Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think, act, and learn like humans [
1]. The core objective of A.I. is to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. The historical journey of artificial intelligence (AI) began in the mid-20th century with the wish to forge creations endowed with human-like intelligence. From 1950, when Alan Turing proposed the concept of a universal machine that could perform any conceivable mathematical computation [
2] until today, AI applications have evolved considerably, offering a range of applications that enhance both personal and professional tasks [
3]. In personal use, A.I. is found in smart assistants like Siri and Alexa, responding to voice commands for managing devices or providing information. In entertainment, A.I. systems recommend personalised content on platforms like Netflix.
Moreover, generative A.I. applications such as ChatGPT are extensively utilised daily by a vast audience and students [
4], indicating their significant impact on enhancing human-computer interaction [
5,
6]. In the workplace, A.I. applications automate and optimise various processes, such as data analysis. Furthermore, A.I. systems assist in diagnostics, tailor medical devices, and provide healthcare [
7].
In the last two years, there has been a marked increase in the use of A.I. applications by higher education students [
8]. Many applications (e.g. ChatGPT, etc.) [
9] are used for various purposes. Since then, an intensive exchange of views has started in the public debate in the international educational community, mainly at the higher education level [
8], and there are even academic institutions that choose to ban the use of AI, an action that most researchers consider to be wrong [
10,
11,
12]. However, researchers propose that the most appropriate solution is the critical inclusion of AI in the educational process, based on a specific framework of norms and the integration of AI in teaching practice, learning, and learning assessment [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. In this framework, many projects suggest and develop A.I. applications to support students' learning in higher education. For example, the augMENTOR aims to develop a novel pedagogical framework that promotes both basic skills and 21
st-century competencies by integrating emerging technologies. This framework will be supported by an open-access AI-boosted toolkit that builds on the strengths of big data and learning analytics to provide different types of stakeholders with explainable recommendations for smart search and identification of educational resources, as well as for designing personalised learning profiles that take into account individual actors' characteristics, needs, and preferences. augMENTOR will leverage advancements in the fields of Pedagogical Design, Creative Pedagogy, Explainable Artificial Intelligence, and Knowledge Representation and Reasoning for instructional purposes [
18]
To properly use these applications, it is necessary to investigate students' experiences [
8] and the factors that seem to explain the intention to use them in the future [
19]. However, limited studies have been conducted in the European Union e.g. [
20], and according to the authors’ knowledge, no previous attempt has been reported in Greece. Previous studies mainly use the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), e.g. [
21,
22] and, to a lesser degree, the Unified Theory of Acceptance and, to a lower degree, the Use of Technology (UTAUT) e.g. [
19,
23,
24,
25,
26]. Moreover, these works investigate the possible factors with participants from various scientific disciplines without specification in a scientific field. Considering that most of these A.I. applications (e.g. ChatGPT, Grammarly, Gemini, etc.) are mainly utilised as writing and brainstorming assistants (e.g. facilitate literature searching, summarise readings, etc.) [
4,
27,
28], we consider that is very important to investigate these possible factors with students who studied in the humanities and social sciences [
28].
This work tries to cover the previous gap by using the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology—UTAUT 2 [
29]—and investigating the factors influencing higher education students' intention and actual use of A.I. technology. Therefore, this work investigates the factors that explain the actual use and intention of Greek students of Humanities and Social Sciences to use A.I. applications for academic purposes.
The findings of this work could enhance our understanding of educational systems, providing insights for potential improvements and reforms. Finally, these insights could foster the development of new academic applications tailored to meet the evolving needs of students in a technology-driven landscape. In addition, faculty members and policymakers could create a framework for the responsible and effective utilisation of these applications to enhance teaching and learning in higher education.
The manuscript's structure follows: Student usage of A.I. applications, the conceptual model UTAUT2, and the corresponding hypotheses are presented. The study's analytical methodology is then presented in sequence. Finally, the study's results are presented in detail and discussed in the next section regarding the findings of previous studies.
