Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Phased Antenna Arrays
2.1. Structure of Antenna Arrays
3. Taguchi Method
3.1. Amplitude Synthesis of Antenna Array Radiation Pattern under Constraints
3.1.1. 10-Element Antenna Array
First Step: Initialization Problem
Second Step: Designating Input Parameters
| Experiment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 8 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 13 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 14 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 15 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 16 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 17 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 18 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 19 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 20 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 21 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 22 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 23 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 24 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 25 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| 26 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 27 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Experiment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 4 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 6 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 7 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 9 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| 12 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| 13 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| 14 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| 15 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 16 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 18 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| 19 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| 21 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 |
| 22 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| 23 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 |
| 24 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 |
| 26 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 27 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
Third Step: Conducting Experiments and Building a Response Table
- n: Number of parameters
- m: Number of levels (1, 2, 3)
- N: Number of level combinations
- i: i-th iteration
| Experiment | Fitness R | (S/N) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 12.97 | -22.26 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 11.19 | -20.98 |
| 3 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 10.56 | -20.47 |
| 4 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 9.91 | -19.92 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 9.70 | -19.73 |
| 6 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 13.86 | -22.83 |
| 7 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 8.67 | -18.76 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 15.53 | -23.82 |
| 9 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 16.81 | -24.51 |
| 10 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 9.32 | -19.39 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 9.31 | -19.38 |
| 12 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 7.61 | -17.63 |
| 13 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 8.28 | -18.36 |
| 14 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 9.88 | -19.90 |
| 15 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 10.99 | -20.82 |
| 16 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 9.03 | -19.12 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 13.93 | -22.88 |
| 18 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 11.27 | -21.04 |
| 19 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 6.84 | -16.70 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 10.13 | -20.11 |
| 21 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 9.70 | -19.73 |
| 22 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 8.26 | -18.34 |
| 23 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 10.97 | -20.81 |
| 24 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 10.95 | -20.78 |
| 25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 8.28 | -18.36 |
| 26 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 7.90 | -17.96 |
| 27 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 21.51 | -26.65 |
| Elements | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | -19.02 | -19.63 | -19.92 | -20.83 | -21.18 |
| Level 2 | -20.62 | -20.17 | -20.95 | -21.03 | -20.82 |
| Level 3 | -21.61 | -21.46 | -20.38 | -19.39 | -19.24 |
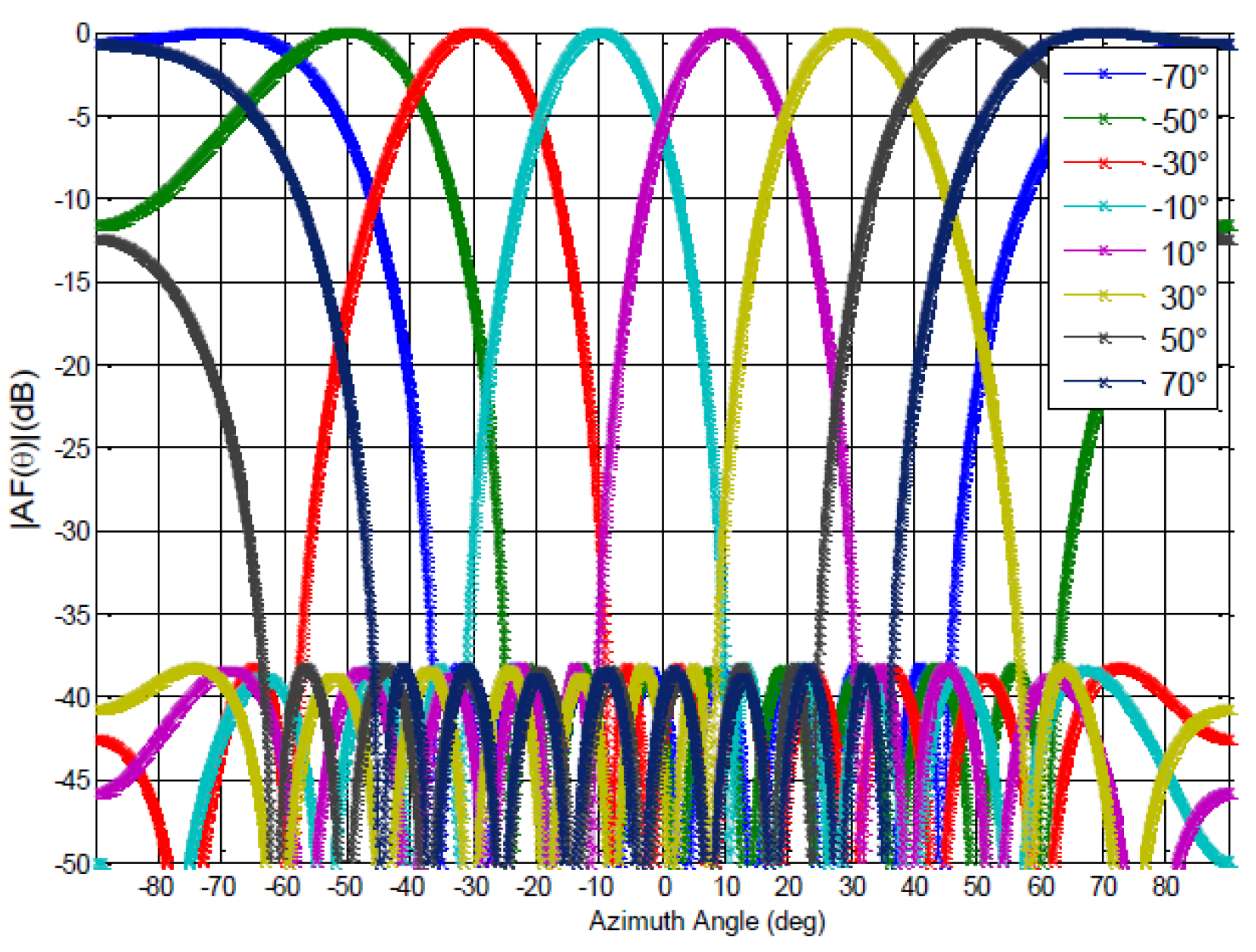
| Optimized values of | Maximum SLL |
|---|---|
| 1.0000 | -13.1526 |
| 0.8413 | -22.8982 |
| 0.9322 | |
| 0.7675 | |
| 0.6049 | |
| 0.5715 | |
| 0.4746 | |
| 0.4877 |
| Elements | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights | 1.0000 | 0.8984 | 0.7187 | 0.5015 | 0.3857 |
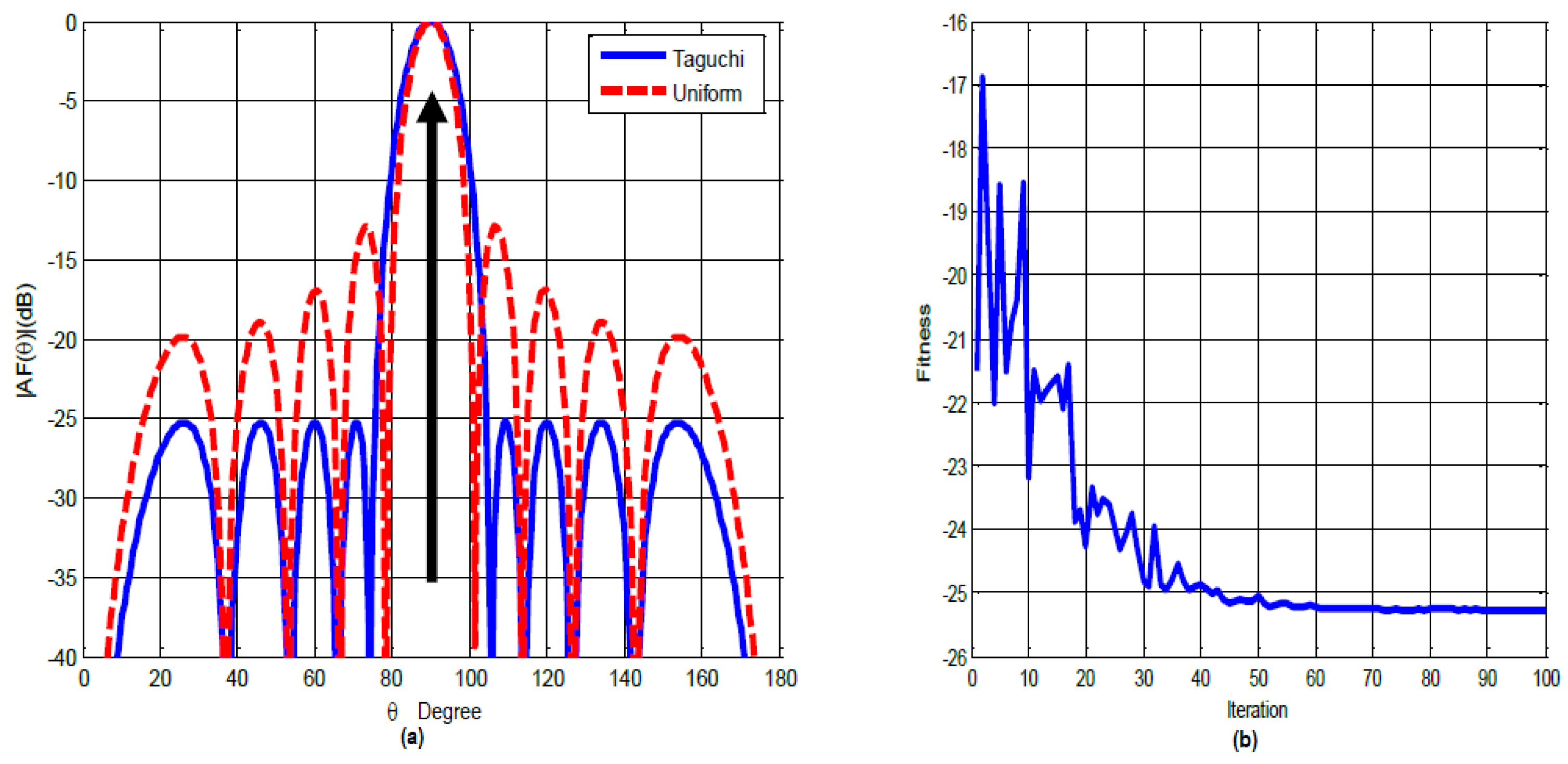
- A gain of 0.6 dB in terms of secondary lobes minimization.
