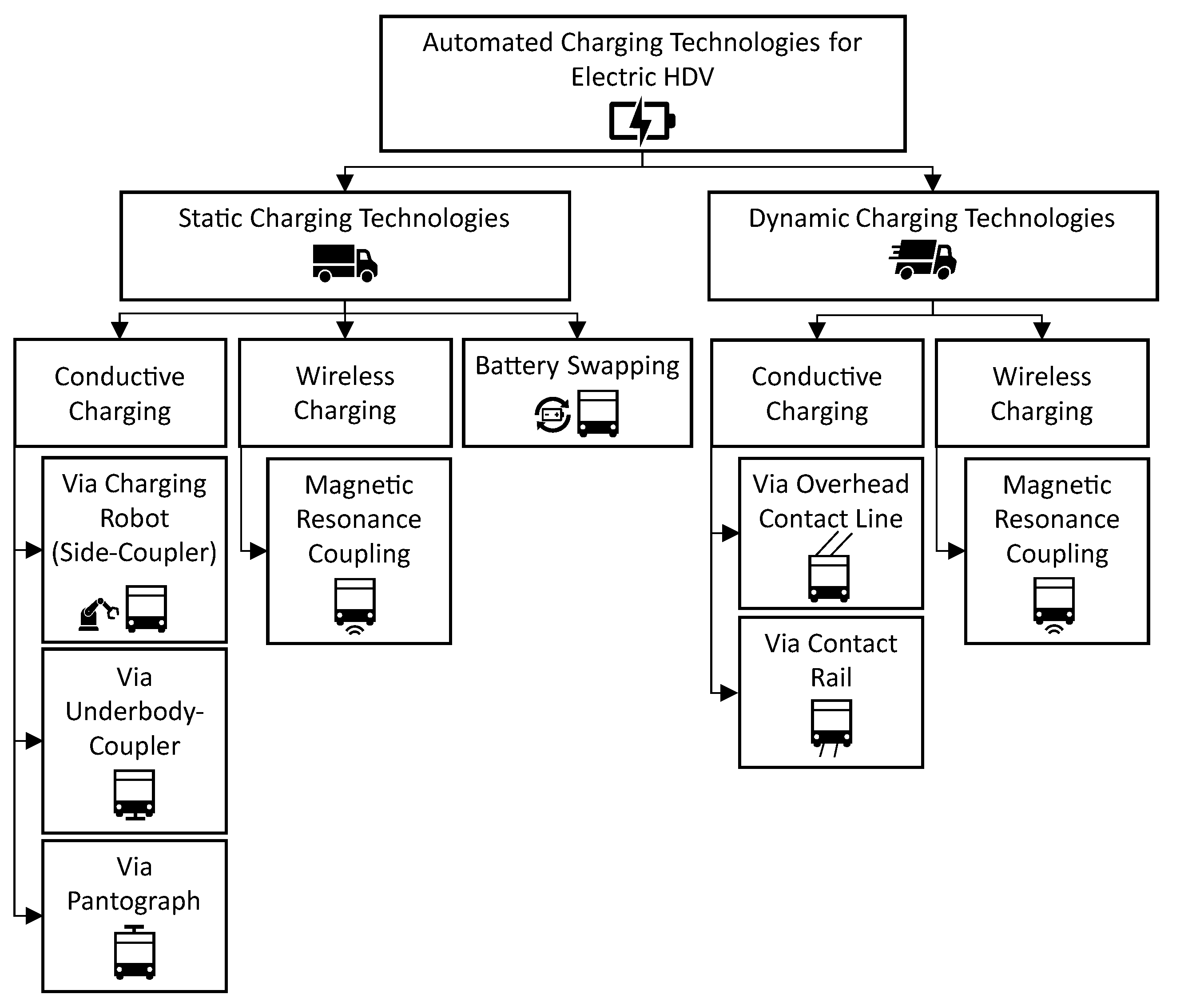
This section examines the functioning and the set-up of leading and emerging, automated charging technologies for electric HDVs. Additionally, it explores the advantages, the potentials, the challenges and the development status of each charging technology. This information is then used to determine a specific TRL for each charging technology. The TRLs constitute a TRL-scale, which was originally developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and is the most widely used tool to assess and compare the maturity of technologies [
20]. The TRL-scale designed by NASA was adopted by the EU for its research and innovation funding program Horizon2020. The emerging EU Horizon2020 TRL-scale is employed in this study [
20,
21]. To map each charging technology with a TRL the current development statuses of exemplary charging systems are investigated.
2.1. Static Conductive Charging via Charging Robot
The static conductive charging technology utilizing a charging robot is based on the method of charging with a charging cable, which represents the most advanced and most widely used charging method amongst HDVs [
13]. Besides the conductor, this method requires a rectifier and a transformer, which can be located in- and/or outside the vehicle. Depending on the arrangement, the vehicle can be charged with alternating current (AC), direct current (DC) or both alternately [
9]. At present charging powers of up to 43 kW (AC) and 500 kW (DC) are possible [
22]. The MCS (Megawatt Chagring System) standard currently under development will make it possible to transmit an even higher charging power of more than1 MW.
When charging with a charging cable, a communication system and protection measures are required. DC-Charging can additionally demand a temperature management system [
9].
To automate charging with a charging cable a robot can be placed at the charging station. The robot is equipped with a camera-based object detection system, which detects and identifies the vehicle to receive vehicle-specific data, such as the position of the charging socket and the required charging power. Based on this information, the charging robot first aligns the charging plug with the charging socket, then inserts the plug into the socket and finally removes the plug from the socket. The robot’s accuracy depends on the accuracy of its vision, control and motion systems, the components’ tolerance ranges and the current temperature, vibrations and environmental conditions. The operating range of the charging robot and the installed charging plug determine the chargeable vehicle types and the possible socket locations. To enable mobile charging the robot can be mounted on a movable platform or an automated vehicle [
22].
A summary of the advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the static conductive charging technology using a charging robot is given in
Table 1.
Besides being based on a widespread charging method, the static conductive charging technology using a charging robot has the advantage that it does not entail extra vehicle components, which would result in extra costs, extra weight and extra space requirements [
13,
16]. Additionally, standards for the conductive charging using a robot are under development, e. g. IEC 63407, IEC TS 61851-27 and ISO TS 5474-5, and the charging technology has the potential to use the already developed standards for manual charging with a cable [
23]. Furthermore, due to the set-up of the charging system, it is not limited to electric HDVs, there is the possibility for a mobile charging robot and the potential to gradually scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs [
11,
22].
The charging technology faces various challenges. First, it requires a parking area designed for charging. Second, the charging robot requires additional space [
16]. Third, both the charging robot and the charging process are conspicuous [
6,
16]. Fourth, the charging technology necessitates maintenance and repair expenses of the moving and connecting parts [
6]. Moreover, the connected parts result in any movements of the vehicle, e. g. when (un-)loading, being transmitted to the robot. Fifth, due to its positioning beside the parking area, the charging infrastructure is susceptible to accidental damage and misuse [
16]. Further challenges are the charging-related vehicle downtime, which depends on the charging power and the battery system, and the need for standards for the location, the orientation, the (security) cover and the opening- and closing mechanism of the charging socket. The parking position and the vehicle payload, the tire pressure and the springs and dampers scenario also influence the socket position [
24]. The robot’s operating range determines the parking requirements. Additional challenges are the developed charging interface, e. g. the shape of the plug and the socket, not being well suited for automation and the robot’s camera-based socket detection system being susceptible to lighting and surface conditions [
22]. Finally, the charging cables represent a safety hazard and a challenge regarding handling, especially the heavy and stiff cables used for high-power charging [
7,
24]. To ensure the safety of the users collaborative robots are necessary [
25].
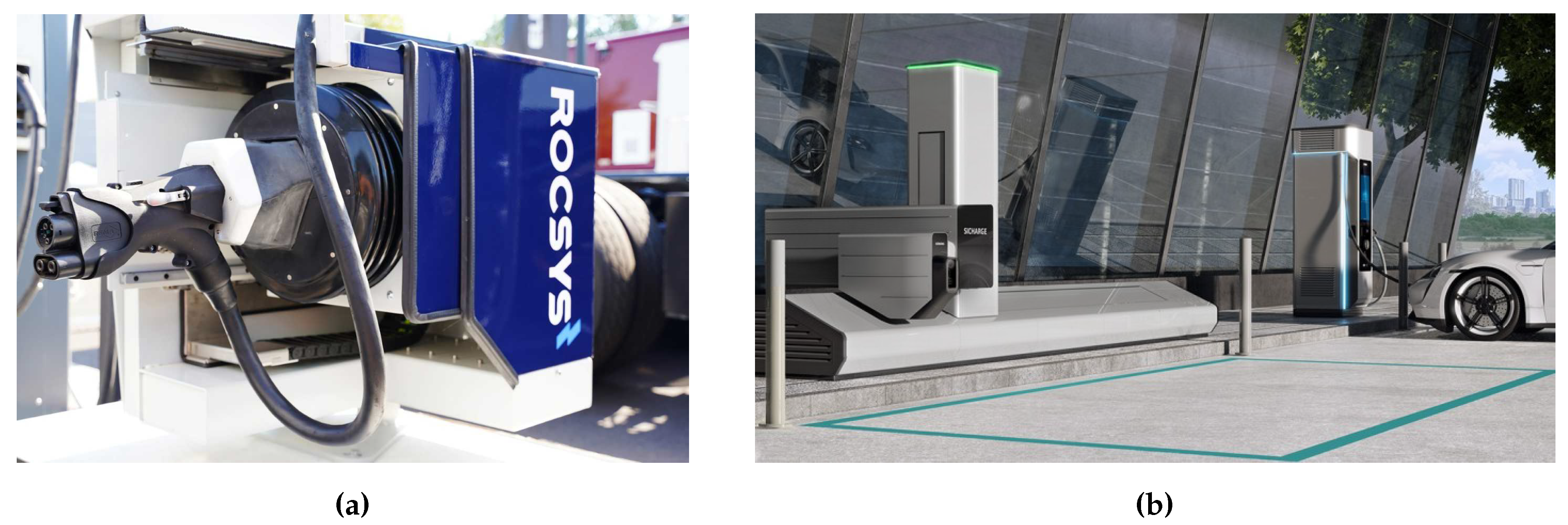
The charging technology using a charging robot is currently being developed for the use in electric HDVs. Two of the developing companies and their charging systems (see
Figure 2) are presented below.
