Submitted:
13 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Patients and Methods
Ethical Statement
Type of the Study
Place and Date of the Study
Source of Animal Models
Inclusion Criteria for Animal Models
Exclusion Criteria for Animal Models
Instruments
| Instrument | Model and manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Autoclaves | Tomy, japan |
| Aerobic incubator | Sanyo, Japan |
| Digital balance | Mettler Toledo, Switzerland |
| Oven | Binder, Germany |
| Deep freezer -70 0C | Artiko |
| Refrigerator 5 | whirlpool |
| PH meter electrode | Mettler-toledo,UK |
| Deep freezer -20 0C | whirlpool |
| Gyrator shaker | Corning gyrator shaker, Japan |
| 190-1100nm Ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer | UV1600PC, China |
| Light(optical) microscope | Amscope 120X-1200X, China |
Material
Isolation of Myxococcus fulvus 124B02 Producing Myxopyronin Antibiotics
Detection of Fruiting Bodies of Myxobacteria
Identification Myxopyronin A producing bacterial isolates:
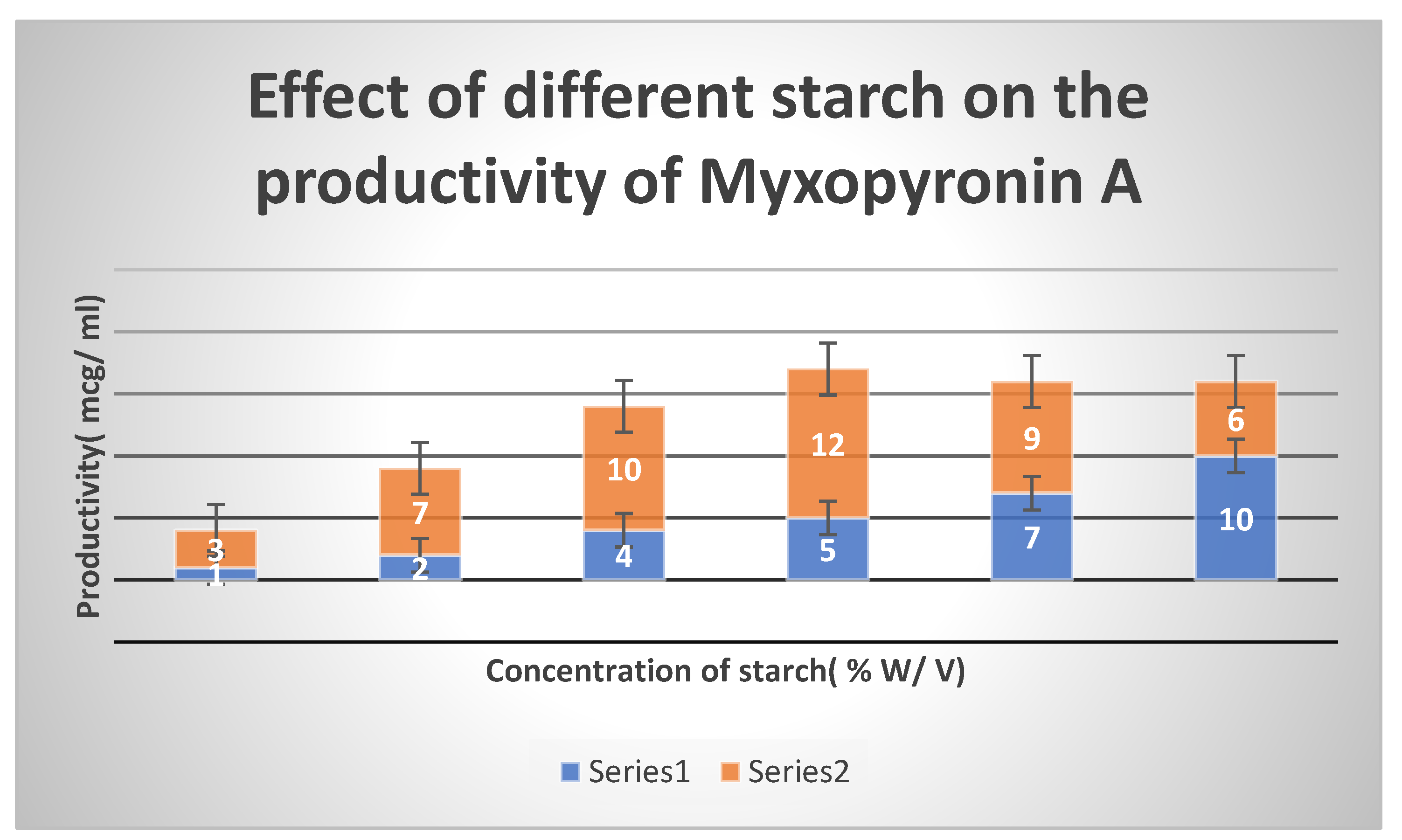
Effect of Different Carbon Sources
Purification of Myxopyronin A Antibiotic
Procedure of Broth Dilution Assay for Determination of MICs of Myxopyronin A
Agar Diffusion Assay with Paper Discs Procedure for the Determination of Myxopyronin A Antimicrobial Activity
| Pathogenic m.o | No of strains | Isolation media |
|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis | 5 | Mannitol egg yolk polymixin agar( MEYP) |
| Bacillus cereus | 7 | Polymixin egg yolk mannitol bromothymol blue agar( PEMBA) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 6 | Salt mannitol agar( SMA) |
| Pneumococci | 13 | Todd Hewitt broth with yeast extract |
| coli | 17 | Sorbitol- Macconkey agar |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 10 | Pseudomonas isolation agar( PSA) |
| Candida albicans | 1 | Potato dextrose agar( PDA) |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 5 | Sabourad dextrose agar( SDA) |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 4 | Bismuth sulfite agar( BSA) |
| Haemophilus influenza | 3 | Enriched chocolate agar |
| Gonococci | 4 | Thayer martin medium |
| Meningococci | 6 | Mueller Hinton agar |
| Serratia Marcescens | 4 | Caprylate thallous agar medium |
| Mucor hiemalis | 1 | Potato dextrose broth |
| Shigella dysenteriae | 8 | Hekteon enteric agar |
| Micrococcus luteus | 1 | Tryptic soy agar |
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 | Blood agar |
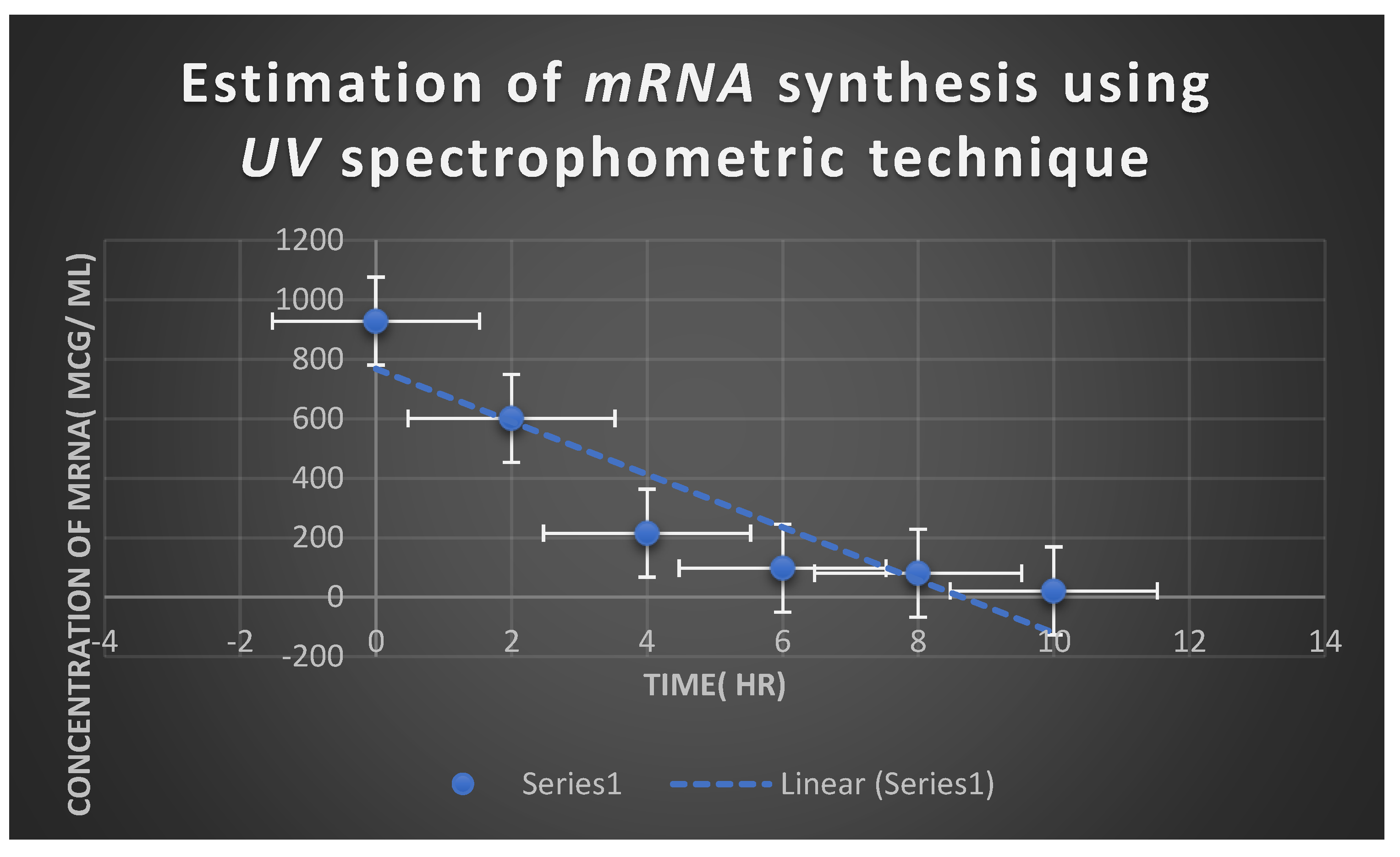
Estimation of Myxopyronin A Effect on Bacterial RNA Synthesis
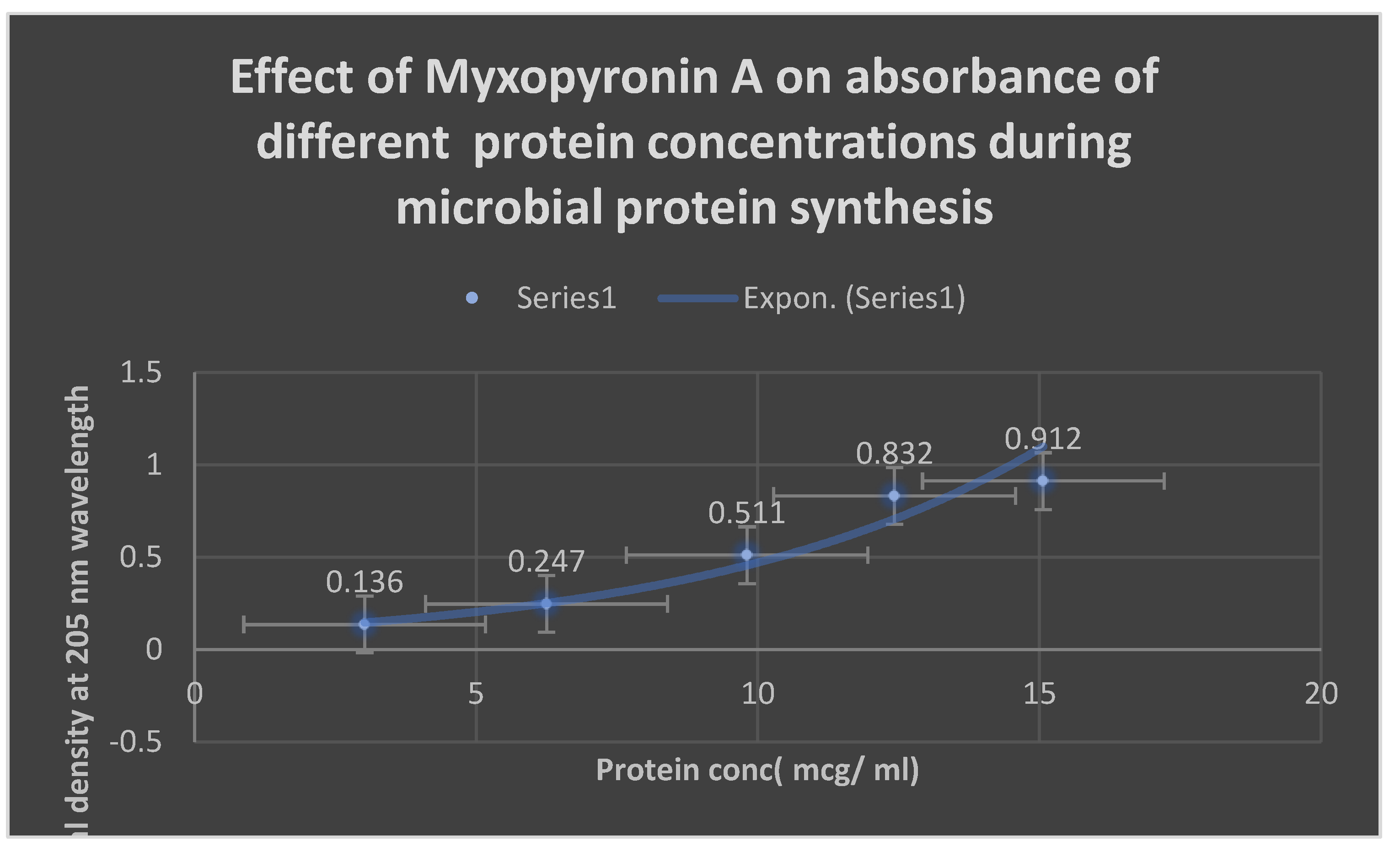
