Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
12 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Anatomical Characterization of Particles
2.2. Multilayer Panel Production
2.3. Characterization of the Panels
2.4. Life Cycle Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and Anatomical Properties of Particles
3.2. Panel Physical and Mechanical Properties
3.3. Particleboard Microstructural Analysis
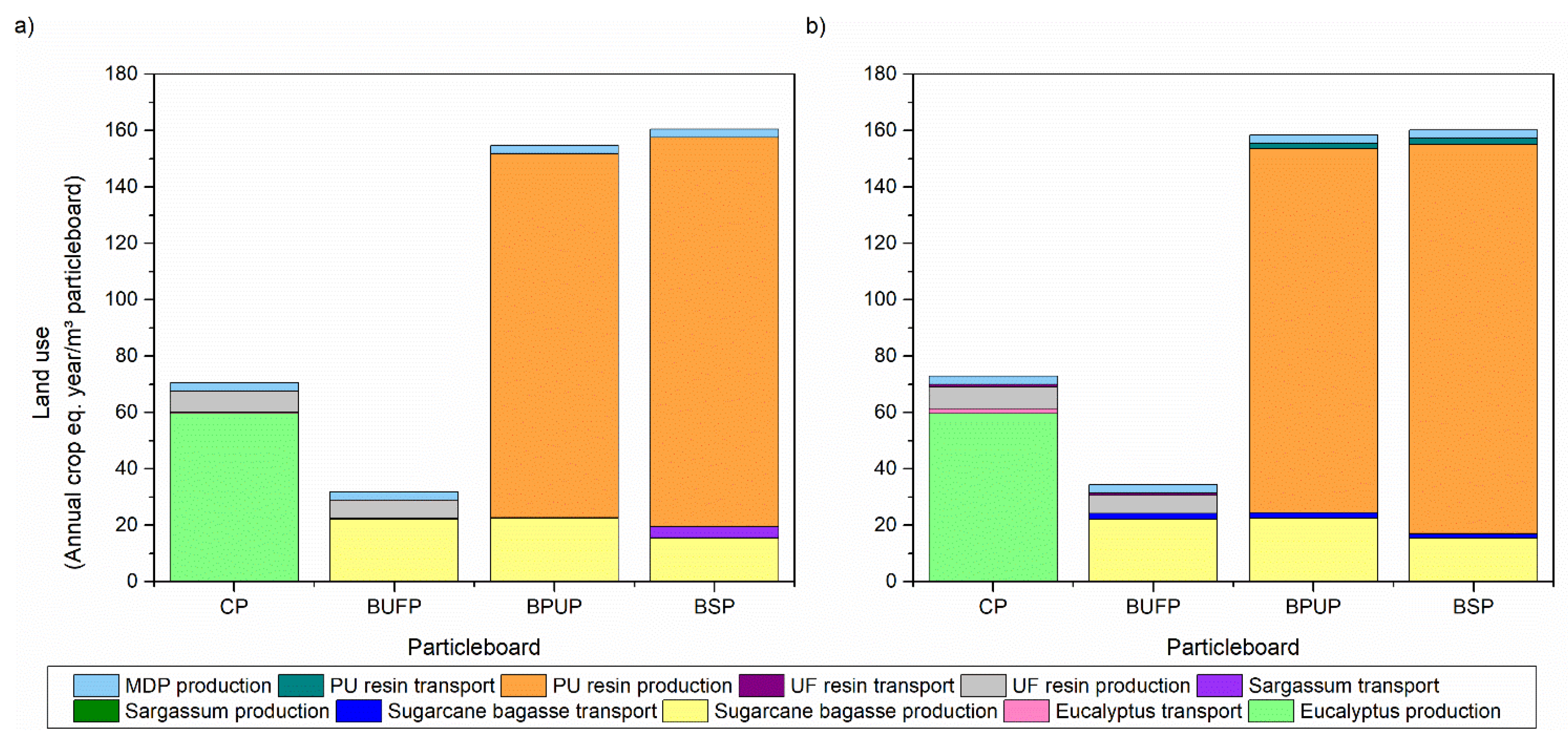
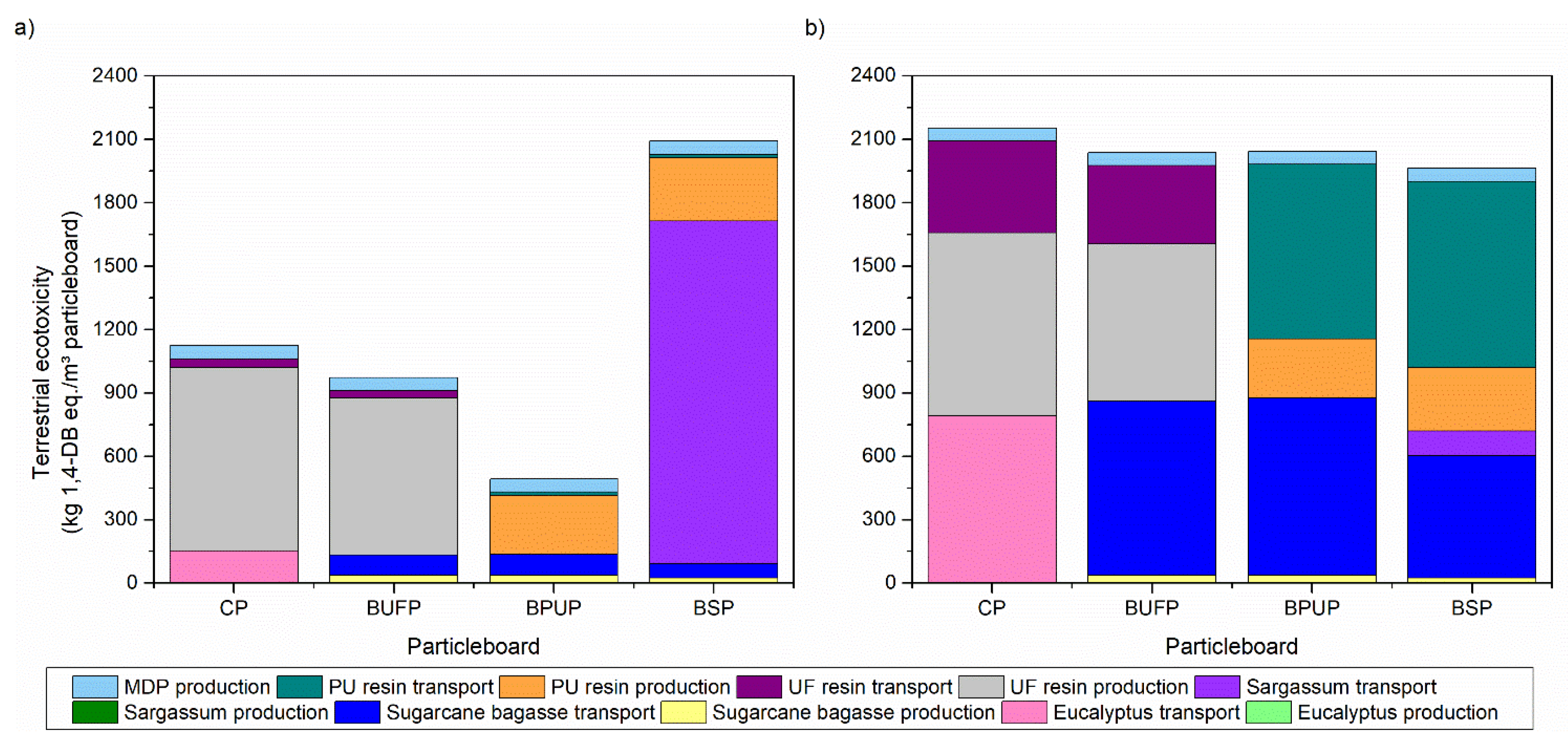
3.4. Life Cycle Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- H.S.J. Roe, D. Freestone, F. Sapsford, The Sargasso Sea High Seas EBSA After Ten Years: Is It Still Relevant and How Has It Helped Conservation Efforts?, Front. Mar. Sci. 9 (2022) 1–12. [CrossRef]
- L.M. Martin, M. Taylor, G. Huston, D.S. Goodwin, J.M. Schell, A.N.S. Siuda, Pelagic Sargassum morphotypes support different rafting motile epifauna communities, Mar. Biol. 168 (2021) 1–17. [CrossRef]
- M.T.M. de Széchy, P.M. Guedes, M.H. Baeta-Neves, E.N. Oliveira, Verification of Sargassum natans (Linnaeus) Gaillon (Heterokontophyta: Phaeophyceae) from the Sargasso Sea off the coast of Brazil, western Atlantic Ocean, Check List 8 (2012) 638–641. [CrossRef]
- M. Wang, C. Hu, B.B. Barnes, G. Mitchum, B. Lapointe, J.P. Montoya, The great Atlantic Sargassum belt, Science (80-. ). 364 (2019) 83–87. [CrossRef]
- E.M. Johns, R. Lumpkin, N.F. Putman, R.H. Smith, F.E. Muller-Karger, D. T. Rueda-Roa, C. Hu, M. Wang, M.T. Brooks, L.J. Gramer, F.E. Werner, The establishment of a pelagic Sargassum population in the tropical Atlantic: Biological consequences of a basin-scale long distance dispersal event, Prog. Oceanogr. 182 (2020) 102269. [CrossRef]
- S. Djakouré, M. Araujo, A. Hounsou-Gbo, C. Noriega, B. Bourlès, On the potential causes of the recent Pelagic Sargassum blooms events in the tropical North Atlantic Ocean, Biogeosciences Discuss. (2017) 1–20. [CrossRef]
- V. Chávez, A. Uribe-Martínez, E. Cuevas, R.E. Rodríguez-Martínez, B.I. van Tussenbroek, V. Francisco, M. Estévez, L.B. Celis, L.V. Monroy-Velázquez, R. Leal-Bautista, L. Álvarez-Filip, M. García-Sánchez, L. Masia, R. Silva, Massive influx of pelagic sargassum spp. On the coasts of the mexican caribbean 2014–2020: Challenges and opportunities, Water (Switzerland) 12 (2020) 1–24. [CrossRef]
- B.E. Lapointe, R.A. Brewton, L.W. Herren, M. Wang, C. Hu, D.J. McGillicuddy, S. Lindell, F.J. Hernandez, P.L. Morton, Nutrient content and stoichiometry of pelagic Sargassum reflects increasing nitrogen availability in the Atlantic Basin, Nat. Commun. 12 (2021) 1–10. [CrossRef]
- N. Skliris, R. Marsh, K. Appeaning Addo, H. Oxenford, Physical drivers of pelagic sargassum bloom interannual variability in the Central West Atlantic over 2010–2020, Ocean Dyn. 72 (2022) 383–404. [CrossRef]
- E. Magaña-Gallegos, M. García-Sánchez, C. Graham, A. Olivos-Ortiz, A.N.S. Siuda, B.I. van Tussenbroek, Growth rates of pelagic Sargassum species in the Mexican Caribbean, Aquat. Bot. 185 (2023). [CrossRef]
- M.N. Sissini, M.B.B. de Barros Barreto, M.T.M. Széchy, M.B. de Lucena, M.C. Oliveira, J. Gower, G. Liu, E. de Oliveira Bastos, D. Milstein, F. Gusmão, J.E. Martinelli-Filho, C. Alves-Lima, P. Colepicolo, G. Ameka, K. de Graft-Johnson, L. Gouvea, B. Torrano-Silva, F. Nauer, J.M. de Castro Nunes, J.B. Barufi, L. Rörig, R. Riosmena-Rodríguez, T.J. Mello, L.V.C. Lotufo, P.A. Horta, The floating Sargassum (Phaeophyceae) of the South Atlantic Ocean – likely scenarios, Phycologia 56 (2017) 321–328. [CrossRef]
- J. Gower, S. King, The distribution of pelagic Sargassum observed with OLCI, Int. J. Remote Sens. 41 (2020) 5669–5679. [CrossRef]
- C.B. Machado, G.-M. Maddix, P. Francis, S.-L. Thomas, J.-A. Burton, S. Langer, T.R. Larson, R. Marsh, M. Webber, T. Tonon, Pelagic Sargassum events in Jamaica: Provenance, morphotype abundance, and influence of sample processing on biochemical composition of the biomass, Sci. Total Environ. 817 (2022) 152761. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Rossignolo, A.J. Felicio Peres Duran, C. Bueno, J.E. Martinelli Filho, H. Savastano Junior, F.G. Tonin, Algae application in civil construction: A review with focus on the potential uses of the pelagic Sargassum spp. biomass, J. Environ. Manage. 303 (2022) 114258. [CrossRef]
- B.B. Solarin, D.A. Bolaji, O.S. Fakayode, R.O. Akinnigbagbe, Impacts_of_an_invasive_seaweed_Sargassum.pdf, 7 (2014) 1–6.
