1. Introduction
Meat is an indispensable part of the human diet, offering a rich array of nutrients including proteins, lipids, trace elements, and minerals that are essential for human health and well-being [
1]. China holds a prominent position in the global meat industry, leading the world in both meat production and consumption [
2]. As the living standards in the nation rise, there is an increasing demand for high-quality meat that is not only nutritious but also safe for consumption. This heightened awareness has made the quality control of meat products a critical concern for both consumers and producers.
The tenderness of meat is a pivotal attribute that significantly influences the eating experience and is often the primary criterion used by consumers to assess meat quality. Tenderness encompasses the resistance of meat to shearing forces and its overall texture, which is influenced by factors such as the cross-linking of connective tissues, interactions between muscle protein molecules, water content, and collagen levels [
3,
4,
5]. The post-slaughter biochemical processes that muscles undergo can dramatically alter the tissue's conditions, thereby impacting the meat's quality. These changes can adversely affect consumer interests and the reputation of meat enterprises, underscoring the importance of rapid and accurate tenderness assessment in ensuring the quality and safety of meat products [
6,
7,
8].
Current methods for assessing meat tenderness include traditional and rapid non-destructive testing approaches. Traditional testing methods, such as shear force and chemical analyses, are often time-consuming and can result in sample damage, posing challenges in meeting the demands of modern, high-throughput production environments. In contrast, improved rapid non-destructive testing techniques that leverage spectroscopy, electrical, and magnetic properties have been developed to enable swift and accurate assessments without compromising the samples’ inherent physical and chemical properties. These advancements have significantly enhanced detection efficiency, reduced costs, and expanded the scope of their application in the rapid quality assessment of meat products [
9,
10,
11,
12].
This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the recent advancements in rapid and non-destructive detection techniques for meat tenderness. It will explore the application of these techniques in various contexts, discuss the limitations and challenges associated with their use, and highlight the potential for overcoming these obstacles. By doing so, the paper seeks to offer valuable insights and inspiration for the further development and application of these cutting-edge technologies in the field of meat quality assessment. Through this examination, the paper aspires to contribute to the continuous improvement and innovation in China's meat production and processing industry, ultimately enhancing the quality and safety of meat products for consumers.
2. Application Progress of Rapid Non-Destructive Detection Technologies for Meat Tenderness
Rapid non-destructive testing technology has emerged as a cutting-edge approach in modern analytical techniques, employing sophisticated instruments to evaluate the external features and internal composition of samples without causing any damage. This innovative method harnesses the inherent properties of the materials being tested, such as optical, acoustic, and electromagnetic characteristics, to gain insights into the physical, mechanical, and structural attributes of the samples. The technology draws upon a diverse array of disciplines, including acoustics, optics, electrical engineering, thermodynamics, and magnetism, among others [
13,
14,
15].
The utilization of advanced techniques such as near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, hyperspectral imaging (HSI), Raman spectroscopy, airflow-optical fusion detection, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology [
16,
17,
18] has revolutionized the way samples are analyzed. These methods offer a robust and versatile toolkit for non-invasive assessment, providing detailed information about the sample's properties and composition. The rapid non-destructive testing technology stands out for its comprehensive capabilities, offering a wide range of applications across various industries. In the context of meat and meat products, this technology presents enormous potential for development. It enables the accurate assessment of key quality parameters such as tenderness, freshness, and composition, without the need for labor-intensive and time-consuming traditional methods. The adoption of these technologies in the meat industry is poised to bring about significant improvements in efficiency, safety, and quality control. By providing detailed and precise information about the internal structure and composition of meat products, these non-destructive techniques can enhance the overall quality assurance processes, ensuring that consumers receive high-quality and safe products. In this paper, we aim to explore the recent advancements and applications of rapid non-destructive testing technology in the field of meat and meat products. We will delve into the specific techniques of NIR spectroscopy, HSI, Raman spectroscopy, airflow-optical fusion detection, and NMR technology, discussing their strengths, limitations, and potential areas for future development. By examining these technologies, we hope to shed light on their transformative potential in enhancing the quality, safety, and overall value of meat products, paving the way for innovative and sustainable practices in the industry.
2.1. Spectroscopy Technology
Spectroscopic detection is an analytical method utilized to identify physical properties and determine chemical composition based on the unique spectrum of a substance. It operates on the fundamental principle of analyzing characteristic wavelengths and intensities of light absorption, emission, or scattering to ascertain the chemical composition and material structure. This interaction between light and matter varies with wavelength, with different substances exhibiting distinct behaviors in terms of light absorption, emission, or scattering across various wavelength regions [
19]. Given the intricate composition of meat products, assessing their quality presents significant challenges. However, spectral detection technology's inherent characteristics adeptly address this challenge, rendering it a widely adopted method in meat quality assessment.
2.1.1. NIR Spectroscopy
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, spanning from 700 ~ 2500 nm (14286 ~ 4000 cm
-1), lies between ultraviolet visible light (UV Vis) and mid-infrared light (MIR). It delineates short-wave (700 ~ 1100 nm) and long-wave (1100 cm
-1 to 2500 nm) NIR regions [
20]. Operating on the principle of molecular vibration transitions, NIR spectroscopy records frequency doubling and combined absorption, mainly of hydrogen-containing group vibrations (X-H, where X=C, N, O). This analytical method measures substance absorption, reflection, or transmission within the NIR range, facilitating precise determination of molecular structure and compound identification [
21,
22,
23]. Due to its capability to discern hydrocarbon organic substance composition and properties, NIR spectroscopy is well-suited for various applications.
In tenderness detection of meat products, NIR spectroscopy coupled with successive projection algorithm (SPA) has yielded promising results. By scanning wavelengths between 900 and 1800 nm, raw data is preprocessed using multivariate scattering correction (MSC) and modeled using partial least squares (PLS). This approach achieved a prediction accuracy of 0.96329, demonstrating the feasibility of non-destructive meat tenderness testing [
24]. Furthermore, NIR spectroscopy has been leveraged for moisture content detection in pork, achieving a model prediction accuracy of 90.48% [
25]. These findings underscore NIR spectroscopy's potential in developing portable non-destructive testing equipment for tenderness evaluation.
Integrating NIR reflectance spectroscopy with visible light, Balage et al. attempted pork tenderness detection. Although achieving a prediction accuracy of 78%, challenges arose possibly due to sample composition variations impacting light scattering effects [
26]. Similarly, Wyrwisz et al. developed an online meat tenderness measurement system using NIR spectroscopy combined with fiber optic systems. Despite efforts, model accuracy remained a concern, with occasional RPD values surpassing 2 [
27]. Nonetheless, stepwise regression in the MLR method exhibited promising results, hinting at NIR spectroscopy's adaptability with different algorithms and instruments for enhanced detection [
28].
However, NIR spectroscopy's indirect nature necessitates extensive experimental samples for model establishment, impacting calibration model applicability and data accuracy. The efficacy of calibration models and econometric method selection critically influences analysis outcomes. Moreover, NIR spectroscopy is ill-suited for analyzing dispersed samples with frequent variations. Therefore, the paramount objective in NIR spectroscopy development is establishing universal, representative calibration models to ensure data accuracy.