- A convergence speed of 80 iterations for the Taguchi method.
- The real-time required for our digital optimization tool is approximately 10 seconds.
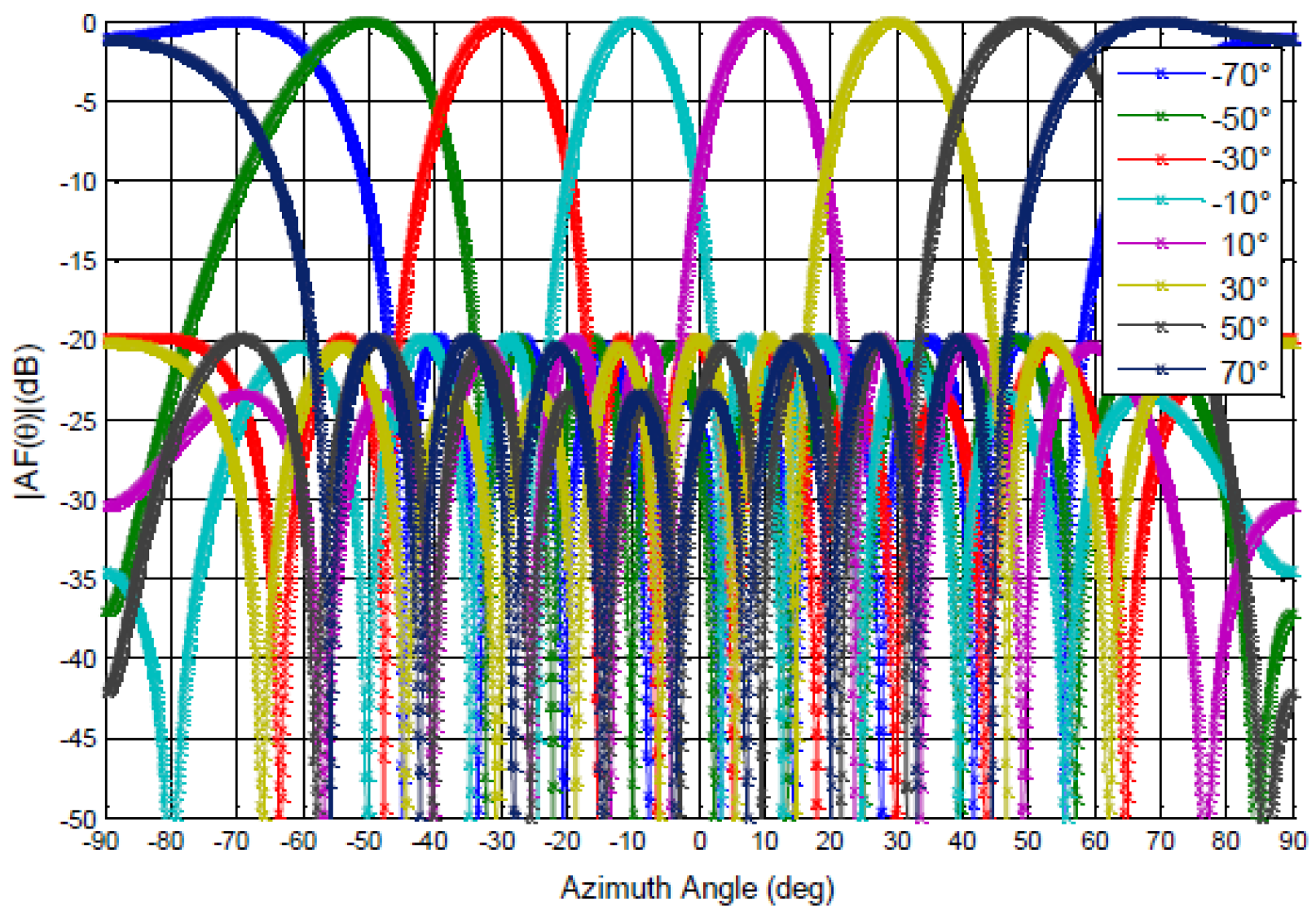
3.1.2. 16-Element Antenna Array
- Step 1: Determine the number of parameters ().
- Step 2: Determine the number of levels ().
- Step 3: Determine the strength ().
- Step 4: Determine the OA experimental design ().
- Step 5: Determine the reduced function ().
- Step 6: Determine the convergence value .
- As shown in Figure 5(b), the optimization objective is achieved after 66 iterations.
- The excitation weights of this optimized antenna array using the Taguchi method are indicated in Table 8.
-
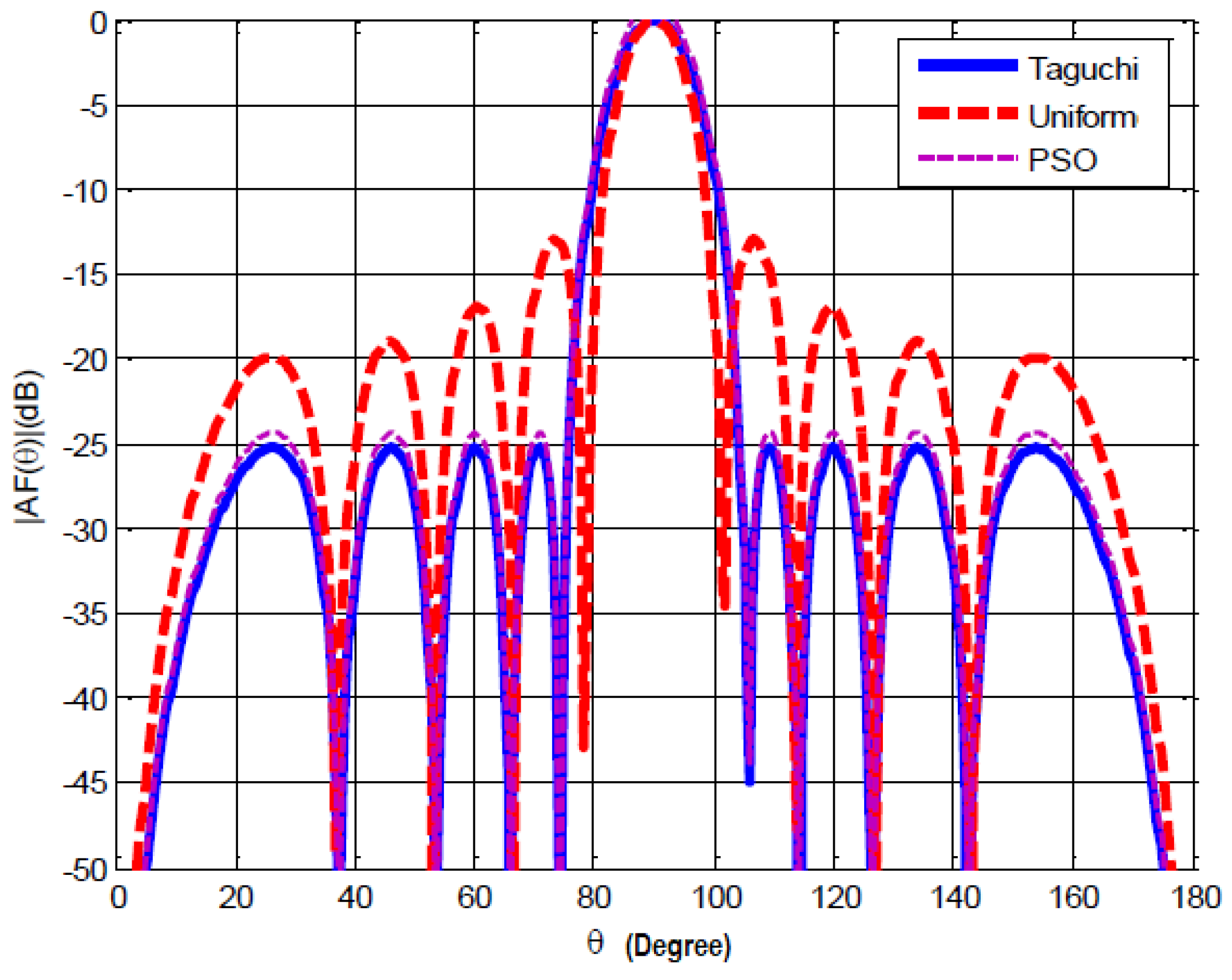
The results obtained compared to those of PSO (Figure 5) show that:
- -
- A gain of 0.8 dB in terms of minimizing the side lobes.
