Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
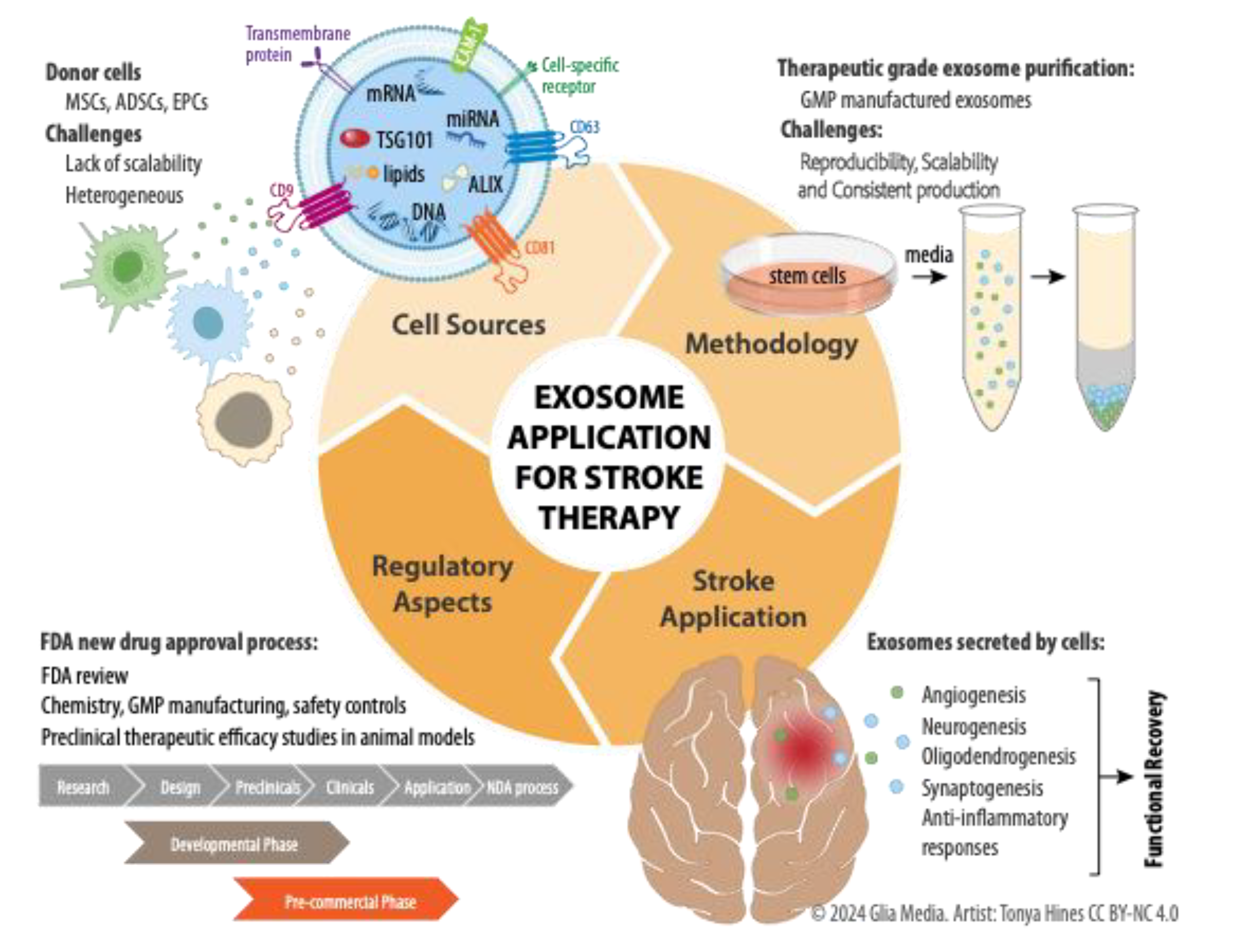
1. Introduction
2. Defining Exosomes
3. Therapeutic Potential for Stroke: Stem Cells versus Exosomes
4. Advantages of Exosome Application in Stroke Therapy
5. Purification Methods and Characterization of Exosomes
6. Stroke Animal Models
6.1. Source of Exosomes in Stroke Therapy
6.2. Delivery of Exosomes in Stroke Therapy
6.3. Biodistribution
6.4. Functional Improvement
6.5. Infarct Volume
6.6. Histological Findings
6.7. Mechanism of Action
7. Clinical Trials and a Perspective on Potential Future Directions for Exosome Therapy in Stroke
8. Conclusion
| Studies | Source of exosomes | Animal models | Purification methods | Characterization | Administration dose | Administration route | Evaluation methods and times for observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xin et. al., [58] | Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) | Adult male Wistar rat transient (2 hours) MCAO model | Ultracentrifugation | expression of Alix | 100 µg total protein of MSC-derived exosomes | Intravenous injection at 24 hrs after stroke | Neurologic severity score (NSS) and foot-fault test at 1, 3, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days |
| Doeppner et. al. [20] | Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) | 10-wk old mice transient MCAO | Polyethyleneglycol (PEG) precipitation and ultracentrifugation | expression of TSG101 and CD81 | 2 x 106 BMSC-EV | Intravenous injection at 24 hrs after stroke at 3 consecutive time points (24 hr, 3 and 5 days) after stroke | Rotarod, corner test and tightrope test, neurologic severity score (NSS) at 7, 14, and 28 days after stroke |
| Ophelders et. al. [19] | Human MSC | Ovine model of preterm hypoxia-ischemia (HI) min in sheep fetuses at 102 days of gestation. | Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and low-speed centrifugation | Particle size (99-123 nm) and expression of CD81 and TSG101 | 2.0 x 107 MSC-EV | Intravenous injection 2 consecutive time points, at 1 hr and 4 days post HI | 1) Baroreceptor reflex on days 0-6 post HI, 2) Collect seizure burden data continuously until 7 days’ post HI |
| Lee et. al. [22] | Human adipose MSC exposed to normal rat brain extract (NBE-MSC), stroke-injured rat brain extract (SBE-MSC) or not exposed to any extract (MSC) | Permanent MCA stroke model in male Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | No molecular or EM characterization | 0.2 mg EV/kg rat body weight | the common carotid artery 48 hrs after stroke | Neurologic function (open field, foot fault, beam balance, prehensile traction and torso-twisting) at 0-, 3- and 7-days post MV injection |
| Chen et. al. [66] | ADSCs and ADSC-exosomes isolated from xenogenic pigs | Mini pigs using the KISOTM System | Ultracentrifugation | Particle size (30-90 nm) using TEM and expression of CD63, TSG101 and ß-catenin | 300 µg exosomes | Intravenous injection at 3 hours after stroke | 1) Sensorimotor functional (Corner Test) studies on day 0, 1, 3, 7, 14 and 28 after stroke, 2) MRI on days 3 and 28 post stroke and 3) euthanized 60 days after stroke. |
| Otero-Ortega et. al. [64] | ADMSC obtained from allogeneic adipose tissue of Sprague-Dawley rats | Ischemic stroke in adult male rats by injection of 1ul of endothelin-1 or of 0.5 U collagenase type IV into the striatum | miRCURY Exosome Isolation Kit | size (<100nm) using NanoSight and by the expression of CD81 and Alix | 100 µg EV | Intravenous injection at 24 hours after stroke | 1) Behavior studies (beam walk, rotarod, modified Rogers test) on 48 hrs, 7 and 28 days after stroke and 2) MRI imaging performed 7 and 28 days after stroke. |
| Webb et. al. [21] | Human neural stem cells (NSC) and human MSC (MSC) differentiated from the H9 hESCs | Thromboembolic model of stroke in aged mice. | Ultracentrifugation | size (<300 nm) using NanoSight and expression of CD63 and CD81 | three dose regiment of EV with 2.7 x 1011 EV | Intravenous injection at 2, 14, and 38 hrs post stroke | 1) Cerebral Doppler measurements at 6 and 38 hrs post injection断2) novel object recognition (NOR) testing to test Episodic memory |
| Xiao et. al. [16] | Endothelial cells exposed to ischemia (6 hr)- reperfusion (24 hr) in vitro | Transient remote ischemic preconditioning cerebral I/R (MCAO/R) in parallel to remote ischemic preconditioning (RIP) by temporary clamping of the femoral artery using adult male and female Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | size (40-100 nm) with a JEOL-1010 TEM and expression of CD63, HSP70 and TSG101 by immunohistochemistry, western blot and flow cytometry | NA | NA | NA |
| Han et. al. [65] | BMSC from Wistar rat | intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in adult male Wistar rats | ExoQuick exosome isolation | BCA Protein assay and qNano nanopore-based exosome detection system断断Alix by断Western blot, and electron microscopy | 100 μg protein of MSC-derived exosomes | Intravenous injection at 24 hrs post ICN | Modified Morris water maze (mMWM), modified Neurological Severity Score (mNSS), and social odor–based novelty recognition tests at days 1, 7, 14, 21 and 25 |
| Huang et al [59] | 1) rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) isolated from rat 断2) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)-overexpressing ADSC | MCAO model using adult male Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | expression of CD9, CD63, CD81, and TSC101 | 100 μg of EVs per kg | Intravenous injection | Oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) experiments |
| Jiang et al [60] | miR30d-5p overexpressing rat ADSCs | MCAO model using adult male Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | size distribution of ADs-Exos, Nanosizer™ technology (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), specific exosome markers CD9, CD63, CD81, and TSC101 | 80 μg of EVs | Intravenous injection | N/A |
| Geng et. al. [61] | Human MI ADSCs (Age: 57-69) and miR-126 loaded ADSCs | MCAO model using 8-12 weeks Sprague-Dawley rats | ExoQuickTM Exosome Precipitation Solution | N/A | N/A | Intravenous injection | Foot-fault test and a modified neurologic severity score (mNSS) at days 1,3,7, and 14 post stroke |
