Submitted:
10 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Endothelial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
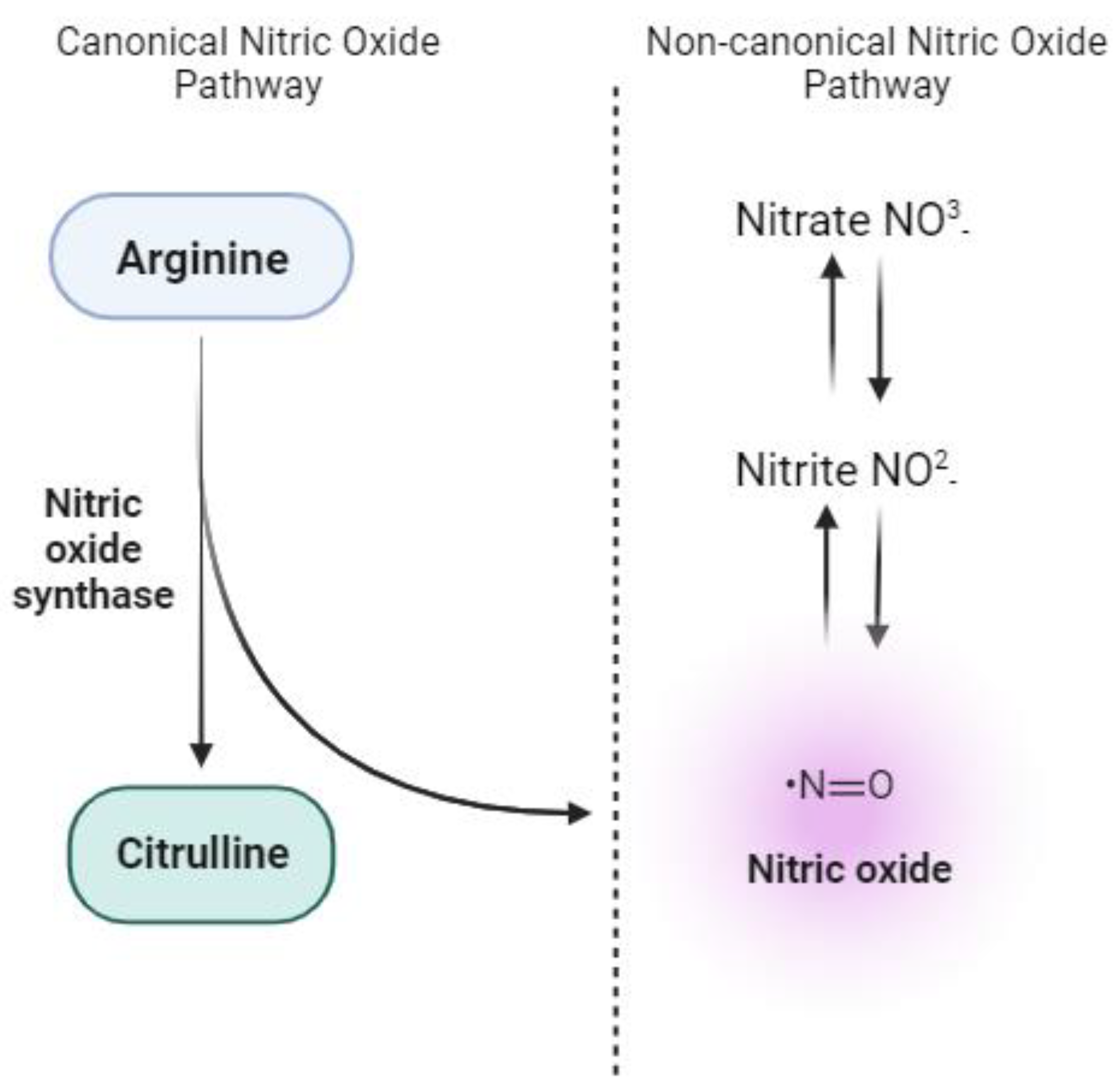
3. Nitrate-Nitrite-NO Pathway: Antioxidant Dynamics and Therapeutic Potential
4. Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet Gynecol 2020, 135, e237–e260. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; Bauersachs, J.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Cifkova, R.; De Bonis, M.; Iung, B.; Johnson, M.R.; Kintscher, U.; Kranke, P. , et al. 2018 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy. Eur Heart J 2018, 39, 3165–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggins, N.; Lai, S. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Emerg Med Clin North Am 2023, 41, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.; An, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, R. Impact of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia on low birthweight and small-for-gestational-age infants in China: A large prospective cohort study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2021, 23, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, D.D.; Avagliano, L.; Ferrazzi, E.; Fuse, F.; Sterpi, V.; Parasiliti, M.; Stampalija, T.; Zullino, S.; Farina, A.; Bulfamante, G.P. , et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Fetal Growth Restriction: Clinical Characteristics and Placental Lesions and Possible Preventive Nutritional Targets. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispi, F.; Miranda, J.; Gratacos, E. Long-term cardiovascular consequences of fetal growth restriction: biology, clinical implications, and opportunities for prevention of adult disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2018, 218, S869–S879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.W., Jr.; LaMarca, B. Risk of cardiovascular disease, end-stage renal disease, and stroke in postpartum women and their fetuses after a hypertensive pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2018, 315, R521–R528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metoki, H.; Iwama, N.; Hamada, H.; Satoh, M.; Murakami, T.; Ishikuro, M.; Obara, T. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: definition, management, and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. Hypertens Res 2022, 45, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.M.; Garovic, V.D. Drug treatment of hypertension in pregnancy. Drugs 2014, 74, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaomang, J.; Yanling, W. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation during pregnancy on high risk factors - a randomized controlled trial. J Perinat Med 2021, 49, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarena Pulido, E.E.; Garcia Benavides, L.; Panduro Baron, J.G.; Pascoe Gonzalez, S.; Madrigal Saray, A.J.; Garcia Padilla, F.E.; Totsuka Sutto, S.E. Efficacy of L-arginine for preventing preeclampsia in high-risk pregnancies: A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial. Hypertens Pregnancy 2016, 35, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monari, F.; Menichini, D.; Pignatti, L.; Basile, L.; Facchinetti, F.; Neri, I. Effect of L-arginine supplementation in pregnant women with chronic hypertension and previous placenta vascular disorders receiving Aspirin prophylaxis: a randomized control trial. Minerva Obstet Gynecol 2021, 73, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesdaghinia, E.; Shahin, F.; Ghaderi, A.; Shahin, D.; Shariat, M.; Banafshe, H. The Effect of Selenium Supplementation on Clinical Outcomes, Metabolic Profiles, and Pulsatility Index of the Uterine Artery in High-Risk Mothers in Terms of Preeclampsia Screening with Quadruple Test: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial : Selenium and preeclampsia. Biol Trace Elem Res 2023, 201, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.H.; Bondonno, C.P.; Croft, K.D.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Rich, L.; Ward, N.C.; Vita, J.A.; Hodgson, J.M. Effects of a nitrate-rich meal on arterial stiffness and blood pressure in healthy volunteers. Nitric Oxide 2013, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovski, E.; Bosco, L.; Khan, K.; Au-Yeung, F.; Ho, H.; Zurbau, A.; Jenkins, A.L.; Vuksan, V. Effect of Spinach, a High Dietary Nitrate Source, on Arterial Stiffness and Related Hemodynamic Measures: A Randomized, Controlled Trial in Healthy Adults. Clin Nutr Res 2015, 4, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanaway, L.