Theoretical Framework
Students' Use of AI for Academic Purposes
Although AI and its applications and implications for education have been discussed for over a decade [
30,
31], the evolution and popularisation of AI over the past couple of years have sparked new interest, concerns, and debates. AI models allow for generating multimodal content such as text, images, and video from textual prompts. Examples of applications include ChatGPT and CoPilot for text-to-text generation, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E and Midjourney for text-to-image, and DeepBrain AI and Sora for text-to-video generation [
32,
33]. AI offers tremendous potential to disrupt current practices in business, education, healthcare, and the content generation industry [
33]. The case of Large Language Models such as ChatGPT in particular and its extremely rapid adoption by the public, in comparison to platforms such as Twitter or Facebook [
32], has been the focus of a largely expanding body of research focusing on their impact on education and learning.
Studies focusing on the applications and benefits of ChatGPT, particularly in Higher Education, have identified benefits such as the potential for the personalisation of learning, personalised feedback and learning tasks, the impact and the shifting paradigms for students' assessment and evaluation, increased motivation and engagement of the students, improvement of communication abilities in language learning, and support in the decision-making process of students regarding academic decisions [
13,
34,
35]. Applications include language translation, increased access to information, summarisation of relevant information personalised to the student's queries, question answering, support of teacher practices, facilitating research such as data analysis and interpretation, and advice on data collection methods [
34,
36].
Technology Acceptance Model of A.I.
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 (UTAUT2) is an extension of the original UTAUT model that was developed by Venkatesh, Morris, Davis, and Davis and was introduced in their 2003 paper titled "User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View", [
37]. The UTAUT2 was developed to understand better the factors influencing technology adoption and usage, particularly in the context of consumer use, by Venkatesh, along with Thong and Xu, who introduced their extension in their 2012 paper titled "Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology" [
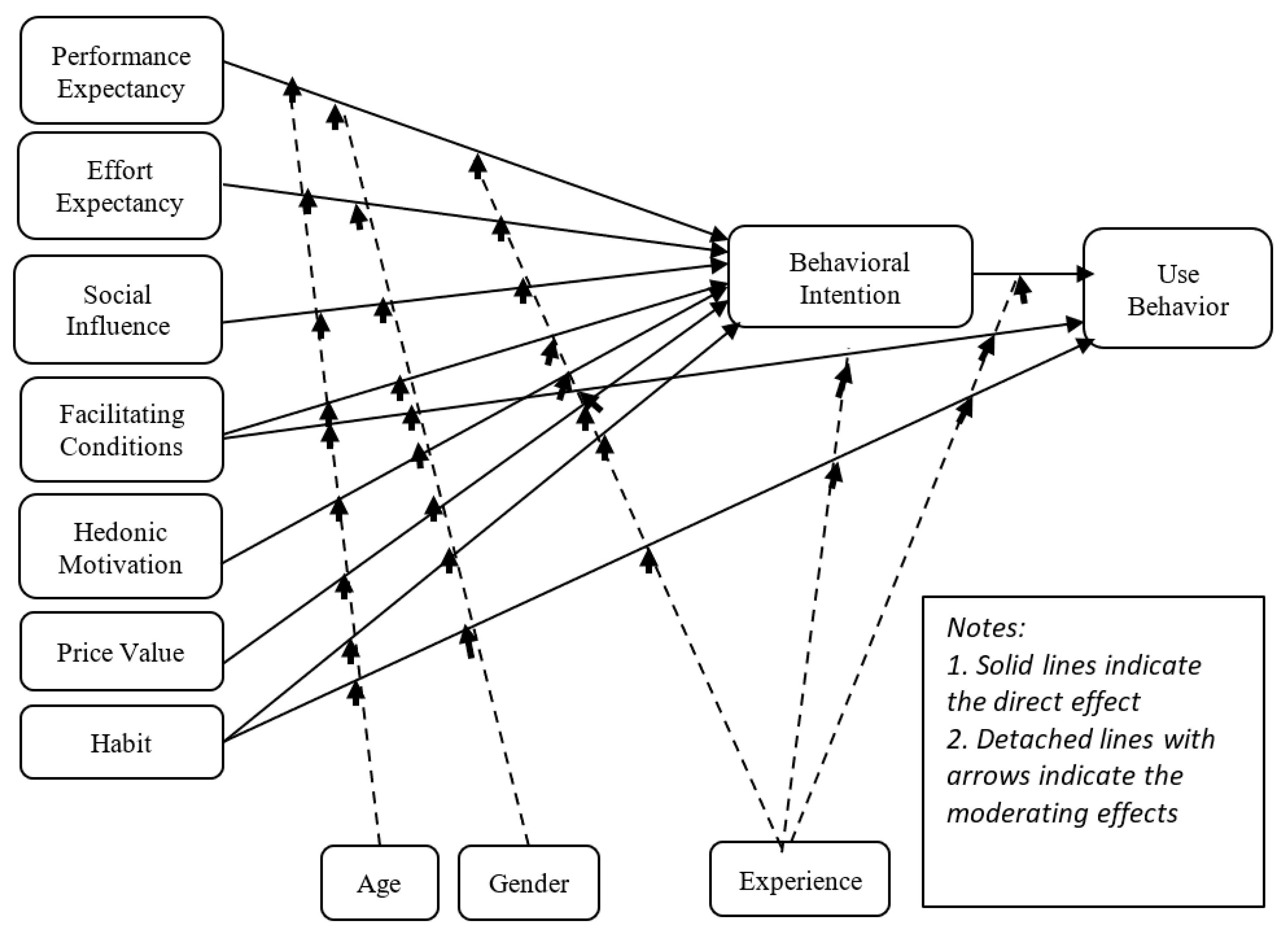
29]. Regarding the context of students' usage of A.I. applications, the construct Performance Expectancy (PerExp) refers to the degree to which using A.I. applications will provide benefits in performing certain activities. Effort Expectancy (EfExp) is the ease associated with using A.I. applications. Social Influence (SocInf) involves how students perceive that essential others believe they should use A.I. applications. Facilitating Conditions (FacCon) are the degree to which a student believes that technical and organisational infrastructure exists to support the use of A.I. applications. Behavioral Intention (BehInt) is the degree of one's intention to use the A.I. applications, and Use Behavior (UsBeh) is the actual use of A.I. applications.