| Liu et. al [62] | Enkephalin overexpressing rat BMSCs | MCAO model using 8-12 weeks Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis, Nanoparticle tracking analysis, specific exosome markers HSP70, CD63, and TSC101 | N/A | Intravenous injection at 12-hour post stroke | NSS test and inclined board test at 1 an d3 weeks |
| Moon et. al [63] | Rat MSCs (p4) or fibroblasts | MCAO model using Sprague-Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | NTA analysis, TEM | 10, 30, 100, or断300 μg rMSC-EVs | Intravenous injection at 24-hour post stroke | 1) mNSS test days 1, 7 and 14 after stroke, and 2) The cylinder and ladder rung walking tests at 28 days post-injury |
| Tian et al. [56] | Neural progenitor cells with RGD-C1C2-fusion | MCAO model using C57BL/6 mice (8 weeks old) | Ultracentrifugation | NTA analysis, TEM | 100 μg (2.5-3.7 × 1010) | Intravenous injection at 1 h of MCAO and 12 h of reperfusion | N/A |
| Yang et al [37] | Hypoxic pre-treated mouse ADSCs | MCAO model using C57BL/6 mice | Ultracentrifugation | TEM and light scattering utilizing Nanosizer (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). | N/A | 1 day postoperatively via an intraperitoneal injection. | Sensorimotor functional recovery prior to MCAO and 3, 5, 7, and 10 days post-MCAO was measured Rotarod exam (IITC Life Science, NY, USA) to define sensorimotor coordination, the adhesive removal test |
| Jiang X et al [92] | Hypoxic preconditioning of neural stem cells (NSCs) | MCAO model using C57BL/6 mice | Ultracentrifugation | BCA protein assay kit, TEM; Nano ZS90 for size and zeta potential; CD9 and CD63 were analyzed via Western Blot; CXCR4 measured using ELISA | 10 µg EV | Intravenous injection at 1 Day after MCAO procedure | Complex motor ability on mNSS adhesive removal test, ladder rung task weekly until day 28th |
| Li et al [97] | M2 microglia | MCAO model using C57BL/6 mice | ExoQuickTC kit from System Biosciences, USA. | TEM, Western blot, PKH26 Red Fluorescent Cell Linker Kit. | M2-Exos (100 μg/mL) EV | Intravenous injection at 2h after MCAO | M2-Exos had a certain effect on alleviating neuronal apoptosis in the MCAO/R model, but had no significant effect on the indicators of neuronal autophagy and ferroptosis |
| Hong et al [93] | UC-MSCs | MCAO model using 8 weeks male Sprague Dawley rats | Ultracentrifugation | TEM, western blot fro CD63, Alix, and TSG101; PKH26 | 50 μg EV | Intravenous injection at 4h after MCAO once a day per 3 days | Neurologic at 2, 4, and 8 hours after the onset of occlusion and then daily until sacrifice. |
| Wang et al [98] | Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs) | MCAO male SD Rats | Ultracentrifugation 断exosome isolation kit from Umibio, China | TEM, western blot, NTA | 200 µg EV | Intravenous injection at the beginning of reperfusion | Stainless steel brain molds were used to freeze the brains rapidly for 5 min at 20°C; the olfactory bulbs and cerebellum were removed before freezing the brain. 2-mm coronal brain sections were prepared, followed by incubation in 2% TTC (Solarbio, China) at RT in the dark. Infarct volumes were calculated using ImageJ software after TTC staining. |
| Zhang et al [91] | NSCs | MCAO male C57BL/6 mice (age: 7–8week, weight: 22-24g) | Ultracentrifugation | TEM, NTA (Malvern Nano ZS90) | NSC (5 × 105 NSCs in 5 μl PBS)断NSC + Exo ( 5 × 105 NSCs with 10 μg exosomes in 5 μl PBS) | lateral ventricle injection at 7 days post MCAO Stereoscopic apparatus (RWD, China). For (AP+0, ML-1, DV-2.25 mm) | Presence and persistence of cerebral edema evaluated by TTC staining at 1 and 7 days post-MCAO/R.断Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation at 3 days post-treatment.断Behavioral assessments (balance beam, ladder rung, rotarod, modified neurological severity score) conducted at 0-8 weeks post-treatment.断Histological examinations performed at 8 weeks post-treatment. MRI for infarct volume |
| Xiao et al [17] | Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) | MCAO C57BL/6 mice (male, 8-week) | Total Exosome Isolation reagent from Thermo Fisher Scientific | TEM, western blot, NTA | 100 µg EV | Intravenous injection Once per day for 3 days after MCAO | Neurological evaluations used the Longa neurological scoring system. |
| Studies | Therapeutic outcomes | Mechanism of action |
|---|---|---|
| Xin et. al.[58] | Enhanced NSS, synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis | 1) Bielschowsky silver and Luxol fast blue staining: Increase neurite remodeling and 2) increased synaptophysin immunoreactivity, increased number of BrdU+/Dcx+ cells and BrdU+/vWF+ cells in IBZ* |
| Doeppner et. al. [20] | Improved neurological impairment and brain remodeling, comparing to 1 x 106 MSC, peripheral lymphodemia was reversed no infiltrating monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, dendritic cells or neutrophils into the brain | 1) Neuroangiogenesis at 28 days post stroke: increased NeuN+ cell density, NeuN+/BrdU+ cell number, Dcx+/BrdU+ cell number and CD31/BrdU+ cell number; 2) Reversed peripheral lymphodemia at D6, no infiltrating monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, dendritic cells or neutrophils into the brain |
| Ophelders et. al. [19] | Reduced baroreflex sensitivity | 1) reduce white matter injury (measured by myelin basic protein) and 2) not impact the normal microglial response to HI (measured by IBA-1 immunoreactivity) |
| Lee et. al. [22] | Reduced infarct volume and improvement in neurologic function was similar in animals treated with either MV isolated from MSC exposed to normal rat brain extract or extract from rat brain after stroke | 1) increased number of DCX+ cells in the ipsilateral **SVZ, increased alpha-smooth muscle actin and reduced GFAP+ cells, 2) increase in the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TSG-6 and attenuation of the pro-inflammatory factors TNF-alpha and progranulin |
| Chen et. al. [66] | 1) Sensorimotor function: No difference was seen between treatments of ADSC, ADSC-EV and combination, 2) MRI and histological studies: greatest reduced infarct volumes showed in the ADMSC plus exosome group, 3) Biodistribution at 60 days: no exosomes or ADMSC | Inflammation, edema, fibrosis, necrosis and apoptosis: greatest reduction in the ADMSC plus exosome group |