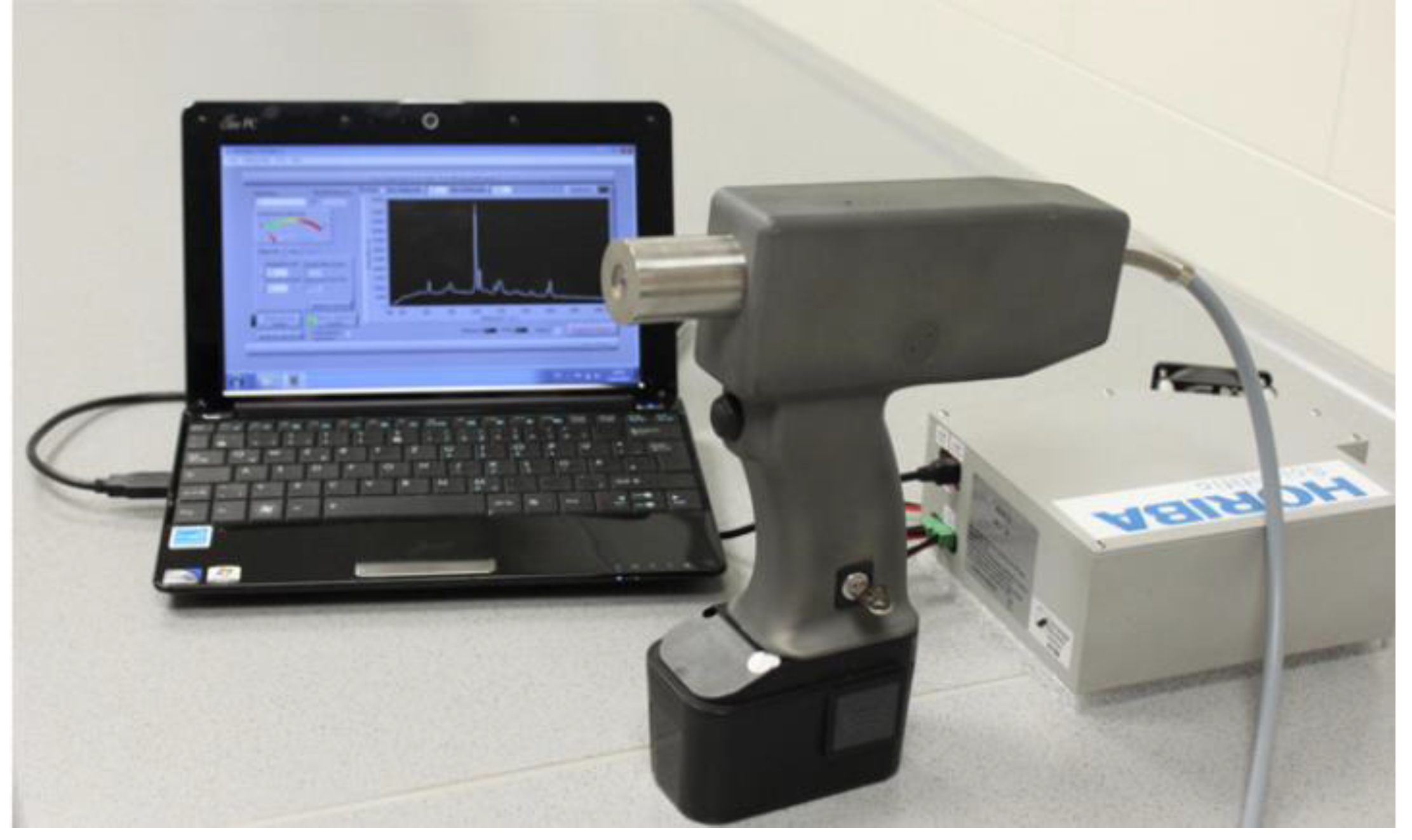
Figure 1.
Working principle diagrams of detection device. This figure shows the main structure of the device. Note: 1. Spectral acquisition unit; 2. Distance measuring unit; 3. Sample placement table; 4. Sample transmission unit.
Figure 1.
Working principle diagrams of detection device. This figure shows the main structure of the device. Note: 1. Spectral acquisition unit; 2. Distance measuring unit; 3. Sample placement table; 4. Sample transmission unit.
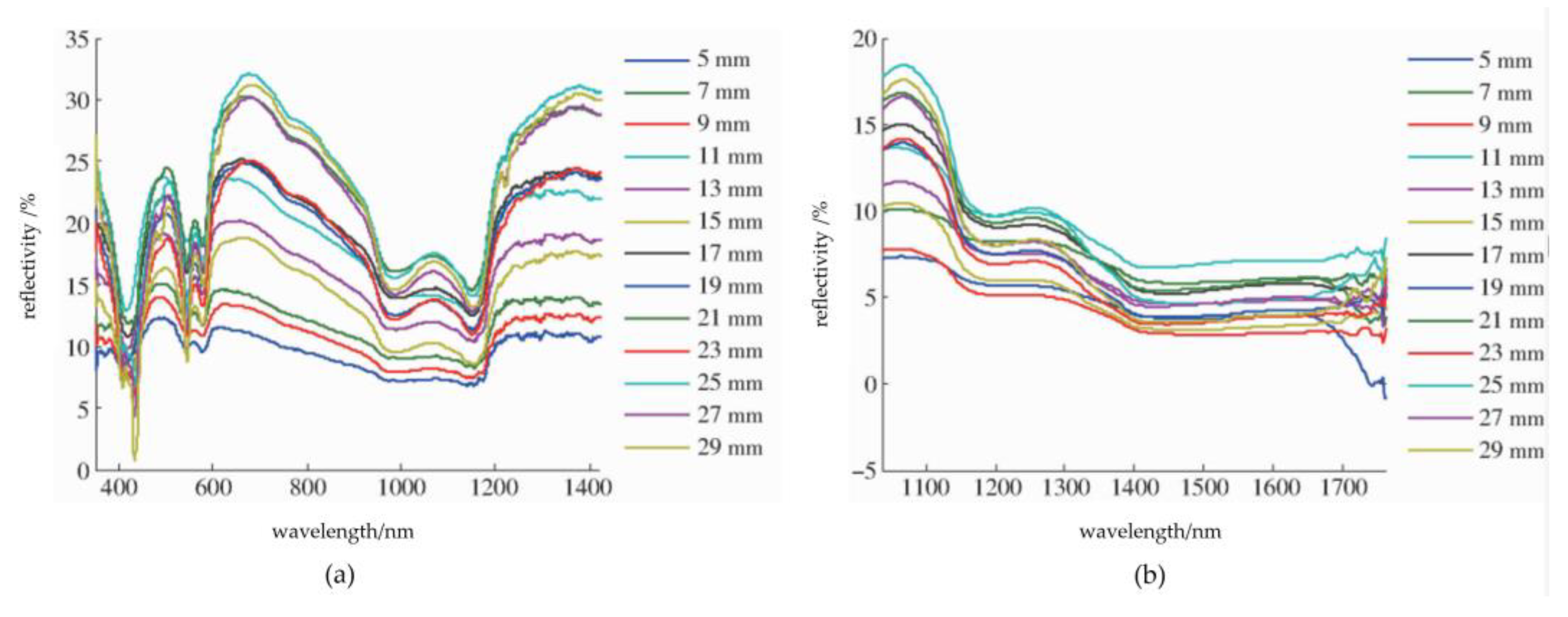
Figure 2.
Original spectrum at different distances of the first band and second band. This figure shows the analysis process of the raw data. Note: (a). First band; (b). Second band.
Figure 2.
Original spectrum at different distances of the first band and second band. This figure shows the analysis process of the raw data. Note: (a). First band; (b). Second band.
2.1.2. HSI Technology
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) is an innovative non-destructive testing technology that seamlessly integrates spectroscopy, information processing, and computer vision techniques. This advanced technology is characterized by its unique "Image Spectral Integration," which enables simultaneous acquisition of both imaging and spectral data from the test samples without the need for any sample damage or preprocessing. Its benefits include high analytical efficiency, straightforward operation, and cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred choice for various applications [
29,
30].
The versatility of HSI technology allows for a comprehensive assessment of meat product quality. By leveraging imaging technology, it can detect external features of meat products, while spectral technology reveals internal quality and food safety information. This dual capability facilitates an in-depth evaluation of meat tenderness, establishing HSI as a reliable and user-friendly non-destructive testing method [
31,
32]. Numerous scholars worldwide have employed HSI for assessing meat tenderness, utilizing the results to evaluate the overall quality of meat products comprehensively.