ROCSYS: In 2021 ROCSYS together with the companies Grivix and VDL ETS developed a charging robot to automate the static conductive charging of electric HDVs [
26]. To integrate the robot into existing systems ROCSYS offers i. a. an automated socket cover, a communications unit and an interface to control and monitor the robot [
27]. The charging robot is equipped with a Combined-Charging-System (CCS)-, a Megawatt-Charging-System (MCS)- or an Euro-Din-charging plug and a 3D-Camera and is not limited to specific vehicle or charger types [
27,
28]. In 2021 ROCSYS’ charging robots were employed by the companies eVersum and Ebusco to automate the charging of electric shuttles and buses [
29,
30]. In 2022 the robots were installed at a public charging station for electric medium- and HDVs in Portland, OR, USA, and at the Oakland Harbor, CA, USA, where they charge tractors operated by the firm SSA Marine [
31,
32]. The charging station is managed by Daimler Truck North America and Portland General Electric and contains 12 charging points [
32]. In 2023 ROCSYS partnered with the companies Taylor Machine Works and Hyster to automate the charging of electric container handlers and terminal tractors [
33,
34].
Siemens: In 2021 Siemens presented a prototype of an automated charging station for BEVs. This charging station incorporates a charging robot, which connects to the CCS-socket of the vehicle using optical sensors and artificial intelligence in around one minute. The vehicle is charged with a power of up to 300 kW. The charging station was tested in cooperation with the truck manufacturer EINRIDE. To fulfill the requirements of the end-users successive charging stations will have a charging power of up to 1 MW [
35].
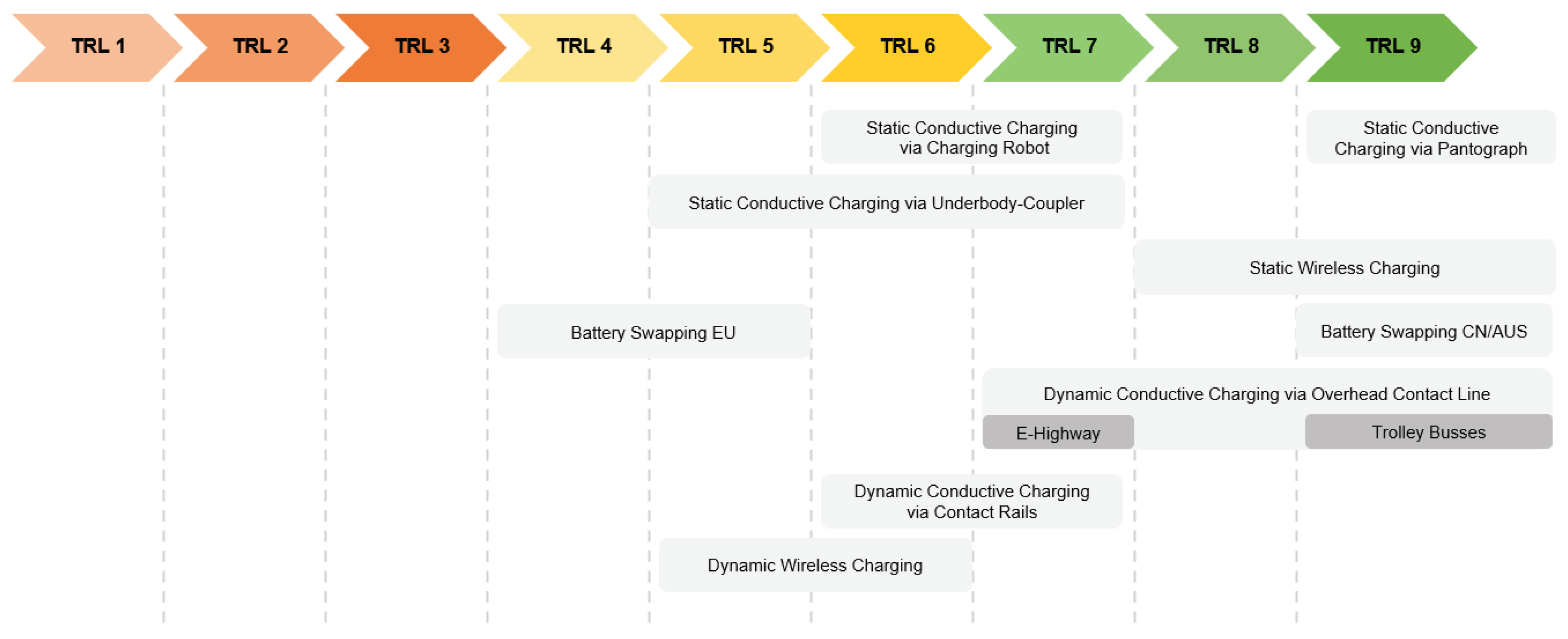
In the evaluation of the TRL the 2023 partnership between ROCSYS and Hyster stands out as a key determinant. In this context, the system is actively demonstrated and further enhanced with a particular focus on the performance in challenging environments [
34]. This endeavor, along with several preceding projects, suggests a progression to a TRL 7, which is indicative of a system prototype’s demonstration in an operational setting. Simultaneously, the Autonomous Charging System developed by Siemens was tested in collaboration with the truck manufacturer EINRIDE. This points to a TRL 6, confirming that the technology has been demonstrated in a relevant environment [
35].
2.2. Static Conductive Charging via Underbody-Coupler
As can be seen in
Figure 1, the static conductive charging technologies can be categorized into side-coupling-, underbody-coupling- and over the vehicle’s roof coupling-systems. This subsection focuses on the underbody-coupling-systems.
An underbody-coupling-system consists of a fixed or a movable ground unit and a fixed or a movable vehicle unit. Whereas the ground unit is embedded in or placed on the surface of the charging station, the vehicle unit is attached to the underbody of the vehicle. To charge the vehicle the ground unit and the vehicle unit must be aligned [
22]. The extent of possible misalignment depends on the specific charging system. However, a benchmark is set at ±150 mm from the optimal parking position along the vehicle’s longitudinal and transversal axes. To maximize the parking accuracy assistance systems can be employed. As soon as the ground unit and the vehicle unit are aligned, their electrical interfaces must be physically connected [
16]. For this the connector of the movable unit moves onto the fixed unit and in doing so can be assisted by a specific interface layout and guided by magnetic, visual or ultra-sound systems [
22]. Besides the ground unit and the vehicle unit, the charging technology requires a rectifier, a transformer, a communication system and a management system to monitor and control the charging process [
36].
A summary of the advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the static conductive charging technology using an underbody-coupler is presented in
Table 2).
In comparison to the charging technology using a charging robot, the charging technology employing an underbody-coupler requires no additional space for its charging infrastructure, as it is installed underneath the parking vehicle. As the charging process takes place unseen underneath the vehicle and the ground unit is embedded in the road pavement, the charging technology using an underbody-coupler is also less conspicuous. If both the ground unit and the vehicle unit are additionally equipped with protective covers, the charging technology is also less susceptible to accidental damage and misuse [
16]. In comparison to the charging technology using a robot, the charging technology employing an underbody-coupler, is not based on a widespread, standardized and manual charging method, resulting in it being wholly designed for automation. Further advantages and potentials are the standards ISO TS 5474-5, IEC TS 61851-26, which are already being developed, the fact that the charging technology is not limited to electric HDVs and the possibility for a mobile ground unit [
23]. Additionally, there is the potential to gradually scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs.
