previous comorbidity of the patients but the SOFA score as an indicator of organ dysfunction at the time of admission to the ICU. In our study, we analyzed the diagnoses of patients upon arrival in the ICU. This study, which covers a longer period and a larger number of patients, confirmed that both Candida isolation and mortality are associated with patient comorbidities. The most significant indicators of a higher frequency of candidiasis are heart, metabolic and respiratory diseases and coagulopathy.
Heart diseases, among which atrial fibrillation is dominant, are significantly more common in our population with
Candida isolation than in the control group of all surgical ICU patients. Previous atrial fibrillation is rarely cited as a risk factor for candidiasis in surgical patients. Other factors that can contribute to more frequent candidiasis in heart patients are their significant hemodynamic instability, the need for an invasive approach, and catheterization of central veins and arteries. Candidemia is a frequent cause of infective endocarditis and new-onset atrial fibrillation
[11]. A series of studies confirmed the association of candida with the presence of foreign bodies which are commonly used in patients with atrial fibrillation, such as central venous catheters, intraarterial catheters, urinary catheters, endotracheal tubes, or parenteral nutrition [
9,
12]. Therefore, one of the possible ways to reduce candidiasis could be the application of the ERAS protocol in emergency patients, who make up most of our population. These measures are faster removal of the nasogastric tube and drains, reduction of catheterization time, earlier mobilization, and earlier initiation of patient feeding [
13].
In diabetic patients, who have a higher risk of being admitted to the ICU from the emergency room, the application of the ERAS protocol could be particularly significant[
14]. In our population with candidiasis, there are twice as many of them as in the control group. New therapies such as Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2), which inhibit renal glucose reabsorption and cause glucosuria, favor candida colonization and candiduria [
15,
16]. Due to the increased frequency of heart disease and diabetes in emergency patients, early recognition of this risk group, application of the ERAS protocol, differentiation of colonization from infection and early initiation of therapy could reduce poor outcomes of these patients [
14,
17].
Respiratory diseases were significantly associated with
Candida isolation in our study. This is consistent with the observation of Krause et al. that candida was never isolated from the lungs of healthy patients [
18]. They compared isolates obtained from patients undergoing elective plastic surgery after intubation, who did not receive antibiotic therapy, with a group that was mechanically ventilated without antibiotic therapy and with a group that was not mechanically ventilated but received antibiotics for other infections. They confirmed that the presence of
Candida is frequent from respiratory specimens in ICU patients who were mechanically ventilated, or who received antibiotics, and that it reflects lower respiratory tract dysbiosis [
18,
19]. The diagnosis of
Candida pneumonia is demanding because the clinical presentation and radiological findings are nonspecific, and the
Candida isolate should be interpreted with caution and individually for each patient [
19,
20].
Some authors believe that
Candida is a marker of a greater burden of illness and that it is not clear whether it should be actively treated or is only an indicator of immunosuppression in patients [
21,
22,
23,
24] Although the guidelines of professional societies do not recommend routine therapy in patients with colonization of the lower respiratory tract, most of them recommend that every clinical case with
Candida isolation should be considered in the context of the clinical presentation [
23,
25]. These newer recommendations are based on the results of clinical observations and preclinical studies [
26,
27]. In a group of 200 ICU patients in whom
Candida was confirmed in lower respiratory tract samples, Lanigan et al. observed a mortality rate of 80% [
27]. The authors confirmed that antifungal treatment was associated with better outcomes, and that mortality was higher in patients who did not receive antifungal therapy [
27].
The duration of mechanical ventilation is significantly higher in our patients with
Candida isolation than in the control population. Similar results were confirmed by Huang et al. in a meta-analysis that included 1661 mechanically ventilated adult patients in the ICU. They compared all those who were positive with
Candida with those who were negative and excluded immunocompromised patients [
28]. In their study, the
Candida-colonized population had a higher 28-day mortality (RR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.27-2.12), although probably due to the higher mortality, the duration of treatment in the ICU was not different between groups [
28]. According to the results of published studies, NAC is often isolated in patients who had previous antifungal therapy, diabetes on SGLT-2 therapy, and those who were immunocompromised [
12,
15,
29]. In our study, prolonged mechanical ventilation was associated with the presence of any
Candida, and especially with NAC. Considering that NAC is the most frequent cause of sepsis in our patients, their impaired condition caused by sepsis may result in prolonged mechanical ventilation. Other associated comorbidities such as diabetes, which was also associated with NAC in our study, may contribute to prolonged mechanical ventilation.
Non-elective patients represent about 90% of all patients with
Candida isolation, and they are mainly admitted after emergency abdominal surgeries, commonly in septic shock.