- B.I. van Tussenbroek, H.A. Hernández Arana, R.E. Rodríguez-Martínez, J. Espinoza-Avalos, H.M. Canizales-Flores, C.E. González-Godoy, M.G. Barba-Santos, A. Vega-Zepeda, L. Collado-Vides, Severe impacts of brown tides caused by Sargassum spp. on near-shore Caribbean seagrass communities, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 122 (2017) 272–281. [CrossRef]
- R. Rodríguez-Muñoz, A.I. Muñiz-Castillo, J.I. Euán-Avila, H. Hernández-Núñez, D.S. Valdés-Lozano, R.C. Collí-Dulá, J.E. Arias-González, Assessing temporal dynamics on pelagic Sargassum influx and its relationship with water quality parameters in the Mexican Caribbean, Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 48 (2021) 102005. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Maurer, K. Gross, S.P. Stapleton, Beached Sargassum alters sand thermal environments: Implications for incubating sea turtle eggs, J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 546 (2022) 151650. [CrossRef]
- D. Resiere, R. Valentino, R. Nevière, R. Banydeen, P. Gueye, J. Florentin, A. Cabié, T. Lebrun, B. Mégarbane, G. Guerrier, H. Mehdaoui, Sargassum seaweed on Caribbean islands: an international public health concern, Lancet 392 (2018) 2691. [CrossRef]
- D. Davis, R. Simister, S. Campbell, M. Marston, S. Bose, S.J. McQueen-Mason, L.D. Gomez, W.A. Gallimore, T. Tonon, Biomass composition of the golden tide pelagic seaweeds Sargassum fluitans and S. natans (morphotypes I and VIII) to inform valorisation pathways, Sci. Total Environ. 762 (2021) 143134. [CrossRef]
- M. Wang, C. Hu, Satellite remote sensing of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae: The power of high resolution and deep learning, Remote Sens. Environ. 264 (2021) 112631. [CrossRef]
- F. Amador-Castro, T. García-Cayuela, H.S. Alper, V. Rodriguez-Martinez, D. Carrillo-Nieves, Valorization of pelagic sargassum biomass into sustainable applications: Current trends and challenges, J. Environ. Manage. 283 (2021) 112013. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Alamsjah, L. Sulmartiwi, K.T. Pursetyo, M.N.G. Amin, K.A.K. Wardani, M.D. Arifianto, Modifying bioproduct technology of Medium Density Fibreboard from the seaweed waste Kappaphycus alvarezii and Gracilaria verrucosa, J. Indian Acad. Wood Sci. 14 (2017) 32–45. [CrossRef]
- D. Garcia-Garcia, L. Quiles-Carrillo, N. Montanes, V. Fombuena, R. Balart, Manufacturing and Characterization of Composite Fibreboards with Posidonia oceanica Wastes with an Environmentally-Friendly Binder from Epoxy Resin, Materials (Basel). 11 (2017) 35. [CrossRef]
- E. Rammou, A. Mitani, G. Ntalos, D. Koutsianitis, H.R. Taghiyari, A.N. Papadopoulos, The Potential Use of Seaweed (Posidonia oceanica) as an Alternative Lignocellulosic Raw Material for Wood Composites Manufacture, Coatings 11 (2021) 69. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Alamsjah, L. Sulmartiwi, K.T. Pursetyo, M.N.G. Amin, K.A.K. Wardani, M.D. Arifianto, Modifying bioproduct technology of Medium Density Fibreboard from the seaweed waste Kappaphycus alvarezii and Gracilaria verrucosa, J. Indian Acad. Wood Sci. 14 (2017) 32–45. [CrossRef]
- J. Fiorelli, S.B. Bueno, M.R. Cabral, Assessment of multilayer particleboards produced with green coconut and sugarcane bagasse fibers, Constr. Build. Mater. 205 (2019) 1–9. [CrossRef]
- E.G. Milagres, R.A.G.S. Barbosa, K.F. Caiafa, G.S.L. Gomes, T.A.C. Castro, B.R. Vital, Properties of particleboard panels made of sugarcane particles with and without heat treatment, Rev. Árvore 43 (2019). [CrossRef]
- B.B.R. Yano, S.A.M. Silva, D.H. Almeida, V.B.M. Aquino, A.L. Christoforo, E.F.C. Rodrigues, A.N. Carvalho Junior, A.P. Silva, F.A.R. Lahr, Use of sugarcane bagasse and industrial timber residue in particleboard production, BioResources 15 (2020) 4753–4762. [CrossRef]
- A.J.F.P. Duran, W.E. Lopes Junior, M. Pavesi, J. Fiorelli, Assessment of medium density panels of sugarcane bagasse, Ciência Florest. 33 (2023) e69624. [CrossRef]
- D.A.L. Silva, F.A.R. Lahr, R.P. Garcia, F.M.C.S. Freire, A.R. Ometto, Life cycle assessment of medium density particleboard (MDP) produced in Brazil, Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 18 (2013) 1404–1411. [CrossRef]
- D.A.L. Silva, F.A.R. Lahr, A.L.R. Pavan, Y.M.B. Saavedra, N.C. Mendes, S.R. Sousa, R. Sanches, A.R. Ometto, Do wood-based panels made with agro-industrial residues provide environmentally benign alternatives? An LCA case study of sugarcane bagasse addition to particle board manufacturing, Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 19 (2014) 1767–1778. [CrossRef]
