Submitted:
09 April 2024
Posted:
10 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1
3.1.1. Differential Expression of Genes Associated Immune Response, GO, KEGG Pathways by RNA-Seq
3.1.2. Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Immune Response by RT-qPCR
3.2. Experiment 2
Differential Expression of Genes, GO, KEGG Pathways and PPI in Response to NDV Vaccination in Harderian Glands and Trachea
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Ed.; Fourteenth edition.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-37117-5.
- Transboundary Animal Diseases in Sahelian Africa and Connected Regions; Kardjadj, M., Diallo, A., Lancelot, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-25384-4.
- Rehan, M.; Aslam, A.; Khan, M.-R.; Abid, M.; Hussain, S.; Umber, J.; Anjum, A.; Hussain, A. Potential Economic Impact of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Wild Birds on Commercial Poultry Industry of Pakistan: A Review. HV 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Taylor, T.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Crossley, B.M.; Killian, M.L.; Bergeson, N.H.; Torchetti, M.K.; Afonso, C.L.; et al. Pathogenicity and Transmission of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus from the 2018–2019 California Outbreak and Related Viruses in Young and Adult Chickens. Virology 2019, 531, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samal, S.K. Avian Virology: Current Research and Future Trends; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UNITED KINGDOM, 2019; ISBN 978-1-912530-11-3.
- Jay Shendure, H.J. Next-Generation DNA Sequencing. 2008.
- Fabio Luciani; Rowena A. Bull; Andrew R. Lloyd Next Generation Deep Sequencing and Vaccine Design: Today and Tomorrow. 2012.
- Deist, M.S.; Gallardo, R.A.; Bunn, D.A.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Zhou, H.; Lamont, S.J. Resistant and Susceptible Chicken Lines Show Distinctive Responses to Newcastle Disease Virus Infection in the Lung Transcriptome. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deist, M.S.; Gallardo, R.A.; Bunn, D.A.; Kelly, T.R.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Zhou, H.; Lamont, S.J. Novel Analysis of the Harderian Gland Transcriptome Response to Newcastle Disease Virus in Two Inbred Chicken Lines. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saelao, P.; Wang, Y.; Gallardo, R.A.; Lamont, S.J.; Dekkers, J.M.; Kelly, T.; Zhou, H. Novel Insights into the Host Immune Response of Chicken Harderian Gland Tissue during Newcastle Disease Virus Infection and Heat Treatment. BMC Veterinary Research 2018, 14, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kaiser, M.G.; Deist, M.S.; Gallardo, R.A.; Bunn, D.A.; Kelly, T.R.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Zhou, H.; Lamont, S.J. Transcriptome Analysis in Spleen Reveals Differential Regulation of Response to Newcastle Disease Virus in Two Chicken Lines. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, H.; Adam, F.A.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Insights into the Chicken Bursa of Fabricius Response to Newcastle Disease Virus at 48 and 72 Hours Post-Infection through RNA-Seq. Veterinary Microbiology 2019, 236, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Nie, F.; Huang, A.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of Chicken Immune Response to Infection of Different Doses of Newcastle Disease Vaccine. Gene 2021, 766, 145077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, P.T.K.; Low, W.Y.; Ren, Y.; Tearle, R.; Hemmatzadeh, F. Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII Gene Expression in Experimentally Infected Birds. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Tang, D.; Yan, S.; Fan, H.; Li, G.; Shahid, M.S.; Mahmood, T.; Guo, Y. Effects of Age on Immune Function in Broiler Chickens. J Animal Sci Biotechnol 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Miller, P.J. Immune Responses of Poultry to Newcastle Disease Virus. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2013, 41, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, K.; Lee, D.-H.; Criado, M.F.; Balzli, C.L.; Killmaster, L.F.; Kapczynski, D.R.; Swayne, D.E. Maternal Antibody Inhibition of Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus Vectored Vaccine in a Primary or Booster Avian Influenza Vaccination Program of Broiler Chickens. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6361–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, N. National Research Council Nutrient Requirements of Poultry - Ninth Revised Edition (1994). The Journal of Applied Poultry Research 1994, 3, 101–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-Based Genome Alignment and Genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-Genotype. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, G.H.; Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Pimanda, J.E.; Zanini, F. Analysing High-Throughput Sequencing Data in Python with HTSeq 2.0. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: Contributors. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/contributors.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Lun, A.T.L.; Smyth, G.K. From Reads to Genes to Pathways: Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Experiments Using Rsubread and the edgeR Quasi-Likelihood Pipeline. F1000Res 2016, 5, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlston Org.Gg.Eg. Available online: http://bioconductor.org/packages/org.Gg.eg.db/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Research 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J Proteome Res 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, D.; Tang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, J. CytoCluster: A Cytoscape Plugin for Cluster Analysis and Visualization of Biological Networks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2017, 18, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepusz, T.; Yu, H.; Paccanaro, A. Detecting Overlapping Protein Complexes in Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/products/discovery-and-translational-research/pcr-qpcr-dpcr/qpcr-assays-and-instruments/mrna-incrna-qpcr-assays-panels/rt2-profiler-pcr-arrays (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Raimundo Espejo, Cassandra Breedlove, Haroldo Toro Changes in the Transcriptome Profile in Young Chickens after Infection with LaSota Newcastle Disease Virus. 2024.