Additionally, UTAUT2 introduces three constructs specific to consumer contexts, such as habit (Hab) and the extent to which students perform behaviours automatically due to learning. It underscores the role of past behaviour and experience in predicting future A.I. application use. Hedonic Motivation (HedMot) represents the fun or pleasure derived from using A.I. applications. Price Value (PrVal) is the cognitive trade-off between the perceived benefits of the applications and the monetary cost of using A.I. applications. Finally, Gender, Age, and experience are considered moderating variables that can influence the strength and the direction of relationships between the model’s core constructs and outcomes like BehInt and UsBeh. The UTAUT2 model offers a nuanced understanding of how various factors, including enjoyment, cost, and habit, collectively influence A.I. application adoption and sustained use in a personal context. This makes it a valuable framework for investigating students, and teachers' technology usage for educational purposes, as it accounts for both the practical and affective dimensions of technology adoption [
38].
Despite the growing interest in AI in recent years, there are only a few research studies on the use of AI by students worldwide [
39]. Recently, but scarcely similar studies utilising the UTAUT model across various countries have highlighted a consistent set of factors influencing students' behavioural intentions and acceptance of A.I. in general [
19,
25] and specifically in chatbot technologies [
23,
24,
26]. Some of them have investigated the factors that explain only the behavioural intention of usage AI applications [
19,
24], and only one work that investigated the moderating effect (only two of them, study years, and gender of students) was found [
40]. Moreover, three studies have investigated the previous factor with a sample from the European Union: England [
23], Spain [
26], and Poland [
40].
Mainly, Alzahrani [
19], using a combination of TAM and UTAUT models with 350 students from universities in Saudi Arabia, investigated the factors that explain only the behavioural intention of students to use A.I. applications in general. Performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and facilitating conditions significantly affected behavioural intention. Similarly, Alshammari and Alshammari [
24], using a UTAUT model with 136 from the same Country, found that performance expectancy and facilitating conditions explain the behavioural intention of students to use ChatGPT. In addition, Dahri et al. [
25], using the UTAUT model with 305 university students (203 from Pakistan and 102 from Malaysia), found performance expectancy and facilitating conditions that explain the behavioural intention of students to use A.I. applications. Moreover, behavioural intention explains their actual use.
