Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
12 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
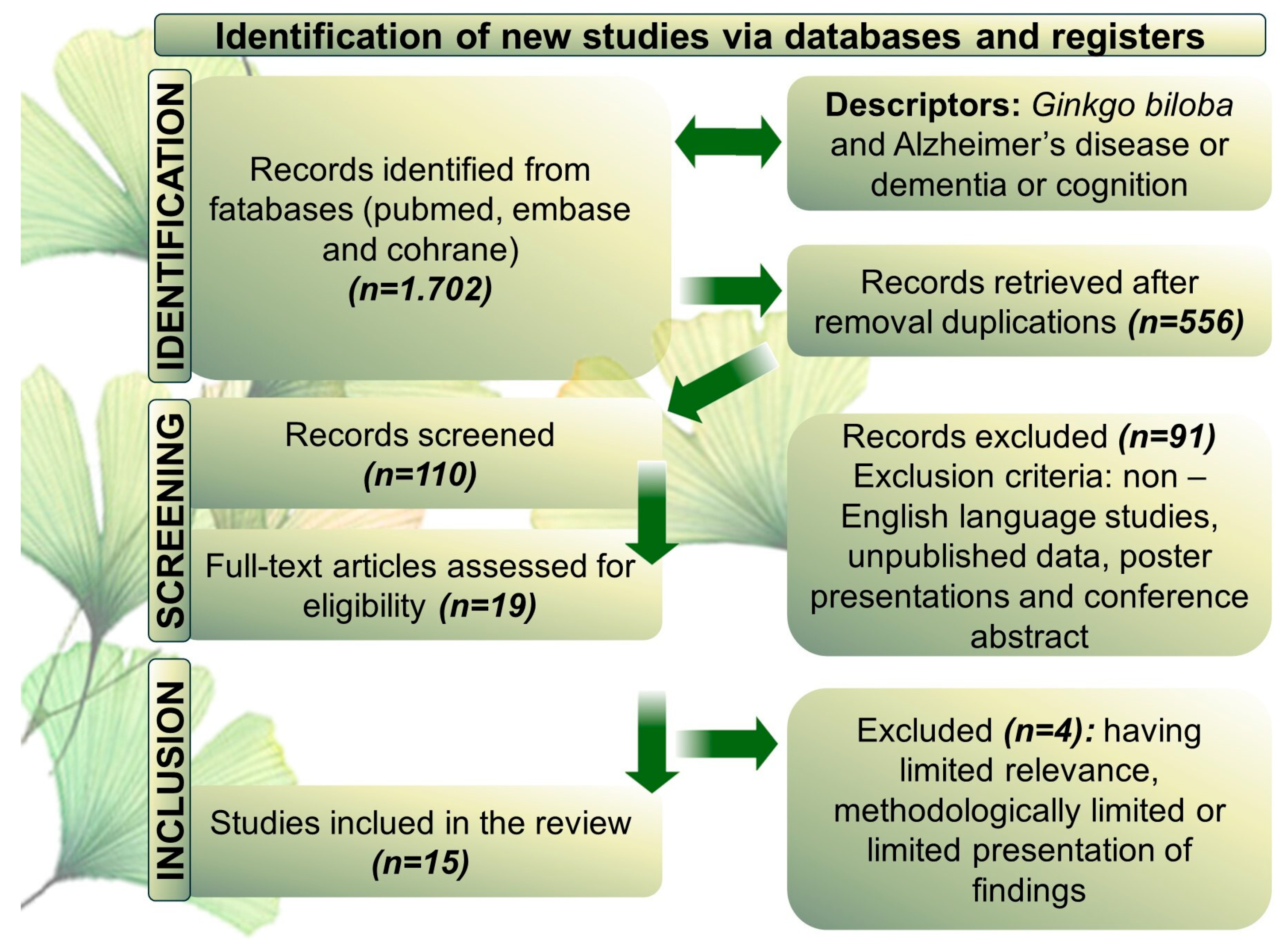
2. Methods
3. Overview of the Included Studies and Result Findings
4. Discussion
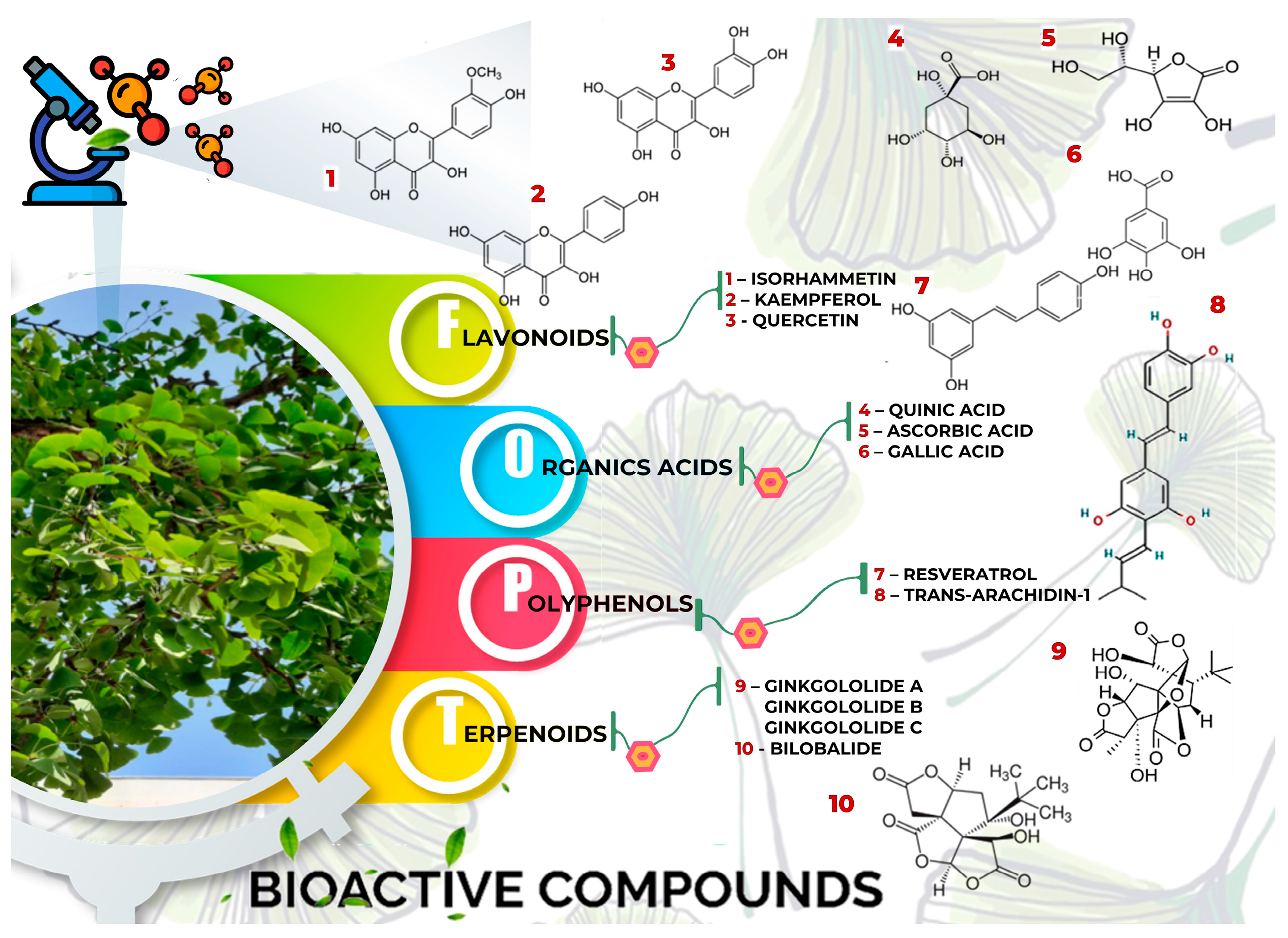
4.1. Ginkgo Biloba, General Aspects
4.2. Ginkgo Biloba and Antioxidant Effects
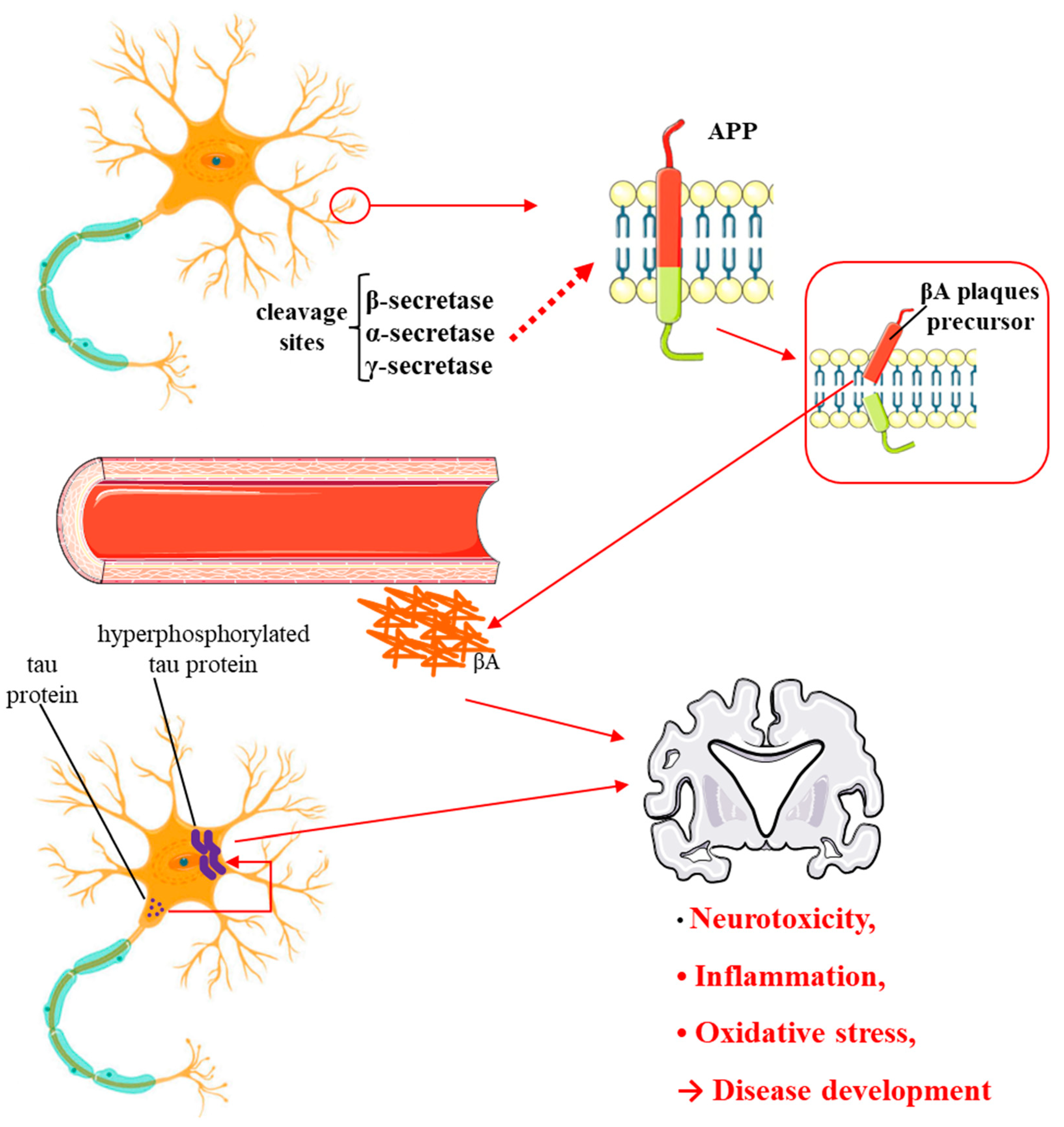
4.3. Ginkgo Biloba and Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia: Evidence from Cellular and In Vivo Studies
4.4. Ginkgo Biloba and Neurotransmitters Related to Alzheimer's Disease
4.4.1. Acetylcholine
4.4.2. Glutamate and Dopamine
4.4.3. Serotonin - 5HT
4.5. Ginkgo Biloba and miAlzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: The Results of Clinical Trials
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Alzheimer, A. Uber eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. All Z Psychiatr 1907, 64, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Scheyer, O.; Rahman, A.; Hristov, H.; Berkowitz, C.; Isaacson, R.S.; Diaz Brinton, R.; Mosconi, L. Female Sex and Alzheimer's Risk: The Menopause Connection. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2018, 5, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, L.; Knoefel, J.; Bhaskar, K. The neuropathology and cerebrovascular mechanisms of dementia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016, 36, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, M.W.; Edmonds, E.C.; Salmon, D.P. Alzheimer's Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2017, 23, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neural Correlates and Molecular Mechanisms of Memory and Learning. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Körtési, T.; Szok, D.; Tajti, J.; Vécsei, L. From CGRP to PACAP, VIP, and Beyond: Unraveling the Next Chapters in Migraine Treatment. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Editorial: Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 2023, 17, 1268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, P.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I. The essential elements of Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem 2021, 296, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, J.V.L.; Nonato, M.B.; Gheler, L.; Prandini, M.N. Structural Volume of Hippocampus and Alzheimer's Disease. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2020, 66, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, L. The Structural Basis of Amyloid Strains in Alzheimer's Disease. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2020, 6, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafian, H.; Zadeh, E.H.; Khan, R.H. Review on Alzheimer's disease: Inhibition of amyloid beta and tau tangle formation. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 167, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumori, A.; Feilen, L.P.; Steiner, H. Substrate recruitment by γ-secretase. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2020, 105, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, J.Y. γ-Secretase in Alzheimer's disease. Exp Mol Med 2022, 54, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Mustafa, M.; Yuede, C.M.; Salazar, S.V.; Kong, P.; Long, H.; Ward, M.; Siddiqui, O.; Paul, R.; Gilfillan, S.; et al. Anti-human TREM2 induces microglia proliferation and reduces pathology in an Alzheimer's disease model. J Exp Med 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsky, J.; Pichlerova, K.; Hanes, J. Tau Protein Interaction Partners and Their Roles in Alzheimer's Disease and Other Tauopathies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer's Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bulck, M.; Sierra-Magro, A.; Alarcon-Gil, J.; Perez-Castillo, A.; Morales-Garcia, J.A. Novel Approaches for the Treatment of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos, D.; Lőrinczi, B.; Szatmári, I.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. The Impact of C-3 Side Chain Modifications on Kynurenic Acid: A Behavioral Analysis of Its Analogs in the Motor Domain. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Schmidt, A.; Hassel, S.; Tanaka, M. Editorial: Case reports in neuroimaging and stimulation. Frontiers in psychiatry 2023, 14, 1264669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, D.; Tuka, B.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L.; Telegdy, G. Memory Enhancement with Kynurenic Acid and Its Mechanisms in Neurotransmission. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Di Fazio, C.; Mazzà, M.; Tamietto, M.; Avenanti, A. Targeting Human Glucocorticoid Receptors in Fear Learning: A Multiscale Integrated Approach to Study Functional Connectivity. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, F.; Battaglia, S. Advances in EEG-based functional connectivity approaches to the study of the central nervous system in health and disease. Advances in clinical and experimental medicine : official organ Wroclaw Medical University 2023, 32, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neurodegeneration in Cognitive Impairment and Mood Disorders for Experimental, Clinical and Translational Neuropsychiatry. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J. Anti-Amyloid Monoclonal Antibodies are Transformative Treatments that Redefine Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutics. Drugs 2023, 83, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valotto Neto, L.J.; Reverete de Araujo, M.; Moretti Junior, R.C.; Mendes Machado, N.; Joshi, R.K.; dos Santos Buglio, D.; Barbalho Lamas, C.; Direito, R.; Fornari Laurindo, L.; Tanaka, M.J.A. Investigating the Neuroprotective and Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Bacopa monnieri: A Systematic Review Focused on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis. 2024, 13, 393.