Estimation of Myxopyronin A Effect on Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Estimation of Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Effects of Myxopyronin A during Experimental Animal Testing in Preclinical Clinical Trials
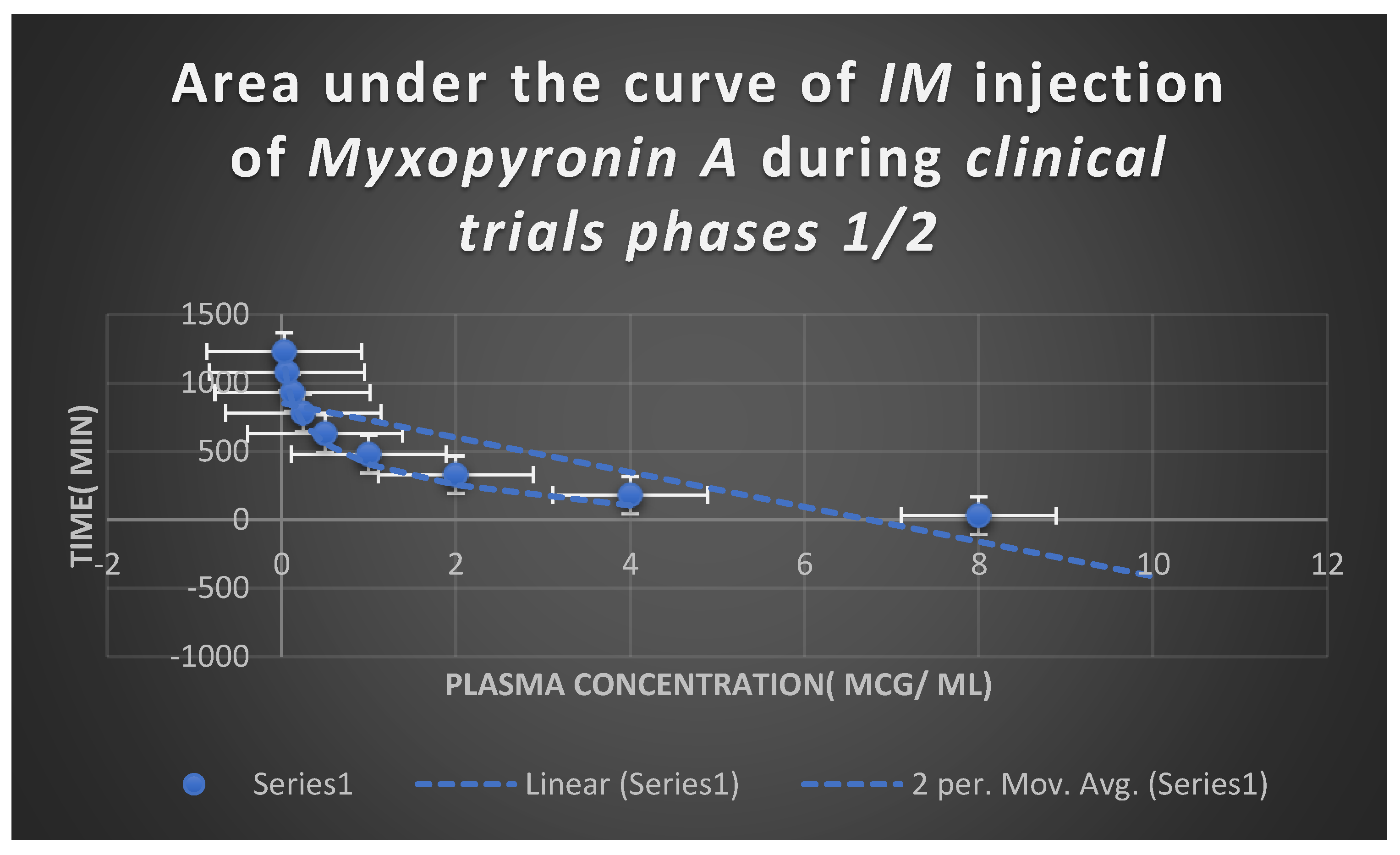
Estimation of Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Effects of Myxopyronin A in Randomized Human Clinical Trials Phases 1/2
Estimation of of Phototoxicity, Mutagenicity and Carcinogenicity of the Test Antibiotic
The Determination of Toxokinetics and Toxodynamic Effects
The Determination of Maximum Bactericidal Activity of Myxopyronin A
Determination of Plasma Protein Binding Capacity of Myxopyronin A
Determination of Liver, Kidney and Heart Function Tests
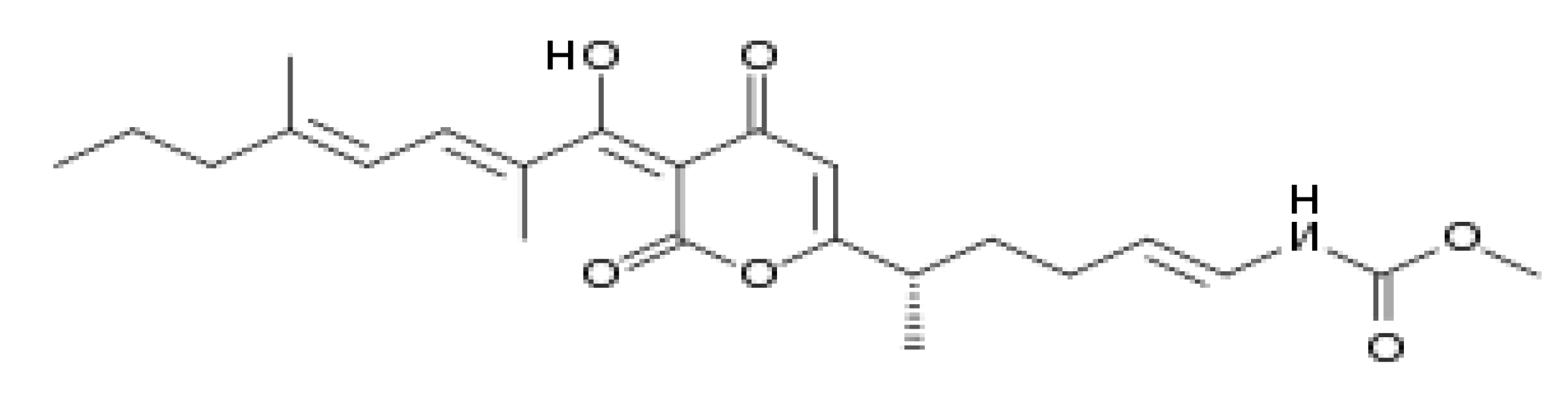
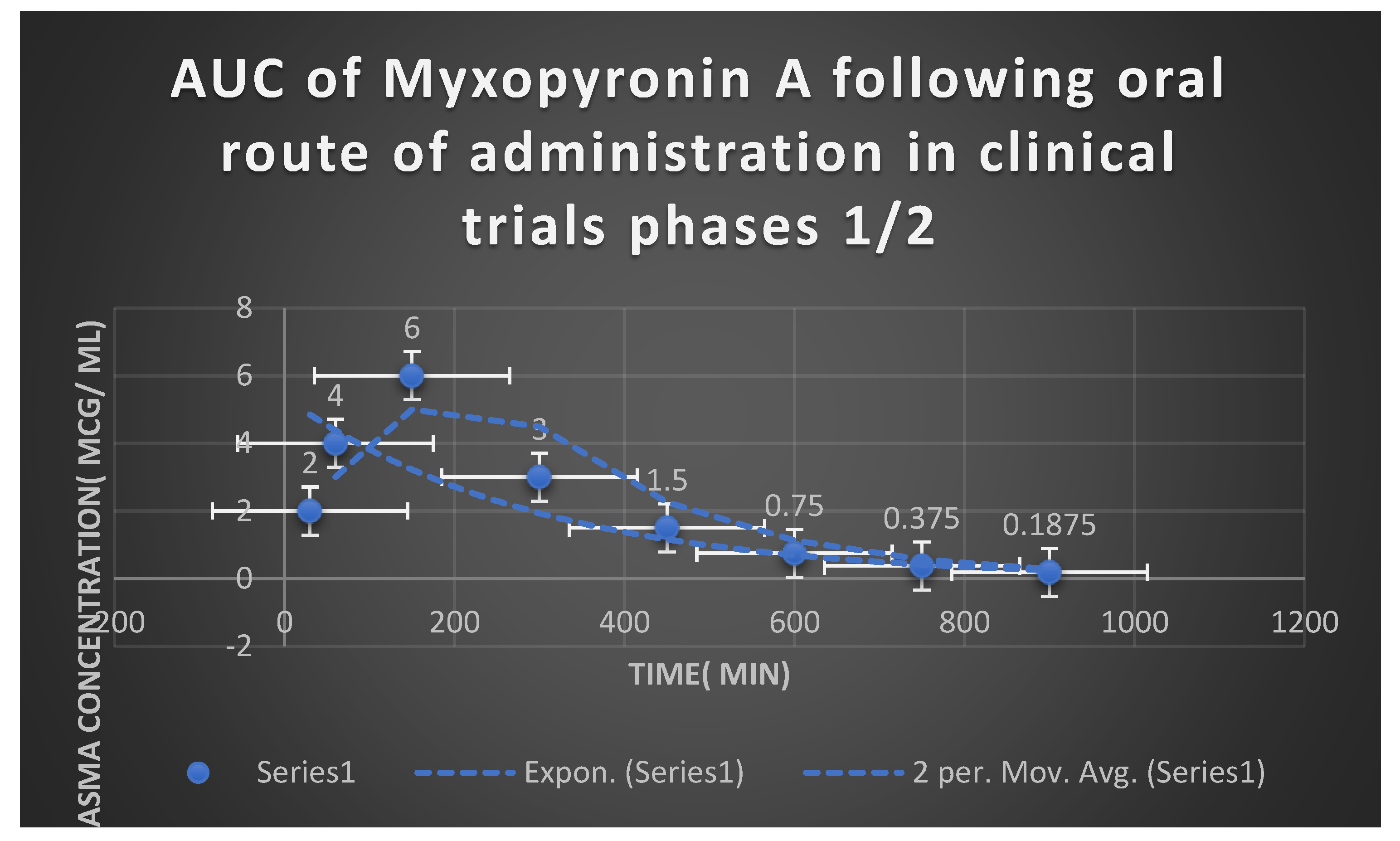
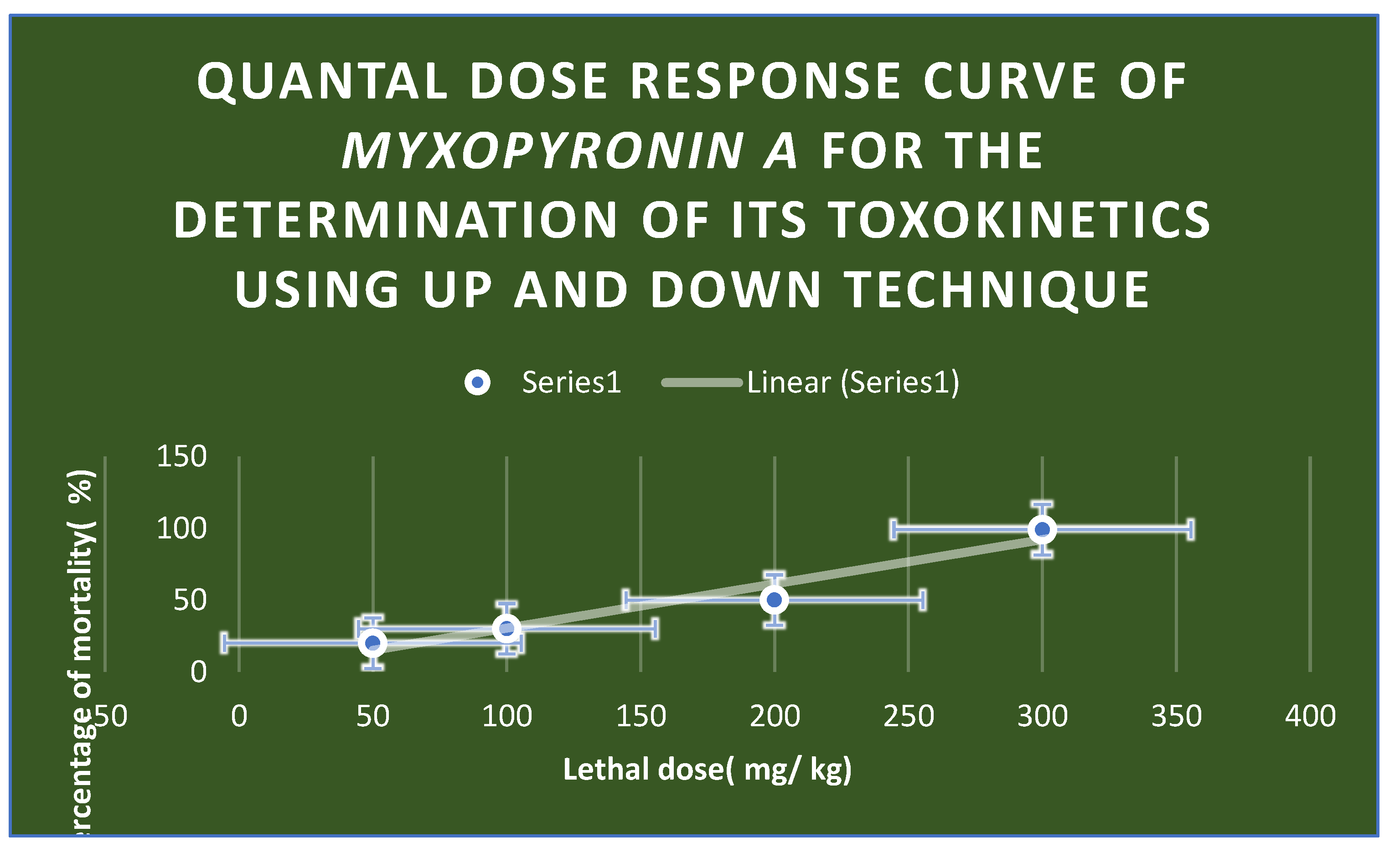
Statistical Analysis
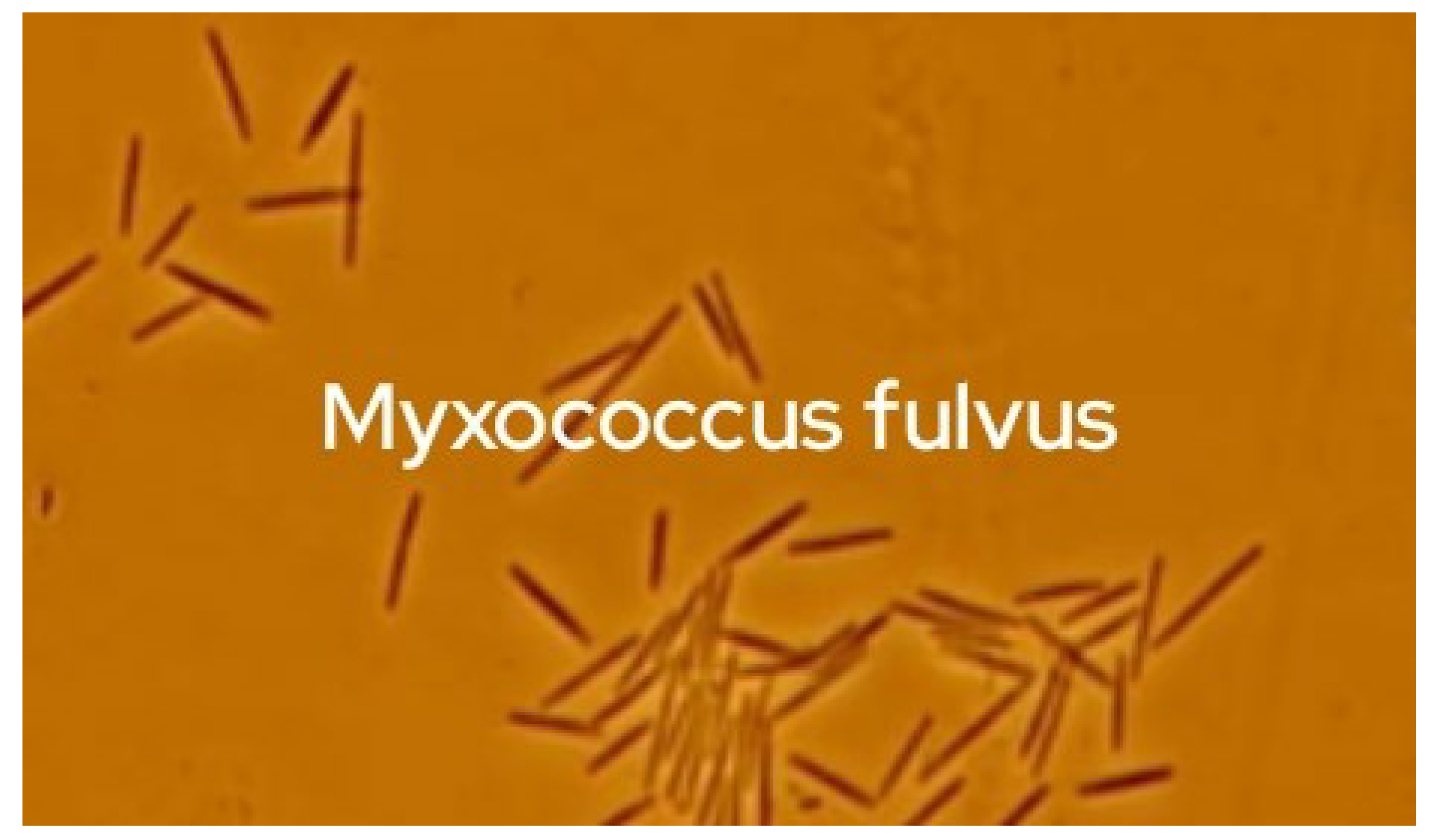
Results
| No of +ve bacterial isolates producing Myxopyronin A | No of -ve bacterial isolates producing Myxopyronin A |
| 19 | 31 |
| Test antibiotic | Degree of purity( %) |
|---|---|
| Myxopyronin A | 80 |
| Myxopyronin B | 20 |
| Description | Scientific Name | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E value | Per. ident |
| Myxococcus fulvus 124B02, complete genome | Myxococcus fulvus 124B02 | 597 | 1167 | 99% | 6.00E-166 | 98.81 |
| Myxococcus sp. MH1 DNA, complete genome | Myxococcus sp. MH1 | 525 | 1051 | 99% | 3.00E-144 | 94.94 |
| Myxococcus sp. SDU36 chromosome, complete genome | Myxococcus sp. SDU36 | 436 | 870 | 99% | 1.00E-117 | 90.15 |
| Myxococcus hansupus strain mixupus chromosome, complete genome | Myxococcus hansupus | 126 | 126 | 65% | 3.00E-24 | 77.23 |
| Cystobacter fuscus strain DSM 52655 chromosome, complete genome | Cystobacter fuscus | 124 | 124 | 54% | 1.00E-23 | 78.92 |
| Cystobacter fuscus strain Cbf 8 chromosome, complete genome | Cystobacter fuscus | 124 | 124 | 54% | 1.00E-23 | 78.92 |
| Test organism | MIC( µg/ ml) | Diameter of inhibition zone( mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis | 5 | 12 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 7 | 18 |
| Streptococcus pneumonae | 13 | 9 |
| Escherichia coli | 108 | 11 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 120 | 0 |
| Candida albicans | 105 | 0 |
| Sacchromyces cerevisiae | 100 | 0 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 101 | 17 |
| Bacillus cereus | 16 | 10 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 21 | 13 |
| Serratia Marcescens | 105 | 9 |
| Mucor hiemalis | 0 | 19 |
| Shigella dysentery | 113 | 7 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 139 | 6 |
| Pathogenic m.o | MIC( µg/ ml) |