- -
- A convergence speed of 66 iterations for the Taguchi method.
- -
- 9 seconds as real-time required for our digital optimization tool.
| Elements | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights | 1.0000 | 0.9500 | 0.8575 | 0.7317 | 0.5861 | 0.4381 | 0.2988 | 0.2552 |
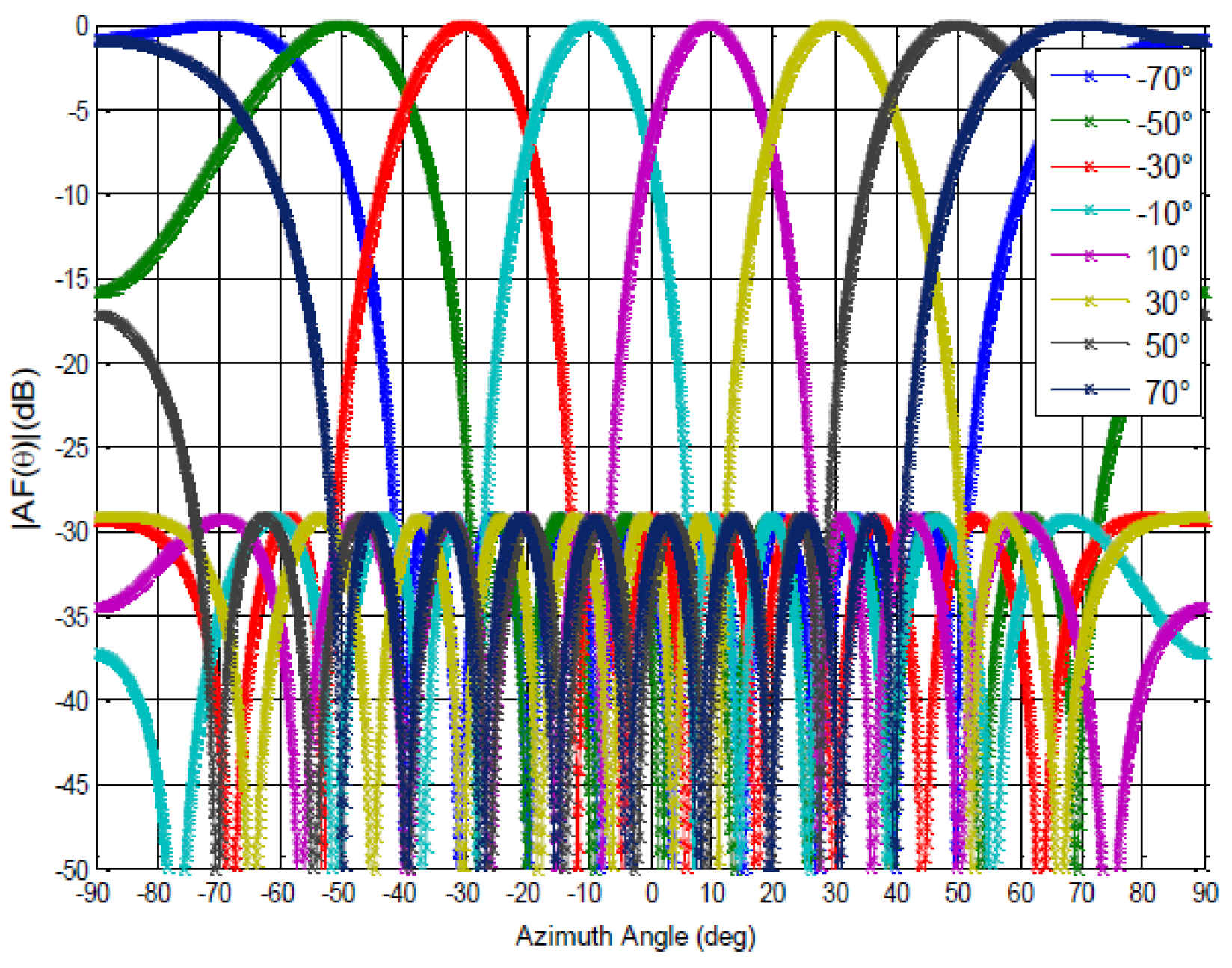
3.1.3. 24-Element Antenna Array
- Step 1: Determine the number of parameters ().
- Step 2: Determine the number of levels ()
- Step 3: Determine the strength ().
- Step 4: Determine the OA experimental design ().
- Step 5: Determine the reduced function ().
- Step 6: Determine the convergence value .
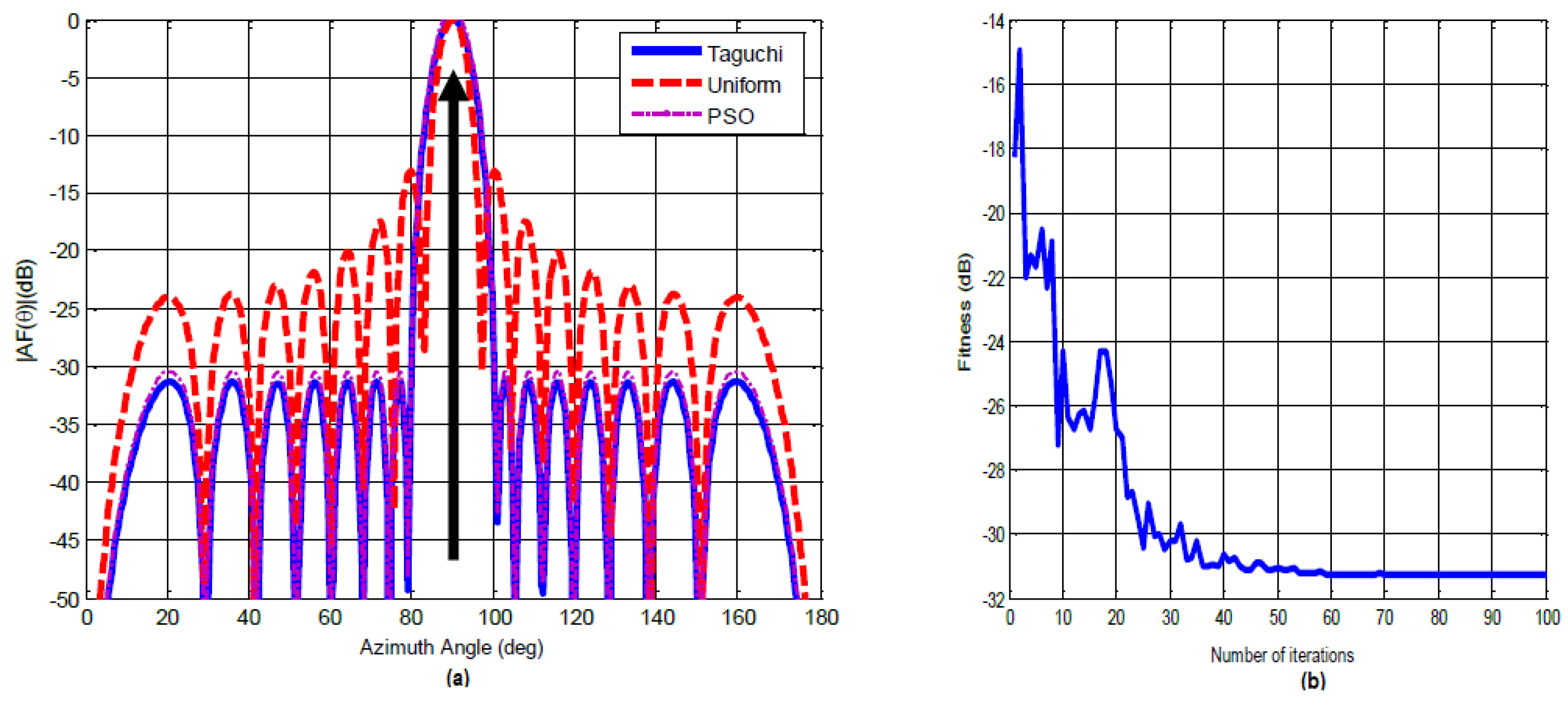
- The optimized maximum SLL by the Taguchi method = -39.2263 dB (Figure 6 (a)).
- The gain = 25.2718 dB (since the level of side lobes of the uniform array is SLL = -13.9545).
- The number of iterations = 73 (Figure 6 (b)).
- The excitation weights of the optimized antenna array by the Taguchi method are listed in Table 9.