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastav, S.; Castellani, R.J.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Perry, G. Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract Against AD and Other Neurological Disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Direito, R.; Laurindo, L.F.; Marton, L.T.; Guiguer, E.L.; Goulart, R.A.; Tofano, R.J.; Carvalho, A.C.A.; Flato, U.A.P.; Capelluppi Tofano, V.A.; et al. Ginkgo biloba in the Aging Process: A Narrative Review. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminifard, T.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The effects of ginseng on the metabolic syndrome: An updated review. Food Sci Nutr 2021, 9, 5293–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, O.L.; Chang, Y.; Ives, D.G.; Snitz, B.E.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Carlson, M.C.; Rapp, S.R.; Williamson, J.D.; Tracy, R.P.; DeKosky, S.T.; Kuller, L.H. Blood amyloid levels and risk of dementia in the Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory Study (GEMS): A longitudinal analysis. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2019, 15, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.J.A.I.M. Liberat i A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.J.T.C.d.o.s.r. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2019, 2019. 2019.
- Yakoot, M.; Salem, A.; Helmy, S. Effect of Memo®, a natural formula combination, on Mini-Mental State Examination scores in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Clin Interv Aging 2013, 8, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellas, B.; Coley, N.; Ousset, P.-J.; Berrut, G.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Dubois, B.; Grandjean, H.; Pasquier, F.; Piette, F.; Robert, P. Long-term use of standardised Ginkgo biloba extract for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease (GuidAge): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology 2012, 11, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NM, N.; MA, B.; MR, N.; F, R.; SN, N. Efficacy of rivastigmine in comparison to ginkgo for treating Alzheimer's dementia. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2012, 62. [Google Scholar]
- R, I.; M, T.; N, B. Efficacy and tolerability of a once daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia: results from a randomised controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2012, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H, H.; A, N.; S, L.; I, S.; R, H.; S, S. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in dementia with neuropsychiatric features: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial to confirm the efficacy and safety of a daily dose of 240 mg. Journal of psychiatric research 2012, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihl, R.; Bachinskaya, N.; Korczyn, A.D.; Vakhapova, V.; Tribanek, M.; Hoerr, R.; Napryeyenko, O.; Group, G.S. Efficacy and safety of a once-daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia with neuropsychiatric features: a randomized controlled trial. International journal of geriatric psychiatry 2011, 26, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäurle, P.; Suter, A.; Wormstall, H. Safety and effectiveness of a traditional ginkgo fresh plant extract - results from a clinical trial. Forsch Komplementmed 2009, 16, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheva, S.; Ihl, R.; Nikolova, G.; Panayotov, P.; Schlaefke, S.; Hoerr, R. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761(R), donepezil or both combined in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease with neuropsychiatric features: a randomised, double-blind, exploratory trial. Aging Ment Health 2009, 13, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeKosky, S.T.; Williamson, J.D.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Kronmal, R.A.; Ives, D.G.; Saxton, J.A.; Lopez, O.L.; Burke, G.; Carlson, M.C.; Fried, L.P.; et al. Ginkgo biloba for prevention of dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 2008, 300, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napryeyenko, O.; Borzenko, I. Ginkgo biloba special extract in dementia with neuropsychiatric features. A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Arzneimittelforschung 2007, 57, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.; Capuano, A.; Bria, P.; Mazza, S. Ginkgo biloba and donepezil: a comparison in the treatment of Alzheimer's dementia in a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Eur J Neurol 2006, 13, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QX, Z.; T, S.; DY, T.; R, D.; ZZ, L.; XJ, Z. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extracts on trichloroethylene-induced human keratinocyte cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Skin pharmacology and physiology 2005, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, v.D.; E, v.R.; A, K.; H, S.; P, K. Ginkgo for elderly people with dementia and age-associated memory impairment: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of clinical epidemiology 2003, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bars, P.L.; Kieser, M.; Itil, K.Z. A 26-week analysis of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2000, 11, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, M.C.; van Rossum, E.; Kessels, A.G.; Sielhorst, H.J.; Knipschild, P.G. The efficacy of ginkgo for elderly people with dementia and age-associated memory impairment: new results of a randomized clinical trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2000, 48, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, B.; Hua, X.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. A near-complete genome assembly of the allotetrapolyploid Cenchrus fungigraminus (JUJUNCAO) provides insights into its evolution and C4 photosynthesis. Plant Commun 2023, 4, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, P.; Singh, R.; Ahuja, P. Biology and chemistry of Ginkgo biloba. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohier, C. Plant biotechnology: An avant-garde research for an ancestral tree, the Ginkgo biloba. In Proceedings of the Annales Pharmaceutiques Francaises; 2002; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gertz, H.J.; Kiefer, M. Review about Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb 761 (Ginkgo). Curr Pharm Des 2004, 10, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bai, P.P.; Gu, K.J.; Yang, S.Z.; Lin, H.Y.; Shi, C.G.; Zhao, Y.P. Dynamic transcriptome and network-based analysis of yellow leaf mutant Ginkgo biloba. BMC Plant Biol 2022, 22, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Sowiński, P. 2, 3-Dihydrobiflavone from Ginkgo biloba. Planta medica 1999, 65, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, J.; Vengalasetti, Y.V.; Bredesen, D.E.; Rao, R.V. Neuroprotective Herbs for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions involving Ginkgo biloba. Drug Metab Rev 2013, 45, 353–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Geng, Z.; Lau, B.H. Ginkgo biloba attenuates oxidative stress in macrophages and endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 1996, 20, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, B.K.S.; Pedroso, A.P.; Machado, M.M.F.; Neto, N.I.P.; Perestrelo, B.O.; de Sá, R.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.C.; Nogueira, F.N.; Oyama, L.M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; et al. Ginkgo biloba Extract Modulates the Retroperitoneal Fat Depot Proteome and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YR, Q.; CQ, M.; DP, W.; QQ, Z.; MR, L.; HR, Z.; JH, J.; Q, F. Bilobalide alleviates neuroinflammation and promotes autophagy in Alzheimer's disease by upregulating lincRNA-p21. American journal of translational research 2021, 13. [Google Scholar]
- J, L.; L, X.; K, L.; X, Z.; X, W.; X, D.; Y, L.; Y, C.; X, L. Bilobalide: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and safety. Phytotherapy research : PTR 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, B.; CY, Y.; Q, X.; Y, C.; F, C. Bilobalide Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L, W.; Y, Z.; Z, S.; K, Z.; P, L.; T, X. Ginkgolide A targets forkhead box O1 to protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiomyopathy. Phytotherapy research : PTR 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K, Z.; Y, L.; Z, Z.; Y, M.; X, W.; D, H.; Y, Y.; P, L. Ginkgolide A alleviates cardiac remodeling in mice with myocardial infarction via binding to matrix metalloproteinase-9 to attenuate inflammation. European journal of pharmacology 2022, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H, H.; J, G.; S, Y.; Y, W.; Y, L.; Y, L.; X, L. Ginkgolide A downregulates transient receptor potential (melastatin) 2 to protect cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats through the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway: Ginkgolide A improve acute renal injury. Human & experimental toxicology 2023, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J, C.; Z, O.; T, G.; Y, Y.; A, S.; H, X.; Y, C.; Z, L. Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2022, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y, Y.; Q, W.; X, S.; H, Z.; J, W.; Y, H.; J, C.; Z, L. Ginkgolide B attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through disrupting NCOA4-FTH1 interaction. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2024, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q, W.; S, N.; L, L.; S, W.; H, X.; Z, R. Ginkgolide B Blocks Vascular Remodeling after Vascular Injury via Regulating Tgf β 1/Smad Signaling Pathway. Cardiovascular therapeutics 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y, H.; D, Z.; P, C.; B, G.; Y, H.; DS, G.; M, G.; A, J.-P.; X, L.; Y, L. Matrix-Based Sensitivity Assessment of Soil Organic Carbon Storage: A Case Study from the ORCHIDEE-MICT Model. Journal of advances in modeling earth systems 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Um, J.-Y.; Ahn, K.S.J.I.j.o.m.s. Anti-neoplastic effect of ginkgolide C through modulating c-met phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 2020, 21, 8303.