- V. Uemura Silva, M.F. Nascimento, P. Resende Oliveira, T.H. Panzera, M.O. Rezende, D.A.L. Silva, V. Borges de Moura Aquino, F.A. Rocco Lahr, A.L. Christoforo, Circular vs. linear economy of building materials: A case study for particleboards made of recycled wood and biopolymer vs. conventional particleboards, Constr. Build. Mater. 285 (2021) 122906. [CrossRef]
- P.J. Van Soest, Nutritional ecology of the ruminant, Second edi, Cornell University Press, New York, 1994. http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.7591/j.ctv5rf668.
- J. Fiorelli, D.D. Curtolo, N.G. Barrero, H. Savastano, E.M. de Jesus Agnolon Pallone, R. Johnson, Particulate composite based on coconut fiber and castor oil polyurethane adhesive: An eco-efficient product, Ind. Crops Prod. 40 (2012) 69–75. [CrossRef]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas, 2018. NBR 14810-2. Medium density particleboards: Part 2: Requirements and test methods. Rio de Janeiro: 2018.
- International Organization for Standardization, 2016. ISO 16893: Wood-based panels - Particleboard. Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
- International Organization for Standardization, 2006a. ISO 14040: Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Principles and Framework, 2006.
- International Organization for Standardization, 2006b. ISO 14044: Environmental Management - Life Cycle Assessment -Requirements and Guidelines, 2006.
- D.L. Faria, I.L. Guimarães, T.B. Sousa, T.D.P. Protásio, L.M. Mendes, J.B. Guimarães Junior, Technological properties of medium density particleboard produced with soybean pod husk and Eucalyptus wood, Sci. For. 48 (2020). [CrossRef]
- D.P. Ribeiro, A.P. Vilela, D.W. Silva, A. Napoli, R.F. Mendes, Effect of Heat Treatment on the Properties of Sugarcane Bagasse Medium Density Particleboard (MDP) Panels, Waste and Biomass Valorization 11 (2020) 6429–6441. [CrossRef]
- C. Bueno, J.A. Rossignolo, L.M. Gavioli, C.C.A. Sposito, F.G. Tonin, M.M. Veras, M.J.B. de Moraes, G.P. Lyra, Life Cycle Assessment Applied to End-of-Life Scenarios of Sargassum spp. for Application in Civil Construction, Sustain. 15 (2023). [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, Y. Hu, Novel lignocellulosic hybrid particleboard composites made from rice straws and coir fibers, Mater. Des. 55 (2014) 19–26. [CrossRef]
- J. Fiorelli, C.A. Gomide, F.A.R. Lahr, M.F. do Nascimento, D. de Lucca Sartori, J.E.M. Ballesteros, S.B. Bueno, U.L. Belini, Physico-chemical and anatomical characterization of residual lignocellulosic fibers, Cellulose 21 (2014) 3269–3277. [CrossRef]
- M.G. Borines, R.L. de Leon, J.L. Cuello, Bioethanol production from the macroalgae Sargassum spp., Bioresour. Technol. 138 (2013) 22–29. [CrossRef]
- I. Ali, A. Bahadar, Red Sea seaweed (Sargassum spp.) pyrolysis and its devolatilization kinetics, Algal Res. 21 (2017) 89–97. [CrossRef]
- R.P. John, G.S. Anisha, K.M. Nampoothiri, A. Pandey, Micro and macroalgal biomass: A renewable source for bioethanol, Bioresour. Technol. 102 (2011) 186–193. [CrossRef]
- S.G. Wi, H.J. Kim, S.A. Mahadevan, D.-J. Yang, H.-J. Bae, The potential value of the seaweed Ceylon moss (Gelidium amansii) as an alternative bioenergy resource, Bioresour. Technol. 100 (2009) 6658–6660. [CrossRef]
- L. Alzate-Gaviria, J. Domínguez-Maldonado, R. Chablé-Villacís, E. Olguin-Maciel, R.M. Leal-Bautista, G. Canché-Escamilla, A. Caballero-Vázquez, C. Hernández-Zepeda, F.A. Barredo-Pool, R. Tapia-Tussell, Presence of Polyphenols Complex Aromatic “Lignin” in Sargassum spp. from Mexican Caribbean, J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9 (2020) 6. [CrossRef]
- D. Fengel, G. Wegener, Wood chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions, Walterde Gruyter, Berlin, 1984. [CrossRef]
- A. Nourbakhsh, F.F. Baghlani, A. Ashori, Nano-SiO2 filled rice husk/polypropylene composites: Physico-mechanical properties, Ind. Crops Prod. 33 (2011) 183–187. [CrossRef]
- H.B. Ahmed, M.H. Helal, M.H. Abdo, M.M. Fekry, A.E. Abdelhamid, Disarmament of micropollutants from wastewater using nylon waste/chitosan blended with algal biomass as recoverable membrane, Polym. Test. 104 (2021) 107381. [CrossRef]
- N. Harris, D. Gibbs, Forests Absorb Twice As Much Carbon As They Emit Each Year, World Resour. Inst. (2021). https://www.wri.org/insights/forests-absorb-twice-much-carbon-they-emit-each-year (accessed February 6, 2024).
- Empresa de Pesquisa Energética, 2023. National Energy Balance - BEN 2022, Empresa de Pesquisa Energética. https://www.epe.gov.br/pt/publicacoes-dados-abertos/publicacoes/balanco-energetico-nacional-2022 (accessed 20 January 2023).

