1. Introduction
Doppler renal resistive index (RRI) has been used for many decades to predict renal dysfunction in a range of patient presentations [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Despite its widespread use in the assessment of pathology in both native and transplant kidneys, the determinants of RRI are poorly understood. This makes interpretation of RRI values difficult and has led to neglect of this potentially useful marker in some areas of practice.
This paper explores the theoretical and patient factors that influence RRI and their relative impact. Better understanding of these will inform interpretation of RRI measurements in the presence of pathology and as a predictor of progressive renal dysfunction.
2. Methods
A range of subject-specific electronic data bases were used to identify relevant papers including EMBASE, Pubmed, Web of Science, Scopus, BioMed Central, EBSCO Medical databases, Medline and the Cochrane library. No date limitations were set.
Key search terms emerged from an initial scoping search and reflect the varied terminology used in papers exploring the determinants of RRI. English language papers reporting the use of Doppler renal resistive index use a variety of synonymous terms and abbreviations including renal RI, renal resistive index, renal Doppler, RI and RRI. In subsequent stages of the search these terms were used to identify studies of Doppler ultrasound investigation of renal blood flow parameters.
A narrative interpretive review of studies was undertaken exploring the theoretical, experimental, and clinical evidence for factors affecting RRI.
3. What Is Renal Resistive Index (RRI) and What Does It Measure?
RRI is essentially an expression of the percentage reduction in end diastolic flow in relation to maximum flow at peak systole within a selected renal vessel.
Any physiological or pathological influences that affect relative flow velocities at diastole and systole will change the value of RI. Emerging initially as a measure of renal function in patients with renal artery stenosis [
6] RRI was assumed to be associated directly with altered resistance to flow within the kidney and with a range of renal pathological structural changes. However, subsequent experimental and in vivo studies have demonstrated that RRI is more closely associated with several systemic factors [
7,
8] .
Ironically, repeated clinical studies have demonstrated that RRI appears to have very little dependence on renal vascular resistance [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14] . For this reason, use of RRI as a useful (direct) indicator for renal disease has been challenged. However, in recent studies, RRI has been shown to be affected by a number of extra-renal factors that explain the observed value of RRI as a strong prognostic indicator for patients with renal damage and a potential predictor of acute kidney injury (AKI) risk.
3.1. Theoretical Determinants of RI
Despite the term ‘resistive index’, this dimensionless ratio is more accurately an indicator of flow pulsatility. Simplified analysis demonstrates that this model of RI is largely independent of vascular resistance [
12].
Although luminal cross-sectional area and pressure within the vessel will change during systole and diastole, renal vascular resistance is unlikely to alter during the time frame of a single cardiac cycle [
11,
12].
Therefore, if R remains constant between systole and diastole, then
This simplified model outlined by O’Neil explains in part the relative independence of RRI from vascular resistance but, does not take into account the complexity associated with distal vascular compliance (capacitance) or non-uniform flow throughout the cardiac cycle. Once impedance of the distal vascular bed is considered, RI does demonstrate some dependence on resistance [
12].
3.2. Key Haemodynamic Determinants of RRI
Whilst experimental and in vivo studies demonstrate an inconsistent relationship between RRI and vascular resistance, three haemodynamic parameters emerge that appear to have a direct impact on RRI.
Ratio of diastolic to systolic blood pressure
Combined effect of interstitial and venous pressure
Ratio of lumen area in systole and diastole at the sample site
O’Neil [
12] clarifies the mathematical relationship between these factors and the simplified flow equation below.
P0 = Combined interstitial and venous pressure.
Ratio of diastolic to systolic blood pressure (Pdiast and Psyst )
The ratio of Pdiast and Psyst is an inverse function of pulse pressure and is affected primarily by cardiac output and systemic arterial compliance (vessel stiffness).
Experimental data confirm a strong correlation between RI and aortic pulse pressure [
9,
11,
12]. This is supported by the findings of several clinical studies where pulse pressure appears to be the main determinant of renal RI [
10,
14].
Pulse pressure is affected by:
These factors are explored further here.