- M, G.-A.; I, G.-L.; H, C.-U.; I, E.; M, G.; MP, C.; MP, P.; S, G.-Z. Anti-Obesity Effects of Isorhamnetin and Isorhamnetin Conjugates. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Guan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, S.; Luan, X.; Zhang, H. Isorhamnetin: A review of pharmacological effects. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2020, 128, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL, X.; RC, C.; KY, Z.; KW, L.; AJ, G.; D, B.; H, X.; DT, L.; TT, D.; KW, T. Isorhamnetin, A Flavonol Aglycone from Ginkgo biloba L., Induces Neuronal Differentiation of Cultured PC12 Cells: Potentiating the Effect of Nerve Growth Factor. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, P.; K, P.; IA, B.; EM, P.; DC, P.; A, C.; RS, C.; C, S.; C, C.; DO, C. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MY, Q.; MI, K.; SH, A.; AK, V.; FA, A.-S.; AM, A.; AA, A.A. Therapeutic Importance of Kaempferol in the Treatment of Cancer through the Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Giri, L.; Bahukhandi, A.; Tariq, M.; Kewlani, P.; Bhatt, I.D.; Rawal, R.S. Chapter 3.19 - Ginkgo biloba. In Nonvitamin and Nonmineral Nutritional Supplements, Nabavi, S.M., Silva, A.S., Eds.; Academic Press: 2019; pp. 241–250.
- Shukla, R.; Pandey, V.; Vadnere, G.P.; Lodhi, S. Chapter 18 - Role of Flavonoids in Management of Inflammatory Disorders. In Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases (Second Edition), Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: 2019; pp. 293–322.
- Sathya, S.; Pandima Devi, K. Chapter 15 - The Use of Polyphenols for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Role of the Mediterranean Diet in the Brain and Neurodegenerative Diseases, Farooqui, T., Farooqui, A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: 2018; pp. 239–252.
- Luo, Y.; Shang, P.; Li, D. Luteolin: A Flavonoid that Has Multiple Cardio-Protective Effects and Its Molecular Mechanisms. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanezi, F.G.; Meireles, L.M.; de Christo Scherer, M.M.; de Oliveira, J.P.; da Silva, A.R.; de Araujo, M.L.; Endringer, D.C.; Fronza, M.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Scherer, R. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of gold nanoparticles capped with quercetin. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2019, 27, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczyova, K.; Kalocayova, B.; Bartekova, M. Potential Implications of Quercetin and its Derivatives in Cardioprotection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Verma, A.K.; Aloliqi, A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Potential Therapeutic Targets of Quercetin, a Plant Flavonol, and Its Role in the Therapy of Various Types of Cancer through the Modulation of Various Cell Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2021, 26, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, L.; He, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Mei, G.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Yao, P.; Tang, Y. Quercetin Attenuates Atherosclerotic Inflammation by Inhibiting Galectin-3-NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2021, 65, 2000746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Drent, M.; de Boer, V.C.J.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. Quercetin reduces markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in sarcoidosis. Clinical Nutrition 2011, 30, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Fang, J. Therapeutic Effects of Quercetin on Inflammation, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes. Mediators of Inflammation 2016, 2016, 9340637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Hu, F.B.; Ros, E.; Sabaté, J. The role of tree nuts and peanuts in the prevention of coronary heart disease: multiple potential mechanisms. The Journal of nutrition 2008, 138, 1746s–1751s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Do, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, M.; Lim, O.K.; Kim, S.Y. Inhibitory Effect of Arachis hypogaea (Peanut) and Its Phenolics against Methylglyoxal-Derived Advanced Glycation End Product Toxicity. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, S.V.; Kudva, A.K.; Krishnamurthy, R.G.; Mudgal, J.; George, T.; Baliga, M.S. Neuroprotective effects of dietary plants and phytochemicals against radiation-induced cognitive and behavioral deficits: a comprehensive review of evidence and prospects for future research. Food & function, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante de Freitas, P.G.; Rodrigues Arruda, B.; Araújo Mendes, M.G.; Barroso de Freitas, J.V.; da Silva, M.E.; Sampaio, T.L.; Petrilli, R.; Eloy, J.O. Resveratrol-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles: The Effects of D-α-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol 1000 Succinate (TPGS) on Physicochemical and Biological Properties against Breast Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrou, L.; Guo, S.; Ho, C.T.; Bai, N. Review on chemical compositions and biological activities of peanut (Arachis hypogeae L.). Journal of food biochemistry 2022, 46, e14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eungsuwan, N.; Chayjarung, P.; Pankam, J.; Pilaisangsuree, V.; Wongshaya, P.; Kongbangkerd, A.; Sriphannam, C.; Limmongkon, A. Production and antimicrobial activity of trans-resveratrol, trans-arachidin-1 and trans-arachidin-3 from elicited peanut hairy root cultures in shake flasks compared with bioreactors. Journal of biotechnology 2021, 326, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.A.; Medina-Bolivar, F.; Martin, E.M.; Engelberth, A.S.; Villagarcia, H.; Clausen, E.C.; Carrier, D.J.J.B.p. Purification of resveratrol, arachidin-1, and arachidin-3 from hairy root cultures of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) and determination of their antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity. 2010, 26, 1344–1351.
- Condori, J.; Sivakumar, G.; Hubstenberger, J.; Dolan, M.C.; Sobolev, V.S.; Medina-Bolivar, F.J.P.P. ; Biochemistry. Induced biosynthesis of resveratrol and the prenylated stilbenoids arachidin-1 and arachidin-3 in hairy root cultures of peanut: Effects of culture medium and growth stage. 2010, 48, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M. Inflammation and fibrosis. Matrix Biol 2018, 68-69, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C. Review: systemic inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2013, 39, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Nazzi, C.; Thayer, J.F. Genetic differences associated with dopamine and serotonin release mediate fear-induced bradycardia in the human brain. Translational psychiatry 2024, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gregorio, F.; Steinhauser, M.; Maier, M.E.; Thayer, J.F.; Battaglia, S. Error-related cardiac deceleration: Functional interplay between error-related brain activity and autonomic nervous system in performance monitoring. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 2024, 157, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Nazzi, C.; Thayer, J.F. Heart's tale of trauma: Fear-conditioned heart rate changes in post-traumatic stress disorder. Acta psychiatrica Scandinavica 2023, 148, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, N.N.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Sharma, M.; Luo, W. The complexity of tau in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 2019, 705, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Barger, S.; Barnum, S.; Bradt, B.; Bauer, J.; Cole, G.M.; Cooper, N.R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Emmerling, M.; Fiebich, B.L.; et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2000, 21, 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farlow, M.R.; Miller, M.L.; Pejovic, V. Treatment Options in Alzheimer’s Disease: Maximizing Benefit, Managing Expectations. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008, 25, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.B.; Rui, Y.C.; Yang, P.Y.; Li, T.J.; Qiu, Y. Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on expressions of IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-10 in U937 foam cells. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2007, 42, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samandar, F.; Tehranizadeh, Z.A.; Saberi, M.R.; Chamani, J. CB1 as a novel target for Ginkgo biloba's terpene trilactone for controlling chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Journal of molecular modeling 2022, 28, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yao, X.; Hao, F.; Yu, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. Ginkgolide A Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses In Vitro and In Vivo. International journal of molecular sciences 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, P.O. Identification of proteins differentially expressed in cerebral cortexes of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761)-treated rats in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model--a proteomics approach. Am J Chin Med 2011, 39, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Ai, D.; Sun, L.; Xu, X.; Cao, X. EGb 761 inhibits Aβ1-42-induced neuroinflammatory response by suppressing P38 MAPK signaling pathway in BV-2 microglial cells. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Palkhede, J.D.; Kim, S.Y. Anti-Glucotoxicity Effect of Phytoconstituents via Inhibiting MGO-AGEs Formation and Breaking MGO-AGEs. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, W.C.; Jiang, W.P.; Huang, G.J. Attenuation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Hispolon in Mice, Through Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways, and Suppressing Oxidative Stress-Mediated ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Tao, S.; Xia, P.; Chaudhry, N.; Kaura, S.; Stone, S.S.; Liu, M. Ginkgo Biloba Extract Reduces Cardiac and Brain Inflammation in Rats Fed a HFD and Exposed to Chronic Mental Stress through NF-κB Inhibition. Mediators Inflamm 2022, 2022, 2408598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnesen, M.G.; Anderson, D.C.; Springer, T.A.; Knedler, A.; Avdi, N.; Henson, P.M. Adherence of neutrophils to cultured human microvascular endothelial cells. Stimulation by chemotactic peptides and lipid mediators and dependence upon the Mac-1, LFA-1, p150,95 glycoprotein family. J Clin Invest 1989, 83, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.T.; Huang, H.; Chang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.D.; Cai, Z.H.; Efferth, T.; Fu, Y.J. Biflavonoids from Ginkgo biloba leaves as a novel anti-atherosclerotic candidate: Inhibition potency and mechanistic analysis. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.B.; Rui, Y.C.; Li, T.J.; Yang, P.Y.; Qiu, Y. Expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in brain of atherosclerotic rats and effects of Ginkgo biloba extract. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005, 26, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Qin, M.; He, S.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J. Ginkgo Biloba Extract Inhibits Metastasis and ERK/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer. Med Sci Monit 2019, 25, 6836–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, P.O. Gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) prevents increase of Bad-Bcl-XL interaction following cerebral ischemia. Am J Chin Med 2009, 37, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhamel, T.A.; Xu, Y.-J.; Arneja, A.S.; Dhalla, N.S. Targeting platelets for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets 2007, 11, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudhary, M.; Zhang, C.; Song, S.; Ren, X.; Kong, L. Ginkgo biloba delays light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties. Exp Ther Med 2021, 21, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, G.; Wang, H.; He, S.; Zhu, Y. A preparation of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extract inhibits the apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in post-stroke mice via regulating the expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and Caspase-3. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2021, 280, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, II; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem Biol Interact 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, B.C.; Chang, C.J. Chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species in signaling or stress responses. Nat Chem Biol 2011, 7, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatgilialoglu, C.; Ferreri, C.; Krokidis, M.G.; Masi, A.; Terzidis, M.A. On the relevance of hydroxyl radical to purine DNA damage. Free Radic Res 2021, 55, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N.; Arnaud, D. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism and functions in plants. New Phytol 2019, 221, 1197–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.S.; Dighe, P.A.; Mezera, V.; Monternier, P.A.; Brand, M.D. Production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide from specific mitochondrial sites under different bioenergetic conditions. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 16804–16809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neha, K.; Haider, M.R.; Pathak, A.; Yar, M.S. Medicinal prospects of antioxidants: A review. Eur J Med Chem 2019, 178, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Rong, J.; Lai, Y.; Tao, L.; Yuan, X.; Shu, X. The Degree of Helicobacter pylori Infection Affects the State of Macrophage Polarization through Crosstalk between ROS and HIF-1alpha. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 5281795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Jozaki, M.; Tanabe, M.; Shirafuta, Y.; Mihara, Y.; Shinagawa, M.; Tamura, I.; Maekawa, R.; Sato, S.; Taketani, T.; et al. Importance of Melatonin in Assisted Reproductive Technology and Ovarian Aging. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezhnina, V.; Ebeigbe, O.P.; Poe, A.; Kondratov, R.V. Circadian Control of Mitochondria in Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal 2022, 37, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feduska, J.M.; Tse, H.M. The proinflammatory effects of macrophage-derived NADPH oxidase function in autoimmune diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 125, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brieger, K.; Schiavone, S.; Miller, F.J., Jr.; Krause, K.H. Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease. Swiss Med Wkly 2012, 142, w13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milisav, I.; Ribarič, S.; Poljsak, B. Antioxidant Vitamins and Ageing. Subcell Biochem 2018, 90, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hass, D.T.; Barnstable, C.J. Uncoupling proteins in the mitochondrial defense against oxidative stress. Prog Retin Eye Res 2021, 83, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorieux, C.; Calderon, P.B. Catalase, a remarkable enzyme: targeting the oldest antioxidant enzyme to find a new cancer treatment approach. Biol Chem 2017, 398, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzu, V.; Jastroch, M.; Divakaruni, A.S.; Brand, M.D. The regulation and turnover of mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010, 1797, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Ji, W. Ginkgolide A attenuated apoptosis via inhibition of oxidative stress in mice with traumatic brain injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Alzahrani, T. Ginkgo Biloba. In StatPearls; Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Talal Alzahrani declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi Zonouz, A.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The molecular mechanisms of ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) activity in signaling pathways: A comprehensive review. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, G. Ginkgo biloba extract alleviates CCl(4)-induced acute liver injury by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Chen, J.; Jiang, M.; Yan, R.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Liao, Y.; Huang, G. Neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of different polarity parts of the extracts of the Ginkgo biloba leaf and Zingiber officinale rhizome from Yongzhou. Front Chem 2022, 10, 984495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Jin, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Gu, S.; Zong, S.; Zhou, J.; et al. Antioxidant effects of ginkgolides and bilobalide against cerebral ischemia injury by activating the Akt/Nrf2 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cell Stress Chaperones 2019, 24, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klomsakul, P.; Aiumsubtub, A.; Chalopagorn, P. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activities and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Effects of Ginkgo biloba Tea Extract. ScientificWorldJournal 2022, 2022, 4806889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achete de Souza, G.; de Marqui, S.V.; Matias, J.N.; Guiguer, E.L.; Barbalho, S.M. Effects of Ginkgo biloba on Diseases Related to Oxidative Stress. Planta Med 2020, 86, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, C.; Quispe, C.; Jamaddar, S.; Hossain, R.; Ray, P.; Mondal, M.; Abdulwanis Mohamed, Z.; Sani Jaafaru, M.; Salehi, B.; Islam, M.T.; et al. Therapeutic promises of ginkgolide A: A literature-based review. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2020, 132, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strømgaard, K.; Nakanishi, K. Chemistry and biology of terpene trilactones from Ginkgo biloba. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2004, 43, 1640–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Jin, W.; Ao, M.; Zhai, S.; Xu, H.; Yu, L.J.F. ; function. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory properties of the active constituents in Ginkgo biloba for the treatment of pulmonary diseases. 2019, 10, 2209–2220. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Lyu, S.J.O.m.; longevity, c. Ginkgo biloba leaf extract protects against myocardial injury via attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic ApoE−/− mice. 2018, 2018. 2018.
- Trebaticka, J.; Ďuračková, Z.J.O.m.; longevity, c. Psychiatric disorders and polyphenols: can they be helpful in therapy? 2015; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, S.; Kumar, P.; Malik, J.J.P.R. Plants and phytochemicals for Huntington's disease. 2013; 7, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Unger, M.J.D.m.r. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions involving Ginkgo biloba. 2013; 45, 353–385. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, A.S.; Taliyan, R.; Sharma, P.L.J.P.m. Protective effect and mechanism of Ginkgo biloba extract-EGb 761 on STZ-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. 2014; 10, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Wang, B.; Cui, H.; Wu, H.; Lv, J.-R.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, J.-S.; Liu, S.; Qi, L.-W.J.J.o.e. Suppression of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms in the mice by treatment with Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761). 2013; 150, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Hao, S.; Wang, J.; Ren, M.J.M.s.m.i.m.j.o.e.; research, c. Ginkgo Biloba L. extract reduces H2O2-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cytotoxicity by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways and oxidative stress. 2018, 24, 3159.