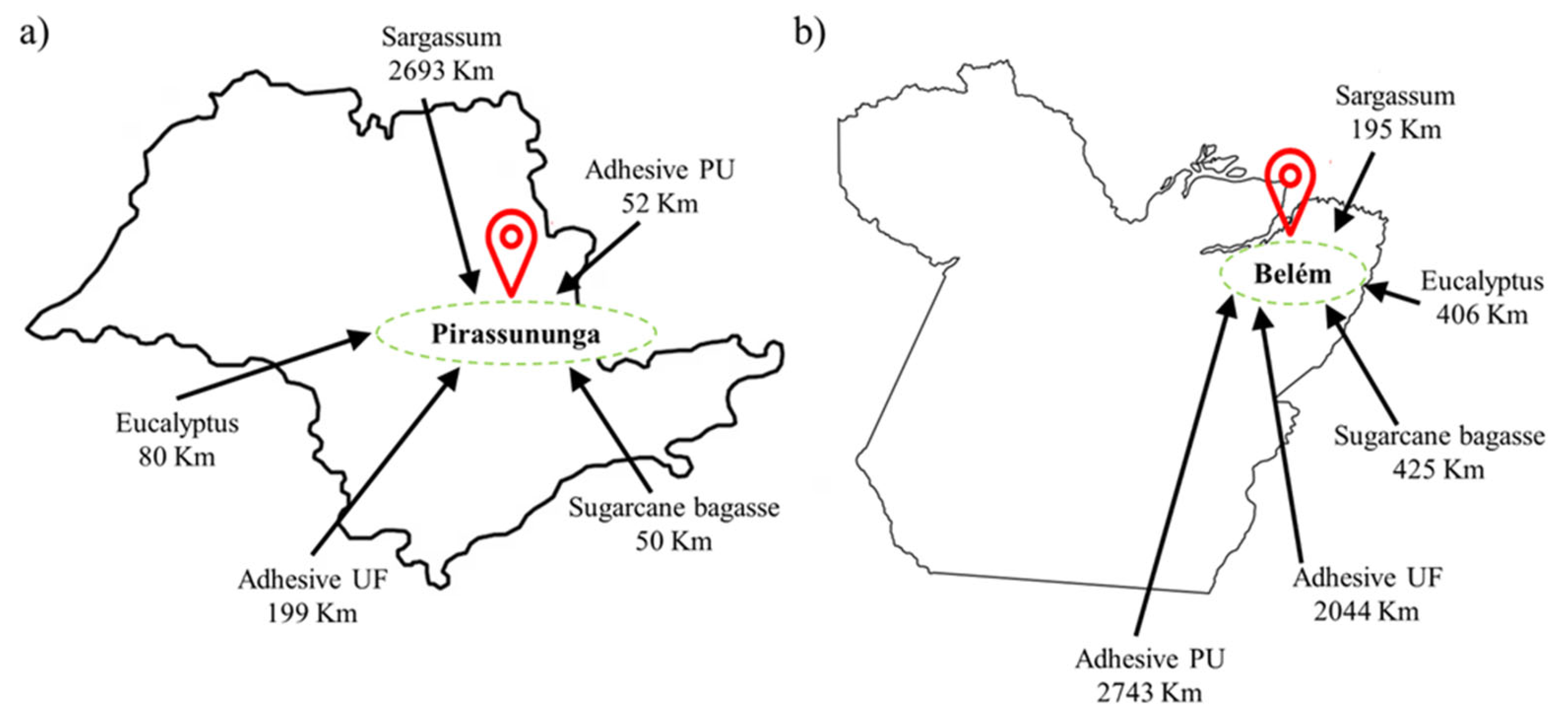
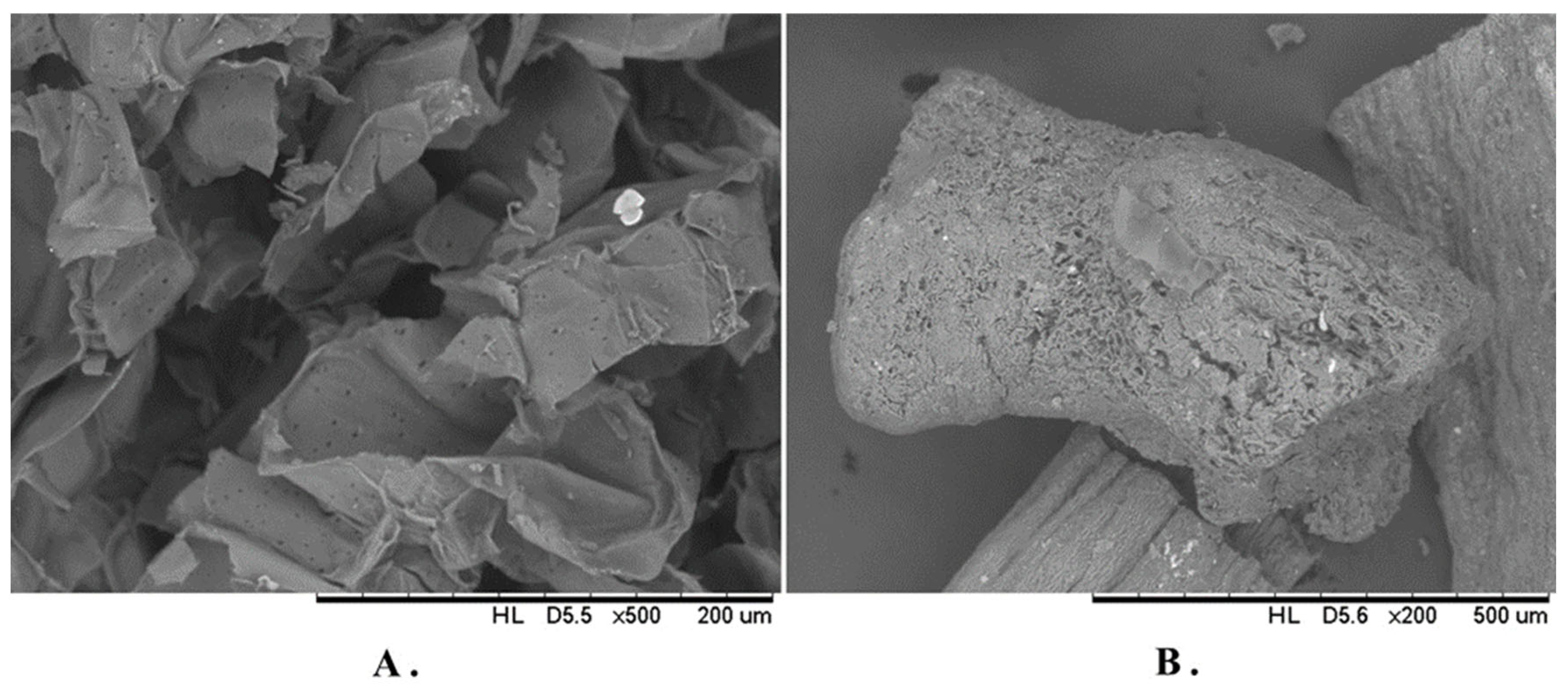

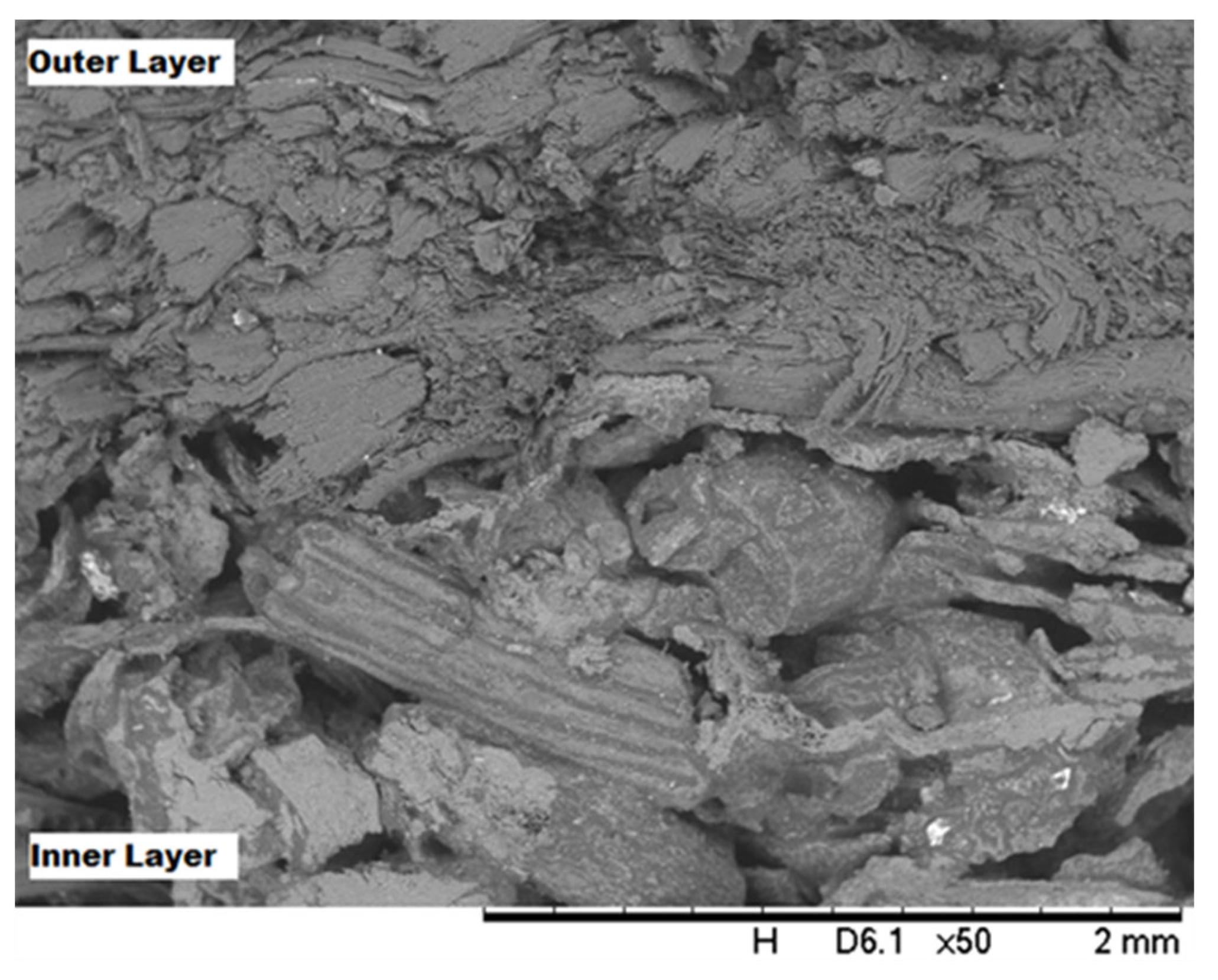
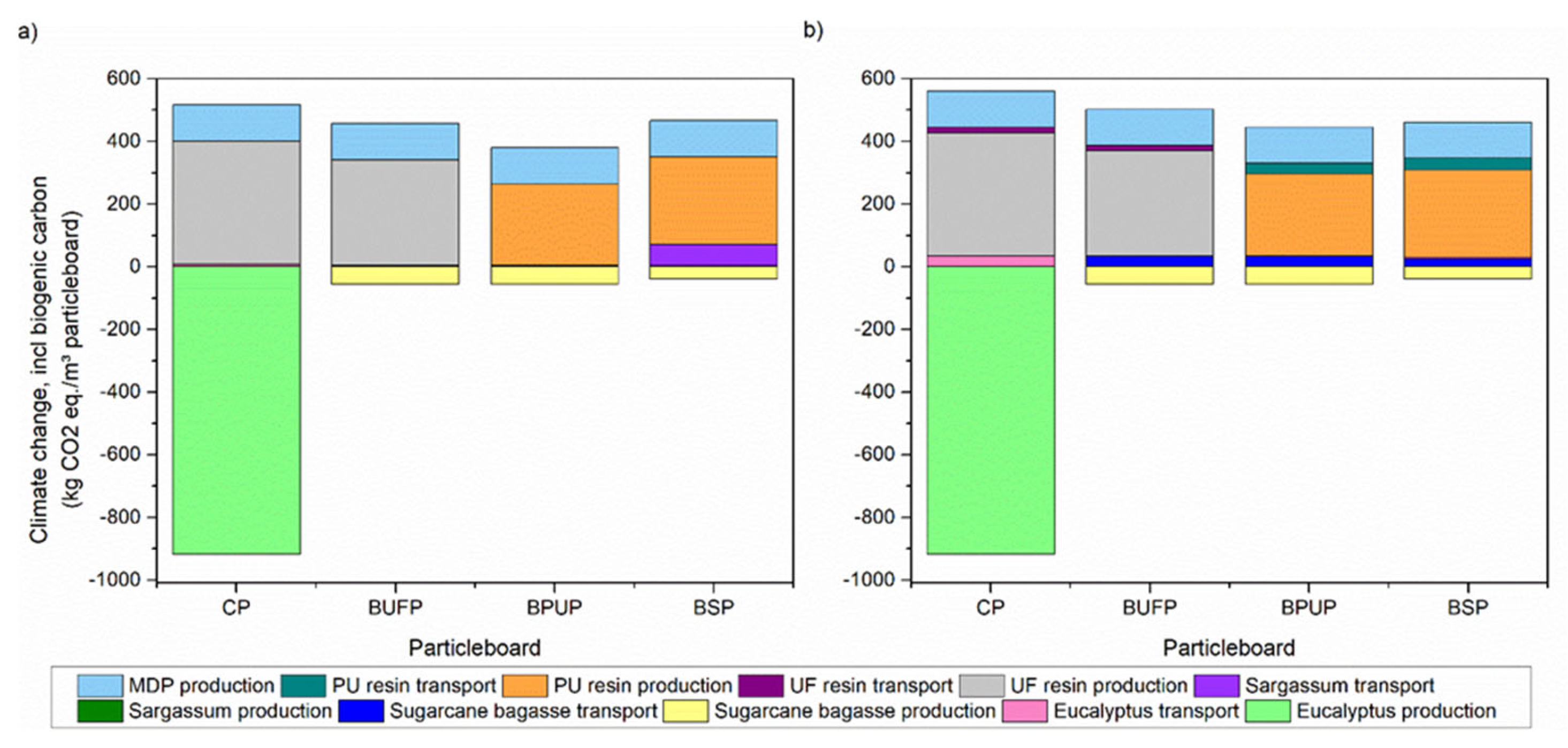
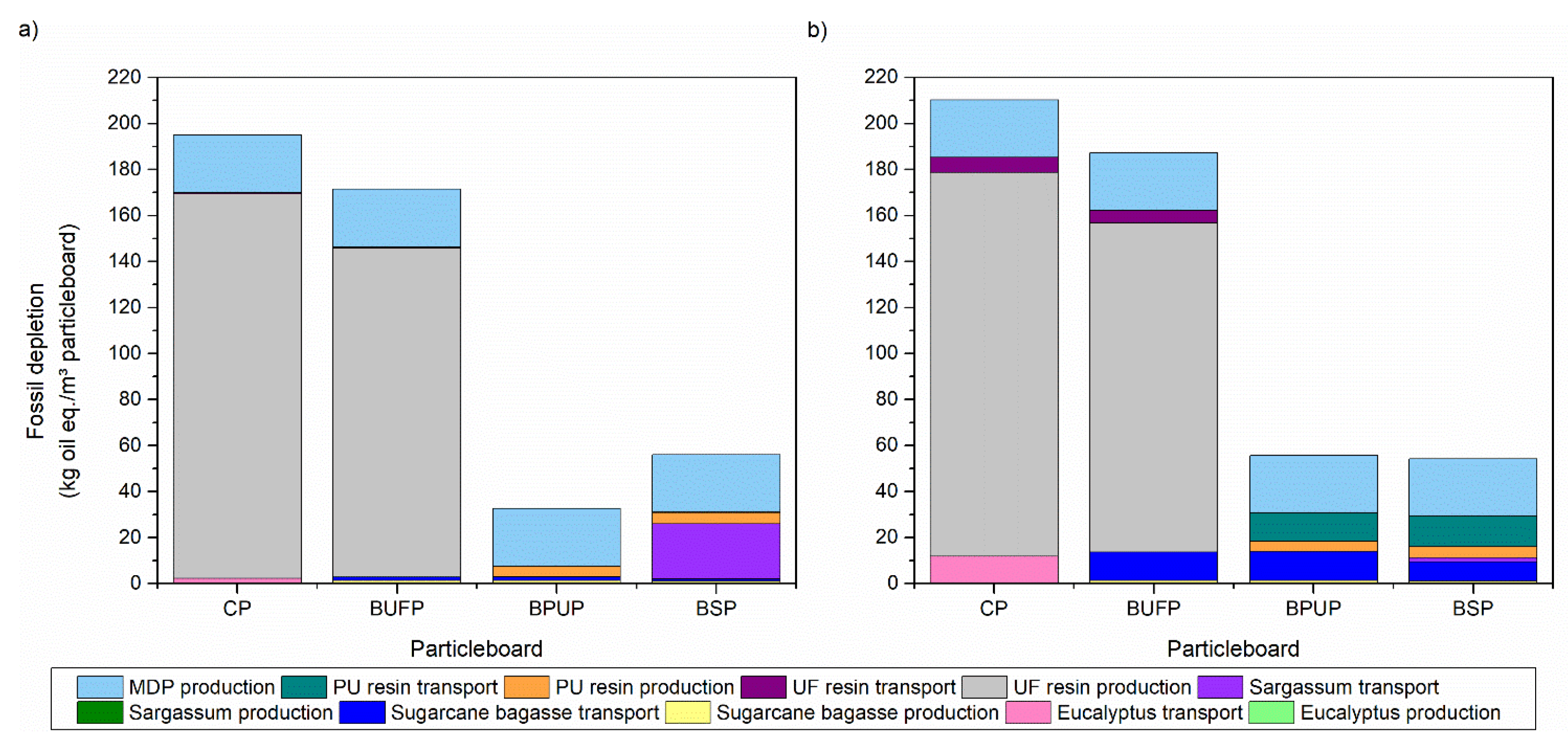
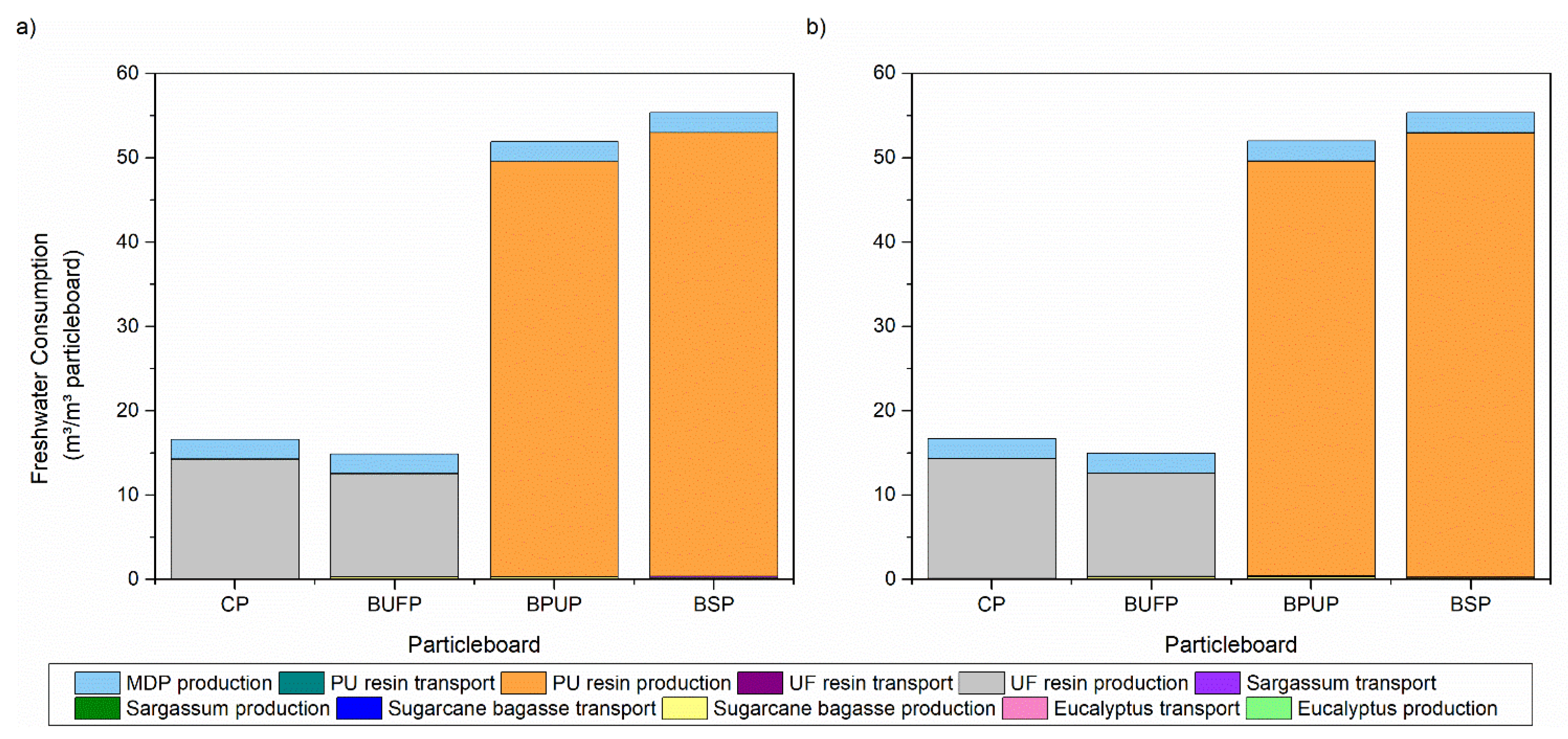
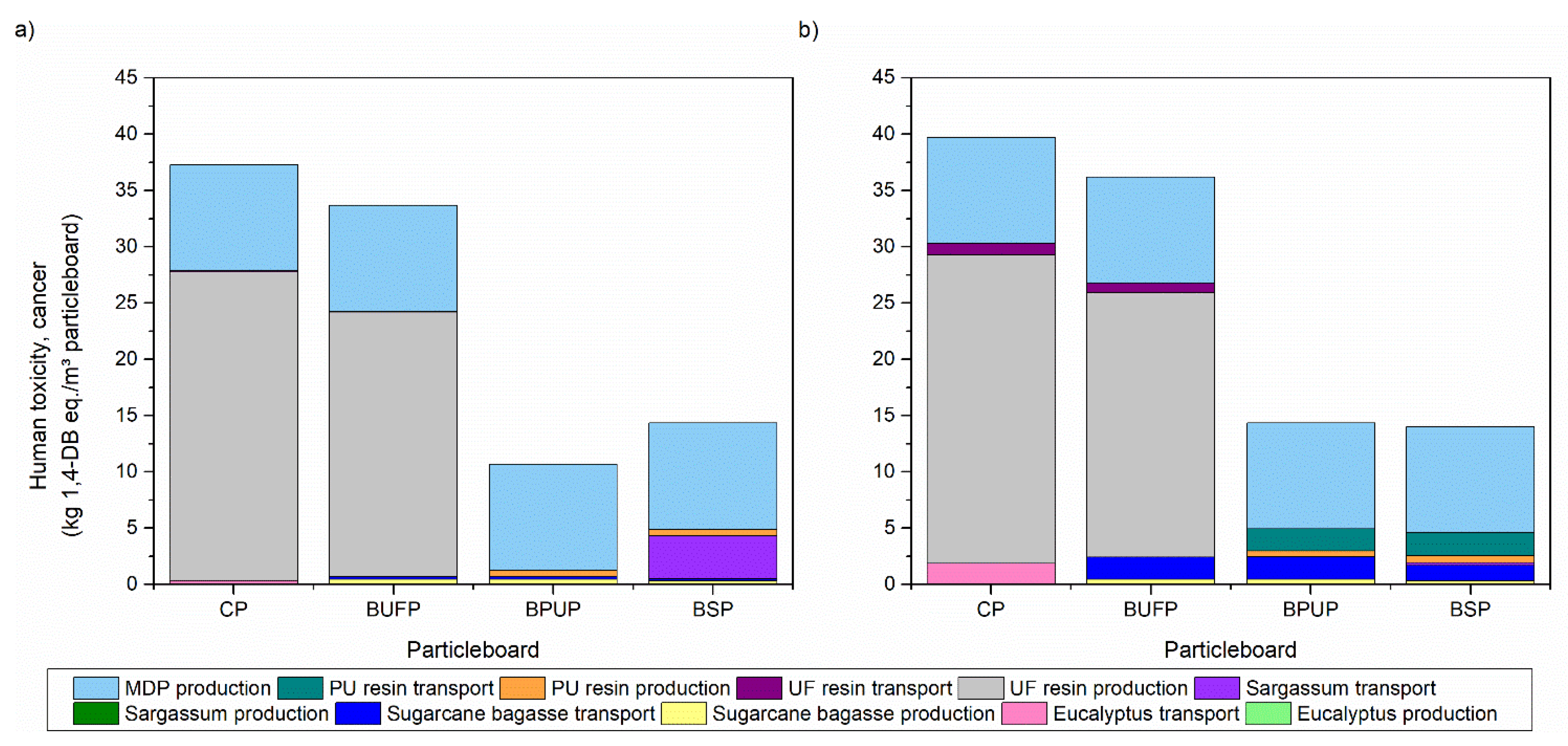
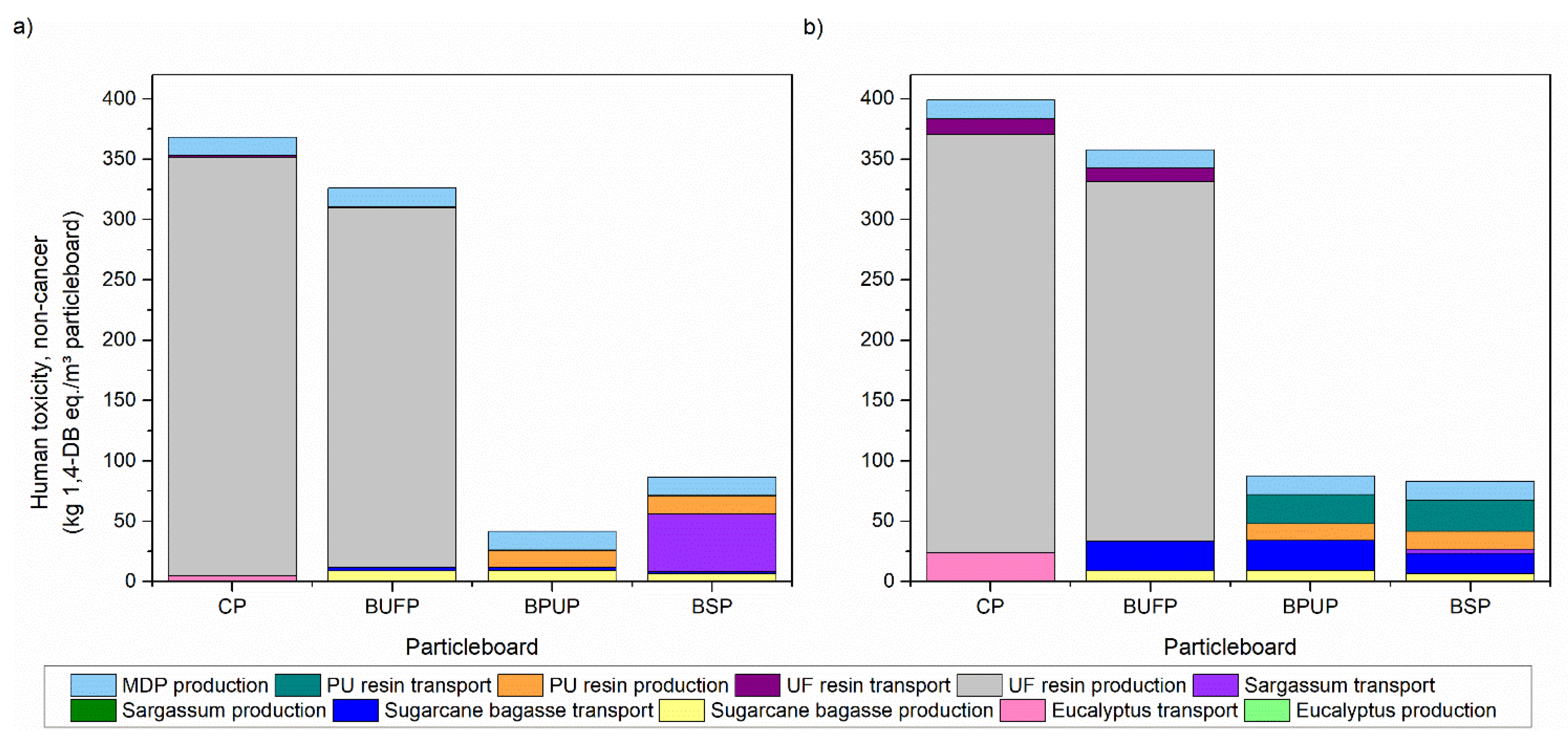
| Panels | Panel Composition | |||||
|
Eucalyptus (kg) |
Sugarcane bagasse (kg) |
Sargassum (kg) |
Urea-Formaldehyde resin (UF) (kg) |
Castor bean Polyurethane resin (PU) (kg) |
Reference | |
| CP | 630 | - | - | 70 | - | Faria et al. [40] |
| BUFP | - | 640 | - | 60 | - | Ribeiro et al. [41] |