In the European Union, Almahri et al. [
23], using an adapted UTAUT2 model without moderating effects with 431 higher education students from the U.K., found that performance expectancy, expected effort, and Habit explain the behavioural intention of students to use ChatGPT. Moreover, behavioural intention explains their actual use. Similarly, Romero-Rodríguez et al. [
26], using the UTAUT2 without moderating effects with 400 students from various universities in Spain, found that performance expectancy, hedonic motivation, price value, and habit explain the behavioural intention of students to use ChatGPT. Moreover, habit, facilitating conditions and behavioural intention explain their actual use. Finally, Strzelecki [
40], using the UTAUT2 model with moderating effect only the gender and the years of study of 534 students from various universities of Polish found habit, performance expectancy, hedonic motivation, effort expectance, and social influence explain the behavioural intention of students to use ChatGPT. Moreover, habit, facilitating conditions and behavioural intention explain their actual use. Finally, moderating effects were not revealed.
Research hypotheses
Based on the UTAUT2 model, we examined eleven hypotheses (see
Figure 1) consisting of the main effects and the interactions influenced by the moderating factors (gender, age, and experience with A.I.):
H1: Expected Performance positively affects students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (PerExp -> BehInt).
H2: Expected effort positively affects students’ intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (EfExp -> BehInt).
H3: Social Influence positively affects Students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (SocInf -> BehInt).
H4: Facilitating Conditions positively affect Students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (FacCon -> BehInt).
H5: Hedonic Motivation positively affects Students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (HedMot -> BehInt).
H6: Price value positively affects Students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (PrVal -> BehInt).
H7: Habit positively affects Students’ Intention to use A.I. applications for academic purposes (Hab -> BehInt).
H8: Intention to Use positively affects students' use of A.I. applications for academic purposes (BehInt -> UsBeh).
H9: Facilitating conditions positively affect students’ use OF A.I. applications for academic purposes (FacCon -> UsBeh).
H10: Habit positively affects students’ use OF A.I. applications for academic purposes (Hab -> UsBeh).
H11: Gender, age, and experience moderate the use of A.I. applications for academic purposes.
Research Methods
The study was conducted in November and December 2023 and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Department of Educational Science and Early Childhood Education of the University of Patras (85812/09-11-2023). This cross-sectional study was based on a quantitative educational research strategy, and the data was collected using an online questionnaire [
41].
Research instrument
The survey questionnaire, which consisted of two sections of questions, initially included the objective, instructions for completion, and our assurance of respondent anonymity [
42]. The first question section included questions regarding the demographic information of the student participants, such as gender, age, year of study, and frequency of experience with A.I. applications for academic purposes. The second section consisted of 27 statements corresponding to the nine constructs of the UTAUT2 model. Students could answer on a five-point scale (1 strongly disagree to 5 strongly agree). These statements, three for each construct, are an adaptation of the corresponding valid and reliable research instrument used in the work of Nikolopoulou et al. [
38]. These researchers used the UTAUT2 model to investigate the factors that explain Greek higher education students' usage of mobile devices for academic purposes [
38]. Specifically, the adaptation involved replacing the term "mobile devices" with the term "A.I. applications" (see Appendix for the corresponding statements for each construct).
The Strategy of Data Analysis
The R environment [
43] and the “seminr” package [
44] were used for data analysis. The method for structural equation modelling (Partial Least Squares - Structural Equation Modeling "PLS-SEM") that allows the estimation of complex cause-effect relationships in path models with latent variables was utilised [
45]. This method is considered suitable for the UTAUT2 model since it is complex and includes many constructs (nine and three moderator variables), indicators (27 statements), and model relationships. Moreover, this method offers satisfying solutions with small sample sizes where the model consists of many constructs, as in this study [
46]. The guidelines of Hair et al. [
46] were used to present the results of PLS-SEM. The bootstrapping method was utilised to estimate the parameters (e.g., path coefficients and their confidence intervals) of both the measurement model and the structural model, according to which 2000 random samples with replacement from the original dataset were created [
45]. Finally, the validity and reliability issues of the measurement tool are detailed in the measurement model.