The combined effect of interstitial and venous pressure (Po) is essentially the renal capil lary wedge pressure. Anything that changes interstitial or venous pressure will therefore affect RI.
The kidney is encapsulated by a thin fibrous sheath that provides a degree of stability and protection for the organ. In the presence of hydronephrosis, acute inflammation, oedema or haematoma, the kidney volume increases. However, this expansion of the kidney is limited, with the renal capsule providing the major opposing force [
15]. Intrarenal pressure therefore increases under these conditions. Even excessive pressure applied through the ultrasound transducer can result in an increase in interstitial pressure that may influence RRI [
16]. This is particularly relevant in transplant kidneys that are relatively superficial. Similarly, venous pressure may change due to renal vein thrombosis, hypovolaemia or vasoplegia (due to sepsis or post-surgery).
Ratio of lumen area in systole and diastole at the sample site
Vessel lumen cross sectional area (LA) changes throughout the cardiac cycle.
The relative cross sectional area at systole and diastole is a theoretical determinant of RRI and is affected by
3.3. Determinants of RRI: Evidence from Clinical and Experimental Studies
Numerous clinical and experimental studies highlight the complexity of these associations between RRI and systemic haemodynamic factors. Early investigations (primarily of patients presenting with renal artery stenosis) focused on renal recovery, identifying poor outcome in patients with raised RRI [
6,
11]. Subsequent studies in critical care have generated a wealth of evidence supporting the close association of RRI with a number of outcome measures including renal recovery, need for long term renal replacement therapy and death [
7,
17].
Despite the promising role of raised RRI in patient prognosis and predication of renal recovery, research evidence confirms that systemic factors are the key determinants of RRI and that RRI cannot be considered a useful direct indicator of renal disease. Interpretation of these somewhat contradictory findings requires a better understanding of the complex association between non-renal haemodynamic factors, individual patient characteristics, how these affect renal blood flow and their potential influence on risk of renal damage. The impact and relative contribution of these factors as determinants of RRI are explored further.
3.3.1. Systemic Factors - How is RRI Affected by Blood Pressure?
The observed relationship between RRI and the components of blood pressure (steady and pulsatile) are consistent with the theoretical understanding of RRI, and offer some insight into how these systemic factors may result in renal injury. General population studies [
13] and studies of hypertensive patients [
11,
18] demonstrate a somewhat surprising but consistent inverse relationship between RRI and mean arterial pressure (MAP) that appears to be independent of other co-variables [
8]. Whilst this is not a direct indicator of renal function, reduced MAP over time would be consistent with a pattern of poor renal perfusion. However, this relationship does not appear to hold in critically ill patients with sepsis where poor correlation between RRI and MAP is noted [
19,
20]. This suggests that, in these patients, other factors affecting renal circulation may have a more dominant role in RRI. (Whilst this effect is poorly understood, this does limit the use of RRI in management of fluid balance in these sick patients.)
3.3.2. Influence of Pulse Pressure on RRI
A key determinant of pulse pressure is compliance of the large arteries. In a normal patient, as blood is ejected from the heart, expansion of the aorta effectively dampens the pulse. This effect contributes to maintenance of continuous steady flow to the kidneys. Where compliance of the aorta is reduced due to vessel wall stiffening, this damping effect is absent, and the renal microvasculature is exposed to high pulse pressure. In a review of studies exploring the association between aortic stiffening and microvascular disease, O’Rourke et al [
21] proposed that these high-pressure fluctuations (increasing markedly with age of the patient) may result in epithelial damage leading to renal insufficiency.
These findings led to a plethora of studies that explore the relationship between RRI and central pulse pressure (cPP) or peripheral pulse pressure (pPP) [
9,
13,
22,
23,
24]. In all cases, a consistent and significant positive association was noted.
One of the key challenges of studies exploring this association was the difficulty of separating the contributory effects of renal and non-renal factors. This was further complicated by the fact that a high proportion of studies were undertaken in critical care, where patients have multiple confounding co-morbidities and high incidence of chronic renal disease. This has been resolved (at least in part) by studies of transplant kidneys where RRI is also noted to be strongly dependent on aortic pulse pressure of the
recipient rather than the donor [
9,
10,
25,
26].