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R Package for the Visualization of Intersecting Sets and Their Properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, C. When PARPs Meet Antiviral Innate Immunity. Trends in Microbiology 2021, 29, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachinger, N.; Fischer, S.; Böhme, I.; Linck-Paulus, L.; Kuphal, S.; Kappelmann-Fenzl, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Loss of Gene Information: Discrepancies between RNA Sequencing, cDNA Microarray, and qRT-PCR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Gibson, M.S.; Wash, R.S.; Ferrara, F.; Wright, E.; Temperton, N.; Kellam, P.; Fife, M. Chicken Interferon-Inducible Transmembrane Protein 3 Restricts Influenza Viruses and Lyssaviruses In Vitro. Journal of Virology 2013, 87, 12957–12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Shiraishi, T.; Qin, J.; Konno, H.; Akiyama, N.; Shinzawa, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Takizawa, N.; Yanai, H.; Ohashi, H.; et al. Mitochondria–Nucleus Shuttling FK506-Binding Protein 51 Interacts with TRAF Proteins and Facilitates the RIG-I-Like Receptor-Mediated Expression of Type I IFN. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e95992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Xing, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C. The Matrix Protein of Newcastle Disease Virus Inhibits Inflammatory Response through IRAK4/TRAF6/TAK1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 218, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Ahn, D.