- The comparative study between the results obtained by the Taguchi method and those by the PSO method indicates a considerable gain of approximately 3.7 dB [46].
| Elements | Weights | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0000 | 7 | 0.5292 |
| 2 | 0.9717 | 8 | 0.4203 |
| 3 | 0.9171 | 9 | 0.3182 |
| 4 | 0.8399 | 10 | 0.2275 |
| 5 | 0.7454 | 11 | 0.1512 |
| 6 | 0.6397 | 12 | 0.1262 |
3.2. Phase Synthesis of Antenna Array Radiation Pattern
- : distance between sources
- : amplitude
- : phase
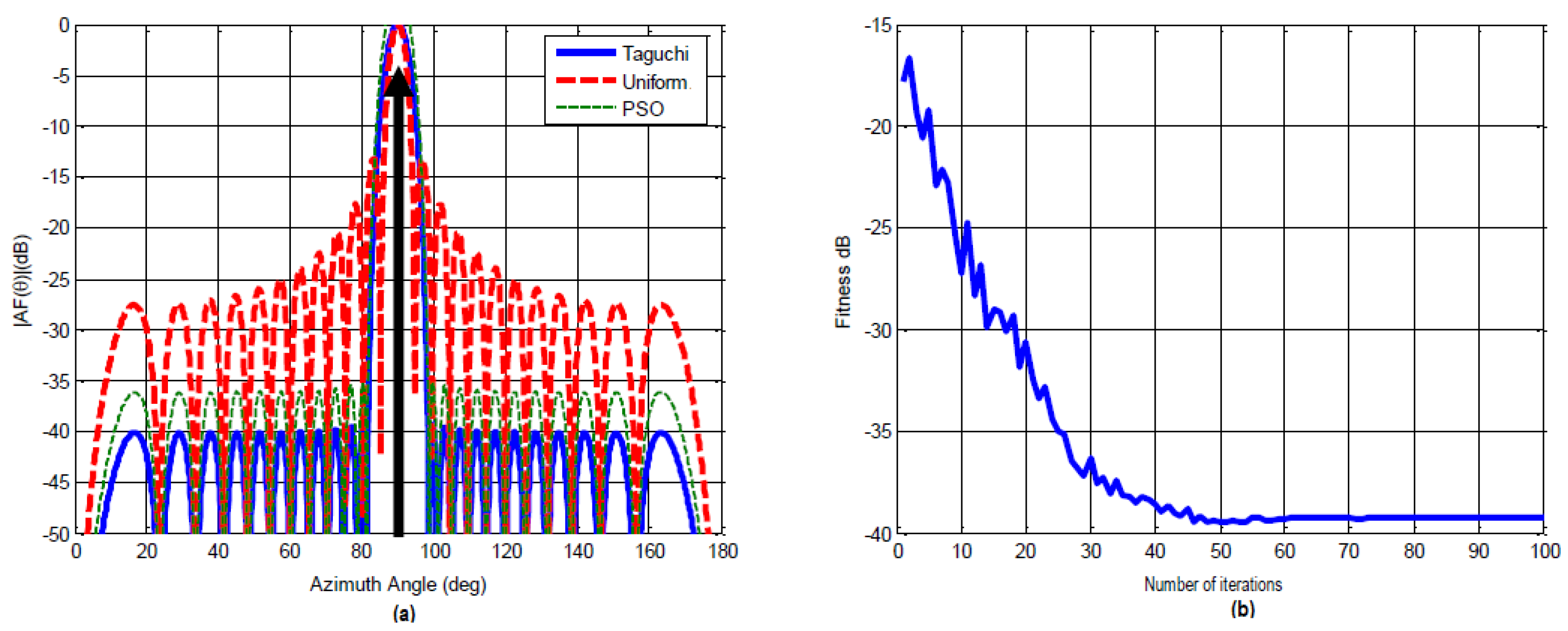
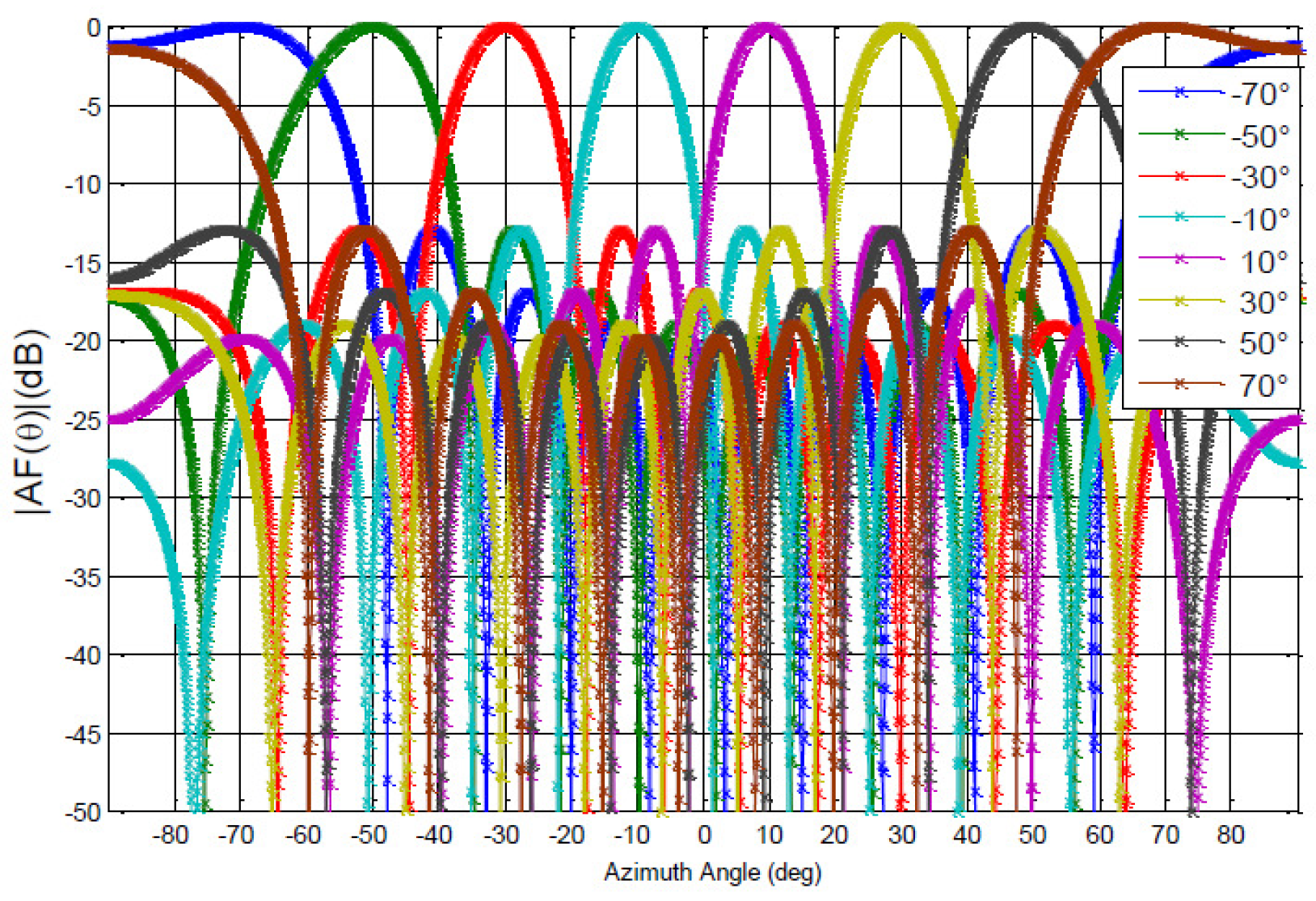
3.2.1. 10-Element Antenna Array
- Step 1: Determine the number of parameters ()
- Step 2: Determine the number of levels ()
- Step 3: Determine the strength ()
- Step 4: Determine the OA experimental design ()
- Step 5: Determine the reduced function ()
- Step 6: Determine the convergence value
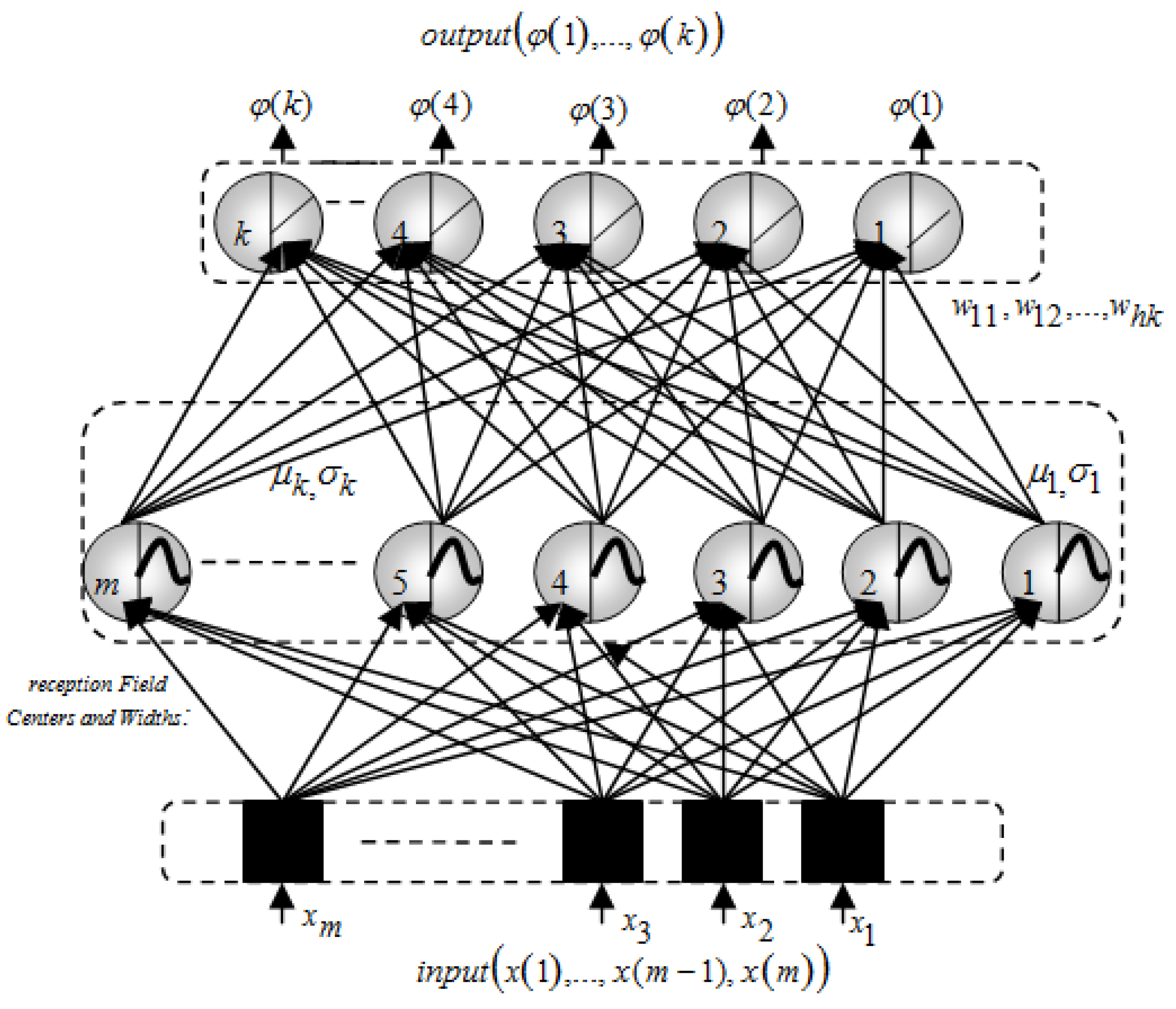
4. Neural Networks for Synthesis and Optimization of Antenna Arrays
- Data Collection: Gather data on antenna parameters, such as element positions, excitation coefficients, and desired radiation characteristics.
