Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield
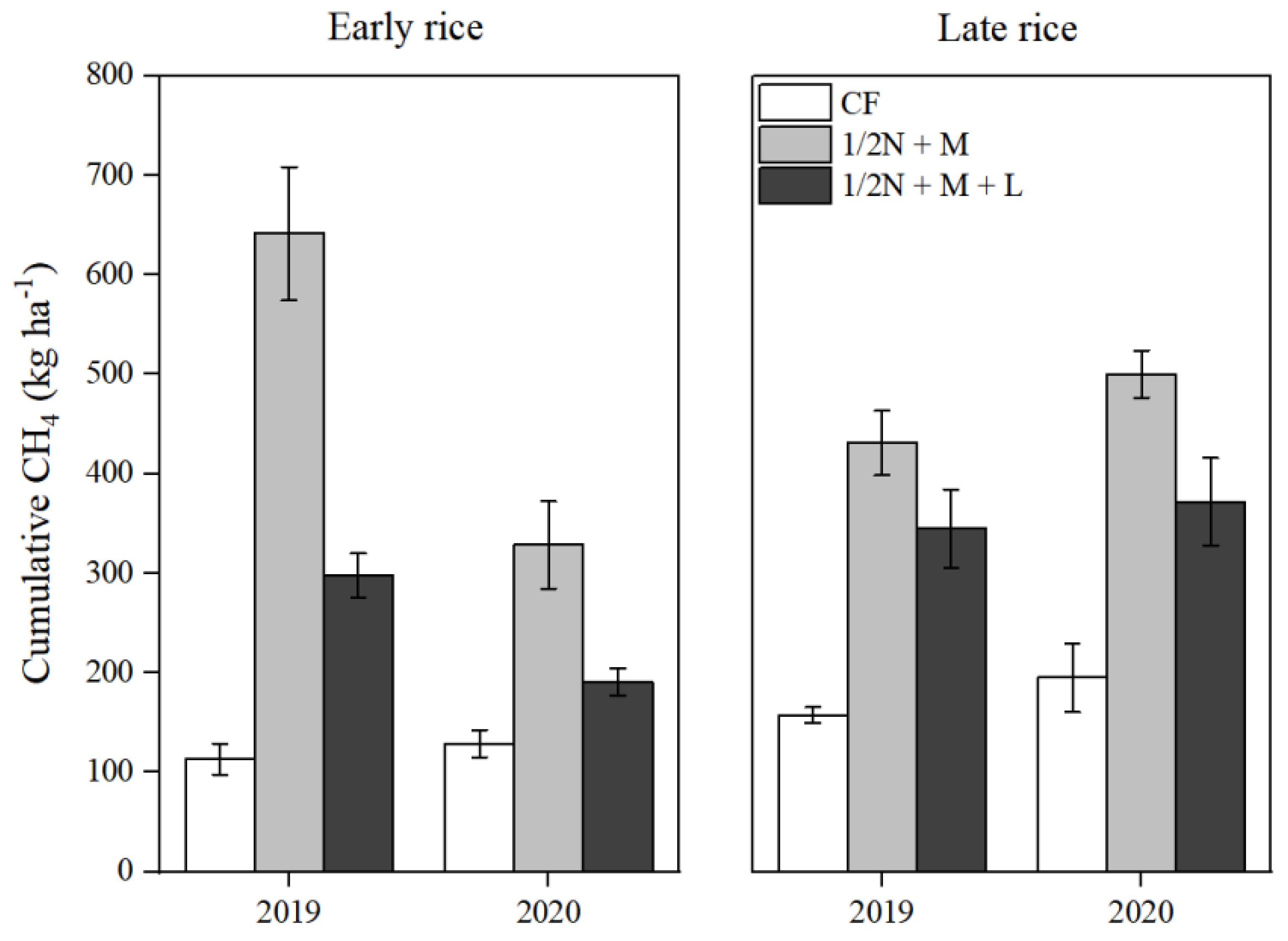
3.2. CH4 Emissions
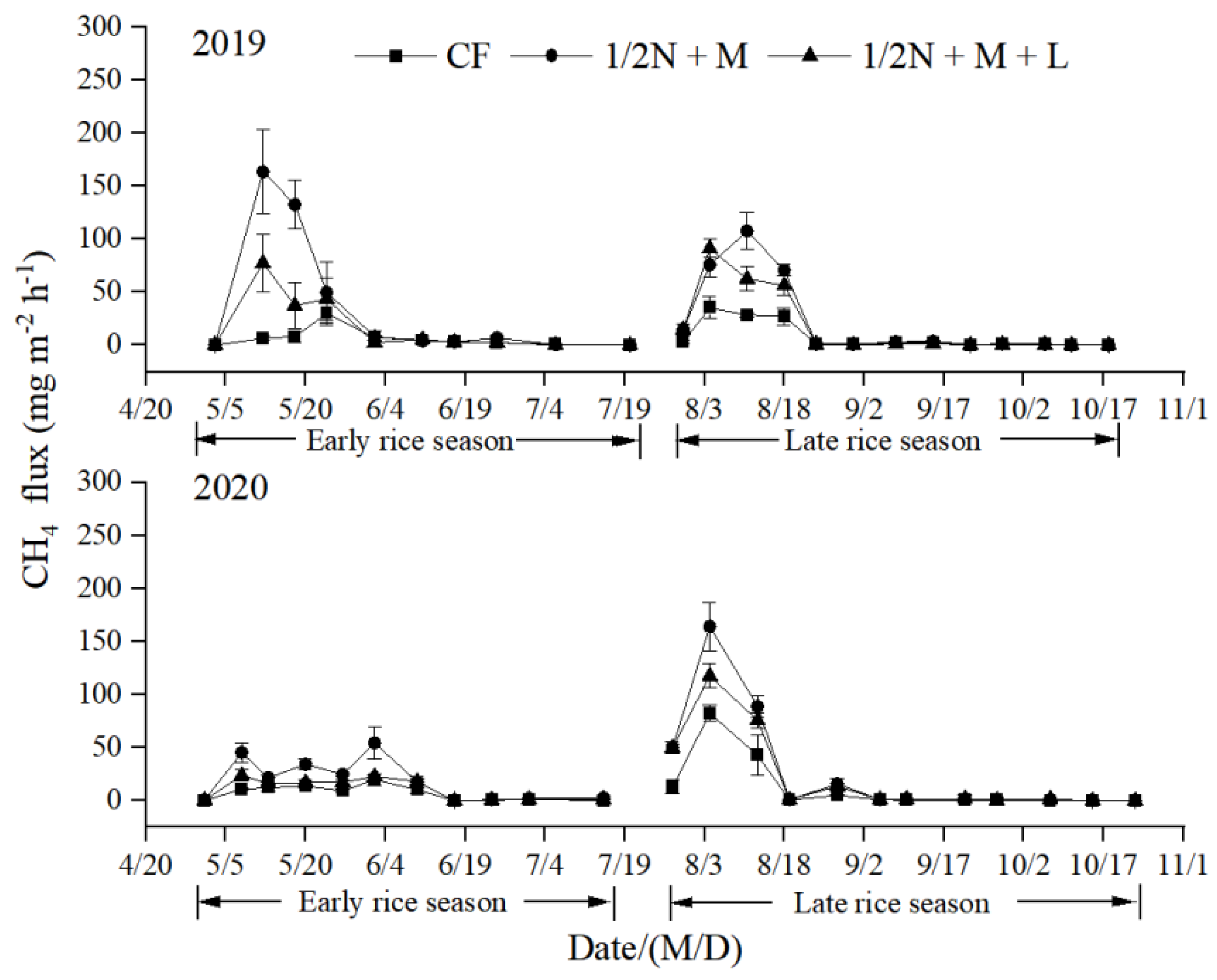
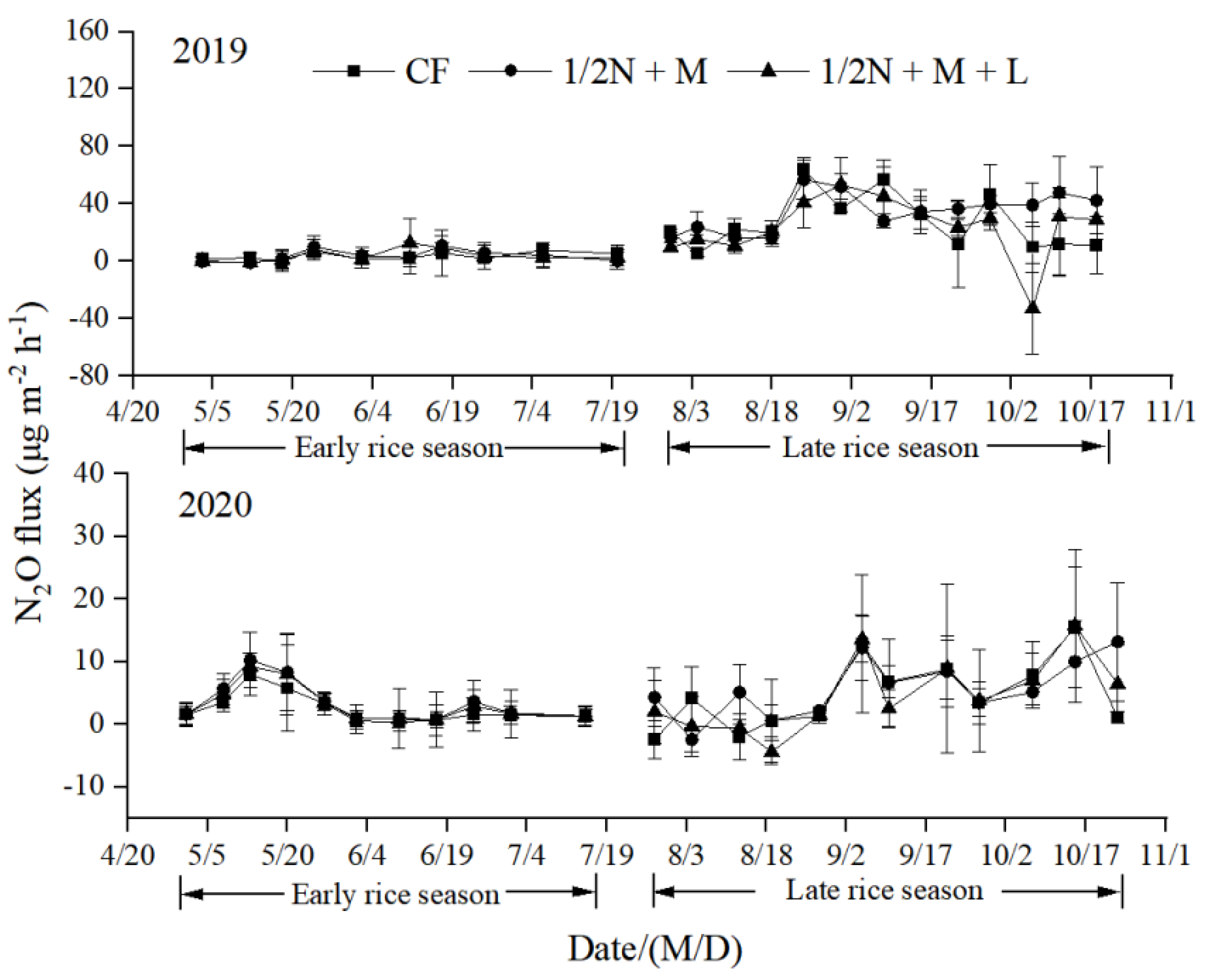
3.3. N2O Emissions
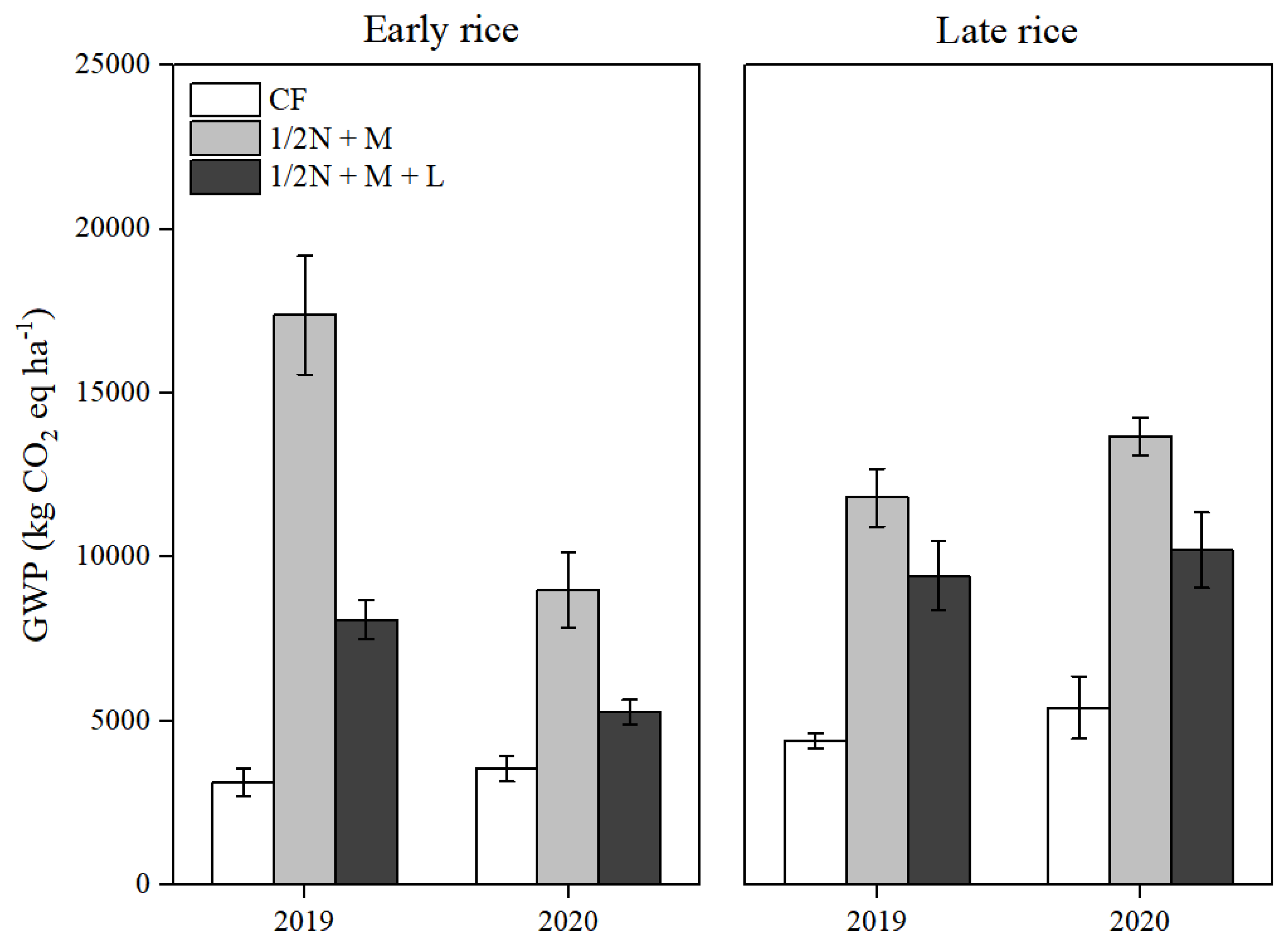
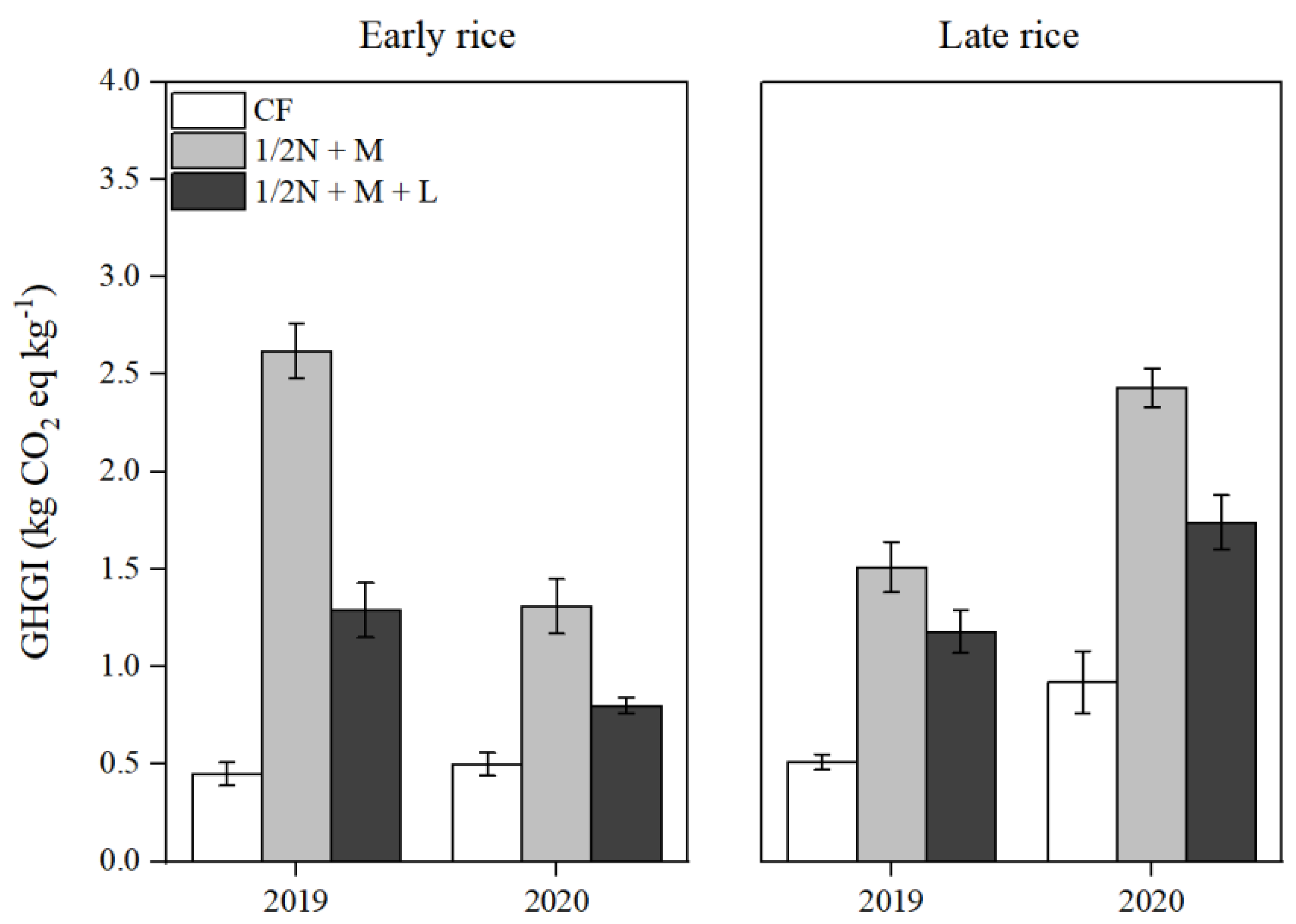
3.4. GWP and GHGI
3.5. Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Pig Manure Substitution on Rice Yield, CH4 and N2O Emissions
4.2. Effect of Liming on Rice Yield, CH4 and N2O Emissions under Pig Manure Substitution