| BPUP | - | 651 | - | - | 99 | Duran et al. [30] |
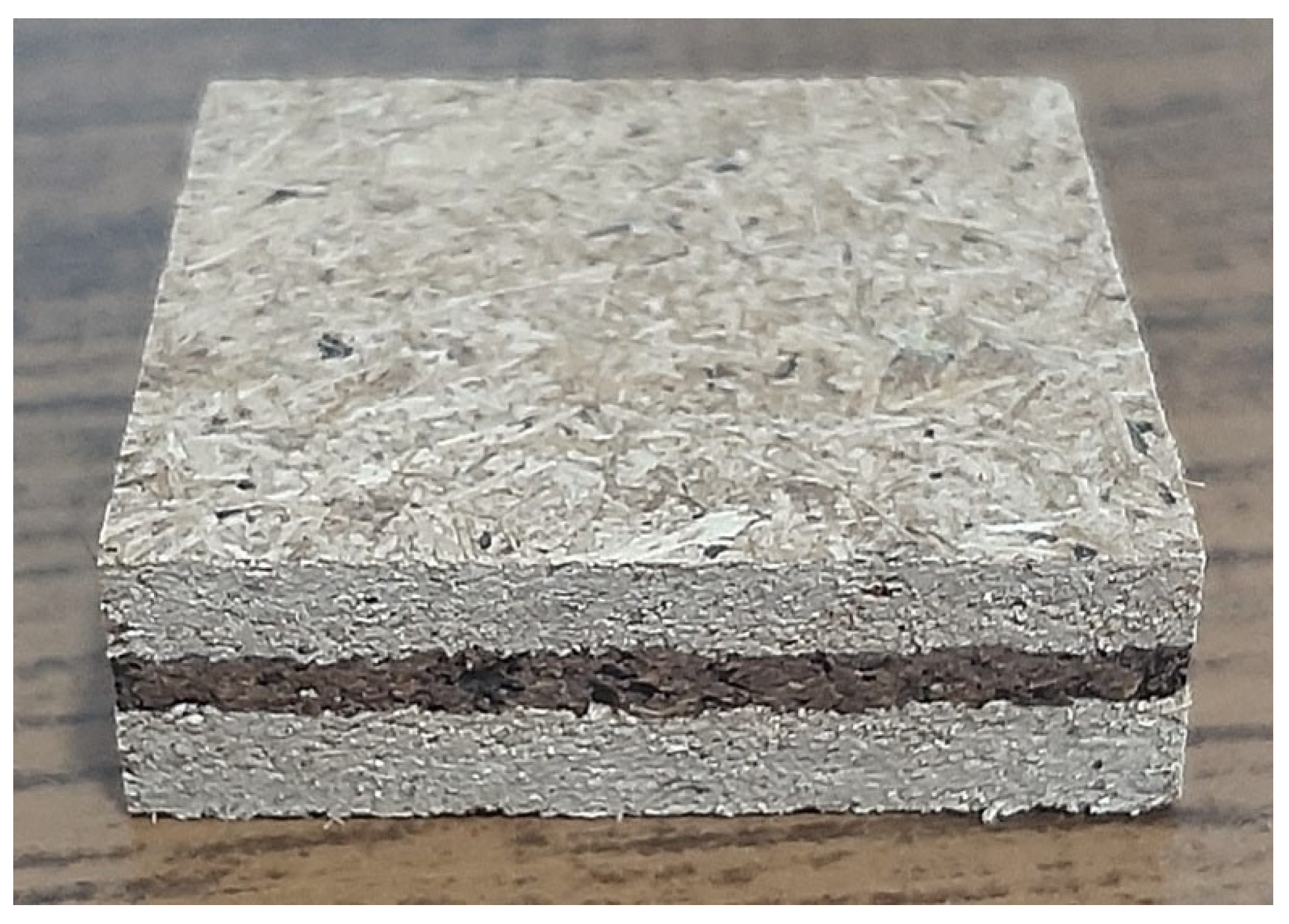
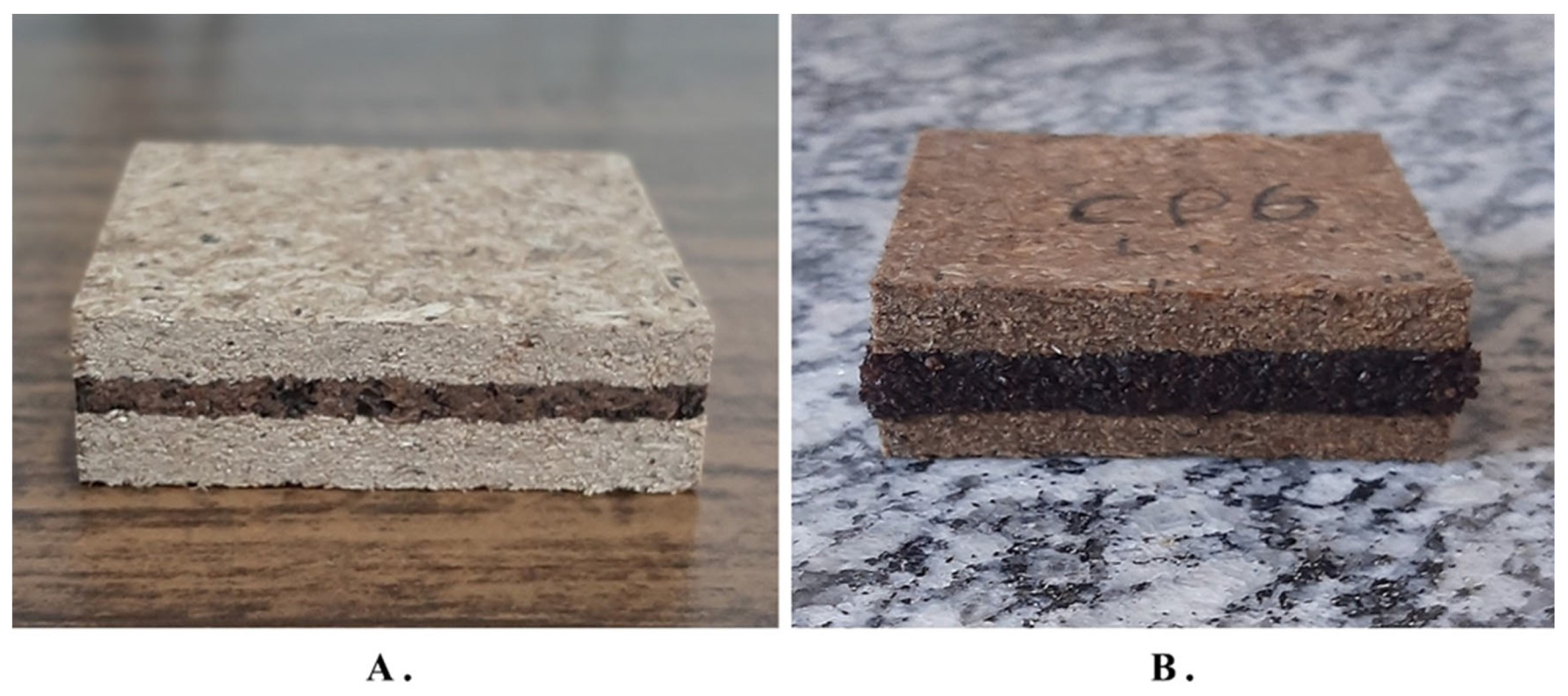
| BSP | - | 447 | 198 | - | 106 | Study |
| Processes inputs and outputs | Data source |
|---|---|
| Inputs | |
| Materials | |
| Sargassum particle | Bueno et al. [42] |
| Eucalyptus | SICV Brazil |
| Sugarcane bagasse; BR: market for bagasse, from sugarcane | Ecoinvent 3.7.1 |
| Castor oil-based polyurethane resin; EU-28: 2-component PUR adhesive based on polyether and castor oil (modified energy consumption based on a Brazilian industry) | |