|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis | 8 |
| Bacillus cereus | 7 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 13 |
| Pneumococci | 15 |
| E.coli | 110 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 142 |
| Candida albicans | 0 |
| Sacchromyces cerevisiae | 0 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 103 |
| Haemophilus influenza | 0 |
| Gonococci | 127 |
| meningococci | 134 |
| Serratia Marcescens | 105 |
| Mucor hiemalis | 0 |
| Shigella dysenteriae | 113 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 0 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 0 |
| Pathogenic m.o | MBC( µg/ ml) |
|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis | 24 |
| Bacillus cereus | 21 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 39 |
| Pneumococci | 46 |
| E.coli | 331 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 412 |
| Candida albicans | 0 |
| Sacchromyces cerevisiae | 0 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 307 |
| Haemophilus influenza | 0 |
| Gonococci | 370 |
| meningococci | 390 |
| Serratia Marcescens | 320 |
| Mucor hiemalis | 0 |
| Shigella dysenteriae | 303 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 0 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 0 |
Discuss
Conclusion
Publication Consent
Ethical Statement:
Conflicts of Interests
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
References
- Dalhoff, A. Selective toxicity of antibacterial agents-still a valid concept or do we miss chances and ignore risks? Infection. 2021 Feb;49(1):29-56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings MI, Truman AW, Wilkinson B. Antibiotics: past, present and future. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2019 Oct;51:72-80. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wencewicz, TA. Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 2019 Aug 23;431(18):3370-3399. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepe JA, Martínez-Martínez L. Resistance mechanisms in Gram-negative bacteria. Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2022 Jul;46(7):392-402. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila J, Marco F. Lectura interpretada del antibiograma de bacilos gramnegativos no fermentadores [Interpretive reading of the non-fermenting gram-negative bacilli antibiogram]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2010 Dec;28(10):726-36. Spanish. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq S, Vickers A, Woodford N, Livermore DM. WCK 4234, a novel diazabicyclooctane potentiating carbapenems against Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter with class A, C and D β-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Jun 1;72(6):1688-1695. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin SV, Fisher P, Graham E, Malek A, Robidoux A. Sulfites inhibit the growth of four species of beneficial gut bacteria at concentrations regarded as safe for food. PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0186629. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong S, Lee Y, Yun CH, Park OJ, Han SH. Propionate, together with triple antibiotics, inhibits the growth of Enterococci. J Microbiol. 2019 Nov;57(11):1019-1024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell. 2007 Sep 7;130(5):797-810. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer M, Herrmann J, Zühlke D, Müller R, Riedel K, Sievers S. Myxopyronin B inhibits growth of a Fidaxomicin-resistant Clostridioides difficile isolate and interferes with toxin synthesis. Gut Pathog. 2022 Jan 6;14(1):4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doundoulakis T, Xiang AX, Lira R, Agrios KA, Webber SE, Sisson W, Aust RM, Shah AM, Showalter RE, Appleman JR, Simonsen KB. Myxopyronin B analogs as inhibitors of RNA polymerase, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Nov 15;14(22):5667-72. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lira R, Xiang AX, Doundoulakis T, Biller WT, Agrios KA, Simonsen KB, Webber SE, Sisson W, Aust RM, Shah AM, Showalter RE, Banh VN, Steffy KR, Appleman JR. Syntheses of novel myxopyronin B analogs as potential inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Dec 15;17(24):6797-800. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy TI, Daniel A, Hardy C, Jackson A, Rehrauer O, Hwang YS, Zou D, Nguyen K, Silverman JA, Li Q, Murphy C. Evaluating the activity of the RNA polymerase inhibitor myxopyronin B against Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011 Jun;319(2):176-9. [PubMed]
- Srivastava A, Talaue M, Liu S, Degen D, Ebright RY, Sineva E, Chakraborty A, Druzhinin SY, Chatterjee S, Mukhopadhyay J, Ebright YW, Zozula A, Shen J, Sengupta S, Niedfeldt RR, Xin C, Kaneko T, Irschik H, Jansen R, Donadio S, Connell N, Ebright RH. New target for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase: 'switch region'. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011 Oct;14(5):532-43. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosaei H, Harbottle J. Mechanisms of antibiotics inhibiting bacterial RNA polymerase. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):339-350. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucipto H, Sahner JH, Prusov E, Wenzel SC, Hartmann RW, Koehnke J, Müller R. In vitro recontruction of α-pyrone ring formation in myxopyronin biosynthesis. Chem Sci. 2015 Aug 1;6(8). 