In contrast to the side-coupling-systems, the underbody-coupling-systems require additional vehicle components [
16]. In the case of a movable ground unit, the vehicle unit can be small, lightweight, simple and easy to integrate, which reduces the negative effects of additional vehicle components [
37]. However, in this case complex robotic kinematics and control systems are required [
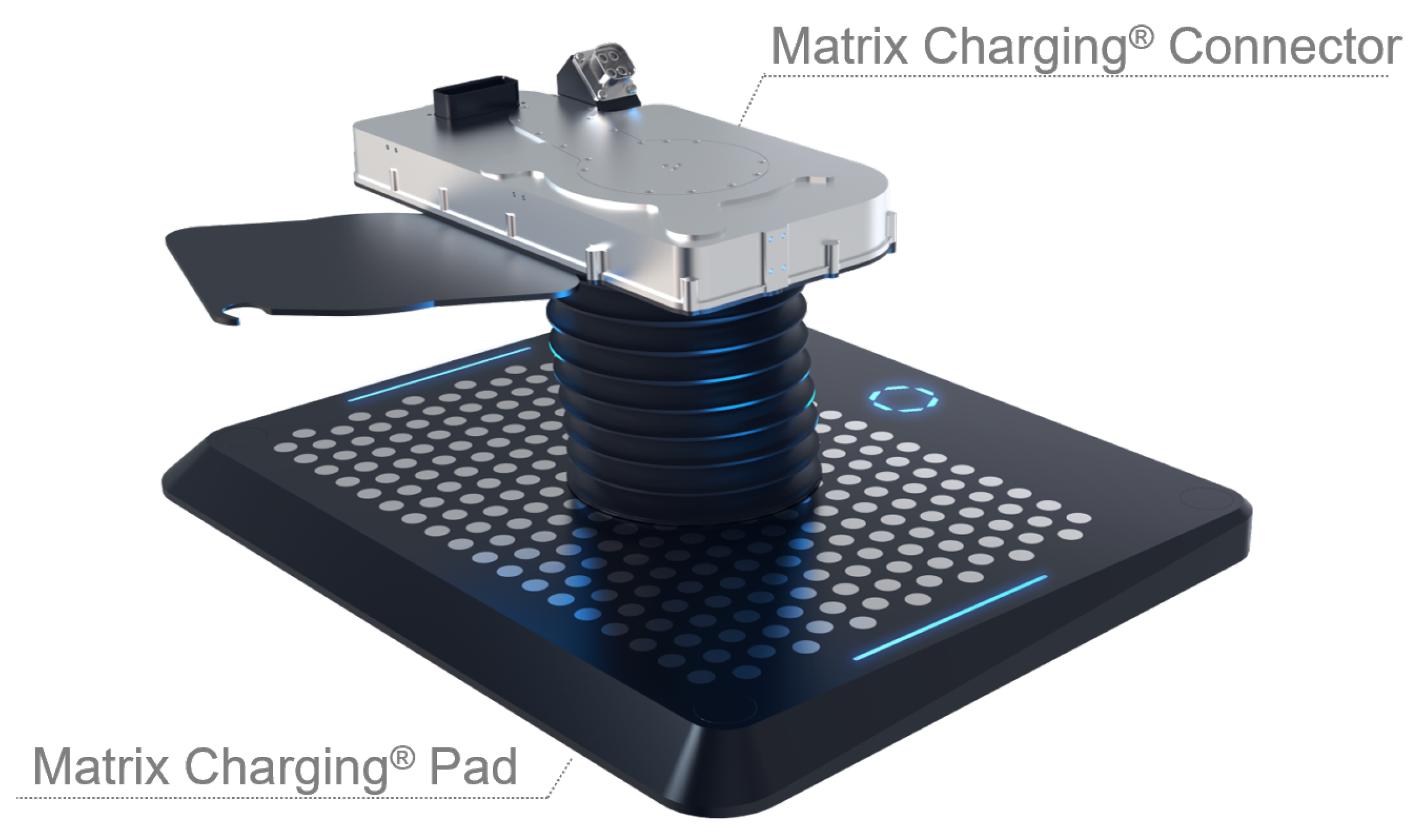
22]. If the ground unit is fixed and implemented as a pad, misalignment of the vehicle unit can be corrected without requiring moving parts. Such a charging system was developed by the company Easelink (see
Figure 3). The ground unit in the shape of a pad is equipped with a multitude of contact points that can be individually switched on and off. The connector of the vehicle unit must only perform a vertical movement to connect to the pad. As only one degree of freedom is required, the connector’s complexity, cost, maintenance and repair expenses and space requirements are reduced. Additionally, the high space availability of the ground area is used [
16,
22,
36]. Further challenges are the specific parking area required for charging, the charging-related vehicle downtime, the maintenance and repair expenses of the moving and connecting parts and the need for standardization of the charging interface. Additionally, the necessary parking accuracy is higher than that required for charging with a robot [
22].
The static conductive charging technology using an underbody-coupler is being developed for the use in electric HDVs. Four of the developing companies and research institutions including their charging systems (see
Figure 4) are introduced below.
Volterio: The Volterio PRO is an underbody-coupling-system developed by the company Volterio to charge electric HDVs. The charging system’s ground unit can supply a charging power of up to 2 MW, is embedded in the road pavement, resembles a manhole cover and can withstand being driven over by HDTs. Before charging, the ground unit’s cover performs an upwards and then sideways motion to expose a parallel robot, which connects the connector to its counterpart attached to the vehicle’s underbody. The charging system enables AC- and DC-charging and does not require a high parking accuracy [
38].
Fraunhofer Institute for Transportation and Infrastructure Systems IVI: The underbody-coupling-system developed by the Fraunhofer IVI can supply a charging power of up to 2 MW to electric HDVs [
39]. The charging system consists of a fixed vehicle unit, which is retrofitted, weighs around 2 kg and is equipped with a protective cover, and a movable ground unit, which is lowered roughly 700 mm into the ground, is equipped with a heating system and a protective cover and employs an electromagnet to increase the contact force [
39,
40,
41]. This charging system will be demonstrated, tested and enhanced within the scope of the Mega-Laden-Project [
42,
43].
Schunk Transit Systems: A third prototype is being developed by the company Schunk Transit Systems. Their charging system consists of a movable ground unit, a fixed vehicle unit and a vehicle positioning and identification system. The prototype can correct parking deviations and is suitable for private and public use [
44]. The vehicle battery can be charged with a charging power of up to 1 MW [
45].
Elonroad: Besides the charger, the underbody-coupling-system developed by the company Elonroad consists of a fixed contact rail and a movable energy collector. The contact rail, which is attached to the ground, is 3.2 m long, 0.25 m wide, 0.04 m high and weighs 50 kg. The energy collector, which is attached to the vehicle’s underbody, is 2.25 m long, 0.85 m wide, 0.035 m high and weighs 20 kg. The contact rail currently supplies a charging power of up to 60 kW. In 2024 it will be increased to 150 kW [
46]. The underbody-coupling-system is being tested by the Swedish company Martin & Servera, where it charges an electric HDT during (un-)loading [
47].
The underbody-coupling-system developed by Volterio is being tested for electric passenger vehicles within the framework of the AC/DC-Project in Graz, Austria. As this charging system is the first of its kind, a TRL 5 is proposed [
48]. Similarly, the underbody-coupling-systems developed by the Fraunhofer IVI and the company Schunk Transit Systems were successfully tested for electric passenger vehicles within the scope of the AULA-Project and will be demonstrated for electric HDVs within the framework of the Mega-Laden-Project [
39,
42,
43,
49]. Therefore, also a TRL 5 is determined for this system for the HDV use-case. The underbody-coupling-system developed by Elonroad is being tested by an end-user in its operational environment, which indicates a TRL 7 [
47].
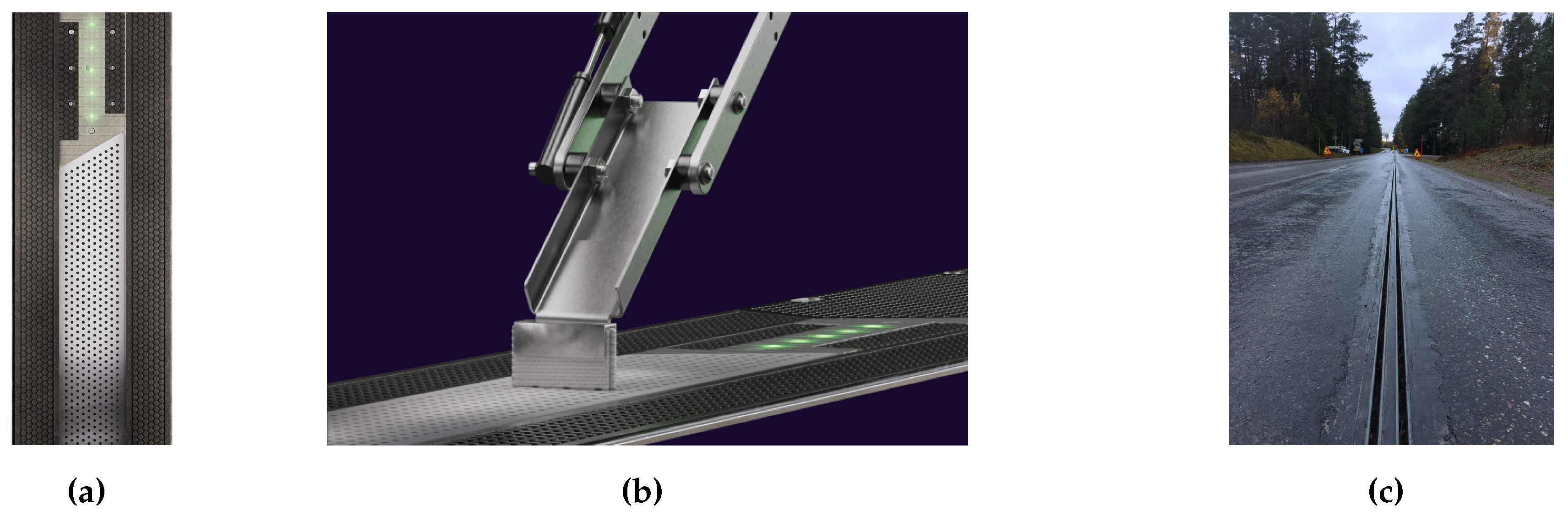
2.3. Static Conductive Charging via Pantograph
The third category of static conductive charging technologies encompasses the over the vehicle’s roof coupling-systems. These systems employ pantographs to transfer energy from the grid to the vehicle battery [
22]. A pantograph can be installed on the side of either the infrastructure (inverted) or the vehicle (roof-mounted) and connects to an interface located on the respective other side. An inverted pantograph can have different interfaces with the vehicle. The most common interface are four contact rails placed in rows of two in parallel on the vehicle’s roof. The contact rails entail an additional weight of 15 kg - 20 kg. The choice of interface only barely affects the charging parameters [
50]. As soon as the vehicle comes to a standstill, the inverted pantograph, which is attached to a mast, is automatically lowered onto the contact rails. Prior to charging, safety checks are performed. Once the battery is fully charged or the charging process is interrupted, the pantograph automatically disconnects from the rails [
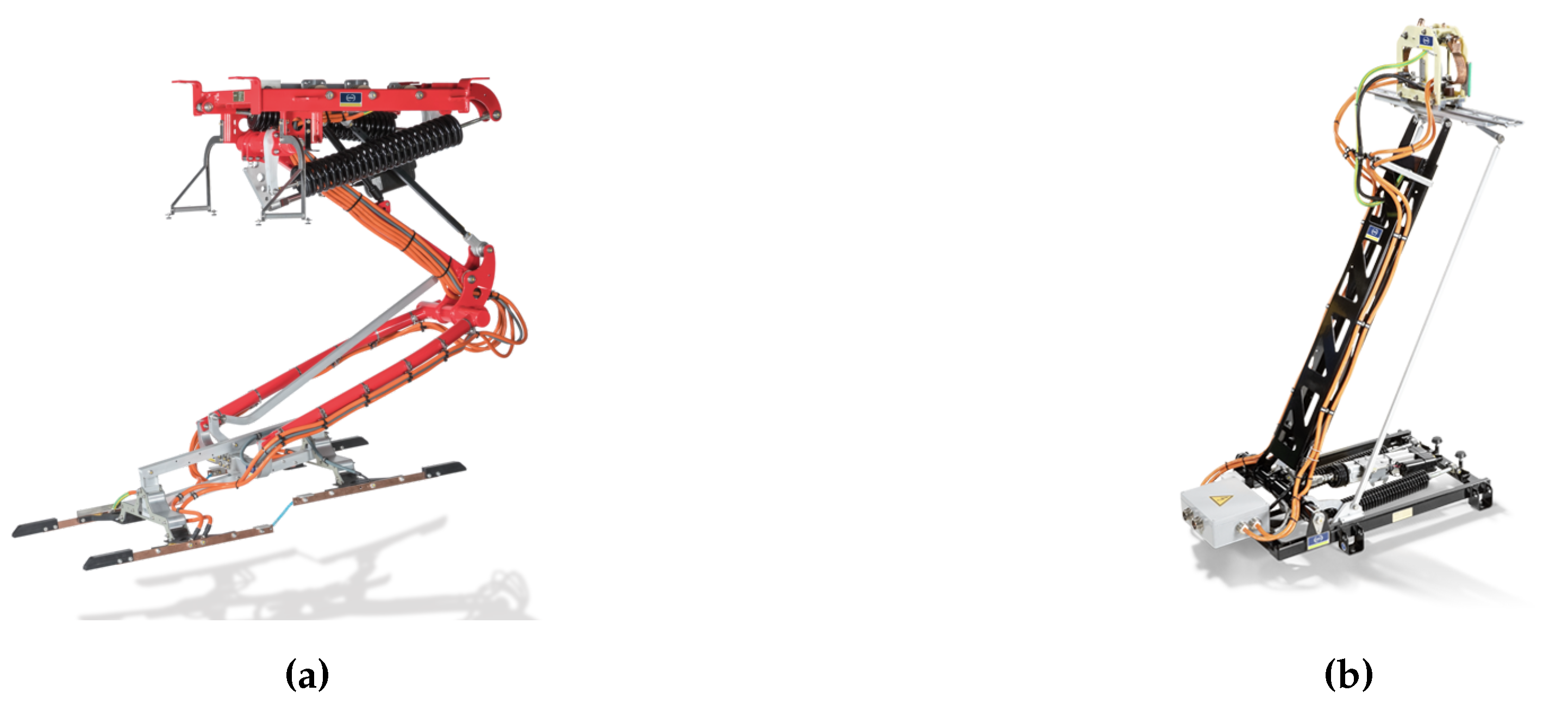
51]. Based on the SLS201, an inverted pantograph manufactured by the company Schunk Transit Systems, it can be stated that inverted pantographs have a range of 0.7 m - 2.3 m, connect with a force of 500 N and weigh 175 kg - 180 kg. The SLS201 is depicted in
Figure 5. When employing a roof-mounted pantograph, an additional resting frame, attached to the vehicle’s roof, and a contact dome, representing the interface with the infrastructure, are required [
50]. In this case the pantograph is automatically raised once the vehicle comes to a standstill underneath the contact dome [
52]. According to the SLS102, a roof-mounted pantograph developed by Schunk Transit Systems, roof-mounted pantographs have a range of 1.5 m - 1.8 m, deliver a force of 250 N - 275 N and weigh 85 kg (see
Figure 5) [
50].
The pantographs offered by Schunk Transit Systems are equipped with 2-, 3-, 4- or 5-pin connectors, correct parking deviations and vehicle movements of up to ±500 mm in driving direction, ±250 mm perpendicular to driving direction and 4° kneeling and can be used for depot, opportunity and pulse charging. Additionally, the pantographs manage 400.000 charging cycles and establish a connection within 5 s [
45].
Besides the pantograph, the interface and the energy supply, the charging technology requires a communication system and an assistance system, e. g. a passive advanced driver assistance system or road and curb markings, to position the vehicle [