In a landmark study in 2013, Naesens et al [
10] compared baseline RRI and RRI at the time of biopsy in 321 transplant recipients. Unlike studies of native kidneys, in transplant patients, the relative contribution of renal and systemic factors on RRI can be explored. This allowed close scrutiny of the relationship between RRI measurements and renal histology. In this study, the strongest independent factor for increased RRI was recipient age (P<0.001). However, there was also close association with increased pulse pressure and reduced MAP. The authors conclude that serial measurements of RRI at the time of biopsy reflect characteristics of the
recipient rather than the graft. This important study supports the conclusion that RRI is of limited use as a
direct indicator of renal function. However, in the same study population, RRI was closely associated with recipient survival and provides useful prognostic stratification in sick patients.
3.3.3. Relationship between RRI and Cardiac Output
Normal renal function is dependent on a constant blood supply which is, in turn, dependent on cardiac output. Renal autoregulation is essential in maintaining stable glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The heart and kidneys also play a closely associated role in maintaining haemodynamic stability and severe dysfunction in either of these organs is unlikely to occur in isolation [
27].
The amount of blood available to the kidney (roughly 20% of total cardiac output) is dependent on total blood volume and on left ventricular output. Kuznetsova et al [
13] explored the relationship between RRI and left ventricular outflow in a general population study (n = 171). Doppler assessment of left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and transmitral peak velocities demonstrated significant association of RRI with central pulse pressure and left ventricular systolic and diastolic Doppler blood flow indexes. (RRI was significantly and positively associated with LVOT and E peak velocities (P ≤ 0.012) and VTIs (P ≤ 0.010).) Although the precise causal relationship is unclear (acknowledged by the authors), this study demonstrates that, in an unselected population, the Doppler spectral profile within the intrarenal arteries is influenced by cardiac hemodynamic factors. However, in the same study, the correlation between RRI and cardiac factors was not as strong as that observed with central pulse pressure (P < 0.0001).
The findings of this study (of well patients) are difficult to translate to a sick or elderly in-hospital population where cardiac output is likely to be compromised. No studies are identified that explore simultaneous longitudinal changes in cardiac and renal haemodynamics. However, altered cardiac output in critically unwell or acute presentations is likely to be of more significance than this study suggests. This could be particularly relevant in older patients presenting with reduced left heart function in combination with hypovolaemia or vasoplegia associated with fluid loss or sepsis.
4. Discussion: Renal Causes of Altered RRI
The experimental and clinical studies reviewed here provide compelling evidence that changes in RRI are determined predominantly by systemic haemodynamics rather than isolated renal pathology. However, there are instances where a direct causal link with renal factors is demonstrated.
4.1. Interstitial Pressure and Vascular Compliance
RRI clearly reflects renal artery pulsatility [
8,
13] and as such may be a useful indicator of early-stage renal microvascular damage. From the mathematical model outlined by O’Neil [
12], raised interstitial pressure (iP) will also affect RRI. The impact of moderately increased iP may be masked by autoregulation. However, where iP is more markedly increased, luminal cross-sectional area and end diastolic velocity (EDV) are likely to be affected. These predicted findings are confirmed by experimental study of ex-vivo hydronephrotic kidneys [
28]. Although RRI appears to be largely independent of vascular resistance (the ratio of pressure to flow) [
11,
25,
28] experimental evidence supports the hypothesis that changes in
compliance of the renal vascular bed and interstitium are contributory factors in the raised RRI values observed where renal disease is present. Direct evaluation of the stiffness and elasticity of intrarenal arteries is problematic. However, in an elegant study of isolated perfused rabbit kidneys, Murphy et al [
29] explored this effect indirectly by inducing raised interstitial pressure via incremental increase in ureteral pressure.