-G.; Syed, G.H.; Siddiqui, A. The Essential Role of Mitochondrial Dynamics in Antiviral Immunity. Mitochondrion 2018, 41, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liang, Z.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, B.; Lin, Q.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; et al. Newcastle Disease Virus Activates the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway by Targeting PHLPP2 Degradation to Delay Cell Apoptosis and Promote Viral Replication. Veterinary Microbiology 2024, 289, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Antiviral Signaling Through Pattern Recognition Receptors. The Journal of Biochemistry 2007, 141, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilden, H.; Fournier, P.; Zawatzky, R.; Schirrmacher, V. Expression of RIG-I, IRF3, IFN-β and IRF7 Determines Resistance or Susceptibility of Cells to Infection by Newcastle Disease Virus. International Journal of Oncology 2009, 34, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Chu, Z.; Hu, R.; Ren, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; et al. High Level Expression of ISG12(1) Promotes Cell Apoptosis via Mitochondrial-Dependent Pathway and so as to Hinder Newcastle Disease Virus Replication. Veterinary Microbiology 2019, 228, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.E.; Busse, D.C.; Binter, S.; Weston, S.; Diaz Soria, C.; Laksono, B.M.; Clare, S.; Van Nieuwkoop, S.; Van den Hoogen, B.G.; Clement, M.; et al. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 1 Restricts Replication of Viruses That Enter Cells via the Plasma Membrane. Journal of Virology 2019, 93, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhakumar, D.; Rohaim, M.A.M.S.; Hussein, H.A.; Hawes, P.; Ferreira, H.L.; Behboudi, S.; Iqbal, M.; Nair, V.; Arns, C.W.; Munir, M. Chicken Interferon-Induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 5 Antagonizes Replication of RNA Viruses. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Tan, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Liao, Y.; Xu, C.; Ren, T.; Ding, C.; et al. A Role for the Chicken Interferon-Stimulated Gene CMPK2 in the Host Response Against Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Single-Cell Transcriptome Atlas of Newcastle Disease Virus in Chickens Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Microbiology Spectrum 2023, 11, e05121–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
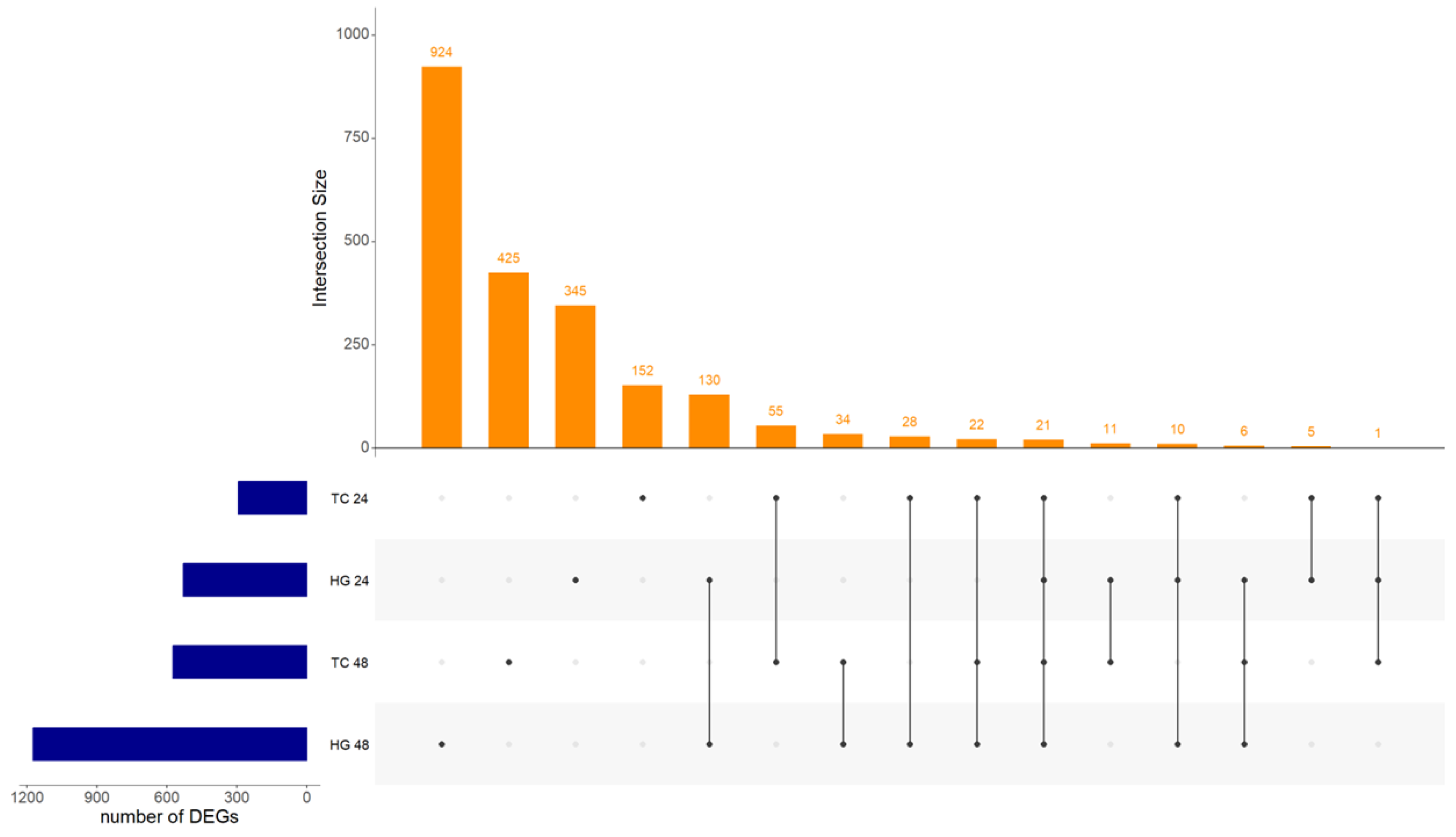
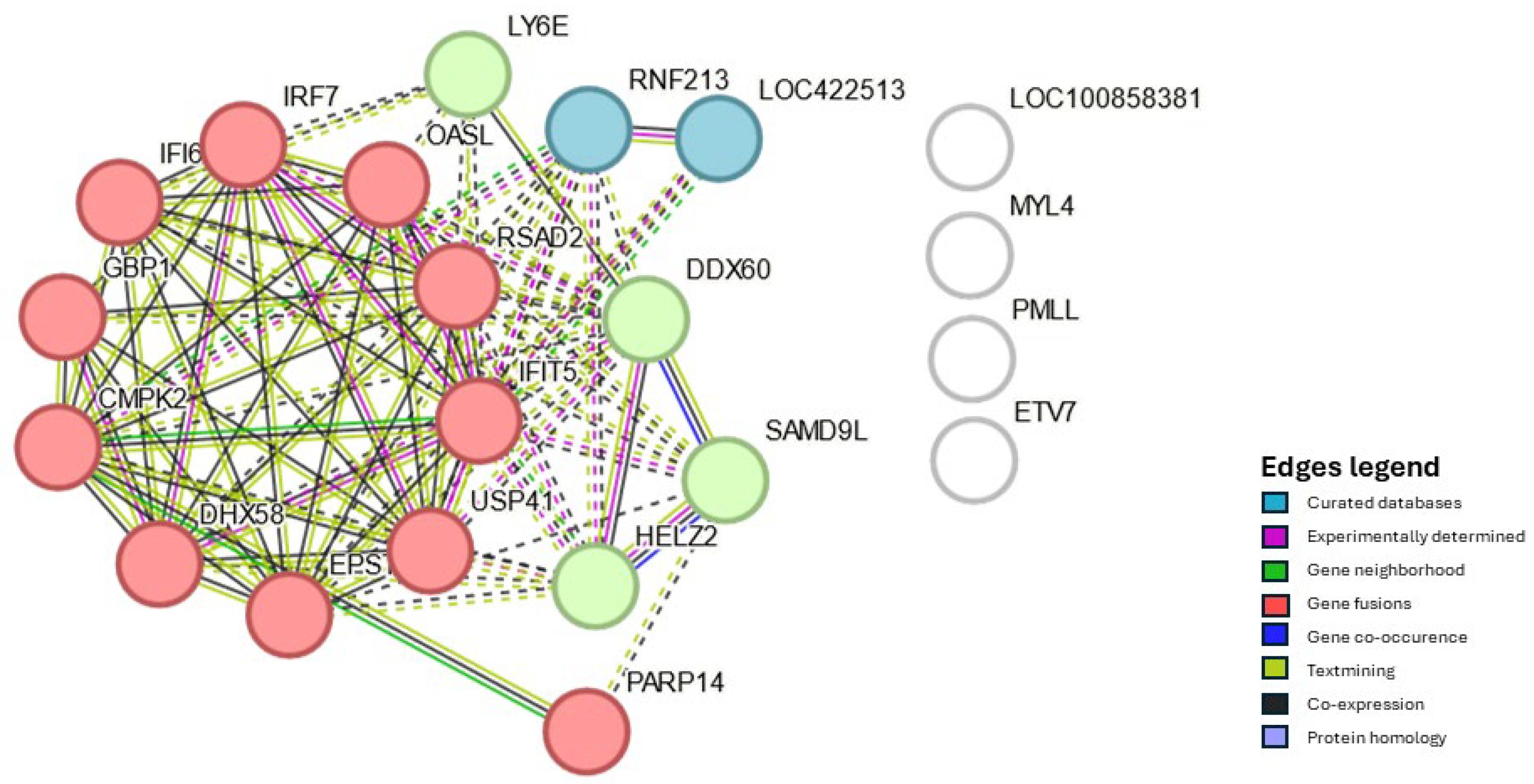
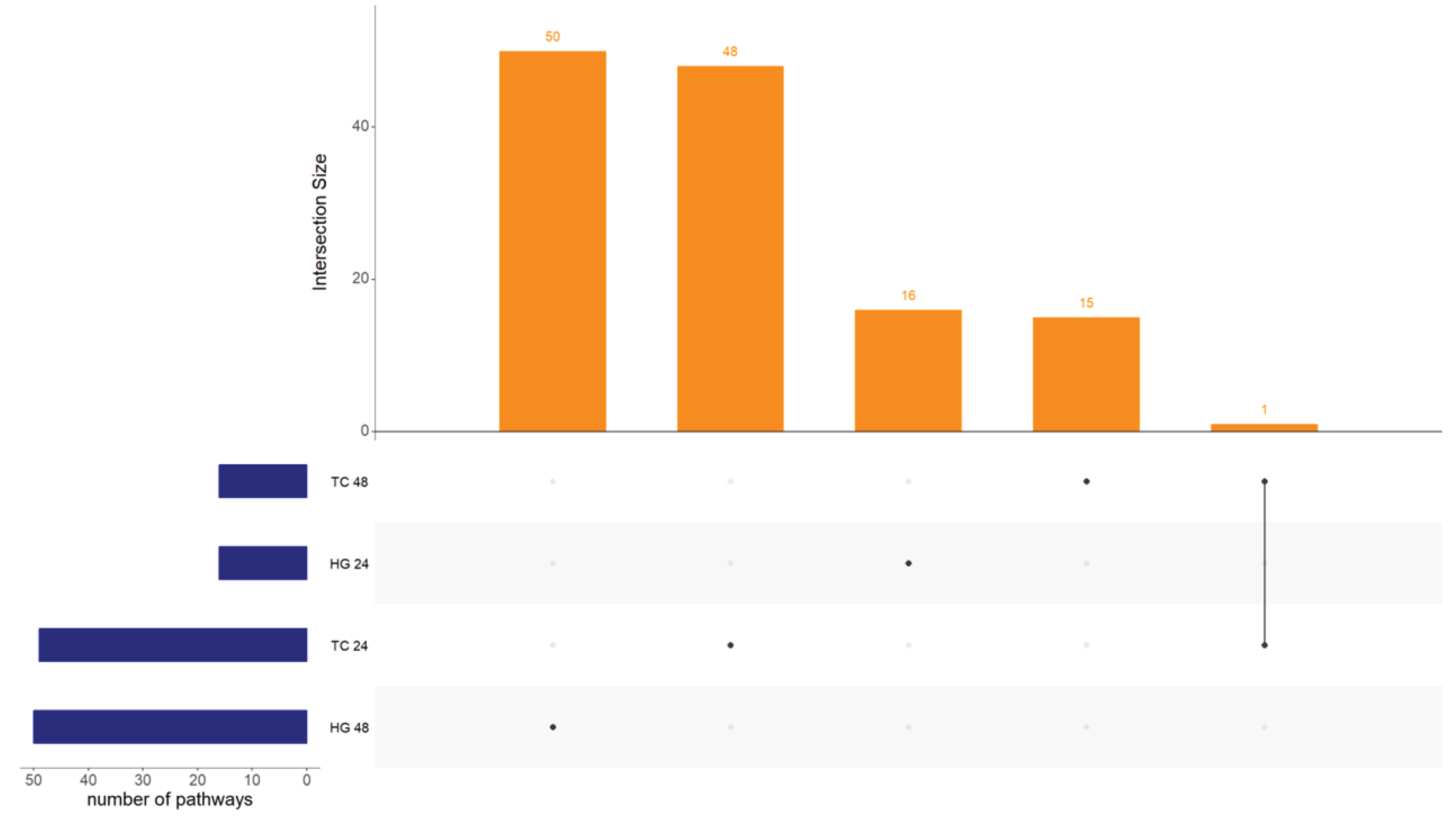
| Organ | Hours post vaccination | Control group | Vaccinated group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA-seq | RT-qPCR | RNA-seq | RT-qPCR | ||
| Harderian glands | 12 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| 24 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| 48 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | |
| Tracheas | 12 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 24 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 48 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | |
| Main factor or interaction |
