Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
Radio Occultation Concept
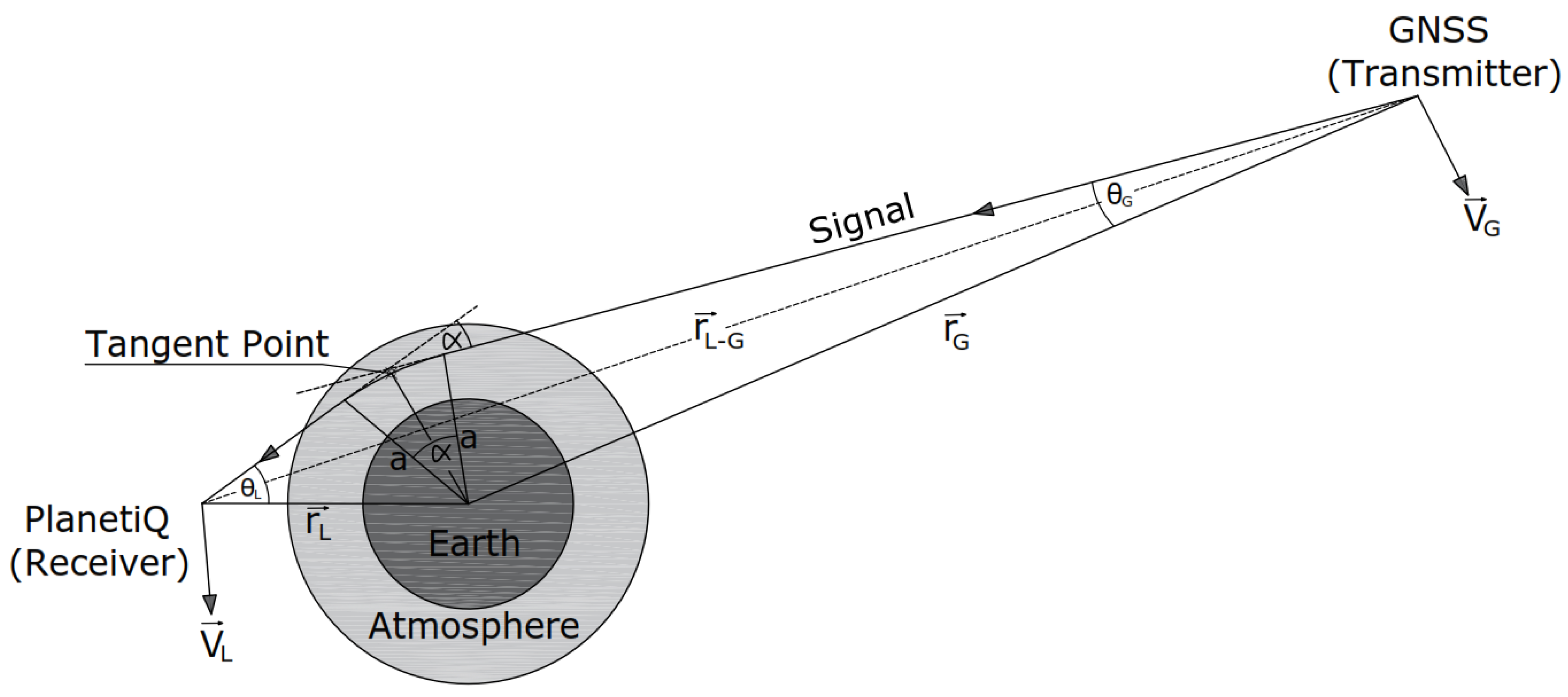
3. Research Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. PlanetiQ Observations Spatial and Temporal Distribution
4.2. PlanetiQ-COSMIC Profiles Comparison
4.2.1. Single Profile Comparison
4.2.2. Multi-Profile Comparison
4.3. PlanetiQ-NWP Models Comparison
4.3.1. PlanetiQ-GFS Model Comparison
4.3.3. PlanetiQ-ECMWF Model Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflict of Interests
Ethical approval
Informed consent
References
- Ghoniem, I. F., Mousa, A. E.-K., & El-Fiky, G. Optimization of GNSS-RO LEO satellite orbits for Egypt and the Middle East region. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2020, 59, 389–397. [CrossRef]
- PlanetiQ. (2024, February 1). Technology. PlanetiQ. https://planetiq.com/technology/.