As a surrogate measure of overall distensibility of the vascular bed, vascular conductance (ratio of flow to pressure) was measured (along with mean flow, mean pressure and RRI) under different driving arterial pressures. They hypothesized that the raised iP caused by obstruction of the kidney would restrict distension of the intrarenal arteries and arterioles. In this landmark study, increase in ureteral pressure was associated with:
consistent and reproducible increase in RRI
increase in RVR (overall mean renal vascular resistance)
significant reduction in flow
significant reduction in mean conductance
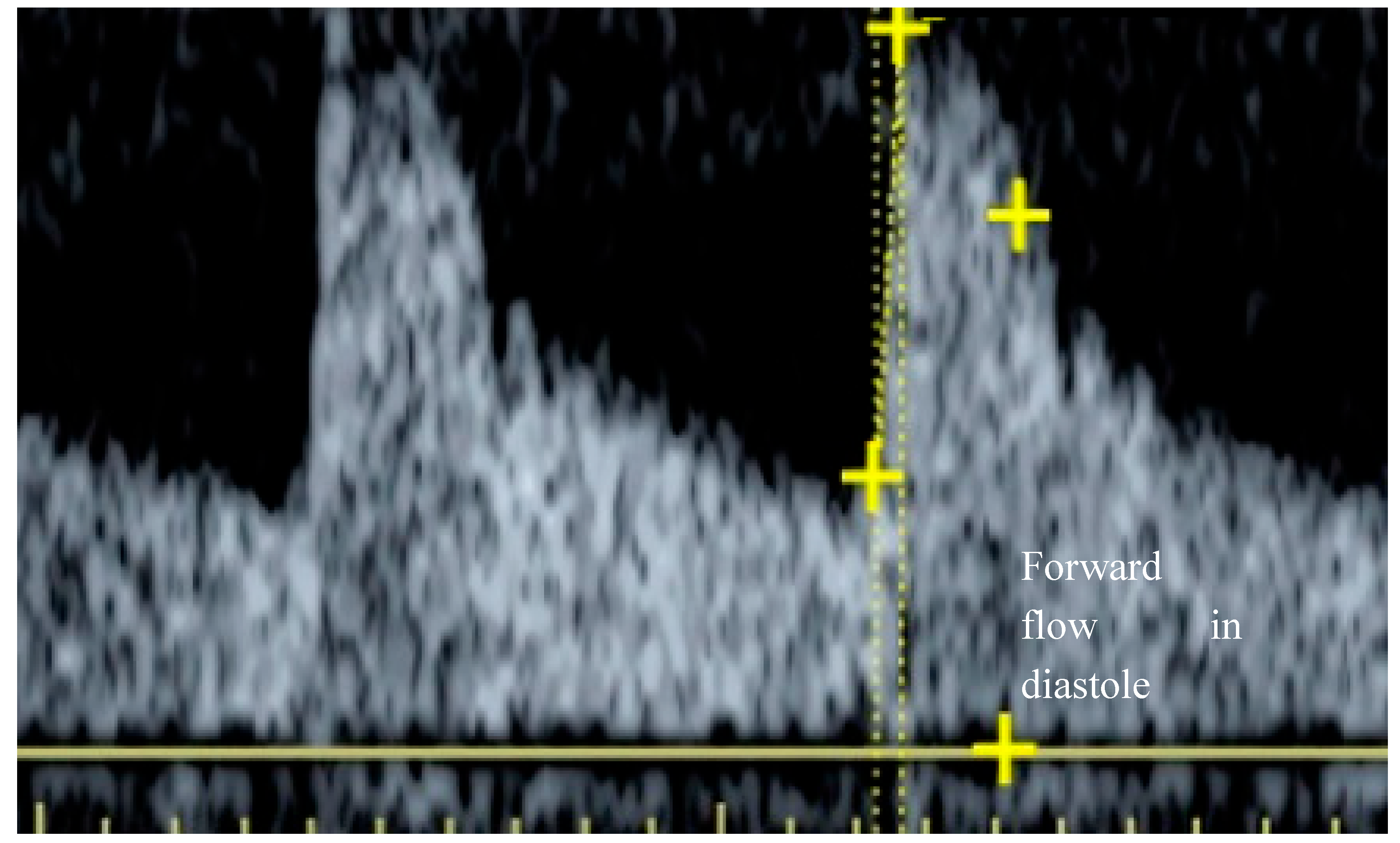
(P< 0.05 for all values) Of particular note was the relative reduction of conductance measured at systole and diastole. A greater proportional reduction (and hence flow) was observed during diastole. The kidney is inherently a low resistance structure, evidenced by the positive flow throughout diastole seen in a normal spectral waveform (
Figure 1).