50,
51,
53].
A summary of the advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the static conductive charging technology using a pantograph is given in
Table 3.
Similarly to the static charging technology using a robot, which is based on the conventional charging with a cable, the charging technology employing a pantograph is based on the widespread and standardized railway technology [
12]. Also, the charging technology using a pantograph is similarly susceptible to accidental damage. However, resulting from the charging process occurring out of reach of the users, it is less susceptible to misuse. Further advantages and potentials are the already developed standard DIN EN 50696, the standard IEC 63407, which is currently being developed, and the possibility to gradually scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs [
6,
23]. Finally, the charging technology is specifically designed for automation, which results in a high possible charging power and therefore a reduced charging duration [
52].
In contrast to the charging technology using a robot, the charging technology employing a pantograph requires additional vehicle components. If an inverted pantograph is employed, the negative effects of the additional vehicle components can be reduced [
6]. However, if a roof-mounted pantograph is installed, the infrastructure costs can be decreased and, in the case of the pantograph being damaged, not all vehicles are affected [
6,
54]. The inverted and the roof-mounted pantograph systems are incompatible [
50]. Further challenges are that for safety reasons the connection between the interface and the pantograph can only be established while driving forward and that, due to the layout of the charging technology, it is limited to electric HDVs [
53]. Additionally, a specific parking area is required for charging, a charging-related vehicle downtime is unavoidable and maintenance and repair expenses of the moving and connecting parts are necessary. In comparison to the charging technology using a robot, the charging technology employing a pantograph has larger additional space requirements for the charging infrastructure and therefore a more conspicuous charging infrastructure. The charging process, however, is similarly conspicuous.
The charging technology using a pantograph has been commercialized. Examples of manufacturers and their market solutions are presented below.
Schunk Transit Systems GmbH: This company offers a variety of pantograph-based charging systems. For example: A roof-mounted pantograph with a charging power of 150 kW to 1 MW, an inverted pantograph for depot charging with a power of up to 200 kW and an inverted pantograph with a charging power of up to 600 kW. The company’s inverted pantographs can connect to contact rails, covers or funnels installed on the vehicles’ roofs [
45].
ABB Ltd.: The company ABB supplies a roof-mounted and an inverted pantograph, which each deliver a charging power of up to 600 kW and can be used to charge buses of different makes [
55,
56]. The inverted pantograph is based on a standard called OppCharge [
56]. OppCharge was developed by the Volvo Bus Corporation and encompasses a standardized interface in the form of contact rails and a standardized communications protocol, which manufacturers can draw on as long as no international standards have been defined [
57].
Heliox Energy: Heliox Energy is a company that acquires pantograph systems and embeds them into designed, constructed, maintained and monitored charging infrastructures for electric buses, trucks, passenger cars and mining, port and marine vehicles [
50,
58]. For example: Heliox Energy has fitted 31 electric buses in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, three electric buses in Jena, Germany, 55 electric buses in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 100 electric buses at Amsterdam Schiphol Airport, the Netherlands, and eight electric buses in Cologne, Germany, with roof-mounted pantographs and peripheral components [
59,
60,
61,
62,
63].
Further companies offering pantograph systems are Siemens and Stemmann Technik [
64,
65]. The static charging technology using a pantograph is currently being employed by bus operators in eleven German cities [
60,
63,
66]. Examples of manufacturers offering vehicles with the charging technology are Scania, Volvo, Mercedes-Benz and Solaris [
67,
68,
69,
70].
As presented above, the charging technology is offered by numerous manufacturers, including vehicle manufacturers, and there is extensive, long-term experience from its application in city buses across the world [
67,
68,
69,
70]. Hence a TRL 9 is proposed, pointing out that the charging technology is proven in an operational environment.
2.4. Static Wireless Charging
The next static charging technology to be examined more closely is the wireless charging technology. Wireless charging of BEVs can be realized with a variety of coupling techniques with the most developed and widespread being the magnetic resonance coupling technique [
9,
18]. A charging system applying this technique encompasses a wallbox, including a rectifier and a high-frequency inverter, a ground unit, a vehicle unit, an onboard charger, including a rectifier and a transformer, and a battery management system [
9,
10]. The wallbox is connected to the electricity grid and has the task to increase the frequency of the AC, as a high frequency results in a high efficiency. From there the energy is transmitted to the ground unit, which is embedded in the road pavement and contains a primary coil [
9,
15,
71]. When the high-frequency AC flows through the primary coil, it generates an alternating magnetic field. This passes through the secondary coil, located opposite the primary coil in a vehicle unit attached to the vehicle’s underbody, where it induces an alternating voltage [
9,
13,
15]. The resulting AC is rectified by the onboard charger, before being used to charge the vehicle battery [
9]. Besides the coils, both the vehicle unit and the ground unit contain shielding materials, elements to optimize the magnetic flux distribution and compensation networks. These networks are composed of reactive components such as capacitors and have the task to match the resonant frequencies of the primary and the secondary coil to the frequency of the alternating magnetic field. As a result, the charging system’s degree of efficiency and the transmission distance are increased [
10,
18,
72,
73]. Furthermore, the magnetic leakage flux resulting from the distance between the coils is compensated, which increases the degree of efficiency further [
9].
Wireless charging requires the use of a wireless communication system and a foreign object detection system [
9,
15]. The latter has the task to detect foreign objects located between the vehicle unit and the road pavement, as they do not only reduce the charging system’s efficiency, but might also present a safety risk, due to induced currents and subsequent warming [
9,
18]. Furthermore, living object protection systems can be employed in areas, where the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements can not be met, which are, however, accessible to living objects. These systems automatically reduce the charging power in case of a living object penetrating a respective area [
9].