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.; Page, R.; Wong, M.; Jirangrat, W.; Teh, K.H.; Ali, A. Acute Supplementation with Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Causes a Greater Increase in Plasma Nitrite and Reduction in Blood Pressure of Older Compared to Younger Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, W.C. Endothelium as an organ system. Crit Care Med 2004, 32, S271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endemann, D.H.; Schiffrin, E.L. Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004, 15, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possomato-Vieira, J.S.; Khalil, R.A. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertensive Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Adv Pharmacol 2016, 77, 361–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Aranguren, L.C.; Prada, C.E.; Riano-Medina, C.E.; Lopez, M. Endothelial dysfunction and preeclampsia: role of oxidative stress. Front Physiol 2014, 5, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.D.; De Long, N.E.; Wang, R.C.; Yazdi, F.T.; Holloway, A.C.; Raha, S. Angiogenesis in the placenta: the role of reactive oxygen species signaling. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 814543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Murtaza, G.; Metwally, E.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Kalhoro, M.S.; Rahu, B.A.; Sahito, R.G.A.; Yin, Y.; Yang, H.; Chughtai, M.I. , et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Balance in Pregnancy. Mediators Inflamm 2021, 2021, 9962860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, H.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, L.; Fu, Y.; Qi, H.; Baker, P.N.; Tong, C. Reactive Oxygen Species are Essential for Placental Angiogenesis During Early Gestation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 4290922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouache, R.; Biquard, L.; Vaiman, D.; Miralles, F. Oxidative Stress in Preeclampsia and Placental Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechend, R.; Viedt, C.; Muller, D.N.; Ugele, B.; Brandes, R.P.; Wallukat, G.; Park, J.K.; Janke, J.; Barta, P.; Theuer, J. , et al. AT1 receptor agonistic antibodies from preeclamptic patients stimulate NADPH oxidase. Circulation 2003, 107, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raijmakers, M.T.; Dechend, R.; Poston, L. Oxidative stress and preeclampsia: rationale for antioxidant clinical trials. Hypertension 2004, 44, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.L.; Brockman, D.; Campos, B.; Myatt, L. Expression of NADPH oxidase isoform 1 (Nox1) in human placenta: involvement in preeclampsia. Placenta 2006, 27, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Gori, T.; Munzel, T. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Hypertens Res 2011, 34, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myatt, L.; Rosenfield, R.B.; Eis, A.L.; Brockman, D.E.; Greer, I.; Lyall, F. Nitrotyrosine residues in placenta. Evidence of peroxynitrite formation and action. Hypertension 1996, 28, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggensack, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Davidge, S.T. Evidence for peroxynitrite formation in the vasculature of women with preeclampsia. Hypertension 1999, 33, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Ploska, A.; Wieronska, J.M.; Dobrucki, L.W.; Kalinowski, L. Endothelial dysfunction due to eNOS uncoupling: molecular mechanisms as potential therapeutic targets. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2023, 28, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoswa, W.N.; Khaliq, O.P. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy (Preeclampsia, Gestational Hypertension) and Metabolic Disorder of Pregnancy (Gestational Diabetes Mellitus). Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 2021, 5581570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukor, Z.; Valent, S.; Toth, M. Regulation of nitric oxide synthase activity by tetrahydrobiopterin in human placentae from normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Placenta 2000, 21, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatre, L.; Ducat, A.; Spradley, F.T.; Palei, A.C.; Chereau, C.; Couderc, B.; Thomas, K.C.; Wilson, A.R.; Amaral, L.M.; Gaillard, I. , et al. Increased NOS coupling by the metabolite tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) reduces preeclampsia/IUGR consequences. Redox Biol 2022, 55, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, B.M.; Cook, L.G.; Danchuk, S.; Puschett, J.B. Uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase and oxidative stress in a rat model of pregnancy-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2007, 20, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Baek, B.S.; Song, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Huh, J.I.; Shim, K.H.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.H. Xanthine dehydrogenase/xanthine oxidase and oxidative stress. Age (Omaha) 1997, 20, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, M.; Polito, L.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine oxidoreductase: One enzyme for multiple physiological tasks. Redox Biol 2021, 41, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, I.; Talosi, G.; Papp, A.; Boda, D. Xanthine oxidase activation in mild gestational hypertension. Hypertens Pregnancy 2002, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, A.B.; Kafkasli, A.; Burak, F.; Gozukara, E.M. Maternal and fetal plasma adenosine deaminase, xanthine oxidase and malondialdehyde levels in pre-eclampsia. Cell Biochem Funct 2005, 23, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, O.J.; Hickey, A.J.R.; Alvsaker, A.; Moran, S.; Hedges, C.; Chamley, L.W.; Perkins, A.V. Changes in mitochondrial respiration in the human placenta over gestation. Placenta 2017, 57, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, F.J.; Gupta, M.B.; Myatt, L.; Powell, T.L.; Glenn, J.P.; Cox, L.; Jansson, T. Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Promotes the Expression of Genes Encoding Electron Transport Chain Proteins and Stimulates Oxidative Phosphorylation in Primary Human Trophoblast Cells by Regulating Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aye, I.L.M.H.; Aiken, C.E.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Smith, G.C.S. Placental energy metabolism in health and disease-significance of development and implications for preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2022, 226, S928–S944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, O.J.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Dekker Nitert, M.; Callaway, L.; Kwan Cheung, K.A.; Radenkovic, F.; Perkins, A.V. Placental mitochondrial adaptations in preeclampsia associated with progression to term delivery. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, R.; Chiarello, D.I.; Abad, C.; Rojas, D.; Toledo, F.; Sobrevia, L. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020, 1866, 165961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gubory, K.H.; Fowler, P.A.; Garrel, C. The roles of cellular reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and antioxidants in pregnancy outcomes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2010, 42, 1634–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, V.A.F.; Melo, A.D.; Santos, H.L.; Barros-Pinheiro, M. Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in subtypes of preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Placenta 2023, 132, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, S.; Ulas, T.; Eren, M.A.; Aydogan, H.; Camuzcuoglu, A.; Kucuk, A.; Yuce, H.H.; Demir, M.E.; Vural, M.; Aksoy, N. Relationship between oxidative stress parameters and cystatin C levels in patients with severe preeclampsia. Medicina (Kaunas) 2013, 49, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaarawy, M.; Aref, A.; Salem, M.E.; Sheiba, M. Radical-scavenging antioxidants in pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1998, 60, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.F.; Palei, A.C.; Machado, J.S.; da Silva, L.M.; Montenegro, M.F.; Jordao, A.A.; Duarte, G.