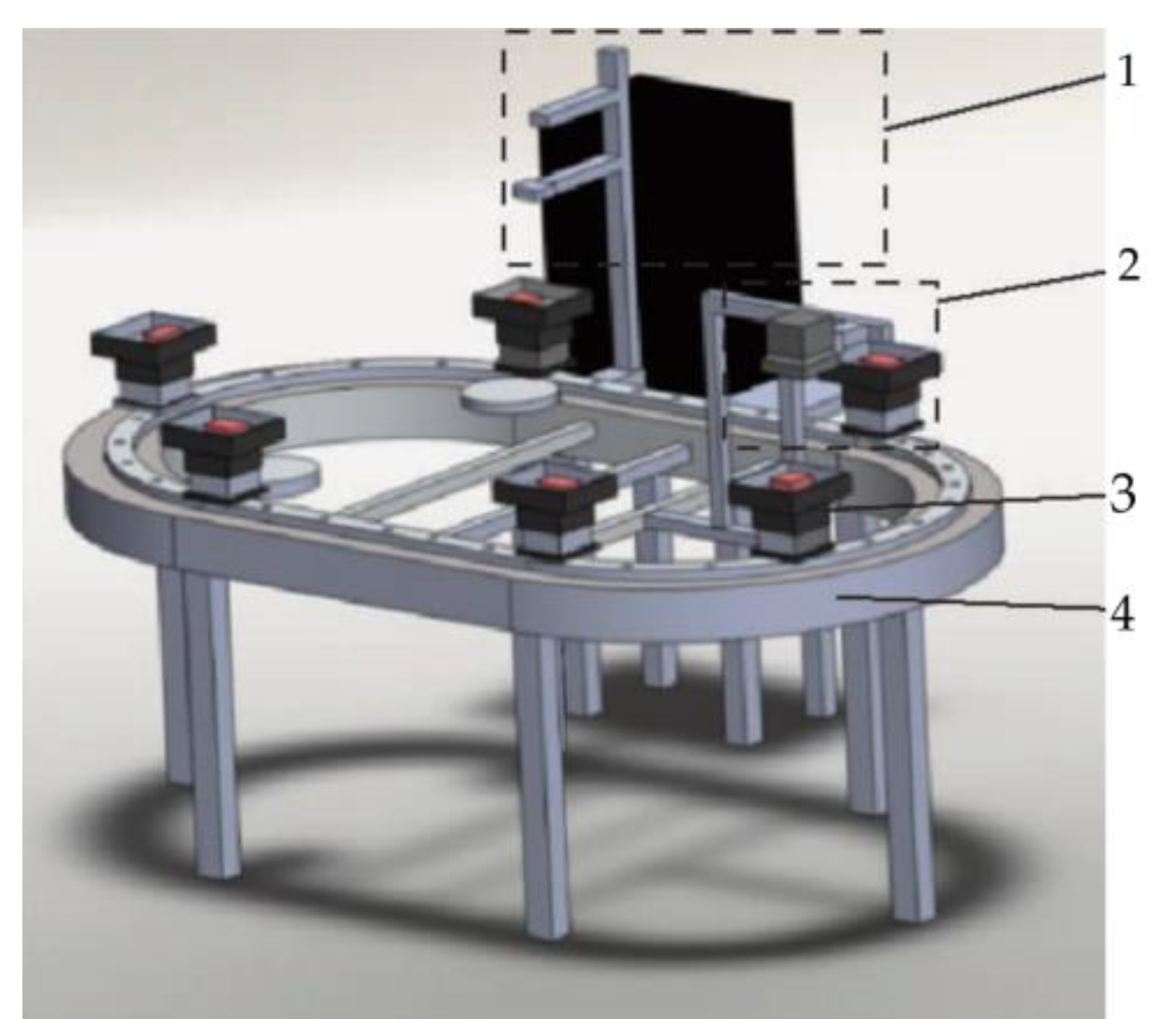
In previous studies, HSI technology has been effectively utilized for rapid tenderness assessment of beef. The configured HSI system, as depicted in
Figure 3, gathers data from samples and employs an enhanced Lorentz function to fit the light scattering curves at various wavelengths. By integrating Principal Component Analysis (PCA), a linear discriminant model is formulated, achieving a prediction accuracy of 75% in the validation set. Intriguingly, the presence of fat spots was found to have negligible impact on tenderness prediction accuracy when a larger diameter incident beam was used on whole steaks, highlighting a marked enhancement in system robustness [
33].
Balage et al. explored the application of HSI for evaluating beef tenderness, utilizing a hyperspectral camera to scan samples across the 928 ~ 2524 nm spectrum with a spectral resolution of 6.3 nm and a spatial resolution of 10 μm. They applied Partial Least Squares combined with Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) for data processing and analysis, developing both local and full sample models. The findings indicated that local models, with a 72% accuracy rate, were more effective in discerning beef tenderness, underscoring the importance of clearly defining HSI application objectives to establish more accurate and robust models [
34].
Zhao et al. established a robust connection between models and samples by extracting reflective spectral information from the samples. They employed a stepwise regression algorithm coupled with a Genetic Algorithm (GA) to identify the characteristic bands associated with the Warner-Bratzler Shear Force (WBSF) value of beef. Furthermore, they utilized PCA to extract three principal components from the samples and developed tenderness level discrimination models based on Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). The study revealed that the PCA-based prediction model outperformed the feature band image model, with the LDA model exhibiting higher recognition accuracy than the SVM model, achieving a discrimination accuracy of 94.44% [
35]. This research offers valuable insights for analyzing the distribution of quality characteristics in whole beef samples and for evaluating beef tenderness comprehensively.
Studies leveraging HSI technology's "Image Spectral Integration" have also been conducted on Ningxia Tan sheep meat. A hyperspectral system captured 128 images of Tan sheep meat within the 400 ~ 1000 nm range. The original spectra, when combined with the Savitzky-Golay (SG) convolutional smoothing preprocessing method, facilitated the extraction of nine characteristic wavelengths. Both Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) and Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) were employed for modeling and analysis. The results indicated that the PLSR model, which integrated feature wavelengths and surface fat distribution image features for predicting lamb tenderness, demonstrated superior predictive performance, with a correlation coefficient of 0.89 in the prediction set [
36]. This study provides a theoretical foundation for the effective application of hyperspectral technology in lamb tenderness detection.
Recognizing the impact of refrigeration on meat product tenderness, Wang et al. utilized HSI technology to conduct non-destructive tenderness testing on chicken samples that had been refrigerated for 0 ~ 6 days. The spectral scanning range was 900 ~ 1700 nm. After acquiring the raw data, SG convolutional smoothing and baseline correction were applied for data preprocessing. A detection model was established using PLSR, and it was observed that the model, post-SG preprocessing of spectral data, exhibited the best predictive performance, with a correlation coefficient of 0.94 in the prediction set [
37]. This research offers a novel approach for meat product enterprises to rapidly measure tenderness and evaluate product quality during the production process, showcasing significant practical application potential.
Yu et al. designed a hyperspectral image acquisition system for the rapid and non-destructive detection of cold and fresh lamb meat tenderness. They employed Minimum Spanning Tree (MSC) for spectral data preprocessing and combined PCA with Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) to extract image feature information. Both Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) and SVM logarithmic data were utilized for modeling and analysis. The study found that the BPNN model provided better predictive performance than SVM, with a correlation coefficient of 0.85 in the prediction set [
38]. This research serves as a reference for researchers aiming to design portable or miniaturized hyperspectral non-destructive testing instruments for lamb tenderness.