A summary of the static wireless charging technology’s advantages, chances and challenges is given in
Table 4.
In comparison to the static conductive charging technologies, the static wireless charging technology has the advantage that it does not require any moving and connecting parts. Consequently, the maintenance and repair expenses are reduced [
9]. Additionally, the wireless charging technology can draw on already developed standards, e. g. DIN EN IEC 61980-1 and ISO 19363 [
23]. Further advantages are the facts that the charging technology is not limited to electric HDVs, that it is specifically designed for automation and that it requires no additional space for its charging infrastructure. In comparison to the charging technology employing a robot, the wireless charging technology is less conspicuous and less susceptible to accidental damage and misuse [
9]. Finally, there is the potential to gradually scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs and the possibility for a mobile ground unit [
11].
With these advantages and potentials come challenges. First, additional vehicle components are necessary [
9]. Second, a specific parking area is required for charging. Third, in comparison to the charging technology using a robot, a higher parking accuracy is required. Fourth, the charging efficiency depends on the horizontal misalignment and the vertical distance between the coils [
22]. To combine a high efficiency and a large distance there is the possibility to lower the vehicle unit ahead of charging. This, however, entails the challenges of moving parts [
9]. The efficiency of the charging system can be increased further by employing a parking assistant, ferrite plates in both units, a large secondary coil, special coil designs and geometries and a variable transmission frequency [
9,
10,
18]. Also the ground clearance and the loading condition of an electric HDV affect the distance between the coils and thereby the efficiency [
14]. Further challenges are the charging-related vehicle downtime and the fact that the wireless charging technology can not build on a widespread and standardized charging method.
As can be seen from
Table 4 the static wireless charging technology has been commercialized. A selection of manufacturers is introduced below.
InductEV: This company develops static wireless charging systems for private, public and commercial transport vehicles, port vehicles and industrial equipment [
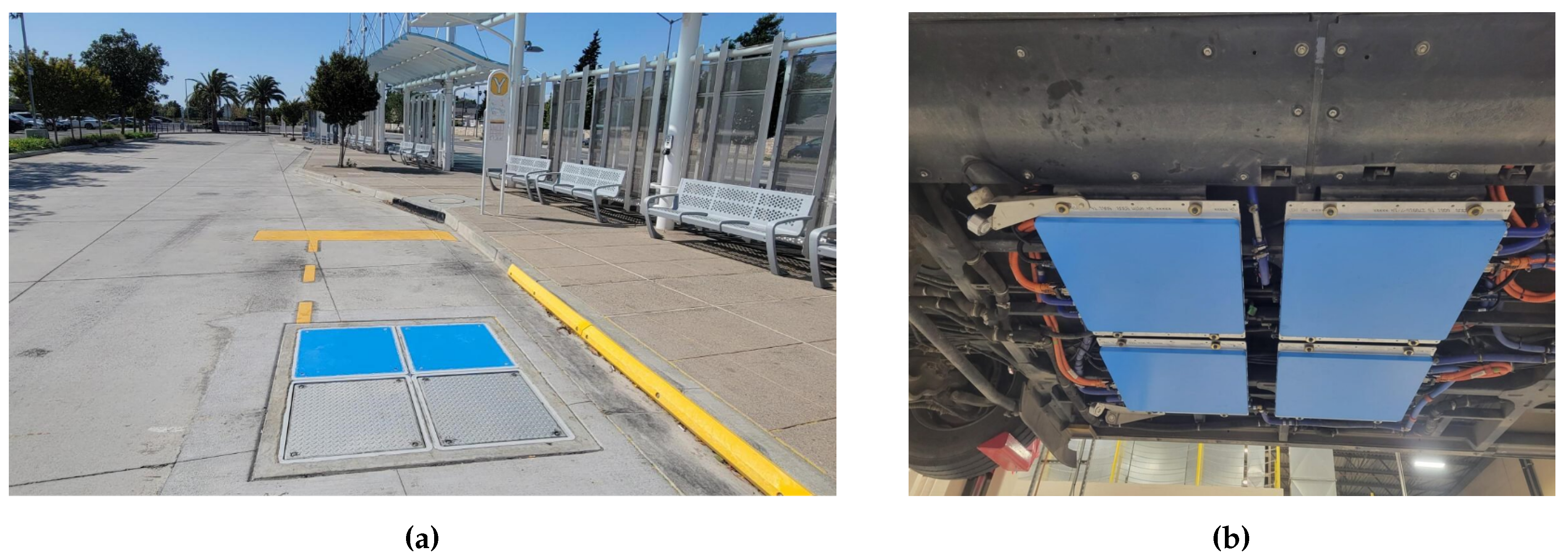
74]. Such a charging system encompasses modular charging pads, which can supply 50 kW (one pad) - 450 kW (six pads) of charging power with an efficiency of over 90% and a response time of 2 s (see
Figure 6) [
75,
76]. Currently, 115 vehicles linked to twelve customers are equipped with InductEV’s charging system and are in operation [
77]. Customer examples are Gillig, BYD, Kansas City International Airport, IndyGo, Link Transit, OshKosh and Green Power Motor Company [
75,
76].
Electreon: Electreon offers both a static and a dynamic wireless charging technology with the static charging technology being commercially deployed since 2022. In 2022 the static charging systems were installed at city bus stops across Israel to charge 200 electric buses, following a successful pilot project at the Tel Aviv University train station in Israel [
78]. By order of a second Israeli bus operator Electreon will fit 30 more buses with their static wireless charging technology to charge at a bus depot in 2023 [
79]. Also in 2023 Electreon will install two wireless charging points for an electric bus in Balingen, Germany, following a second pilot project in Karlsruhe, Germany [
80].
WAVE Charging: This company offers a static wireless charging technology to charge electric medium- and HDVs during scheduled stops and dwell times. The charging technology can deliver a charging power of 125 kW - 500 kW with an efficiency of up to 92%. The company has deployed its charging technology in six locations across the USA [
81].
WiTricity: WiTricity’s static charging technology supplies a charging power of 3.6 kW - 22 kW with an efficiency of 90% - 93% over an air gap of 100 mm - 250 mm. Additionally, it offers the possibility for bidirectional energy transfer [
82].
Concerning the technological readiness of the static wireless charging technology, the announced commercial deployment of the charging system developed by Electreon indicates a TRL up to 9 [
78]. Additionally, the charging system developed by the company InductEV is offered as a factory option by the bus manufacturer BYD in the USA [
83]. However, as acquiring a CE-marking is still underway, a TRL 8 - 9 is suggested [
74]. Owing to the high number of deployments across the USA, a minimum TRL 7 is proposed for the charging system developed by the company WAVE Charging [
81]. In 2023 WiTricity announced a collaboration with a Chinese manufacturer of autonomous buses. As the company’s charging system has previously only been installed in passenger vehicles, a TRL 5 is suggested [
84]. Although there is a strong deviation between the TRLs of the different manufacturers, a higher TRL for static inductive charging can be determined by the commercial availability of the systems of some manufacturers. Overall a TRL between 8 and 9 is identified.
2.5. Battery Swapping
Besides the conductive and the wireless charging, there is the possibility to swap the depleted battery for a fully charged battery in a battery swapping station (BSS) [
19]. The battery swap technology therefore both temporally and spatially decouples the battery charging from the BEV and its driving patterns. Generally, there are two types of BSSs:
- (1)
Centralized: The swapping and the charging occur in different locations.
- (2)
Distributed: The swapping and the charging occur in the same location [
85].
Irrespective of the type of BSS, the main components of a BSS are the swapping robots, the battery storage racks, the battery charging racks, the chargers, the batteries, the rectifiers, the transformers and the management and control systems.
The swapping process begins with the BSS receiving a swapping-request from a vehicle. This includes the vehicle’s current position, its expected time of arrival and battery- and vehicle-specific data, which enable the BSS to prepare a fitting battery. Once the vehicle arrives at the BSS, the driver is identified, authenticated and then guided to the swapping lane [
19]. There the removing and the reinstalling of the battery is performed by one or two robots [
85]. Either way, the battery is dismounted from the side, the rear, the underbody or the roof of the vehicle, while the vehicle is stationary or moving [
19]. Once removed, the battery is placed in the charging rack if necessary via a storage rack [
85]. Before the charging of the battery begins, its state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), remaining charge, age and number of charge and discharge-cycles are determined. Then, depending on the demand, the battery is charged with a low or a high charging power. Normally a BSS works according to the "first come, first served"-principle. The communication between the vehicle and the BSS takes place via an information system. For example, the information system receives the vehicle’s swapping request and transmits it to the BSS [
19]. The multitude of batteries charged in one location necessitates an extensive temperature management system and additional safety measures [
85,
86].
A summary of the advantages, the potentials and the challenges associated with the battery swap technology is given in
Table 5.
The main advantage of the battery swap technology is that the battery swapping can be performed within five minutes [
19]. It thereby overcomes one of the major drawbacks of BEVs, namely the relatively long charging time compared to refueling with diesel. The second advantage is that the BSS has a flexible energy demand, meaning its energy demand does not necessarily depend on the consumer demand for battery swaps. This reduces the investments in power lines, storage systems and power generation capacities [
87]. If the consumer demand is low or back-up batteries are available, the batteries can be charged with a low charging power during off-peak hours, which also reduces the electricity costs, increases the battery lifetimes and flattens the load curve [
13,
19,
87]. During peak hours the batteries can feed energy into the grid to generate revenue [
19]. With the battery swapping decoupled from the battery charging pricing might present a challenge [
88]. Further advantages are the existing standards, e. g. DIN EN IEC 62840-2 and PD IEC PAS 62840-3, and the fact that the battery swapping is performed within in enclosed area, which ensures that the swapping and the charging systems are less exposed to the environment, accidental damage and misuse than the other static charging technologies [
23]. Also the battery swap technology is not limited to electric HDVs. However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there is no BSS, which is used to swap the batteries of both passenger vehicles and HDVs. Another potential is that the reinstalled battery can be chosen according to the user’s needs and preferences regarding e. g. capacity [
85]. Finally, there is the possibility to gradually scale-up of the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs and the fact that the battery swap technology is mostly designed for automation.