Candida in the abdominal cavity is considered a serious infection that requires immediate treatment [
4,
30]. Bassetti et al. in their research proved that the most common form of invasive candidiasis are candidemia and intraabdominal candidiasis, with a frequency of about 5% at admission to the intensive care unit, while the 30-day mortality was 42% [
4]. Risk factors for increased mortality include age, severe liver failure, septic shock, and increased SOFA score. In our patients with
Candida isolation, there were 90% non-elective, i.e., emergency patients. The majority were admitted to ICU with peritonitis, their SAPS II score was significantly higher, as well as the frequency of heart and respiratory diseases, coagulopathy, and sepsis. Sepsis was associated with soft tissue infections such as Fournier’s gangrene, abdominal and pelvic abscesses. In the multivariate analysis, sepsis was confirmed as the most important factor that contributed to mortality in our entire population. Candidemia and septic shock with increased mortality were associated with NAC in our patients, which was also reported in other studies [
31]. Routsi et al. observed the incidence of candidemia was 10.2% during COVID-19, which is significantly higher compared to the two pre-pandemic periods when the incidence of candidemia was 3.2% and 4.2%, respectively [
32]. Comparable to the results of other authors, an increase in fluconazole resistant strains was also observed in our patients in the post-COVID-19 era [
24,
32].
Candiduria in asymptomatic patients without risk factors may be treated by changing the urinary catheter, while in high-risk patients fluconazole is necessary to prevent invasive candidiasis [
33,
34,
35]. According to Dias, in critically ill ICU predisposed inpatients with numerous comorbidities, any candiduria, asymptomatic or symptomatic, may be the only clue of a severe infection [
33]. Catheterization of the urinary bladder is the most common risk factor for candidiasis in patients in ICUs, followed by use of antibiotics, prolonged hospital stay, extreme age, diabetes mellitus, female gender, immunosuppressive therapy [
34,
35,
36]. We expected that urine cultures would be positive more often in diabetics than in other patients with
Candida, which was not confirmed (Spearman’s correlation coefficient ρ = 0.002, P= 0.972). Marchena-Gomez et al. confirmed that candidiasis is not only related to mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU but is common in general surgery wards. The frequency of candida is like that in our study, but in their patients, candida was not the most common in urine cultures (18.6%) but is highest in surgical wounds in which the frequency of isolation was 25% [
37]. Anemia was an independent factor of mortality in their study [
37].
In our population of surgical ICU patients with
Candida isolation, there was a significant predominance of
C. albicans, which was isolated in 68.2% of patients, while NAC was less common. Other studies have confirmed similar ratios, but a slightly higher frequency of NAC. Dimopoulos et al. study finds 35.7% of NAC, while Aguilar et al. find 41%. [
9,
12]. According to the results of recent studies, the frequency of fluconazole-resistant NAC strains has increased after the COVID-19 pandemic. This increase in resistant strains is probably related to the longer use of antibiotics and the greater invasiveness of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Therefore, our study emphasizes the importance of reduced antibiotic use and prevention of fungal colonization. We also want to emphasize that early diagnosis of
Candida infection and the use of scoring systems can facilitate the differentiation of patients at low and high risk. These measures, combined with diagnostic tests, can assist in identifying patients who should receive preventive treatment [
12,
38].
The limitation of our study is that, except for invasive candidiasis, we did not associate the isolated
Candida species with the specific site of infection. Thus, patients were not classified according to whether they had colonization or signs of infection of the site from which the samples were taken. Another limitation of this study is its retrospective character. Since the aim of the study was to correlate
Candida isolation with comorbidities, we did not analyze the antibiotics the patients received before taking the samples. We also did not analyze the use of antifungal therapy within the
Candida isolation group and the use of other medications, such as corticosteroids,.. Since most of the patients were admitted to the ICU with complicated infections, respiratory failure, and sepsis, the administration of these drugs was expected. Earlier studies confirmed increased frequency of
Candida infection in patients who received antibiotics for a long time, and the association of
Candida isolation with corticosteroid therapy [
3,
9], so we believe that this was also the case in our patients. The association of all these factors could be better examined in a future prospective study.
4. Materials and Methods
We conducted a cross–sectional study in which we analyzed patient data from 2016 to 2023 admitted to the Intensive Care Unit, Osijek University Hospital, Croatia. The study included adult patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit in whom Candida was isolated, regardless of the type of sample, the number of yeasts, or whether it was infection or colonization. The control group was patients without positive Candida findings in microbiological isolates. The control group was formed by subtracting from the electronic database all consecutive patients admitted to the surgical intensive care during the three-month period in the year before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic from March to the end of May 2019 (N=160), and the same number of patients after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, from March to the end of June 2020 (N=161). A total of 497 patients were analyzed, of which 236 (47.4%) had isolated Candida, and 261 (52.6%) were in the control group.