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Cavalli, R.C.; Sandrim, V.C. Assessment of oxidative status markers and NO bioavailability in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Hum Hypertens 2013, 27, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiga, U.; D'Souza, V.; Kamath, A.; Mangalore, N. Antioxidant activity and lipid peroxidation in preeclampsia. J Chin Med Assoc 2007, 70, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrim, V.C.; Palei, A.C.; Metzger, I.F.; Cavalli, R.C.; Duarte, G.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Interethnic differences in ADMA concentrations and negative association with nitric oxide formation in preeclampsia. Clin Chim Acta 2010, 411, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socha, M.W.; Stankiewicz, M.; Zolniezewicz, K.; Puk, O.; Wartega, M. Decrease in Nitric Oxide Production as a Key Mediator in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia and a Potential Therapeutic Target: A Case-Control Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobko, T.; Reinders, C.I.; Jansson, E.; Norin, E.; Midtvedt, T.; Lundberg, J.O. Gastrointestinal bacteria generate nitric oxide from nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 2005, 13, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosby, K.; Partovi, K.S.; Crawford, J.H.; Patel, R.P.; Reiter, C.D.; Martyr, S.; Yang, B.K.; Waclawiw, M.A.; Zalos, G.; Xu, X. , et al. Nitrite reduction to nitric oxide by deoxyhemoglobin vasodilates the human circulation. Nat Med 2003, 9, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlstrom, M.; Montenegro, M.F. Therapeutic value of stimulating the nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway to attenuate oxidative stress and restore nitric oxide bioavailability in cardiorenal disease. J Intern Med 2019, 285, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, V.; Milsom, A.B.; Okorie, M.; Maleki-Toyserkani, S.; Akram, F.; Rehman, F.; Arghandawi, S.; Pearl, V.; Benjamin, N.; Loukogeorgakis, S. , et al. Inorganic nitrate supplementation lowers blood pressure in humans: role for nitrite-derived NO. Hypertension 2010, 56, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Im, M.W.; Pai, S.H. Nitric oxide production increases during normal pregnancy and decreases in preeclampsia. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2002, 32, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiessl, B.; Strasburger, C.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Mylonas, I.; Jeschke, U.; Kainer, F.; Friese, K. Plasma- and urine concentrations of nitrite/nitrate and cyclic Guanosinemonophosphate in intrauterine growth restricted and preeclamptic pregnancies. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2006, 274, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, M.F.; Amaral, J.H.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Sakamoto, E.K.; Ferreira, G.C.; Reis, R.I.; Marcal, D.M.; Pereira, R.P.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Sodium nitrite downregulates vascular NADPH oxidase and exerts antihypertensive effects in hypertension. Free Radic Biol Med 2011, 51, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.J.; Patel, N.; Loukogeorgakis, S.; Okorie, M.; Aboud, Z.; Misra, S.; Rashid, R.; Miall, P.; Deanfield, J.; Benjamin, N. , et al. Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 2008, 51, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.H.; Ferreira, G.C.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Montenegro, M.F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Consistent antioxidant and antihypertensive effects of oral sodium nitrite in DOCA-salt hypertension. Redox Biol 2015, 5, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Tian, R.; Lu, N. NADPH oxidase is a primary target for antioxidant effects by inorganic nitrite in lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in mice and in macrophage cells. Nitric Oxide 2019, 89, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Peleli, M.; Zollbrecht, C.