1. Introduction
Progress in the creation of new constructions, machine parts and mechanisms is largely related to the problem of obtaining materials with given structure-sensitive characteristics [
1,
2].
Of considerable interest are nanostructured metal-ceramic materials, representing compositions, in which the particles of the second phase are distributed in a metal matrix.
Recently in this direction are carried out intensive research in connection with the prospect of improving the properties of such materials by optimizing the choice of material dispersed particles and their distribution in the matrix. At the same time it is possible to expect improvement of composite properties, in particular, mechanical, electro- and thermophysical, magnetic properties.
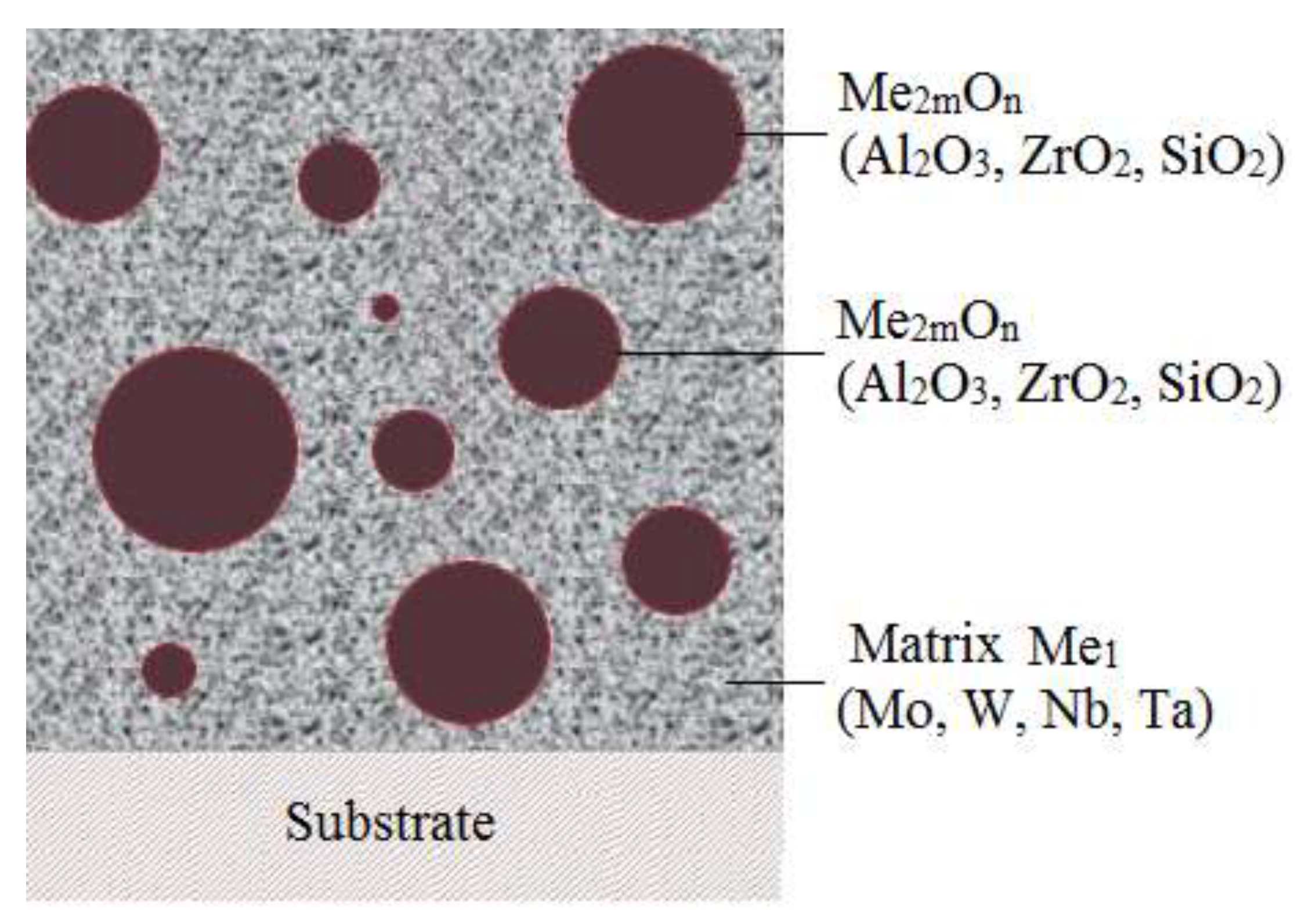
Of particular interest are "molecular" composite materials in which the particles of the second phase (high enthalpy ceramic compounds - oxides, nitrides, carbides) are in a highly dispersed state (100 Å) in the metal matrix.
In this paper,
Section 2 presents the results of our experimental studies on obtaining two-phase materials with ultradisperse structure, studied their structure, composition, some electrophysical properties [
3,
4]. The anomalies of the electrophysical characteristics caused, probably, by the deformations of the electronic spectrum of the materials caused by the ensemble of ultradispersed particles in the matrix were revealed [
5].
In
Section 3, the effect of an ensemble of nanoparticles with an output work different from that of the matrix material on the change in the electron density in composite materials was theoretically considered [
6,
7].
The distribution of the concentration of free carriers around a single lobe was calculated, and estimates were made for the ensemble of microparticles, taking into account the results obtained.
The effect of an ensemble of microparticles on the change in electron density in composite materials was investigated. It is shown that the introduction of ~1 % ultra-dispersed (~100 A) particles with j0 = 0,3 eV reduces the electron density in the matrix at 1200K by about an order of magnitude. Reducing the temperature leads to a strengthening of the effect, which allows the above nanocompositions to be considered as candidate materials with adjustable electrophysical properties.
When considering the distribution of electron density in nanocomposites with j0 < 0, it is shown that the average values of electron density in the matrix when 1% of particles with a radius of 50 A are introduced increase by more than two orders of magnitude. This effect provides a basis for expanding the class of materials with adjustable free carrier densities.
Possible ways of nanodisperse structures formation are discussed. The possibilities of creating ultradisperse compositions using radiation-plasma methods are considered [
6,
7].