In a normal kidney, iP is approximately zero. Arterioles have high cross sectional area and these small compliant vessels are free to expand during systole. The distensibility of a vessel is dependent on wall stiffness, the pressure exerted through the wall (transmural pressure) and the compliance of the surrounding interstitium. Murphy et al [
29] hypothesised that, when iP is raised, arterioles will dilate to approximately full extension during systole, but will collapse down to close to occlusion during diastole. End diastolic flow is therefore reduced. As RRI is a ratio of peak systolic to end diastolic flow (PSV – EDV / PSV) this would account for the observed increase in RRI. The relative contribution of renal vascular resistance and compliance in raising RRI is difficult to determine from this study. However, previous experimental work by the same authors confirmed that even marked increase in vascular resistance (through pharmacologically induced vasoconstriction) resulted in only minimal increase in RRI [
25,
29]. They conclude that the impact of raised iP on conductance (particularly at diastole) seems to be the reason why RRI rises with increased ureteral pressure.
Results from these important studies suggest that, in addition to pulse pressure, raised interstitial pressure has an important role in increasing RRI. This raises the possibility that RRI could be a direct indicator of renal pathologies that increase interstitial pressure or reduce vessel distensibility.
4.2. Patient Characteristics Affecting RRI
In addition to the haemodynamic factors considered here, several patient anthropometric characteristics have also been linked with RRI. General population studies
13,24 show a strong positive correlation between RRI and subject age, female gender and body weight and a negative correlation with height. In addition to these independent patient characteristics, in large studies of hypertensive patients [
9,
22,
23] multi-variate analysis demonstrates a positive correlation between RRI, hypercholesterolemia and use of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors. In general, patient age is identified in all studies as the strongest independent determinant of RRI.
4.3. Reduced Renal Functional Reserve and Risk of Acute Kidney Injury
Review of the studies considered here identifies significant historic confusion regarding the determinants of RRI, which was long regarded as a direct reflection of renal vascular resistance [
7,
29]. This view of RRI, based on early experimental data from animal studies, led to speculation that RRI could provide a useful non-invasive measure of renal perfusion and intrarenal pathology. However, as a better understanding of the influence of systemic haemodynamic factors has emerged, it is more useful to think of raised RRI as an indicator of reduced renal functional reserve. As such, raised RRI can be considered a
‘red flag’ marker for the conditions in which AKI
risk is increased.
The aetiology of AKI is highly complicated with multiple contributory factors and complex associations between pathological conditions, acute events and renal auto regulatory response. Individual risk of the rapid functional decline associated with AKI is dependent on pre-existing chronic renal damage and the severity of acute insult. In broad terms, the picture emerging from review of recent literature is that there is significant overlap between the determinants of RRI and age-related risk factors (such as arterial stiffening) that result in gradual functional decline. This pattern is consistent with evidence from critical care that indicates that raised RRI performs better than all other independent patient characteristics at predicting outcome of an episode of AKI [
29,
32,
33,
35,
36].
Although the key determinants of RRI discussed here are systemic, there is compelling evidence that RRI can also be influenced directly by raised interstitial and venous pressure. This suggests that, as well as acting as a marker for chronic reduced functional reserve, raised RRI may also have potential as a marker for sub-clinical AKI in patients who are acutely unwell. The association between systemic and renal determinants of RRI and raised risk of AKI are summarised in
Table 2 and Table 3.
Table 1.
Systemic determinants of RRI associated with renal functional decline.
Table 1.