| Urea-formaldehyde resin; RER: melamine formaldehyde resin production | |
| Lubricanting oil; RER: lubricanting oil production | |
| Diesel; BR: diesel, import from Row | |
| Heavy fuel oil; BR: heavy fuel oil, import from Row | |
| Transport | |
| Transport; RoW: transport, freight, lorry, all sizes, EURO3 to generic market for transport, freight, lorry, unspecified. | Ecoinvent 3.7.1 |
| Electricity consumption | |
| Electricity; BR: electricity, high voltage, production mix | Ecoinvent 3.7.1 |
| Outputs | |
| Medium-density multilayer panels | - |
| Waste | Cellulose (%*) |
Hemicellulose (%*) |
Lignin (%*) |
Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pelagic Sargassum | 41.48 | 3.21 | 16.94 | Study |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 50.47 | 30.56 | 10.74 | Fiorelli et al. [44] |
| Pinus spp | 51.13 | 15.10 | 27.29 | Fiorelli et al. [44] |
| Medium density panels | ρ | Adhesive | TS | MOR | MOE | IB | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg/m³) | (%) | (MPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | |||
| 24h | |||||||
| Sugarcane bagasse and Sargassum | 750 | PU | 19.81 | 16.31 | 2162 | 0.49 | Study |
| (sd) | 0.84 | 1.30 | 273.25 | 0.15 | |||
| Sugarcane bagasse | 700 | UF | 9.9 | 15.6 | 2021 | 0.48 | Ribeiro et al. [41] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 750 | PU | 14.99 | 15.48 | 1885 | 1.02 | Duran et al. [30] |
| Eucalyptus | 700 | UF | 11.50 | 18.71 | 1841 | 0.65 | Faria et al. [40] |
| NBR 14810-2:2018 - Non-structural use in dry conditions (P2) | 551 - 750 | 22 | 11 | 1600 | 0.35 | ||
| ISO 16893 - 2016 - General purpose for use in dry conditions | - | - | 10 | - | 0.24 | ||
| ISO 16893 - 2016 - Forniture grade for use in dry conditions | - | - | 11 | 1600 | 0.35 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