2. Experimental Studies of Metal-Ceramic Materials and Coatings Production
2.1. Application of Nanostructured Metal-Ceramic Coatings from Two-Phase Alloys by CVD Method Using Nonequilibrium Plasma
Nanostructured metal-ceramic materials, which are compositions in which the particles of the second phase are distributed in a metallic matrix, have recently been studied quite intensively in connection with the prospect of improving the properties of such materials (mechanical electrical, magnetic, thermal, etc.) at high temperatures. Of particular interest are "molecular" composite materials in which the second phase particles (high enthalpy ceramic compounds - oxides, nitrides, carbides) are in a highly dispersed state (100 Å) in a metal matrix.
Usually such materials are obtained by methods of powder metallurgy, as well as by chemical deposition from solutions of salts or hydroxides with subsequent reduction [
8,
9,
10,
11]. The possibility of obtaining "molecular" two-phase alloys Mo- Al
2O
3 by hydrogen reduction of molybdenum trioxide and aluminum hydrochloride is indicated in [
12]. Fine-dispersed Ni-Cr-SiO alloys were obtained by co-deposition from the gas phase [
13]. Nb-Al
2O
3 compositions with oxide particle sizes less than 30 Å can be obtained by cathodic sputtering [
14].
The following methods exist for gas-phase deposition of oxide films [
15,
16].
Decomposition must be carried out in an oxidizing environment containing H2O, CO2 or O2 to regulate the stoichiometry of the resulting oxide.
- 2.
Hydrolysis of metal halide on a heated surface.
In this hydrolysis, water vapor produced by the gas reaction is used, but the metal halide may be transported to the coated surface where the reaction that produces the oxide is localized by the H2-CO2 mixture (inactive if the halide vaporization temperature is below the temperature at which the water gas reaction begins to proceed at a noticeable rate.
Hydrolysis of metal halides by means of the water-gas reaction is more thermodynamically advantageous at high temperatures than at low ones. This difference in the changes of free energy in both reactions is due to the water-gas reaction itself.
We have conducted studies on the development of processes for obtaining two-phase alloys by co-reduction of metal chlorides in the CO
2 process using low-temperature nonequilibrium plasma [
3,
4,
17], which schematically can be represented by the reaction
The metallic component (Me1) in such systems is W, Mo, Nb, Ta, and the ceramic component (Me2mOn) is aluminum, zirconium or silicon oxides. The principle possibility of obtaining such materials by chemical vapor deposition stems from the fact that the optimum temperatures for obtaining the above metals lie in the same range as for aluminum, zirconium and silicon oxides, and the thermodynamic stability of these oxides is higher than that of matrix oxides and intermetallides.
Nanoparticles are 50-200 A in size, i.e. they already have individuality (their own volume and surface) and can be characterized to a certain extent by thermodynamic and physical-mechanical characteristics inherent to the nanoparticle material.
A distinctive feature of these methods of obtaining composite materials is that particle and matrix materials are formed simultaneously in the process of crystallization, as a result of which particles and matrices are equilibrated to each other in the absence of ultimate stresses, which accounts for many features of molecular compositions.
2.2. The Structure of Metal-Ceramic Coatings
In works [
3,
4], the processes of obtaining metal-ceramic coatings Mo - ZrO
2 by the CVD method in the "СО
2-process" were investigated.
The main characteristics of the samples are given in
Table 1.
Deposition rate and properties of ZrO2 depend on the deposition temperature and composition of the vapor-gas mixture. As the deposition temperature increases the growth rate of the coating increases, reaching a maximum at 1200-1300°C. With further increase in temperature a decrease in deposition rate is observed due to the course of the homogeneous process in the gas phase. Temperature dependence of zirconium oxide density behaves similarly: it reaches maximum at 1100-1200°C, and density decreases with further rise in temperature.
Studies of the dependence of ZrO2 density and deposition rate on the total pressure in the reactor at the same partial pressure of metal chloride and carbon dioxide show that with increasing pressure at the same deposition temperature, a decrease in density is observed.
As the deposition temperature increases, the degree of crystallinity increases. At temperatures in the 1400-1600°C range, the average size of crystalline grains is ~20-25 μm, but the density of such coatings is lower than at lower deposition temperatures.
At a pressure of 50 mm Hg and temperature of 1300°C cellular coatings are formed, while at a pressure of 150 mm Hg coatings are practically not formed (oxide powder is deposited on the reactor walls), which is associated with the course of the reaction in the gas phase.
The deposition temperature (900-1600°C) and the ratio of partial pressures of metal chlorides were chosen as varied independent parameters in the study of the kinetics of two-phase Mo-ZrO2 alloys. The prepared samples were investigated by metallographic, phase X-ray, electron microscopic and microprobe X-ray analyses. Ceramic concentrations were determined by chemical and quantitative X-ray microprobe analysis.
As the temperature increases up to 1100°C, the growth rate for all systems increases, after which some decrease in growth rate is observed, reaching a minimum at 1200°C. With further increases in temperature, the rate increases and reaches a maximum at 1500°C. At temperatures of 1600-1700°C there is practically no deposition of metal-ceramic materials on the substrate. Changing the flow geometry, substrate geometry, etc. affects the state of the maxima, but the qualitative nature of the dependence is maintained.
The ratio of chloride partial pressures also has a significant effect on the deposition rate. An increase in the ratio at constant substrate temperature T=1300°С leads to a decrease in the deposition rate (it is important to emphasize that the ratio change was performed by varying the partial pressure of chlorides forming the metal matrix, P1 and P2, while P=const).
The microstructure of metal-ceramic coatings has a columnar character, which is characteristic of materials obtained by crystallization from the gas phase. however, the grain size is smaller than that of metal coatings. This seems to be due to the fact that oxide particles inhibit recrystallization and prevent grain growth.
At thicknesses up to 10 μm, the coatings had a strong adhesion to the lining.
The metal-ceramic samples showed a very high microhardness level of 2000-2500 kg/mm2.
The samples based on metals Mo, W, Nb, and ceramic components Al
2O
3 and ZrO
2, similar to those used in the study of coalescence in two-phase alloys Mo-Al
2O
3 and Mo-ZrO
2 were used for X-ray structure and electronographic studies [
3,
4].