Systemic determinants of RRI associated with renal functional decline.
| Patient factor |
Key haemodynamic determinant |
Impact on intrarenal blood flow |
Impact on RRI |
Significance of factor as determinant of RRI |
Potential link to immediate (or future) AKI risk |
| Hypertension |
↑ systolic pressure |
↑ PSV |
↑ RRI |
major |
Microvascular trauma over time → ↓ functional reserve |
| Increased central pulse pressure |
↑ systolic pressure |
↑ PSV |
↑ RRI |
major |
Microvascular trauma over time → ↓ functional reserve |
| Increased systemic arterial stiffness |
↓ aortic compliance |
↑ PSV |
↑ RRI |
major |
Microvascular trauma over time → ↓ functional reserve |
| Left heart failure → decreased flow LVOT |
↓ diastolic pressure |
↓ EDV |
↑ RRI |
minor |
Long term hypo-perfusion → ischemic damage → ↓ functional reserve |
| Reduced mean arterial pressure (MAP) |
Poor renal perfusion over time |
↓ EDV |
↑ RRI |
minor |
Long term hypo-perfusion → ischemic damage → ↓ functional reserve |
| Bradycardia |
Increased diastolic duration |
↓ EDV |
↑ RRI |
minor |
Long term hypo-perfusion → ischemic damage → ↓ functional reserve |
Table 2.
Acute determinants of RRI associated with rapid renal functional decline.
Table 2.
Acute determinants of RRI associated with rapid renal functional decline.
| Patient factor |
Key haemodynamic determinant |
Impact on intrarenal blood flow |
Impact on RRI |
Potential link to immediate (or future) AKI risk |
Hydronephrosis
Acute inflammation
Oedema
Haematoma |
↑ interstitial pressure |
↓ EDV
↑ ratio of luminal CSA |
↑ RRI |
Impact may be masked by auto-regulation. |
Renal vein thrombosis
Hypovolaemia
Vasoplegia (sepsis or post-surgery). |
↑ venous pressure |
↓ EDV |
↑ RRI |
Tubular ischemia due to hypo-perfusion |
Trauma
Rhabdomyolysis
+ hypovolaemia |
*renal vaso-constriction
↓ renal blood flow |
↓ EDV |
↑ RRI |
Tubular ischemia due to hypo-perfusion |
5. Summary and Conclusion
Use of RRI as a marker for renal disease has something of a checkered history. As recognition of the importance of systemic determinants emerged, the concept of RI as a direct indicator of declining renal function, particularly in native kidneys, has been largely rejected. However, a plethora of studies over the last decade have identify RRI as a useful prognostic indicator for a range of co-morbidities in patients who are acutely unwell. RRI more accurately reflects the complex combined effects of systemic circulation and renal microcirculation and is now rightly understood to be a marker of systemic cardiovascular risk rather than an isolated prognostic indicator for renal recovery [
30]. However, high RRI (≥ 0.7) compares favourably with conventional markers (albuminuria and low eGFR) as an early indicator of diabetic kidney disease, and as a potential marker for sub-clinical acute kidney injury (AKI) and post procedural AKI risk [
7,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36].
There are no curative therapies for the damage caused by these acute or chronic conditions, both of which result in irreversible reduction in renal function. Therefore, outcomes can only be improved by preventive care and early intervention. Despite high level focus on this as a research priority, a reliable method of early detection and assessment of individual risk of AKI is still proving to be elusive [
37]. The current method of AKI diagnosis is based on assessment of changes in serum creatinine level (sCr) which typically will rise 2-3 days after the initial renal insult and on reduced urine output over more than 6 hours [
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. Both markers have poor sensitivity and specificity and are limited by an inherent time lag between observed changes and the time of initial injury to the kidney.
Evidence for the re-emergence of RRI as a marker for renal compromise is largely from point-of-care studies of acutely unwell patients in critical care and may be difficult to translate into a general population. However, these studies have highlighted the significant potential for RRI as a useful alternative to conventional protocols for staging and management of long-term conditions that impact on renal functional reserve. In an aging population, early detection and preventive care would have significant potential cost savings. This may have further significance as the long-term impact of COVID-19 continues to emerge and the reported association of this condition with AKI risk is better understood [
43].