| Otero-Ortega et. al. [64] | 1) Significant improvement in the behavioral tests at 28 days and 2) MRI: a decrease in lesion size and improved mean axial diffusivity at 28 days (No difference in functional outcome or MRI at 24 hours and 7 days after treatment. 3) Biodistribution: EV found in the brain, lung, liver, and spleen 24 hrs after administration | Promoting white matter repair after stroke involves proteins identified in extracellular vesicles (EVs) proteome. These proteins play roles in hydrolase activity, tubulin binding, protein kinase regulator activity, kinase regulator activity, and catalytic activity. While growth factor activity isn't the predominant function, the proteins identified could still contribute to functional recovery after EVs administration. There's potential for enhancing therapeutic effects by selectively manipulating the expression of these molecules. |
| Webb et. al. [21] | 1) Significant functional improvements of sensorimotor tests (i.e., balance beam walking, the number of footfalls, hanging wire, and tail suspension performance and declarative memory 14 days post-TEMCAO in aged rodents 2) Biodistribution: the presence of EV in the brain infarct area at 1 hr after injection and still present in the liver, lungs, and spleen at 24 hrs after injection | Smaller infarct volumes (TTC staining) and higher amounts of circulating M2 macrophages and T regulatory cells and lower amounts of TH17 T-cells at 96 hrs after administration of NSC-EV compared to both MSC-EV treated and control animals. Promoting tissue repair and reduce inflammation by modulating immune responses and facilitating communication between cells in the CNS. Crossing the blood-brain barrier for delivering therapeutic molecules directly to the brain. |
| Xiao et. al. [16] | Evaluating smaller infarct volumes using TTC-staining | Reduction the rate of apoptosis through downregulation of Bax and caspase-3 and upregulation of Bcl-2 in SH-SY5Y nerve cells. |
| Han et. al. [65] | Significant improvement in the neurological function of spatial learning and motor recovery measured at 26–28 days by mMWM and starting at day 14 by mNSS | Increased newly generated endothelial cells in the hemorrhagic boundary zone, neuroblasts and mature neurons in the subventricular zone, and myelin in the striatum without altering the lesion volume. 1) EBA staining for mature vascular detection, 2) DCX, TUJ1, and MAP2 for neurogenesis and 3) BrdU-positive, indicating that there were newly generated neuroblasts (BrdU-DCX, BrdU-TUJ1) and newly generated immature neurons (BrdU-MAP2) around the hematoma and the SVZ. |
| Huang et al [59] | Suppressed MCAO-induced cerebral injury (TTC staining 3 days after MCAO). | PEDF-modified ADSCs ameliorated cerebral I/R injury by activating autophagy and suppressing neuronal apoptosis. |
| Jiang et al [60] | Reduction of the cerebral injury area of infarction at day 3 post stroke | Increased anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4, IL-10. Suppression of autophagy (Beclin-1 and Atg5) and inflammatory factors, TNF-a, IL-6 and iNOS |
| Geng et. al. [61] | MiR-126 exosomes: significant reduction ischemic stroke and MCAO ratsImproved functional recovery | Significant increase of the expression of vWF (an endothelial cell marker) and doublecortin (a neuroblasts marker), suppression of microglial cell by Iba1. Decrease of neuron cell death (TUNEL) and increase of cell proliferation. |
| Liu et. al [62] | Exosomes crossed the blood-brain barrier Improvement of the neurological score. | Reduction of Neurons Injury: LDH, p53, caspase-3, and NO. Improvement of brain neuron density. at days 3 and 7: NeuN. |
| Moon et. al [63] | Biodistribution: larger amounts of hMSCs were trapped within the lung after injection and rMSC-EVs accumulated in the infarcted hemisphere in a dose-dependent manner (30–300 μg), but not in the lung and liver. | miRNA-184 and miRNA-210 were essential for promoting neurogenesis and angiogenesis of MSC-EVs.Ki-67 (proliferating cells), DCX (immature progenitor neurons), and vWF (angiogenesis) of both ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres, 14 days after tMCAO. significantly increased coexpression of Ki-67 and DCX in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of both the contralateral and ipsilateral hemispheres |
| Tian et al. [56] | Biodistribution: 24 hours later, the brains were dissected and analyzed by NIRF imaging. the accumulation of undecorated EVReN or Scr-EVReN was most predominant in the liver, followed by the ischemic brain and then the spleens and lungs, whereas the RGD-EVReN had a significantly stronger signal in the ischemic brain | Strong suppression of the inflammatory response (TNFa, IL1b and IL-6). RNA sequencing revealed a set of 7 miRNAs packaged in the EVs inhibited MAPK, an inflammation related pathway. |
| Yang et al [37] | Improved cognitive function by decreasing neuronal damage in the hippocampus after cerebral infarction. | Delivery of circ-Rps5, downstream targets, SIRT7 and miR-124-3p, which promoted M2 microglia/macrophage polarization |
| Jiang X et al 17 | 1) Survival Improvement: MCAO mice treated with hypoxia-preconditioned exosomes (H-EXO) showed a 25% increase in survival compared to standard exosome treatment. 2) Motor Function Recovery:H-EXO-treated mice exhibited superior motor function recovery, outperforming standard exosome treatment in neurological severity scores and behavioral tests. 3) Sensory Acuity and Motor Ability:H-EXO significantly enhanced sensory acuity recovery, restoration of complex motor abilities, and early recovery in ladder-crossing tests. 4) Infarct Volume Reduction: H-EXO treatment resulted in a substantial reduction in infarct volume relative to the whole brain, as observed through MRI and TTC staining. 5) Pathological Examination: Pathological examination revealed that H-EXO reduced spongy tissue, widened cell gaps, and protected neurons, showcasing improved ischemic brain repair capacity. | miR-216a-5p and miR612, are upregulated in hypoxic stem cell-derived exosomes, providing stronger neuroprotection. Additionally, hypoxic stimulation increases the presence of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (HIF-1a) in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes, leading to enhanced vascularization of endothelial cells. |