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, M.F.; de Vries, W.; Bonten, L.T.C.; Zhu, Q.C.; Hao, T.X.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, M.G.; Shi, X.J.; Zhang, F.S.; Shen, J.B. Model-based analysis of the long-term effects of fertilization management on cropland soil acidification. Environmental Science & Technology 2017, 51, 3843–3851. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.Z.; Xu, W.X. Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019, 180, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makara, A.; Kowalski, Z.; Lelek, L.; Kulczycka, J. Comparative analyses of pig farming management systems using the Life Cycle Assessment method. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 241, 118305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Islas, M.E.; Güereca, L.P.; Sosa-Rodriguez, F.S.; Cobos-Peralta, M.A. Environmental assessment of energy production from anaerobic digestion of pig manure at medium-scale using life cycle assessment. Waste Management 2020, 102, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.X.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.P.; Smith, P.; Li, L.Q.; Qiu, D.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Xu, X.B.; Shen, S.Y.; Chen, X.M. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region.; China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ma, X.F.; Shen, J.L.; Chen, D.; Zheng, L.; Ge, T.D.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. ; Reduction in net greenhouse gas emissions through a combination of pig manure and reduced inorganic fertilizer application in a double-rice cropping system: Three-year results. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2022, 326, 107799. [Google Scholar]
- Mockeviciene, I.; Repsiene, R.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K.; Karcauskiene, D.; Slepetiene, A.; Lepane, V. Effect of long-term application of organic fertilizers on improving organic matter quality in acid soil. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 2022, 68, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Shen, L.Y.; Ma, M.Y.; Xu, B.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Sha, C.Y.; Ye, C.M.; Xiong, L.J.; Huang, S.F. Effects of Pig Manure and Its Organic Fertilizer Application on Archaea and Methane Emission in Paddy Fields. Land (Basel) 2022, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, 2013.