In all systems studied, according to the phase X-ray analysis, there is only the metal Mo, W, Nb, and the ceramic component. No other compounds were detected. The size of the ceramic particles in the obtained samples is very small. As electron microscopic studies of thin films showed [
3], the particles are evenly distributed in the metal matrix and their size does not exceed 50-100 A. The uniformity of the component distribution was confirmed by X-ray microprobe analysis.
Dispersed particles have a great influence on the molybdenum structure, which manifests itself in an increase in lattice parameters, a decrease in block sizes and the presence of significant distortions of types II and III. The lattice parameter of molybdenum in the samples studied at room temperature is 3.148-3.153 A (for pure molybdenum a = 3.147 A), and there is a tendency for the parameter to grow with increasing concentration of the oxidizing phase. The type II stress and block size D also significantly depend on the concentration of dispersed particles. At concentration wt. 10 % Al2O3 ~30-50 kg/mm2 and D=300-400 A, and at wt. 50 % Al2O3 ~300-400 kg/mm2 and D=30-50 A.
Table 2 shows the results of X-ray phase analysis of Ta-ZrO
2 sample. Only tantalum and zirconium dioxide were also detected in all the samples of this system studied.
Electronographic analysis of the surface of the two-phase Nb-ZrO2 alloy shows that the alloy consists of niobium and zirconium dioxide (table 3). Niobium oxides or other compounds were not detected.
The results of the X-ray phase analysis agree well with the electronography data.
2.3. Thermal Stability
One of the essential requirements to structural materials is thermal stability at high temperatures, the absence of significant grain growth of the structure, which is the key to maintaining high mechanical characteristics at these temperatures.
The study of the thermal stability of two-phase alloys (heterogeneous structures synthesized from unmelted components) is becoming increasingly important due to the increased use of such materials in modern engineering. At present, a significant number of studies on the growth rate of dispersed particles in composite materials have been performed [
18,
19,
20].
The study of thermal stability of the metal-ceramic coatings obtained by us has shown [
3,
4] that they retain their structure during annealing up to temperatures of 1400°С. The study of thermal stability of two-phase metal-ceramic systems was of particular interest, since the microstructure evolution can lead to changes not only in mechanical, but also in electrophysical properties of materials.
From the obtained data extremely high stability of metal-ceramic compositions follows. The size of ceramic particles even after annealing at 1900°C for 5 hours does not exceed 1 μm. While type II stresses are almost completely removed as a result of such heat treatment, type Ш stresses remain significant. The microhardness of metal ceramics decreases with increasing temperature and annealing time, but remains sufficiently high even after annealing at 1900°С (1100-1800 kg/mm2).
The phase composition does not change in the process of annealing. The uniformity of ceramic distribution over the layer thickness does not change as compared to the original samples. In the process of annealing a significant decrease in the grain size of metal-ceramics is observed due to the effect of ceramic particles on the recrystallization process.
Most researchers process the experimental results using formula (1) and draw conclusions about the growth process mechanism during annealing based on the obtained values of п and ΔН
However, often the values obtained in different heat treatment modes refer to different mechanisms, which can lead to incorrect conclusions, so criteria for selecting experimental results referring to a single mechanism are needed.
In composite materials, the growth of dispersed particles can occur by the following mechanisms: 1) growth of a supersaturated solid solution; in this case the number of particles in the system remains unchanged, only their sizes increase. This mechanism may occur if supersaturation of solution is large; 2) coagulation (agglomeration) - association of particles as a whole; 3) coalescence itself - diffusive growth of large particles at the expense of small ones.
Given the very low solubility of refractory oxides in refractory metals, as well as the significant size of dispersed particles (~50 A), it should be assumed that the role of the first two mechanisms is small.
The main mechanism of particle growth in refractory metal-metal oxide systems at high temperatures is coalescence [
19].
The coalescence process may be limited by the following stages: a) dissociation of the oxide on the surface of the smallest particles; b) dissolution of the oxide components in the metal matrix; c) its diffusion in the matrix; d) adsorption and chemical reaction on the surface of large particles.
For each of these stages theoretically obtained expressions for particle growth rate.
Following [
4], we will consider the methods of processing the experimental data on the growth of precipitates during high-temperature annealing and their interpretation based on different models.
To study the growth parameters in the Mo-ZrO
2 system, samples with zirconium dioxide content of 5-30 wt % were annealed in vacuum at temperatures of 1500-1900°C for 1-20 h. The dimensions of zirconia particles were measured from electron microscopic photographs. Since r - the average particle size is a statistical parameter, it is necessary to perform a large number of measurements, processing of which requires the use of a computer. For each sample, 400-500 measurements were taken and processed using statistical methods. Average particle size was determined for each standard in thermal treatment mode by using a computer
and their dispersion
The values of = f (t, T) were processed by the least-squares method using equation (1).
The obtained values of parameters п and ΔН for different samples differing in the initial particle size distribution function and ZrO
2 concentration are presented in
Table 4. The available scatter in values of parameters п ~2 - 4.5 and ΔН ~20 - 100 kcal/mol does not allow making unequivocal conclusions on the mechanism of coalescence process in the system studied.
Let us consider in more detail the processing of experimental data and the interpretation of the results based on some theoretical models. As the initial distribution function we used a narrow Gaussian curve and a lognormal distribution, which is often realized in engineering during milling, crushing, etc., and is therefore quite possible in composite materials obtained by powder metallurgy methods.
The most reasonable regarding coalescence in such systems are the Exner-Fischmeister [
21], Wagner [
22], and Lifshitz-Slezov [
23] models.
The above models differ both in the values of p and ΔH parameters and in the type of the particle size distribution function. In order to process experimental data for any of the models, it is first necessary to establish the closeness of the experimental distribution function to the selected theoretical difference of heights of two neighboring columns, a very large number of measurements (in our case, 8000-10 000 for each sample) is required, which is extremely laborious without automation of the one and only for the points where there is such agreement, to determine п and ΔН.
The easiest way to check the closeness of the experimental distribution to the selected theoretical distribution is to construct histograms. However, in order for statistical fluctuations not to exceed the measurement process.
Comparison of experimental distribution functions with theoretical distributions mentioned above was performed by us on a computer using Pearson's goodness-of-fit criterion (χ
2 criterion) [
24].