Optimization of algorithms and enhancement of models are crucial for advancing non-destructive testing technology in HSI. A study predicting lamb meat tenderness without damage used hyperspectral and chemometric methods. Hyperspectral spectra of lamb meat were collected across two bands, 400 ~ 1000 nm and 900 ~ 1700 nm, with the original spectral data in both bands preprocessed using MSC, de rendering, baseline, SNV, normalization, and SG. SPA, Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling (CARS), and Variable Combination Population Analysis (VCPA) were used, with the Interval Variable Iterative Space Shrink Approach (IVISSA) optimizing feature wavelengths for preprocessed data. Models were developed using the PLSR algorithm, and various numerical values were compared. The study found that the OS-IVISSA-PLSSR tenderness prediction model had the highest predictive performance index, with a correlation coefficient of 0.79 for the prediction set [
39]. This outcome demonstrates that model optimization can significantly reduce computational operations, enhance detection efficiency, and improve model accuracy and stability, ultimately increasing detection precision.
HSI technology excels at capturing fine spectral features of samples and can be paired with various models for multi-indicator detection, tailored to specific application scenarios. However, several challenges remain. Firstly, HSI is susceptible to environmental factors such as lighting, shadows, and climatic conditions, which can alter the spectral signatures of samples. Secondly, the high spectral dimensionality and data redundancy complicate calculations, leading to the confusion of normal spectra, background content, and abnormal spectra, potentially distorting content. Additionally, the significant storage space required for image data poses logistical challenges.
To address these issues, future developments in HSI non-destructive testing technology should focus on upgrading hardware, refining detection model accuracy and robustness, reducing spectral dimensions, and simplifying data and calculations. These advancements will further enhance the practicality and effectiveness of HSI technology in diverse applications.
2.1.3. Raman Spectroscopy Technology
Raman spectroscopy is a sophisticated light scattering technique that provides a wealth of information about a sample's chemical composition and structure. This technique operates by exposing a sample to high-intensity incident light from a laser source, which results in two types of scattering: elastic and inelastic. Both of these scattering phenomena are collectively known as Raman scattering. The resulting Raman spectrum, which is based on the interaction between light and the chemical bonds within the material, is typically composed of multiple Raman peaks. Each peak corresponds to a specific wavelength position and intensity of the Raman scattered light [
40,
41]. These peaks offer researchers valuable insights into the sample, such as chemical structure identification, pH value determination, assessment of sample crystallinity, shear force measurement, and detection of impurities, making Raman spectroscopy a versatile analytical tool [
42,
43,
44]. The non-destructive nature of Raman spectroscopy, characterized by its straightforward operation, rapid measurement time, high sensitivity, and the ability to analyze samples without causing damage, ensures its development prospects remain stable and ever-improving.
Capitalizing on the strengths of Raman spectroscopy, numerous scholars worldwide have explored its application in non-destructive testing for meat tenderness. As far back as 2004, researchers utilized Raman spectroscopy to investigate how proteins reflect the tenderness of beef. They designed and implemented a Raman spectroscopy-based non-destructive detection system, discovering that the ratio of α-helix to β-sheet structures in proteins and the hydrophobicity of muscle fibers are critical factors influencing beef tenderness. By employing the Partial Least Squares (PLS) algorithm for spectral data analysis, a strong correlation between Raman spectral data and beef tenderness was established, with an R
2 value of 0.65 [
45]. This finding underscores the significant potential of Raman spectroscopy in predicting meat tenderness.
Bauer et al. employed a 671nm Raman system to non-destructively test beef tenderness. They scanned spectral data in the 340 ~ 2100 cm
-1 range and preprocessed the data using Extended Multiplication Scattering Correction (EMSC). They then constructed a prediction model based on PLSR and PLS-DA algorithms. The PLS-DA model demonstrated the highest accuracy, reaching 80%, with classification accuracy improving as the set threshold increased [
46]. This outcome confirms the feasibility of developing Raman spectroscopy-based non-destructive testing equipment for meat tenderness and offers valuable insights for researchers in equipment development.
Building upon the handheld Raman microprobe, a lamb tenderness data collection system was designed, as illustrated in
Figure 4. Savitzky-Golay (SG) smoothing was used for spectral data preprocessing, while PLS was applied for modeling and analysis. The model fitting revealed a strong correlation between the Raman spectra generated by the detection and the actual sample tenderness, with R
2 values of 0.79 and 0.86 for the two datasets, respectively, indicating a robust predictive capability [
47]. The development of more convenient equipment signifies technological advancement, and this finding confirms that utilizing portable devices can enhance work efficiency, increase the number of testing samples, and thereby strengthen the data training for prediction models, improving their generalizability.
Cama Moncunell et al. utilized a 780 nm wavelength laser with 120 mW power, a charge-coupled device (CCD) detector, and a universal platform sampling (UPS) with a 50um gap aperture as their Raman spectroscopy data acquisition platform for beef tenderness detection. They recorded Raman intensities within the 250 ~ 3381 cm
-1 shift range and preprocessed the data using five different methods, including SG. They iteratively selected the most crucial Raman bands using PLS combined with cross-validation (CV) and projection variable importance (VIP) to fit a new PLS model. Unfortunately, the model's prediction results were suboptimal, with the highest correlation coefficient reaching only 0.48. The low accuracy may stem from changes in the protein's secondary and tertiary structures, which can obscure the α-helix signal, leading to unclear spectra and mixed bands. Additionally, the tryptophan signal in the 760 ~ 880 cm
-1 band of the tertiary structure does not contribute to tenderness prediction, complicating the detection process. The presence of unrelated signals in the model may also contribute to its low accuracy [
48]. This study's contribution lies in its examination of Raman spectral bands for detecting WBSF and in summarizing the reasons behind the low accuracy of their detection model, providing valuable lessons for future researchers to avoid similar pitfalls.
Despite its extensive applications in non-destructive testing, Raman spectroscopy has certain limitations. Firstly, many compounds lack Raman activity, and those that possess it may emit fluorescence at specific excitation frequencies, which can overshadow Raman signals and impede analysis. Secondly, nonlinear curves are common in Fourier transform spectroscopy analysis. Thirdly, overlapping vibrational peaks and variations in Raman scattering intensities can be influenced by optical system parameters. Addressing these challenges requires enhancing Raman signal strength, bolstering the robustness of detection models, and improving the stability and fault tolerance of Raman spectroscopy systems, which are now key research focal points.
2.2. Airflow - optical fusion detection technology
Airflow-optical fusion detection technology represents a novel frontier in non-destructive testing, offering a unique approach to assess the quality characteristics of meat products. The fundamental premise of this technology is to utilize gas as a medium, employing pressure devices like pumps to compress the gas. By altering the cross-sectional area of a flow pipeline, the gas is transformed into a high-velocity jet that emanates from a small-diameter straight-hole nozzle in a near-radial pattern. When a test sample is positioned beneath the nozzle, the force exerted by the high-speed airflow can induce surface deformation. Concurrently, optical sensors are deployed to monitor the sample's deformation, yielding a series of test data that can be analyzed for non-destructive evaluation of meat attributes such as tenderness and freshness [
49,
50,
51,
52]. This technology has garnered extensive research and application, with airflow laser technology and airflow structured light three-dimensional (3D) vision technology being particularly noteworthy.
Lee et al. devised an innovative laser blowing system that harnesses airflow-optical fusion detection technology to gauge the tenderness of chicken meat. By applying high-speed airflow to the chicken meat, a laser sensor positioned above the airflow nozzle simultaneously recorded detection data. This data was then modeled using Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) and Partial Least Squares (PLS) algorithms, yielding promising results with a resolution accuracy of up to 85%. Interestingly, this system was found to be particularly adept at detecting tender meat, likely due to the low airflow pressure that is insufficient to cause deformation in tougher meat [
53]. In contrast, spectral technology may encounter overlapping spectral signals when distinguishing between tender and tough meat, necessitating complex data preprocessing to mitigate this issue. This observation suggests that, in the realm of tenderness detection, airflow-optical fusion technology possesses greater developmental potential than single optical technology.