With advantages and potentials come challenges. First, there is a need for standardized batteries. The standardization extends to the batteries’ physical dimensions, mounting and dismounting procedures and electrical connections to the vehicle. The batteries’ capacities, voltages, powers and management systems must not necessarily be standardized [
87]. However, they must be compatible with different vehicle systems [
19]. The standardization of the batteries limits the innovative power and the flexibility of both the vehicle and the battery manufacturer and the uniqueness and the design of the products [
19,
89]. Besides being standardized, the batteries must be robust, as they have to withstand frequent removals and installations [
19]. Second, there is a need for an additional and standardized BSS-battery-vehicle interface in the shape of a battery-contacting-system and an interlocking system [
90]. A third challenge is that, in comparison to the other static charging infrastructures, the BSS is larger, more conspicuous and more complex, as it requires swapping, storage and charging systems to handle the batteries [
19,
85]. To reduce the large space requirements the BSS can be built upward [
13]. A fourth challenge lies in the battery swap technology requiring more batteries than BEVs, which results in additional costs, resource consumption and emissions. A fifth challenge is developing a leasing model for the batteries [
19]. Finally, a specific parking area is required for charging, the moving and connecting parts of the BSS result in maintenance and repair expenses and the battery swap technology is not based on a widespread and standardized charging technology.
Examples of existing battery swap technologies are introduced below.
SANY: In 2022 the company put its first intelligent BSS into operation. This BSS requires 50 m
2 of space, can be installed within one day, stores eight batteries, charges a battery in one hour and can perform 168 battery swaps per day. The BSS serves SANY’s HDTs, dump trucks, concrete mixer trucks and truck loaders. The battery swapping process begins with an electric HDV docking at the BSS and the driver scanning a QR-Code. If authenticated, the vehicle is unlocked, the battery is swapped and the vehicle is locked again. With the help of an assistance vehicle the process is completed within five minutes [
91]. In 2022 the companies SANY and CATL announced a project to demonstrate the battery swap technology for electric HDTs and dump trucks in the Fujian province, China [
92].
Geely: This company offers a battery swap technology for cement mixers and semi-trailer trucks. The batteries of these vehicles are located behind the passenger cabins and can be accessed from the top. A crane positioned above the vehicle in the BSS drops down, lifts the battery up and transports it to the storage area, where a charged battery is waiting. The entire swapping process takes five minutes. Similarly to the BSS developed by SANY, the driver is authenticated using a QR-Code, the BSS can store eight batteries and the batteries can be charged in one hour. Geely’s BSS requires 19 m
2 of space, is equipped with solar panels and can serve up to 50 vehicles [
93].
Janus Electric: Janus Electric is an Australian company that fits existing HDV with its battery swap technology. Once installed, the batteries can be swapped at BSSs within four minutes. The BSSs are powered by renewable energies and enable a bidirectional energy transfer [
94]. Following the presentation of the first prototype in 2021 and a 12-month-trial involving five prototypes, the battery swap technology is currently commercially available in Australia [
94,
95].
Project eHaul: The project’s primary aim is to develop and implement an automated BSS for electric HDVs. This BSS, which is the first of its kind in Germany, will be tested by two semi-trailer trucks for several months. Besides the BSS, a business model will be designed [
96]. In April 2023, the electric trucks were put into operation. In October 2023, the build-up of the BSS was be completed (see
Figure 7). Once all the components are synchronized, the testing will begin [
97].
Similarly to the static wireless charging technology, the TRL of the battery swap technology differs greatly. For example, in November 2023 Europe’s first automated BSS for electric HDVs was opened in Germany [
98]. As testing under experimental conditions is currently in progress, a TRL 4 - 5 is proposed. In contrast, the battery swap technology offered by the company Janus Electric is commercially available in Australia indicating a TRL 9 [
94]. In China, 49.5% of the 36.000 electric HDTs sold in 2022 are swap-capable, which also implies a TRL 9 [
99].
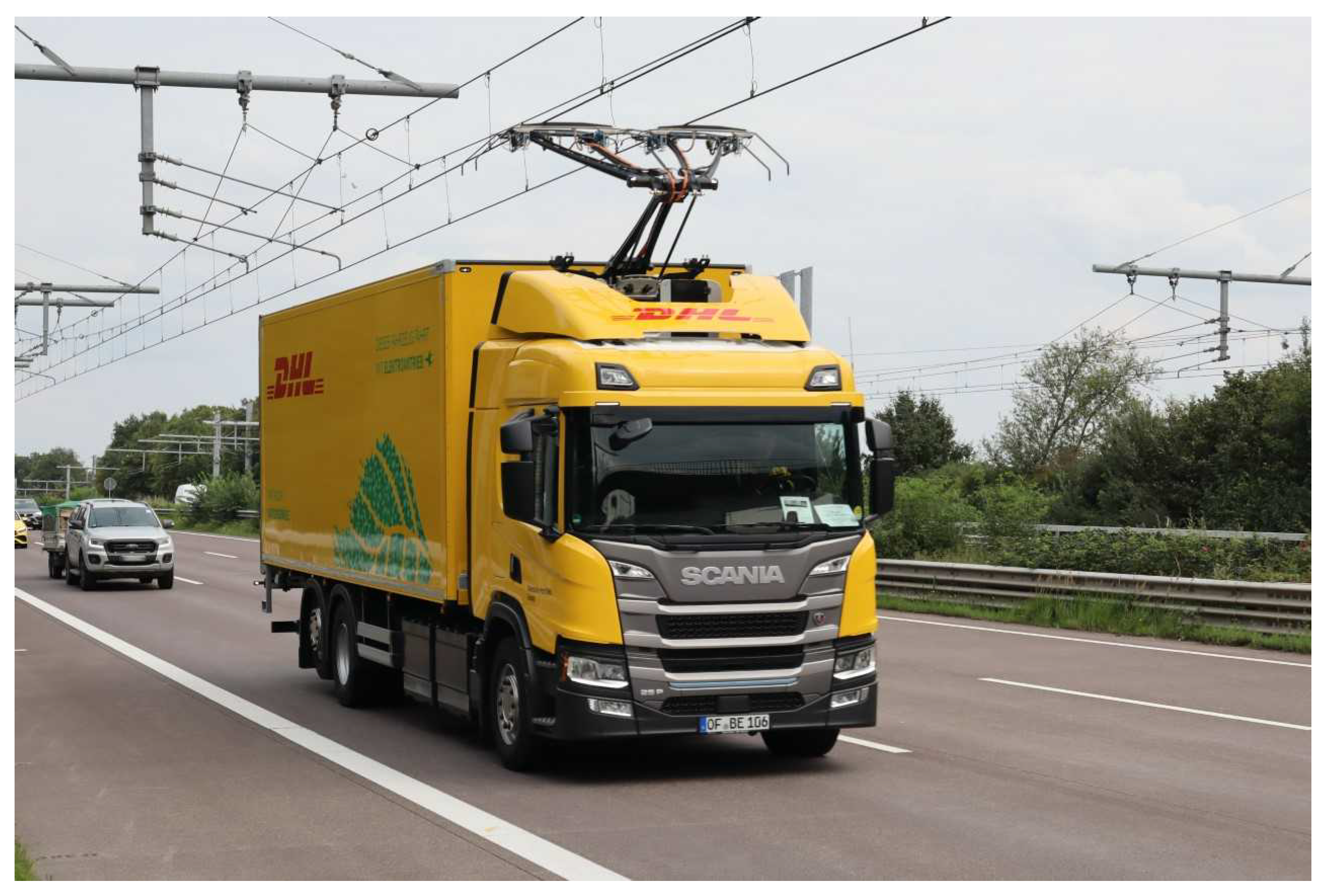
2.6. Dynamic Conductive Charging via Overhead Contact Line
Next, the dynamic charging technologies are investigated, beginning with the conductive charging technology using an overhead contact line.
Charging via an overhead contact line requires three main components:
The rectifier substations supply energy to the contact line [
100]. Therefor, they rectify and transform the high or medium voltage AC provided by the grid into the low voltage DC required by the batteries [
12,
101]. The final voltage levels usually range from 600 V - 750 V. The substations are placed every 1 km - 10 km alongside the road and typically provide 2 MW - 4 MW of power per substation [
102]. The exact positions, powers and the total number of stations depend on the route and the number of charging vehicles [
12,
102]. Besides the rectifier and the transformer, a substation contains switches, control systems and an inverter to operate the charging system and to feed the recuperated energy into the grid [
12,
100]. In contrast to train systems, the charging system for electric HDVs requires a two-pole overhead contact line. The reason for this is that the current can not be returned via rails [
12]. The positive and the negative pole are realized as two contact wires included in two separate catenary systems. Next to the contact wires, which at a height of around 5.1 m run parallel to the road, each catenary system consists of a messenger cable and droppers. The catenary systems are held by brackets and add-on-parts attached to masts and each cover 1.5 km of road. The masts are placed every 60 m [
100]. The overhead contact line of the eHighway in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, is depicted in
Figure 8. To charge a vehicle via an overhead contact line, a pantograph must be installed on the roof [
89]. As soon as the vehicle is located below the contact line, the arm of the pantograph extends and connects four carbon contact strips to the two contact wires [
103] (see
Figure 8). If the supplied energy exceeds the energy required to propel the vehicle, a battery can be charged. This battery can then power the vehicle on non-electrified road sections [
89]. It is important to notice that the power supplied to the vehicle is used to propel the vehicle and to charge the battery [
104]. Besides the three main components safety measures, such as restraint systems located alongside the road, are necessary [
100].