Participants
The convenience sample for this study consists of 197 students from various departments at the School of Humanities and Social Sciences of the University of Patras, such as Philosophy, Educational Sciences, Early Childhood Education, and Philology.
Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics of these participants.
Results
Initially, the measurement model will be presented, providing evidence about the reliability and validity of the research instrument. This model follows the structural model, namely the check of the hypotheses of the conceptual model.
Measurement Model
Table 2 presents descriptive statistics and reliability and convergent validity indices for each construct of the UTAUT2 model. All the Cronbach's Alphas are close to .7 or exceed .7, but Composite reliability exceeds 7, indicating satisfactory internal consistency reliability for all constructs [
45]. Moreover, all items’ loadings are very close or exceed .7, and simultaneously, the Average Extracted Variance for each construct exceeds .5, indicating a satisfactory level of convergent validity for all constructs [
45].
In addition, Pearson’s linear correlation coefficients among the constructs are significant (see
Table 3). Finally, the Fornell-Larcker criterion [
47] indicates satisfactory discriminant validity of constructs since the square roots of the average variance extracted (see on diagonal cells) for each construct are higher from all their correlations.
Structural Model
The analysis did not reveal collinearity problems since all variance inflation factor (VIF) coefficients are lower than 3 [
46]. The explained variance in the two endogenous constructs (R2 of BehInt = 75% and R2 of UsBeh= = 67%) indicates moderate to substantial predictive power [
45]. Regarding the testing of the eleven hypotheses (see
Table 2), only six of them are supported (zero is not included in the corresponding 95% confidence interval). Indeed, in these confirmed hypotheses, the corresponding direct effect coefficients indicate small to medium effects [
45]. Finally, the hypothesis of moderating effects of Gender, Age, and Experience with A.I. applications was not confirmed.
Table 2.
Testing the assumptions of the conceptual model: Direct effect coefficients (b) and their 95% confidence intervals based on bootstrapping (2000 samples).
Table 2.
Testing the assumptions of the conceptual model: Direct effect coefficients (b) and their 95% confidence intervals based on bootstrapping (2000 samples).
| Hypotheses |
Direct effect |
95% CI |
Results |
| H1 |
PerExp -> BehInt |
.422 |
.232 |
.571 |
Supported |
| H2 |
EfExp -> BehInt |
-.058 |
-.176 |
.084 |
Not supported |
| H3 |
SocInf -> BehInt |
.081 |
-.025 |
.217 |
Not supported |
| H4 |
FacCon -> BehInt |
.010 |
-.114 |
.138 |
Not supported |
| H5 |
HedMot -> BehInt |
.184 |
.052 |
.315 |
Supported |
| H6 |
PrVal -> BehInt |
-.034 |
-.153 |
.108 |
Not supported |
| H7 |
Hab -> BehInt |
.335 |
.187 |
.488 |
Supported |
| H8 |
BehInt -> UsBeh |
.423 |
.262 |
.558 |
Supported |
| H9 |
FacCon -> UsBeh |
.187 |
.078 |
.292 |
Supported |
| H10 |
Hab -> UsBeh |
.284 |
.151 |
.420 |
Supported |
| H11 |
Moderating effects |
Not supported |
Conclusions and Discussion
In this work, we investigated the factors according to the UTAUT2 technology acceptance model that explains the intention and actual use of artificial intelligence applications by humanities and social sciences students for academic purposes. The data analysis confirms the robust structure of the UTAUT2 model and the satisfactory fit with the data related to the factors explaining the intention of higher education students to use A.I. applications [
23,
26,
40]. Also, the explanatory power of the model, the percentage of explained variance regarding students' intention and actual use of A.I. applications, is similar to previous research [
26,
40].