The calculations were performed as follows. An ordered sample r containing experimental values r
i was divided into
L intervals with an equal number of points т
i and the function was defined
where
is the probability of finding points in the
i-th interval given by the tested theoretical distribution function
f (х).
If χ2 < (χ2)0 , where (χ2)0 is the table function at a certain confidence probability P, then with probability P we can say that the theoretical distribution function describes the experimental data well.
The results of testing different theoretical models using Pearson's goodness-of-fit test are presented in
Table 5. As can be seen from this table, at no point in the coalescence process can the distribution function be represented by a lognormal distribution. At the initial sites of coalescence, the experimental distribution is close enough to the normal Gaussian distribution. As the particles grow, the distribution function becomes blurred and departs from the normal distribution more and more. This suggests that the formation of dispersed particles during crystallization of the material in our case obeys Gaussian law.
At later stages, coalescence is very well described by the asymptotic Lifshitz-Slezov distribution, and, as can be seen from
Table 5, starting from some point, the process can be described by a single mechanism (u
0=0 corresponds to volume diffusion).
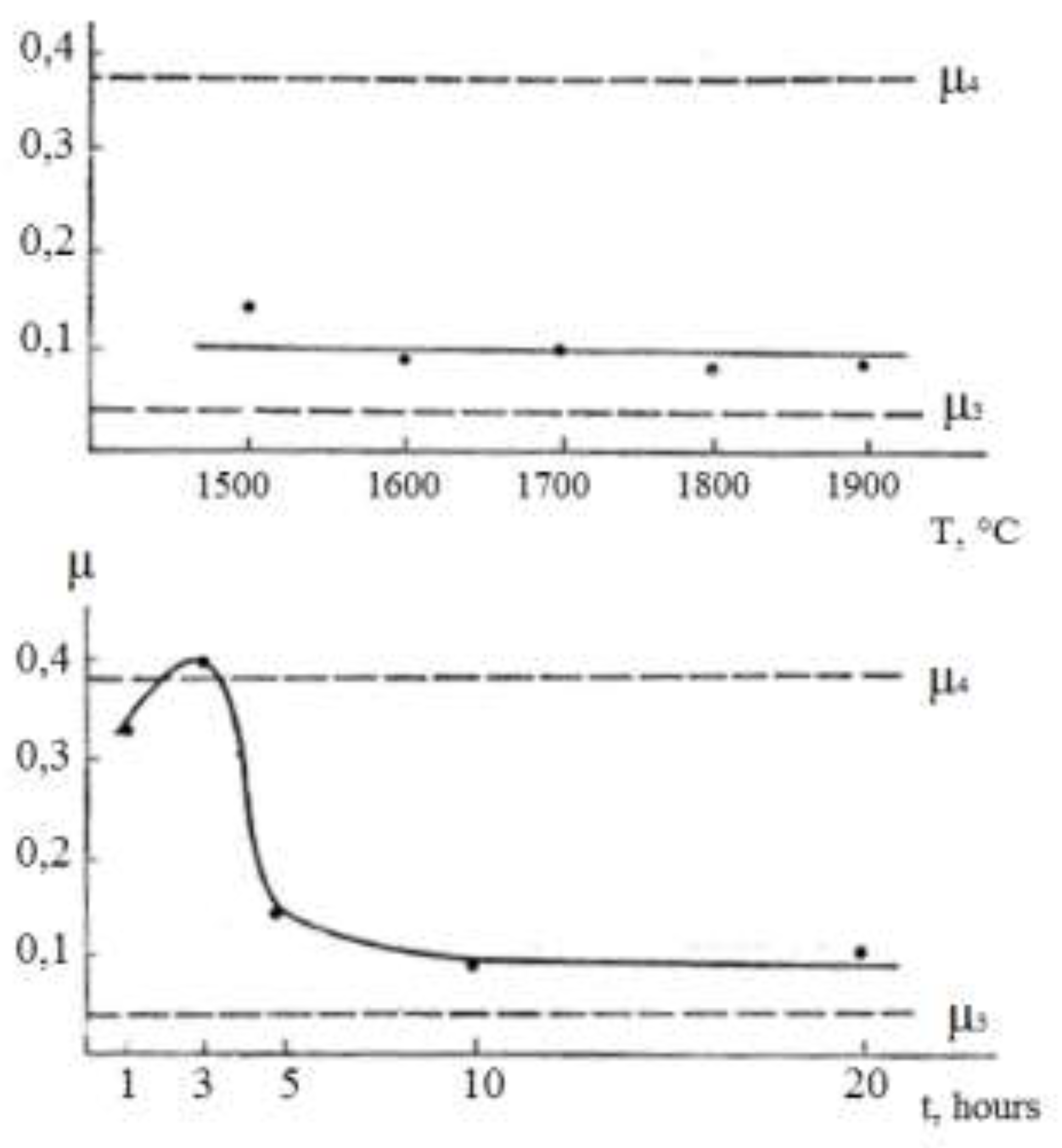
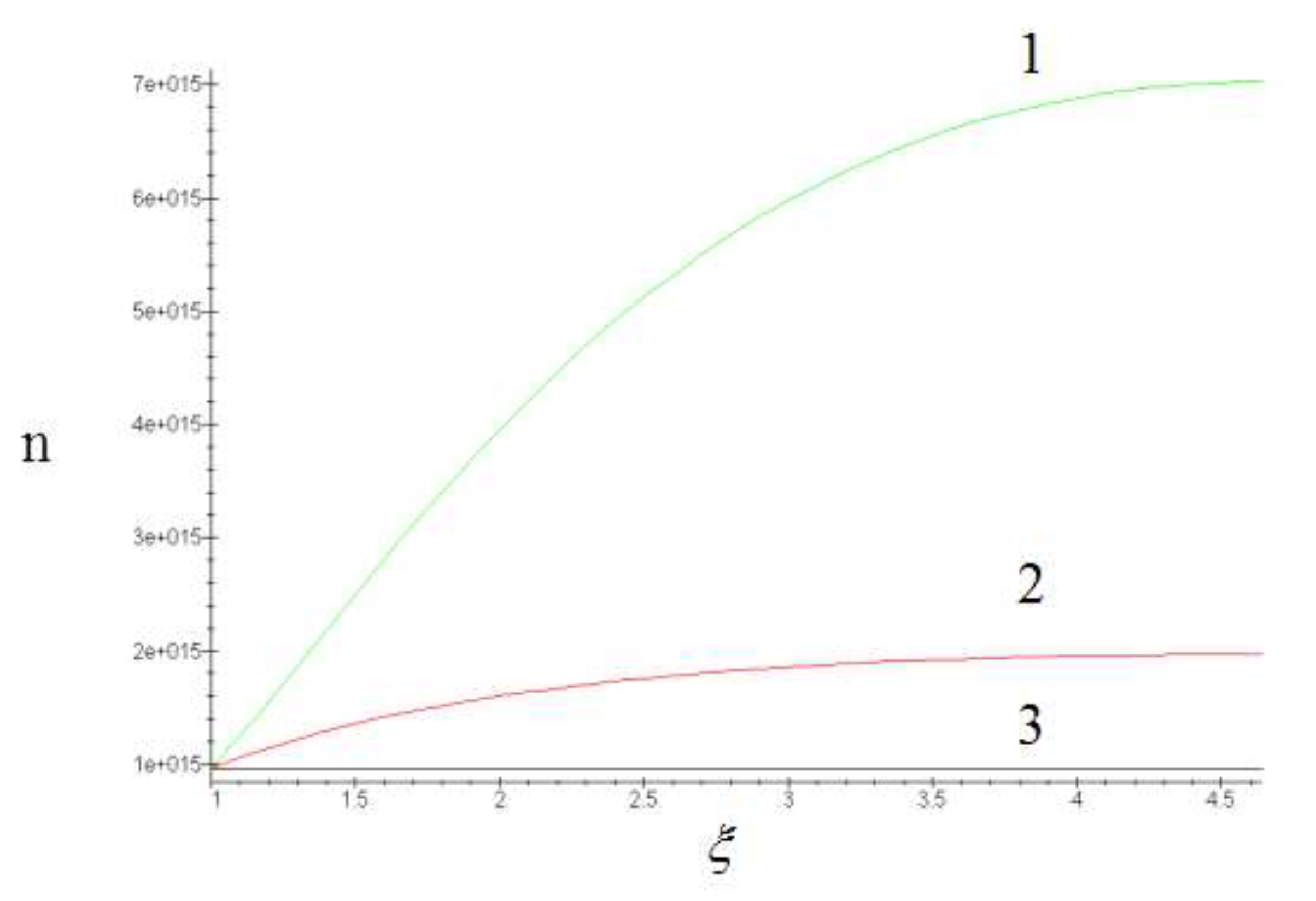
Figure 1a.
Dependence of the variability coefficient µ on temperature (a) and annealing time (b).
Figure 1a.
Dependence of the variability coefficient µ on temperature (a) and annealing time (b).
The theoretical values of the coefficients µ
3 and µ
4 were calculated on a computer.
Only those points that correspond to the same mechanism should be processed by the least-squares method.
It is easier to determine whether different points belong to the same mechanism by examining the behavior of the coefficient of variability µ(T, t) = σ/r. If this coefficient remains constant within a wide range, it indicates that the distribution function is unchangeable.
Figure 1а shows experimental coefficients of variability µ obtained on a computer. As can be seen, not all points correspond to the same coalescence mechanism. Hence, the source of errors in processing the experimental results is clear. If we process all points corresponding to different mechanisms by the method of least squares, we obtain some average values of п and ΔН that do not make any physical sense.
At the same time the least squares processing of points corresponding to one mechanism of coalescence gives п = 3 and ΔН = 56 kcal/mol. The value of p is in very good agreement with the predictions of the Lifshitz-Slezov theory [
23]. The value of ΔН can be compared with the activation energy of zirconium diffusion mass transfer in molybdenum.
2.4. Study of Comprehensive Elastic Deformation in Two-Phase Alloys [5]