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Persson, A.E.; Carlstrom, M. NADPH oxidase in the renal microvasculature is a primary target for blood pressure-lowering effects by inorganic nitrate and nitrite. Hypertension 2015, 65, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, X.M.; Tarnawski, L.; Peleli, M.; Zhuge, Z.; Terrando, N.; Harris, R.A.; Olofsson, P.S.; Larsson, E.; Persson, A.E.G. , et al. Dietary nitrate attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injuries by modulation of immune responses and reduction of oxidative stress. Redox Biol 2017, 13, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Herrera, I.; Kozyra, M.; Zhuge, Z.; McCann Haworth, S.; Moretti, C.; Peleli, M.; Caldeira-Dias, M.; Jahandideh, A.; Huirong, H.; Cruz, J.C. , et al. AMP-activated protein kinase activation and NADPH oxidase inhibition by inorganic nitrate and nitrite prevent liver steatosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetta, H.S.; Politis-Barber, V.; Petrick, H.L.; Dennis, K.; Kirsh, A.J.; Barbeau, P.A.; Nunes, E.A.; Holloway, G.P. Nitrate attenuates high fat diet-induced glucose intolerance in association with reduced epididymal adipose tissue inflammation and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species emission. J Physiol 2020, 598, 3357–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DesOrmeaux, G.J.; Petrick, H.L.; Brunetta, H.S.; Holloway, G.P. Independent of mitochondrial respiratory function, dietary nitrate attenuates HFD-induced lipid accumulation and mitochondrial ROS emission within the liver. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2021, 321, E217–E228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlstrom, M.; Persson, A.E.; Larsson, E.; Hezel, M.; Scheffer, P.G.; Teerlink, T.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. Dietary nitrate attenuates oxidative stress, prevents cardiac and renal injuries, and reduces blood pressure in salt-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 2011, 89, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindler, A.L.; Fleenor, B.S.; Calvert, J.W.; Marshall, K.D.; Zigler, M.L.; Lefer, D.J.; Seals, D.R. Nitrite supplementation reverses vascular endothelial dysfunction and large elastic artery stiffness with aging. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem J 2016, 473, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.C.; Mustafa, M.R.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Murugan, D.D. Chronic administration of sodium nitrite prevents hypertension and protects arterial endothelial function by reducing oxidative stress in angiotensin II-infused mice. Vascul Pharmacol 2018, 102, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, M.J.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; Santos-Parker, J.R.; Ziemba, B.P.; Lubieniecki, K.L.; Johnson, L.C.; Poliektov, N.E.; Bispham, N.Z.; Woodward, K.A.; Nagy, E.E. , et al. Inorganic Nitrite Supplementation Improves Endothelial Function With Aging: Translational Evidence for Suppression of Mitochondria-Derived Oxidative Stress. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashor, A.W.; Chowdhury, S.; Oggioni, C.; Qadir, O.; Brandt, K.; Ishaq, A.; Mathers, J.C.; Saretzki, G.; Siervo, M. Inorganic Nitrate Supplementation in Young and Old Obese Adults Does Not Affect Acute Glucose and Insulin Responses but Lowers Oxidative Stress. J Nutr 2016, 146, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamy, V.M.; Lepe, J.; Catalan, A.; Retamal, D.; Escobar, J.A.; Madrid, E.M. Oxidative stress is closely related to clinical severity of pre-eclampsia. Biol Res 2006, 39, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmiak, P.; Wojnarowicz, O.; Szymkowiak, M. Malondialdehyde and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as Markers of Oxidative Stress in Small for Gestational Age Newborns from Hypertensive and Preeclamptic Pregnancies. Biomed Res Int 2022, 2022, 9246233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratacos, E.; Casals, E.; Deulofeu, R.; Cararach, V.; Alonso, P.L.; Fortuny, A. Lipid peroxide and vitamin E patterns in pregnant women with different types of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998, 178, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noris, M.; Todeschini, M.; Cassis, P.; Pasta, F.; Cappellini, A.; Bonazzola, S.; Macconi, D.; Maucci, R.; Porrati, F.; Benigni, A. , et al. L-arginine depletion in preeclampsia orients nitric oxide synthase toward oxidant species. Hypertension 2004, 43, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.W.; Vaughan, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd. Placental