More specifically, in explaining students' intention to use A.I. applications, the factors of Performance Expectancy (direct effect =.422), Habit (direct effect =.335), and Hedonic Motivation (direct effect =.184) play a dominant role. These positive effects suggest that high values of students' perceptions of the performance expectancy of A.I. applications in their academic support, when other factors included in the model are held constant, are more likely to lead to their utilisation in the future. Similarly, the more students perceive that specific applications have become a habit, the more likely they will use them. Similarly, the more pleasure they derive from utilising these applications, the more likely they will use them. Other researchers have reported the explanatory role of students' attitudes towards the Expected Performance of A.I. applications [
19,
23,
24,
25,
26,
40]. Similar to previous research is the explanatory role of habit [
23,
26,
40] and hedonic motivation [
26,
40].
To explain the actual use of A.I. applications by students, the factors of intention to use (direct effect=.423), habits (direct and indirect effect=.425), and facilitating conditions (direct and indirect effect=.191) play a dominant role. These positive effects suggest high student perceptions that they will use A.I. applications for academic support when other factors included in the model are held constant and are more likely to lead to actual use. Previous studies also report this effect [
23,
25,
26,
40]. Also, the more students perceive that these applications have become a habit, the more likely they are to adopt them for academic support. Previous studies also reported this effect [
26,
40]. In the same vein, but to a lesser extent, the more they perceive that adequate technical support is provided for these applications, the more likely they are to adopt them for their academic support. This small effect has also been reported in previous studies [
26,
40].
Finally, other studies confirm the non-support of moderation effects, as supported in the UTAUT2 model [
40]. However, it is worth emphasising that this study [
40] only considered gender and years of study, not experience with A.I. applications.
Given the above, several suggestions for practical applications and future research are suggested. Academics and lecturers should explain and demonstrate the usefulness of A.I. applications as supporting tools for students in their academic careers. This means that in the context of courses, student seminars, and workshops on the use of technology, these applications should be included by demonstrating to students their benefits and advantages, which increase their efficiency [
34] and academic performance [
25]. In this context, ways of implementation, general functions, and features of A.I. applications that excite students could be presented. Also, these applications could be included in the existing curriculum. Finally, the creators of these applications need to provide technical support in the form of feedback instructions, making it easier for the users to address any problems during its utilisation effectively.
As in any research, some limitations should be considered in reading and interpreting the findings, which will also feed the avenue for further research. The presented effects between variables should be considered mainly as correlations since this research is cross-sectional [
41]. Furthermore, using self-reports in the study increases the possibility of measurement bias and socially desirable results [
48]. Future longitudinal studies should explore these hypotheses with a representative sample, such as a cluster sample including students across different departments, universities, and countries. Also, for a complete picture regarding factors explaining the intention as well as the actual use of A.I. applications, other factors such as perceived trust [
21] or information accuracy [
25] and perceived satisfaction [
22,
25] should be investigated. Finally, a qualitative approach with semi-structured interviews could provide rich insights regarding the previous possible factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, K.L., V.K., I.V., and N.K.; Methodology, K.L., S.P., S.A. and V.K.; Software, A.F. and S.A.; Validation, K.L., S.P. and N.K.; Formal analysis, K.L. and S.A.; Investigation, K.L.; Resources, S.P., A.F. and A.A.; Data curation, K.L., S.A. and A.A.; Writing – original draft, K.L. and V.K.; Visualization, N.K.; Supervision, K.L., V.K. and N.K.; Project administration, K.L. and S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted by the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Department of Educational Science and Early Childhood Education of the University of Patras (85812/09-11-2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and analysed during the current study are available from the first author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to the students of the university departments for their continued support. This research was carried out in the context of the European Union Horizon 2020 project augMENTOR (“Augmented Intelligence for Pedagogically Sustained Training and Education”, HORIZON-CL2-2021-TRANSFORMATIONS-01-05), co-funded by the European Commission under Grant Agreement ID: 101061509.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix
PerExp1. I find Artificial Intelligence applications such as ChatGPT useful in my studies.
PerExp2. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT helps me to complete various activities related to my studies faster
PerExp3. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT increases productivity in my studies
EfExp1. It is easy to learn using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT.
EfExp2. My interaction with Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT is clear and understandable
EfExp3. Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT are easy to use.