Anecdotally, RRI measurement in patients presenting to central imaging departments in the UK does not form part of routine imaging protocols. In view of the wealth of recent evidence emerging from point-of-care studies, this is perhaps worth revisiting. However, in all contexts, a good appreciation of the complexity of RRI is essential if diagnostic confusion is to be avoided. In this review, the key haemodynamic determinants of RRI have been outlined and their relative importance explored. By gaining a better understanding of the systemic and renal factors that influence RRI, ultrasound users will be better prepared to understand and interpret changes in RRI across a range of patient presentations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, HV; methodology, HV.; formal analysis, HV.; writing—original draft preparation, HV.; writing—review and editing, RIL and MS.; supervision, RIL and MS. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this literature-based review.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created for this narrative review of published literature. All data quoted are available from the referenced publications.
References
- Darmon M, Schortgen F, Vargas F, Liazydi A, Schlemmer B, Brun-Buisson C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of Doppler renal resistive index for reversibility of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Medicine. 2011, 37, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbani F, Boddi M, Cammelli R, Cecchi A, Spinelli E, Bonizzoli M, et al. Prognostic value of doppler-based renal arterial resistive index in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: Preliminary results. Intensive Care Medicine. 2010, 36, S177. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D, Darmon M. Renal Doppler to assess renal perfusion in the critically ill: a reappraisal. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1751–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viazzi F, Leoncini G, Derchi LE, Pontremoli R. Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the management of the hypertensive patient. J Hypertens. 2014, 32, 149–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinot PG, Bernard E, Abou Arab O, Badoux L, Diouf M, Zogheib E, et al. Doppler-based renal resistive index can assess progression of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia. 2013, 27, 890–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radermacher J, Chavan A, Bleck J, Vitzthum A, Stoess B, Gebel MJ, et al. Use of Doppler ultrasonography to predict the outcome of therapy for renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2001, 344, 410–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddi M, Bonizzoli M, Chiostri M, Begliomini D, Molinaro A, Tadini Buoninsegni L, et al. Renal Resistive Index and mortality in critical patients with acute kidney injury. European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2016, 46, 242–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauwenberghs N, Kuznetsova T. Determinants and Prognostic Significance of the Renal Resistive Index. Pulse. 2016, 3, 172–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto J, Ito S. Central pulse pressure and aortic stiffness determine renal hemodynamics: pathophysiological implication for microalbuminuria in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011, 58, 839–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens M, Heylen L, Lerut E, Claes K, De Wever L, Claus F, et al. Intrarenal resistive index after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2013, 369, 1797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos JA, Townsend RR. Systemic arterial hemodynamics and the "renal resistive index:" What is in a name? Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 2014, 16, 170–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, WC. Renal Resistive Index A Case of Mistaken Identity. Hypertension. 2014, 64, 915–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova T, Cauwenberghs N, Knez J, Thijs L, Liu YP, Gu YM, et al. Doppler indexes of left ventricular systolic and diastolic flow and central pulse pressure in relation to renal resistive index. Am J Hypertens. 2015, 28, 535–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee MK, Hsu PC, Chu CY, Lee WH, Chen SC, Chen HC, et al. Significant Correlation between Brachial Pulse Pressure Index and Renal Resistive Index. Acta Cardiologica Sinica. 2015, 31, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert LA, Stuart KA, Stemper JA. Whole kidney volume/pressure relationships. Kidney International. 1975, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozniak MA, Kelcz F, Stratta RJ, Oberley TD. Extraneous factors affecting resistive index. Invest Radiol. 1988, 23, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninet S, Schnell D, Dewitte A, Zeni F, Meziani F, Darmon M. Doppler-based renal resistive index for prediction of renal dysfunction reversibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Critical Care. 2015, 30, 629–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabia J, Torguet P, Garcia I, Martin N, Mate G, Marin A, et al. The relationship between renal resistive index, arterial stiffness, and atherosclerotic burden: The link between macrocirculation and microcirculation. Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 2014, 16, 186–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitte A, Coquin J, Meyssignac B, Joannes-Boyau O, Fleureau C, Roze H, et al. Doppler resistive index to reflect regulation of renal vascular tone during sepsis and acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2012, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Lahmer T, Rasch S, Schnappauf C, Schmid RM, Huber W. Influence of volume administration on Doppler-based renal resistive index, renal hemodynamics and renal function in medical intensive care unit patients with septic-induced acute kidney injury: a pilot study. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1327–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Rourke MF, Safar ME. Relationship between aortic stiffening and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension. 2005, 46, 200–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco MA, Natale F, Mocerino R, Tassinario G, Calabro R. Renal resistive index and cardiovascular organ damage in a large population of hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens. 2007, 21, 291–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stea F, Sgro M, Faita F, Bruno RM, Cartoni G, Armenia S, et al. Relationship between wave reflection and renal damage in hypertensive patients: A retrospective analysis. Journal of Hypertension. 2013, 31, 2418–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte B, Pruijm M, Ackermann D, Vuistiner P, Eisenberger U, Guessous I, et al. Reference values and factors associated with renal resistive index in a family-based population study. Hypertension. 2014, 63, 136–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tublin ME, Tessler FN, Murphy ME. Correlation between renal vascular resistance, pulse pressure, and the resistive index in isolated perfused rabbit kidneys. Radiology. 1999, 213, 258–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgul A, Sasak G, Basaran C, Colak T, Ozdemir FN, Haberal M. Relationship of Renal Resistive Index and Cardiovascular Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients. Transplantation Proceedings. 2009, 41, 2835–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock JS, Gottlieb SS. Cardiorenal syndrome: New perspectives. Circulation. 2010, 121, 2592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bude RO, Rubin JM. Relationship between the resistive index and vascular compliance and resistance. Radiology. 1999, 211, 411–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybraniec MT, Bożentowicz-Wikarek M, Chudek J, Mizia-Stec K. Pre-procedural renal resistive index accurately predicts contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with preserved renal function submitted to coronary angiography. International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 2016; 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Darabont R; Mihalcea D; Vinereanu D. Current insights into the significance of the renal resistive index in kidney and cardiovascular disease. Diagnostics, 2023; 13, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah M, Nafisi-Moghadam R, Nouri N. Relationship between Intra-renal Arterial Resistance Index (RI) and Albuminuria in Diabetic Patients. Iran J Diabetes Obes 2012, 4, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhamid Y, Fawzy M, Abd Al-Salam R, Gouda Y, Salem M. Relation between resistivity and pulsatility indices of renal and intrarenal arteries and degree of albuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients. Kasr Al Ainy Med J 2017, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables HK, Wiafe YA, Adu-Bredu TK. Value of Doppler ultrasound in early detection of diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound 2020, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty P, Szatjnic S, Ferre F, Conil J-M, Mayeur N, Fourcade O, et al. Doppler renal resistive index for early detection of acute kidney injury after major orthopaedic surgery: a prospective observational study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2015, 32, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J. B. Doppler-based renal resistive index for prediction of renal dysfunction reversibility: There are still some questions. Journal of Critical Care 2015, 30, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustiniano, E., Meco, M., Morenghi, E., Ruggieri, N., Cosseta, D., Cirri, S., et al. (2014). May renal resistive index be an early predictive tool of postoperative complications in major surgery? Preliminary results. BioMed Research International, 2014.
- Gudsoorkar PS; Nysather J; Thakar CV. Definition, Staging, and Role of Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of Cardiovascular Interventions. Interv Cardiol Clin, 2023; 12, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Darmon, M.; Ostermann, M.; Joannidis, M. Predictions are difficult…especially about AKI. Intensive Care Medicine, 2017, 43, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Johnson C, Karvellas CJ, Kutsiogiannis DJ, et al. Review article: Acute kidney injury in critical illness. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia-Journal Canadien D Anesthesie. 2010, 57, 985–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang CH, Lin CY, Tian YC, Jenq CC, Chang MY, Chen YC, et al. ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY CLASSIFICATION: COMPARISON OF AKIN AND RIFLE CRITERIA. Shock. 2010, 33, 247–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci Z, Cruz DN, Ronco C. Classification and staging of acute kidney injury: beyond the RIFLE and AKIN criteria. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011, 7, 201–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewington A, Kanagasundaram S. Renal Association Clinical Practice Guidelines on Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clinical Practice. 2011, 118, C349–C90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 rapid guideline: acute kidney injury in hospital NICE guideline [NG175]Published date: 06 May 2020 (accessed online 21/10/2020).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).