The charging of buses via overhead contact lines (trolley buses) was introduced in the 20
th century. However, due to the vehicles’ inflexibility regarding the route, the use was limited. In the last decade trolley buses equipped with batteries were developed and tested. Generally, the charging system for trolley buses resembles that for electric HDTs [
105].
The advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line are summarized in
Table 6.
The first advantage of the charging technology using an overhead contact line is that it is based on the widespread and standardized trolley systems for trains, trams and trolley buses [
100]. The second advantage is that the charging does not require any downtime, which results in less vehicles and less drivers having to be deployed [
106]. Additionally, the reduced downtime leads to the dynamic charging technologies suiting automated vehicles best, as they do not require a driver-related break. With dynamic charging technologies charging while driving is possible. Consequently, the existing infrastructure, i. e. the roads, are used for charging and no specific parking area is required. This, however, results in the road and the charging system influencing each other, for example regarding maintenance [
12]. It is not necessary to electrify the entire road. Gaps can be left, where a battery or an internal combustion engine propels the vehicle [
101]. On the one hand, this reduces the infrastructure costs, on the other, it entails an increase in battery costs or greenhouse gas emissions [
101,
107]. Furthermore, as the vehicle is propelled by the electricity provided by the overhead contact line, the battery capacity can be reduced and thereby also the battery weight, space requirements and costs, the resource consumption and the grid connection power, while the payload can be increased [
6,
9,
12]. This is possible, provided that the distance travelled on the non-electrified roads is limited [
12]. If a large number of kilometers is electrified, the vehicles can have a high range without requiring large battery capacities and the charging power and the local grid connection power can be reduced [
6,
12]. Additionally, frequent shallow charging with dynamic charging technologies is better than sporadic deep charging with static charging technologies regarding battery lifetime [
108]. Another possibility lies in exploiting synergies with the static charging technology using a pantograph regarding e. g. standardization [
9,
89]. Standards for the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line are under development [
102]. The dynamic charging technologies were specifically designed for automation. Finally, in comparison to the static charging technology using a robot, the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line is less susceptible to misuse. However, as the vehicles are moving, it is more susceptible to accidental damage. It also has larger space requirements and has a more conspicuous charging infrastructure and charging process. The dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line requires additional vehicle components in the shape of a pantograph. Due to the minimum height of the contact wires and the restricted reach of the pantograph, the charging technology is limited to electric HDVs [
100,
101]. The extended pantograph results in an increased air resistance and therefore also in increased energy costs [
103,
109]. As the charging technology is both conductive and dynamic, also the wear and tear is increased. This results in higher maintenance and repair expenses in comparison to the static charging technologies. Further challenges are the possible negative effects of the charging infrastructure on the avifauna and the fact that the charging technology can require changes in the driving speed and the distance and lane management [
110]. Additionally, the authentication and payment process must be implemented while driving, the scale-up of the charging infrastructure can not entirely occur in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs and there is a need for a standardized charging interface [
6]. Finally, the charging technology using an overhead contact line faces the challenge of high infrastructure costs ranging from 0.4 - 1.1 million Euros per kilometer. However, the charging technology is expected to become a cost-competitive option regarding costs per vehicle-kilometer once high-frequented roads are electrified [
102].
In Germany there are currently three pilot projects testing the charging technology using an overhead contact line for electric HDTs (see
Table 7). The projects employ a technology developed by Siemens. Part of this technology is a pantograph, which can connect to or disconnect from the overhead contact line up to driving speeds of 90 km/h and automatically disconnects in the case of the vehicle swerving or indicating [
111].
Regarding trolley buses, there are at least 277 trolley bus systems operating worldwide [
105]. Vehicle manufacturers offering trolley buses are Solaris, Hess and Iveco [
122,
123,
124].
To determine the TRL for the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line for electric HDTs, the comparatively high number of research and demonstration projects employing the same technology, the already elapsed parts of the project durations, the many involved transport companies, the use of the operational environments and the ongoing testing has to be taken into account [
12,
89]. This indicates a TRL 7. However, it is also necessary to consider the trolley buses, which are offered by the manufacturers Solaris, Hess and Iveco and therefore exhibit a TRL 9 [
122,
123,
124].
2.7. Dynamic Conductive Charging via Contact Rails
The second option to charge a vehicle both dynamically and conductively are contact rails. Contact rails are placed in the road pavement and are accessible via a movable contact arm attached to the vehicle’s underbody [
101]. The charging system’s build-up is similar to that using an overhead contact line, as it also requires rectifier substations. The substations are placed every 1 km - 2 km alongside the road [
104,
125]. In addition, cables to supply the contact rails with energy and switching cabinets including sensors to detect the vehicles and energize the respective sections of the rails are installed. Generally, there are three types of contact rails:
Two parallel flush-mounted contact rails.
Two parallel embedded contact rails.
One segmented flush-mounted contact rail.
Each type of contact rails has its advantages and challenges. If the contact rails are flush-mounted, the contact arm can effortlessly establish a connection. However, as humans, animals and other vehicles can easily come in contact with the rails, additional safety-related efforts are required. If the contact rails are embedded, the safety of the road-users is increased. In this case though, the process of connecting the contact arm with the contact rails is more difficult and dirt and wear debris can accumulate within the rails. Additionally, the embedded rails might represent a safety hazard for (motor-)cyclists. A single segmented flush-mounted contact rail offers the advantage that only the rail segment located below the vehicle is energized. Therefore, the safety is increased. However, an exact energizing of the contact rails, which also takes the vehicle length and vehicle speed into account, is required. This necessitates a reliable communication system. The different types of contact rails are incompatible. In contrast to the charging technology using an overhead contact line, the contact arm is realized as a pick-up shoe [
104].
Table 8 summarizes the advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the charging technology using contact rails.
The charging technology using contact rails shares many of its advantages and potentials with the charging technology using an overhead contact line. For instance, charging while driving is possible, the existing infrastructure, i. e. the road, is used, it is not necessary to electrify the entire road, there is the possibility to reduce the battery capacity and still ensure a high electric range and there is no charging-related downtime required. Technology-specific advantages are that the contact rails are accessible to all vehicle types and that, in comparison to the charging technology using an overhead contact line, the charging occurs unseen underneath the vehicle, resulting in a less conspicuous charging process and charging infrastructure [
125]. Additionally, the charging technology using contact rails requires less space than that using an overhead contact line. Further advantages and potentials are that the charging technology can draw on the experience of the railway traffic with contact rails, that the charging technology was specifically designed for automation and that standards for the dynamic charging via contact rails are under development, e. g. DIN CLC/TS 50717 [
126]. Finally, there is the possibility to exploit synergies with the static charging technology using an underbody-coupler [
127]. In comparison to the charging technology using an overhead contact line, the charging technology employing contact rails is less susceptible to accidental damage, but, due to the system layout, more susceptible to misuse. Considering the static charging technologies, the charging technology using contact rails necessitates increased maintenance and repair expenses and results in higher energy costs. Furthermore, vehicle adaptations in the shape of a contact arm are necessary, there is a need for a standardized charging interface and a need to implement the authentication and payment process while driving. Similarly to the charging technology using an overhead contact line, a change in driving behaviour regarding distance and lane management might be required. The infrastructure costs of the charging technology using contact rails exceed those of the charging technology using an overhead contact line [
128]. Finally, there only is a limited possibility to scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs, as, aside from the length of the electrified section, there is no room for maneuver.
Two companies located in Sweden offer charging technologies using contact rails.
Elonroad: The contact rail developed by the company Elonroad can be used for both static and dynamic charging of various vehicle types [
125,
127]. The rail designed for dynamic charging is 9.2 m long, weighs 250 kg, supplies a charging power of up to 300 kW and enables a driving speed of up to 160 km/h. As the charging system is designed as a single flush-mounted contact rail, the polarity of the rail segments must alternate for the rail to be energized. Between each negative segment there is a segment that can be both positive and negative. The substations energize these segments once an authenticated vehicle is detected above. According to Elonroad, the charging system can transfer energy with an efficiency of up to 97%. Only the vehicles equipped with a specific current collector can charge from the contact rails. The size of the current collector equals that of an A-segment passenger car, a city car. Besides the current collector, an onboard charger is required [
125]. Since 2019 Elonroad has been demonstrating and testing its dynamic charging technology by charging i. a. an electric bus on a public road in Lund, Sweden. This project is scheduled to end in 2024 [
129]. Additionally, the company Aisin has chosen to install Elonroad’s dynamic charging technology at their 1 km-test track in Mons, Belgium, to explore the electrified road-systems and to develop their onboard charging equipment. The test track will be installed in 2024 [
130]. The contact rail and current collector designed by Elonroad can be seen in
Figure 9.
Elways: The charging system developed by the company Elways consists of a contact rail embedded in the road pavement (see
Figure 9). By placing the rail in a trench, energizing only sections of the rail, linking the current supply to a minimum driving speed and installing a turn-off device Elways ensures the safety of its technology. To detect road obstacles Elways employs a radar. The water and the snow that accumulate in the trench are ploughed by either the contact arms or a special vehicle and the ice is melted by a heating system [
131]. Since 2018 Elways has been testing its charging technology using an electric 18 t-truck and a road near Arlanda Airport, Sweden. The truck was charged with 200 kW of power at a driving speed of 60 km/h [
132].
As the dynamic charging technology using contact rails is currently being demonstrated within the scope of two projects, which have been carried out since several years, partly incorporate transport companies and represent the first projects of their kind, a TRL 6 - 7 is suggested, indicating that the system is demonstrated in relevant and operational environments [
129,
132].