Lou et al. explored the use of airflow in conjunction with structured light 3D vision technology for rapid, non-destructive detection of beef tenderness. A structured light 3D camera was used to capture the three-dimensional point cloud deformation data on the surface of beef following the application of airflow. Employing algorithms such as point cloud segmentation, down sampling, and rotation, they extracted nine features from the beef surface, including six deformation and three point cloud features. Their findings indicated that a model based on the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) algorithm exhibited a strong predictive capability for beef tenderness, with a R of 0.8356. Moreover, the ELM model achieved an impressive correct classification accuracy of 92.96% for tender beef [
54].
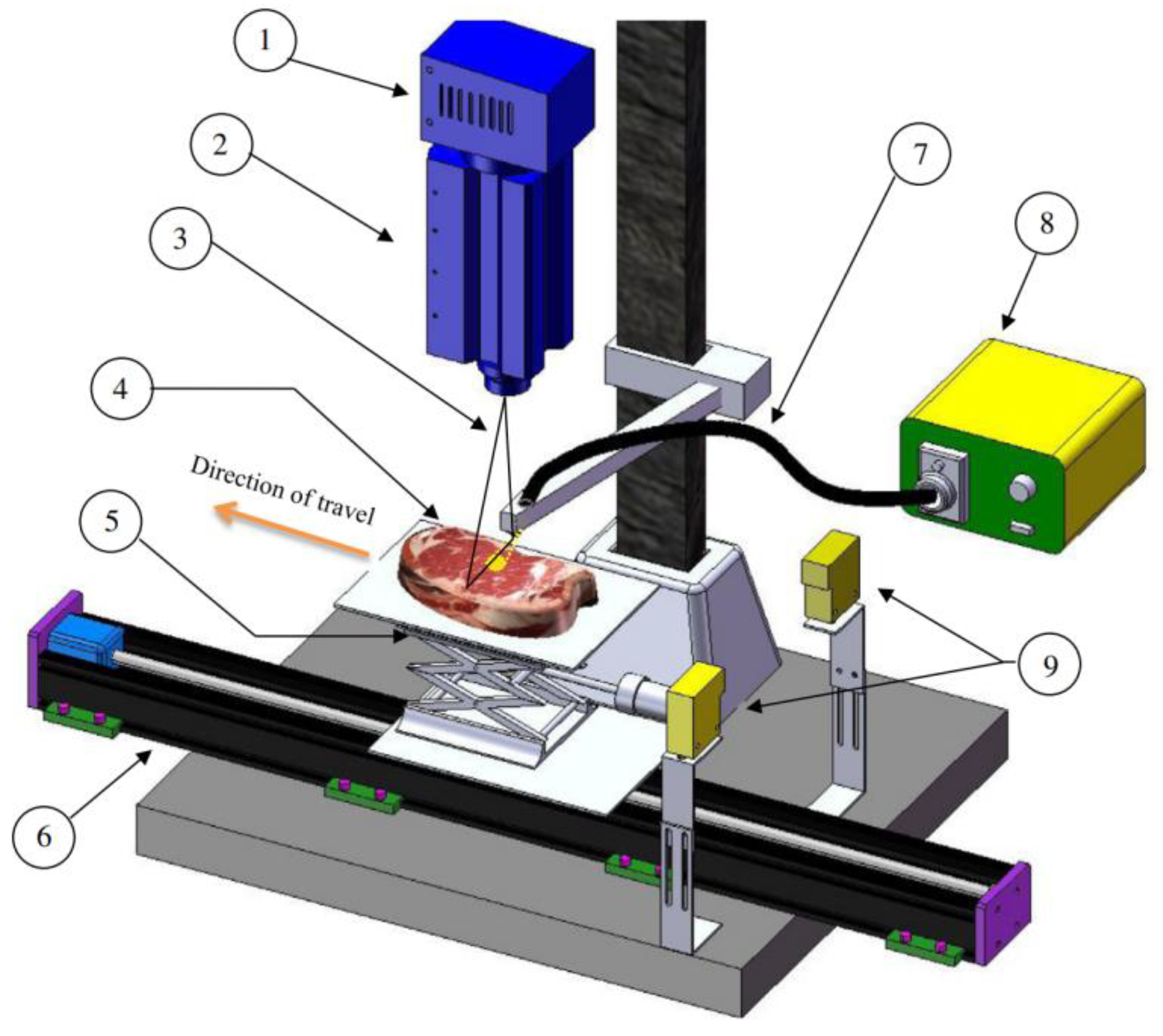
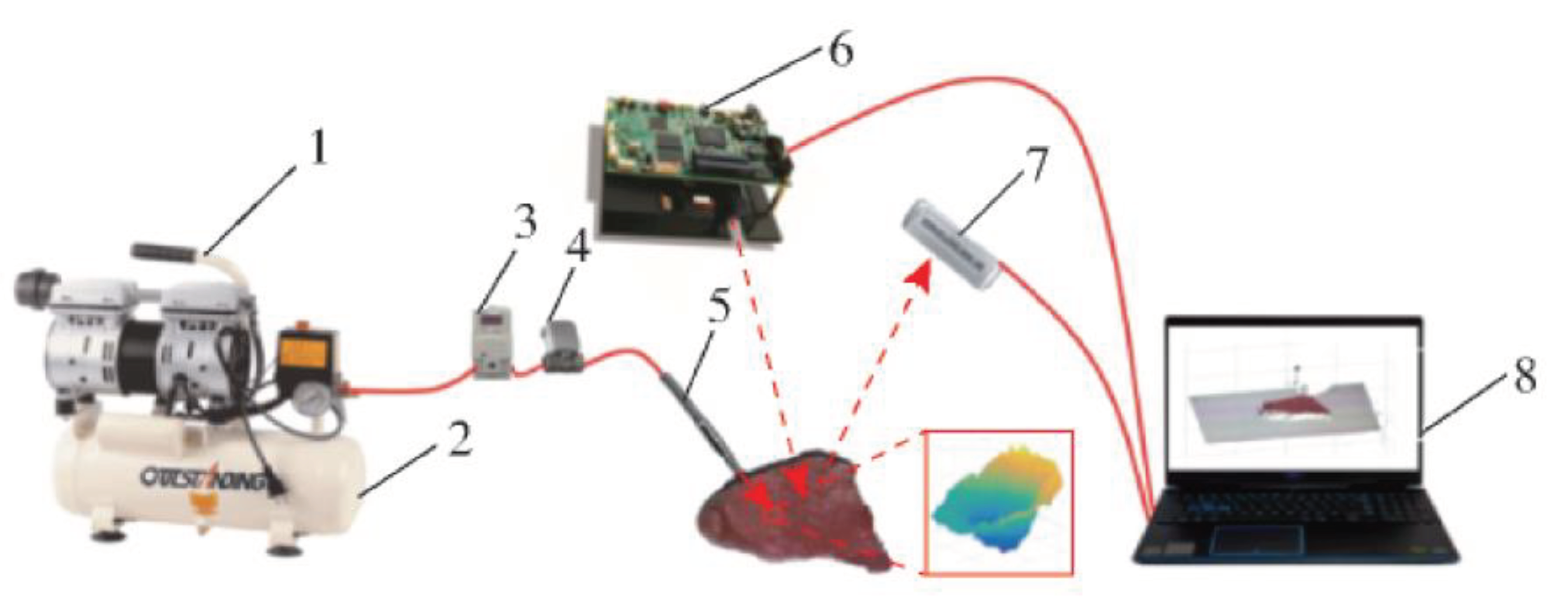
Xu et al. developed a non-destructive testing apparatus leveraging controllable airflow-laser detection technology to assess the tenderness of chicken meat, as depicted in
Figure 5. They employed Support Vector Machine (SVM) and global variable PLS algorithms, combined with Savitzky-Golay (SG) preprocessing, to construct models for dynamic and static detection modes, such as transient, creep recovery, and stress relaxation. Their results indicated that the dynamic mode outperformed the static mode, with the transient mode demonstrating superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative assessments. The correlation coefficients for the validation set were an impressive 0.95 and 0.913, respectively [
55].