| Li et at [97] | OIP5-AS1 could reduce cerebral infarct size, brain edema and mNSS scores in MCAO/R mice and inhibit the expression levels of pyroptosis-related proteins in brain tissue, suggesting that M2 microglia-derived exosomal OIP5-AS1 can alleviate CIRI and inhibit neuronal pyroptosis.M2-Exos had a certain effect on alleviating neuronal apoptosis in the MCAO/R model but had no significant effect on the indicators of neuronal autophagy and ferroptosis. | OIP5-AS1 can alleviate MCAO/R-induced brain damage via the pyroptosis-related proteins indicating that OIP5-AS1 could inhibit the expression of pyroptotic proteins. OIP5-AS1 attenuates neuron damage by reducing the protein stability of TXNIP, thereby inhibiting neuron pyroptosis and reducing CIRI. |
| Hong et al [93] | MSCs-derived exosomes ameliorated cerebral I/R injury via enhancing circBBS2 expression. circBBS2 served as an endogenous sponger of miR-494 to upregulate SLC7A11, resulting in ferroptosis inhibition. | UC-MSCs-derived exosomes protected against H/R-induced ferroptosis in SH-SY5Y cells via delivering circBBS2. |
| Wang et al [98] | Infarct volume was decreased more evidently of the miR-193b-5p Exos group compared with the Exos group (P<0.01). The infarct volume differed not obviously between the Exos and inhibitor Exos groups (P>0.05). These findings showed that exosomes overexpressing miR-193b-5p aggravate ischemic injury caused by pyroptosis. | miR-193b-5p, which is overexpressed in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. These exosomes mediate the activation of the AIM2 inflammasome and induce cell pyroptosis, a form of programmed cell death. The exosomes are absorbed by OGD/R-induced PC12 cells and ischemic penumbra of cerebral tissue, influencing the inflammatory response and cell death associated with ischemic stroke. |
| Zhang et al [91] | Combination therapy (NSCs and exosomes) significantly reduces tissue loss compared to NSC treatment alone. Exosomes further decrease neuronal loss in the postlesional hemisphere. Combination therapy superior therapeutic effects compared to individual treatments. Improved motor function and reduced brain infarction in MCAO/R mice. Accelerated and enhanced therapeutic effects with the addition of NSC-derived exosomes. | Delivery of miRNAs to recipient cells and brain tissues, which then regulate the expression of target genes such as STAT3, PTPN1, and CHUK. |
| Xiao et al [17] | BMSC-derived exosomes contribute to functional recovery after ischemic stroke by promoting angiogenesis and reducing neuronal cell damage. Role of Egr2 in this process, which binds to the promoter of SIRT6, enhancing its expression. Increased SIRT6 then suppresses Notch signaling, leading to improved outcomes in cell injury and angiogenesis under OGD/R conditions. BMSC-derived exosome-mediated mitigation of OGD/R-caused cell injury and reduced angiogenesis was dependent on Egr2. Exosomes carrying Egr2 can mitigate brain damage caused by MCAO/R in mice, offering a promising avenue for exosome-based ischemic stroke therapy. | Transferring mRNAs and microRNAs, exosomes with overexpressed microRNA-138-5p from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells can confer neuroprotection to astrocytes after ischemic stroke by inhibiting LCN2. Exosomes derived from BMSCs with overexpressed CXCR4 promote the activation of microvascular endothelial cells during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauldin, P. D.; Simpson, K. N.; Palesch, Y. Y.; Spilker, J. S.; Hill, M. D.; Khatri, P.; Broderick, J. P.; Interventional Management of Stroke, I. I. I. I. Design of the economic evaluation for the Interventional Management of Stroke (III) trial. Int J Stroke 2008, 3, 138–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C. W.; Aday, A. W.; Almarzooq, Z. I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A. Z.; Bittencourt, M. S.; Boehme, A. K.; Buxton, A. E.; Carson, A. P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; Elkind, M. S. V.; Evenson, K. R.; Eze-Nliam, C.; Ferguson, J. F.; Generoso, G.; Ho, J. E.; Kalani, R.; Khan, S. S.; Kissela, B. M.; Knutson, K. L.; Levine, D. A.; Lewis, T. T.; Liu, J.; Loop, M. S.; Ma, J.; Mussolino, M. E.; Navaneethan, S. D.; Perak, A. M.; Poudel, R.; Rezk-Hanna, M.; Roth, G. A.; Schroeder, E. B.; Shah, S. H.; Thacker, E. L.; VanWagner, L. B.; Virani, S. S.; Voecks, J. H.; Wang, N. Y.; Yaffe, K.; Martin, S. S. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adeoye, O.; Hornung, R.; Khatri, P.; Kleindorfer, D. Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator use for ischemic stroke in the United States: a doubling of treatment rates over the course of 5 years. Stroke 2011, 42, 1952–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D. A.; Duncan, P. W.; Nguyen-Huynh, M. N.; Ogedegbe, O. G. Interventions Targeting Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Stroke Prevention and Treatment. Stroke 2020, 51, 3425–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Flores, S.; Rabinstein, A.; Biller, J.; Elkind, M. S.; Griffith, P.; Gorelick, P. B.; Howard, G.; Leira, E. C.; Morgenstern, L. B.; Ovbiagele, B.; Peterson, E.; Rosamond, W.; Trimble, B.; Valderrama, A. L.; American Heart Association Stroke, C.; Council on Cardiovascular, N.; Council on, E. ; Prevention; Council on Quality of, C. ; Outcomes, R., Racial-ethnic disparities in stroke care: the American experience: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011, 42, 2091–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeme, S.; Kottenmeier, E.; Uzochukwu, G.; Brinjikji, W. Evidence-Based Disparities in Stroke Care Metrics and Outcomes in the United States: A Systematic Review. Stroke 2022, 53, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A. I.; Baskett, W. I.; Huang, W.; Shyu, D.; Myers, D.; Raju, M.; Lobanova, I.; Suri, M. F. K.; Naqvi, S. H.; French, B. R.; Siddiq, F.; Gomez, C. R.; Shyu, C. R. Acute Ischemic Stroke and COVID-19: An Analysis of 27 676 Patients. Stroke 2021, 52, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, N.; Noval, M. G.; Kaur, R.; Amadori, L.; Gildea, M.; Sajja, S.; Das, D.; Cilhoroz, B.; Stewart, O.; Fernandez, D. M.; Shamailova, R.; Guillen, A. V.; Jangra, S.; Schotsaert, M.; Newman, J. D.; Faries, P.; Maldonado, T.; Rockman, C.; Rapkiewicz, A.; Stapleford, K. A.; Narula, N.; Moore, K. J.; Giannarelli, C. SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers pro-atherogenic inflammatory responses in human coronary vessels. Nat Cardiovasc Res 2023, 2, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriakose, D.; Xiao, Z. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 10. Thery, C.; Witwer, K. W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M. J.; Anderson, J. D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G. K.; Ayre, D. C.; Bach, J. M.; Bachurski, D.; Baharvand, H.; Balaj, L.; Baldacchino, S.; Bauer, N. N.; Baxter, A. A.; Bebawy, M.; Beckham, C.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Benmoussa, A.; Berardi, A. C.; Bergese, P.; Bielska, E.; Blenkiron, C.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Boilard, E.; Boireau, W.; Bongiovanni, A.; Borras, F. E.; Bosch, S.; Boulanger, C. M.; Breakefield, X.; Breglio, A. M.; Brennan, M. A.; Brigstock, D. R.; Brisson, A.; Broekman, M. L.; Bromberg, J. F.; Bryl-Gorecka, P.; Buch, S.; Buck, A. H.; Burger, D.; Busatto, S.; Buschmann, D.; Bussolati, B.; Buzas, E. I.; Byrd, J. B.; Camussi, G.; Carter, D. R.; Caruso, S.; Chamley, L. W.; Chang, Y. T.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Cheng, L.; Chin, A. R.; Clayton, A.; Clerici, S. P.; Cocks, A.; Cocucci, E.; Coffey, R. J.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Couch, Y.; Coumans, F. A.; Coyle, B.; Crescitelli, R.; Criado, M. F.; D'Souza-Schorey, C.; Das, S.; Datta Chaudhuri, A.; de Candia, P.; De Santana, E. F.; De Wever, O.; Del Portillo, H. A.; Demaret, T.; Deville, S.; Devitt, A.; Dhondt, B.; Di Vizio, D.; Dieterich, L. C.; Dolo, V.; Dominguez Rubio, A. P.; Dominici, M.; Dourado, M. R.; Driedonks, T. A.; Duarte, F. V.; Duncan, H. M.; Eichenberger, R. M.; Ekstrom, K.; El Andaloussi, S.; Elie-Caille, C.; Erdbrugger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J. M.; Fatima, F.; Fish, J. E.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Forsonits, A.; Frelet-Barrand, A.; Fricke, F.; Fuhrmann, G.; Gabrielsson, S.; Gamez-Valero, A.; Gardiner, C.; Gartner, K.; Gaudin, R.; Gho, Y. S.; Giebel, B.; Gilbert, C.; Gimona, M.; Giusti, I.; Goberdhan, D. C.; Gorgens, A.; Gorski, S. M.; Greening, D. W.; Gross, J. C.; Gualerzi, A.; Gupta, G. N.; Gustafson, D.; Handberg, A.; Haraszti, R. A.; Harrison, P.; Hegyesi, H.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A. F.; Hochberg, F. H.; Hoffmann, K. F.; Holder, B.; Holthofer, H.; Hosseinkhani, B.; Hu, G.; Huang, Y.; Huber, V.; Hunt, S.; Ibrahim, A. G.; Ikezu, T.; Inal, J. M.; Isin, M.; Ivanova, A.; Jackson, H. K.; Jacobsen, S.; Jay, S. M.; Jayachandran, M.; Jenster, G.; Jiang, L.; Johnson, S. M.; Jones, J. C.; Jong, A.; Jovanovic-Talisman, T.; Jung, S.; Kalluri, R.; Kano, S. I.; Kaur, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Keller, E. T.; Khamari, D.; Khomyakova, E.; Khvorova, A.; Kierulf, P.; Kim, K. P.; Kislinger, T.; Klingeborn, M.; Klinke, D. J., 2nd; Kornek, M.; Kosanovic, M. M.; Kovacs, A. F.; Kramer-Albers, E. M.; Krasemann, S.; Krause, M.; Kurochkin, I. V.; Kusuma, G. D.; Kuypers, S.; Laitinen, S.; Langevin, S. M.; Languino, L. R.; Lannigan, J.; Lasser, C.; Laurent, L. C.; Lavieu, G.; Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Le Lay, S.; Lee, M. S.; Lee, Y. X. F.; Lemos, D. S.; Lenassi, M.; Leszczynska, A.; Li, I. T.; Liao, K.; Libregts, S. F.; Ligeti, E.; Lim, R.; Lim, S. K.; Line, A.; Linnemannstons, K.; Llorente, A.; Lombard, C. A.; Lorenowicz, M. J.; Lorincz, A. M.; Lotvall, J.; Lovett, J.; Lowry, M. C.; Loyer, X.; Lu, Q.; Lukomska, B.; Lunavat, T. R.; Maas, S. L.; Malhi, H.; Marcilla, A.; Mariani, J.; Mariscal, J.; Martens-Uzunova, E. S.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Martinez, M. C.; Martins, V. R.; Mathieu, M.; Mathivanan, S.; Maugeri, M.; McGinnis, L. K.; McVey, M. J.; Meckes, D. G., Jr.; Meehan, K. L.; Mertens, I.; Minciacchi, V. R.; Moller, A.; Moller Jorgensen, M.; Morales-Kastresana, A.; Morhayim, J.; Mullier, F.; Muraca, M.; Musante, L.; Mussack, V.; Muth, D. C.; Myburgh, K. H.; Najrana, T.; Nawaz, M.; Nazarenko, I.; Nejsum, P.; Neri, C.; Neri, T.; Nieuwland, R.; Nimrichter, L.; Nolan, J. P.; Nolte-'t Hoen, E. N.; Noren Hooten, N.; O'Driscoll, L.; O'Grady, T.; O'Loghlen, A.; Ochiya, T.; Olivier, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, L. A.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Ostergaard, O.; Ostrowski, M.; Park, J.; Pegtel, D. M.; Peinado, H.; Perut, F.; Pfaffl, M. W.; Phinney, D. G.; Pieters, B. C.; Pink, R. C.; Pisetsky, D. S.; Pogge von Strandmann, E.; Polakovicova, I.; Poon, I. K.; Powell, B. H.; Prada, I.; Pulliam, L.; Quesenberry, P.; Radeghieri, A.; Raffai, R. L.; Raimondo, S.; Rak, J.; Ramirez, M. I.; Raposo, G.; Rayyan, M. S.; Regev-Rudzki, N.; Ricklefs, F. L.; Robbins, P. D.; Roberts, D. D.; Rodrigues, S. C.; Rohde, E.; Rome, S.; Rouschop, K. M.; Rughetti, A.; Russell, A. E.; Saa, P.; Sahoo, S.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Sanchez, C.; Saugstad, J. A.; Saul, M. J.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Schneider, R.; Schoyen, T. H.; Scott, A.; Shahaj, E.; Sharma, S.; Shatnyeva, O.; Shekari, F.; Shelke, G. V.; Shetty, A. K.; Shiba, K.; Siljander, P. R.; Silva, A. M.; Skowronek, A.; Snyder, O. L., 2nd; Soares, R. P.; Sodar, B. W.; Soekmadji, C.; Sotillo, J.; Stahl, P. D.; Stoorvogel, W.; Stott, S. L.; Strasser, E. F.; Swift, S.; Tahara, H.; Tewari, M.; Timms, K.; Tiwari, S.; Tixeira, R.; Tkach, M.; Toh, W. S.; Tomasini, R.; Torrecilhas, A. C.; Tosar, J. P.; Toxavidis, V.; Urbanelli, L.; Vader, P.; van Balkom, B. W.; van der Grein, S. G.; Van Deun, J.; van Herwijnen, M. J.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.; van Niel, G.; van Royen, M. E.; van Wijnen, A. J.; Vasconcelos, M. H.; Vechetti, I. J., Jr.; Veit, T. D.; Vella, L. J.; Velot, E.; Verweij, F. J.; Vestad, B.; Vinas, J. L.; Visnovitz, T.; Vukman, K. V.; Wahlgren, J.; Watson, D. C.; Wauben, M. H.; Weaver, A.; Webber, J. P.; Weber, V.; Wehman, A. M.; Weiss, D. J.; Welsh, J. A.; Wendt, S.; Wheelock, A. M.; Wiener, Z.; Witte, L.; Wolfram, J.; Xagorari, A.; Xander, P.; Xu, J.; Yan, X.; Yanez-Mo, M.; Yin, H.; Yuana, Y.; Zappulli, V.; Zarubova, J.; Zekas, V.; Zhang, J. Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zheutlin, A. R.; Zickler, A. M.; Zimmermann, P.; Zivkovic, A. M.; Zocco, D.; Zuba-Surma, E. K., Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750.