- Wang, J.Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Ma, Y.C.; Sun, L.Y.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Huang, Q.W.; Sheng, Q.R. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions as affected by organic–inorganic mixed fertilizer from a rice paddy in southeast China. Journal of Soil and Sediments 2013, 13, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.S.; Zhan, Y.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhou, M.H.; Yan, G.X.; Wang, L.; Werner, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Potential benefits of liming to acid soils on climate change mitigation and food security. Global Change Biology 2021, 27, 2807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C.; Elsgaard, L.; Cheng, Y.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Abalos, D. Liming modifies greenhouse gas fluxes from soils: A meta-analysis of biological drivers. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2022, 340, 108182. [Google Scholar]
- Paradelo, R.; Virto, I.; Chenu, C. Net effect of liming on soil organic carbon stocks: A review. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2015, 202, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, J.; Brye, K.R.; Rector, C.; Gbur, E.E. Methane emissions from rice across a soil organic matter gradient in Alfisols of Arkansas, USA. Geoderma Regional 2019, 16, e00200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Rong, H.; Hallett, P.D.; Mooney, S.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, H.; Peng, X.H. Impact of soil puddling intensity on the root system architecture of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Soil & Tillage Research 2019, 193, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Gurajala, H.K.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environmental Pollution 2020, 257, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalos, D.; Liang, Z.; Dörsch, P.; Elsgaard, L. Trade-offs in greenhouse gas emissions across a liming-induced gradient of soil pH: Role of microbial structure and functioning. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2020, 150, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOA. Ministry of Agriculture of China. http://www.moa.gov.cn.
- Zhu, Q.C.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.X.; Zeng, M.F.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S. Enhanced acidification in Chinese croplands as derived from element budgets in the period 1980-2010. Science of the Total Environment 2018, 618, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.X.; Zeng, M.F.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S.; de Vries, W. Cropland acidification increases risk of yield losses and food insecurity in China. Environmental Pollution 2019, 256, 113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT. https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/EMN (accessed 4 November 2022).
- Jin, S.Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Han, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Ren, C.C.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wei, X.; Wu, Y.; Arthur, P.J.M.; Stefan, R.; Gu, B.J.; Chen, J. Decoupling livestock and crop production at the household level in China. Nature Sustainability 2021, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liao, P.; van Gestel, N.; Sun, Y.N.; Zeng, Y.J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W.J.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Lime application lowers the global warming potential of a double rice cropping system. Geoderma 2018, 325, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.H.; Chen, X.B.; Zheng, S.M.; Gunina, A.; Ning, Z.; Hu, Y.J.; Tang, H.M.; Rui, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, H.B.; Huang, D.Y.; Su, Y.R. Manure application accumulates more nitrogen in paddy soils than rice straw but less from fungal necromass. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2021, 319, 107575. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.D.; Liu, Y.R.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Fu, Q.L.; Chen, J.Z.; Hu, H.Q.; Huang, Q. Y Influence mechanisms of long-term fertilizations on the mineralization of organic matter in Ultisol. Soil & Tillage Research 2020, 201, 10459. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. The Earth’s Energy Budget.; Climate Feedbacks.; and Climate Sensitivity. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press.; 2021.
- Shang, Q.Y.; Yang, X.X.; Gao, C.M.; Wu, P.P.; Liu, J.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Zou, J.W.; Guo, S.W. Net annual global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in Chinese double rice-cropping systems: a 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Global Change Biology 2010, 17(6), 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods.; Springer Science & Business Media Press: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 327–342. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Ali, I.; Yuan, P.L.; Khan, A.; Hua, Z.; Wei, S.Q.; Jiang, L.G. Partial substation of organic fertilizer with chemical fertilizer improves soil biochemical attributes, rice yields, and restores bacterial community diversity in a paddy field. Frontiers in plant science 2022, 13, 895230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.A.; Shu, A.P.; Song, W.F.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.G.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, Z.B.; Gao, Z. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Q.; Liu, Y.R.