If the components of a dispersion-strengthened material, which is a composite in which the second phase particles are distributed in a metallic matrix, have significantly different properties, we can expect that, depending on the elastic properties, thermal expansion coefficients and other material properties of the matrix and dispersed particles, there will be comprehensive elastic deformations in the composite when it cools from the receiving temperature to T0 temperature.
Suppose a composite material obtained at the temperature Tp, in which spherical disperse isotropic particles of the same radius are uniformly distributed in an isotropic matrix, cooled to the temperature T0. When calculating average strains in such a system, one can approximately reduce the problem to calculating strains of an area per one particle, with zero displacement at the boundary of this area. Physically, this is justified by the fact that the median regions are subjected to elimination of all symmetrically arranged particles which compensate each other on average. Under such consideration the rest of the medium is characterized by some averaged values.
The elastic displacements of such a system with different elastic and thermal properties of the matrix and the separations are described by equations
with the following boundary conditions:
where
),
Т
п – Т
0,
,
-- average distance between disperse particles,
--- modulus of elasticity,
-- Poisson's coefficient,
-- coefficient of thermal expansion, I and II refer to the materials of disperse particles and matrix, respectively.
Solving equation (1) with limit conditions (2) - (4), we can calculate the all-round elastic strain:
where
- – is the volume part of dispersed particles. As can be seen from expression (5), if the materials of particles and matrix are such that
and ΔT > 0, in such a system there appears an all-round tensile state. At
and ΔT > 0 in the matrix there is a state of all-round compression. When heating the composition above Tn (ΔT < 0), an all-round tensile state is possible at
. If T
0 is above the plastic deformation temperature of the matrix materials and (or) particles, stress relaxation will lead to a decrease in the all-round elastic deformation.
In the case of a polydisperse particle system, there are local regions of elastic deformation. Naturally, when measuring the local properties of the matrix, it is necessary to take into account the particle size distribution function and heterogeneity of distribution in the volume, but if l means the average distance between particles, the above estimates are also correct for the polydisperse system when compared with the experimental values that are averaged over the volume when measured.
We carried out X-ray studies of "molecular" two-phase alloys Mo-Al
2O
3 and Mo-ZrO
2. For measurements were used samples similar to those used in the study of coalescence in two-phase alloys [
4], where it was shown that in the initial samples the oxide particles distributed in the molybdenum matrix are 50A in size.