isoprostane is significantly increased in preeclampsia. FASEB J 2000, 14, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Souza J, M.P.; Harish, S.; Pai, V.R.; Shriyan, C. Increased Oxidatively Modified Forms of Albumin in Association with Decreased Total Antioxidant Activity in Different Types of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Indian J Clin Biochem 2017, 32, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, C.; Watanabe, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Mori, T.; Matsushita, H.; Shinohara, K.; Wakatsuki, A. The severity of hypoxic changes and oxidative DNA damage in the placenta of early-onset preeclamptic women and fetal growth restriction. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013, 26, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilali, N.; Kocyigit, A.; Demir, M.; Camuzcuoglu, A.; Incebiyik, A.; Camuzcuoglu, H.; Vural, M.; Taskin, A. DNA damage and oxidative stress in patients with mild preeclampsia and offspring. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013, 170, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Peleli, M.; Zollbrecht, C.; Giulietti, A.; Terrando, N.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Carlstrom, M. Inorganic nitrite attenuates NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide generation in activated macrophages via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med 2015, 83, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.M.; Quinn, P.A.; Jennings, S.C.; Ng, L.L. NADPH oxidase activity in preeclampsia with immortalized lymphoblasts used as models. Hypertension 2003, 41, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezeck Nunes, P.; Cezar Pinheiro, L.; Zanetoni Martins, L.; Alan Dias-Junior, C.; Carolina Taveiros Palei, A.; Cristina Sandrim, V. A new look at the role of nitric oxide in preeclampsia: Protein S-nitrosylation. Pregnancy Hypertens 2022, 29, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Chen, F.; Kovalenkov, Y.; Pandey, D.; Moseley, M.A.; Foster, M.W.; Black, S.M.; Venema, R.C.; Stepp, D.W.; Fulton, D.J. Nitric oxide reduces NADPH oxidase 5 (Nox5) activity by reversible S-nitrosylation. Free Radic Biol Med 2012, 52, 1806–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollbrecht, C.; Persson, A.E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Carlstrom, M. Nitrite-mediated reduction of macrophage NADPH oxidase activity is dependent on xanthine oxidoreductase-derived nitric oxide but independent of S-nitrosation. Redox Biol 2016, 10, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashmore, T.; Fernandez, B.O.; Branco-Price, C.; West, J.A.; Cowburn, A.S.; Heather, L.C.; Griffin, J.L.; Johnson, R.S.; Feelisch, M.; Murray, A.J. Dietary nitrate increases arginine availability and protects mitochondrial complex I and energetics in the hypoxic rat heart. J Physiol 2014, 592, 4715–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlstrom, M.; Liu, M.; Yang, T.; Zollbrecht, C.; Huang, L.; Peleli, M.; Borniquel, S.; Kishikawa, H.; Hezel, M.; Persson, A.E. , et al. Cross-talk Between Nitrate-Nitrite-NO and NO Synthase Pathways in Control of Vascular NO Homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal 2015, 23, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.C.; Murugan, D.D.; Lau, Y.S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Mustafa, M.R. Sodium nitrite exerts an antihypertensive effect and improves endothelial function through activation of eNOS in the SHR. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 33048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damacena-Angelis, C.; Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Crevelin, E.J.; Portella, R.L.; Moraes, L.A.B.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Nitrate decreases xanthine oxidoreductase-mediated nitrite reductase activity and attenuates vascular and blood pressure responses to nitrite. Redox Biol 2017, 12, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Feng, Y.; Shu, C.; Yuan, R.; Bu, L.; Jia, M.; Pang, B. Dietary Nitrate Protects Against Skin Flap Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats via Modulation of Antioxidative Action and Reduction of Inflammatory Responses. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, E.F.; Peixoto, L.G.; Teixeira, R.R.; Justino, A.B.; Puga, G.M.; Espindola, F.S. Potential Benefits of Nitrate Supplementation on Antioxidant Defense System and Blood Pressure Responses after Exercise Performance. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 7218936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.D.; Capo, X.; Reynes, C.; Quetglas, M.; Salaberry, E.; Tonolo, F.; Suau, R.; Mari, B.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. , et al. Dietary Sodium Nitrate Activates Antioxidant and Mitochondrial Dynamics Genes after Moderate Intensity Acute Exercise in Metabolic Syndrome Patients. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Walsh, S.W. Antioxidant activities and mRNA expression of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase in normal and preeclamptic placentas. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1996, 3, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osunkalu, V.O.; Taiwo, I.A.; Makwe, C.C.; Akinsola, O.J.; Quao, R.A. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Enzyme Level and Antioxidant Activity in Women with Gestational Hypertension and Pre-eclampsia in Lagos, Nigeria. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2019, 69, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y. Impaction of factors associated with oxidative stress on the pathogenesis of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia: A Chinese patients based study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e23666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira-Dias, M.; Viana-Mattioli, S.; de Souza Rangel Machado, J.; Carlstrom, M.; de Carvalho Cavalli, R.; Sandrim, V.C. Resveratrol and grape juice: Effects on redox status and nitric oxide production of endothelial cells in in vitro preeclampsia model. Pregnancy Hypertens 2021, 23, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweider, N.; Huppertz, B.; Wruck, C.J.; Beckmann, R.; Rath, W.; Pufe, T.; Kadyrov, M. A role for Nrf2 in redox signalling of the invasive extravillous trophoblast in severe early onset IUGR associated with preeclampsia. PLoS One 2012, 7, e47055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chigusa, Y.; Tatsumi, K.; Kondoh, E.; Fujita, K.; Nishimura, F.; Mogami, H.; Konishi, I. Decreased lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor 1 (LOX-1) and low Nrf2 activation in placenta are involved in preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012, 97, E1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadir, F.; Rahimi, Z.; Ghanbarpour, A.; Vaisi-Raygani, A. Nrf2 rs6721961 and Oxidative Stress in Preeclampsia: Association with the Risk of Preeclampsia and Early-Onset Preeclampsia. Int J Mol Cell Med 2022, 11, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.H.; Rizzi, E.S.; Alves-Lopes, R.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Tostes, R.C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Antioxidant and antihypertensive responses to oral nitrite involves activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 141, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, T.; Renshall, L.J.; Nihlen, C.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.; David, A.L.; Tsatsaris, V.; Stuckey, D.J.; Wareing, M.; Greenwood, S.L. , et al. Beetroot juice lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function in pregnant eNOS(-/-) mice: importance of nitrate-independent effects. J Physiol 2020, 598, 4079–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormesher, L.; Myers, J.E.; Chmiel, C.; Wareing, M.; Greenwood, S.L.; Tropea, T.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Nihlen, C.; Sibley, C.P. , et al. Effects of dietary nitrate supplementation, from beetroot juice, on blood pressure in hypertensive pregnant women: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled feasibility trial. Nitric Oxide 2018, 80, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, T.; Ormesher, L.; McBain, A.J.; Humphreys, G.J.; Myers, J.E.; Singh, G.