- Bai, W., Deng, N., Sun, Y., Du, Q., Xia, J., Wang, X., ... & Tan, G. Applications of GNSS-RO to Numerical Weather Prediction and Tropical Cyclone Forecast. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1204. [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E. R., Hajj, G. A., Schofield, J. T., Linfield, R. P., & Hardy, K. R. Observing Earth's atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the Global Positioning System. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 1997, 102(D19), 23429-23465.
- Qiu, C., Wang, X., Zhou, K., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Li, H., ... & Yuan, H. Comparative Assessment of Spire and COSMIC-2 Radio Occultation Data Quality. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5082. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Huangfu, J., Wang, X., Chen, W., Peng, W., Tang, Q., ... & Xue, Z. Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4958. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I. F., Abd El-Fatah, M. A., Mousa, A. E.-K., & El-Fiky, G. Analysis of the differences between GPS radio occultation and radiosonde atmosphere profiles in Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science 2022, 25, 491–500. [CrossRef]
- Melbourne, W. G., Davis, E., Duncan, C., Hajj, G., Hardy, K., Kursinski, E., ... & Yunck, T. P. (1994). The application of spaceborne GPS to atmospheric limb sounding and global change monitoring. JPL Publ. 94–18, Pasadena, CA.
- Rocken, C., Anthes, R., Exner, M., Hunt, D., Sokolovskiy, S., Ware, R., ... & Zou, X. Analysis and validation of GPS/MET data in the neutral atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 29849–29866. [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A., Aoyama, Y., & Tsuda, T. A simulation analysis to optimize orbits for a tropical GPS radio occultation mission. Earth Planets Space 2006, 58, 919–925.
- Pavelyev, A., Pavelyev, A., Matyugov, S., Yakovlev, O., Liou, Y.-A., Zhang, K., & Wickert, J. (2013). Radio Wave Propagation Phenomena from GPS Occultation Data Analysis. InTech. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Yue, X., Wan, W., & Schreiner, W. (2020). Characterizing Ionospheric Effect on GNSS Radio Occultation Atmospheric Bending Angle. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Zou, X., Shao, H., Anthes, R., Chang, J., Tseng, J-H., & Wang, B. Impact of GPS/MET bending angle profiles on assimilation and forecasts for the period June 20-30. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 31771–31786.
- Fjeldbo, G., Kliore, J., & Eshleman, V. The neutral atmosphere of Venus as studied with the Mariner V radio occultation experiments. The Astronomical Journal 1971, 76, 123–140.
- Prol, F. S., Hoque, M. M., Hernández-Pajares, M., Yuan, L., Olivares-Pulido, G., von Engeln, A., ... Study of Ionospheric Bending Angle and Scintillation Profiles Derived by GNSS Radio-Occultation with MetOp-A Satellite. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1663. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z., He, Q., Li, L., Zhang, K., & Wu, S. (2020). Daily Climatological Fields Based on GNSS Radio Occultation Measurements: A Feasibility Study. In: Sun, J., Yang, C., & Xie, J. (Eds.), China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2020 Proceedings: Volume I. Springer. [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Lara, S. (2016). Current and Future GNSS and Their Augmentation Systems. In: Pelton, J., Madry, S., & Camacho-Lara, S. (Eds.), Handbook of Satellite Applications. Springer. [CrossRef]
- Innerkofler, J., Kirchengast, G., Schwärz, M., Marquardt, C., & Andres, Y. GNSS radio occultation excess-phase processing for climate applications including uncertainty estimation. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 2023, 16, 5217–5247. [CrossRef]
- Pirscher, B. (2010). Multi-satellite climatologies of fundamental atmospheric variables from radio occultation and their validation (Ph.D. thesis), Wegener Center Verlag Graz, Austria, Sci. Rep. 33-2010.
- Alizadeh, M., Wijaya, D., Hobiger, T., Weber, R., & Schuh, H. (2013). Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy. [CrossRef]
- Born, M., & Wolf, E. (1964). Principles of Optics. New York, NY: Pergamon.
- Xie, F., Syndergaard, S., Kursinski, E. R., & Herman, B. M. An approach for retrieving marine boundary layer refractivity from GPS occultation data in the presence of superrefraction. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 1629–1644.