High-temperature X-ray studies of two-phase alloys were carried out using a high-temperature diffractometer attachment that allowed the determination of thermal expansion coefficients in the temperature range 20-1500°C in a vacuum of 2·10-4 mmHg method without using a standard with alignment of the X-ray beam relative to the sample plane before each new measurement.
Judging by the temperature dependences of the lattice parameters of molybdenum in the compositions Mo- Al2O3 and Mo- ZrO2, at all temperatures studied the lattice parameter of the composite material molybdenum matrix is higher than that for pure molybdenum,
The increase in the interplanar distances indicates the presence of all-round tensile stresses in the molybdenum matrix at temperatures 293-1473K. Significant distortions of type III (~0.2-0.4 Å) characterize the mixing of atoms from positions corresponding to the lattice symmetry, and changes in the electron density distribution.
At temperatures of 2073K the lattice parameter of molybdenum in the two-phase alloy approaches to that of pure molybdenum. Thermal expansion of molybdenum in two-phase alloys differs by significantly higher value of KTR in the temperature range 573-1073K (
=6.8-10
-6 deg
-1 (573-1073K in Mo- Al
2O
3),
=6.3-10
-6 deg
-1 (573-1073K in Mo-ZrO
2). For comparison,
= 5.2-10
-6 deg
-1,
= 9.0-10
-6 deg
-1 (273-1273K [
25],
= 8.7-10
-6 deg
-1 (273-1273K [
25].
In the region of temperatures 1073-1273K an anomalous change of KTR is observed, and KTR at these temperatures is less than that of pure molybdenum.
It is likely that such deviations are caused by a change in the electronic structure of molybdenum under the action of highly dispersed particles.
Similar results obtained in high-temperature X-ray studies of Nb-ZrO2 alloys show that up to 1373K niobium is in a tensile state. Comparison of the lattice parameter of the matrix in the Nb-ZrO2 alloy (a=3.425 A) with the lattice parameter of pure niobium (a=3.295 A) shows that the matrix is in a state of strong all-round stretching.
This circumstance can be further used in obtaining gradient coatings to harmonize the properties of the base and coating.
Dispersed particles have a strong influence on the structure of molybdenum, which is manifested by an increase in lattice parameters, a decrease in block sizes and the presence of significant distortions of type II and III, as evidenced by the blurring of diffraction maxima and a decrease in the intensity of second-order reflection lines.
The lattice parameter of molybdenum in the samples studied at room temperature is 3.148-3.153 A (for pure molybdenum a = 3.147 A). The type II stress and block size D also significantly depend on the concentration of dispersed particles. Thus, at a weight concentration of 10 % Al2O3 ~ 30-50 kg/mm2 and D=300-400A, and at a weight concentration of 50 % Al2O3 ~300-400 kg/mm2 and D=30-50A.
The increase in the interplanar distances indicates the presence of tensile stresses in the molybdenum matrix. Significant distortions of type III (~0.2-0.4 Å) characterize the displacement of atoms from positions corresponding to the lattice symmetry and a change in the electron density distribution.
Two-phase Mo-SiO2 alloys were investigated at room temperature. The lattice parameter of molybdenum in such alloys is 3.139-3.146 Å, i.e. the molybdenum matrix is in an all-round compressed state, which is in a good agreement with equation (5).
At all investigated temperatures the lattice parameter of the molybdenum matrix of the composite material is higher than that of pure molybdenum, which indicates the presence of all-round stretching in the molybdenum matrix at temperatures 300-1473K. At 2073K the lattice parameter of molybdenum in the two-phase alloy approaches that of pure molybdenum. Thermal expansion of molybdenum in two-phase alloys differs by significantly higher value of KTR in the temperature range 573-1073K (=6,8·10-6 deg-1 (573-1073K in Mo-Al2O3), = 6,3·10-6 deg-1 (573-1073K in Mo-ZrO2). For comparison (=5,2·10-6 deg-1, = 9,0·10-6 deg-1 (273-1273K, = 8,7·10-6 deg-1 (273-1273K). In the region of temperatures 1073 - 1273K an anomalous change of KTR is observed, and KTR at these temperatures is less than that of pure molybdenum.
When cooling the material, the temperature dependence of the lattice parameter remains approximately the same as when heated, but at room temperature the parameter increases slightly. Repeated heating leads to a shift of the area of anomalous changes in the LTR in the direction of lower temperatures. Up to the temperatures of 1073K a non-uniform increase in the molybdenum lattice parameter depending on the crystallographic directions was observed, which, apparently, was connected with the distortion of the molybdenum lattice symmetry. At temperatures of 1073-1273K there are anomalies in the change of distortions of type II and block size. Probably, such deviations are caused by the change of electronic structure of molybdenum under the action of highly dispersed particles or by the blocking of molybdenum grains by the oxide phase. The presence in the matrix of a comprehensive tensile stress of sufficient magnitude can lead to an electronic phase transition, such as the Adler type [
26], which causes the restructuring of the electronic spectrum.
It is known that such large all-round elastic deformations are not observed when similar composite materials are obtained by powder metallurgy methods. This is probably due to the greater friability of the separation-matrix boundaries in such materials, which causes a partial relaxation of the arising thermal stresses. In addition, a much larger particle size apparently leads to a much greater relaxation of stress by dislocation loop disruption. It is possible that comprehensive elastic deformations exist in such materials, but their magnitude due to relaxation by the above mechanisms is insufficient for a radical rearrangement of the electronic spectrum.
2.5. Electrophysical Properties of Metal-Ceramic Materials
As already noted, due to the high degree of dispersion of ceramic particles "molecular" two-phase alloys can have a number of interesting properties. In this section we present some results on the measurement of electrical conductivity and thermal emf of two-phase alloys [
27,
28].
Measurements of electrical conductivity of samples in the form of coatings on a molybdenum substrate were made by the usual two-probe method at temperatures 295...1873K in vacuum at a pressure of 10-4 Pa. The electrical conductivity of tube samples obtained by coating deposition on a tube followed by full etching of the substrate in acid was measured by the four-probe method.
Thermo-eds were measured on a semi-automatic thermo-eds recorder by resonance extraction of a useful signal followed by synchronous detection [
29].