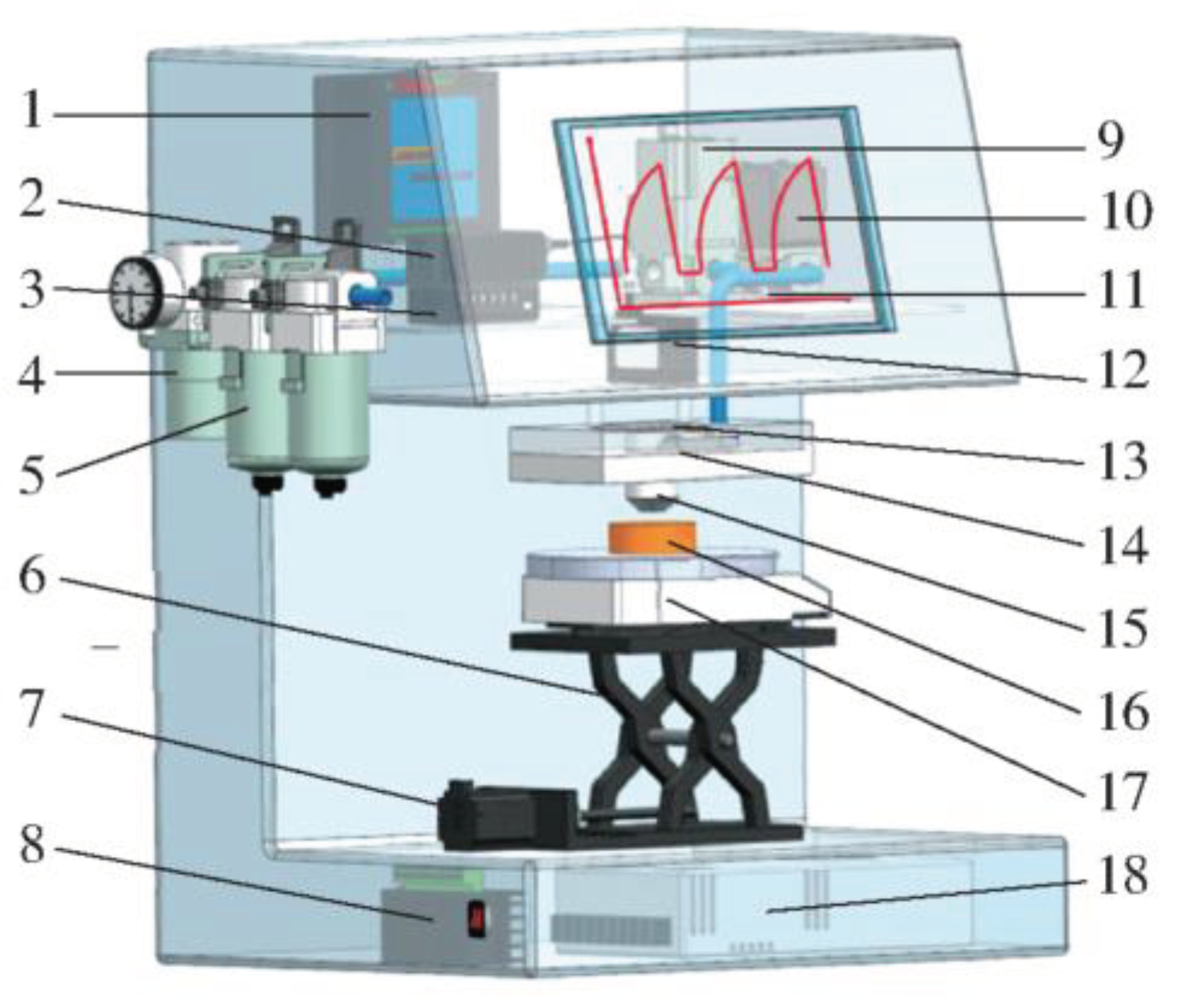
Lu et al. introduced a rapid, non-destructive testing method for beef tenderness, integrating airflow pulses with structured light 3D imaging to address the limitations of traditional tenderness testing methods in terms of speed and accuracy. The detection system, shown in
Figure 6, utilized high-speed airflow to impact the beef surface and structured light 3D imaging to capture three-dimensional point cloud information from the concave area formed on the beef surface. Through denoising, point cloud segmentation, and surface fitting algorithms, they extracted various effective data from the concave area. Additionally, they established beef tenderness prediction models based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LS-SVR), Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN), and Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN). The GRNN model emerged as the most accurate predictor, with a correlation coefficient of 0.975 for the prediction set. Furthermore, the researchers utilized a GRNN neural network based on K-fold cross-validation to predict the tenderness levels of beef, achieving a perfect grading accuracy of 100% for tender beef [
56].
Despite the promising potential of airflow-optical fusion detection technology in meat product quality assessment, several challenges remain. Current research predominantly focuses on establishing correlations between meat product quality characteristics and prediction models, with less emphasis on the development of dedicated detection equipment. Moreover, existing equipment tends to be bulky and inconvenient to transport. The control methods for these systems are often limited, relying on hardware to regulate airflow output. Once the airflow exits the nozzle, it becomes uncontrollable, leading to an entrainment effect with the surrounding air, resulting in uneven force distribution on the sample surface and complicating the deformation area's output signal. To address these issues, it is essential to expedite research on equipment portability and miniaturization and to enhance the key structures and associated software of the detection systems. Improving the robustness and fault tolerance of detection models will significantly boost the capabilities of airflow-optical fusion detection technology.
2.3. NMR Technology
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is an analytical tool that is both information-rich and non-destructive in nature. The fundamental principle of NMR is based on the behavior of atomic nuclei in a constant magnetic field, where they undergo a precession effect around the external magnetic field. By introducing a fixed frequency electromagnetic wave and adjusting the strength of the external magnetic field to match the precession frequency with the electromagnetic wave frequency, nuclear precession synchronizes with the electromagnetic waves, a phenomenon known as NMR. This technology exploits the intrinsic magnetic properties of specific atomic nuclei to absorb and emit energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. This process induces nuclear transitions and generates NMR signals that reveal the molecular structure, dynamic processes, and chemical reactions within the sample, enabling non-invasive, non-destructive, and quantitative analysis and research [
57,
58,
59]. As NMR is a magnetic field imaging method devoid of radioactivity, it is inherently safe and poses no harm to researchers. In recent years, NMR technology, characterized by its low cost, rapid non-destructive testing capabilities, and precision, has seen widespread application in the food, agriculture, and industrial sectors.
In their study, Kelly et al. employed NMR technology to investigate the migration and distribution characteristics of myofibrillar water in muscle tissues. They used a desktop low-field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) transverse relaxation (T2) instrument to characterize the distribution and fluidity of water in meat, as well as the structural characteristics that directly influence water retention capacity (WHC). Their research demonstrated that the T2 relaxation time can serve as an indicator of meat's water holding capacity. Given that water content is a critical factor in meat tenderness studies, this work has established the feasibility of using NMR technology for non-destructive testing of meat tenderness [
60].
Focusing on Tan lamb as their subject, Ma et al. applied LF-NMR technology to study the water distribution and migration in cold and fresh Tan lamb during storage to analyze and differentiate the tenderness levels. Using an NMR imaging analyzer, they sampled and imaged the lamb. Post-image analysis with a curve regression model revealed a highly significant correlation between the transverse relaxation time T2 and shear force, with a correlation coefficient of -0.996 (p < 0.01) and a fitting regression coefficient of 0.942. Similarly, the total peak area A exhibited a highly significant negative correlation with shear force, with a correlation coefficient of -0.991 (p < 0.01) and a fitting regression coefficient of 0.960 [
61].