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.J.P.R. Ginkgo biloba extract attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis in mouse cochlear neural stem cells. 2016; 30, 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Sharma, N.; Nehru, B.J.I. Anti-inflammatory effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neuronal injury. 2018; 26, 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.K.; Muller, W.E. Multi-target drugs for the treatment of cognitive impairment and fatigue in post-COVID syndrome: focus on Ginkgo biloba and Rhodiola rosea. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2024, 131, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Fang, J.; Han, Y.; Hu, X.; Meng, J.; Huang, F.; Xu, H.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Effects and safety of Ginkgo biloba on blood metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1231053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.; Zhu, T.; Wang, W.; Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X. Green Synthesis of Narrow-Size Silver Nanoparticles Using Ginkgo biloba Leaves: Condition Optimization, Characterization, and Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Du, X.; Xu, L. Radioprotective effect of Ginkgolide B on brain: the mediating role of DCC/MST1 signaling. Int J Radiat Biol 2024, 100, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yao, X.; Hao, F.; Yu, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.J.I.J.o.M.S. Ginkgolide A ameliorates LPS-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. 2017, 18, 794.
- Zhang, W.; Song, J.-k.; Yan, R.; Li, L.; Xiao, Z.-y.; Zhou, W.-x.; Wang, Z.-z.; Xiao, W.; Du, G.-h.J.A.P.S. Diterpene ginkgolides protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion damage in rats by activating Nrf2 and CREB through PI3K/Akt signaling. 2018, 39, 1259–1272.
- Chen, W.S.-T.; Lin, T.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Hsieh, D.J.-Y.; Kuo, W.-W.; Liao, S.-C.; Kao, H.-C.; Ju, D.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.J.A. Ginkgolide A improves the pleiotropic function and reinforces the neuroprotective effects by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in 6-OHDA-induced cell model of Parkinson’s disease. 2023; 15, 1358. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, J.J.J.o.E. A RNA-seq approach for exploring the protective effect of ginkgolide B on glutamate-induced astrocytes injury. 2021; 270, 113807. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P.-D.; Mungur, R.; Zhou, H.-J.; Hassan, M.; Jiang, S.-N.; Zheng, J.-S.J.N.R.R. Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro. 2018; 13, 1204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lei, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xu, W.; Dong, W.; Ran, J.; Shi, Q.; Fu, J.J.F.i.C.N. Ginkgolide B maintains calcium homeostasis in hypoxic hippocampal neurons by inhibiting calcium influx and intracellular calcium release. 2021; 14, 627846. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, C.-J.; Lai, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-L.; Wei, C.-H.; Huang, W.-C.J.E.-B.C.; Medicine, A. Ginkgolide C suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the AMPK signaling pathway. 2015; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tchantchou, F.; Lacor, P.N.; Cao, Z.; Lao, L.; Hou, Y.; Cui, C.; Klein, W.L.; Luo, Y.J.J.o.A.s.d. Stimulation of neurogenesis and synaptogenesis by bilobalide and quercetin via common final pathway in hippocampal neurons. 2009; 18, 787–798. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Wu, F.; Xu, J.; Zou, J.J.N.i. Bilobalide regulates soluble amyloid precursor protein release via phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase-dependent pathway. 2011; 59, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.; Gao, N.; Zhang, T.J.T.l. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative damage through activating mitophagy in an in vitro model of Alzheimer’s disease. 2018; 282, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, T.J.N. Resveratrol decreases the insoluble Aβ1–42 level in hippocampus and protects the integrity of the blood–brain barrier in AD rats. 2015; 310, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Foudah, A.I.; Devi, S.; Alam, A.; Salkini, M.A.; Ross, S.A.J.F.i.P. Anticholinergic effect of resveratrol with vitamin E on scopolamine-induced Alzheimer’s disease in rats: Mechanistic approach to prevent inflammation. 2023; 14, 1115721. [Google Scholar]
- Kehr, J.; Yoshitake, S.; Ijiri, S.; Koch, E.; Nöldner, M.; Yoshitake, T.J.I.p. Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb 761®) and its specific acylated flavonol constituents increase dopamine and acetylcholine levels in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: possible implications for the cognitive enhancing properties of EGb 761®. 2012; 24, S25–S34. [Google Scholar]
- Fang XianYing, F.X.; Jiang Yan, J.Y.; Ji Hui, J.H.; Zhao LinGuo, Z.L.; Xiao Wei, X.W.; Wang ZhenZhong, W.Z.; Ding Gang, D.G. The synergistic beneficial effects of Ginkgo flavonoid and Coriolus versicolor polysaccharide for memory improvements in a mouse model of dementia. 2015.
- Chopin, P.; Briley, M. Effects of four non-cholinergic cognitive enhancers in comparison with tacrine and galanthamine on scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Psychopharmacology 1992, 106, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, H. Models of memory dysfunctions. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1985, 444, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristofiková, Z.; Klaschka, J. In vitro effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on the activity of presynaptic cholinergic nerve terminals in rat hippocampus. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders 1997, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, E. Effects of an extract of Ginkgo biloba on learning and memory in mice. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior 1991, 38, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewski, A.; Hensch, S.A. Ginkgo biloba and memory for a maze. Psychological reports 1999, 84, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, U.; Kimber, S.; Hindmarch, I. The effects of acute doses of standardized Ginkgo biloba extract on memory and psychomotor performance in volunteers. Phytotherapy research : PTR 1999, 13, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, G.S.; Shovlin, C.; Wesnes, K.A. A double-blind, placebo controlled study of Ginkgo biloba extract ('tanakan') in elderly outpatients with mild to moderate memory impairment. Current medical research and opinion 1991, 12, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Ai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y. The Efficacy and Safety of Alzheimer's Disease Therapies: An Updated Umbrella Review. Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2022, 85, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, S.S.; Koochekpour, S. Glutamate, glutamate receptors, and downstream signaling pathways. International journal of biological sciences 2013, 9, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K.; Pham, H.T.; Dinh, L.D. Interaction of Plant Extracts with Central Nervous System Receptors. Medicines (Basel, Switzerland) 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitake, T.; Yoshitake, S.; Kehr, J.J.B.J.o.P. The Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® and its main constituent flavonoids and ginkgolides increase extracellular dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex. 2010; 159, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, R.G. Modulação do sistema glutamatérgico: estudo dos efeitos do ácido quinolínico e dos derivados da guanina. 2005.
- Hornykiewicz, O.J.P.r. Dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) and brain function. 1966; 18, 925–964. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, K.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Tai, M.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-F.J.N. Ginkgo biloba extract enhances noncontact erection in rats: the role of dopamine in the paraventricular nucleus and the mesolimbic system. 2011, 189, 199–206.
- Tian, J.; Guo, L.; Sui, S.; Driskill, C.; Phensy, A.; Wang, Q.; Gauba, E.; Zigman, J.M.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Kroener, S.J.S.t.m. Disrupted hippocampal growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1α interaction with dopamine receptor D1 plays a role in Alzheimer′ s disease. 2019; 11, eaav6278. [Google Scholar]
- Butters, M.A.; Young, J.B.; Lopez, O.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Mulsant, B.H.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; DeKosky, S.T.; Becker, J.T. Pathways linking late-life depression to persistent cognitive impairment and dementia. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience 2008, 10, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Fujii, T.; Kawashima, K. Enhancement of cortical and hippocampal cholinergic neurotransmission through 5-HT1A receptor-mediated pathways by BAY x 3702 in freely moving rats. Neuroscience letters 1999, 265, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranger, K.; Giannoni, P.; Girard, S.D.; Girot, S.; Gaven, F.; Stephan, D.; Migliorati, M.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Bockaert, J.; Marchetti-Gauthier, E.; et al. Chronic treatments with a 5-HT(4) receptor agonist decrease amyloid pathology in the entorhinal cortex and learning and memory deficits in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 2017, 126, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehr, J.; Yoshitake, S.; Ijiri, S.; Koch, E.; Nöldner, M.; Yoshitake, T. Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb 761®) and its specific acylated flavonol constituents increase dopamine and acetylcholine levels in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: possible implications for the cognitive enhancing properties of EGb 761®. International psychogeriatrics 2012, 24 Suppl 1, S25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, K.A.; Gross-Isseroff, R.; Israeli, M.; Biegon, A. Autoradiographic analysis of serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding in the human brain postmortem: effects of age and alcohol. Brain research 1991, 554, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huguet, F.; Drieu, K.; Piriou, A. Decreased cerebral 5-HT1A receptors during ageing: reversal by Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761). The Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology 1994, 46, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, N.; Chan, Y.F.; Chen, C.; Dasig, D.; Dominguez, J.; Han, S.H.; Jia, J.; Kim, S.; Limpawattana, P.; Ng, L.L.J.C.n.; therapeutics. Strategies for the use of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb 761®, in the treatment and management of mild cognitive impairment in Asia: Expert consensus. 2021, 27, 149–162.
- Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.; Yew, D.T. Ginkgo biloba extract in Alzheimer's disease: from action mechanisms to medical practice. International journal of molecular sciences 2010, 11, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, S.; Asl, S.S.; Komaki, A.; Hashemi-Firouzi, N. The effect of chronic stimulation of serotonin receptor type 7 on recognition, passive avoidance memory, hippocampal long-term potentiation, and neuronal apoptosis in the amyloid β protein treated rat. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, P.; Rojas, C.; Ebadi, M.; Montes, S.; Monroy-Noyola, A.; Serrano-García, N. EGb761 pretreatment reduces monoamine oxidase activity in mouse corpus striatum during 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium neurotoxicity. Neurochemical research 2004, 29, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blecharz-Klin, K.; Piechal, A.; Joniec, I.; Pyrzanowska, J.; Widy-Tyszkiewicz, E. Pharmacological and biochemical effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on learning, memory consolidation and motor activity in old rats. Acta neurobiologiae experimentalis 2009, 69, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrschaft, H.; Nacu, A.; Likhachev, S.; Sholomov, I.; Hoerr, R.; Schlaefke, S. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in dementia with neuropsychiatric features: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial to confirm the efficacy and safety of a daily dose of 240 mg. J Psychiatr Res 2012, 46, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihl, R.; Bachinskaya, N.; Korczyn, A.D.; Vakhapova, V.; Tribanek, M.; Hoerr, R.; Napryeyenko, O. Efficacy and safety of a once-daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia with neuropsychiatric features: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2011, 26, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Farlow, M.R.; Tariot, P.N.; Hoerr, R.; Kieser, M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of two doses of Ginkgo biloba extract in dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Curr Alzheimer Res 2005, 2, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Model/Country | Population | Intervention/Comparison | Outcomes | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [34] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study design in an outpatient setting/Egypt. | 60 individuals complaining of memory impairment or forgetfulness and satisfying the clinical criteria for mild cognitive impairment, 27 ♂, 33 ♀, 50-80y. | The subjects were divided into 2 groups: G1 received one Memo capsule (combination of 750 mg of lyophilized royal jelly with standardized extracts of GB 120mg) 1x/d/4 weeks, and G2 received placebo. | Only the group treated with MEMO exhibited a statistically significant improvement in MMSE score after 4 weeks. The mean change in MMSE was +2.067 versus +0.133, respectively. | Neither group reported any serious AE (mild nausea, transient headache, and palpitation). |
| [35] | Randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled GuidAge clinical trial/France. | 2820 patients who spontaneously reported memory complaints, 940 ♂, 1880 ♀, 70y or older. | Patients were divided into 2 groups: G1 received 120 mg standardized GB extract (EGb761) 2x/d, and G2 received placebo. | The study did not provide evidence for the protective effect of GB extract on incidence of AD. | Both groups presented serious events such as death, stroke, bleeding, or cardiac disorders. |
| [36] | Randomized, double-blind clinical trial/Iran. | 56 patients with primary degenerative dementia of the AD type, 51 completed the study, 23 ♂, 28 ♀, 50-75y. | Patients were divided into G1 received GB (120 mg) 1x/d/24w, and G2 received rivastigmine (4.5 mg) 1x/d/24w. | This trial establishes GB efficacy and tolerability in Alzheimer's dementia; however, it is not to the same level as rivastigmine. | Group 2: one adverse event was observed but not specified. |
| [37] |
Randomized, controlled, double- blind, multi-center trial/Ukraine. | 333 patients diagnosed with mild to moderate dementia AD, 113 ♂, 220 ♀, 50y or more; and 71 patients diagnosed with VaD, 19 ♂, 52 ♀, 50y or more. |
Patients were divided into G1, received 240mg of GB extract EGb 761®, 1x/d/24w and G2, which received placebo. Patients diagnosed with VaD were divided into two groups: G1 received 240 mg of GB extract EGb 761, 1x/d/24w, and G2 received placebo. |
EGb 761® improved cognitive function, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and functional abilities in both types of dementia. Significant differences were observed in SKT and NPI scores, and in most secondary outcomes, with no notable variations between AD and VaD subgroups. | Both groups presented headache, respiratory tract infection, increased blood pressure, and dizziness. |
| [38] | Multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled/Republic of Belarus, Republic of Moldova, and Russian Federation. |
410 patients suffering from mild to moderate AD or VaD, of those 402 were counted into consideration, 123♂, 279♀, 50y or more. |
Patients were randomized into 2 groups: G1 received GB (240 mg) 1x/d/24w and G2 received placebo. | After the interaction, G1 showed that EGb 761® 1xd at 240mg effectively treats dementia, significantly improving cognitive performance and neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients (p < 0.001). | G1 and G2: headache: dizziness, respirator tract infection, hypertension: somnolence; upper abdominal pain., |
| [39] | Multi-center, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group clinical trial/Ukraine. | 410 individuals with: probable AD (NINCDS-ADRDA criteria); possible AD with CVD (NINDS-AIREN criteria); or probable VaD (NINDS- AIREN criteria); (symptoms of dementia had to be present for at least 6 m), 132♂, 272♀, 50y or older. | Population was divided into 2 groups: G1 received a once-daily tablet with 240 mg of EGb 761®; G2 received placebo. A screening period up to 4 weeks was necessary and was followed by a 24-week treatment period. | EGb 761® was better than placebo for improving SKT and NPI total score (placebo group worsened in SKT, and did not show alteration on the NPI total score). | G1 and G2 showed similar side effect rates (headache, respiratory tract infection, hypertension, dizziness). |
| [40] | Open, uncontrolled, clinical trial/Switzerland. | 59 patients (DemTect score > 12, no obvious symptoms of dementia, and with the presence of at least two of the following symptoms: forgetfulness, impaired concentration, or impaired memory), 15 ♂, 44 ♀, 60y or older. | All patients received 90mg of fresh plant GB extract 2x/d/6w. | At the final visit, SF-12 mental score significantly increased from 48.3 ± 10.1 to 51.3 ± 7.9, but SF-12 body score (44.5 ± 9.2 to 45.3 ± 8.1) and DemTect score (15.9 ± 2.0 to 16.0 ± 2.3) did not change significantly. About half of the patients experienced memory and concentration improvement and fewer forgetfulness symptoms. | Twenty-seven patients reported 39 AE, which were not specified. |
| [41] | Randomized, double-blind exploratory trial/Bulgaria. | 96 patients meeting the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria for probable AD, scored below 36 on the TE4D, below 6 on the CDT, between 9 and 23 on the SKT, and at least 5 on the 12-item NPI, 29 ♂, 65 ♀, 50y or older. | Patients were divided in 3 groups: G1 received EGb 761 120 mg 2x/d; G2 received donepezil at a daily dose of 5 mg during the first 4 weeks and 10 mg for the remaining 18 weeks; G3 received both drugs at recommended doses. It was established a 22-week-treatment period. | During treatment, patients of 3 groups showed improvements over baseline values in all tests and rating scales. No statistically significant or clinically relevant differences could be detected between treatments. | 26 AE were documented for 10 patients treated with EGb 761, 51 for 24 patients taking donepezil, and 29 for 18 patients receiving combined treatment. The most frequent: headache, insomnia, diarrhea, and fatigue. |