When measuring the thermo-EDs at high temperatures, great difficulties arise due to the need to separate the useful signal from the interference created by the furnace powered by alternating current. This is especially felt when measuring small thermo-eds of high-resistance materials. We have developed a scheme that allows to largely eliminate these disadvantages [
29]. In the presence of calibrated thermocouples, very small temperature differences can be measured with this method. Processing of measurement results was performed using a computer. Performed measurements of thermal emfs of monocrystalline and polycrystalline molybdenum are in good agreement with the literature data.
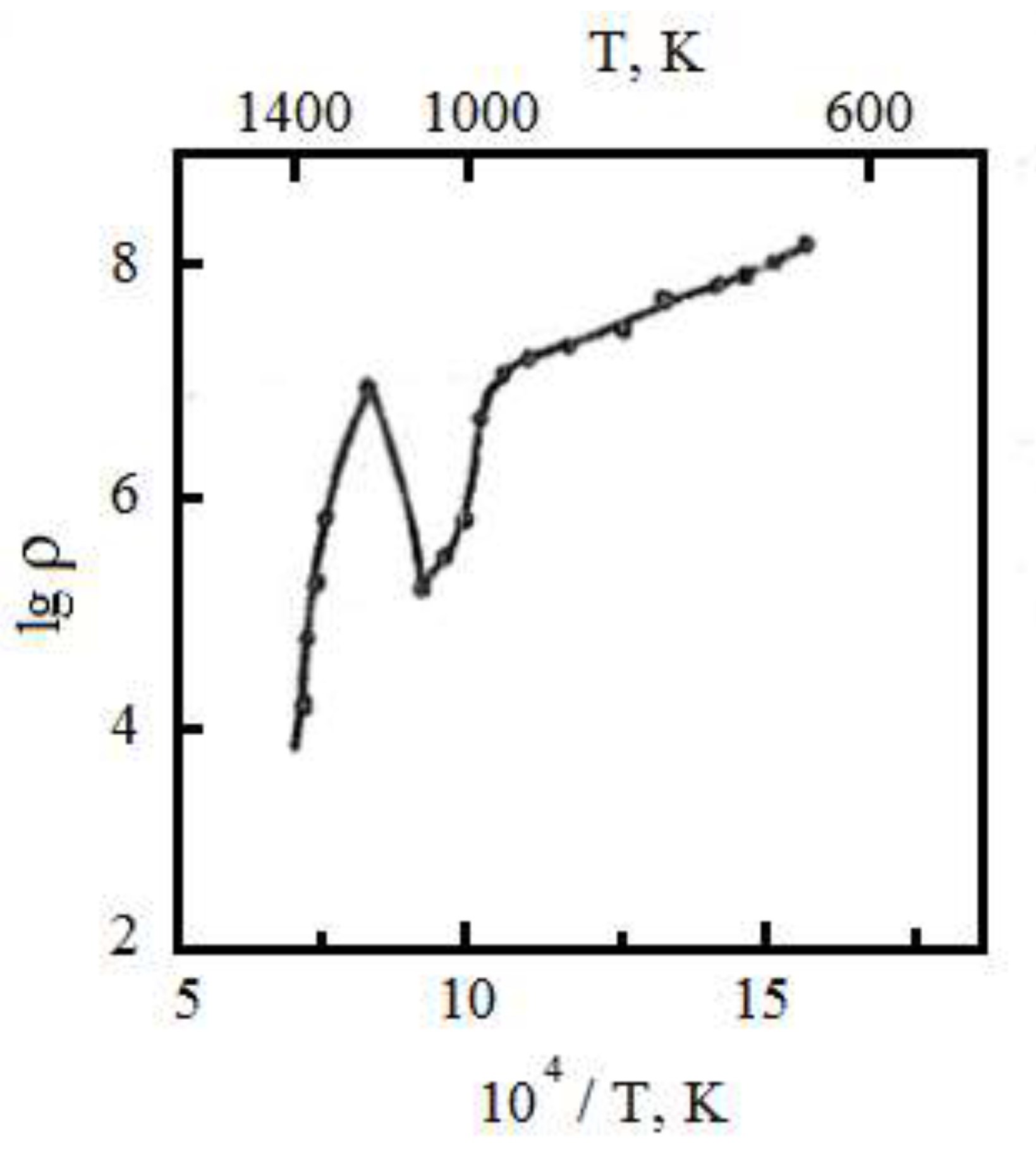
Conducted measurements of temperature dependences of the resistivity of samples Mo-ZrO2 showed that with increasing temperature in the range of 300-1000K resistivity of different samples decreases exponentially with a bandgap width E = 2-3 eV.
At temperatures of 700-750°C a sharper drop in resistivity was observed (the width of the forbidden zone E = 0.1-0.3 eV). A further increase in temperature from 1000 to 1273K leads to an increase in the resistivity of the alloy, reaching for some samples 2-4 orders of magnitude. For this temperature interval the presence of large jumps in the value of electrical resistance is characteristic. At higher temperatures the resistivity decreases monotonically again.
Figure 2 shows the temperature dependence of the logarithm of resistivity of the Mo-ZrO
2 alloy. At 295K the resistivity of different samples with ceramic content of 10...30 wt.% is 10
9...10
14 0m-cm.
With increase in temperature in the interval 295...973K the resistivity exhibits semiconductor character with the band gap width ΔE = 2...3 eV. At temperatures 973...1023K a sharper decrease of resistance is observed (ΔE = 0.1...0.3 eV). Further increase in temperature from 1023 to 1273K leads to increase in resistivity of two-phase alloys, reaching for some samples 2...4 orders of magnitude.
For this temperature interval the presence of large jumps in the value of electrical resistance is characteristic. At higher temperatures the resistivity again monotonically decreases and at 1873K is 103...102 0m·cm.
The resistivity of the studied materials is affected by the concentration of the oxide component and the degree of dispersion of the second phase particles. At low oxide concentrations, the resistance is metallic in nature, while at concentrations of 8...10 wt. % a sharp transition to semiconductor properties is observed. Obviously, it is connected with that at such maintenance of the ceramic component all-round deformations in a matrix reach the value sufficient for rearrangement of an electronic spectrum of a matrix that leads to change of electrophysical properties of the disperse-strengthened two-phase alloys.