Fabíola et al. explored the use of time-domain Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (TD-NMR) technology for beef tenderness detection. They collected attenuation signals from Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) and Continuous Wave-Free Precession (CWFP) sequences using a TD-NMR spectrometer and constructed a multiple regression model using Partial Least Squares (PLS) to fit the data. Their results indicated a strong correlation between CPMG tenderness data and reference data, with r>0.65. The study also highlighted that each beef sample could be measured in less than 1 second, confirming that this detection method not only offers good predictive performance but also boasts extremely high detection efficiency [
62]. TD-NMR detection technology provides researchers with a non-destructive and reliable analysis method, which can inform the design and manufacture of more user-friendly NMR non-destructive testing equipment.
While NMR technology is a convenient and swift detection method widely utilized in the medical field, its application in agriculture and food industries is less prevalent. There are several reasons for this discrepancy: 1. The application research in the food industry lacks systematic approach, and there is a scarcity of detection data. 2. NMR testing of different agricultural products necessitates specific research for each product, which is time-consuming. 3. The cost of NMR-related equipment is relatively high, which to some extent curtails the advancement of NMR technology. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to intensify data collection efforts, establish a more comprehensive NMR spectral database, and conduct research into low-cost, portable non-destructive testing equipment. These initiatives will be pivotal in propelling the development and broader adoption of NMR technology in various fields.
3. Research Development Trends and Prospects
As technology continues to evolve, the rapid non-destructive testing technologies for meat tenderness mentioned earlier are poised to become pivotal in the field.
Table 1 encapsulates the diverse applications of each technology, showcasing their potential for enhancing the quality assessment of meat products. However, several challenges remain in the development and implementation of these rapid non-destructive testing technologies.
Firstly, technologies such as near-infrared spectroscopy, hyperspectral imaging, and nuclear magnetic resonance face limitations due to the bulkiness of equipment, high costs, and portability issues, which hinder their widespread adoption and application. Secondly, the existing databases and models are often tailored to specific meat types, lacking the versatility to generalize the quality characteristics across various meat categories. This necessitates a targeted approach to data analysis, which limits the universality of the models.
To address these challenges, a multifaceted strategy is required. Firstly, there is a need to foster the integration and exploration of technologies, enhancing the capacity to merge multiple technologies into more precise and stable testing equipment. Secondly, upgrading and transforming key components of current testing equipment will improve the accuracy of meat tenderness assessments. Thirdly, intensifying research into the intelligence, miniaturization, and efficient data processing capabilities of testing equipment is crucial for increasing testing efficiency.
Additionally, establishing a comprehensive, multi-source, and open non-destructive testing database for meat tenderness is essential. This database would facilitate more robust data comparison and enhance overall testing capabilities. Fifthly, a holistic summary of existing testing models, coupled with the integration of multi-source information, will pave the way for the development of a more universal and robust non-destructive testing model for meat tenderness.
The rapid advancement of big data and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to significant improvements in computing power and algorithms. Currently, detection methods are often confined to specific algorithms, and the models developed are relatively singular. However, by harnessing AI, these limitations can be transcended. AI can analyze and compare original detection data with existing algorithms and models, distilling from vast datasets the most suitable algorithms and models for non-destructive testing. By recording these findings in a database and iteratively refining the AI, there is an expectation of establishing detection models with greater universality and stability.
Over time, as data accumulates, AI may even devise previously unknown algorithms and models that are better suited for non-destructive testing. This development is instrumental in simplifying the intelligence required for non-destructive testing and holds immense potential for the future.
With the accelerating pace of technological innovation and the growing focus on intelligent instrumentation research and development globally, it is anticipated that in the near future, the convergence of rapid non-destructive testing and AI technology will lead to significant enhancements in related instruments and methodologies. This integration will not only improve the efficiency and accuracy of meat tenderness assessments but also expand the applicability of these technologies across various industries, marking a new era in quality control and assurance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, Y.L., H.W. and Z.Y.; software, T.H. and X.W.; validation, Z.Y., W.W.; investigation, Z.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, review and editing, Y.L. and Z.Y.; project administration and funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32102055, the Science and Technology General Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission, grant number KM202310853002, the Young Teachers Research Ability Enhancement Program, grant number BGY2022KY-03QT, Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Modern Agricultural Engineering in Ordinary Higher Education Institutions of the Education Department of the Autonomous Region, grant number TDNG2023107.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the four funds for supporting this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yang, T.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Luo, F.; Yang, L.; Li, K.Y.; Qin, M.; Ge, Q.F.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.G.; Liu, R. Research advances in effect of cooking on meat quality and nutrition properties. J. Res. Diet. Sci. Cult. 2022, 39, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; He, Z.F. Research progress in meat detection technology. Meat Res. 2006, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 1180-2006, Determination of meat tenderness. Determination of shear force [S].
- Wang, H.F.; Qu, G.J.; Qin, G.X. The factor of affect meat tenderness and tenderization technology. Jilin Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2010, 31, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, J. A theoretical approach of the relationships between collagen content, collagen cross-links and meat tenderness. Meat Sci., 2007, 76, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lei, Q.X.; Cao, D.G.; Huang, T.R.; Huang, M. Effects of different ages on the slaughter performance, muscle quality and nutritional characteristics of 817 broilers. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2023, 46, 59–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, S.Z.; Zhao, G.M.; Sun, B.Z. Development status and countermeasures of beef cattle slaughtering and processing industry in China. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2023, 45, 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M.; Gu, L.W.; Zhou, L. Analysis and research on the transfer trend of pig slaughtering capacity in China. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 58, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L. Application of new non-destructive testing technology in meat quality testing. Mod. Food 2023, 29, 104–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Wang, J.H.; Lu, A.X. Research development on non-destructive determination technology for meat product quality. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 4083–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q. Application of new non-destructive testing technology in meat quality detection. Meat Ind. 2012, 8, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.Q.; Huang, S.Z. Non-destructive measurement techniques for meat quality detection. Meat Res. 2008, 8, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zaukuu, J-L. Z.; Tsyawo, E.C. Rapid and non-destructive detection of ponceau 4R red colored pork. Meat Sci. 2024, 209, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulladosa, E.; Duran-Montgé, P.; Serra, X.; Picouet, P.; Schimmer, O.; Gou, P. Estimation of dry-cured ham composition using dielectric time domain reflectometry. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.J.; Liu, G.S.; He, J.G.; Wan, G.L.; Ma, C.; Ban, J.J.; Ma, L.M. Non-destructive assessment of the myoglobin content of Tan sheep using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2020, 167, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, M. Optical sensing as analytical tools for meat tenderness measurements - A review. Meat Sci. 2023, 195, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres-Nevado, J.M.; Garrido-Varo, A.; De Pedro-Sanz, E.; Tejerina-Barrado, D.; Pérez-Marín, D.C. Non-destructive Near Infrared Spectroscopy for the labelling of frozen Iberian pork loins. Meat Sci. 2021, 175, 108440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antequera, T.; Caballero, D.; Grassi, S.; Uttaro, B.; Perez-Palacios, T. Evaluation of fresh meat quality by Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A review. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, C.Z.; Dong, J.; Bai, M.Y.; Hui, T. Research progress of rapid non-destructive detection technology in the field of apple mold heart disease. Molecules 2023, 28, 7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.S.; Xiao, X.Q. Vis/NIR based spectral sensing for SSC of table grapes. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 2023, 43, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Song, Y.; Zou, X.B.; Cai, J.R. Research progress of sensing detection and monitoring technology for fruit and vegetable quality control. Smart Agric. 2021, 3, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Raúl, G.; Antonio, J.S.; Joel, G.; Eugenio, I.; Ana, F.; Jose, M.B. Nondestructive assessment of freshness in packaged sliced chicken breasts using SW-NIR spectroscopy. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 0–337. [Google Scholar]