- Data Preprocessing: Normalize and preprocess the collected data to improve the neural network training process.
- Model Design: Design the architecture of the neural network, including the number of layers, neurons per layer, and activation functions.
- Training: Train the neural network using the collected and preprocessed data, adjusting weights and biases to minimize the difference between predicted and target radiation patterns.
- Validation: Validate the trained neural network using separate datasets or cross-validation techniques to ensure generalization to unseen data.
- Optimization: Utilize the trained neural network for antenna array optimization, adjusting antenna parameters to achieve desired radiation characteristics.
4.1. Taguchi-Neural Network Architectures
| Abbreviation | Algorithm | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| LM | Levenberg-Marquardt | High convergence rate |
| BFG | BFGS Quasi-Newton | Fast convergence |
| RP | Resilient Backpropagation | Robust to noise |
| BR | Bayesian Regularization | Effective for small data |
| SCG | Scaled Conjugate Gradient | Memory efficient |
| CGB | Conjugate Gradient with Powell/Beale Restarts | Balanced performance |
| CGF | Fletcher-Powell Conjugate Gradient | Stable convergence |
| CGP | Polak-Ribiére Conjugate Gradient | Good for sparse data |
| OSS | One-Step Secant | Fast convergence |
| GDX | Variable Learning Rate Backpropagation | Adaptive learning rate |
| GD | Basic Gradient Descent | Simple, easy to implement |
| GDM | Gradient Descent with Momentum | Accelerated convergence |

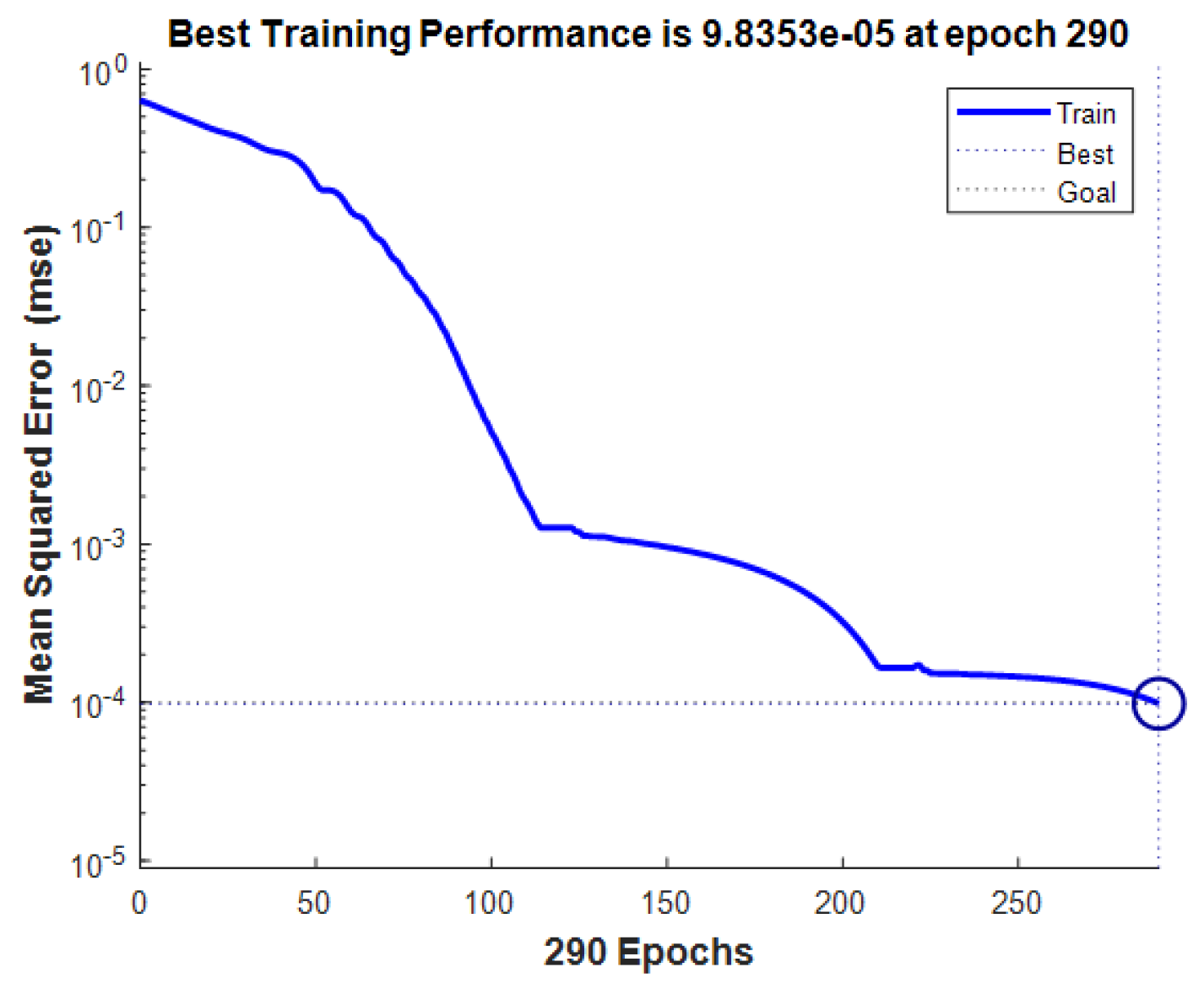
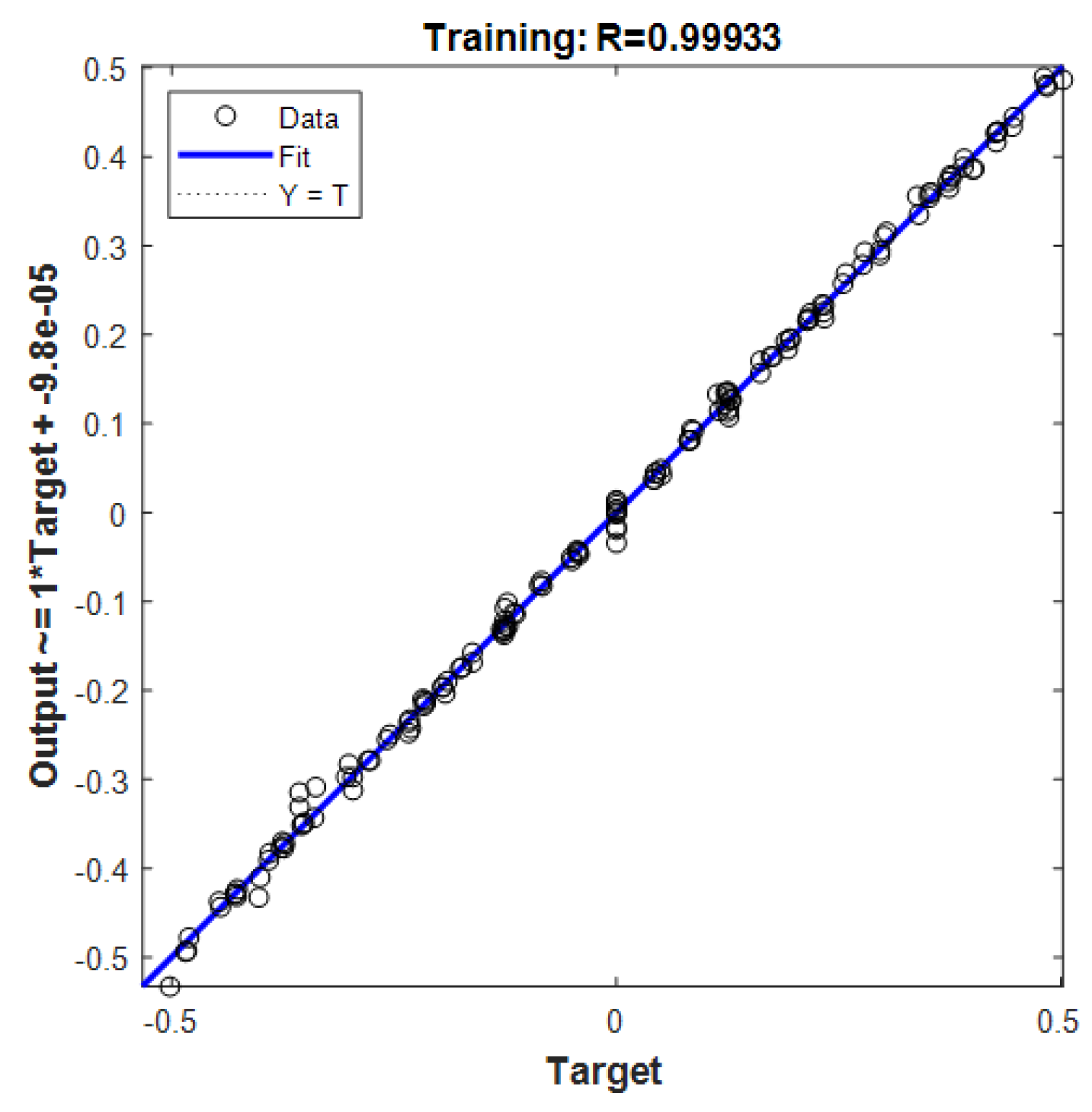
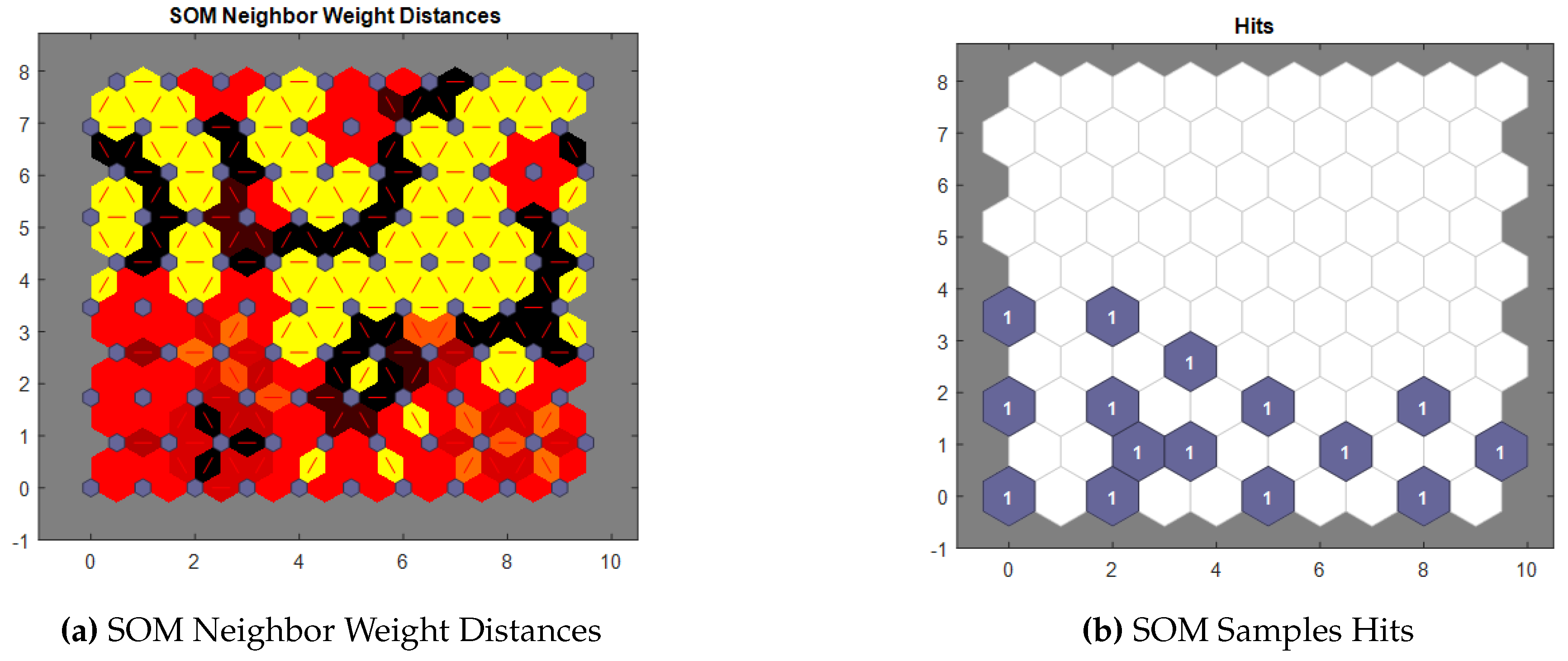
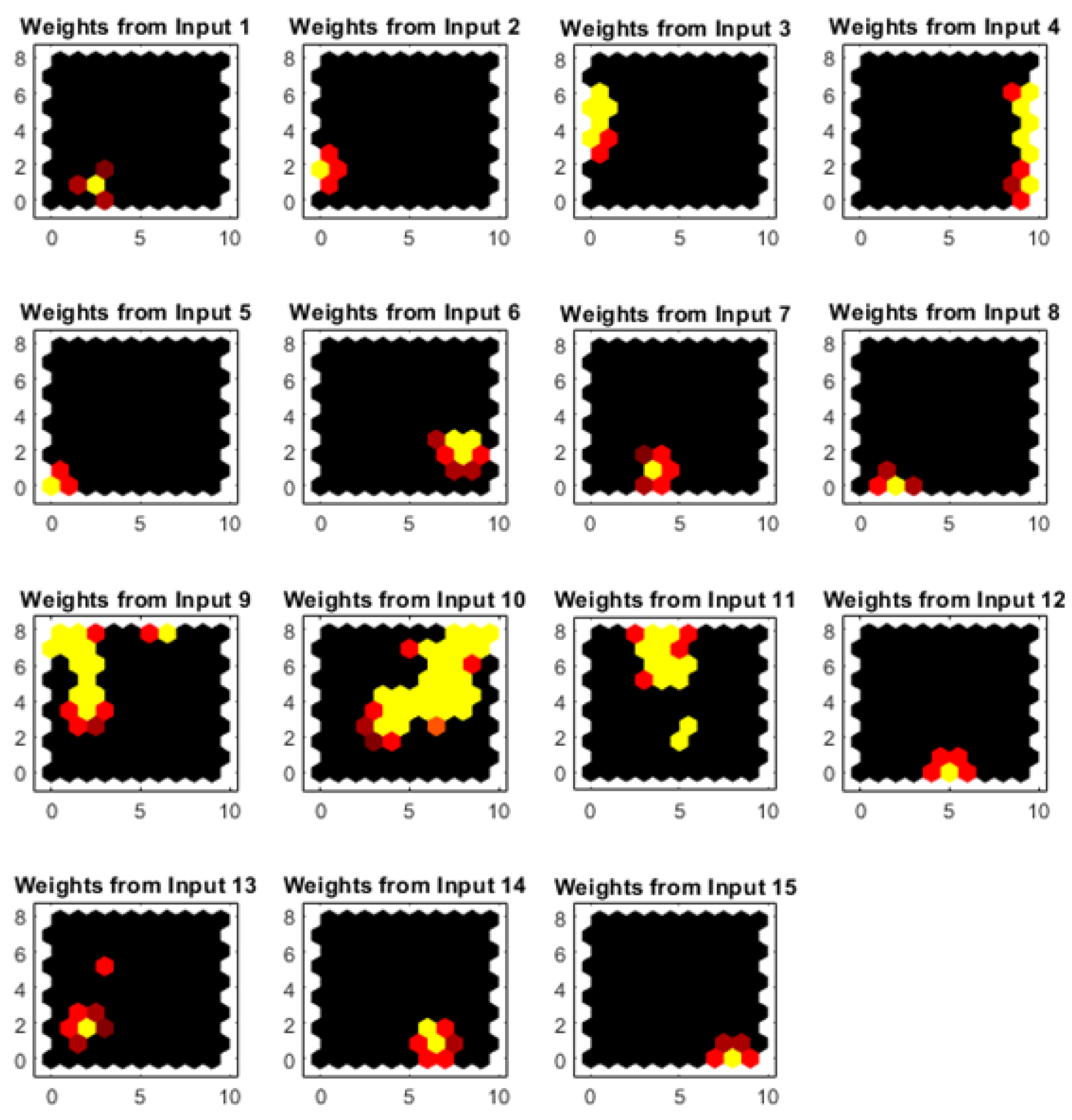
5. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| SOM | Self-Organizing Maps (SOMs) |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| BMU | Best Matching Unit |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| DACs | Digital-to-Analog Converters |
| ADCs | Analog-to-Digital Converters |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| OA | Orthogonal Array |
| FDTD | Finite-Difference Time-Domain |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Angles (Degrees) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -70 | -60 | -50 | -40 | -30 | -20 | -10 | 0 |
| 84.1463 | 77.4561 | 68.4900 | 58.3565 | 45.5440 | 30.3652 | 15.2609 | 0 |
| -106.7147 | -126.6421 | -153.5394 | 173.1063 | 134.6896 | 92.9003 | 46.6549 | 0 |
| 62.5153 | 29.3031 | -15.5709 | -70.2386 | -134.2522 | 154.4626 | 78.0024 | 0 |
| -128.3519 | -174.4535 | 122.4385 | 45.5405 | -44.1573 | -144.8638 | 109.4055 | 0 |
| 40.8783 | -17.9783 | -99.6457 | 160.2969 | 45.0250 | -83.2515 | 140.8011 | 0 |
| - 40.8783 | 17.9783 | 99.6457 | -160.2969 | -45.0250 | 83.2515 | -140.8011 | 0 |
| -128.3519 | 174.4535 | -122.4385 | -45.5405 | 44.1573 | 144.8638 | -109.4055 | 0 |
| -62.5153 | 29.3031 | 15.5709 | 70.2386 | 134.2522 | -154.4626 | -78.0024 | 0 |
| 106.7147 | 126.6421 | 153.5394 | -173.1063 | -134.6896 | -92.9003 | -46.6549 | 0 |
| -84.1463 | -77.4561 | -68.4900 | -58.3565 | -45.5440 | -30.3652 | -15.2609 | 0 |
| Angles (Degrees) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