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Nihlen, C.; Cottrell, E.C. Altered Oral Nitrate Reduction and Bacterial Profiles in Hypertensive Women Predict Blood Pressure Lowering Following Acute Dietary Nitrate Supplementation. Hypertension 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said Abasse, K.; Essien, E.E.; Abbas, M.; Yu, X.; Xie, W.; Sun, J.; Akter, L.; Cote, A. Association between Dietary Nitrate, Nitrite Intake, and Site-Specific Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Patarata, L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Fraqueza, M.J. Nitrate Is Nitrate: The Status Quo of Using Nitrate through Vegetable Extracts in Meat Products. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Dong, Q.; Liu, L.; Wei, Q. Red and processed meat consumption and cancer outcomes: Umbrella review. Food Chem 2021, 356, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, O.M.; Stephan, B.C.M.; Minihane, A.M.; Mathers, J.C.; Siervo, M. Nitric Oxide Boosting Effects of the Mediterranean Diet: A Potential Mechanism of Action. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2018, 73, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinnato, J.A., 2nd; Freire, S.; Pinto, E.S.J.L.; Cunha Rudge, M.V.; Martins-Costa, S.; Koch, M.A.; Goco, N.; Santos Cde, B.; Cecatti, J.G.; Costa, R. , et al. Antioxidant therapy to prevent preeclampsia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2007, 110, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Liu, A.H.; Croft, K.D.; Ward, N.C.; Yang, X.; Considine, M.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Short-term effects of nitrate-rich green leafy vegetables on blood pressure and arterial stiffness in individuals with high-normal blood pressure. Free Radic Biol Med 2014, 77, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. The functional nitrite reductase activity of the heme-globins. Blood 2008, 112, 2636–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.; Sanchez-Valverde, F.; Gil, F.; Clerigue, N.; Aznal, E.; Etayo, V.; Vitoria, I.; Oscoz, M. Methemoglobinemia induced by vegetable intake in infants in northern Spain. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2013, 56, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, L.; Spyker, D.A. NADH-methemoglobin reductase activity: adult versus child. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2018, 56, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Model | Source | Dose | Time | Mainly outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidative Stress Hypertension | Nitrite Nitrate |
10-5 mol/L 10-2 mol/L |
30 minutes 1 week |
↓ NADPH oxidase activity ↓ Hypertension |
[64] |
| Renal Ischaemia-Reperfusion | Nitrate | 1 mmol/kg/day | 2 weeks | ↓ O2•− levels ↓ IL-12p70, IL-1β, IL-6 |
[65] |
| High-fat diet | Nitrate | 1.0 mmol.kg-1.d-1 | 7 weeks | ↓ NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide and hydrogen peroxide ↓ p67phox protein expression |
[66] |
| High-fat diet | Nitrate | 4 mM | 8 weeks |
↓ Mitochondrial ROS ↓ 4-HNE |
[67] |
| High-fat diet | Nitrate | 4 mM | 8 weeks | ↓ H2O2 mitochondrial emission ↓ TBARs adducts ↓ N3 |
[68] |
| Renal and cardiovascular disease | Nitrate | 0.14 or 1.4 NaNO3 kg -1 | 11 weeks | ↓ Hypertension ↓ Cardiac and renal damage ↓ MDA, 8-OHdG and iPF2α |
[69] |
| Aging | Nitrite | 50 mg/L | 3 weeks | ↑ eNOS expression ↓ Nitrotyrosine levels ↓ IL-1B, IL-6, IFNg and TNF-α |
[70] |
| Hypertension | Nitrite | 50 mg/L | 2 weeks | ↓ Blood pressure ↓ ROS levels ↓ Superoxide Anion ↓ Nitrotyrosine ↓ Nox-4 protein |
[72] |
| Age-associated vascular endothelial dysfunction | Nitrite | 50 mg/L | 8 weeks | ↓ Mitochondrial ROS production ↑ Nrf2 |
[73] |
| 2K1C hypertension | Nitrite | 0.5, 5 and 50mM | 4 weeks | ↓ hypertension ↓ MDA, 8-isoprostane ↓ vascular ROS production ↓ NADPH oxidase activity |
[60] |
| DOCA-salt hypertension | Nitrite | 15 mg/kg | 4 weeks | ↓ hypertension ↓ MDA, 8-isoprostane ↓ NADPH oxidase activity ↓ XOR activity |
[62] |
| Hypoxia | Nitrate | 0.7 mmol-1 | 2 weeks | ↑ Complex I activity ↓ Protein Carbonyls ↓Nitroso-compounds |
[88] |
| IR injury Skin Flap | Nitrate | 5 mmol/L | 7 days before surgery | ↓ histological lesions and protected cells from apoptosis ↑ SOD, GSH-Px, CAT activity ↓MDA ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 |
[92] |
| 2K1C hypertension | Nitrite | 15 mg/kg | 4 weeks | ↓ Hypertension ↓ ROS levels ↑ Nrf2 ↑ SOD1, CAT, GPx2, TRDX-1, TRDX-2 mRNA expression ↑SOD and GPx activity |
[103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