- Crescitelli, R.; Lasser, C.; Szabo, T. G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzas, E. I.; Lotvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, P.; Landmesser, U. Role of microRNAs in stem/progenitor cells and cardiovascular repair. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 93, 614–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H. S.; Tong, H. S.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, C. Y.; Bin, J. P.; Su, L. Differential Expression Pattern of Exosome Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in Vascular Endothelial Cells Under Heat Stroke. Med Sci Monit 2018, 24, 7965–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chopp, M. Exosome Therapy for Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.; Katakowski, M.; Wang, F.; Qian, J. Y.; Liu, X. S.; Ali, M. M.; Buller, B.; Zhang, Z. G.; Chopp, M. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke 2017, 48, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Chai, Y.; Lv, S.; Ye, M.; Wu, M.; Xie, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Z. Endothelial cell-derived exosomes protect SH-SY5Y nerve cells against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Med 2017, 40, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y. BMSC-Derived Exosomal Egr2 Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke by Directly Upregulating SIRT6 to Suppress Notch Signaling. Mol Neurobiol 2023, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Alonso-Lopez, E.; Perez-Mato, M.; Laso-Garcia, F.; Gomez-de Frutos, M. C.; Diekhorst, L.; Garcia-Bermejo, M. L.; Conde-Moreno, E.; Fuentes, B.; de Lecinana, M. A.; Bravo, S. B.; Diez-Tejedor, E.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, M. Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Proteins and MicroRNA Profiles in Subcortical and Cortical-Subcortical Ischaemic Stroke. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophelders, D. R.; Wolfs, T. G.; Jellema, R. K.; Zwanenburg, A.; Andriessen, P.; Delhaas, T.; Ludwig, A. K.; Radtke, S.; Peters, V.; Janssen, L.; Giebel, B.; Kramer, B. W. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Protect the Fetal Brain After Hypoxia-Ischemia. Stem Cells Transl Med 2016, 5, 754–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeppner, T. R.; Herz, J.; Gorgens, A.; Schlechter, J.; Ludwig, A. K.; Radtke, S.; de Miroschedji, K.; Horn, P. A.; Giebel, B.; Hermann, D. M. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med 2015, 4, 1131–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R. L.; Kaiser, E. E.; Scoville, S. L.; Thompson, T. A.; Fatima, S.; Pandya, C.; Sriram, K.; Swetenburg, R. L.; Vaibhav, K.; Arbab, A. S.; Baban, B.; Dhandapani, K. M.; Hess, D. C.; Hoda, M. N.; Stice, S. L. Human Neural Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Improve Tissue and Functional Recovery in the Murine Thromboembolic Stroke Model. Transl Stroke Res 2018, 9, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Y.; Kim, E.; Choi, S. M.; Kim, D. W.; Kim, K. P.; Lee, I.; Kim, H. S. Microvesicles from brain-extract-treated mesenchymal stem cells improve neurological functions in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 33038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Newcomb, J.; Garbuzova-Davis, S.; Davis Sanberg, C.; Sanberg, P. R.; Willing, A. E. Human Umbilical Cord Blood Cells Have Trophic Effects on Young and Aging Hippocampal Neurons in Vitro. Aging Dis 2010, 1, 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, N.; Kawao, N.; Okada, K.; Okumoto, K.; Teramura, T.; Ueshima, S.; Umemura, K.; Matsuo, O. Systemic transplantation of embryonic stem cells accelerates brain lesion decrease and angiogenesis. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 575–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mo, X.; Qin, C.; Zheng, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C. Transplantation of differentiated bone marrow stromal cells promotes motor functional recovery in rats with stroke. Neurol Res 2013, 35, 320–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Yuan, P.; Zhao, H.; Yi, Y.; Qin, Y.; Dong, Z.; Cao, L.; Ren, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Lu, B.; Liang, A.; Xu, G. T.; Zhu, H.; Gao, Z.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Human adipose-derived stem cells partially rescue the stroke syndromes by promoting spatial learning and memory in mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Stem Cell Res Ther 2015, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, P.; Kassis, I.; Levin, N.; Paul, F.; Backner, Y.; Benoliel, T.; Oertel, F. C.; Scheel, M.; Hallimi, M.; Yaghmour, N.; Hur, T. B.; Ginzberg, A.; Levy, Y.; Abramsky, O.; Karussis, D. Beneficial effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain 2020, 143, 3574–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, A.; Srivastava, M. V.; Mohanty, S.; Bhatia, R.; Kumaran, S. S.; Bose, S. Stem cell therapy: a clinical trial of stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013, 115, 1003–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeppner, T. R.; Hermann, D. M. Stem cell-based treatments against stroke: observations from human proof-of-concept studies and considerations regarding clinical applicability. Front Cell Neurosci 2014, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T. L.; Baskaran, R.; Tsai, S. T.; Huang, C. Y.; Chuang, M. H.; Syu, W. S.; Harn, H. J.; Lin, Y. C.; Chen, C. H.; Huang, P. C.; Wang, Y. F.; Chuang, C. H.; Lin, P. C.; Lin, S. Z. Intracerebral transplantation of autologous adipose-derived stem cells for chronic ischemic stroke: A phase I study. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2022, 16, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeppner, T. R.; Ewert, T. A.; Tonges, L.; Herz, J.; Zechariah, A.; ElAli, A.; Ludwig, A. K.; Giebel, B.; Nagel, F.; Dietz, G. P.; Weise, J.; Hermann, D. M.; Bahr, M. Transduction of neural precursor cells with TAT-heat shock protein 70 chaperone: therapeutic potential against ischemic stroke after intrastriatal and systemic transplantation. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R. H.; Pulin, A. A.; Seo, M. J.; Kota, D. J.; Ylostalo, J.; Larson, B. L.; Semprun-Prieto, L.; Delafontaine, P.; Prockop, D. J. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibe, F.; Klein, O.; Klose, J.; Priller, J. Mesenchymal stromal cells rescue cortical neurons from apoptotic cell death in an in vitro model of cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2012, 32, 567–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tredget, E. E.; Wu, P. Y.; Wu, Y. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One 2008, 3, e1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J. Y.; Wang, H. W.; Chang, S. J.; Liao, K. H.; Lee, I. H.; Lin, W. S.; Wu, C. H.; Lin, W. Y.; Cheng, S. M. Mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e72604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Fang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Candi, E.; Wang, J.; Hua, D.; Shao, C.; Shi, Y. The secretion profile of mesenchymal stem cells and potential applications in treating human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tu, Z.; Yang, D.; Hu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, B.; Hou, S. Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Neurosci Lett 2022, 769, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G. Y.; Wang, Y. Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells promote microglia M2 polarization and neurological recovery in a mouse model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, T.; Niu, X.; Hu, L.; Cheng, J.; Guo, D.; Ren, H.; Zhao, R.; Ji, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y. ADSC-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial infarction injury by promoting miR-205-mediated cardiac angiogenesis. Biol Direct 2023, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, L.