| -15.1075 | -31.1920 | -45.4145 | -58.3105 | -69.3280 | -78.4109 | -84.1271 |
| -46.2167 | -91.7536 | -135.2755 | -173.9426 | 153.8277 | 126.7011 | 106.7805 |
| -77.2720 | -154.1821 | 135.8536 | 70.4664 | 16.0056 | -30.0311 | -63.2958 |
| -108.3717 | 144.2690 | 45.0192 | -45.1731 | -121.7617 | -180.7680 | 127.5157 |
| -140.4088 | 83.7520 | -43.9049 | -160.8637 | 100.5142 | 18.2899 | -41.5726 |
| 140.4088 | -83.7520 | 43.9049 | 160.8637 | -100.5142 | -18.2899 | 41.5726 |
| 108.3717 | -144.2690 | -45.0192 | 45.1731 | 121.7617 | 180.7680 | -127.5157 |
| 77.2720 | 154.1821 | -135.8536 | -70.4664 | -16.0056 | 30.0311 | 63.2958 |
| 46.2167 | 91.7536 | 135.2755 | 173.9426 | -153.8277 | -126.7011 | -106.7805 |
| 15.1075 | 31.1920 | 45.4145 | 58.3105 | 69.3280 | 78.4109 | 84.1271 |
Appendix A.2
| Elements | @ -20dB | @ -25dB | @ -29dB | @ -38dB |
| 1 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 2 | 0.9383 | 0.8986 | 0.8763 | 0.8551 |
| 3 | 0.7445 | 0.7188 | 0.6651 | 0.6158 |
| 4 | 0.6478 | 0.5020 | 0.4240 | 0.3590 |
| 5 | 0.5906 | 0.3853 | 0.3590 | 0.1672 |
Appendix B
| Algorithm 1:Taguchi Antenna Array Optimization Algorithm |
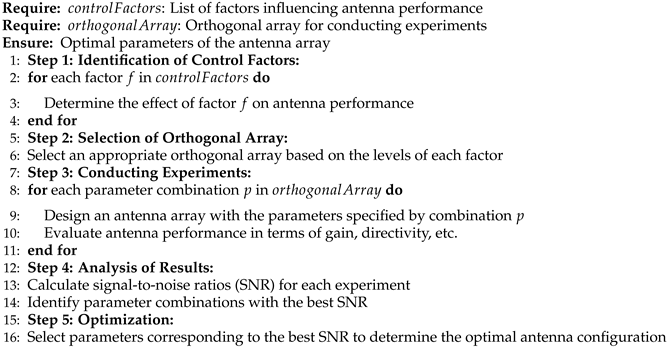 |
References
- Kim, J., Kim, J. H., & Kim, Y. H. (2007). Application of Taguchi method in the optimization of diesel engine operating parameters for simultaneous reduction of NOx and particulate emissions. Fuel, 86(7-8), 1039-1046.
- Chakraborty, S., & Ghoshal, S. (2008). Multi-response optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters using Taguchi based grey relational analysis. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 199(1-3), 335-347.
- Hagan, M. T., & Menhaj, M. B. (1994). Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE transactions on neural networks, 5(6), 989-993.
- Huang, C. L., & Wang, C. J. (2006). A GA-based feature selection and parameters optimization for support vector machines. Expert Systems with Applications, 31(2), 231-240.
- Gupta, R., Jain, V. K., & Kumar, A. (2010). Application of Taguchi and response surface methodologies for geometric optimization of multiple performance characteristics in turning. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 51(9-12), 919-928.
- Chen, C. H., & Lin, Y. Y. (2006). A hybrid Taguchi–genetic algorithm for optimization of back propagation learning in neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 31(2), 231-240.
- Jamaludin, A., Shuib, N. L. M., & Razak, Z. A. (2018). Multi-Objective Optimization of Injection Molding Process Parameters Using Taguchi Based Grey Relational Analysis (GRA) Coupled with Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Materials, 11(1), 17.
- Garg, G., Gupta, N., Bansal, A., & Kumar, A. (2019). Optimization of WEDM Process Parameters using Taguchi Approach: A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 4662-4669.
- Rao, R. V., & Pawar, P. J. (2008). A hybrid approach of Taguchi method and genetic algorithm for optimization of machining parameters in turning operations. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 207(1-3), 275-288.
- Sharma, S., Goyal, V., & Kumar, A. (2020). Optimization of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining Process Parameters Using Taguchi Method: A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 1028-1033.