SocInf1. The people who are important to me (e.g., friends and family) believe I should use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT for my studies.
SocInf2. The people influencing my behaviour believe I should use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies.
SocInf3. The people whose opinions I value prefer that I use Artificial Intelligence applications, like ChatGPT, for my studies as well
FacCon1. It is easy to find user instructions for Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT.
FacCon2. I have the knowledge necessary to use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT.
FacCon3. The Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT that I use in my studies align well with other applications I use
HedMot1. The use of Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies is enjoyable.
HedMot2. The use of Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies is pleasant.
HedMot3. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies is very entertaining.
PrVal1. The cost of Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT is reasonable
PrVal2. The cost of the services I access through Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT is worth the money.
PrVal3. Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT are worth their cost.
Hab1. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT has become a habit for me.
Hab2. I must use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT.
Hab3. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT is self-evident for me.
UsBeh1. I intend to continue using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies.
UsBeh2. I will always strive to use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies.
UsBeh3. I plan to use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT frequently in my studies.
BehInt1. Using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT is a pleasant experience.
BehInt2. I use Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT to support my studies.
BehInt3. I spend much time using Artificial Intelligence applications like ChatGPT in my studies
References
- Jackson, P.C. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence, 3rd ed.; Courier Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luger, G.; Chakrabarti, C. From Alan Turing to modern AI: Practical solutions and an implicit epistemic stance. AI & Society 2017, 32, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electronic Markets 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassopoulos, S.; Manoli, P.; Gouvi, M.; Lavidas, K.; Komis, V. The use of ChatGPT as a learning tool to improve foreign language writing in a multilingual and multicultural classroom. Adv. Mob. Learn. Educ. Res. 2023, 3, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Nie, J.; Ding, Y.; Yue, J.; Wu, Y. How Close is ChatGPT to Human Experts? Comparison Corpus, Evaluation, and Detection. ArXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, A.; Kumari, K.; Fereidooni, H.; Sadeghi, A. To ChatGPT, or not to ChatGPT: That is the question! ArXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Jain, A.; Araveeti, S.R.; Adhikari, S.; Garg, H.; Bhandari, M. FDA-Approved Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices: An Updated Landscape. Electronics 2024, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel-Villarreal, R.; Vilalta-Perdomo, E.; Salinas-Navarro, D.E.; Thierry-Aguilera, R.; Gerardou, F.S. Challenges and Opportunities of Generative AI for Higher Education as Explained by ChatGPT. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, W. Unlocking the Power of ChatGPT: A Framework for Applying Generative AI in Education. ECNU Review of Education 2023, 6, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasadi, E.A.; Baiz, C.R. Generative AI in education and research: Opportunities, concerns, and solutions. Journal of Chemical Education 2023, 100, 2965–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, J.; Distler, R. Schools shouldn't ban access to ChatGPT. Time Magazine. 2023. Available online: https://time.com/6246574/schools-shouldnt-ban-access-to-chatgpt/.