2015. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Toole, GA. Classic Spotlight: How the Gram Stain Works. J Bacteriol. 2016 Nov 4;198(23):3128. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhur J, Chan H, Kachappilly B, Mohamed A, Morlot C, Awad M, Lyras D, Taib N, Gribaldo S, Rudner DZ, Rodrigues CDA. A dynamic, ring-forming MucB / RseB-like protein influences spore shape in Bacillus subtilis. PLoS Genet. 2020 Dec 14;16(12):e1009246. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin Y, Faheem A, Hu Y. A spore-based portable kit for on-site detection of fluoride ions. J Hazard Mater. 2021 Oct 5;419:126467. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeen MT, Jacobs-Wagner C. Bacterial cell shape. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Aug;3(8):601-10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang Q, Xiao L, He Q, Liu S, Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang Z, Nie F, Guo Y, Zhang L. Comparison of haemolytic activity of tentacle-only extract from jellyfish Cyanea capillata in diluted whole blood and erythrocyte suspension: diluted whole blood is a valid test system for haemolysis study. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Nov;64(7-8):831-5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubay MM, Acres J, Riekeles M, Nadeau JL. Recent advances in experimental design and data analysis to characterize prokaryotic motility. J Microbiol Methods. 2023 Jan;204:106658. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang C, Zhang Y, Luo H, Zhang H, Li W, Zhang WX, Yang J. Iron-Based Nanocatalysts for Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction. Small Methods. 2022 Oct;6(10):e2200790. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu CY, Cheng HY, Yao XM, Li LZ, Liu HW, Guo WQ, Yan LS, Fu JL. Biodegradation and decolourization of methyl red by Aspergillus versicolor LH1. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;51(7):642-649. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu D, Wu L, Yao H, Zhao L. Catalase-Like Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, and Their Applications. Small. 2022 Sep;18(37):e2203400. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik A, Stefanek S, Janusz G. Properties, Physiological Functions and Involvement of Basidiomycetous Alcohol Oxidase in Wood Degradation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 9;23(22):13808. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro JT, Sellers W. Blood coagulation test for citrate utilization. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):168-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajang M, Malairuang K, Sukna J, Rattanapradit K, Chamsart S. Single-step ethanol production from raw cassava starch using a combination of raw starch hydrolysis and fermentation, scale-up from 5-L laboratory and 200-L pilot plant to 3000-L industrial fermenters. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Mar 16;14(1):68. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerwin, BA. Polysorbates 20 and 80 used in the formulation of protein biotherapeutics: structure and degradation pathways. J Pharm Sci. 2008 Aug;97(8):2924-35. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueba FJ, Neijssel OM, Woldringh CL. Generality of the growth kinetics of the average individual cell in different bacterial populations. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1048-55. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea KW, Xie J, LaCross N, Patel M, Mukundan D, Murphy TF, Marrs CF, Gilsdorf JR. Relationships of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae strains to hemolytic and nonhemolytic Haemophilus haemolyticus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Feb;46(2):406-16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogawat A, Vadassery J, Verma N, Oelmüller R, Dua M, Nevo E, Johri AK. PiHOG1, a stress regulator MAP kinase from the root endophyte fungus Piriformospora indica, confers salinity stress tolerance in rice plants. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 16;6:36765. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry AL, Feeney KL. Two quick methods for Voges-Proskauer test. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1138-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang J, Su Y, Jia F, Jin H. Characterization of casein hydrolysates derived from enzymatic hydrolysis. Chem Cent J. 2013 Apr 4;7(1):62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bie TH, Witkamp RF, Balvers MG, Jongsma MA. Effects of γ-aminobutyric acid supplementation on glucose control in adults with prediabetes: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023 Sep;118(3):708-719. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endoh R, Horiyama M, Ohkuma M. D-Fructose Assimilation and Fermentation by Yeasts Belonging to Saccharomycetes: Rediscovery of Universal Phenotypes and Elucidation of Fructophilic Behaviors in Ambrosiozyma platypodis and Cyberlindnera americana. Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 5;9(4):758. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu Z, Guo W, Liu C. Isolation, identification and characterization of novel Bacillus subtilis. J Vet Med Sci. 2018 Mar 24;80(3):427-433. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao Y, Meng K, Fu J, Xu S, Cai G, Meng G, Nielsen J, Liu Z, Zhang Y. Protein engineering of invertase for enhancing yeast dough fermentation under high-sucrose conditions. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2023 Apr;68(2):207-217. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irschik H, Gerth K, Höfle G, Kohl W, Reichenbach H. The myxopyronins, new inhibitors of bacterial RNA synthesis from Myxococcus fulvus (Myxobacterales). J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1983 Dec;36(12):1651-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(2):163-75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J Pharm Anal. 2016 Apr;6(2):71-79. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell'Anno A, Fabiano M, Duineveld GCA, Kok A, Danovaro R. Nucleic acid (DNA, RNA) quantification and RNA/DNA ratio determination in marine sediments: comparison of spectrophotometric, fluorometric, and HighPerformance liquid chromatography methods and estimation of detrital DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Sep;64(9):3238-45. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonian, MH. Spectrophotometric determination of protein concentration. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;Appendix 3:Appendix 3B. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rox K, Becker T, Schiefer A, Grosse M, Ehrens A, Jansen R, Aden T, Kehraus S, König GM, Krome AK, Hübner MP, Wagner KG, Stadler M, Pfarr K, Hoerauf A. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) of Corallopyronin A against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):131. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu J, Jin H, Zhu H, Zheng M, Wang B, Liu C, Chen M, Zhou L, Zhao W, Fu L, Lu Y. Oral bioavailability of rifampicin, isoniazid, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide in a 4-drug fixed-dose combination compared with the separate formulations in healthy Chinese male volunteers. Clin Ther. 2013 Feb;35(2):161-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utku Türk EG, Jannuzzi AT, Alpertunga B. Determination of the Phototoxicity Potential of Commercially Available Tattoo Inks Using the 3T3-neutral Red Uptake Phototoxicity Test. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022 Feb 28;19(1):70-75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas DN, Wills JW, Tracey H, Baldwin SJ, Burman M, Williams AN, Harte DSG, Buckley RA, Lynch AM. Ames Test study designs for nitrosamine mutagenicity testing: qualitative and quantitative analysis of key assay parameters. Mutagenesis. 2023 Dec 19:gead033. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, YY. , Huang, YF., Liang, J. et al. Improved up-and-down procedure for acute toxicity measurement with reliable LD50 verified by typical toxic alkaloids and modified Karber method. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. [CrossRef]