- Zhang, J., & Wang, J. (2007). Neural network ensemble based on Taguchi optimization method for software reliability prediction. Journal of Systems and Software, 80(5), 759-767.
- Lin, C. J., & Cheng, C. H. (2010). Multi-response optimization of drilling parameters on CFRP laminates by Taguchi method and grey relational analysis. Materials & Design, 31(1), 153-158.
- Salehi, M., & Bagherpour, R. (2020). Optimization of electrical discharge machining parameters using the Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 25, 616-621.
- Ravi, S., & Murugan, N. (2019). Optimization of machining parameters in electric discharge machining using Taguchi coupled Grey Relational Analysis (GRA) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 1524-1530.
- Garg, A., Rathi, R., & Kansal, H. K. (2018). Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining using Taguchi and genetic algorithm: A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(3), 9636-9643.
- Tang, Z., & Yang, H. (2003). Taguchi method based genetic algorithm for neural networks optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 25(2), 343-352.
- Chen, Y., & Liu, Z. (2019). A hybrid optimization algorithm based on Taguchi method and neural network for chip breaker design. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 30(7), 2875-2889.
- Mohanty, A. R., Rao, P. V., & Garg, D. (2020). Optimization of drilling parameters on glass fiber reinforced polymer composites using Taguchi and neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 1185-1191.
- Pandian, A., & Sathish Kumar, T. (2017). Optimization of process parameters in machining of GFRP composite using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 4(2), 1612-1620.
- Srivastava, A. K., & Singh, T. P. (2019). Optimization of process parameters of electrochemical machining using Taguchi-based GRA coupled with PCA. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 3482-3488.
- Kar, S., & Mandal, S. (2009). A hybrid neural network–Taguchi approach for optimization of micro-EDM parameters. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 44(5-6), 439-451.
- Rahman, M. A., Rahman, M. M., & Rahaman, M. A. (2015). Prediction and optimization of surface roughness in electrical discharge machining (EDM) using artificial neural network (ANN) and Taguchi technique. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2(4-5), 2299-2308.
- Sahoo, A. K., & Sahoo, R. K. (2019). Optimization of EDM process parameters using Taguchi based Grey-Taguchi method coupled with PCA. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 4462-4468.
- Kar, S., & Mandal, S. (2016). Hybrid optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process using Taguchi and grey relational analysis. Materials Today: Proceedings, 3(10), 3439-3448.
- Sutha, S., Rajendran, I., & Sekar, A. D. (2020). Optimization of machining parameters in WEDM process using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 25, 1008-1013.
- Sanjay, R., & Rajendran, I. (2015). Optimization of machining parameters in WEDM process using Taguchi method coupled with artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Procedia Engineering, 97, 2051-2060.