- Popenici, S. Artificial Intelligence and Learning Futures: Critical Narratives of Technology and Imagination in Higher Education, 1st ed.; Routledge, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, T.; Kaya, M.H.; Cansu, F.K. Revolutionizing education with AI: Exploring the transformative potential of ChatGPT. Contemporary Educational Technology 2023, 15, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Dede, C. Navigating a world of generative AI: Suggestions for educators. In The Next Level Lab at Harvard Graduate School of Education; President and Fellows of Harvard College: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bahroun, Z.; Anane, C.; Ahmed, V.; Zacca, A. Transforming Education: A Comprehensive Review of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Educational Settings through Bibliometric and Content Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Campbell, T.; Melville, W.; Park, B.Y. Navigating Opportunities and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence: ChatGPT and Generative Models in Science Teacher Education. Journal of Science Teacher Education 2023, 34, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Integrating Generative AI in Education: How ChatGPT Brings Challenges for Future Learning and Teaching. Journal of Advanced Research in Education 2023, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavidas, K.; Papadakis, S.; Filippidi, A.; Karachristos, C.; Misirli, A.; Tzavara, A.; Komis, V.; Karacapilidis, N. Predicting the Behavioral Intention of Greek University Faculty Members to Use Moodle. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, L. Analysing Students' Attitudes and Behavior Toward Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Higher Education. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. (IJRTE) 2023, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodríguez, J. Use of ChatGPT at University as a Tool for Complex Thinking: Students' Perceived Usefulness. Journal of New Approaches in Educational Research 2023, 12, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, G. Factors influencing students' intention to adopt and use ChatGPT in higher education: A study in the Vietnamese context. Educ Inf Technol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, R.S.; Thiyyagura, D. An empirical evidence on the continuance and recommendation intention of ChatGPT among higher education students in India: An extended technology continuance theory. Educ Inf Technol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahri FA, J.; Bell, D.; Merhi, M. Understanding Student Acceptance and Use of Chatbots in the United Kingdom Universities: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information Management (ICIM), London, UK, 27-29 March 2020; IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, S.H.; Alshammari, M.H. Factors Affecting the Adoption and Use of ChatGPT in Higher Education. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Educ. 2024, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahri, N.A.; Yahaya, N.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; et al. Investigating AI-based academic support acceptance and its impact on students’ performance in Malaysian and Pakistani higher education institutions. Educ Inf Technol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodríguez, J.-M.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.-S.; Buenestado-Fernández, M.; Lara-Lara, F. Use of ChatGPT at University as a Tool for Complex Thinking: Students’ Perceived Usefulness. Journal of New Approaches in Educational Research 2023, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan CK, Y.; Hu, W. Students’ voices on generative AI: Perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2023, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeti̇şensoy, O.; Karaduman, H. The effect of AI-powered chatbots in social studies education. Education and Information Technologies 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. MIS Quarterly 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.S.; Hawn, A. Algorithmic Bias in Education. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education 2022, 32, 1052–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Law, N. Mapping Artificial Intelligence in Education Research: A Network-based Keyword Analysis. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education 2021, 31, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, F.M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ferris, J.A.; Knoth, S.; Jones-Farmer, L.A. (2023). How generative AI models such as ChatGPT can be (mis)used in SPC practice, education, and research? An exploratory study. Quality Engineering, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Nah, F.F.-H.; Zheng, R.; Cai, J.; Siau, K.; Chen, L. Generative AI and ChatGPT: Applications, challenges, and AI-human collaboration. J. Inf. Technol. Case Appl. Res. 2023.
- Azaria, A.; Azoulay, R.; Reches, S. ChatGPT is a Remarkable Tool – For Experts. 2023. arXiv:2306.03102. [CrossRef]
- Firat, M. What ChatGPT means for universities: Perceptions of scholars and students. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves de Castro, C. A Discussion about the Impact of ChatGPT in Education: Benefits and Concerns. Journal of Business Theory and Practice 2023, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.; Davis, G.; Davis, F. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, K.; Gialamas, V.; Lavidas, K. Acceptance of mobile phone by University students for their studies: An investigation applying UTAUT2 model. Education and Information Technologies 2020, 25, 4139–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro-Rueda, M.; Fernández-Cerero, J.; Fernández-Batanero, J.M.; López-Meneses, E. Impact of the Implementation of ChatGPT in Education: A Systematic Review. Computers 2023, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interactive Learning Environments 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, A. Social Research Methods; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lavidas, K.; Petropoulou, A.; Papadakis, S.; Apostolou, Z.; Komis, V.; Jimoyiannis, A.; Gialamas, V. Factors Affecting Response Rates of the Web Survey with Teachers. Computers 2022, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2023. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Ray, S.; Danks, N.; Calero Valdez, A. Seminr: Building and Estimating Structural Equation Models_. R package version 2.3.2, 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=seminr (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Hair, J.F.; Hult GT, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (pls-sem), 3rd ed.; SAGE, 2021.
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of pls-sem. European Business Review 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavidas, K.; Papadakis, S.; Manesis, D.; Grigoriadou, A.S.; Gialamas, V. The Effects of Social Desirability on Students’ Self-Reports in Two Social Contexts: Lectures vs. Lectures and Lab Classes. Information 2022, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).