Organ and sampling time point (hours) | Unique DEGs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg 24 hpv | Hg 48 hpv | Tc 24 hpv | Tc 48 hpv | ||||||
| up | down | up | down | up | down | up | down | ||
| Vaccination | 490 | 39 | 114 | 1,061 | 168 | 126 | 74 | 503 | 2,169 |
| Age | 347 | 54 | 194 | 1,069 | 108 | 201 | 94 | 547 | 2,235 |
| Type | 1,947 | 736 | 336 | 612 | 116 | 370 | 103 | 600 | 3,919 |
| Type × Age | 1,278 | 3,614 | 412 | 109 | 324 | 83 | 521 | 84 | 5,715 |
| Vacc × Age | 81 | 459 | 826 | 44 | 97 | 214 | 632 | 234 | 2,333 |
| Vacc × Type | 384 | 1,185 | 375 | 152 | 267 | 166 | 561 | 72 | 2,692 |
| Vacc × Type × Age | 1,939 | 403 | 113 | 188 | 307 | 312 | 172 | 464 | 2,333 |
| Main factor or interaction |
Organ and sampling time point (hours) | Unique pathways | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg 24 | Hg 48 | Tc 24 | Tc 48 | ||||||
| up | down | up | down | up | down | up | down | ||
| Vaccination | 16 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 30 | 20 | 8 | 8 | 130 |
| Age | 0 | 0 | 7 | 43 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 9 | 68 |
| Type | 49 | 1 | 16 | 34 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 110 |
| Type × Age | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 128 |
| Vacc × Age | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 2 | 48 | 15 | 35 | 149 |
| Vacc × Type | 0 | 50 | 43 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 107 |
| Vacc × Type × Age | 45 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 149 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