- Suresh, S., Natarajan, U., & Senthilkumar, K. (2017). Optimization of machining parameters in WEDM process using Taguchi method and neural network. Procedia Engineering, 174, 918-926.
- Ali, H. M., & Abouelatta, O. B. (2013). Optimization of WEDM process parameters using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 65(9-12), 1433-1442.
- Chen, X., Zhu, H., Zhang, Z., & Lu, X. (2015). Optimization of WEDM process parameters using Taguchi method and BP neural network. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 76(5-8), 1037-1044.
- Gupta, R., Jain, V. K., & Kumar, A. (2017). Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters in WEDM process using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 91(1-4), 653-669.
- Gupta, A., Kumar, R., & Kumar, S. (2018). Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(1), 1420-1427.
- Cheng, L., Zhu, X., & Li, Z. (2015). Optimization of cutting parameters in wire electrical discharge machining process using Taguchi method and response surface methodology. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29(9), 3811-3818.
- Prakash, C., & Pal, S. K. (2016). Modeling and optimization of process parameters of wire electrical discharge machining using hybrid Taguchi-genetic algorithm. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 82(5-8), 969-978.
- Mukherjee, A., & Ghosh, A. (2020). Optimization of process parameters in turning of AISI 304 using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 1759-1764.
- Panja, S., & Dey, A. (2020). Optimization of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining Process Parameters Using Taguchi Method Coupled with Principal Component Analysis and Artificial Neural Network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 1708-1715.
- Guo, J., & Zhang, W. (2016). Surface roughness optimization in dry turning of AISI 4140 using Taguchi method and neural network. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 31(10), 1341-1347.
- Gouda, A. M., Hussein, H. A., & Elbestawi, M. A. (2018). Optimization of cutting parameters in CNC turning process using Taguchi method and neural network. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 33(5), 500-508.
- Pathak, S., & Bhaduri, A. K. (2018). Optimization of Surface Roughness in Turning of AISI 4340 Steel using Taguchi Method Coupled with Grey-Taguchi Analysis. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(2), 5272-5277.
- Zhang, L., & Wang, Z. (2017). Optimization of drilling parameters using Taguchi method and neural network. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 39(8), 3245-3254.
- Singh, G., & Kumar, R. (2020). Optimization of micro-wire electrical discharge machining (MWEDM) process parameters using Taguchi-grey relational analysis and ANN-GA. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31(4), 975-990.
- Mukhopadhyay, S., Paul, S., & Datta, S. (2018). Application of Taguchi coupled with grey relational analysis (GRA) for optimization of machining parameters in turning operations. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(3), 8690-8699.
- Tobing, T. A. J., Rahim, R. A., & Hafiyyan, M. S. (2019). Optimization of abrasive waterjet machining process parameters using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 1989-1997.
- Das, R., Sahoo, A. K., & Panda, A. (2020). Optimization of drilling parameters on GFRP composites using Taguchi method and ANN. Materials Today: Proceedings, 25, 903-908.
- Das, A., Panda, A., & Biswal, B. B. (2019). Optimization of machining parameters on CNC turning operation of AISI 304 using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 1023-1030.
- Ghayoula, E., Bouallegue, A., Ghayoula, R., & Chouinard, J. Y. (2014). Capacity and Performance of MIMO systems for Wireless Communications. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 7(3), 34.
- Smida, A., Ghayoula, R., Nemri, N., Trabelsi, H., Gharsallah, A., & Grenier, D.. Phased arrays in communication system based on Taguchi-neural networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 27(12), 4449-4466, 2014.
- Ghayoula, E., Ghayoula, R., Haj-Taieb, M., Chouinard, J. Y., & Bouallegue, A. (2016). Pattern Synthesis Using Hybrid Fourier-Neural Networks for IEEE 802.11 MIMO Application. Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, 67, 45-58.
- Hammami, A., Ghayoula, R., & Gharsallah, A. (2011). Antenna array synthesis with Chebyshev-Genetic Algorithm method. In 2011 International Conference on Communications, Computing and Control (pp. 12).
- Nemri, N., Smida, A., Ghayoula, R., Trabelsi, H., & Gharsallah, A. (2011). Phase-only array beam control using a Taguchi optimization method. In 2011 11th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS) (pp. 97-100).
- Gargouri, L., Ghayoula, R., Fadlallah, N., Gharsallah, A., & Rammal, M. (2009). Steering an adaptive antenna array by LMS algorithm. In 2009 16th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (pp. 11).
- Kai Yang and Basem El-Haik. "Taguchi’s Orthogonal Array Experiment," in Design for Six Sigma: A Roadmap for Product Development, McGraw-Hill, 2008, pp. 469-497.
- C. F. Jeff Wu and Michael Hamad, "Full Factorial Experiments at Two Levels," in Experiments: Planning, Analysis, and Parameter Design Optimization, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2000, p. 112.
- Basar, M. R., Hussain, Z. M., Bae, S. H., & Kim, N. S. (2019). Smart Antenna Arrays for 5G and Beyond: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Wireless Communications, 26(2), 173-179.
- Yang, C., Yang, S., & Zhou, W. (2020). A Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Network Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access, 8, 71998-72008.
- Huang, M., Liu, L., Chen, S., Yang, J., & Lin, Z. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Reinforcement Learning in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 7(2), 540-548.
- Chen, W., Zhang, X., Tang, J., & Wang, L. (2020). Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis via Deep Learning. IEEE Access, 8, 138349-138357.
- Zhang, Z., Chen, K., & Lee, C. (2019). 3D Beamforming with Antenna Array Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access, 7, 61819-61829.
- Liu, W., Guo, Y., Li, X., Zhang, J., & Wang, H. (2020). A Survey of Smart Antennas Based on Artificial Intelligence. Wireless Personal Communications, 112(1), 433-453.
- Li, R., Chen, K., Jiang, X., Wu, D., Li, C., & Jin, M. (2021). Deep Learning Based Smart Antenna: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access, 9, 14068-14080.
- Huang, C., Liu, Q., Wu, Q., Wu, W., & Wang, D. (2020). Deep Learning Based Smart Antenna for Mobile Communication: A Review. IEEE Access, 8, 189381-189389.
- Chen, W., Gao, W., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, S. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access, 9, 73886-73896.
- Liu, C., Tian, Y., Yang, X., & Cai, Z. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Network Based on Machine Learning. IEEE Access, 9, 112392-112402.
- Yang, C., & Li, J. (2018). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Neural Networks. IEEE Access, 6, 58711-58720.
- Wu, L., Wang, X., Zhang, J., & Hu, C. (2020). Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Based on Machine Learning. IEEE Access, 8, 12742-12751.
- Li, W., Cao, M., Li, C., Zhang, W., & Tian, S. (2020). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access, 8, 104201-104208.
- Wang, H., Liu, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Using Attention Mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 20(1), 125-138.
- Zhu, J., Chen, W., & Li, J. (2020). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Spiking Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(11), 4667-4678.
- Li, X., Wu, Q., & Chen, W. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Optimization Based on Federated Learning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 20(3), 1866-1878.
- Zhang, Y., Liu, Q., & Wang, H. (2020). Smart Antenna Beamforming with Graph Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 68(12), 8307-8318.
- Wu, L., Liu, Q., & Wang, H. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Capsule Networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(9), 9001-9014.
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Xu, J., & Tang, X. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Based on Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(1), 329-340.
- Chen, S., & Li, J. (2022). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Based on Deep Q-Learning. IEEE Access, 10, 4171-4180.
- Chen, Y., Li, J., & Guo, Y. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(10), 10091-10101.
- Liu, Q., & Yang, Z. (2019). Smart Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Based on Neural Network. IEEE Access, 7, 155470-155476.
- Zhang, H., & Chen, W. (2020). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19(10), 6823-6835.
- Wang, H., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., & Chen, X. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Machine Learning. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 69(6), 3484-3496.
- Guo, S., Hu, Z., & Li, C. (2022). Deep Learning Assisted Smart Antenna Beamforming for 6G Wireless Communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 40(2), 343-353.
- Jin, Y., Ren, J., & Li, Y. (2020). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19(8), 5322-5335.
- Li, Z., Yang, C., & Liu, S. (2022). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Optimization Using Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 71(3), 2289-2298.
- Wang, X., Zhou, H., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19(2), 1341-1353.
- Chen, W., Wu, Q., & Hu, C. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 69(9), 5415-5426.
- Liu, Q., Lin, Y., & Chen, Y. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 39(5), 1388-1399.
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., & Zhao, J. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Based on Deep Q-Learning. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(10), 9842-9854.
- Liu, Q., Liu, S., & Wang, H. (2020). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Using Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 68(7), 4897-4908.
- Chen, W., Li, C., & Wu, Q. (2022). Smart Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Based on Transformer Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 70(1), 174-184.
- Yang, C., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Using Evolutionary Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 71(4), 3789-3801.
- Liu, S., Wu, Q., & Zhang, X. (2021). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 20(8), 5209-5221.
- Wang, H., Zhang, Y., & Liu, Q. (2020). Smart Antenna Array Beamforming Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 68(8), 5721-5732.
- Liu, S., Chen, W., & Wu, Q. (2021). Smart Antenna Beamforming Optimization Using Variational Autoencoders. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 20(5), 3521-3533.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