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Chu, M.; Sha, X.; Zhao, J. Anti-CHAC1 exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of miR-760-3p in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury mice inhibiting neuron ferroptosis. J Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, G. Emerging Role of microRNAs in Stroke Protection Elicited by Remote Postconditioning. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 748709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M. C.; Andriantsitohaina, R. Microparticles in angiogenesis: therapeutic potential. Circ Res 2011, 109, 110–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, O. G.; Van Balkom, B. W.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Bouten, C. V.; Verhaar, M. C. Extracellular vesicles: potential roles in regenerative medicine. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, X.; Gong, Q.; Li, C.; Guo, B.; Jiang, H. Exosomes with Highly Angiogenic Potential for Possible Use in Pulp Regeneration. J Endod 2018, 44, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, G. Stem cell therapy without the cells. Commun Integr Biol 2013, 6, e26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. C.; Liu, X. B.; Huang, S.; Bi, X. Y.; Wang, H. X.; Xie, L. X.; Wang, Y. Q.; Cao, X. F.; Lv, J.; Xiao, F. J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z. K. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells stimulated by hypoxia promote angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cells Dev 2012, 21, 3289–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlan, R. S.; Pisano, S.; Oliveira, M. I.; Ferrari, M.; Mendes Pinto, I. Exosomes as Reconfigurable Therapeutic Systems. Trends Mol Med 2017, 23, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, Y. Exosomes: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets of Diabetic Vascular Complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 720466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castano, C.; Novials, A.; Parrizas, M. Exosomes and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2019, 35, e3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Niu, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalirfardouei, R.; Jamialahmadi, K.; Jafarian, A. H.; Mahdipour, E. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2019, 13, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H. E.; Hasan, A.; Rizzi, R.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Cenciarelli, C.; Caceci, T.; Shuaib, A. Potential of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Ischemic Stroke. Front Neurol 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeppner, T. R.; Kaltwasser, B.; Teli, M. K.; Sanchez-Mendoza, E. H.; Kilic, E.; Bahr, M.; Hermann, D. M. Post-stroke transplantation of adult subventricular zone derived neural progenitor cells--A comprehensive analysis of cell delivery routes and their underlying mechanisms. Exp Neurol 2015, 273, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bexell, D.; Gunnarsson, S.; Tormin, A.; Darabi, A.; Gisselsson, D.; Roybon, L.; Scheding, S.; Bengzon, J. Bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stroma cells act as pericyte-like migratory vehicles in experimental gliomas. Mol Ther 2009, 17, 183–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Chopp, M. Emerging potential of exosomes for treatment of traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 2017, 12, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B. A.; Gao, J. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiltbrunner, S.; Larssen, P.; Eldh, M.; Martinez-Bravo, M. J.; Wagner, A. K.; Karlsson, M. C.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomal cancer immunotherapy is independent of MHC molecules on exosomes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38707–38717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Shang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z. G.; Chopp, M. MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched extracellular particles. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2737–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Exosomes derived from PEDF modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 2018, 371, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, H.; Jin, M.; Yang, X.; Ji, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Wu, G.; Lai, X.; Cai, L.; Hu, R.; Xu, L.; Li, L. Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs Reverse Acute Ischemic Stroke-Induced, Autophagy-Mediated Brain Injury by Promoting M2 Microglial/Macrophage Polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018, 47, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Tang, H.; Luo, S.; Lv, Y.; Liang, D.; Kang, X.; Hong, W. Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified ADSCs promotes functional recovery after stroke in rats by improving neurogenesis and suppressing microglia activation. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, N.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Rapid Enkephalin Delivery Using Exosomes to Promote Neurons Recovery in Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Neuronal p53/Caspase-3. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 4273290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, G. J.; Sung, J. H.; Kim, D. H.; Kim, E. H.; Cho, Y. H.; Son, J. P.; Cha, J. M.; Bang, O. Y. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Stroke: Biodistribution and MicroRNA Study. Transl Stroke Res 2019, 10, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-Garcia, F.; Gomez-de Frutos, M. D.; Rodriguez-Frutos, B.; Pascual-Guerra, J.; Fuentes, B.; Diez-Tejedor, E.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, M. White Matter Repair After Extracellular Vesicles Administration in an Experimental Animal Model of Subcortical Stroke. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 44433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Seyfried, D.; Meng, Y.; Yang, D.; Schultz, L.; Chopp, M.; Seyfried, D. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes improve functional recovery after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. J Neurosurg 2018, 131, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. H.; Chen, C. H.; Wallace, C. G.; Yuen, C. M.; Kao, G. S.; Chen, Y. L.; Shao, P. L.; Chen, Y. L.; Chai, H. T.; Lin, K. C.; Liu, C. F.; Chang, H. W.; Lee, M. S.; Yip, H. K. Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74537–74556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. C.; Liu, L.; Ma, F.; Wong, C. W.; Guo, X. E.; Chacko, J. V.; Farhoodi, H. P.; Zhang, S. X.; Zimak, J.; Segaliny, A.; Riazifar, M.; Pham, V.; Digman, M. A.; Pone, E. J.; Zhao, W. Elucidation of Exosome Migration across the Blood-Brain Barrier Model In Vitro. Cell Mol Bioeng 2016, 9, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-Garcia, F.; Gomez-de Frutos, M.; Fuentes, B.; Diekhorst, L.; Diez-Tejedor, E.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, M. Role of Exosomes as a Treatment and Potential Biomarker for Stroke. Transl Stroke Res 2019, 10, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H. X.; He, C. P.; Fan, S.; Zhu, Y. L.; Qi, C.; Huang, N. P.; Xiao, Z. D.; Lu, Z. H.; Tannous, B. A.; Gao, J. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cheng, K. Stem cell-derived exosome versus stem cell therapy. Nat Rev Bioeng 2023, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. G.; Buller, B.; Chopp, M. Exosomes - beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat Rev Neurol 2019, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Guo, W. Z.; Li, X. K. The Unique Immunomodulatory Properties of MSC-Derived Exosomes in Organ Transplantation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 659621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D. K.; Hvam, M. L.; Primdahl-Bengtson, B.; Boysen, A. T.; Whitehead, B.; Dyrskjot, L.; Orntoft, T. F.; Howard, K. A.; Ostenfeld, M. S. Comparative analysis of discrete exosome fractions obtained by differential centrifugation. J Extracell Vesicles 2014, 3, 25011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Pei, F.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Z. Extracellular Vesicles in Liquid Biopsies: Potential for Disease Diagnosis. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 6611244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helwa, I.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M. D.; Zimmerman, A.; Dinkins, M. B.; Khaled, M. L.; Seremwe, M.; Dismuke, W. M.; Bieberich, E.; Stamer, W. D.; Hamrick, M. W.; Liu, Y. A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0170628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauro, B. J.; Greening, D. W.; Mathias, R. A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A. M.; Simpson, R. J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, J. Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mager, I.; Johansson, H. J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O. P.; Hallbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J. J.; Gilthorpe, J.; Davies, T.; Fairchild, P. J.; Gabrielsson, S.; Meisner-Kober, N. C.; Lehtio, J.; Smith, C. I.; Wood, M. J.; El Andaloussi, S. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeyen, E.; Van Mol, K.; Baggerman, G.; Willems, H.; Boonen, K.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, A.; Schildermans, K.; Cho, W. C.; Mertens, I. Ultrafiltration and size exclusion chromatography combined with asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation for the isolation and characterisation of extracellular vesicles from urine. J Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1490143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Y.; Rhim, W. K.; Yoo, Y. I.; Kim, D. S.; Ko, K. W.; Heo, Y.; Park, C. G.; Han, D. K. Defined MSC exosome with high yield and purity to improve regenerative activity. J Tissue Eng 2021, 12, 20417314211008626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monguio-Tortajada, M.; Galvez-Monton, C.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Roura, S.; Borras, F. E. Extracellular vesicle isolation methods: rising impact of size-exclusion chromatography. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76, 2369–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R. P.; Zhou, Y.; Eason, A. B.; Landis, J. T.; Chambers, M. G.; Willcox, S.; Peterson, T. A.; Schouest, B.; Maness, N. J.; MacLean, A. G.; Costantini, L. M.; Griffith, J. D.; Dittmer, D. P. Imaging of surface microdomains on individual extracellular vesicles in 3-D. J Extracell Vesicles 2022, 11, e12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, O. L.; Campbell, A. W.; Christenson, L. K.; Weiss, M. L. Improving Reproducibility to Meet Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 Guidelines in Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE 2021.
- Witwer, K. W.; Goberdhan, D. C.; O'Driscoll, L.; Thery, C.; Welsh, J. A.; Blenkiron, C.; Buzas, E. I.; Di Vizio, D.; Erdbrugger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J. M.; Fu, Q. L.; Hill, A. F.; Lenassi, M.; Lotvall, J.; Nieuwland, R.; Ochiya, T.; Rome, S.; Sahoo, S.; Zheng, L. Updating MISEV: Evolving the minimal requirements for studies of extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 2021, 10, e12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R. L.; Chong, J. Y.; Prabhakaran, S.; Elkind, M. S. Experimental treatments for acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet 2007, 369, 331–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, D. J.; Black, S. E.; Hakim, A. M. ; Heart; Stroke Foundation of Ontario Centre of Excellence in Stroke, R. , Toward wisdom from failure: lessons from neuroprotective stroke trials and new therapeutic directions. Stroke 2002, 33, 2123–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y. D.; Al-Khoury, L.; Zivin, J. A. Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: two decades of success and failure. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard Green, A.; Odergren, T.; Ashwood, T. Animal models of stroke: do they have value for discovering neuroprotective agents? Trends Pharmacol Sci 2003, 24, 402–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.; Feuerstein, G.; Howells, D. W.; Hurn, P. D.; Kent, T. A.; Savitz, S. I.; Lo, E. H.; Group, S. Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke 2009, 40, 2244–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Nan, Z.; Motooka, Y.; Low, W. C. Transplantation of a novel cell line population of umbilical cord blood stem cells ameliorates neurological deficits associated with ischemic brain injury. Stem Cells Dev 2005, 14, 722–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Sternberg, H.; Bignone, P. A.; Murai, J.; Malik, N. N.; West, M. D.; Larocca, D. Clonal and Scalable Endothelial Progenitor Cell Lines from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mao, W.; Niu, L.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.; Cai, M.; Yuan, Z.; Song, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, N.; Wei, J.; Dong, Z. NSC-derived exosomes enhance therapeutic effects of NSC transplantation on cerebral ischemia in mice. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.-C.; Wu, H.-H.; Tabata, Y.; Gao, J.-Q. Biological nano agent produced by hypoxic preconditioning stem cell for stroke treatment. Nano Research 2023, 16, 7413−7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Zhao, T.; He, W.; Xia, J.; Huang, Q.; Yang, J.; Gu, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J. Exosomal circBBS2 inhibits ferroptosis by targeting miR-494 to activate SLC7A11 signaling in ischemic stroke. FASEB J 2023, 37, e23152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; He, C.; Liu, H.; Liao, X.; Dai, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Bihl, J.; Ma, X. Microvascular endothelial cells-derived microvesicles imply in ischemic stroke by modulating astrocyte and blood brain barrier function and cerebral blood flow. Mol Brain 2016, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B. C.; Kang, I.; Yu, K. R. Therapeutic Features and Updated Clinical Trials of Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC)-Derived Exosomes. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M. D.; Sargent, R. G.; Long, J.; Brown, C.; Chu, J. S.; Kessler, S.; Derugin, N.; Sampathkumar, J.; Burrows, C.; Vaziri, H.; Williams, R.; Chapman, K. B.; Larocca, D.; Loring, J. F.; Murai, J. The ACTCellerate initiative: large-scale combinatorial cloning of novel human embryonic stem cell derivatives. Regen Med 2008, 3, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pang, Y.; Hou, L.; Xing, X.; Yu, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y. Exosomal OIP5-AS1 attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by negatively regulating TXNIP protein stability and inhibiting neuronal pyroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 127, 111310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Song, J.; Jia, F.; Wei, W.; Jiang, F.; Li, G.; Zhong, D. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-193b-5p reduces pyroptosis after ischemic stroke by targeting AIM2. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2023, 32, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