2.8. Dynamic Wireless Charging
Just as the static wireless charging technology, the dynamic wireless charging technology employs the magnetic resonance coupling technique. There are, however, differences in the build-ups of the charging technologies. The first difference lies in the layout of the primary coils. The dynamic wireless charging technology can encompass either one long primary coil or a multitude of small, aligned primary coils. The single primary coil is 10 m - 100 m long and can charge several vehicles at once. The aligned primary coils are as large as the secondary coils and are connected either in series or in parallel. When using a single primary coil only one primary coil and one primary station, including a rectifier, a high-frequency inverter and a compensation network, are required. Such a charging system is easy to control, enables a constant mutual induction and features a simple configuration and compensation network [
71]. A single primary coil faces the challenges of high losses and high safety risks, as the coil is permanently energized [
15,
71]. Furthermore, the maintenance and repair expenses are high and the coupling coefficient and therefore also the efficiency is low. When employing many aligned primary coils only the primary coil closest to the secondary coil is energized, which results in reduced losses and a higher safety. Also, the length of the charging track is more flexible. The second possible system layout requires many primary coils, compensation networks and, depending on the design, high-frequency inverters, resulting in high material costs and a high system complexity. Additionally, to eliminate self-coupling the primary coils are separated by large distances, which leads to the mutual inductance and therefore the charging power varying with the position of the secondary coil [
71]. The second difference is that the secondary coil of the dynamic wireless charging technology is mobile. In the case of the aligned primary coils, only the primary coil closest to the secondary coil is energized. Therefor, the mutual inductance is monitored, as it indicates the distance between the coils. The third difference concerns the compensation networks, which, as parts of the dynamic wireless charging technology, encompass both capacitors and coils. This increases the stability and the tolerance of misalignment and enables a bidirectional energy flow and the charging of multiple vehicles simultaneously by one primary coil [
18].
Besides requiring a communication system, the dynamic wireless charging technology necessitates a foreign object detection system, a living object protection system and a driver assistance system to guide the vehicle while charging [
9,
11,
15]. Furthermore, the EMC regarding other electrical systems and the environment must be ensured [
9]. To do so, active or reactive resonant shielding can be employed. Active shielding defines the energizing of external coils to generate a magnetic field opposing that of the primary coil. Reactive resonant shielding extends active shielding by adding reactive components, which are excited by the primary coil’s magnetic field [
18].
Next to the influencing factors mentioned in Sub
Section 2.4, the charging power depends on the driving speed, the number of secondary coils energized by the same primary coil, the power quality and the total number of primary and secondary coils [
14,
133]. There is the possibility to place the secondary coils in the wheels of the vehicle to reduce the distance between the coils and increase the efficiency [
10]. Furthermore, a magnetizable concrete can be installed to direct and confine the magnetic field and thereby increase the efficiency [
71].
A summary of the advantages, the potentials and the challenges of the dynamic wireless charging technology is given in
Table 9).
The dynamic wireless charging technology shares many advantages and potentials with the dynamic conductive charging technologies. For example, charging while driving is possible, the existing infrastructure, i. e. the road, is used, it is not necessary to electrify the entire road, there is the possibility to reduce the battery capacity and still ensure a high electric range and there is no charging-related downtime required. Technology-specific advantages and potentials are the standards, which are currently under development, e. g. ISO TS 5474-6, IEC PT 63243 and IEC PT 63381, the fact that the charging technology can draw on the experience and the standards of the static wireless charging technology and the possible synergies with the static wireless charging technology by employing the same vehicle unit for example [
23,
71,
134]. In comparison to the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line, the dynamic wireless charging technology requires less space and has a less conspicuous charging infrastructure and charging process. Additionally, as no vehicle components are extended while driving, the air resistance and therefore also the energy costs are reduced. Moreover, due to the fact that there is no physical connection between the vehicle and the infrastructure, there is less wear and tear and therefore less maintenance and repair work. Further advantages and potentials are that the dynamic wireless charging technology is not limited to electric HDVs and that it is specifically designed for automation.
The dynamic wireless charging technology also shares many of its challenges with the dynamic conductive charging technologies. For example, vehicle adaptations in the shape of a vehicle unit are required, there is a limited possibility to scale-up the charging infrastructure in parallel to the scale-up of the BEVs, a change in driving behaviour, e. g. a reduced speed, increased gaps and a ban on passing, might be required and there is a need for a standardized charging interface and a mobile authentication and payment procedure [
14]. In comparison to the dynamic charging technology using an overhead contact line, the dynamic wireless charging technology is less susceptible to accidental damage but, due to the system layout, more susceptible to misuse. Further technology-specific challenges are the sensitivity of the ground units to movements of the road surface, the sensitivity of the system efficiency to the horizontal and the vertical misalignment of the coils, operating the charging system at the recommended frequency, as current systems work with lower frequencies, and isolating the ground units so that the failure of a ground unit does not lead to the failure of the system [
14,
71]. The infrastructure costs of the dynamic wireless charging technology exceed those of the dynamic conductive charging technologies [
128]. Finally, in comparison to the dynamic conductive charging technologies, the power capability of the dynamic wireless charging technology is limited [
104].
The company Electreon is developing a dynamic wireless charging technology for electric HDVs. This technology is being/will be demonstrated, explored and tested within the framework of various projects (see
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
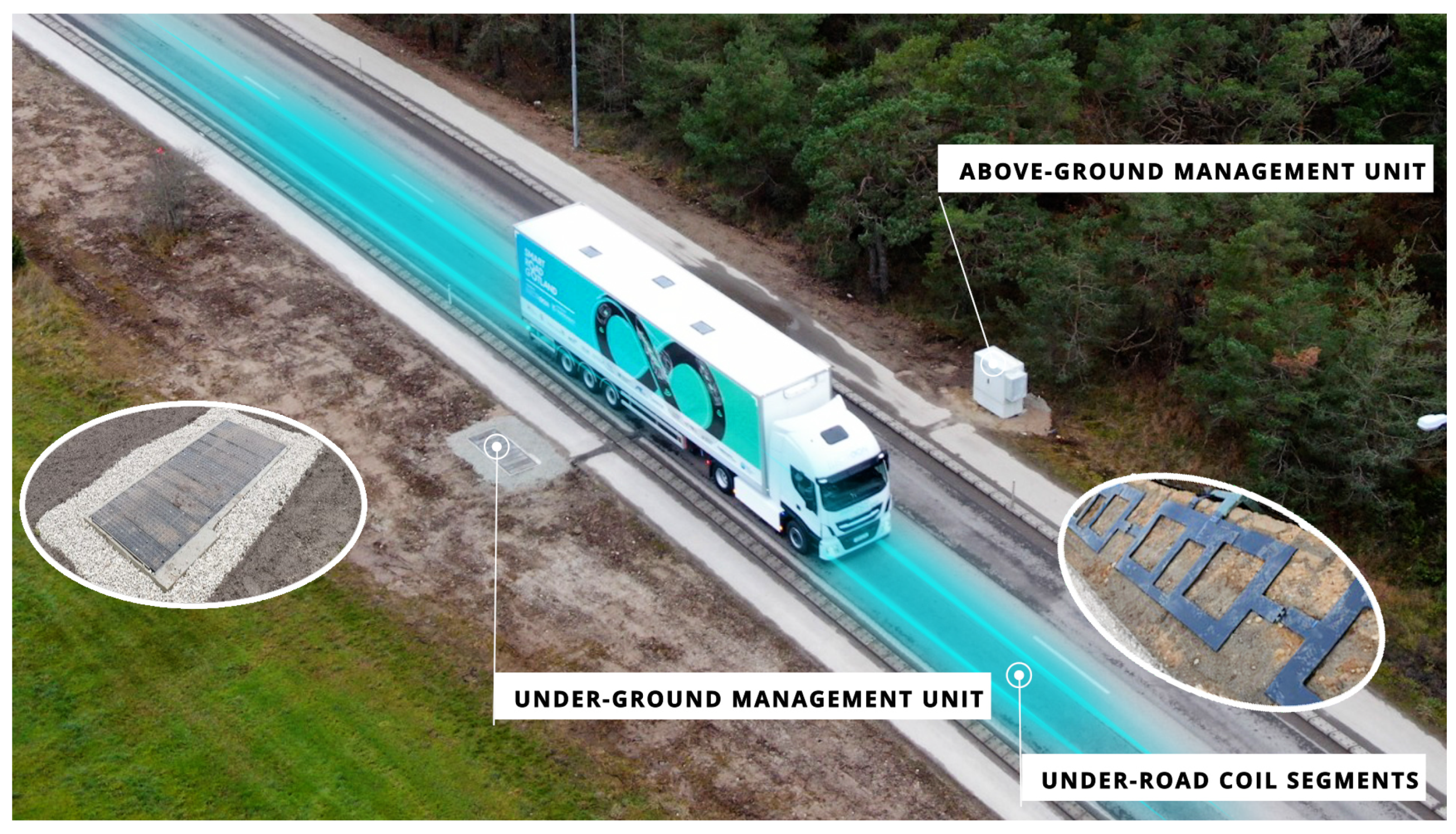
Electreon’s primary coils are embedded in the road pavement, are energized once an authenticated vehicle is located above and can be installed at a rate of 1.6 km of coils per night [
135,
136]. The corresponding primary stations can be installed underground, minimizing the space requirements and the technology’s conspicuousness. The charging technology has a life time of 10 to 20 years, is not affected by snow or ice and can be installed in tunnels if the energy supply is guaranteed [
135]. In Visby, Sweden, an electric truck was charged with an average power of 100 kW while travelling at speeds of up to 80 km/h [
137]. In 2023 and 2024 Electreon is planning to test its charging technology at driving speeds of 120 km/h [
135]. Currently, Electreon is offering a Charging-as-a-Service-Business Model in which the customers pay a monthly subscription fee [
138].
To determine the TRL of the dynamic wireless charging technology the projects employing the charging system designed by Electreon are examined. The primary aim of the completed and the ongoing projects is to validate and demonstrate the charging technology and to display its benefits and feasibility on public roads with different vehicle types and in various use cases [
80,
137,
140,
141,
142,
145]. As a few of the projects already incorporate transport companies, a TRL 5 - 6 is proposed, indicating that the technology has been validated and demonstrated in a relevant environment [
137,
142,
145].