| [42] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial/USA. | 3069 with normal cognition (n = 2587) or MCI (n = 482) (impaired at or below the 10th percentile of Cardiovascular Health Study normative data, stratified by age and education, on at least 2 of 10 selected neuropsychological test scores from each cognitive domain, + CDR global score of 0.5), 1651♂, 1418 ♀, 75y or older. | Patients were randomized into 2 groups: G1 received GB extract (120 mg) 2x/d, and G2 received placebo. There was a median follow-up of 6.1 years). | 523 individuals with dementia (246 placebo, 277 GB); 92% classified as possible/probable AD or AD with brain vascular disease evidence. The rate of total dementia was 3.3 per 100 person-years in the GB group and 2.9 in placebo. GB had no effect on dementia or AD incidence in older people with normal cognition or MCI. | The AE profiles for the groups were similar, and there were no statistically significant differences in the rate of serious AE (death, coronary heart disease, stroke, bleeding). |
| [43] | A randomized, placebo- controlled, double-blind clinical trial/Ukraine. | 400 patients with probable AD, possible AD with CVD or probable VaD, all of them with mild to moderate dementia as evidenced by a total score from 9 to 23 (both inclusive) on the SKT test battery, 110 ♂, 285 ♀, 50y or older. | Patients were allocated to receive either two tablets of EGb 761® 120 mg or placebo per day for 22 weeks, being preceded by a medication-free screening period of up to 4 weeks. |
The patients treated with EGb 761® improved cognitive test performance regarding neuropsychiatric symptoms and activities of daily living; placebo deteriorated slightly on most of the outcome measures or remained unchanged, at best. | 166 patients randomized to EGb 761® reported 302 AE, and 178 patients treated with placebo reported 81 AE (headache, angina pectoris, dizziness, back pain). |
| [44] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study/Italy. | 76 patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type, 35 ♂, 41 ♀, aged 50-80y. | Patients were randomized into 3 groups: G1 received GB 160 mg daily dose, G2 received donepezil 5 mg daily dose, G3 was given placebo for 24 weeks. | Compared with the donepezil group, attention, memory, and cognitive performance (SKT test) showed a comparable important improvement. | The frequency of AE was very low (upper respiratory tract infection, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea). |
| [45] | Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter trial/USA. |
513 outpatients with uncomplicated dementia of the AD type scoring 10 to 24 on the MMSE and less than 4 on the modified HIS, without other serious health problems and not using continuous treatment to any psychoactive drug, 243 ♂, 270 ♀, 60y or older. | Patients were divided into 3 groups: G1 received placebo, G2 received 120 mg of EGb 761® per day (or twice-daily dose of 60 mg), and G3 received 240 mg of EGb 761® per day (or twice-daily dose of 120 mg). They were accompanied for 26 weeks. | No differences between the treatment groups regarding cognitive endpoint. Placebo group did not worsen notably from baseline. At the same time, a similar slight decline was found for both actively treated groups. | The frequency of AE and serious AE was very low (upper respiratory tract infection, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea). |
| [46] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial/ Netherlands. | 214 participants with the diagnosis of Dementia (AD or VaD) or age-associated memory impairment (AAMI). 19 ♂, 104 ♀, 50y or older. | The subjects were randomly allocated to one of 3 treatments: G1: EGb 761® 240mg/d, G2: EGb 761® 160mg/d, and G3 placebo. After the 12-week treatment, the subjects were randomly separated in a second 12-week treatment period to continue their GB treatment or placebo. | No benefit of GB was observed. Small differences regarding SKT and CGI were found in GB group (no significant or clinically meaningful). |
35 AE were registered (Nausea, constipation, diarrhea, hospital entrance, and death) |
| [47] | Multi-center, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial/US. | 309 patients with a diagnosis of uncomplicated AD or multi-infarct dementia (ICD-10 and DSM-III-R criteria), 143 ♂, 166 ♀, 45y or older. | Patients were randomly allocated to either G1 (that received EGb 40 mg 3x/d) or G2 (placebo) for 52 weeks following a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period. | In comparison to the base-line values, placebo showed significant worsening in all domains of assessment; EGb slightly improved cognitive assessment and the daily living and social behavior. | Nausea, constipation, and diarrhea in both groups |
| [48] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial/Netherlands. |
214 patients with a mild or moderate stage of dementia (as assessed by the results of SIDAM interview and by a score of 8 - 23 on the SKT), 34 ♂, 180 ♀, 50y or older. | Patients were divided into 3 groups after a 3-week run-in period on placebo: G1 received EGb 761 120 mg 2x/d; G2 received twice-daily doses of EGb 761 80 mg; G3 continued receiving placebo. Outcomes were evaluated after 12 and 24 weeks of intervention. | In general, any remarkable shift in score on most of the outcome parameters during the intervention, either in the GB group or in the placebo | Dizziness, nervousness, and headache were the most common symptoms. |
| Study | Question focus | Appropriate randomization | Allocation blinding | Double-blind | Losses (<20%) |
Prognostics or demographic Characteristics |
Outcomes | Intention to treat analysis | Sample calculation | Adequate follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [34] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | Yes | Yes |
| [35] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| [36] | Yes | NR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | NR | Yes |
| [37] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [38] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [39] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [40] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | NR | Yes |
| [41] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | NR | Yes |
| [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [43] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [44] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | NR | Yes |
| [45] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [46] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [47] | Yes | NR | NR | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | Yes |
| [48] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bioactive compounds | Molecular structures | Part of the plant | Health effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilobalide | 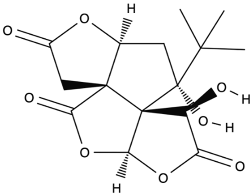 |
Leaves and bark. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-adipogenesis, pro-autophagy, and microcirculation-improving properties. | [59,60,61] |
| Ginkgolide A | 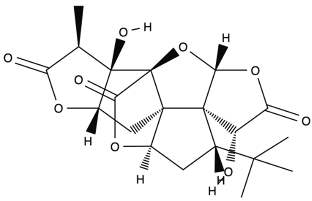 |
Leaves mostly, root and bark. |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic-like, anti-atherosclerosis, anti-thrombosis, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective. | [62,63,64] |
| Ginkgolide B |  |
Leaves mostly, root and bark. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiplatelet aggregation, and anti-shock. | [65,66,67] |
| Ginkgolide C | 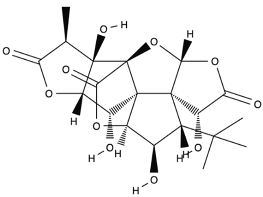 |
Leaves mostly, root and bark. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-adipogenesis. | [68,69] |
| Isorhamnetin | 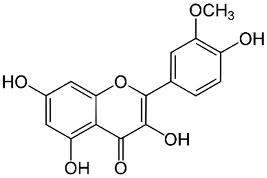 |
Leaves | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and organ protection. | [70,71,72] |
| Kaempferol | 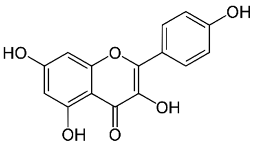 |
Leaves. |
Anti-inflammatoy, antioxidant, anti-cancer, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, and anti-cancer. | [73,74] |
| Luteolin | 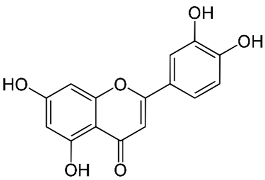 |
Leaves | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, neuroprotective | [35,75,76,77,78] |
| Quercetin | 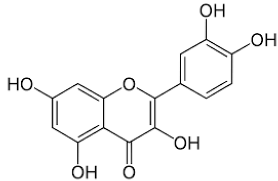 |
Leaves | Anti-inflammator, antioxidant, reduce degradation of serotonin by monoamine oxidases, anticancer |
[75,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
| Resveratrol | 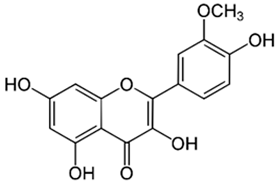 |
Oil, skin, roots, and leaves. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-obesity, antidiabetic, anti-hypertension, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and anti-cancer. | [85,86,87,88] |
| Trans-arachidin-1 | 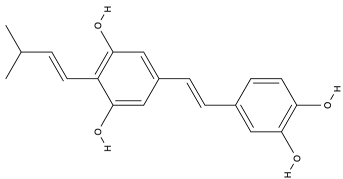 |
Oil, skin, roots, and leaves. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, cardioprotective, and anti-cancer. | [89,90,91,92] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).