- Heuser E, Becker K, Idelevich EA. Bactericidal Activity of Sodium Bituminosulfonate against Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 5;11(7):896. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irschik H, Gerth K, Kemmer T, Steinmetz H, Reichenbach H. The myxovalargins, new peptide antibiotics from Myxococcus fulvus (Myxobacterales). I. Cultivation, isolation, and some chemical and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1983 Jan;36(1):6-12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaus F, Dedić D, Tare P, Nagaraja V, Rodrigues L, Aínsa JA, Kunze J, Schneider G, Hartkoorn RC, Cole ST, Altmann KH. Total Synthesis of Ripostatin B and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Ripostatin Analogs. J Org Chem. 2018 Jul 6;83(13):7150-7172. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennison TJ, Smith JC, Badhan RKS, Mohammed AR. Formulation and Bioequivalence Testing of Fixed-Dose Combination Orally Disintegrating Tablets for the Treatment of Tuberculosis in the Pediatric Population. J Pharm Sci. 2020 Oct;109(10):3105-3113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi WA, Al-Shaer MH, Peloquin CA. Protein Binding of First-Line Antituberculosis Drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jun 26;62(7):e00641-18. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| mRNA concentration( ng/ ml) | Absorbance( optical density) at 260 nm |
|---|---|
| 810 | 0.973 |
| 705 | 0.601 |
| 341 | 0.397 |
| 43 | 0.213 |
| Bacterial protein concentration( mcg/ ml) | Time( hr) |
|---|---|
| 70.3 | 1 |
| 41.06 | 3 |
| 18.62 | 5 |
| 3.01 | 10 |
| 0.79 | 12 |
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| Gram stain | - |
| Cell shape | Elongated bacilli with tapered ends |
| Spore shape | Ellipsoidal |
| Spore site | Central |
| Motility | + via gliding |
| Catalase | + |
| Oxidase | - |
| Blood haemolysis | - |
| Indol | - |
| Methyl red | - |
| Nitrate reduction test | + |
| Vogues proscauer | - |
| Citrate utilization | - |
| Starch hydrolysis | + |
| Casein hydrolysis | + |
| Growth at 45 ℃ | Bacterial isolates did not grow at 45 ℃; but were grown at 10-37 ℃ |
| Tween 80 | + |
| Tolerance salinity | |
| 5% NaCl | - |
| 7% NaCl | - |
| Saccharide fermentation | |
| Glucose | - |
| Fructose | - |
| Maltose | - |
| Sucrose | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