- de Nadai Bonin, M.; da Luz e Silva, S.; Bünger, L.; Ross, D.; Dias Feijó, G.L.; da Costa Gomes, R.; Palma Rennó, F.; de Almeida Santana, M.H.; Marcondes de Rezende, F.; Vinhas Ãtavo, L.C.; et al. Predicting the shear value and intramuscular fat in meat from Nellore cattle using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2020, 163(), 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, N.; Wang, Y.M. Prediction of tenderness of fresh mutton in South Xinjiang by NIRS. J. Tarim Univ. 2020, 32, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.K.; Yang, Q.H.; Wang, W.X. On-line detection and classification of pork moisture based on near-infrared spectra. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Balage, J. M.; da Luz e Silva, S.; Gomide, C.A.; Bonin, M.D.N; Figueira, A.C. Predicting pork quality using Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2015, 108(), 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyrwisz, J.; Moczkowska, M.; Kurek, M.; Karp, S.; Atanasov, A.; Wierzbicka, A. Evaluation of WBSF, color, cooking loss of longissimus lumborum muscle with fiber optic near-infrared spectroscopy (FT-NIR), Depending on Aging Time. Molecules 2019, 24, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Q. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy technology in beef tenderness detection. Chin. Food Saf. Mag. 2017, (36), 75. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yang, F.Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Wang, S.M.; Fu, L.H. Nondestructive identification of soybean protein in minced chicken meat based on hyperspectral imaging and VGG16-SVM. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 125, 105713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Rao, L.; Xie, L; Yan, M. ; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, L.Q.; Xiao, S.J.; Ding, N.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Quantification and visualization of meat quality traits in pork using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2023, 196, 109052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchman, S.; Loeffen, M.P.F.; Reis, M.M.; Craigie, C.R. Robustness of hyperspectral imaging and PLSR model predictions of intramuscular fat in lamb M. longissimus lumborum across several flocks and years. Meat Sci. 2021, 179, 108492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.S.; Xu; M. ; Dai, C.X. Multi-task convolutional neural network for simultaneous monitoring of lipid and protein oxidative damage in frozen-thawed pork using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2023, 201, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cluff, K.; Naganathan, G.K.; Subbiah, J.; Samal, A.; Calkins, C.R. Optical scattering with hyperspectral imaging to classify longissimus dorsi muscle based on beef tenderness using multivariate modeling. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balage, J.M.; Amigo, J.M.; Antonelo, D.S.; Mazon, M.R.; da Luz e Silva, S. Shear force analysis by core location in Longissimus steaks from Nellore cattle using hyperspectral images – A feasibility study. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Peng, Y.K. Distribution of beef tenderness grading based on texture features by hyperspectral image analysis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Wu, L.G.; Kang, N.B.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; He, X.G. Study on Tan-lamb mutton tenderness by using the fusion of hyperspectral spectrum and image information. J. Optoelectronics·Laser 2016, 27, 987–995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; He, H.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Liu, X. , Ma, H.J.; Zhu, M.M.; Gao, H.Y., Zeng, J. Rapid prediction of chicken tenderness by hyperspectral imaging technique. J. Hainan Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 31, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.Q. Detection method for tenderness of chilled fresh lamb based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Fan, N.Y.; Cheng, L.J.; Yu, J.Y.; Yuan, R.R. Hyperspectral model optimization for tenderness of chilled tan-sheep mutton based on IVISSA. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 2020, 40, 2558–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, C.; Li, Y.Z.; Du, S.S.; Geng, Y.C.; Su, M.K.; Liu, H.L. Raman spectroscopy for rapid fingerprint analysis of meat quality and security: Principles, progress and prospects. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Fraser-Miller, S.J.; Jessep, W.T.; Bain, W.E.; Hicks, T.M.; Ward, J.F.; Craigie, C.R.; Loeffen, M.; Gordon, K.C. Rapid discrimination of intact beef, venison and lamb meat using Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.M.; Xie, Y.F.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.H.; Yao, W.R. Non-destructive prediction of colour and water-related properties of frozen/thawed beef meat by Raman spectroscopy coupled multivariate calibration. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.R.; Song, C.; Lin, X.M.; Gao, X. Identification of meat species by combined laser-induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 1064. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.Y.; Xia, L.; Hu, Y.F.; Li, G.K. Fe3O4-WO3−X@AuNPs for magnetic separation, enrichment and surface-enhanced Raman scattering analysis all-in-one of albendazole and streptomycin in meat samples. Sens. Actuators B 2024, 402, 135131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rene; J. B.; Steven, J.B.; Linda, J.F.; Bruce, W.M.; Desmond, P. Preliminary investigation of the application of Raman spectroscopy to the prediction of the sensory quality of beef silverside. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Scheier, R.; Eberle, T.; Schmidt, H. Assessment of tenderness of aged bovine gluteus medius muscles using Raman spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2016, 115(), 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Scheier, R.; Hopkins, D.L. Preliminary investigation on the relationship of Raman spectra of sheep meat with shear force and cooking loss. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cama-Moncunill, R.; Cafferky, J.; Augier, C.; Sweeney, T.; Allen, P.; Ferragina, A.; Sullivan, C.; Cromie, A.; Hamill, R.M. Prediction of Warner-Bratzler shear force, intramuscular fat, drip-loss and cook-loss in beef via Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics. Meat Sci. 2020, 167, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Dong, J. Prediction of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Content of Chilled Beef for Freshness Evaluation by Using Viscoelasticity Based on Airflow and Laser Technique. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Wang, W.J.; Long, Y.; Peng, Y.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Chao, K.L.; Tang, X.Y. A feasibility study of rapid nondestructive detection of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) content in beef based on airflow and laser ranging technique. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.Z.; Sun, Q.M.; Yang, T.X.; He, K.; Tang, X.Y. Nondestructive determination of common indicators of beef for freshness assessment using airflow-three dimensional (3D) machine vision technique and machine learning. J. Food Eng. 2023, 340, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Luo, X.Z.; Sun, Q.M.; Tang, X.Y. Development of beef freshness detection device based on air flow and multi-point laser technique. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Owens, C.M.; Meullenet, J.F. A Novel Laser Air Puff and Shape Profile Method for Predicting Tenderness of Broiler Breast Meat. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Z.; Xiong, L.J.; Gao, X.; Hou, Y.X.; He, M.; Tang, X.Y. Determination of beef tenderness based on airflow pressure combined with structural light three-dimensional (3D) vision technology. Meat Sci. 2023, 202, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.B.; Zhao, Q.L.; He, K.; Li, Y.Y.; Peng, Y.K.; Tang, X.Y. Evaluation of chicken tenderness based on controlled air-flow laser detection technique. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51(S2), 457–465. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Hu, Q.Y.; Dai, D.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Deng, Y.M. Beef Tenderness detection based on pulse air-puff combined with structural light 3D imaging. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- John, W.B.; Dmitry, B.; Andreas, T. Lower than low: Perspectives on zero- to ultralow-field nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 323, 106886. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, T.; Hu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Gan, B.; Xie, J.H.; Yu, Q. Rapid identification and quantitation of pork and duck meat of binary and ternary adulteration in minced beef by 1H NMR combined with multivariate data fusion. Food Control 2023, 154, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.M.; Yang, F.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.H.; Ai, Z.J. Establishment of detection model of water-injected meat based on low field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation spectroscopy. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, L.P.; Katja, R.; Henrik, J.A.; David, L.H. Water distribution and mobility in meat during the conversion of muscle to meat and ageing and the impacts on fresh meat quality attributes — A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.L.; Wu, L.G.; Wang, S.L.; He, X.G.; He, J.G. Detection of tan-sheep meat tenderness based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fabíola, M.V.P.; Sérgio, B.P.; Thaísa, G.; Carolina, L.G.; Pedro, E.D.F.; Luiz, A.C. Fast determination of beef quality parameters with time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and chemometrics. Talanta 2013, 108, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).