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.L.; Muhammad, M.; Lv, Z.Z.; Hou, H.Q.; Lan, X.J.; Ji, J.H.; Waqas, A.; Li, D.C.; Zhang, H.M. Soil nutrients and heavy metal availability under long-term combined application of swine manure and synthetic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. Journal of Soils and Sediments 2020, 20, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Shi, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; He, X.H.; Evgenia, B. Improved nitrogen use efficiency, carbon sequestration and reduced environmental contamination under a gradient of manure application. Soil & Tillage Research 2022, 220, 105386. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.L.; Lam, S. K, Yan, X.Y.; Chen, D.L. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses and soil carbon balance? Environmental Science & Technology 2017, 51(13), 7450–7457. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.J.; Ros, G.H.; Xu, M.G.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Duan, Y.H.; de Vries, W. Long-term impacts of mineral and organic fertilizer inputs on nitrogen use efficiency for different cropping systems and site conditions in Southern China. European Journal of Agronomy 2023, 146, 126797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.R.; Chen, X.P.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.X.; Song, Y.L.; Tan, S.R.; Chen, Y.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.L. Effects of substituting synthetic nitrogen with organic amendments on crop yield.; net greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint: A global meta-analysis. Field Crop Research 2023, 301, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.F.; Zhou, J.; Peng, B.; Li, Q.J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Q.M.; Wang, Y.L. Differences of nitrogen uptake and utilization of conventional rice varieties with different growth duration. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 2011, 44(22), 4570–4582. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Domingo-Olivé, F.; Bosch-Serra, À.D.; Yagüe, M.R.; Poch, R.M.; Boixadera, J. Long term application of dairy cattle manure and pig slurry to winter cereals improves soil quality. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 2016, 104, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Khera, T.S.; Doran, J.W. Mineralization and denitrification in upland, nearly saturated and flooded subtropical soil II. Effect of organic manures varying in N content and C:N ratio. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2000, 31, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, D.C.; Samson, M.I.; Gapas, P. Inhibition of nitrogen mineralization in young humic fractions by anaerobic decomposition of rice crop residues. European Journal of Soil Science 2007, 58, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Fang, Q.C.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F.S. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biology 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.L.; Li, S.Q.; Jin, Y.G.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.W.; Zou, J.W. Linking methane emissions to methanogenic and methanotrophic communities under different fertilization strategies in rice paddies. Geoderma 2019, 347, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.; Klose, M. Dynamics of the methanogenic archaeal community in anoxic rice soil upon addition of straw. European Journal of Soil Science 2006, 57, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Lueders, T.; Friedrich, M.W.; Conrad, R. Methanogenic populations involved in the degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2001, 38, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Decock, C. Effects of organic fertilizers on the soil microorganisms responsible for N2O emissions: a review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.H.; Li, L.L.; Xie, J.H.; Wang, J.B.; Anwar, S.; Du, C.L.; Zhou, Y.J. Substituting inorganic fertilizers with organic amendment reduced nitrous oxide emissions by affecting nitrifiers’ microbial community. Land 2022, 11(10), 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xie, G.X.; Yang, Z.H.; He, N.; Yang, D.; Liu, M.D. Variation in abundance, diversity, and composition of nirK and nirS containing denitrifying bacterial communities in a red paddy soil as affected by combined organic-chemical fertilization. Applied Soil Ecology 2021, 166, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D. Biogeochemistry of N2O uptake and consumption in submerged soils and rice fields and implications in climate change. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2013, 43, 2653–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Qin, T.; Du, X.Z.; Sheng, F.; Li, C.F. Effects of irrigation regime and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and grain yields from paddy fields in central China. Agricultural Water Management 2021, 250, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Yang, C.F.; Carswell, A.M.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.L.; Xu, M.G. Co-amelioration of red soil acidity and fertility with pig manure rather than liming. Soil use and management 2023, 39, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Chang, S.X.; Zhang, Q.P. Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: a global meta-analysis. Journal of Soils and Sediments 2019, 19, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; Van Gestel, N.C.; Zeng, Y.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Liming and straw retention interact to increase nitrogen uptake and grain yield in a double rice-cropping system. Field Crop Research 2018, 216, 217–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.N.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.J.