Demographic and clinical data were collected from electronic databases and medical charts. The following data were analyzed: age, sex, type of admission (emergency, elective), the surgical department from which the patient was admitted to the ICU,, days of ICU stay, type of surgical procedures (craniotomy, laparotomy, thoracotomy), reoperations, initial laboratory findings taken on admission to the ICU, the value of SAPS II score within 24 hours of admission to the ICU and SAPS II score 24 hours before discharge or death, treatment outcome (discharge, death), and period of hospitalization (before and during the COVID-19 pandemic).
Comorbidities at admission were analyzed separately. Heart diseases were atrial fibrillation, previous myocardial infarction, unstable angina, cardiomyopathy and valvular diseases. Arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and peripheral vascular diseases were classified as vascular diseases. Respiratory diseases were asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis or previous tuberculosis. Any previously recognized disease such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, personal history of a stroke, and conditions with a new disorder of the consciousness such as brain trauma were considered neurological diseases. The patient who had a brain tumor with impaired consciousness, was classified as having a neoplasm and a neurological disease. Coagulopathy was considered any condition in which the patient had a coagulation disorder requiring therapeutic intervention upon admission, i.e., thrombophilia, previous therapeutic od preventative use of anticoagulants, or history of deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Trauma and polytrauma were evaluated separately. Renal diseases were considered when acute or chronic kidney failure was confirmed according to KDIGO criteria and kidney tumors. Bladder diseases such as infections, stones or tumors are classified as urological diseases. Gastrointestinal diseases that were known before admission such as tumors, Crohn’s disease, ulcers of the stomach and duodenum were registered, whereas hepatobiliary diseases were a separate category. Due to the high mortality rate, sepsis on admission was considered as an entity, regardless of the source of infection. Diabetes and hyperlipidemia were classified as metabolic diseases, while hypo/hyperthyroidism, parathyroid gland diseases and pituitary gland diseases were considered endocrine diseases. Psychiatric diagnosis was recorded when the patient or his guardian declared that he had the specified diagnosis and/or was taking psychoactive drugs. Soft tissue infections, i.e., neck abscesses, mediastinitis, Fournier gangrene, etc. were considered as specific groups. Neoplasms were considered both in patients whose cancer surgery was the main reason for surgery and admission to the ICU, as well as in those who had trauma and other tumors that were previously or currently under therapy, such as prostate cancer.
Microbiological samples that were analyzed were taken when infection was suspected based on clinical or laboratory signs. Depending on the possible source of infection urine, blood, vascular catheter tips, drains, and wound swabs were collected according to standard guidelines. Respiratory specimens were tracheal aspirates and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). Analyses of the samples received were performed by routine microbiology procedures that account for inoculation onto selective and nonselective agar plates, identification of morphologically different colonies with germ tube test, API Candida© (Bio Merieux, France) and MALDI TOF Bruker Biotyper. Film Array BCID2 Panel was performed if blastoconidiae were observed from positive blood culture samples inoculated onto BACTEC BD © bottles (Becton Dickenson, UK). Susceptibility of identified isolates was performed using ATB Fungus 3 © (BioMerieux, France) and interpreted according to valid EUCAST standards.
Statistical analysis. Categorical data are represented by absolute and relative frequencies. Numerical data are described by the median and the limits of the interquartile range. Differences in categorical variables were tested with the χ2 test. Differences in numerical variables between two independent groups were tested with the Mann-Whitney U test, whereas differences between three or more groups were tested using one-way ANOVA. Differences in variables between two measurements were tested with the Wilcoxon test. Correlation between variables was examined with Pearson’s correlation for parametric variables (r) and Spearman’s correlation (ρ) for non-parametric variables. Factors that were significant in bivariate analysis were tested in multivariate analysis, A P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G.T. and S.K.; methodology, J.G.T., S.K., K.K.; software, K.K, S.K.; validation, S.K., K.K., D.K., M.K.; formal analysis, M.B., D.K., M.K., K:K., S.K.; investigation, J.G.T., A.C., I.K.K.; I.J.P.; data curation, J.G.T., A.C., I.K.K., I.J.P; writing—original draft preparation, J.G.T., S.K., A.C., I.K.K.; writing—review and editing, S.K., J.G.T., A.C., D.K., M.K., M.B.; supervision, S.K, D.K., M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.