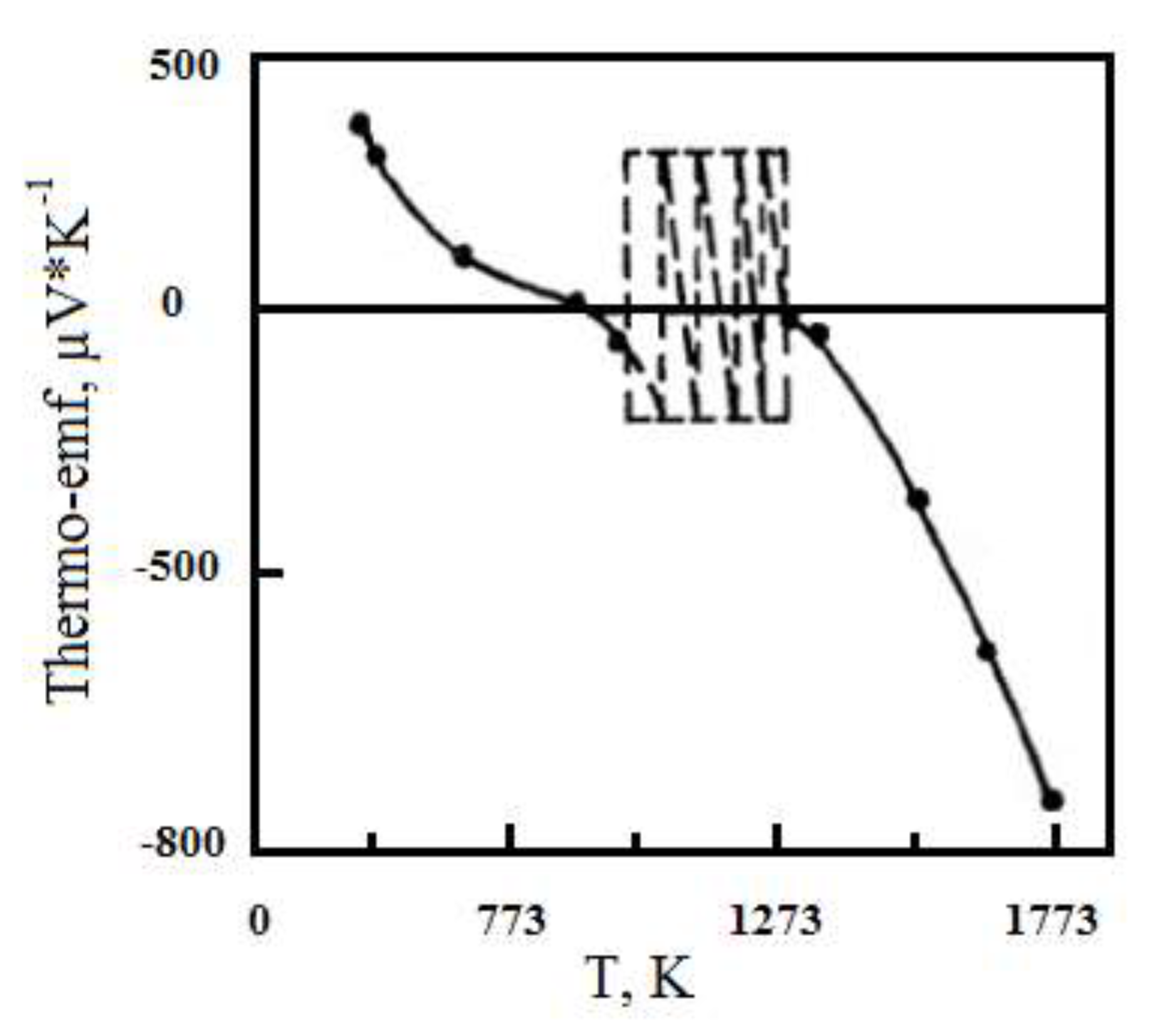
The thermo-edf measurements of Mo-ZrO
2 alloys (
Figure 3) show that in the temperature range of 750-1000°С there is a significant instability of thermo-EDs in magnitude and sign. At temperatures above 1273K thermo-edf increases monotonically, reaching the value E = -900 mV/deg at 1700K. The region of thermo-edf instability correlates well with the region of anomalous changes in resistivity. Especially clearly this correlation is traced at simultaneous measurement of thermo-edf and electric resistance (temperature difference between hot and cold ends of the sample was - 0.1-0.5 degrees).
When the temperature decreases, the course of resistivity and thermo-edf does not repeat the temperature dependence obtained when the temperature rises. In all investigated samples a "hysteresis loop" is observed, that is, as the temperature decreases, the resistivity slowly increases monotonically up to the temperature of 673...773K, where there is a sharp increase in resistance by 3-4 orders of magnitude.
In addition, it was found that repeated heating of the samples to high temperatures leads to a shift of the lattice instability area towards lower temperatures, which is confirmed by measurements of electrical resistance, thermal emfs and the data of high-temperature X-ray radiography.
On the same samples were carried out X-ray high-temperature studies similar to those carried out on similar two-phase alloys in [
5]. It was found that just in this temperature range observed kinks in the temperature dependence curve of the lattice parameter of the metal matrix, jump of the linear expansion coefficient (for example, in the temperature range 573...1073K α
Mo = 6.8•10
-6 deg
-1 in the alloy Mo-Al
2O
3, and in the alloy Mo-ZrO
2 α
Mo = 6.3•10
-6 deg
-1), anomalies in the change in distortions of type II and block size, indicating the course of the phase transition. Observed significant distortions of type III
~ 0.2...0.4 A) testify to the displacement of atoms from the positions corresponding to the lattice symmetry, and the change in the electron density distribution, which can lead to the electronic phase transition, for example Adler type [
30].
This is probably due to a partial relaxation of all-round elastic deformations as well as to a change in the particle size distribution function due to the coalescence process during high-temperature annealing.
Similar patterns in the behavior of resistivity, thermal emfs, and thermal expansion coefficient are typical not only for Mo-ZrO2 samples, but also for other studied Mo-Al2O3, W-ZrO2, and W-Al2O3 systems.
It allows to assume that the observed features of changes in electrical resistance and thermo-edf of the investigated two-phase alloys are caused by a high degree of dispersion of ceramic particles, which leads to a comprehensive deformation of the matrix material and changes in its electronic structure.