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Liming reduces nitrogen uptake from chemical fertilizer but increases that from straw in a double rice cropping system. Soil & Tillage Research 2024, 235, 105873. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ji, X.; Chao, C.; Liu, Z.B.; Zhu, J.; Peng, H. Effects of increasing lime application rates on microbial diversity and community structure in paddy soils. Applied Soil Ecology 2021, 161, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, F.; Bochu, V.; Findeling, A.; Doelsch, E. Repeated pig manure applications modify nitrate and chloride competition and fluxes in a Nitisol. Science of the Total Environment 2015, 511, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Bell, S.M.; Liu, J.S.; Sun, Y.N.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zhang, H.C.; Huang, S. Interaction of lime application and straw retention on ammonia emissions from a double-cropped rice field. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2023, 344, 108309. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Baldock, J.A.; Butterly, C.R.; Gazey, C. Long-term effect of lime application on the chemical composition of soil organic carbon in acid soils varying in texture and liming history. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2016, 52, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.D.; Xu, P.; Zhou, W.; Shaaban, M.; Zhao, J.S.; Ren, T.; Lu, J.W.; Hu, R.G. Prior nitrogen fertilization regulates CH4 emissions from rice cultivation by increasing soil carbon storage in a rapeseed-rice rotation. Applied Soil Ecology 2020, 155, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Palmada, T.; Berben, P.; Saggar, S.; Luo, J.F.; McMillan, A.M.S. Influence of liming-induced pH changes on nitrous oxide emission.; nirS.; nirK and nosZ gene abundance from applied cattle urine in allophanic and fluvial grazed pasture soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2020, 56, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.A.; Tarin, M.W.K.; Guo, J.X.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, G. Soil liming effects on CH4, N2O emission and Cd, Pb accumulation in upland and paddy rice. Environmental Pollution 2019, 248, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnie, N.; Rüdiger, R.; Joseph, P.G.; Mekonnen, G.; Holger, W.; Cargele, M.; Roland, B.; Nicolas, B. Nitrogen fertilization and liming increased CO2 and N2O emissions from tropical ferralsols, but not from a vertisol. Soil Use and Management 2023, 39, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Hink, L.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Archaea produce lower yields of N2O than bacteria during aerobic ammonia oxidation in soil. Environmental Microbiology 2017, 19, 4829–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, E.; Teutscherova, N.; Pastorelli, R.; Lagomarsino, A.; Giagnoni, L.; Renella, G. Liming reduces N2O emissions from Mediterranean soil after-rewetting and affects the size, structure and transcription of microbial communities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2020, 147, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.P.; Khalid, M.S.; Peng, Q.A.; Xu, X.Y.; Wu, L.; Younas, A.; Bashir, S.; Mo, Y.L.; Lin, S.; Zafar-Ul-Hye, M.; Abid, M.; Hu, R.G. Reduction in soil N2O emissions by pH manipulation and enhanced nosZ gene transcription under different water regimes. Environmental Pollution 2018, 235, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, L.; Bergaust, L.; Liu, B.; Frostegard, A. Regulation of denitrification at the cellular level: a clue to the understanding of N2O emissions from soils. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2012, 367, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Elsgaard, L. Nitrous oxide fluxes from long-term limed soils following P and glucose addition: Nonlinear response to liming rates and interaction from added P. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 797, 148933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Chang, S.X.; Xu, M.G.; Cai, Z.C.; Müller, C. Contrasting effects of different pH-raising materials on N2O emissions in acidic upland soils. European Journal of Soil Science 2021, 72, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.C.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Bai, T.S.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wang, H.; Sheng, X.J.; Sean, B.; et al. Intermediate soil acidification induces highest nitrous oxide emissions. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Xiong, Z.Q. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity from the double rice system with integrated soil-crop system management: A three-year field study. Atmospheric Environment 2015, 116, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CH4 (kg ha-1) |
N2O (g ha-1) |
GWP (kg CO2 eq ha-1) |
Yield (kg ha-1) |
GHGI (kg CO2 eq kg-1) |
|
| Treatment (T)a | |||||
| CF | 149c | 413a | 4123c | 7146a | 0.60c |
| 1/2N + M | 475a | 534a | 12973a | 6742b | 1.97a |
| 1/2N + M + L | 301b | 444a | 8257b | 6686b | 1.25b |
| Crop (C)b | |||||
| Early rice | 283b | 330b | 7740b | 6753b | 1.16b |
| Late rice | 333a | 598a | 9162a | 6963a | 1.38a |
| Year (Y)c | |||||
| 2019 | 331a | 405b | 9043a | 7375a | 1.26a |
| 2020 | 286b | 522a | 7860b | 6342b | 1.28a |
| F-values | |||||
| T*C | 11.2*** | NS | 11.2*** | 199*** | 9.6*** |
| T*Y | 13.8*** | NS | 13.8*** | NS | 9.9*** |
| C*Y | 60.4*** | NS | 60.3*** | NS | 246*** |
| T*C*Y | 21.2*** | NS | 21.2*** | NS | 49.6*** |
| pH | SOM (g kg-1) | |
| Treatment (T)a | ||
| CF | 5.4b | 19.0b |
| 1/2N + M | 5.5b | 20.7a |
| 1/2N + M + L | 5.9a | 20.4a |
| Year (Y)b | ||
| 2019 | 5.7a | 20.1a |
| 2020 | 5.6a | 20.0a |
| F-values | ||
| T | 22.3*** | 11.7*** |
| Y | NS | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