- University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. (2024, February 1). UCAR. https://ucar.edu/.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. (2023, December 12). ECMWF, https://www.ecmwf.int/.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. (2023, December 30). NOAA, https://www.noaa.gov/.























| PlanetiQ observations (filestamp) | COSMIC observations (filestamp) | f-test P value (Pres., Temp., WVP, Ref.) |
T-stat (Pres., Temp., WVP, Ref.) |
T-cr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN04.2023.353.18.15.R24 | C2E2.2023.353.18.18.G31 | 0.99, 0.8, 0.45, 0.88 | 0.008, 0.24, -0.75, -0.15 | 1.96 |
| GN02.2023.347.21.41.C20 | C2E1.2023.347.21.39.G31 | 0.99, 0.87, 0.91, 0.97 | 0.003, 0.16, -0.11, -0.03 | |
| GN04.2023.348.08.07.C24 | C2E6.2023.348.08.10.G05 | 0.98, 0.8, 0.29, 0.92 | 0.016, 0.25, 1.07, 0.1 | |
| GN04.2023.340.11.18.G23 | C2E5.2023.340.11.13.R17 | 0.75, 0.73, 0.52, 0.71 | -0.31, -0.33, -0.63, -0.37 | |
| GN04.2023.353.10.22.G07 | C2E2.2023.353.10.22.G07 | 0.99, 0.99, 0.87, 0.99 | -0.01, -0.02, -0.16, -0.02 | |
| GN02.2023.340.06.33.C41 | C2E3.2023.340.06.28.G24 | 0.99, 0.94, 0.73, 0.94 | 0.00, 0.08, 0.35, 0.08 | |
| GN04.2023.348.08.07.E31 | C2E6.2023.348.08.10.G05 | 0.98, 0.84, 0.53, 0.96 | 0.02, 0.2, 0.62, 0.06 | |
| GN04.2023.340.11.18.R17 | C2E5.2023.340.11.13.R17 | 0.99, 0.89, 0.93, 0.98 | 0.00, -0.13, -0.08, 0.02 | |
| GN02.2023.342.14.23.G18 | C2E6.2023.342.14.32.R16 | 0.99, 0.98, 0.75, 0.93 | 0.00, 0.03, 0.31, 0.08 |
| PlanetiQ observations (filestamp) | Model | f-test P value (Pres., Temp., WVP, Ref.) |
T-stat (Pres., Temp., WVP, Ref.) |
T-cr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN02.2023.100.00.10.R20 | GFS ECMWF |
0.98, 0.4, 0.00, 0.98 0.96, 0.17, 0.00, 0.94 |
-0.015, 0.82, 8.4, -0.02 -0.05, 0.01, 8.4, -0.08 |
1.96 |
| GN02.2023.125.00.44.E11 | GFS ECMWF |
0.98, 0.87, 0.6, 0.99 0.99, 0.95, 0.66, 0.99 |
0.03, -0.16, -0.51, 0.01 0.02, -0.07, -0.45, -0.01 |
|
| GN03.2023.200.12.47.G27 | GFS ECMWF |
0.9, 0.98, 0.33, 0.89 0.95, 0.99, 0.87, 0.93 |
-0.12, 0.02, 0.98, -0.135 0.05, -0.02, 0.17, 0.08 |
|
| GN02.2023.250.00.04.G12 | GFS ECMWF |
1, 0.92, 0.18, 0.99 0.99, 1, 0.52, 0.99 |
0.00, -0.1, -1.33, 0.01 -0.01, 0.00, 0.64, 0.01 |
|
| GN02.2023.300.00.25.E09 | GFS ECMWF |
0.93, 0.58, 0.09, 0.88 0.93, 0.69, 0.62, 0.92 |
0.09, -0.54, 1.7, 0.02 0.08, -0.39, 0.49, 0.1 |
|
| GN02.2023.350.01.00.C44 | GFS ECMWF |
0.99, 0.92, 0.87, 0.95 0.97, 0.93, 0.87, 0.93 |
0.01, 0.01, 0.15, 0.05 0.02, -0.02, 0.17, 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





